Water
Water is used to fill heating pipes and radiators more often than any other liquid, since it is the cheapest.
Technical characteristics of water:
- high heat capacity - at 20 ℃ it is 4183 J / kg · deg;
- low viscosity, which minimizes the load on the circulation pump;
- non-toxic substance;
- oxidation processes occur only during contact of steel with water in the presence of oxygen;
- thermal expansion coefficient - 0.03% / deg.
Antifreeze
The main purpose of antifreeze during its development several decades ago was to use it as a filler for water cooling of a car engine in winter. Due to its properties, antifreeze began to be used for filling heating systems. The freezing point of a substance is put down in its marking as a numerical value - 30, 40 or 65.
Antifreeze characteristics:
- low price;
- the average level of heat capacity is 3520 J / kg · deg;
- due to the high viscosity of the substance, the pump for filling the heating system is subjected to significant loads;
- the presence of anti-corrosion additives protects the metal from oxidation;
- it is highly toxic, since it contains the poisonous substance ethylene glycol;
- thermal expansion coefficient - 0.05% / deg.

Please note that an expansion tank is provided in a closed heating system to compensate for thermal expansion when heating the coolant. It should be the greater, the higher the value of this coefficient for the coolant.
Since antifreeze is characterized by zero corrosiveness, the system with such a carrier must be absolutely sealed. Otherwise, any crack will result in a coolant leak. In the case of other liquids, such as water, small defects become clogged with rust or precipitated salts.
Types of coolants
There are several types, mainly liquidsbut also meet gaseous... More often than others they use the following two substances.
Water
It is the standard filler for the pipeline. It tolerates heat well and does not cause chemical reactionsexcept for the oxidation of metals. During operation, the contour partially fills scumformed as the liquid cools.
Important! When using this substance, it is sufficient to carry out annual cleaning the system from solid formations.
Antifreeze
Anti-freeze is used in systems that periodically turn off, especially in the cold season. It is also useful in northern areas. When cooling down, the pipes will not burst, which happens with water. For the infusion of antifreeze, it is recommended to create a system with contour of small diameter, and install radiators panel... This helps to save on fluid consumption.
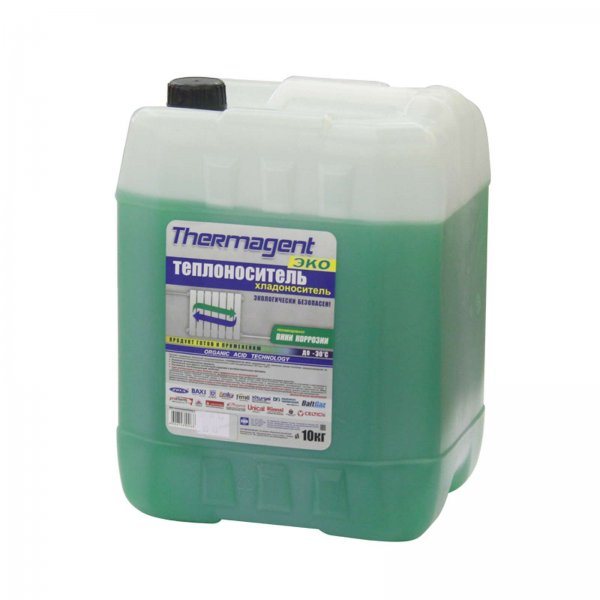


Photo 1. Antifreeze model EKO-30 based on propylene glycol with carboxylate additives, weight - 10 kg,.
In addition, it is much more difficult to fill: the antifreeze cannot be filled directly with a hose or through the tank (in a closed system).
Bay perform in one of two ways:
- From below with a pump. It creates pressure, thanks to which the antifreeze begins to circulate. This will require a special mechanism capable of acting on liquids other than water.
- Through a non-return valve. It is connected to the container, placing it as high as possible. This helps to relieve pressure. After completing the filling, the leftovers are drained.
Propylene glycol
Propylene glycol is used for the production of special anti-freezing fluids, which are used as a heat carrier in heating systems. In its pure form, propylene glycol has a rather low heat capacity (2400 J / kg · deg). Therefore, before pumping the coolant into a closed heating system, it is diluted with water. It significantly increases the heat capacity of a substance. As a result, the solution has a heat capacity index close to antifreeze (depending on concentration - 3500-4000 J / kg · deg).


Other characteristics of propylene glycol:
- high viscosity;
- low corrosiveness due to the presence of additives;
- non-toxic - the cans with the substance are labeled "Eco";
- thermal expansion coefficient - 0.05% / deg.
Filling the system with antifreeze
If, however, various antifreezes are used as a coolant, then the situation is different. The system must be filled from various containers - buckets, cans. Usually they take a bucket, pour antifreeze from the canister into it, and then fill the system with a pump.
The coolant is poured through drain valve.
The heating system must be able to drain the coolant. For this, a drain valve is installed. But through this drain valve, you can not only drain the system, but also fill it!
Such a faucet can be installed on the supply or return pipeline, for this you need to make a tee. Or it can be even simpler - install it instead of a plug on any lower radiator.
To fill the system, you need to lower the submersible pump into a bucket with antifreeze, put a hose on it and put the other end of the hose on the drain valve. Then open the valve and turn on the pump. The system is filled by analogy with the make-up tap from the water supply system - the pressure is pumped up to 1.5 atm, then the air from the radiators is vented. The pressure is again pumped up to 1.5 atmospheres, and so on until all the air leaves the system.
Saline solution
For open-type heating systems with natural circulation of the coolant, one of the possible options for the coolant is a concentrated solution of sodium chloride, calcium chloride or other mineral salts. It is used to prevent the heating circuit pipes from freezing in winter. Moreover, the stronger the salt concentration, the lower the freezing temperature of the solution.
Brine specifications:
- rather low heat capacity - a solution with a salt concentration of 30% gives off 2700 J / kg · deg;
- low viscosity;
- very high corrosive activity - steel pipes "burn out" very quickly from constant contact with salt;
- lack of toxins;
- thermal expansion coefficient - 0.03% / deg;
- low price of salt.
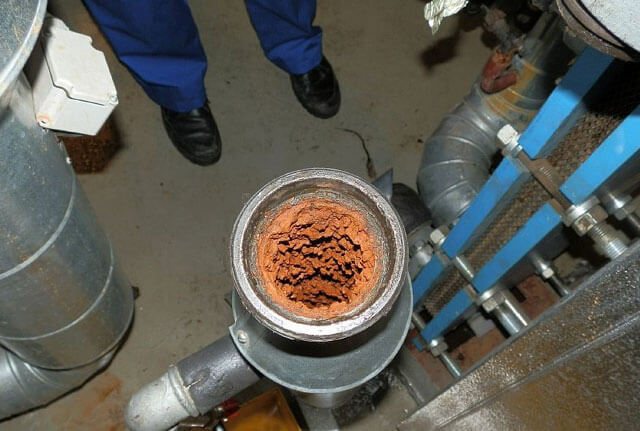


The disadvantage of the solution is that, under the condition of a low circulation rate of the coolant, salt will be deposited on the inner surface of the pipes, reducing their clearance. In addition, salt has a detrimental effect on the components of the circulation pump - the shaft and impeller, since the fouling of crystals leads to a decrease in its performance.
What is the importance of circulating pumps for heating systems
It is believed that there is no particular need to use a circulation pump for heating systems. Supporters of this judgment argue that a pump is a device that unnecessarily consumes a lot of electricity and makes the heating system dependent on it. That is, in the event of power outages, there will be problems with the supply of heat to the house.
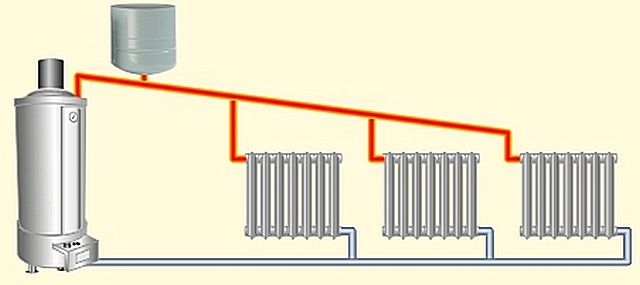

Such a judgment may seem correct. So, if the installation of the heating system is carried out in a small house where the pipeline is not very branched, then it is possible to organize the natural circulation of the coolant from the boiler to the radiators.
With a detailed study of this approach, it becomes obvious that its only advantage is independence from electricity (provided that the heating boiler is non-volatile). For all other characteristics, a system with natural circulation loses, and it is much more difficult to mount it.


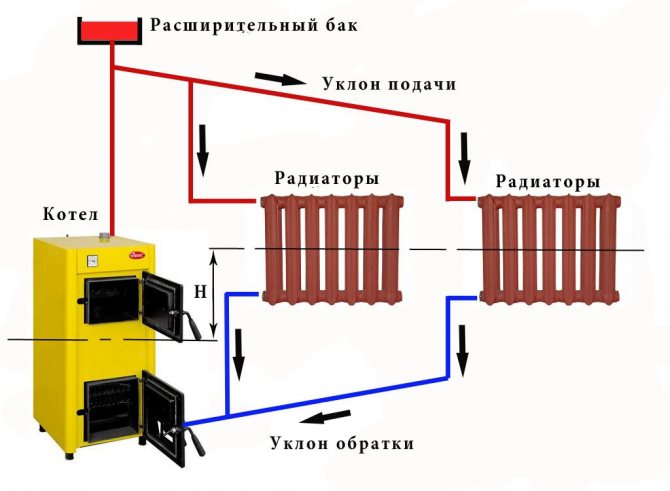
In order to ensure the natural movement of the coolant, pipes in the heating system must be of different diameters (50 mm or more). It is more difficult to install them, moreover, they are more expensive. During installation, it is important to observe the rule - pipes along the entire length of the circuit must have a slope towards the boiler. Often this cannot be achieved without spoiling the appearance of the rooms.
If the heating system with natural circulation has been carefully thought out and well debugged, then the pressure drop due to the temperature difference in the pipes (in both directions of water movement) will still be no more than 0.6 bar. This value is likely to be sufficient for a house that is not large in size. However, if the heating system has ramifications, is characterized by a large length, and there are also large differences in height and pressure, then 0.6 bar is hardly enough. Moreover, the situation can be complicated by hydraulic resistance, due to which the circuit can "lock up".
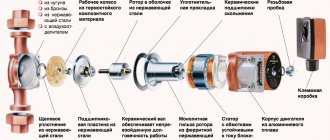
Connecting a circulation pump to the heating system will help solve many problems.


Circulation pumps for heating systems consume quite little electricity, which makes it possible, even if it is turned off, to heat the house from a medium-power UPS for several hours, which is especially important when using a boiler with "intelligence".


However, if the problem of power outages for your home is constant, then it makes no sense to connect the circulation pump to the heating system. In this case, it is necessary to think in a timely manner how to make an effective system with natural circulation.
In heating systems operating with circulation pumps, it is possible to adjust both their operation as a whole, and by rooms, groups of radiators. If the heating system is well thought out, then there will be no problems with multi-way taps, electromechanical regulators and other thermostatic devices during operation.


If it is necessary to "split" the heating system into several sections with different heating temperatures, this will not affect its overall operation in any way (which cannot be said about heating systems with natural circulation). For rooms, you can safely choose the most suitable heating options - using radiators, any convectors, underfloor heating circuits.
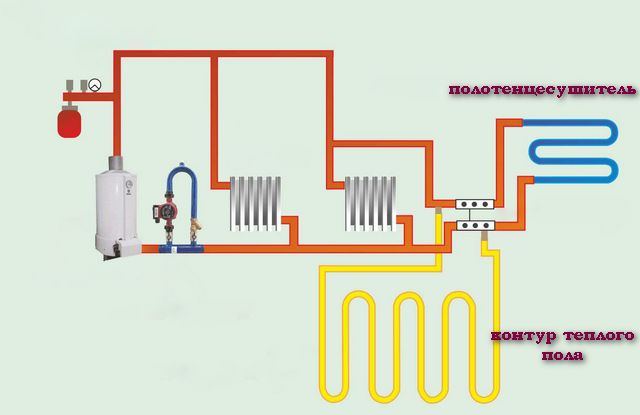

It is impossible to install water floors in houses without connecting a circulation pump for heating systems. A well-thought-out system that works with a pump is characterized by a high efficiency of work, the receipt of which costs money spent on its purchase and payment for the electricity consumed by this equipment. Such a system turns out to be more economical: pipes can be of small diameters, they will simply be hidden in the floor or wall.


The pipe circuits of a heating system with a circulation pump can have as many branches as you like, the number of heated floors can also be any. It is important here to choose the right pump that will create the required pressure. And yet, a heating system powered by a circulation pump is easier to start, maintain and carry out its prevention.
So, the installation of a circulation pump in the heating system has many advantages, which are definitely more than disadvantages, therefore, in almost all cases, you should think about purchasing it.
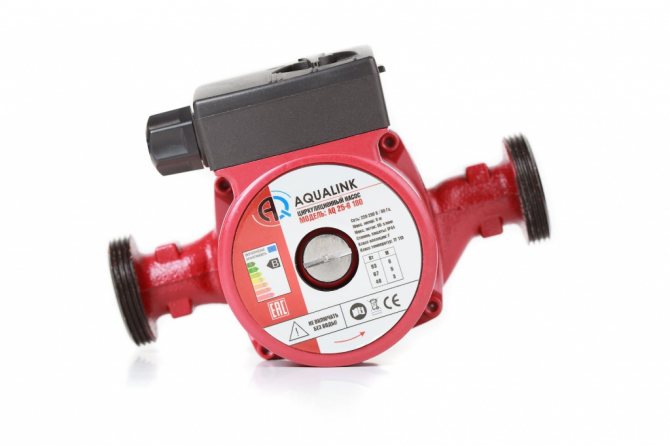


In the event that your home already has a natural circulation heating system, then you can still purchase a circulation pump, the efficiency of which will be evident.
Read the material on the topic: Hot water supply of a private house
Interim findings
So, before filling a closed heating system, you need to assess the conditions for using the heating system.
The conclusions will be as follows:
- Provided that you will use heating all the time, and a positive temperature is maintained in the system, water will be the best option for a heat carrier. Distilled water is best, but you can also just use it from the tap.
- In cases where the house will be heated only from time to time in winter, the best option is to fill the heating system with antifreeze, that is, an ethylene glycol-based coolant.
Filling and discharging the coolant from the system
Filling the heating circuit in a house with a coolant is usually performed in the following cases:
- Initial start-up of heating in a private house.
- Bringing the heating system into working condition after planned or unforeseen repairs or replacement of the boiler, shut-off fittings, and other elements.
- Refilling before the heating period after draining the heating agent from the heating system in a house that has not been heated for a long time.
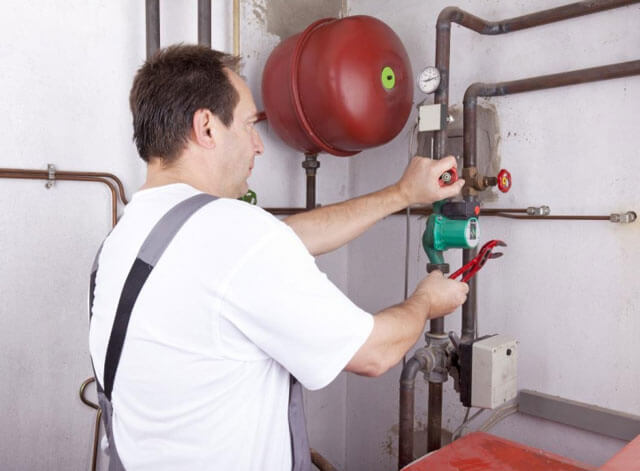


To discharge the coolant, it is necessary to open special valves in the lower part of the circuit, as well as at least one valve for air intake so that water flows freely from the system.
How to properly fill an open heating system
Before adding water to the heating system, it is worth deciding on what scheme it functions.
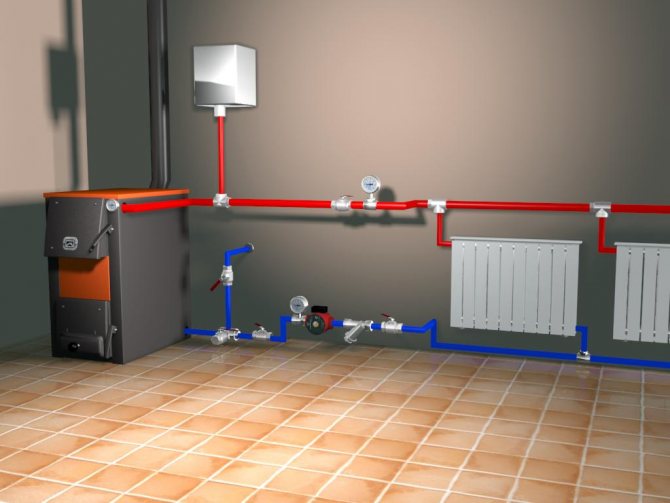
There are two types of heating circuit assembly in a private house:
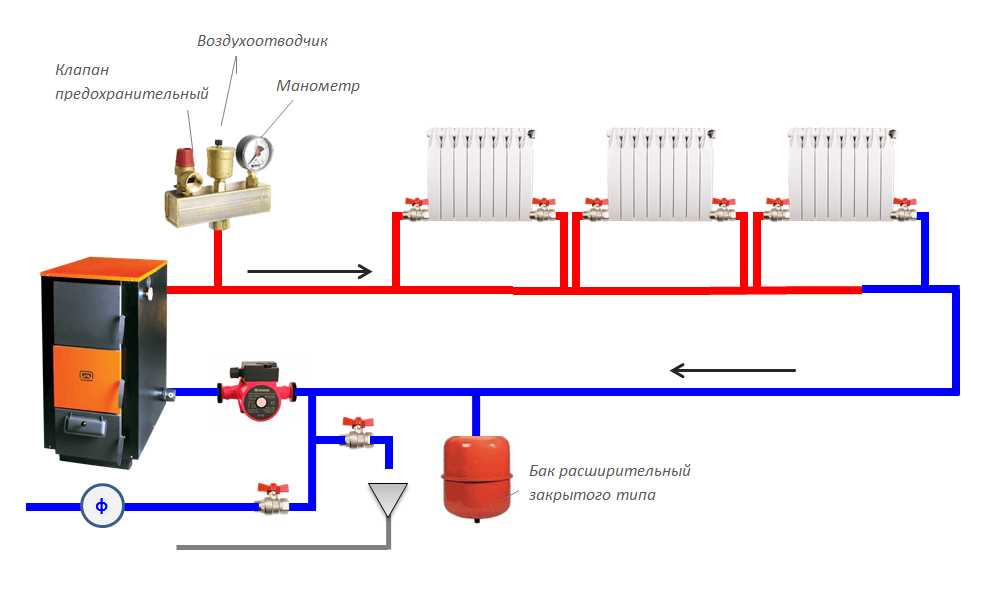
- Open system - the pressure in it is equal to the height of the water column from the lower to the upper point of the circuit. By means of an open expansion tank, the system is in communication with the atmosphere.
- The closed type of heating operates at an overpressure of 1.5-2.5 atmospheres. It contains a membrane tank that compensates for the thermal expansion of the coolant when its temperature rises.
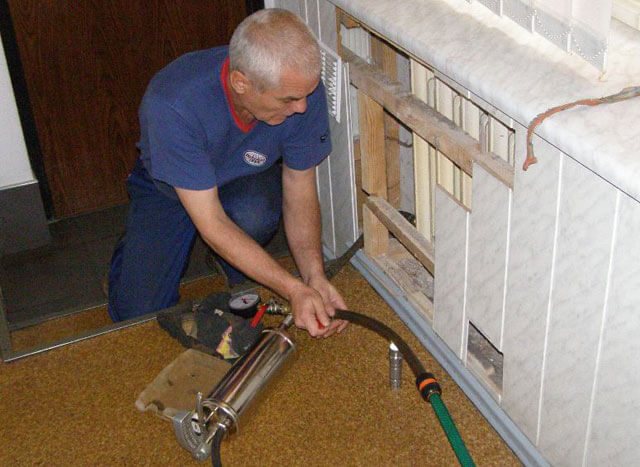


In an open heating system, all pipes of the circuit are laid so as to create a slight slope from the expansion vessel to the top of the circuit.
In this case, you do not have to puzzle yourself how to properly pour water into the heating system. It is fed directly through an expansion tank installed under the ceiling or in the attic. You can fill it with any container, or connect the tap to the central water supply.
Please note that excess air from the system will also escape through the expansion vessel.
Thus, in the case of an open type of heating system - how to properly power it, problems should not arise. After firing up the furnace or boiler, the water will begin to circulate in a natural way, or forcibly after turning on the circulation pump, if it is provided for by the scheme.
Pumps for pressure testing and filling the system: are there any differences
Pressurizing pumps and filling equipment do not have significant differences. Often, one and the same unit is used both to check the strength of the system and to fill it.
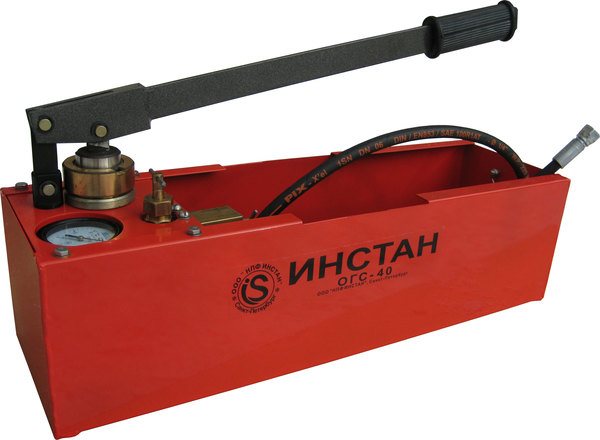


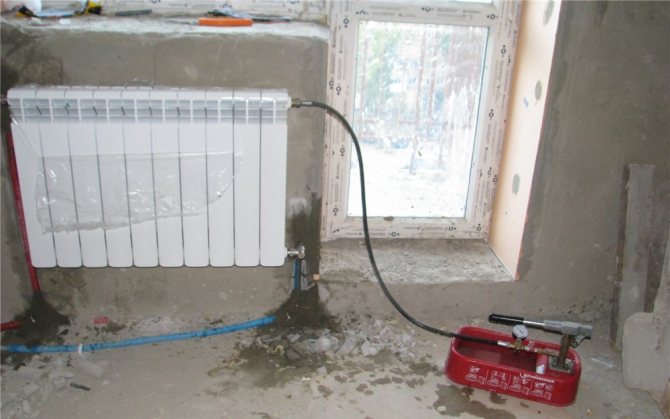
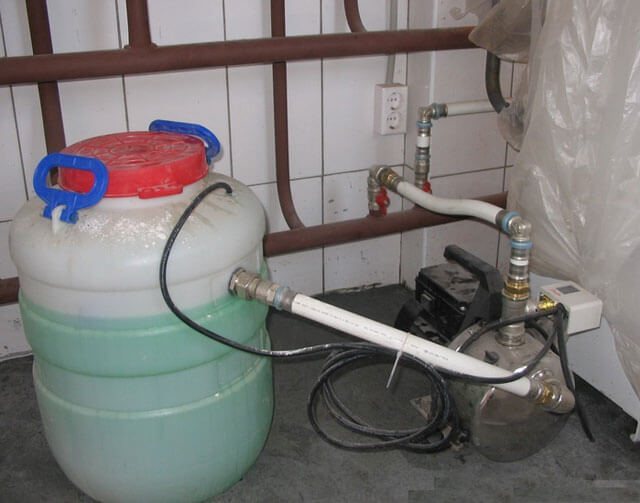
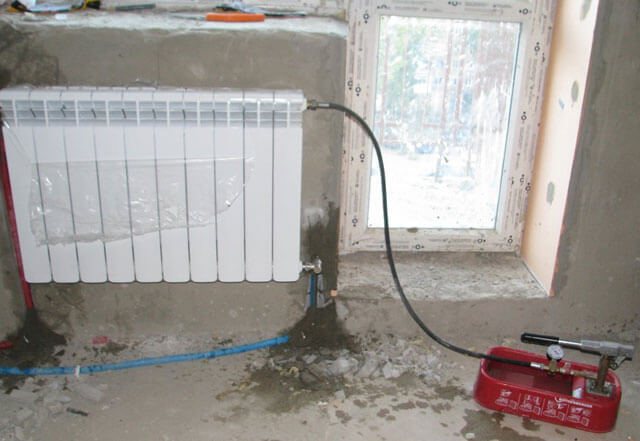
Photo 1. This is how a hand pump for crimping looks like. ...
Modern pressure and injection pumps differ in the type of drive. It can be electric or manual. By the principle of action equipment is subdivided into the following types:
- membrane;
- lamellar-rotary;
- piston.
The principle of operation of the crimper
The principle of operation of a manual crimper is quite simple. Water is poured into the tested heating system up to the maximum possible level.After that, by pressing the lever, the pressure level required for the test is reached (2-3 times higher than the working norm). When the required pressure is obtained, the ball valve on the unit is closed. The operator monitors fluctuations on the pressure gauge.
Attention! In order to prevent excessive pressure inside the heating system during pressure testing, the pumps are equipped with special overflow valve.
If the pressure starts to drop, then the pipe is leaking. Described the procedure is repeated several times. If a defect is detected, work stops until it is eliminated.
The first pressure testing is carried out immediately after the completion of installation work. Then the check is repeated every 5 years after flushing the pipeline aggressive chemicals.