Glass wool is a popular material used by humans for thermal and sound insulation since the distant 1873.
it one of the cheapest and most widely available types of insulation.
Let's figure out what qualities, characteristics and features glass wool has, and why it has been popular for the second century.
About the material
This is a special case of mineral wool - insulation based on mineral fibers. Fibers can be of three types:
- glass;
- stone;
- slag.
Thermal insulation is provided by the presence still air between the fibers... Thermal conductivity is in the range of 0.030 - 0.052 W / mK (when measured dry at 10 ° C or 25 ° C).


Sound insulation is obtained by absorption of sound waves by fibers (the sound absorption coefficient of the fibers can be 0.8 - 0.92).
If we compare the thermal resistance of glass wool and brick, then 5 cm of the thickness of the first material corresponds to 1 m of the thickness of the second.
What are the differences between mineral wool and glass wool?
Both materials are fiber-structured insulation. However, the difference between them is quite large:
- Glass wool
softer and more elastic than mineral wool. It has good hiding power, which allows large areas to be insulated. It is also easier to transport and much cheaper. - Mineral wool
absorbs less moisture, as a result of which it has a lower percentage of shrinkage. The heat resistance index is higher than that of glass wool.
Thus, when choosing between these materials, it is necessary to determine the conditions in the insulated room. For example, it is better to insulate an attic with glass wool due to its covering ability, and a kitchen area with high humidity should be insulated with mineral wool. In the case when the budget issue arises sharply, glass wool is the leader.
Characteristics and properties
Glass wool fibers are located parallel to each other, characterized by significant:
- length - from 15 to 50 mm (this is 2 to 4 times more than stone);
- thickness - from 3 to 20 microns,
This gives products from them strength and resilience - the largest among mineral wool.
Specific strength value of glass fibers exceeds that of steel wire.
The homogeneity of the composition determines the high resistance to vibration, and the low density (11 - 45 kg / m3, compared to 30 - 90 kg / m3 for stone wool) - the minimum impact on building structures.


High compressibility (90%), softness and elasticity make it possible to qualitatively isolate uneven surfaces, structures of complex geometry.
The inorganic base makes the material unsuitable for rodent eating and nesting, is an unsuitable medium for the appearance of mold and mildew.
In addition, glass wool:
- keeps its shape stably;
- does not age;
- does not deform;
- does not cause corrosion of metals in contact with it;
- retains mechanical and thermal insulation properties for decades;
- characterized by frost resistance (used in the range of -60 ° C).
TO disadvantages include:
- increased fiber fragility - to protect against the smallest debris, installation should be carried out in overalls using respiratory protection (for example, respirators), when installed outside, protection from wind is required to prevent fiber migration (for example, installation of glass fibers);
- excessive moisture absorption (the water absorption coefficient for materials of open porosity can be up to 20% by weight, up to 2% by volume); moisture trapped inside the glass wool irreversibly changes the structure to a more fragile one, leading to a loss of more than 40% of its thermal insulation properties;
- shrinkage over time.
To reduce exposure to moisture, cotton wool impregnated with special compounds (oils, silicon organic compounds), water-repellent additives are introduced.
Structure
What is glass wool made of? This material contains both the main components that ensure its properties of both insulation and binders, which allow it to maintain its strength and integrity.


Basic:
- glass or glass broken;
- natural quartz sand;
- limestone (chalk);
- soda ash;
- boric acid;
- borax (sulfate);
- dolomite;
- fluorite.
Binders:
- polymer resin;
- clay;
- spar;
- other substances.
Binder components can be 2.5 - 10% by weight.
The question that arises for some, why is glass in glass wool, can be answered as follows. The presence of this component determines the important properties of the material, namely:
- incombustibility;
- unattractiveness to rodents and mold;
- strength and durability.
If glass wool was in place of glass, say, wood fibers, all these advantages would be reduced to zero.
The harm of glass wool to the skin
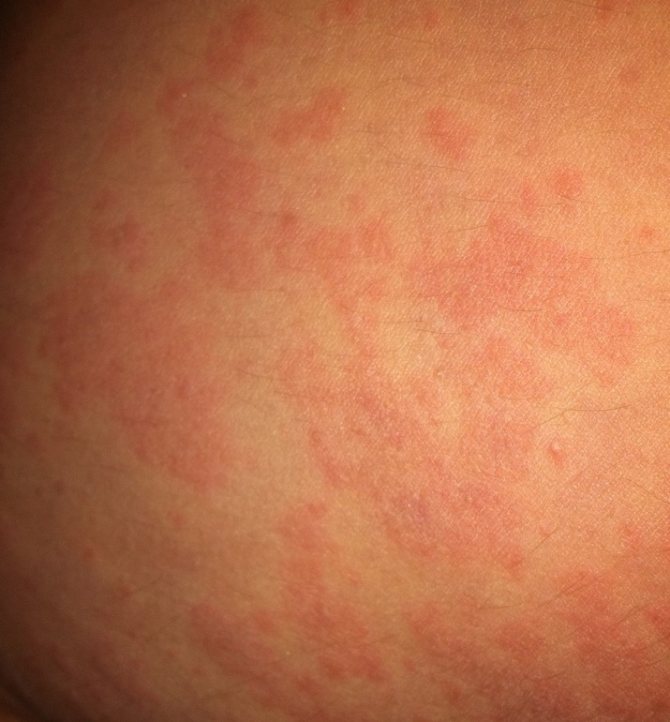
During direct contact of glass wool with human skin, when they work without gloves and overalls during installation, sharp fragments of microparticles penetrate inside and cause skin irritation, at the point of contact it turns red, itching appears.
The particles can injure the skin and penetrate deep into the dermis, causing allergies. It is necessary to refrain from scratching the affected areas. The glass wool should be disposed of under a stream of clean running water.
It is important: All glass wool repairs must be carried out with protective clothing and rubber gloves or tarpaulin gloves.
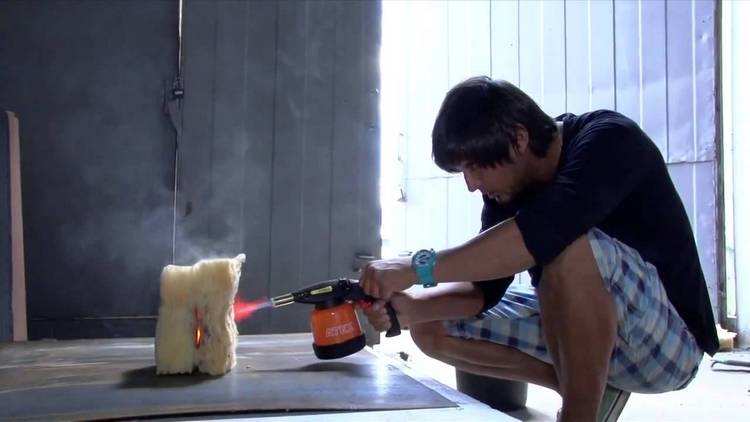
Does glass wool burn?
Glass wool does not support combustion, belongs to the class of non-combustible materials (NG).
Such materials withstand exposure to high temperatures while maintaining the integrity of the structure, strength and other properties, they do not ignite.
The material is sintered at temperatures from 500 to 550 ° C.
The temperature range of use is determined by the composition, more precisely, by the organic resins included in the composition as a binder. For glass wool, the upper limit is 250 to 450 ° C. Exceeding this range can be considered the melting point.
In this case, the upper limit is determined by the temperature of burnout of the resins, as a result of which the material loses its binder, and, consequently, its operational properties.
Under the influence of fire there is no release of toxic and harmful substances.


Applications
If we talk about the industries of application, then these are:
- building;
- heat supply;
- production;
- automotive industry;
- aviation;
- pipeline transportation of materials.
For every sphere different types are selecteddiffering:
- type of fiber
- their location,
- the presence of additional coatings,
- density (maximum possible - 130 kg / m3).
Most common designs glass wool - rolls and soft mats.
Fiberglass insulation is available in the form of:
- continuous filament (rolls);
- staple (cut) fibers (slabs), including those characterized by increased rigidity with facing;
- soft mats;
- reinforced rolls;
- cached technical insulation, including in the form of foil-clad products.


Rolls for a long time and successfully used for insulation of horizontal surfaces - floors, roofs.
Cached View - for insulation of high-temperature pipelines, assemblies and containers.
Mats and slabs used for thermal insulation of various premises and structural elements, namely:
- facades;
- window and doorways;
- interfloor and other floors;
- internal and external partitions of buildings;
- sound and thermal insulation of cabins.
Cotton wool should be fastened in such a way as to provide a free position (for maximum expansion) and at the same time a tight fit without gaps.
Production
Production begins with the introduction of the starting components into the smelting furnace. As a result of the temperature of 1400 ° C, centrifugal forces of centrifuges and steam inflation get glass filaments.
To obtain the finest yarns with the required mechanical properties at the outlet, strict adherence to the recipe composition is required.
The yarns treated with binder solutions of polymers (modified urea, phenol-algid polymers) are sent to a straightening conveyor to be formed homogeneous fiberglass cloth.


This is followed by the stage of polymerization - a temperature of 250 ° C becomes a catalyst for the formation of polymer bonds and removal of excess moisture.
Cooling, cutting with saws and milling cutters, then - pressing (compressed 5-6 times), packaging in polyethylene - we get ready-to-transport rolls and plates.
The use of cullet as the main component deserves special attention.
Modern technologies allow add up to 80% glass powder, obtained by crushing and grinding of commercial glass waste.
The composition of cullet is regulated by national standards - GOST R 52233-2004. According to the provisions of the document, this secondary raw material can be 1 or 2 grades and one of five grades in accordance with the color (BS, PST, PSL, ZS, KS).
Glass wool obtained as a result of the disposal and processing of household and industrial glass waste meets all the requirements for these products.
At the same time, a product made from recycled materials differs lower production costs in comparison with traditional technology, and, as a result, a more affordable price for the consumer.
Many companies are engaged in the production of glass wool using this technology, including:
- Isover;
- URSA;
- Knauf.
Manufacturing standard
Glass wool production regulated by a number of regulatory documents... GOST 19170 2001 is considered the main one.
It describes:
- production methods;
- protective measures when working with material;
- scope of application.


It is allowed to manufacture according to our own, approved in the appropriate order by TU.
Harm to eyes
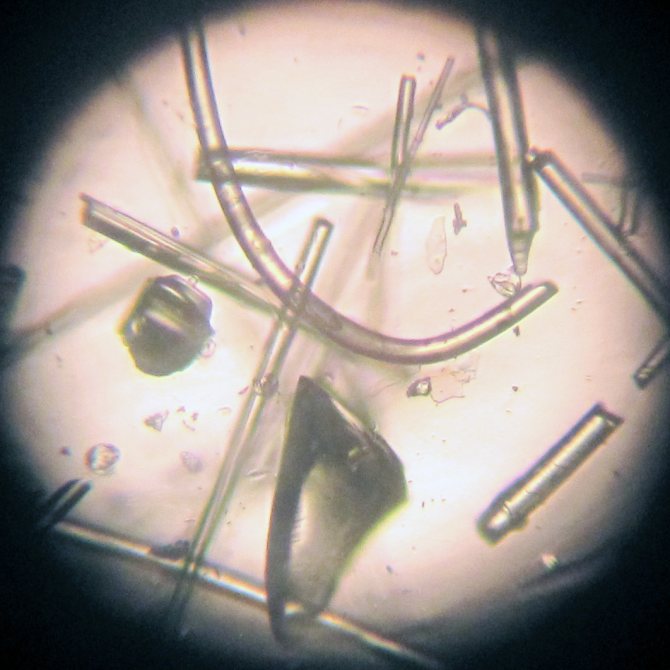
As you know, glass wool is characterized by increased fragility. Sharp and fine debris can penetrate the eyes and cause serious injury. During repairs using glass wool without special glasses, particles can get into the eyes.
Symptoms of getting into:
- acute pain in the eyes;
- lacrimation;
- feeling of discomfort;
- increased painful sensations.
What to do if glass wool dust gets into your eyes? In this case, in case of discomfort, you should consult a doctor.
Pros and cons as insulation
Based on the properties of glass wool, we can distinguish both positive and negative qualities.
The pluses include:
- good heat and sound insulation properties;
- fire safety;
- resistance to biological influences (pests, bacteria);
- light weight;
- ease of transportation;
- low cost (700 - 2100 rubles).
By cons:
- hygroscopicity (the need for additional vapor barrier);
- inconvenience of installation (the need to use protective equipment);
- the appearance of shrinkage after 8 - 10 years of service.
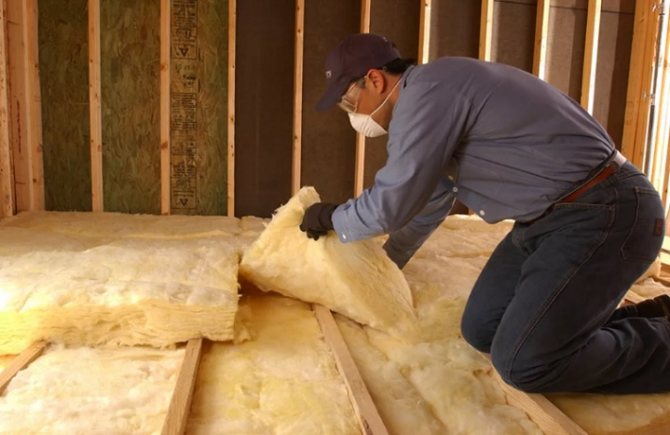
How to work properly with glass wool?
In order to avoid any problems during operation, it is necessary:
- Before starting work, flatten and clean glass wool from crumbling particles;
- When insulating the ceiling, you can use the crate.If there is no lathing, apply waterproofing.
- Apply glue, press the glass wool to the surface, hold for a few minutes.
- Use overalls and protective equipment (gloves, respirator, goggles).
- After finishing work, treat clothes, hands and face.
Is there any harm to human health?
In this question, there is information chaos.
Manufacturers selling glass wool talk about its harmlessness, while competitors offering other insulation materials talk about adverse effects.
We will not argue, we will only report the facts.
Glass wool can be dangerous and pose a threat only during its installation - there is a possibility contact of glass dust on the skin and in the respiratory system.


For protection, it is necessary to use protective clothing, respirators.
There is good news in this matter - modern technologies make it possible to produce materials that do not spread glass dust.
At the end of the installation, glass wool insulation becomes completely harmless.
Overalls are cleaned:
- shake off;
- vacuum cleaning;
- wash with 3-4 rinses;
- re-vacuuming after drying.
If glass wool particles come into contact with your skin, take a cool, strong shower without using detergents.
Why cool? Because hot water expands the pores, and therefore the penetration of glass particles.
Phenol is fraught with health risks
In chronic poisoning with poisonous phenol, a person begins to lose weight, diarrhea appears, heaviness when swallowing, saliva is abundantly secreted, dizzy, urine becomes dark.
If a person has been under the influence of phenol for a long time and breathed in its vapors, then he may feel weakness and muscle pain, and an enlargement of the liver is found during examination. Nervous disorders are observed, accompanied by severe headaches, even leading to loss of consciousness.
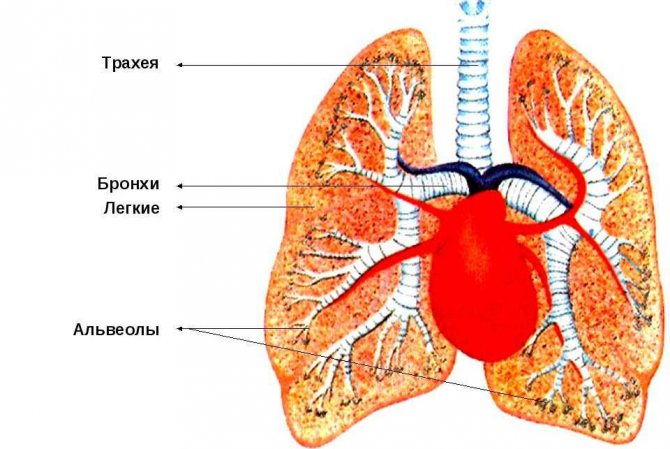
In ordinary living quarters, about 40 kg of dust, consisting of mineral particles of different diameters, is formed during the year. Small ones, with a diameter of less than 5 microns, are in the air. It is these particles that are considered allergenic, which, when inhaled, penetrate the human lungs, and, accumulating there, pose a threat to the respiratory system.
Most of the particles of mineral dust are of a dangerous size - less than 3 - 5 microns, they settle in the lungs along with the vapors of toxic phenol.
Note: it is very important for this reason to constantly ventilate the living area.
Recycling
Glass wool can be obtained by recycling cullet. And how is it disposed of itself?
To date there are three options:
- Burial at special landfills.
- Pure grinding and reuse in road construction, brick making.
- Use in the form of a charge - a solid residue formed during waste incineration. In this case, the glass component can reach 78% of the total volume, almost 20% is clay, 2% is sodium silicate.
The price of the recycling service for the disposal of glass wool fluctuates within from 400 to 1,000 rubles per ton.
There are also installations (mills) for processing (deep grinding to a size of 0.1 - 100 microns) of industrial glass fiber waste and its return to the technological process.