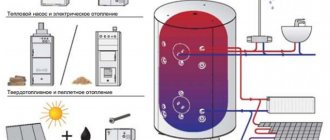
The procedure for calculating heating in residential buildings depends on the availability of heat meters and on how the house is equipped with them. Often, after the next payment of large bills for heating, tenants of multi-storey buildings think that somewhere they were deceived. In some apartments you have to freeze every day, in others, on the contrary, they open the windows to ventilate the premises from the intense heat. In order to completely save yourself from the need to overpay for excess heat and to save money, you need to decide on how exactly the calculation of the amount of heat for heating the home must be performed. Simple calculations will help to solve this, by means of which it will become clear how much heat entering the batteries of houses must have.
Gcal and Gcal / h: what is the difference
If it is necessary to calculate the payment by the consumer for the services of state heat power engineering (heating at home, hot water), such a value as Gcal / h is used. It denotes a reference to time - how many Gigacalories are consumed during heating for a given period of time. Sometimes it is also replaced by Gcal / m3 (how much energy is needed to transfer heat to a cubic meter of water).
The value of Gcal / h can be calculated independently using this formula:
Q = V * (T1 - T2) / 1000, where
- Q is the amount of heat energy;
- V is the volume of liquid consumption in cubic meters / tons;
- T1 is the temperature of the incoming hot liquid, which is measured in degrees Celsius;
- T2 is the temperature of the supplied cold liquid by analogy with the previous indicator;
- 1000 is an auxiliary coefficient that simplifies calculations, eliminating the numbers in the tenth place (automatically converts kcal to Gcal).
This formula is often used to build the principle of operation of heat meters in private apartments, houses or businesses. This measure is necessary in case of a sharp increase in the cost of this utility service, especially when the calculations are generalized based on the area / volume of the room that is heated.
If a closed-type system is installed in the room (hot liquid is poured into it once without additional water supply), the formula is modified:
Q = ((V1 * (T1 - T2)) - (V2 * (T2 - T))) / 1000, where
- Q is the amount of heat energy;
- V1 is the volume of the consumed thermal substance (water / gas) in the pipeline through which it enters the system;
- V2 is the volume of the thermal substance in the pipeline through which it returns back;
- T1 is the temperature in degrees Celsius in the pipeline at the inlet;
- T2 - temperature in degrees Aim in the pipeline at the outlet;
- T is the cold water temperature;
- 1000 is an auxiliary coefficient.
This formula is based on the difference between the inlet and outlet values of the heating medium in the room.
Depending on the use of one or another energy source, as well as the type of thermal substance (water, gas), alternative calculation formulas are also used:
- Q = ((V1 * (T1 - T2)) + (V1 - V2) * (T2 - T)) / 1000
- Q = ((V2 * (T1 - T2)) + (V1 - V2) * (T1 - T)) / 1000
In addition, the formula changes if electrical devices are included in the system (eg underfloor heating).
Why is it needed
Apartment buildings
It's very simple: gigacalories are used in calculations for heat. Knowing how much heat energy is left in the building, the consumer can be billed quite specifically. For comparison, when central heating is operating without a meter, the bill is billed for the area of the heated room.
The presence of a heat meter implies horizontal sequential or collector wiring of heating pipes.supply and return pipe bends are installed in the apartment; the configuration of the apartment system is determined by the owner. Such a scheme is typical for new buildings and, among other things, allows flexible regulation of heat consumption, choosing between comfort and economy.
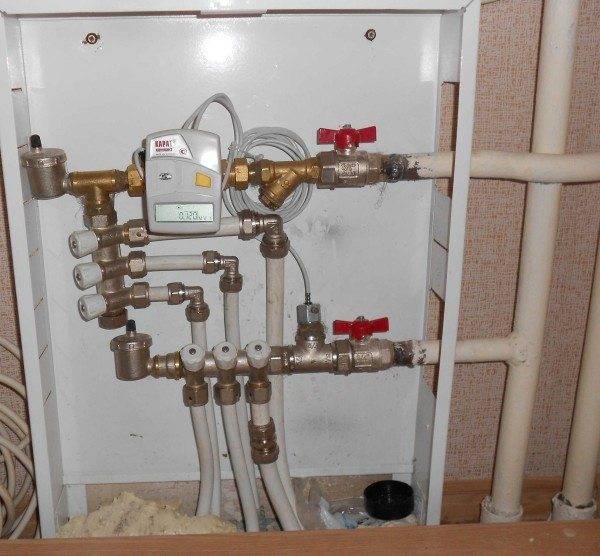


Horizontal collector wiring in the apartment.
How is the adjustment carried out?
- By throttling the heating devices themselves. The throttle allows limiting the radiator's permeability, reducing its temperature and, accordingly, the heat consumption.
- Installation of a common thermostat on the return pipe. The flow rate of the coolant will be determined by the temperature in the room: when the air is cooled, it will increase, and when the air is heated, it will decrease.
Private houses
The cottage owner is primarily interested in the price of a gigacalorie of heat received from various sources. We will allow ourselves to give approximate values for the Novosibirsk region for tariffs and prices in 2013.
The cost of a gigacalorie, taking into account transport costs and the efficiency of the heating installation, rubles