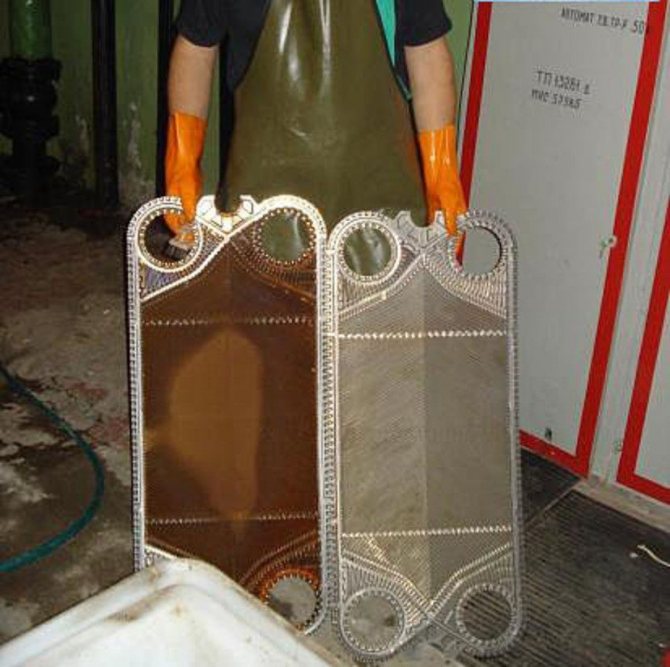
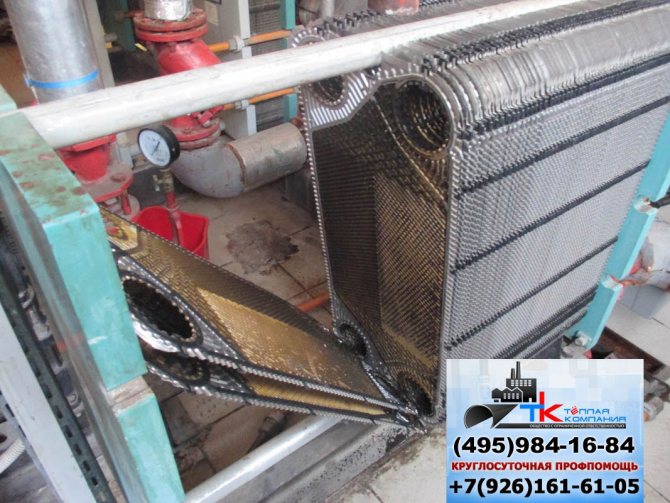
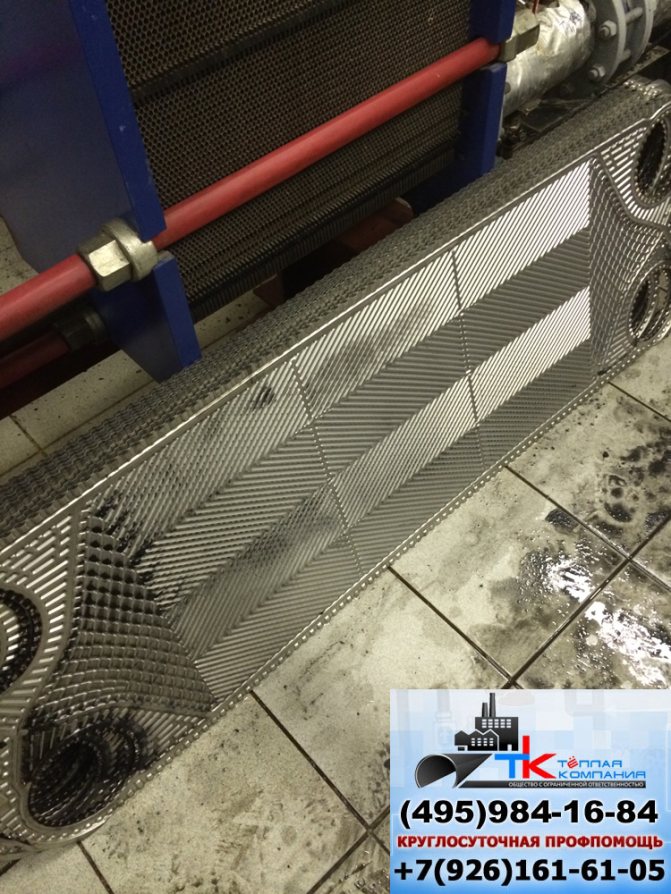
Currently, heat exchange equipment is used in all spheres of human activity. These are engineering systems of buildings (heating, cold supply, hot water supply), technological processes in the production of goods, food, large industrial energy: oil refineries, large plants, thermal power plants, nuclear power plants, and so on. Cold tap water in most Russian regions is hard, which leads to the appearance of various deposits, scale in the heat exchanger, etc. The inner surfaces of pipelines, which have been in operation for ten years, are clogged by more than sixty percent. In the process of operation, any unit becomes contaminated, and as a result, there is a deterioration in heat exchange and permeability of the coolant / product through the heat exchanger. All this leads to loss of heat or disruption of technological processes, which, in turn, leads to high energy consumption and loss of quality or quantity of the product produced. At the same time, the cost of cleaning or repairing the unit is an order of magnitude less than the losses that can result from a faulty unit. And even more so the need to replace equipment partially or completely.
The frequency of flushing is determined by the design of the units and the area of their application (for example, in the food industry, this procedure has to be carried out very often). And the way of flushing - by design features, degree and type of contamination. For the equipment to work properly, the device should be flushed once or twice a year on average. The choice of flushing technology is made by specialists and depends on the design features of the unit and its technical characteristics.
Pros and cons
The use of chemistry for cleaning heat exchangers has both undoubtedly positive and conditionally negative sides. One side,
- the already mentioned disassembly of the units is not required, which significantly reduces labor costs - if necessary, for shell-and-tube heat exchangers, you can limit yourself to dismantling the distribution chamber (s) to facilitate access to each tube of the tube bundle separately; extraction of the bundle from the casing is not required;
- labor costs for carrying out the chemical cleaning of the heat exchanger itself are incomparable with the labor costs for mechanical cleaning: for chemical cleaning, it is enough to introduce the active substance into the heat exchanger system and wait for the recommended time; mechanical cleaning requires careful processing of each section of the structure;
- it is simply impossible to mechanically clean some surfaces - for example, the surface of the "inner" tubes of a tube bundle of a shell-and-tube heat exchanger or thin and fragile parts of a plate; at the same time, the chemical solution will reach these "problem" areas without difficulty.
On the other hand,
- chemicals for flushing have some cost, and their reuse is usually ineffective (however, mechanical cleaning also consumes its "consumables");
- the quality of the cleaning of "problem" areas can be difficult to assess visually (however, the use of a technical endoscope can partially help; the results of thermal and hydraulic tests after washing also give an idea of its effectiveness);
- in the case of the wrong choice of chemistry for flushing heat exchangers, temperature conditions or exceeding the recommended time, negative corrosion processes are possible (however, if all standards are observed, their probability is quite small).
In some cases, chemical and mechanical cleaning can be used together to achieve optimal results; the main issue here is the question of cost justification.
Tools and filters
When comparing water filters and flushing aids, the initial investment in flushing aids will be less, but the amount of use will quickly make them a more expensive option. It will always be cheaper to purify water in the long term than to constantly deal with the consequences of poor quality or poorly treated water. Reagents for flushing plate heat exchangers will always lead to the destruction of surfaces, even if they work carefully with surfaces. The composition of the water, if it is not purified, is unknown, how it will change in the future, it is not known what will get into such water and how the new impurity will react and the old rinsing agent is not clear. One way or another, but flushing the surface with aggressive means is the gradual destruction of surfaces. And as a result, the equipment will still have to be disassembled. The design features of any equipment involve bottlenecks where dissolved impurities can accumulate and clog narrow passages. When using purified water, there will be no such problems at all.
AquaShield
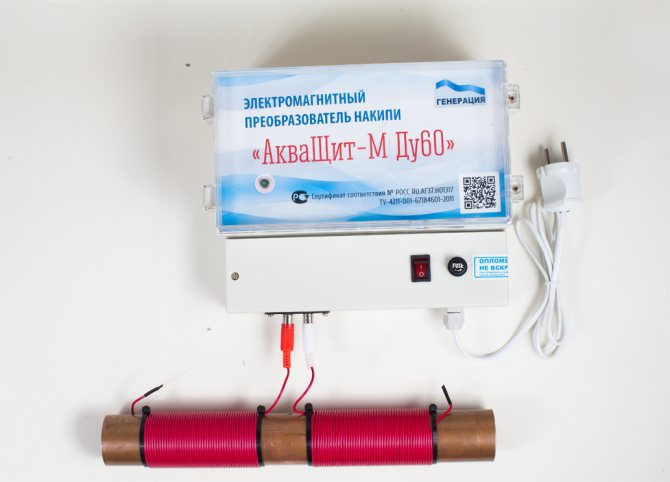

Let's take and compare the cost of chemical cleaning of plate heat exchangers and the price of an ordinary simple AquaShield. Chemical washing in a year can result in the cost of one electromagnetic softener. AquaShield will not allow new scale to form on the surfaces of the equipment during the year. But at the same time, WITHOUT the use of new cleaning agents, it will help remove old scale. And the cost of operating it will be just electricity bills. And the device uses no more electricity than an ordinary light bulb per month. This comparison alone is enough to understand that flushing agents can only be a temporary solution to problems.
Limescale OFF
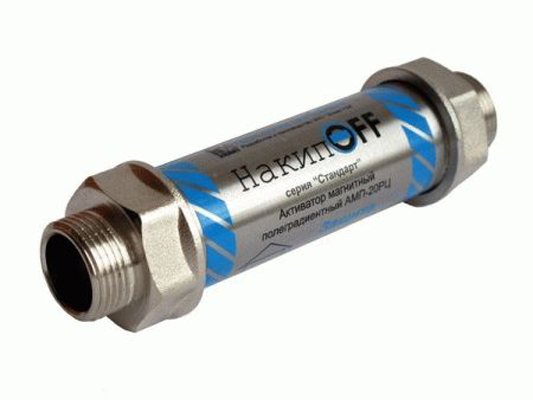


Simple descaler. It looks like it works like Anti-Scale. It is diluted with water, poured into equipment where surfaces need to be cleaned. Depending on the degree of contamination, it is kept in contact with the surface to be cleaned for several hours, then washed with a powerful jet of water. Aggressive agent, before use, you should study the instructions so as not to spoil the working surfaces.
What other equipment can I use to flush plate heat exchangers?
Very often, various electric powered mechanical brushes are used to flush the heat exchangers, which helps to remove old scale between the plates. The second option is a water softener for the boiler, which will help arrange small water shocks in plate heat exchangers, which will help dissolve old lime deposits.
The price of the issue
How much can a descaler cost? On average, the price of the smallest 5-10 liter eggplant ranges from 500-600 rubles per bottle. The price depends on the container, the area of sale and on the chemicals used and on the manufacturing companies. Sometimes chemicals designed for specific equipment are more expensive than bulk products.
Cleaning frequency
There are no strict requirements for the rules on the frequency of flushing of heat exchangers - there are only recommendations indicated in the Operation Manual attached to each device. Recommendations should be adjusted in accordance with the specifics of use - the chemical properties of heat-carrying media, their physical contamination, etc. In particular, it is shown to carry out cleaning if, during a routine inspection, contaminating deposits of any nature with a thickness of more than 0.3 mm are detected on heat exchange surfaces.
In practice, the presence of such deposits may be indicated by an excessive decrease in the thermal characteristics of the apparatus recorded by external measuring instruments. Some manufacturers produce modern heat exchangers with a certain "margin", that is, with the expectation of thermal resistance of pollution. For them, the presence of deposits exceeding 0.3 mm is allowed - if the heat transfer parameters are within the normal range.
Chemical flushing of a plate heat exchanger, cost and nuances
How does chemical washing work? How often? What is the cost of chemical flushing of plate heat exchangers? Why is it sometimes at a price higher than the timely developed and launched water treatment?
The heat exchangers can be flushed with alkalis or acids. Cleaning should be done with diluted products. When working with hazardous chemicals, be sure to remember the safety rules. You need to use respirators, gloves, dilute the funds strictly according to the instructions.
How often should the surfaces of heat exchangers be cleaned? It all depends on the rate of fouling of surfaces by bloom. If the water is too hard, then you will have to clean the surfaces once a month. When working with a plate device, it must be borne in mind that the distance between the plates is narrow, and that the plates themselves are thin, which means it is very easy to damage them.


The same should be taken into account when choosing chemicals, since such processing has its own characteristics. First, the consumer should not think that flushing a plate heat exchanger is cheap. Chemicals may not cost big money, but they will have to be used often, this is the first feature, and any aggressive agent will leave its mark on surfaces. And their cost has nothing to do with it! Any aggressive agent is designed to dissolve any substance and any surface. Therefore, washing with such substances will damage the surfaces. Even they may not dissolve the surfaces themselves, but when removing plaque with the help of mechanics, the surfaces will still not retain their original smoothness. If the thermal system does not include a water softening system, then a quick failure is guaranteed to it. And the most expensive means for flushing plate heat exchangers are not helpers here. And rather, the most expensive means are the most aggressive, which means they will destroy surfaces much more intensively. So, by choosing means for flushing, consumers knowingly reduce the service life of their equipment. A one-time flush may seem like a better investment, though.
Reagents
For chemical washing of heat exchangers, two types of active reagents are used - acidic and alkaline.
- Contrary to popular belief, alkali copes much better with organic deposits: acid can only carbonize serious contamination from the outside, after which its action becomes ineffective. Alkaline eats away organic matter completely. Alkaline reagent can be purchased as a ready-to-use mixture, or you can make it yourself. For moderately soiled surfaces, the following composition is recommended: Based on 100 liters of hot (80 - 90 ° C) water, the following dissolves:
- caustic soda (NaOH) - 0.2 kg;
trisodium phosphate (Na3PO4 x 12H2O) - 0.4 kg;
- sodium nitrite (NaNO2) - 0.25 kg.
For heavy soiling for the same 100 liters:
- caustic soda - 0.4 kg;
- soda ash (Na2CO3) - 0.2 kg;
- sodium nitrite - 0.25 kg.
- 1.5% nitric acid aqueous solution - for moderate deposits;
5 - 10% nitric acid solution - for hard-to-dissolve persistent deposits.
The use of hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid is generally not permitted.The use of the above alkaline solutions is not allowed if there are any aluminum elements in the heat exchanger.
The action of the acid is neutralized with a weak (1 - 1.5%) solution of caustic soda or caustic potash (aka potassium hydroxide, KOH). The alkali action is, accordingly, neutralized by a weak acidic solution. The insoluble salts formed during the neutralization reaction precipitate - it is advisable to wash them with a strong stream of clean water.
Containers for the preparation of reagents must be chemically resistant to their effect. Compliance with the strictest safety measures is mandatory, since these substances can be dangerous to humans both in dry form and even in the form of weak solutions.
What is flushing for and what does it save from?
Since plate heat exchangers are considered, you need to focus on the design features. Here the heat from the heated plates is transferred to the cold medium and then the heat carrier is transferred further. Made, such plates can be of different materials, but the following are most often used:
| Type of heated device | Plate material |
| Heat exchanger | Copper Steel Cast iron Titanium |
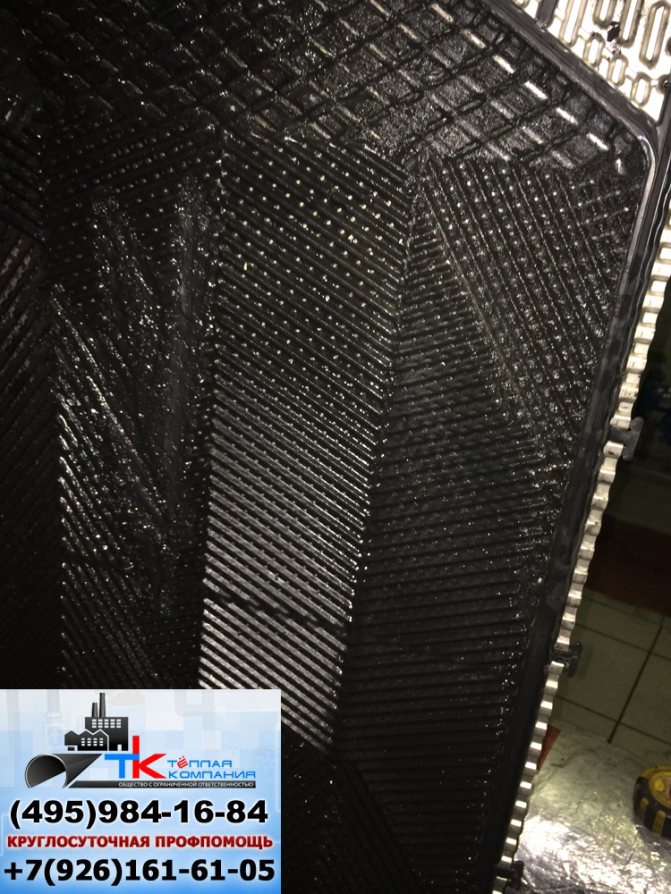
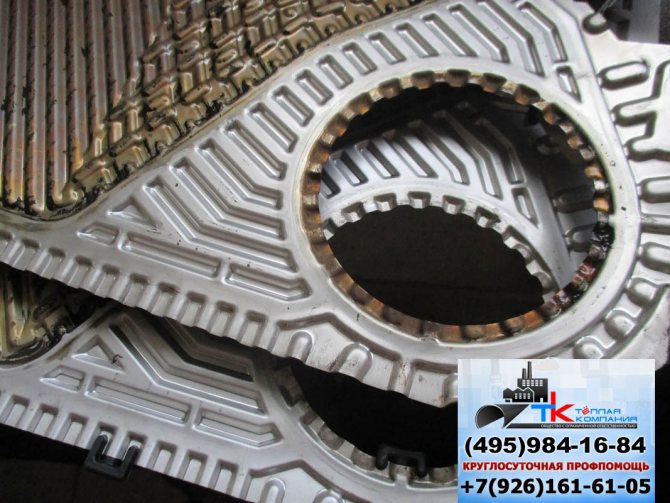
Plates can be corrugated or flat. The plates are located close to each other, and the water wanders between them, gradually heating up. Naturally, if you use lime mineralized water, then very quickly unpleasant growths form between these thin plates.
And the longer you use poor-quality water, the more negative consequences will be. Heating quality will drop dramatically! How does lime water work? When heated, it produces lime salts, which very quickly settle on heated surfaces. The worst thing about limescale is that it is very poor at letting heat through. It turns out that the device starts to junk. Here, even rinsing the plate heat exchanger with your own hands will be of great help. And all because the scale fouling of the plates disrupts the entire operation of the heat exchanger. The water comes out of it barely warm and the heating period increases significantly.
The worst case scenario is when the metal of the heat exchanger plates cannot withstand overloads. What can happen in this case:
- The metal will start to crack;
- The metal will begin to flow;
- The metal will start to explode.
In any case, scale build-up on the surface will damage the equipment. Moreover, a breakdown is such when it becomes impossible to repair the equipment. That is, the reason for the urgent need to use liquid for flushing plate heat exchangers was found out. But this is where the competition between flushing and water treatment comes into play. But you should immediately warn that flushing will always be a loser. She does not save from scale, she does not warn her, she only removes the already formed plaque. And this is exclusively a struggle with the consequences.
What problem does flushing solve? Reagents, chemical liquids help to remove the formed plaque. At least somehow soften it, dissolve it and remove it from the surface. Flushes are used even before mechanical cleaning. The plaque is so insidious that it literally eats into the surface. And it is very difficult to remove it. Even very strong chemicals are powerless.
Procedure
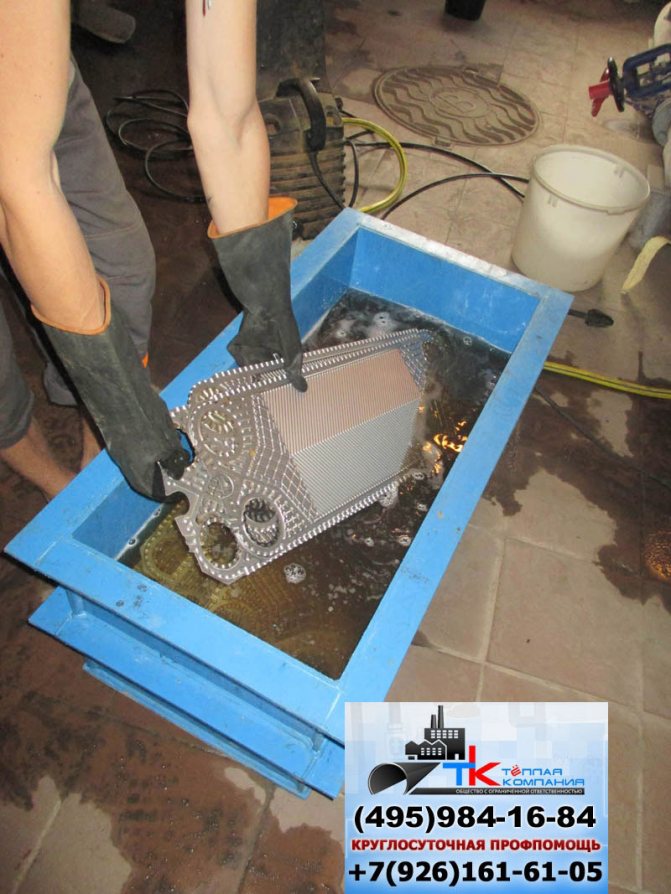
There are two options for chemical cleaning:
- without using additional equipment;
- using a special pump for flushing the heat exchangers.
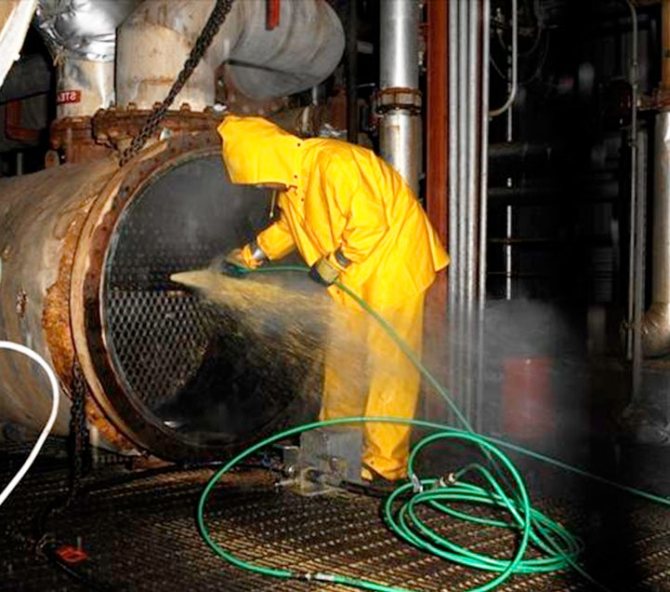
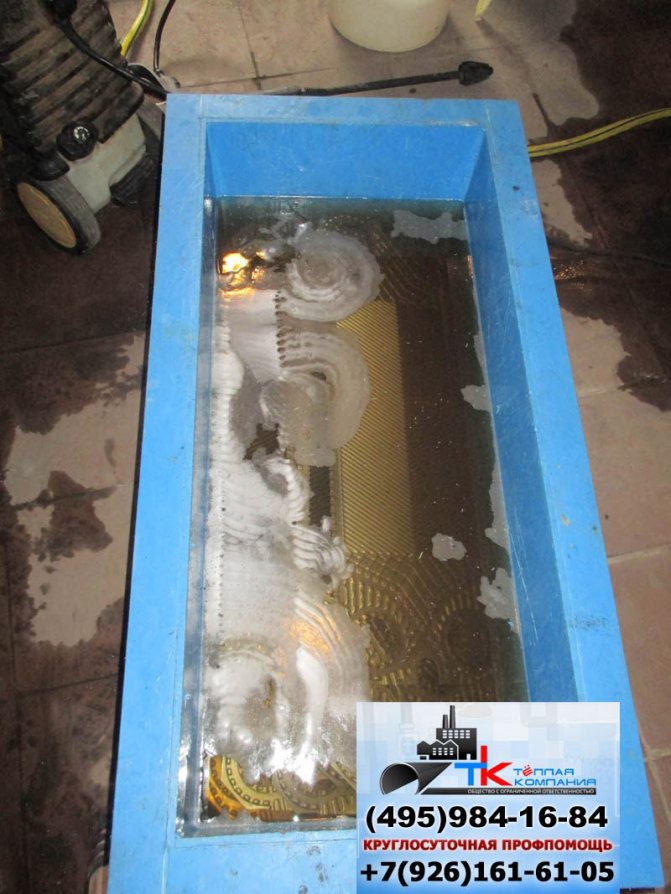
- First option. To carry out chemical cleaning of the heat exchanger:
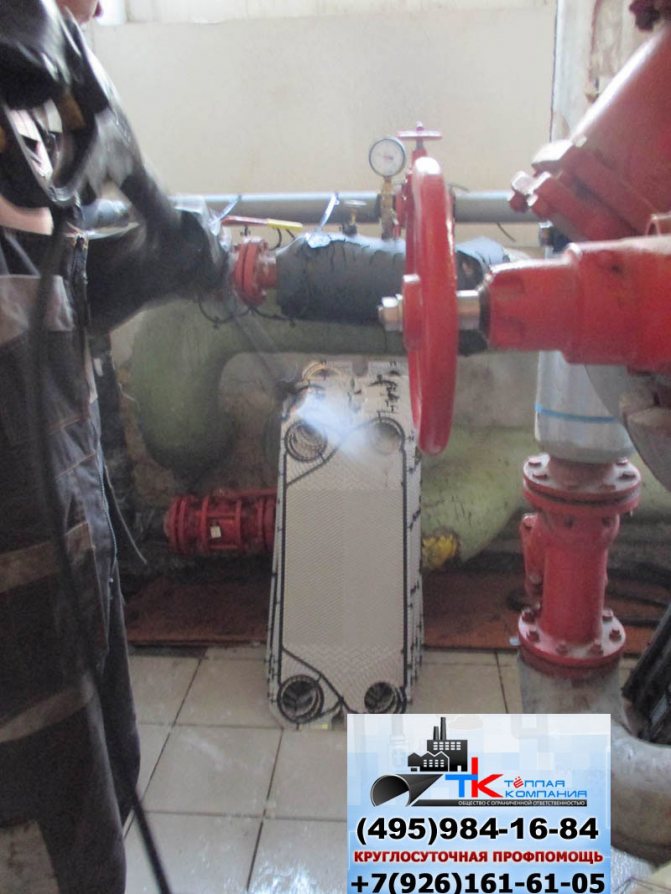
- disconnect the heat exchanger from the heating medium supply and removal system and, if necessary, drain the remaining liquid in it;
seal the outlet pipes with plugs;
- fill the entire heat exchanger through the inlet pipes (in the case of a shell-and-tube heat exchanger, both the space in the tubes of the tube bundle and the annular space) with a chemical reagent heated to a temperature of 80 - 90 degrees Celsius.
- wait 30 - 40 minutes;
- remove the plugs and carefully drain the active solution;
- flush the cavity of the heat exchanger with a neutralizing solution or, in extreme cases, with a large amount of clean water;
- if possible, blow out the heat exchanger with hot air until it is completely dry.
- The second option involves the use of a pump for flushing heat exchangers, combining the pump itself, made of chemically resistant polymers, a container for a reagent and a thermoelectric heater to maintain the desired temperature of the reagent. In modern models, the pump is equipped with two hoses connected to the inlet and outlet of the heat exchanger. Through the first hose, the reagent is pumped under pressure into the heat exchanger, removed through the second hose back into the tank and supplied again. A filter can be installed between the "drain" hose and the container to filter out undissolved dirt particles.
If an incomplete removal of deposits is found prior to the rinsing and drying steps, the cleaning procedure can be repeated with fresh active solution.
Naturally, the heat exchanger is flushed and dried after the pump has been used.
How to clean a heat exchanger
The heat exchanger is cleaned at the end of the heating season. To carry out the work, it is enough to have a standard set of tools available. Before starting work, it is necessary to disconnect the boiler unit from the gas network (main or local) and electricity.
Consider how to clean a floor standing gas boiler
:
- the first step is to dismantle the burner device;
- all wires must be disconnected from the gas valve;
- a thermocouple is removed from the combustion chamber, which is connected to the gas valve by a capillary tube;
- the fuel supply pipe is disconnected;
- bolts or nuts (4 pcs) that fix the plate with the burner are unscrewed, the assembly is removed outward.
It is convenient to clean the gas boiler burner with an old toothbrush. Soot must also be removed from the flame control sensor, igniter, piezoelectric device for automatic ignition.
To get to the boiler heat exchanger, remove the top cover of the unit, disconnect the draft sensor and chimney, remove the insulation, dismantle the casing fasteners and the casing itself. Having gained access to the heat exchanger, it is necessary to remove the turbulators from it.
A soft metal brush is suitable for cleaning the turbulators, and the heat exchanger itself is freed from soot deposits with a miniature scraper made of thin metal. A long-handled brush is also used. First of all, the smoke tubes are cleaned and swept, then the soot that has crumbled on the bottom should be removed.


The wall-mounted boiler is cleaned with a toothbrush
Cleaning the wall-mounted heat generator. After turning off the gas supply, it is necessary to dismantle the front panel of the boiler. Then the front cover is unscrewed, which closes the combustion chamber. It is recommended to cover the nozzles with a sheet of heavy paper to prevent the burner from clogging up with falling soot. Do-it-yourself cleaning of the heat exchanger of a double-circuit boiler is performed using an old toothbrush or a brush with metal bristles. After cleaning is complete, brush around the heat exchanger and carefully remove the paper containing the collected soot. How the procedure is performed, see the video below.
Flushing of a single-circuit and double-circuit gas boiler
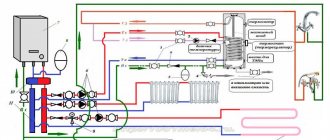
Flushing the heat exchanger of a gas boiler is necessary to remove internal deposits that can disrupt the normal circulation of the coolant in the heating system and cause problems with the supply of hot water to the local DHW system. Also, the sediments may contain substances that destroy the metal.
How often this action is required to be performed depends on the type of coolant. If purified water circulates in the system, it is enough to do prophylaxis every four years, removing deposits. The system with antifreeze should be flushed every two years and the coolant should be changed regularly - under the influence of high temperatures, it changes its properties over time and can become dangerous for the metal elements of the system.
additional information
Since contamination (in particular, scale) can play the role of a kind of "patches" in the heat exchanger, sealing possible cracks or damage to the integrity of the joints, after the procedure of chemical and / or mechanical cleaning, it is mandatory to carry out hydraulic tests of the heat exchanger. If damage is found, it seems reasonable to decide on the economic feasibility of repair or further operation of the apparatus - in some cases (especially when the service life is approaching), it may be more profitable to replace the damaged block element or the entire heat exchanger assembly with a more modern and efficient one.
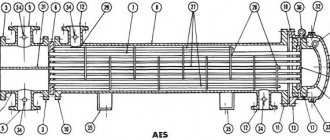
JSC "TSEEVT" produces heat exchangers of standard and improved characteristics, of various designs and purposes, with a wide range of applications. It is possible to use devices manufactured by JSC "CEEVT" both as part of new systems and as a replacement for exhausted heat exchangers. In each case, the calculation of the heat exchanger is made individually, for specific tasks and technical characteristics specified by the customer.
To clarify any technical or practical points, it is enough to contact the company's representative office in any convenient way from those indicated in the "Contacts" section of this site or fill out an application by filling out an electronic form.
Disassembly and removal of soot
For efficient operation of the equipment, it is necessary to clean the gas column. Deposits formed on the walls can disrupt the uninterrupted operation of the device, so there is no need to wait for a complete failure of the equipment, you should periodically carry out preventive cleaning.
Before starting dismantling, it is necessary to block the access to gas and water. Do-it-yourself cleaning of the gas water heater begins with removing the boiler doors and disconnecting the auto ignition wire. Then the thermocouple, piezoelectric element and burner tube are removed
Carefully take out the nozzle and the burner itself
Take out the thermometer sleeve, the boiler cover, and the flue. The gas water heater is cleaned with a brush and brushes, which clean all internal and external elements. The nozzle hole is cleaned with a needle with a smaller diameter in order to avoid enlarging the hole and disturbing the combustion mode. The internal channels of the heat exchanger are blown out with a vacuum cleaner and wiped with a damp cloth.
At the same time, you can carry out minor repairs to the heat exchanger with your own hands: replace the gasket under the pilot burner, check the thermocouple, which is prone to breakdowns due to the specifics of operation, and so on. Such works do not require large investments, but they maintain the boiler performance at a high level, and the thermocouple device is quite simple, and element replacement will not be difficult.
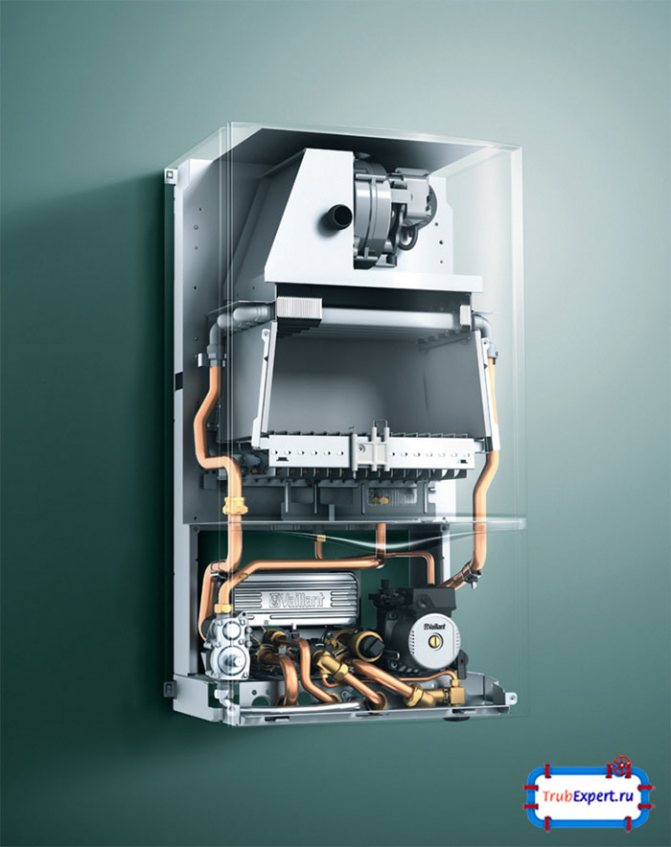


Gas boiler structure
Assembly is carried out upside-down. When connecting the piezoelectric element, it is recommended not to use the tool in order to avoid damage to the ceramic base, it is better to tighten it by hand.
When installing, it is necessary to check the thermocouple on the gas boiler, you need to know that the end of the conductors should be at the level of the place where the flame appears.
How to clean the heat exchanger of a gas boiler
Speaking about how to choose the right tool for cleaning heat exchangers, you should be guided, first of all, by the advice of specialists, many of whom recommend the use of hydrochloric acid.This reagent copes well with plaque, but due to its excessively high degree of acidity, the coating inside the heat exchanger can be damaged.
Alternative methods involve treating the walls of the mechanism with citric acid, which can also solve the problem of scale well.
It is important to remember that timely and proper care of the entire heating system will provide high-quality heating to the entire home, and the owners will be able to save themselves from the risk of damage to any functional part of the equipment. If you have doubts about your own abilities, you can entrust such work to specialists, who also have various photos of heat exchangers and videos on removing deposits in them.
CIP cost (rub.)
| Type of PTO | CIP chemical cleaning (100 plates) | Alfa Laval | Mashinpeks | Swap |
| S04 (U2), M3, VT04, T2 | 10500 | M3, M3M | VT04 | |
| S07 | 12000 | M6, M6M | ||
| S08, GX07 / 08 | 12000 | M6, M6M | VT10 | GC16 / 30, GX16 / 18 |
| S14, M6M, VT10 | 14250 | M6, M6M | ||
| S18 (H17) | 14250 | |||
| S20, H17, GX-016/018 | 15750 | |||
| S21, S22, M10M, M10B, GX-026 | 15750 | M10M, M10V | VT20 | GX26 |
| S38, S37, N35, VT40 | 18000 | VT40 | ||
| S41, S42, A55, Q30, VT80 | 24000 | VT80 | ||
| S47, GX-042 | 24000 | GX42 | ||
| S62, S65, M15B, GX-051 | 31500 | М15М, М15В | NT150 | GX52 |
Mechanical method
Mechanical method: essence, infrastructure, process technology.
Heat exchanger tubes are often mechanically cleaned. The device with which the cleaning work is carried out is quite primitive and has the most elementary structure. It includes:
- a rotating bar equipped with a special tool for cutting deposits;
- a platform that moves translationally along one rail (on which the specified rod is placed).
The movement of the platform occurs in parallel with the simultaneous movement of the rod, which it makes along the heat exchange structure (pipe). The bar itself is located inside the pipe, which is designed to perform two functions: to protect the hands of personnel and to transport water. Water is needed in order to flush out the deposits.
For the mechanical method of cleaning heat exchangers, various tools are used. The most popular among them are brushes and cutters, drills, drilling and cutting tools.
Cleaning of heat exchangers, flushing of heat exchangers - the choice of method!
CIP cleaning of heat exchangers is selected as the main cleaning method in the following cases:
- when it is necessary to flush the heat exchanger, both brazed and semi-welded;
- when the degree of contamination is assessed as low or medium (acid flushing method of heat exchangers).
Dismountable cleaning of heat exchangers is the most effective and is used if the degree of pollution of the heat exchangers is assessed as severe. This may be due to the fact that the channels are completely clogged with deposits and the cleaning of the heat exchangers is necessary. In such cases, manufacturers are advised to resort to the collapsible method, which is guaranteed to remove any contamination.
Scheduled preventive maintenance is less painful, significantly extending their lifespan. Productivity is improving at the same time. The main signs of the need for maintenance are: an increase in pressure losses, failure to ensure the temperature schedule in relation to the passport values. Conclusion of technical experts - cleaning of the heat exchanger is necessary.
A timely and regular procedure for flushing the heat exchanger plates is to remove deposits, scale, dirt, microorganisms of devices of any type, significantly extending the service life, which is much cheaper than its overhaul. Nothing comes as expensive as unplanned production stops.
However, these costs can be avoided as much can be planned before the problem becomes a reality. You just need to outline a plan of preventive measures in advance. For example, seals are subject to wear. However, if they are replaced in time, leaks can be avoided, leading to various costs.The plates can get dirty. Limescale has a negative effect on heat transfer and degrades performance. In some cases, the increased pressure drop can cause serious problems. Timely cleaning and rinsing will help avoid these problems.