Attic ventilation: an overview of current schemes and ways to implement them
It is at least wasteful not to use a spacious attic as an additional room, and that is why ventilation of the under-roof space is so necessary
Planning to use your attic space as a living space, but don't know how to make it comfortable? I will talk about how the ventilation of the attic works. With a proper arrangement of the system for replacing stale air with fresh air, you can make the attic suitable for all-season comfortable living. In addition, the instructions for the installation of ventilation systems will be useful to you, even if the attic in a private house is not supposed to be used as housing.
Four reasons to ventilate attic spaces
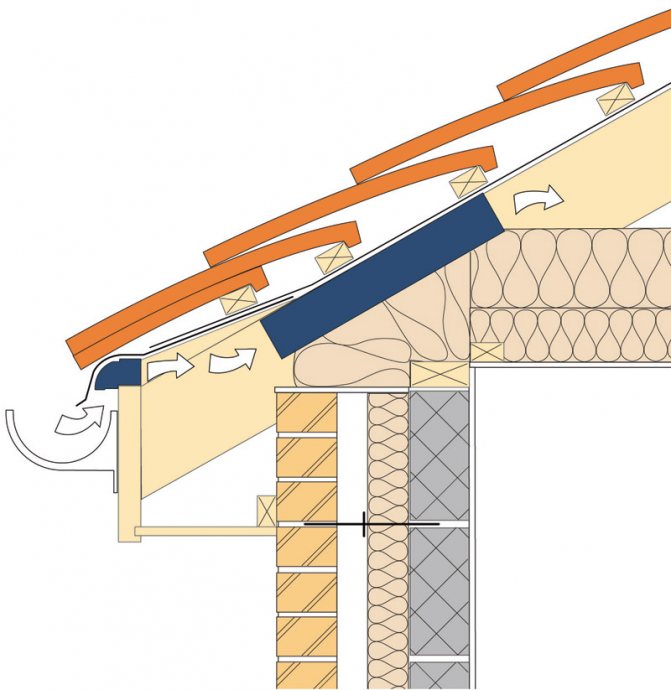
An example of a ventilation device for supply and exhaust ventilation on a modern roof
- The comfort of living in the attic. Clean fresh air is one of the main conditions for comfortable living indoors. Therefore, if the room under the roof is used for living, you need to take care of the normal air exchange even at the design stage of the roof.
- Lack of condensation. Effective air exchange prevents condensation on the windows, which is important if the under-roof space is used as an attic.
- No mold. Timely replacement of warm humid air with fresh air prevents mold on building surfaces. That is, if the air does not stagnate in the attic, mold will not appear in the corners, no matter what materials are used for finishing.
- Long-lasting roofing resource. Excessive air humidity has a detrimental effect on the condition of the roofing material. Moreover, if moist air is not removed from under the roof, condensation will accumulate on the vapor barrier, which can reduce the resource of the insulation. A properly organized ventilation system will increase the life of the roof without the need for repairs.
Attic ventilation as it happens
The best option is a supply and exhaust system that works according to a natural principle, as shown in the diagram.
Under the eaves of the rafter roof, air vents are arranged through which the flow of fresh cold air is provided, while the warmer humid air will go into the skylights or other technological openings in the upper part of the gable or slope.
The preferred option when using modern roofing materials is a counter-grill with ventilation gaps. At the same time, air exchange in the insulated space of the attic is arranged separately, by means of a supply and exhaust system.
Keep in mind that ventilation in the attic must be planned and built as a complete system. That is, the project needs to provide for an air exchange system both in the attic and in the under-roof space, as well as pipe insulation and insulation of other communications. In addition, the ventilation design must be carried out taking into account the type of thermal insulation materials used.
Types of ventilation attic
The disadvantage of the system is excessive dependence on the temperature outside the house. That is, in the warm season, ventilation will be weak.
The advantage of the forced system is that it does not depend on climatic conditions: the exhaust air will be removed with the same efficiency both in winter and in summer.
Methods for venting air to the outside
Under the ridge bar on a pie made of corrugated board or metal tile, a duct is arranged with your own hands, covered with a mesh. The ventilation device is such that the condensate formed during the cold season will not drain into the room, but will flow out onto the slope.
The peculiarity of the solution is that the windows are constantly open, regardless of the season. In order to prevent the entry of animals and birds, decorative grilles are installed over the windows.
The advantage of special aerators over a conventional pipe embedded in the roof is a special design that prevents the formation and penetration of condensate into the room.
There are manual and automated valves on sale.
Attic ventilation: an overview of current schemes and ways to implement them
How to make ventilation in the attic? Read about the schemes and installation methods in the article
Ventilation and insulation of the attic
The advantage of the attic space is that the cost of living space is reduced by 30% compared to a new apartment. The use of an attic for housing allows you to increase the total area of the house by 20-30% and reduce heat losses through the roof by up to 7%.
Attic houses make it possible to organize a clear division of premises into day and night zones, and the second floor is used, as a rule, in the evening and at night. But the most important advantage of attic houses is that with the same composition of premises, they can reduce the occupied land area by 30-40% and, accordingly, reduce the length of the foundations.
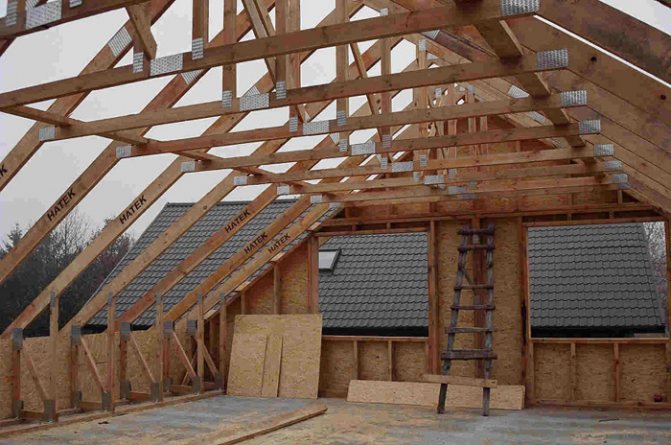
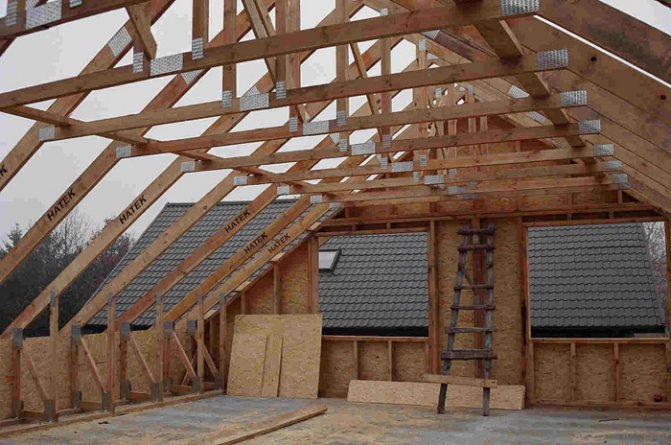
In essence, mansard roofs are the same frame structures, with the only difference that the frame of the attic room is adapted to the geometry of the roof (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Influence of roof geometry on the attic frame:
A - in a sloping roof with a span of no more than 6 m; B - in the frame structure of the attic with a span of 6-12 m: 1 - triangular truss; 2 - racks; 3 - struts of racks; 4 - frame struts; 5 - run; 6 - floor beams; 7 - external walls; 8 - inner wall; 9 - rafters; 10 - crossbar (overlap of the attic); 11 - crate
The role of the outer skin in such a frame is played by the roof covering. However, the specificity of the roof is somewhat different from the specificity of the walls, so there are some peculiarities here that must be taken into account.

Analyzing the accumulated experience in the construction of attics, it should be noted that during their construction a lot of mistakes have been made, both at the design stage and at the construction stage. Since mistakes made at the construction stage are mainly associated with unauthorized simplification of projects, it is very difficult to systematize them.
This is due to the negligence of the performers during the work, and sometimes to the blatant technical ignorance and incompetence. That is why, in any construction, a project must be drawn up, the requirements of which must be strictly followed. However, it should be noted that designers often make mistakes, which subsequently affect the quality of the constructed housing.
A cold roof over an unequipped attic or over a part of it, as a rule, does not create problems for the load-bearing part of the roof, as it is constantly ventilated. The temperature and humidity of the air in the attic are close to the outside, since the roof is directly laid on the lathing with gaps.
Only a thin wall of roofing, which usually does not have heat-saving properties, separates the attic space from the outside air. A warm attic and even more so an attic require adherence to a certain sequence in the placement of heat and waterproofing layers that separate the living space from the outside air.
The most significant mistake that is made during the construction of attic rooms is a violation of the ventilation regime of the roof. And since ventilation ensures the correct operation of the roofing "pie", it is here that the big troubles are laid, which become apparent during the operation of the attic.
With an increase in the moisture content of the insulation, its thermal conductivity increases, which results in the release of condensate, the formation of mold, moistening of rafters and battens, freezing of the roof and damage to the interior decoration of the attic room. Here is a short, sad summary of the lack of professionalism and ignorance of modern roof technology. Let us briefly consider what is the reason for the violation of the ventilation mode of the roof.
For the insulation of modern roofs, mineral wool is mainly used as one of the most effective insulation materials (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 Elements of mansard roof insulation:
1 - mineral wool; 2 - vapor and wind insulation (membrane); 3 - waterproofing; 4 - air flows; 5 - rafter; 6 - roof; 7 - attic sheathing
But, as practice shows, this material has the ability to accumulate moisture in itself not only through direct water absorption, but also drip, in the form of dew and fog. Therefore, measures related to limiting the ingress of moisture into the insulation and ensuring its output to the outside are the basis of the "vital activity" of the entire constructive scheme.
Roof ventilation is one of the most effective moisture control methods. Thanks to ventilation, the roofing material heats up less from the under-roof space, and the snow lying on the roof will melt evenly, which solves the problem of ice formation.
Provided that the roof covering (with proper installation) is reliable both steam and waterproofing, then the ventilation of the insulation is achieved through special units and devices. For this, ventilation gaps are provided in roofing systems (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3 A structure in which the floor beams go out onto the wall frame, and the ends of the rafters, cut at an angle, are laid on the board - "sole". It is the protruding beams that contribute to the formation of an air flow and allow you to lay insulation from the outside of the walls.
1 - floor beam; 2 - frame of the house; 3 - cornice board; 4 - board - "sole"; 5 - rafters; 6 - air flow
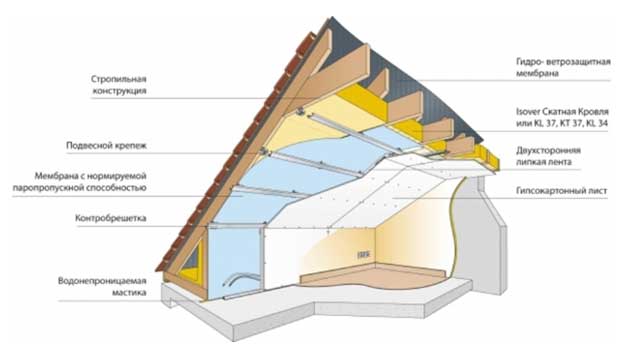
Modern roof structures, as a rule, involve, in addition to the main roofing, an additional layer of waterproofing in the form of a strong synthetic film. Due to the microperforation of the inner structure of these films, air vapor from the interior of the room can pass through the waterproofing membrane into the outer space.
Moisture from the outside does not penetrate through the film. Thus, the film allows you to keep the wooden roof structures dry, removing water vapor outside the attic. A roof insulation protected by a membrane will perform its functions much more efficiently.
Vapor-proof films form a barrier on the inner side of the roof insulation layer. These films protect the structure from heat loss and leakage, prevent the formation of moisture in the insulation. Such films are laid close to the heat-insulating layer, while the inner lining layer should lag behind the film by 4-6 cm. This is due to the fact that warm air coming from the room can also form condensation on the inner side of the film.
Depending on the material of the under-roof waterproofing, there are two ventilation schemes: two-layer and one-layer (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4 Two-layer (scheme A) and single-layer (scheme B) ventilation systems:
1 - vapor barrier; 2 - mineral wool; 3 - waterproofing; 4 - two air streams; 5 - one air flow
According to scheme A, the waterproof film must be installed with a gap in relation to both the roof and the insulation so that two air cavities are formed for free air movement from the eaves to the ridge.
These cavities must be open for air flow at the eaves overhang and for exhaust air at the ridge. With such a constructive solution, moisture that has got under the roof will drain along the film, and the condensed moisture will be eroded by the air flow, drying the insulation and the crate.
In this case, the film should not be allowed to touch the insulation, otherwise the condensation formed in it will moisten the insulation.
It is possible to lay the waterproofing directly on the insulation (Scheme B) only if the vapor-permeable membrane does not allow the penetration of external moisture and freely passes vapors from the insulation. The vapor permeability of such a membrane should be at least 750-1000 g / m2 per day. This is clearly seen in Fig. five.
Fig. 5 Value of ventilation gaps in various roof elements
A - general view of the roof; B - gaps in the ridge - not less than 0.05% of the area of both slopes; B - airflow in the eaves overhang - 0.2% of the slope area; G - the gap in the roof slope - 5 cm2 / m
In the ridge of the roof, the section of the ventilation gap (fragment "B") must be at least 0.05% of the area of both slopes. For one running meter of the ridge of the roof in the given example, the cross-sectional area will be 90 cm2 / m.
The area of the ventilation gap (fragment "D") per 1 m2 of the slope will be 5 cm2 / m2 in this case. In the eaves overhang (fragment "B"), the section of the ventilation gap should be 0.2% of the slope area. The minimum clearances for roofs with different slope lengths are shown in the table.
Minimum ventilation gaps for different roof elements
| Roof ridge | Ventilation area clearance on one side, cm2 / m | 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 |
| Roof slope | Height of vent. the gap between the waterproofing and the crate, cm | 2,4 2,4 2,4 2,4 2,6 2,9 3,1 3,3 3,6 3,8 4,0 4,3 4,5 4,8 |
| Eaves overhang | Ventilation area clearances, cm2 / m | 200 200 200 200 220 240 260 280 300 320 340 360 380 400 |
| Rafters length, m | 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | |
Practice shows that the design gaps are not enough, since errors in the laying of building structures and insulation lead to a narrowing of the gap in some places and, as a result, to a deterioration in roof ventilation with all the ensuing consequences. Therefore, it is not recommended to make a gap of less than 5 cm in order to ensure normal air circulation.
In addition, in complex roof structures and in the presence of various architectural elements (attics, parapets, dormers, etc.), the possibility of air circulation is sharply reduced. As a result, it is necessary to increase the height of the ventilation gap, which leads to an increase in the height and to the complexity of the roof structure. Therefore, it is not recommended to erect roofs of fancy configurations without special need.
Insulation of the roof is the main element on which the comfort of living in the attic depends. It is in the insulation that the builders' mistakes lie when ignoring the heat engineering laws.
As a rule, builders and designers lay down the thickness of the insulation, taking into account the climatic zone of construction and the thermal insulation properties of the material. The structural features of the roof are not taken into account.
In domestic practice, three roof insulation schemes are used:
- with a supporting frame located in a warm area
- with supporting frame located in the cold zone
- with a supporting frame located directly in the insulation
Since the attic floor is subject to heat loss to a greater extent than the lower floors, because it has a large surface of contact with the external environment, special attention must be paid to the problem of thermal insulation.
Considering that in the design and construction of attic rooms, gypsum plasterboard systems with a metal frame are currently very often used (Fig.4 and 5), then it is here that strategic mistakes are hidden, which negatively affect the thermal insulation properties of the enclosing structures.
Insulation of the roof is the main element on which the comfort of living in the attic depends. It is in the insulation that the builders' mistakes lie when ignoring the heat engineering laws. As a rule, builders and designers lay down the thickness of the insulation, taking into account the climatic zone of construction and the thermal insulation properties of the material. The structural features of the roof are not taken into account.
In domestic practice, three roof insulation schemes are used:
- with a supporting frame located in a warm area
- with supporting frame located in the cold zone
- with a supporting frame located directly in the insulation
Since the attic floor is subject to heat loss to a greater extent than the lower floors, because it has a large surface of contact with the external environment, special attention must be paid to the problem of thermal insulation.
Considering that in the design and construction of mansard rooms, gypsum plasterboard systems with a metal frame are currently very often used (Fig. 6 and 7), then it is here that strategic mistakes lie that adversely affect the thermal insulation properties of the enclosing structures.
Fig. 6 Facing attics on a metal frame:
А - fastening of bearing profiles using clamping hangers; B - fastening the bearing profiles using straight suspensions; 1 - putty with reinforcing tape; 2 - bearing profile; 3 - small-format gypsum fiber sheet; 4 - screw for GVL (30 mm); 5 - dowel
Fig. 7 Option for an attic structure using drywall:
1 - plasterboard sheet; 2 - polyethylene film; 3 - mineral wool; 4 - straight suspension; 5 - insulation (expanded polystyrene or mineral wool)
According to the laws of heat engineering, the appearance of a metal element in the insulation layer, in an area equal to 1% of the surface to be insulated, leads to an increase in heat losses through this area by 10 times. That is, if 1 m2 of the surface of the enclosing structure has a metal element in its layer, the area of which is 10 cm2, then we can assume that the insulation layer will work only for 10% of its heat-saving capacity, and the remaining 90% will not work.
Construction practice shows that when choosing the type of insulation, one must be guided by the following rules:
The supporting metal frame should be located in a warm area in cases where:
- the tightening of the rafter legs or metal frames pass inside the attic room
- the building facade is insulated from the outside.
The supporting metal frame should be located in the cold zone when:
- roof beams have a large overhang to the outside, for example, they serve as the supporting structure of a balcony canopy
- there is a need to minimize the construction height of the coating
In all cases of using metal elements in the roof frame, the thickness of the insulation layer should be increased by at least 40%. It is extremely important to carefully study the design of the roof assemblies associated with vapor barrier and waterproofing.
The desire to simplify the laying of these layers leads to the appearance of foci of condensation in the roof structure and to damage to the inner lining of the attic room.
Attic ventilation schemes and options
The specific type and scale of the ventilation system (more precisely, its selection) for the attic depends on several factors. When planning a diagram of how to make ventilation of the attic, the following factors must be taken into account:
- whether it is a residential attic or not;
- insulated or not;
- how often people will be there;
- what is its size (is it big or not).
There are no universal ways of organizing a ventilation system for an attic; in each case, one should proceed from the factors listed above.
Natural, with aerators
The effectiveness of the natural type of ventilation for the attic directly depends on how accurately ("according to the textbook") the insulation materials were installed. The main and mandatory rule for laying insulation materials is to leave ventilation spaces in the interlayer segments of the material used and directly in the under-roof area.
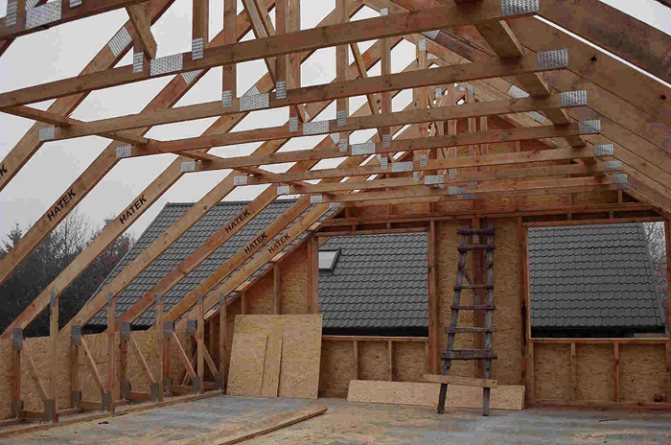


It is necessary to do ventilation of the attic even at the stage of roof construction.
Simply put, there should be a free ventilation space both between each layer of the applied insulation, and directly under the surface of the building's roof. The mechanism of operation of natural ventilation is based on natural (which is natural) draft.
Natural draft easily provides a constant supply of fresh air from the outside. In this case, the total area of ventilation ducts should be about 0.2% of the entire area of the attic. In most cases, it is advisable to use the ventilation installation option, in which the outlet of the ventilation ducts is carried out through the gables.
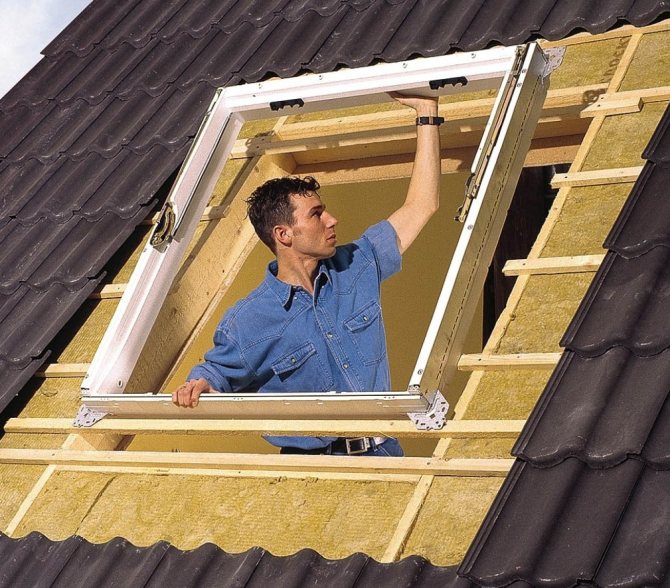
Natural with dormer windows
When implementing this ventilation method and installing dormer windows, one should be guided by the standards prescribed in SNiP 2-26 and SNiP 21-01. These standards state:
- installation of dormer windows is allowed only with a roof slope of at least 35 degrees;
- the minimum dimensions of the flaps should be 0.6x0.8 meters;
- the regulated dimensions of the dormer windows are 1.2x0.8 meters.
The shape of dormer windows installed in a private building can be of a wide variety of shapes, and ultimately depend on the general style of construction. Installation of skylights is carried out using frames at the stage of roof construction, together making up a single structure.
The ventilation system based on the use of skylights significantly improves the aesthetic appearance of the roof and also improves its basic functionality. In most cases, for a pitched roof, the best option would be to use windows with 1 inclined plane.
The installation scheme is quite simple: 2 beams are attached at the distance required by the regulations and then fixed by means of vertical posts, which are joined at the top with a jumper. Then the outer sides should be sheathed with cladding, and at the end on the side of the facade a decorative (with any style at the discretion of the building owners) grille is mounted.
Forced, with an exhaust fan
Given the relatively small area of the vast majority of attics, they do not need a forced flow. In about 95-99% of cases, it will be sufficient to install a forced exhaust system.
How to make an inflow depends on a number of circumstances, but in most cases the classic scheme is suitable. In the classical scheme, the supply system is organized through gaps, windows (due to micro-ventilation or simply opening a window, through a comb), window valves, or through the air duct system, if any.
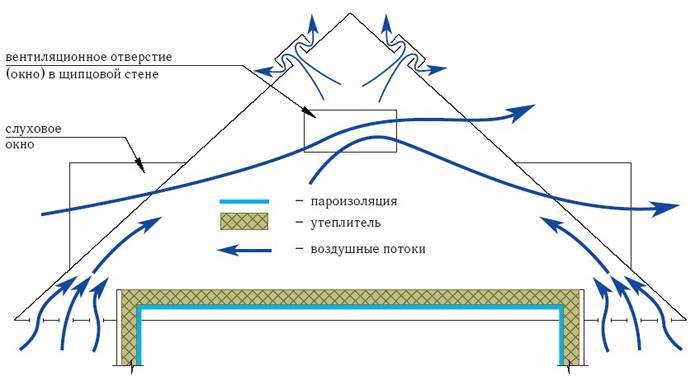

Attic ventilation system diagram
Methods for ventilating the attic through gables
There are several common technological methods that provide ventilation of the inner space of the attic floor and the building structures of which it consists:
- Ventilated pediment. This method consists in forming a ventilation gap between materials with different thermotechnical characteristics.
- Ventilation grills and windows. These elements ensure unobstructed air movement through the attic, which helps to reduce the pressure in the room. It is easiest to embed gratings or windows on the pediment, but installation on roof slopes is also possible.
- Ventilation valves.They are used in supply and exhaust ventilation systems, the movement of air flows can be natural or forced, provided by a fan. Functionally, the valves are equated to ventilation windows.
The listed ventilation methods can be used both individually and in combination with each other. They are also supplemented with aerators, turbo-reflectors and other similar devices.
Roof ventilation in a cold attic
In any room where there is no ventilation, a normal microclimate is impossible. Insufficient air exchange is the cause of stagnant air and high humidity, at the next stage, mold begins to grow on the structural elements and fungus starts. All these factors negatively affect the structure, over time it will begin to deform and lose its purpose. In a private house, the room under the roof can be warm or cold.
Differences between cold and warm roof ventilation
In the first case, the ventilation duct is equipped over the entire area of the slope with the help of a lathing and counter-lathing. Warm air masses enter the under-roof space at the eaves, rise and exit through the aerator in the roof strip. Condensation also leaves through it.
Many owners of private houses, where the premises under the roof are not heated, wonder if roof ventilation is needed in a cold attic, because no one lives there? Such a system should be in this case as well, since it will ensure the safety of the structure itself.
Only for an unheated room, it is arranged differently. In this case, air vents are created in the under-roof cornice for the flow of cold air, while warm air goes into the aerator and dormer windows in the attic in a private house.
Arrangement of roof ventilation for a cold attic
For an attic space, this is the level of the cornice. Holes need to be created here
It is very important to correctly calculate the size of the vents in the attic, so that the air inflow and outflow are the same. Often, owners of private houses use perforated spotlights.
To create an outflow of air from the attic, there are roofing elements such as aerators and a ridge. The direction of movement of streams is formed depending on the characteristics of a particular house:
- if the roof of the house has two slopes, ventilation ducts are made on the gables - loose overhangs or holes in the wall, the area of the channels should be 0.2% of the area of the attic,
- if slate or ondulin is used as a roofing material and no vapor barrier was used, then no additional structures are needed, since air will circulate along the waves of the coating, the ridge will serve as an outflow element,
- if the roof of the house is flexible or made of ceramics, a "turtle" (valve) is formed,
- a system of two grids has proven itself well, one is installed with holes in the downward direction, the other can be adjusted,
- on the hip roof, ventilation can be created using two holes, one of which is located at the bottom at the hem, the other at the ridge at the top,
- also on a hip roof, provided that the overhangs are wooden, you can place beams with a gap of several millimeters.
Sequence of work
- Calculation of air exchange According to SNiP, in cold attics, as in basements, dormer windows or vents are needed for air flow. In total, their area should be 1/400 of the total area of the room.
- The choice of the system of outflow and air inflow. After performing the calculations, you need to choose the system that will be optimal for your home: an aerator or a ridge, windows or air vents. Next, a diagram is drawn up, that is, how many ventilation elements there will be, their sizes, how they will be located.
- Execution of work. When creating a ventilation system in the attic, you should strictly adhere to the scheme.
Let's summarize
From the foregoing, it is clear that the work is not difficult for a home craftsman who knows how to hold a tool in his hands and accurately follow the recommendations of the project. But nevertheless, it is better to entrust the development of documentation to specialists. They will calculate the size of the air vents in the attic, their location and number, according to the characteristics of a particular room. A professionally created project will save you from mistakes and shortcomings, the consequences of which can be dire.
Roof ventilation in a cold attic
The need to create effective roof ventilation in a cold attic is associated with the formation of the required level of comfort in living quarters. Otherwise, heat loss and the formation of condensation are inevitable, and then the appearance of mold and mildew, and even deformation of the house.
Ventilation of the roof space
Ventilation of the space between the base of the roof and the insulation is necessary for several reasons.
- In the summer, depending on the type of roof, the area under the roof is subject to intense heating (especially in the presence of metal tiles). With poor ventilation, humid air accumulates and stagnates, which adversely affects the condition of the roofing elements. In addition, strong heating of the air under the roof contributes to the establishment of heat in the living quarters of a private house.
- In the cold season, when the outside temperature is freezing, and in the attic there is a plus, the snowfalls that accumulate on the roof melt. This leads to the ingress of water under the roof and the formation of ice, which can cause mechanical damage to parts of the roof.
- High humidity can weaken the thermal characteristics of the insulation or completely disable it.
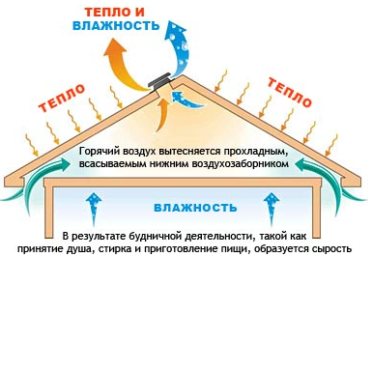

Guided by these factors, ventilation of the attic above the attic equipped with inflow and exhaust.
Roof ventilation purpose
Roof ventilation is designed to remove moisture from the space located between the outer moisture-proof material: tiles, corrugated board, slate, and internal roof structures.
The main functions that it performs:
- preventing the accumulation of unventilated air under the roof. This is especially true for houses with residential attics,
- elimination of the formation of frost and ice in the under-roof cavities,
- timely removal of moisture and dampness from the attic space.
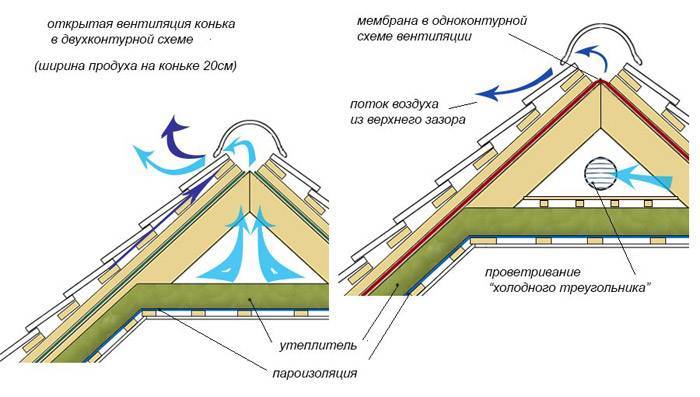

The need to install roof ventilation systems is caused by fluctuations in daily air temperatures, as a result of which condensation forms on the inside of the roof: in the winter in the form of frost, and in the summer - dampness.
This problem can be partially solved thanks to the device of the so-called "roofing pie", which includes a layer of steam and waterproofing. However, waterproofing layers cannot always and everywhere prevent the accumulation of dampness under the roof.
Moisture formed inside the "roofing cake" leads to a sharp drop in its performance. Since mineral wool slabs are usually used as insulation, they become denser under the influence of dampness and lose their thermal insulation properties. In winter, moisture accumulating under the roof turns into ice and, expanding, gradually destroys the attic structures. During the warmer months, dampness leads to the formation of mold and mildew, which can spread to the entire building.
All these problems can be eliminated by roof ventilation.
Device
With a cold roof
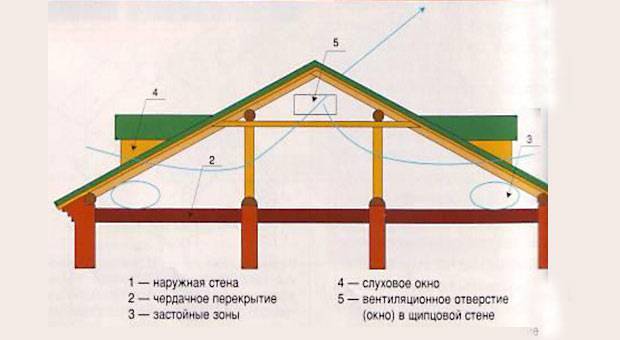

This is the simplest solution to the problem, since the attic space allows large volumes of air to move freely. Air vents located under the eaves, under the ridge strip, in the gables allow air masses to circulate due to natural convection:
- cold air is drawn into the attic from the outside through the eaves vents;
- warm air rises from the ceiling of the dwelling up under the roof and goes out through the ridge vents.
Of course, in this way it is impossible to completely level the temperature difference of the roof surface from the outside and inside, however, usually it is not enough for the formation of condensation on the inside of the attic.
As a rule, the number of vents located at the top and bottom of the slope of pitched roofs of a simple configuration is the same. The only condition under which normal circulation of the air flow is ensured is that the total area of the vents should be about 0.33% or ⅟300 of the slope area.
For a warm roof
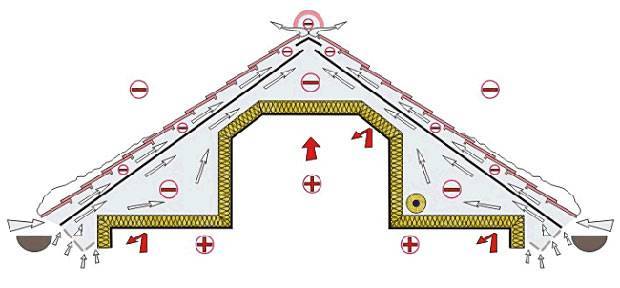

Attic ventilation is somewhat more complicated. In such a design, air cannot circulate freely, since it is almost entirely occupied by attic rooms.
Air circulation in the residential attic located in the under-roof space is provided by a convective flow directed from the eaves towards the ridge. In order for it to pass this path unhindered, additional space is created in the roofing pie between the layers of thermal and waterproofing using a counter-lattice and lathing. The gap must be at least 5 cm high.

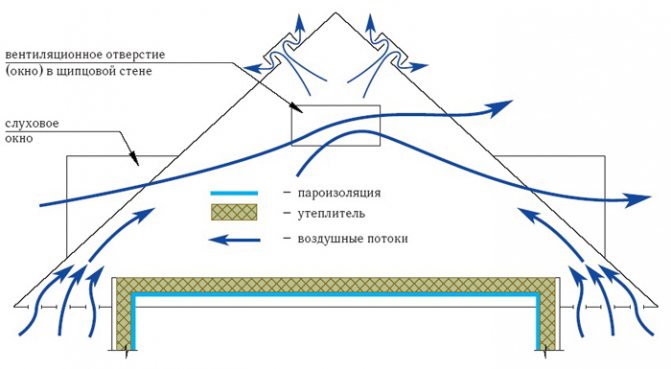
Then, in the space under the roof, a ventilated circuit is formed, that is, they provide the flow of air, as well as its exit with vapors:
- inflow: eaves overhang along the bottom of the roof, then, attic windows (above them), valley or others, where the contour is interrupted;
- exit: ridge, attic windows (under them), junctions, that is, where they need to be made on purpose.
Attention! It is important to ensure the continuity of the circuit in order to exclude the formation of "stagnant zones", places of possible accumulation of condensate

attic ventilation
Roof Ridge Aerator
The ventilation output to the roof is carried out using a ridge aerator, which should:
- ensure effective ventilation of the space under the roof;
- maintain an optimal indoor climate;
- extend the service life of the roof structure.
The modern ridge aerator is suitable for any kind of roof. It is installed in place of the ridge and consists of individual segments: structural ribs, dividing walls, connecting elements and plugs.
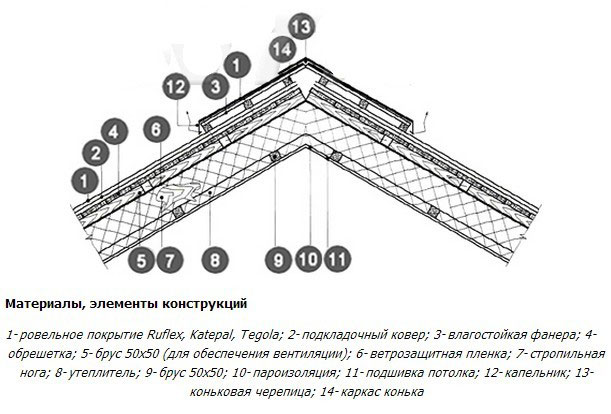

Ridge node of the attic roof with aerator and soft roofing.
Installation of a skate aerator has general rules
- Placement on roofs with a slope of 14-45 °.
- Obligatory presence of ridge vents.
- Installation of a ventilation ridge along the entire ridge girder.
- The location of the ridge cuts at a distance of 30 cm from the chimney, the edges of the outer wall and other through elements of the roof.
- Creation of a sealed ventilation ridge structure.
Required tools for installing the ventilation ridge:
- a circular saw;
- cord for marking (lace);
- a hammer;
- special scissors;
- roulette;
- sealing mastic;
- gun for sealing mastic.
Roof ventilation from metal tiles and corrugated board
If the builders are conscientious, then under the corrugated board (metal tile) they had to lay waterproofing - some kind of appropriate roll material. For what? In cold weather, condensation forms on the inside of the metal, which flows in real streams ... guess where. In addition, moisture can penetrate through the roofing material itself and also flow to the ceiling. In addition, steam penetrates through the ceiling and condenses on the metal tile / corrugated board and also flows down - not like steam, but like water ...
So: we put waterproofing under the metal roofing materials, and ventilation should be carried out between the roofing material and the waterproofing membrane so that moisture can quickly be removed from the waterproofing surface.
It is technically simple to make roof ventilation from corrugated board or metal tile: using a counter-lattice:


The counter-lattice is a slats of 25x50 mm, attached over the waterproofing to the rafters. The counter-lattice also provides the gap necessary for ventilation of the roof.
It is necessary to lay waterproofing under the corrugated board or metal tile, even if the attic is not planned to be made warm, that is, insulation will not be laid between the rafters. And you also need to make a counter-lattice. And in the presence of a warm (residential) attic or attic, ventilation of the roof in the manner discussed above is especially important.
How to make ventilation attic in a private house
At the design stage of the future home, it is important to think not only about the convenient layout of the premises.
Coziness in the house cannot be provided for a long time if you do not pay attention to such an important point as the ventilation of the attic in a private house
This is no less important than the insulation of the attic, because the lack of well-designed ventilation will lead to the fact that living in the house will soon be uncomfortable, and the service life of the house will be drastically reduced


The lack of ventilation can lead to a reduction in the life of the roof due to the appearance of mold on it, and in the house itself you can not hope for a comfortable stay. In summer, when the roof heats up and its temperature becomes more than 100 degrees, it will be very hot in the house, and at low temperatures, condensation will form in the attic. due to which wooden roof structures will rot.
The main purpose of the ventilation system is to provide heat exchange. The temperature of the air and the roof is mixed, and as a result, a comfortable microclimate is created in the house.
Let us consider in more detail the situation when the ventilation of the attic is bad, or there is none at all.
In winter, part of the heat from the room still leaves even through a high-quality insulation. At the same time, the roof heats up, and unevenly, only above the room. Here the snow begins to melt and flows down to the edge of the roof, where it remains cold above the overhang. Ice that forms on the eaves of the roof does not allow melted snow to drain, and it begins to penetrate under the roof. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to ensure that the temperature throughout the roof is leveled and moisture is removed - for this, ventilation of the attic is needed.
What is ventilation in the attic and why is it needed
Air exchange in the under-roof space is important at any time of the year. In the summer, ventilation helps to avoid overheating of the house from the hot roof covering, especially if the latter is made of metal materials.
In winter, warmth and moisture emanating from the house contribute to the formation of frost and, as a result, dampness. This problem cannot be avoided without intensive ventilation.
If, in addition to the lack of ventilation, the heat-insulating layer is not properly made, in winter the roof can heat up to above-zero temperatures, leading to thawing of the lower layer of snow and the formation of an ice crust and icicles during the thaw period.
Without air exchange in the space under the roof, the microclimate throughout the house is disturbed: on sunny summer days, living quarters will quickly heat up, and from autumn to spring, condensation will accumulate under the sheathing. Accordingly, without the release of steam, which is formed as a result of the vital activity of the inhabitants of the house, the humidity will increase in the rooms as well.
But the main danger of the lack of air exchange is that the wooden elements of the roof will wear out much faster than the time allotted to them. Moisture contributes to the accelerated process of decay, fungal and mold damage.


Therefore, ventilation of the roof space is indispensable.
In addition, it is important that the air exchange is efficient. What you need to consider when arranging ventilation in the attic:
- The area of the holes should correspond to the area of the attic. The ideal ratio is 1 to 500 (1 square meter of ventilation per 500 square meters of space).
- The entire internal space of the roof must be involved in the air exchange. If the air stagnates in some areas, condensation or frost will form.
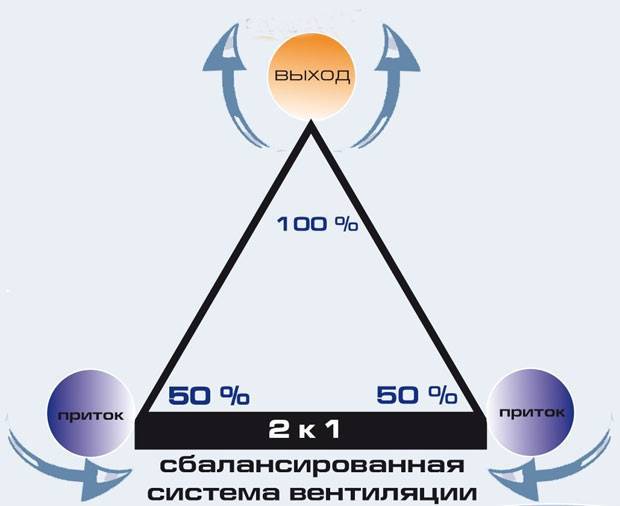
- The ventilation system should have two channels: through one air enters, through the other it goes out into the street.
The most difficult stage of the work is the calculations. Too many or too large air vents are just as bad as insufficient air space. This task is best left to specialists.
How is the ventilation of the attic carried out?
Ventilation of the attic takes place through holes evenly distributed along the entire perimeter of the roof. The cross-sectional area of these holes must correspond to the roof and ceiling area. Violations of these requirements entail large heat losses from the premises, the formation of ice on the roof with all the negative consequences.
The table below shows recommendations for the size of the ventilation holes (the table is a little curve, but another was not found; to enlarge the table, click):
The top line shows the width of the ceiling (5, 6, 7.5, 8.5, 9.5-10 m). In the column "Condition" - exactly which and where to leave the holes. The second column is an explanation of the third: either the number indicates the area of the hole, or the width of the slots.
The most optimal (effective) option is the holes on the bottom and on the ridge (continuous slots on the overhangs and on 2 sides of the ridge):
With such openings, ventilation works in any weather and in any wind. In other conditions, full ventilation occurs only with a sufficiently strong wind.
Of course, for ventilation, you do not need to make holes in the ridge, ridge elements with ventilation are available ready-made.
If it is not possible to leave gaps in the ridge itself, then special elements (aerators) are placed as close to the ridge as possible.
If the roofing material itself has a wavy shape (corrugated board, slate), then there are no problems at all and there is nothing to bother with, live happily ever after with your roof ... or under your roof? 

Is ventilation of the attic floor necessary, and why
It is imperative to equip a ventilation system in the attic space, since it allows you to solve several very serious problems with the microclimate at once. At the same time, you can equip it with your own hands with a relatively small budget for work.


Consequences of lack of ventilation in the attic
Properly done attic ventilation solves the following problems:
- Elimination of excess moisture and prevention of dampness in heat-insulating (insulation) materials. That is, ventilation protects thermal insulation materials from wear and tear and functional damage.
- A significant reduction in the likelihood of the appearance and accumulation of colonies of fungi and mold, which creates additional protection for wooden roofing items (and also protects the health of those living in the building).
- Protection against the drift of too hot air masses into the building during periods of intense heat (heat) in the external environment (outside).
- Protection against moisture accumulation, and, as a result, protection of corrosive phenomena that can damage metal structures.
- Protection against the appearance of icicles under the eaves in winter (especially in severe frosts).
- Significant savings in electricity required for optimal heating of the attic for the winter and, sometimes, autumn periods (in general, during the cold season).
Roof ventilation elements
For the device of the inflow, air vents are used, located under the eaves or roof sheathing. The number and sizes of openings providing air intake are calculated depending on the area and volume of the roof.
The volume of the roof for the same area may differ. This is due to the fact that different shapes of roof slopes have different angles of inclination. This factor should be taken into account when calculating ventilation.
The air vents are covered with ventilation grilles.
Exhaust of humid air takes place in the upper part of the roof (at the ridge). The ridge is the final element of the roof and at the same time the point of maximum accumulation of moisture and stagnant air masses. To remove the latter, ridge vents are used, similar in principle to a pipe deflector. In addition to these devices, ventilation holes, called aerators, are also made on the roof slopes. Their task is to ensure the function of the hood. Depending on the slope of the slope, these holes are closed with a special grid made of flexible tiles.
Ventilation of the attic can also be carried out through openings located on both sides of the house in the gables. This solution is suitable for roofs with a steep slope. In this case, ventilation of a larger space is required.
In some cases ventilation of the attic under-roof space produced by installing dormer windows.
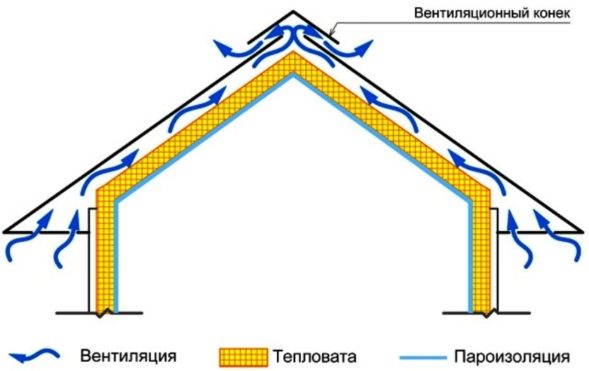

Exhaust ventilation type
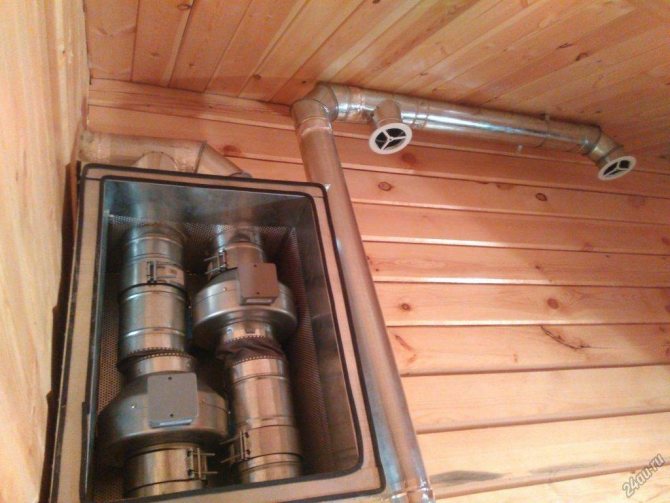


A positive answer to the question whether ventilation is needed in a wooden house is based on many years of experience in the construction and operation of private households. The organization of the air flow is the basis of the principles of exhaust ventilation. The air intake must be unimpeded. Naturally supplied ventilation supplies the house with air from the street. Main advantages:
- profitability;
- simplicity of the ventilation system design;
- availability.
Exhaust ventilation in a private wooden house is provided at the design stage. It is a central highway with branches, which are designed to ensure the outflow of air from all rooms of the house. To increase the efficiency of operation, the exhaust ventilation is equipped with fans mounted at the inlets of the ventilation ducts. The power of the fans is different, therefore it is selected based on the volume of the room. Fans are economical, there are models with automatic operating modes.
Forced ventilation attic
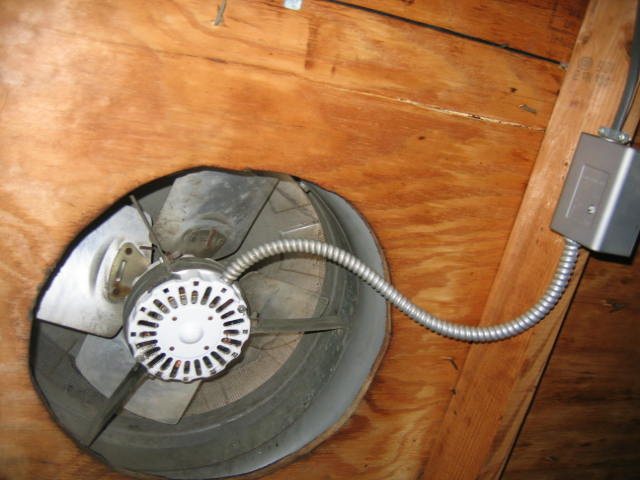


Fan for forced ventilation attic
The forced ventilation system in the attic implies the installation of additional equipment that allows artificial air movement.
Moreover, these devices can be installed both on the air supply system and on the hood. Installation of equipment on both holes is also permissible.
This system is much more effective than the natural one. And first of all, it does not depend on weather conditions. This means that no matter what happens, there will always be fresh air in the attic.
Of the minuses, it should be noted the high cost of equipment, the laboriousness of calculations and installation of the system, as well as significant consumption of electricity required to maintain the operation of the fans.
Mixed ventilation is the most efficient system. In this case, if necessary, air supply is provided by forced draft devices, but a transition to natural air exchange is also possible.
The most efficient ventilation is supply and exhaust. In this case, the fans are installed on the duct for both the supply and discharge of air.
Ventilation system installation
Before starting the installation of the ventilation system of the attic rooms, it is required to make a project and calculate all the necessary parameters.
At the same time, at the design stage, the entire attic of a residential building should be carefully measured and all important dimensions and parameters required for the calculation and installation of the ventilation system should be recorded.
If the choice fell on a forced-type system, it is important to choose a fan of the appropriate power. During installation, you should adhere to a certain order of actions:
During installation, you should adhere to a certain order of actions:
Referring to the diagram, mark all ventilation elements, including valves and a chimney. Make holes in the roof using a special tool.For supply valves, through holes must be made in the cornice or pediment
It is important to take into account that the supply valves are located below the exhaust valves. Install the required valves. The slots must be sealed. A pipe cover is installed on the roof and firmly fixed
Before installing the pipe itself, you need to make sure that all joints are reliably sealed. The pipe must be installed strictly in a vertical position, taking into account all the required distances. Inside the room, a fan is mounted on the pipe, and a deflector is installed outside. The system can then be used.
A test for air exchange in the room is carried out for several days.
Correct installation of ventilation will ensure the most efficient supply of fresh air, and optimal removal of exhaust air. Any violations during the installation of the structure will significantly reduce the efficiency.
Natural ventilation in the attic
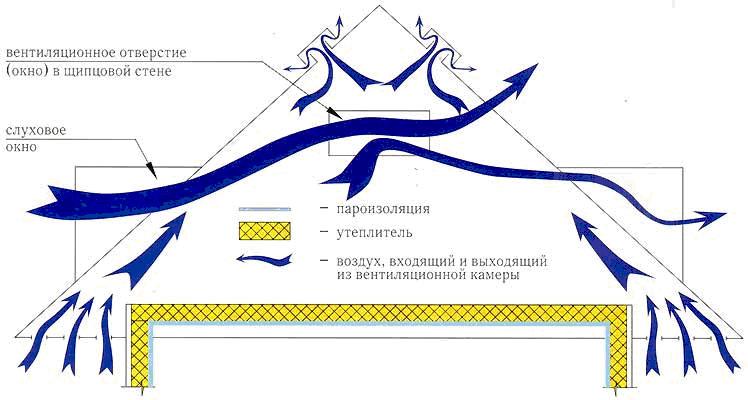

Simple natural ventilation of the attic
The effectiveness of natural ventilation in the attic depends entirely on how correctly insulating materials are laid.
When installing insulation, it is important to ensure the presence of special holes located between its layers and the roof.
The principle of such air exchange is based on physical processes in which warm air rises and cold air descends.
With correctly located supply and exhaust openings, a natural draft is created, which ensures the supply of fresh air and the removal of waste air.
The total area of such a system is calculated based on the fact that the area of the holes should not exceed 0.2% of the total area of the room.
The simplest, but at the same time very effective way is the organization of air exchange through the gables. However, this method is not applicable to stone structures.
The dimensions of the gap that must be left for easy air transmission depend on the material from which the roof is made:
- If the roof is made of metal profiles, metal tiles or shingles, the gap should be made no more than 2.5 cm.
- If soft materials or flat surfaces are used, the allowable gap is no more than 5 cm.
- If, in addition to insulation, waterproofing is also installed, the distance between these layers should be from 2 to 3 cm.
In order for natural air exchange to be effective, it is required to ensure the tightness of the ventilation cavities. It is thanks to this that you can achieve good traction and the absence of "dead zones".
It functions best during the cold season, when the delta between indoor and outdoor temperatures is at its maximum.
Another design solution is the installation of skylights on the roof. The shape of such windows can be any, it all depends on the taste of the owner of the building.
It should be noted that the installation of such structures not only improves the appearance of the house, but also increases the efficiency of natural ventilation.
The advantages of natural air exchange include ease of installation and relative cheapness. Of the minuses, it is important to note that the efficiency of work directly depends on the ambient temperature.
In very hot weather, the attic may generally be left without ventilation.
DIY installation
Before you start arranging the ventilation of the attic with your own hands, you need to create its project, carefully think over the layout of the components included in it, write down the sequence of work on paper. In the process of preparation, it is imperative to inspect all sections of the attic room, make the necessary measurements, and note the design features of the attic. When performing forced ventilation, it is necessary to select an exhaust fan with the appropriate technical characteristics. The sequence of installation work:
- On the diagram, according to the established designations, the fixing points of the valves and the section for laying the exhaust pipe are marked.
- In the roof, you need to drill holes with a drill or punch. These works are carried out very carefully so as not to damage the layers of the roofing cake, the construction of which includes a roof covering, lathing, waterproofing, insulation and vapor barrier layers. Openings for supply valves are made in the cornice or pediment. Be sure to consider the placement of the supply and exhaust ducts. The first ones are equipped below.
- The valves are being installed in the wall. A tube is inserted into the pre-drilled hole, which is closed by a grill from the street side. A filter is installed on the inside and the valve body is attached. All these items are included with the valve. The gaps between the structural elements and the wall surface are carefully sealed.
- On the surface of the roof, where the hole for the pipe is drilled, the overlay is securely fixed, the quality of the sealing of the connecting sections is checked. Next, the pipe is installed strictly vertically. It is imperative to maintain all calculated distances.
- From the inside of the building, a fan is mounted to the pipe, and from the outside, a deflector. The ventilation system is ready for use. The effectiveness of its work is tested for several days.
It is important to understand that properly equipped mansard roof ventilation is one of the conditions for comfortable living in a country house. When arranging it with your own hands, it is imperative to comply with the established building codes, design together with the structure of the house and equip it at the stage of erecting the roof of the building .. https://www.youtube.com/embed/VGCQE8ZgaSE
Single Vented Gap System
When arranging the ventilation system of a pitched roof, it is worth considering that the size of the ventilation duct directly depends on the length of the slopes and the angle of the roof.


Ventzazor is designed during the development of the roof model
According to SNiP II-26-76:
- the height of the gap is no more than 5 cm, an increase in the indicators of which can lead to the formation of turbulence, which will significantly reduce air exchange;
- with a cover length of more than 10 m, forced ventilation is required;
- ventilation system openings must be reliably protected from debris.
Attic ventilation functions


A living attic cannot be without good air exchange
The ventilation system during a particularly hot period allows you to eliminate stuffiness, but in winter it effectively prevents cold and moisture from entering the room. That is why an important point is the correct installation of the ventilation system with your own hands, because:
- the system removes moisture and prevents the formation of dampness in the insulation material - it is thanks to ventilation that the heat insulator retains its functionality for many years, preventing the penetration of heat and cold;
- with properly created ventilation, the formation of fungus and mold is minimized, thereby eliminating the possibility of premature destruction of wooden roof elements;
- in extreme heat, it prevents hot air from entering the house;
- prevents the accumulation of moisture, thereby preventing corrosive manifestations that negatively affect the metal tile;
- eliminates the formation of icicles under the eaves in severe frosts;
- saves energy, thereby reducing the costs required to heat a residential attic in winter.
What is the ventilation of the attic room
Given that the attic belongs to a residential area, then the arrangement of this attic area should be proper. The premises must be safe, and insulation must be carried out taking into account year-round use.
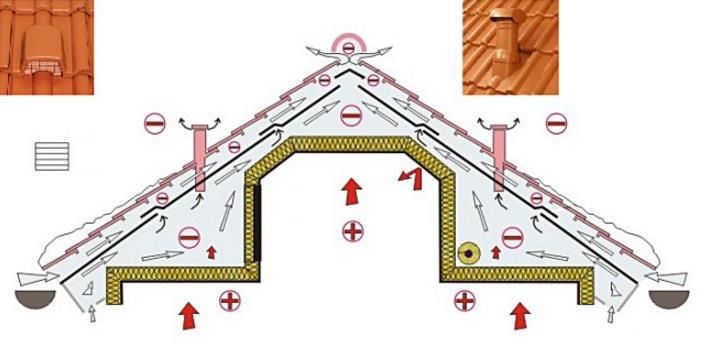

Attic floor ventilation scheme Source bitumka.com
To ensure a favorable microclimate and comfortable living conditions, ventilation of the attic under-roof space must be carefully thought out. It is necessary to ventilate not only the rooms, but also the roof itself for the long-term preservation of the elements of the roof in proper condition.
Ventilation of the attic room can be:
- Natural. In this case, natural draft is used, which is formed with the correct location of the ventilation ducts and openings. This is the least expensive option of all. It is equipped with grilles, aerators, spotlights, ventilation pipes and other elements.
- Forced. It occurs with the help of mechanical action with the use of fans for inflow and outflow, additional devices for heating cold air from the street. This is the most expensive way to ventilate an attic room, especially when using climatic equipment with wide functionality (indicators of temperature, humidity, humidification, ionization, heating).
- Mixed. There is only one mechanical process (air inflow or outflow). More often, a mechanical hood is used with the launch of fresh air in the form of gravity.
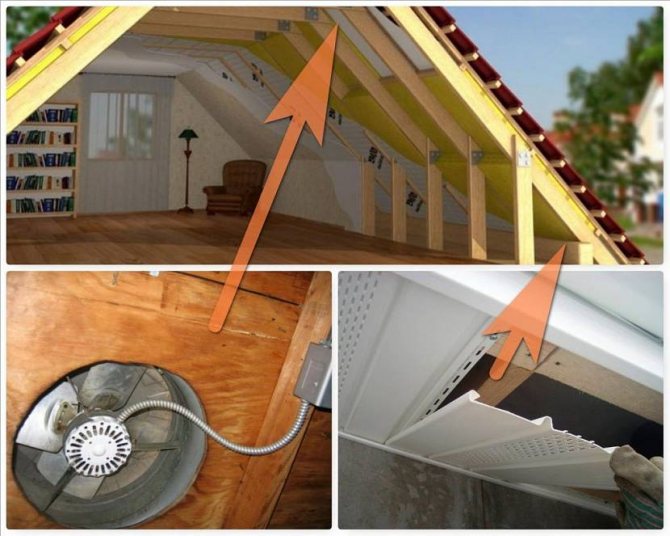


Mixed ventilation operation Source nashicherdaki.ru
See also: Contacts of construction companies that offer roof repair and design services.