Do not overdo it
It should also be noted that 14-15 sections for one radiator is the maximum. It is ineffective to install radiators in 20 or more sections. In this case, divide the number of sections in half and install 2 radiators with 10 sections each. For example, put 1 radiator near the window, and the other near the entrance to the room or on the opposite wall. In general, at your discretion.
Steel radiators are the same story. If the room is large enough and the radiator comes out too large, it is better to put two smaller ones, but with the same total power.
If there are 2 or more windows in a room of the same volume, then a good solution would be to install a radiator under each of the windows. In the case of sectional radiators, everything is quite simple.
14/2 = 7 sections under each window for a room of the same volume
But, since such radiators are usually sold in 10 sections, it is better to take an even number, for example 8. A stock of 1 section will not be superfluous in case of severe frosts. The power will not particularly change from this, however, the inertia of heating of the radiators will decrease. This can be useful if cold air is frequently entering the room. For example, if it is an office space that customers often visit. In such cases, the radiators will heat up the air a little faster.
What to do after calculation
After calculating the power of heating radiators for all rooms, it will be necessary to select a pipeline in diameter, taps. Number of radiators, length of pipes, number of valves for radiators. Calculate the volume of the entire system and select the appropriate boiler for it.
For a person, home is often associated with warmth and comfort.
And in order for the house to be warm, it is necessary to pay due attention to its heating system. Modern manufacturers use the latest technologies for the production of various elements of heating systems
However, without proper planning of such a system, these technologies may be useless for certain premises.
Steel panel radiators are a competitor to the usual section-type heating devices. They are attractive because, in comparison with all sectional models, with smaller dimensions, they have a higher heat transfer coefficient. They consist of panels in which the coolant moves along the formed passages. There can be several panels: one, two or three. The second component is corrugated metal plates, which are called ribbing. It is due to these plates that a high level of heat transfer of these devices is achieved.
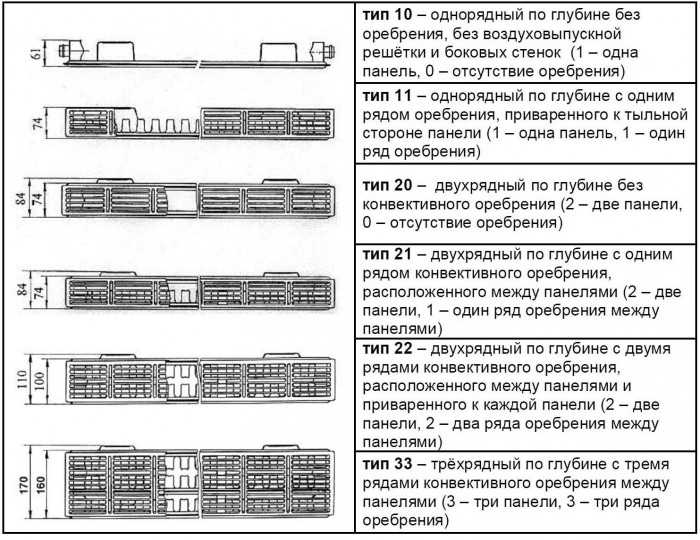
To obtain different heat output, panels and fins are combined in several versions. Each version has a different capacity. To choose the right size and power, you need to know what each of them is. By structure, steel panel batteries are of the following types:
- Type 33 - three-panel. The most powerful class, but also the largest. It has three panels to which three finning plates are connected (therefore it is designated 33).
- Type 22 - two-panel with two fins.
- Type 21. Two panels and between them one corrugated metal plate. These heaters, with equal dimensions, have a lower output compared to type 22.
- Type 11. Single-panel steel radiators with one fins. They have even less thermal power, but also less weight and dimensions.
- Type 10. This type has only one heating medium panel. These are the smallest and lightest models.
All of these types can be of different heights and lengths. Obviously, the power of panel radiators depends on both the type and the size. Since it is impossible to calculate this parameter independently, each manufacturer draws up tables in which he enters the test results.These tables are used to select radiators for each room.
Installation and maintenance features
Each steel radiator Kermi (Fko or FKV, does not matter) is equipped by the manufacturer with a special dividing plug, which must be correctly installed after the device is installed. It is she who separates the coolant, ensuring the sequence of connecting the panels.
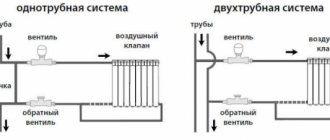
If the bottom connection is made according to the "Leningrad" principle, then the plug is not mounted, and the Therm-X2 effect will not work.
In the event that old heating devices are replaced with Kermi steel radiators, special adapters will be required that adjust the distance between the pipes.
Like other types of heating devices, Kermi brand radiators need regular cleaning. As a rule, they are equipped with lids that tightly seal the inside of the device. They can be removed using a "key", which is the company's logo, made on a plastic plate. It needs to be pulled back slightly so as not to scratch the paint and turned counterclockwise until it comes off. After removing it, you can remove the sides and cover and start cleaning the radiator.
Steel radiator Kermi bottom connection - diagram (pdf):

Recently, it has become popular to change metal pipes to polypropylene ones. Wrapping a panel steel radiator Kermi with polypropylene is a good addition to a quality device.
These pipes are capable of withstanding pressures up to 25 bar and have a long service life of up to 40 years. If the strapping is made by soldering using a special apparatus, then the service life of the radiators can be significantly increased.
Summing up, we can say that Kermi steel panel radiators are one of the highest quality, reliable and powerful heating devices made of this material on the domestic market. Their only drawback is the high price, which is fully compensated by the long battery life.
Determine the power
The power of steel panel radiators must be determined based on the heat loss of the room in which they will be installed. For apartments located in standard buildings, one can proceed from the SNiP standards, which normalize the required amount of heat per 1m 3 of the heated area:
- Premises in brick buildings require 34W per 1m 3.
- For panel houses for 1m 3 it takes 41W.
Based on these standards, you determine how much heat is required to heat each of the rooms.
For example, a room in a panel house 3.2m * 3.5m, ceiling height 3m. Let's calculate the volume 3.2 * 3.5 * 3 = 33.6m 3. Multiplying by the SNiP norm for panel houses, we get: 33.6 * 41 = 1377.6W.
SNiP standards are indicated for the middle climatic zone. For the rest, there are corresponding coefficients depending on the average temperatures in winter:
- -10 o C and above - 0.7
- -15 o C - 0.9
- -20 o C - 1.1
- -25 o C - 1.3
- -30 o C - 1.5
Correction of heat loss is also needed, depending on the number of external walls, because it is clear that the more such walls, the more heat goes through them. Therefore, we take them into account: if one wall goes out, the coefficient is 1.1, if two, we multiply by 1.2, if three, then we increase by 1.3.


Let's make adjustments for our example. Let the average winter temperatures in the region be -25 ° C, there are two outer walls. It turns out: 1378W * 1.3 * 1.2 = 2149.68W, round off 2150W.
Let's use this figure as an example. Provided that the insulation near the house and windows is average, the figure found is quite accurate.
Recalculation of the power of panel radiators depending on the temperature regime
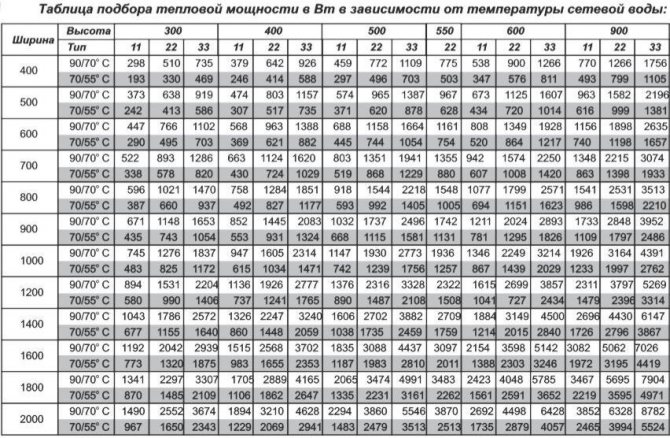
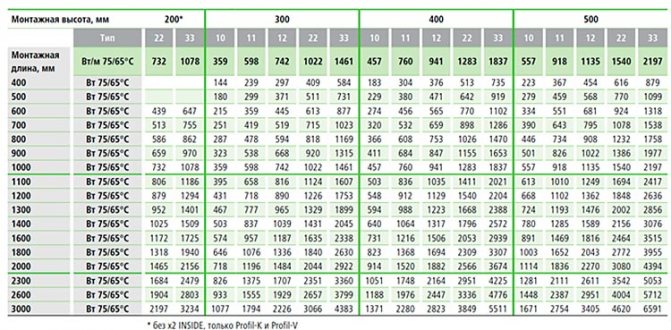
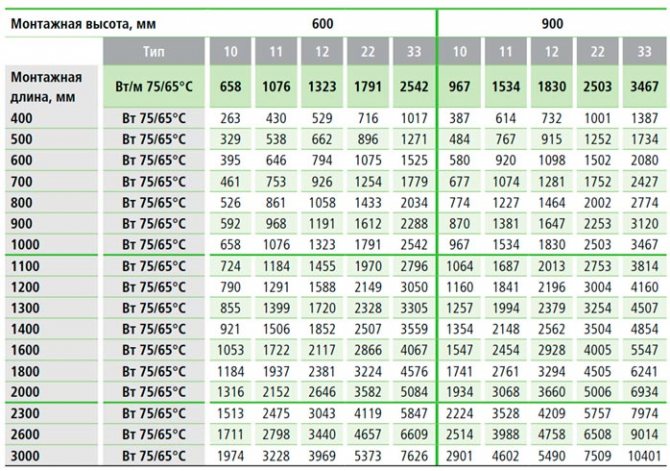
But the values in this table are valid for a system with parameters 75/65/20 (flow temperature 70 ° C, return 65 ° C, the room is maintained at 20 ° C). These values are used to calculate the temperature delta: (75 + 65) / 2-20 = 50 ° C.
If the parameters of your system are different, recalculation is necessary.For such cases, Kermi compiled a table with corrective coefficients.
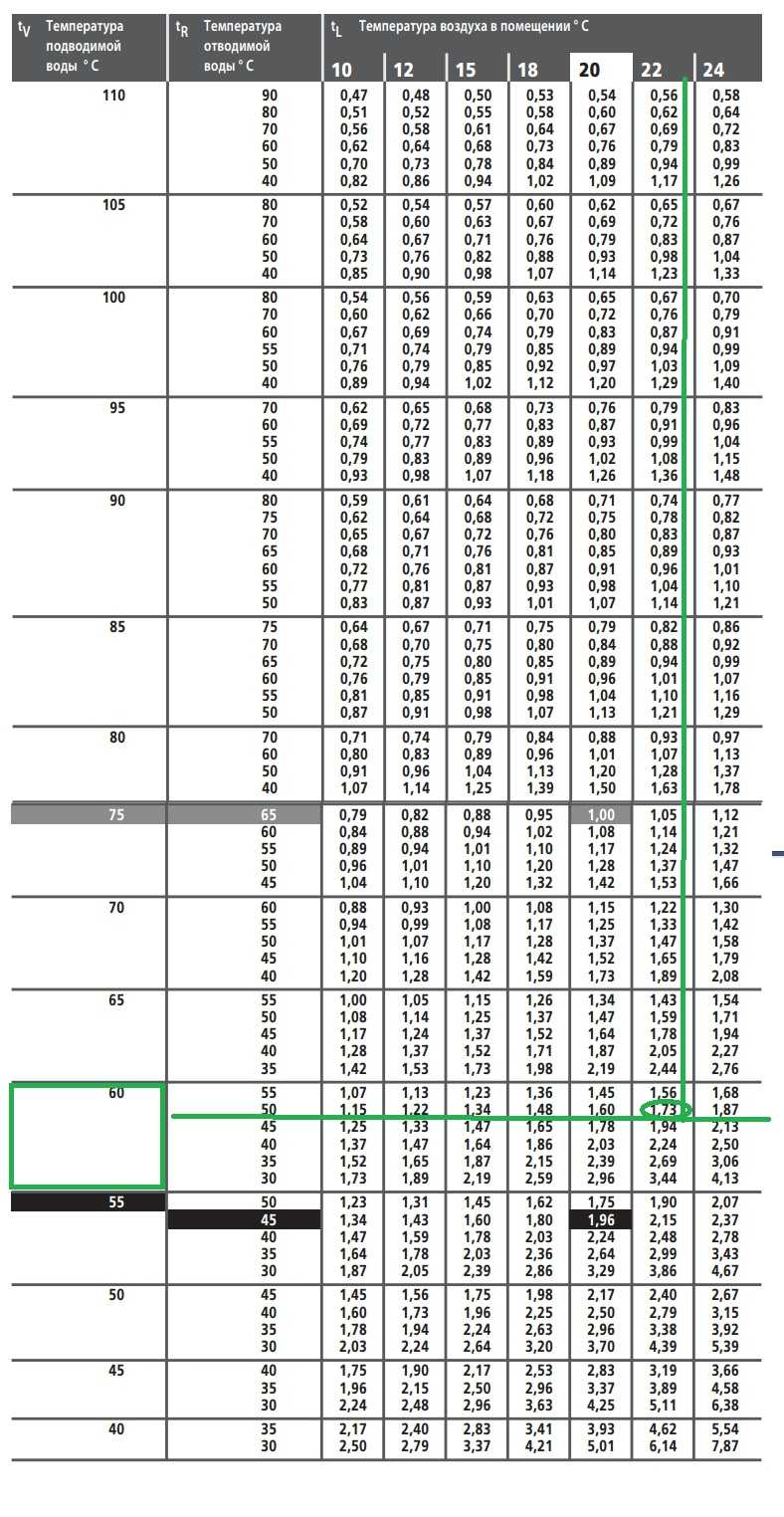

Conversion table depending on the temperatures of the heating system (click to enlarge)
Let us assume a low-temperature system with parameters 60/50/22 (flow temperature 60 ° C, return 50 ° C, the room is maintained at 22 ° C). We calculate the delta of temperatures: (60 + 50) / 2-22 = 33оС. We find in the table a line with the temperature of the flowing water, then with the temperature of the discharged water and we reach the value of the room temperature (22оС in our case). This cell contains the coefficient 1.73 (marked in green).
We multiply the calculated amount of heat loss for our room by it: 2150W * 1.73 = 3719.5W. Now we are looking for suitable options in the capacity table for this case (marked in green). The choice is more modest, but radiators are required much more powerful.
Here is the whole method for determining the power of panel radiators. You can use it to select steel panel batteries for any room and any system.
You may be interested in reading about how to calculate the power of the boiler and how to determine the diameter of the pipes for heating.
Panel steel heating radiators KERMI ThermX2
Made according to all European standards, they have a wavy profile surface, and are notable for their low price. They are only suitable for closed heating systems. A small amount of hot water, coupled with a high heat output, make these devices the most suitable for autonomous heating. Moreover, it is better to use them in systems where the coolant is not excessively hot.
These radiators are made according to the latest patented X2 technology, which significantly increased the efficiency of heating devices. By doubling the radiation of the infrared spectrum, this technology has made radiators very comfortable. The heating time has been accelerated by about a quarter, and the savings have increased by 11%. The essence of the X2 principle is that the front panel heats up first, and only then does the rear. For more details, see the video below.
Video: Technical features of Kermi steel panel radiators
After connecting the panels into the body, the finished product is first thoroughly degreased, then phosphated. The final finishing is done by electrostatic painting. The top layer of paint is processed at a temperature of 180 degrees. Thanks to this, it turns out to be durable. The high-gloss finish gives the batteries a fancy look.
On top and on the side, the radiator has screen grilles. They allow to achieve a significant increase in the efficiency of heat transfer - by 60%. The set includes 4 overlays intended for fastening the equipment.
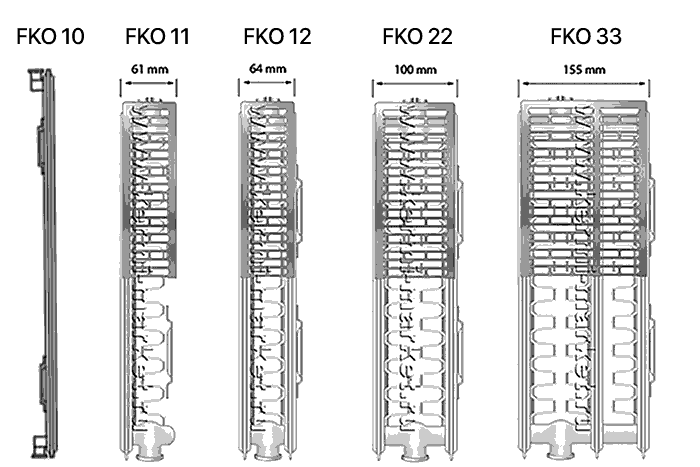
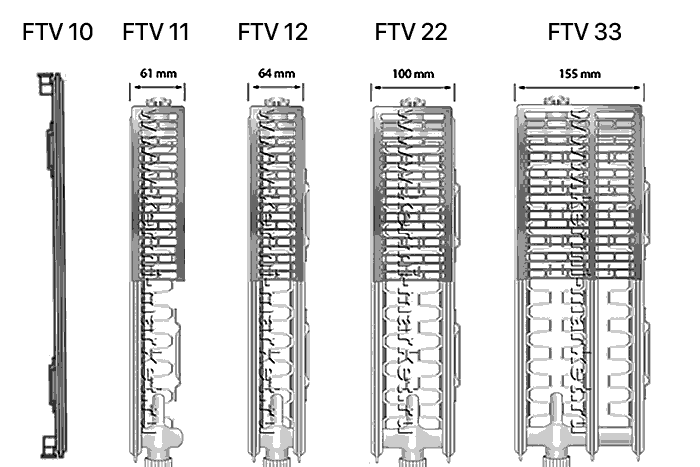
There are 2 lines of Kermi panel radiators, which differ in the place of connection to the heating network. Radiators of the Kermi ThermX2 Profil-K (FKO) line are connected from the side. And devices such as Kermi ThermX2 Profil-V (FKV or FTV) are designed to be connected from below.
Laterally connected Kermi ThermX2 Profil-K
These radiators are equipped with convectors, and their panels are made of two profiled steel sheets joined by welding. On the sides there are screens, and on top there is an overhead grill. Radiators with side connection type are marked with the letter combination FKO. For connection to the system, the Kermi Profil-K FKO has four female threaded sockets (1/2 ″ diameter) on the sides. You can connect the radiator to the pipes from either side.
Technical characteristics of heating radiators Kermi ThermX2 FKO:
- Connecting thread: 4 x G1 / 2 ”(female)
- Height: 300, 400, 500, 600, 900
- Center distance: total height minus 50 mm
- Length: 400mm to 3000mm
- Depth: type 10 and 11 - 61mm, type 12 - 64mm, type 22 - 100mm, type 33 - 155mm
- Working pressure - 10 atm. (1.0 MPa)
- Pressure test - 13 atm. (1.3 MPa)
- Max. heating medium temperature: 110 ° C
- Working temperature - 95 °
Bottom-connected Kermi ThermX2 Profil-V
All these radiators have a thermal valve built into the structure. Its thread is right-handed, with a pitch of M30x1.5. The temperature controller is not included in the delivery set, it must be purchased separately. The thread at the branch pipe is external, its diameter is 3/4 ″. The center-to-center distance is 5 cm. This design is intended for two-pipe heating systems. If you need to connect to a one-pipe system, then they purchase special fittings.
Kermi ThermX2 FKV specifications:
- Connecting thread: 2 x G3 / 4 "(external),
- Radiator heights: 300, 400, 500, 600, 900
- Radiator length: 400mm to 3000mm
- Distance between supply pipes: 50mm
- Radiator depth: type 10 and 11 - 61mm, type 12 - 64mm, type 22 - 100mm, type 33 - 155mm
- Working pressure - 10 atm. (1.0 MPa)
- Pressure test - 13 atm. (1.3 MPa)
- Maximum temperature of the heating medium: 110 ° C
- Working temperature - 95 ° С
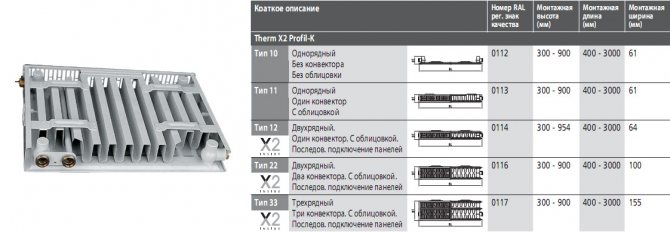
In addition to the connection methods, panel radiators differ in types. In total Kermi manufactures 5 types of steel panel radiators:
Type 10 - single-row, has a depth of 6.1 cm. There is no cladding and convector. Manufactured by prior order only.


Type 11 - single-row, faced, depth - 6.1 cm. There is one convector.


Type 21 - double-row, lined, with a depth of 6.4 cm. One convector.


Type 22 - double-row, lined. Two convectors.


Type 33 - three-row, lined. Three convectors.


The most popular and frequently used type is 22.
KERMI radiator range
Some of the best panel radiators are appliances German company KERMIwhich are considered the best in their class in terms of performance. They are made from cold-rolled sheet steel 1.25 mm thick and are perfect for Russian conditions - severe frosts and sudden temperature changes. KERMI batteries can be used in rooms of any size, although they are small in size. Height can be 30-50 cm, width - 0.7-1 m. The main feature is three depth options: 59, 64, 100 mm. Even the deepest batteries do not recede much from the wall, therefore almost invisible.
The surface of all batteries from this manufacturer is varnished. Any of them can be connected to both centralized and autonomous heating, to a one-pipe and two-pipe system. According to the type of connection, all devices are divided into FTV (bottom connection and ¾ ″ external thread) and FKO (with side connection and ½ ″ internal thread).
Each species three series:
- 11- single row (one convector);
- 22- two-row (two convectors);
- 33- three-row (three convectors).
In the production of all models, the Therm X2 technology is used - the front panel (with direct current) heats up first, only then the rear panel (from the reverse flow of water), which serves as a heat shield. The surface of the batteries is degreased and covered with a primer, then varnish (by immersing the device in it). The final layer is heat-treated epoxy-polyester enamel. Such the coating is almost impossible to spoil... In addition, KERMI does not use formaldehyde in the production process, which makes the devices environmentally friendly.
The choice of a radiator based on the calculation
Steel radiators


Let's leave in brackets a comparison of different types of heating radiators and note only the nuances that you need to have an idea about when choosing a radiator for your heating system.
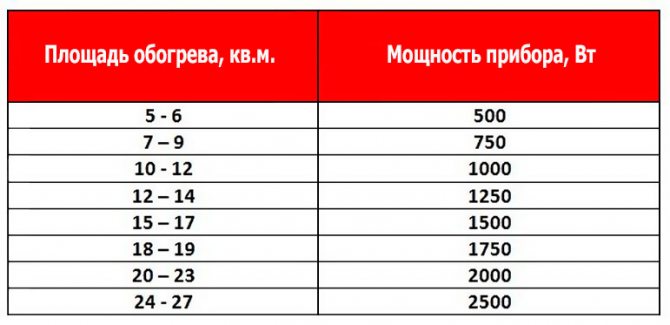
In the case of calculating the power of steel heating radiators, everything is simple. There is the required power for an already known room - 2025 watts. In this case, we look at the table and look for steel batteries that produce the required number of watts. Such tables are easy to find on the websites of manufacturers and sellers of similar goods.
Here is an example of such a table:
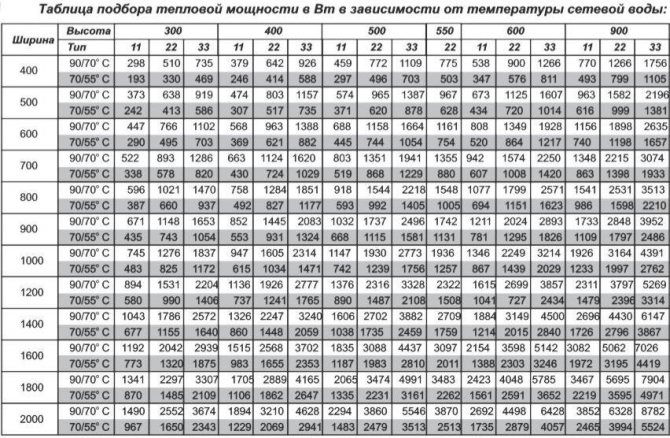

The table indicates the type of radiator, in this example we take type 22, as one of the most popular and quite decent in terms of consumer qualities.And a 600 × 1400 radiator is perfect for us. The power of the heating radiator will be 2020 W. But it's better to take a little more than a little less power.
Aluminum and bimetallic radiators


In this case, there is one important difference in calculating the power of radiators. Aluminum and bimetallic radiators are often sold in sections
And the capacity in tables and catalogs is indicated for one section. Then it is necessary to divide the power required to heat a given room by the power of one section of such a radiator, for example:
2025/150 = 14 (rounded up)
And we got the required number of sections of such a radiator for a 45 cubic meter room.
Calculation of sections by the volume of the room
Knowing the height of the room and its area - you can calculate heating radiator sections, it is enough to calculate the building volume of the room. This selection method is suitable for rooms with non-standard heights. According to building codes, indicators for heating 1m3:
- for brick houses, 34 W / 1m3 should be taken;
- panel houses - 41 W / 1m3;
- new houses built according to all requirements - 20 W / 1 m3.

The selection is made according to the formula:
n = (S x Qnorm) / qsec,
where: n is the required number of sections, pcs;
V is the building volume of the heated room, m2;
Qnorm - rated load in terms of heat consumption, W;
qsec - section heat transfer, W.
The calculation results are increased upward.
Important! In the case of a cold winter, or too low a coolant temperature, it is worth adding a margin of 10 to 20% for the thermal power of the device.
Power calculation
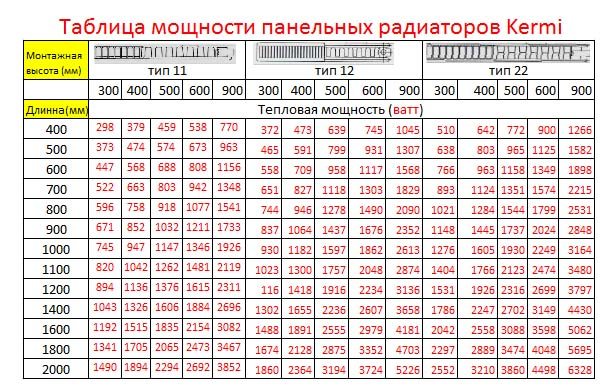

One of the options for calculating the power of a radiator involves the use of a comparative method, when a typical cast-iron 12-section battery is taken as a basis. It is known from the studies carried out that with such dimensions, it provides heat transfer of the order of 1444 W.
The capacity of the internal volume of the cast iron sample filled with the coolant is 13 liters.
From the passport of Kermi batteries, it is easily recognized that the heat transfer from a typical one-section unit under the code 10 is about 2100 W (with a working volume of 6.3 liters). Using these data when replacing cast-iron batteries with new samples, you can be sure that their heat transfer will be no worse, and even slightly higher.


To correctly determine the required power and the radiator connection diagram, a tabular calculation is used. To implement it, you will need the following additional data:
- the amount of heat loss in the apartment;
- parameters of the liquid carrier;
- estimated room average temperature.
When choosing, the dimensions of the radiator are also taken into account, after which the appropriate adjustments are made to the selection algorithm. The desired heat transfer value is determined by the summary table provided by the manufacturer of a specific radiator from the popular Kermi line. The required model is in the corresponding column, opposite to which the power value suitable for it is indicated. Experts advise taking this indicator with a small margin, which guarantees the desired result.
After all the parameters are taken into account, the user will be able to more accurately determine the model suitable for specific operating conditions.
Choosing the type of Kermi radiator, taking into account the required power
The table shows the power of the various radiators of the brand. Values suitable for our case are highlighted in red. These batteries can be installed in a room with similar characteristics.
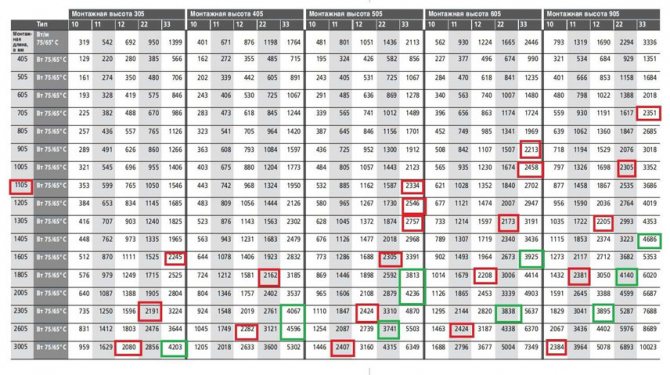

But for Kermi radiators, the power table works only if the average temperatures of the coolant and air in the room are observed:
- coolant t (supply) - 70 degrees;
- coolant t (return) - 65 degrees;
- t air - 20 degrees.
If the system characteristics differ from the average, it is required to multiply the received power by one more factor. The latter can be determined using a table.
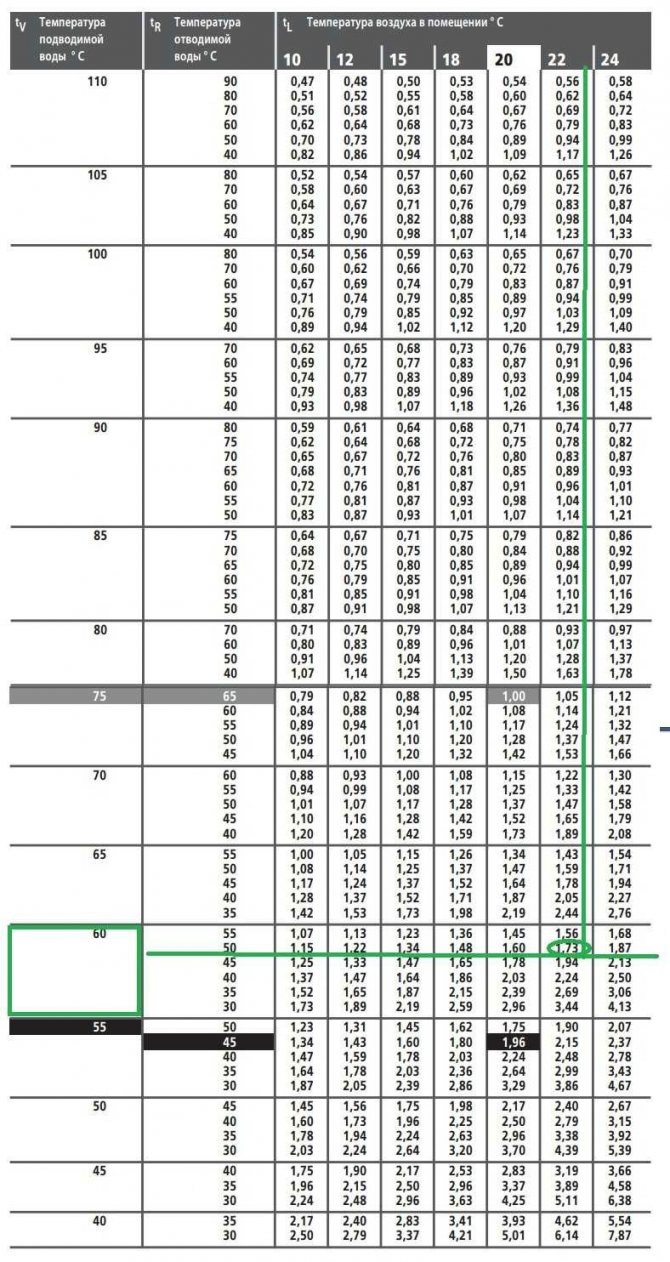

For example, the system parameters in our case (respectively) are 65/50/24. Then the required coefficient is 1.71.It remains to calculate the value and decide on the option of Kermi batteries - the power table again comes to the rescue. For our example, the product is 2480x1.71 = 4240 W. Suitable options are highlighted in green.
- Back to
- Forward