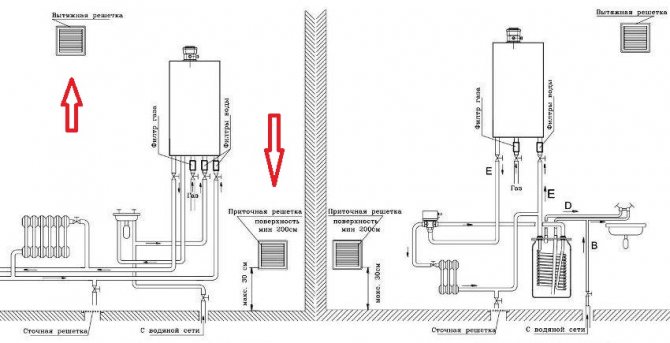
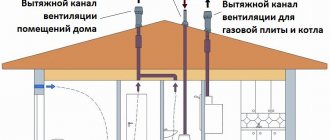
- There must be a ventilation outlet on the ceiling. The boiler room should be connected to the entire ventilation system of the house, if any.
- How to make ventilation in the boiler room of a private house: the wall in which the chimney passes must be punched in two places: in one the chimney outlet from the wall, the supply to the boiler and the second place below to clean the garbage accumulated in the chimney, but at the same time not less than 25 cm from the upper output (which is connected to the boiler).
- Air is supplied to the boiler room through the openings at the bottom of the door or through the ventilation duct.
- The air intake holes are calculated as follows: 8 cm² for each kW of boiler output, if the air intake is from the street. Respectively 30 cm² if the air intake is from the inside.
- Also, be sure to study the documentation for the boiler, for sure the requirements for your specific boiler model are described there.
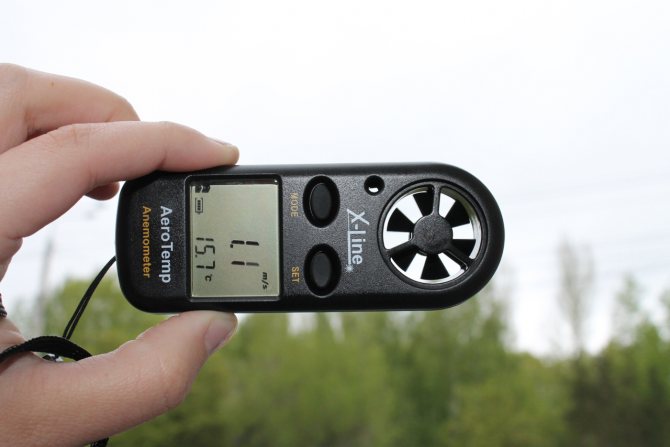
The need for air circulation in a gas boiler room
Even with a small presence of carbon monoxide, the well-being of the residents of the house worsens. Headache, pain in the eyes, lethargy - this is the least that accompanies a person with gas poisoning.
Its most dangerous leaks, as it often leads to an explosion or fire. And also an incorrectly calculated hood directly affects the boiler performance.
This is due to the fact that fresh oxygen is needed for normal fuel combustion. And if it is not enough due to poor ventilation, then the gas burns worse and, accordingly, the boiler gives off less heat.
ATTENTION! A bad exhaust hood with a floor-standing boiler serves as a source of gas and burning inside the exhaust pipe, as a result of which its passage decreases, draft deteriorates and the room becomes smoky.
Exhaust requirements
In gas boiler houses, increased demands are made on the ventilation system.
Moreover, such premises may be equipped with:
- As a separate building.
- Attach houses to the building.
- In the basement.
- In a dedicated room in a building.
If the equipment is designed for liquefied gas, then basements and attics cannot be used for these purposes, since the specific gravity of gas is greater than that of air.
As a result, it sinks in the event of leaks and will be explosive. Along with the allocation of separate rooms, modern wall-mounted boilers are allowed to be placed in the kitchen.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with: Ventilation in a frame house
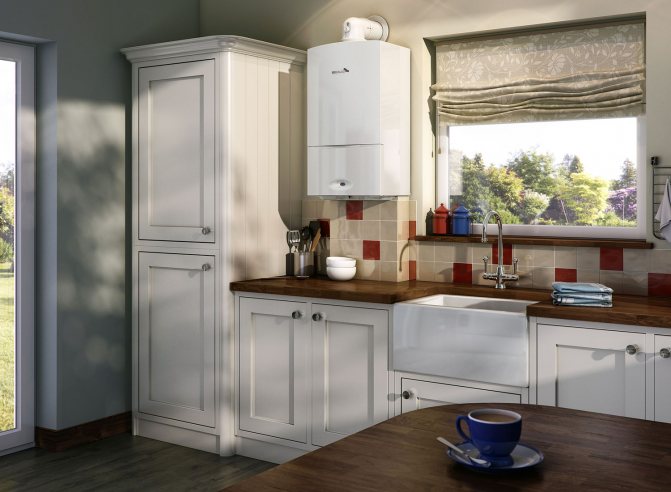


Despite the coaxial chimney, the rooms for them must meet the following requirements:
- The area is about 12 m2.
- Height to ceilings over 220 cm.
- The size of the window must be at least 0.05m2 per 1m³ of the room volume.
- The presence of a window or an opening window.
- The boiler is hung on a wall made of non-combustible material, while the distance from the adjacent partition must be at least 20 cm.
- Adequate openings for air inlet from the adjacent room.


How to make a hood


Types of boilers for a private house
Before equipping the hood in your home, it is important to correctly determine the necessary equipment (including the type of boiler), the materials used and the type of branch ducts. You should start with a set of equipment, selected taking into account the following factors:
- the area of the future boiler room;
- safe distance to flammable objects;
- the type of the room itself;
- the amount of estimated costs.
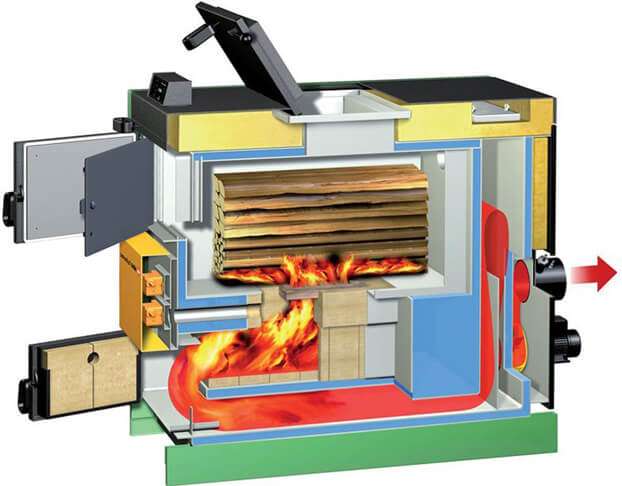
It is also important to decide on the type of boiler chosen for heating a private home. The best option for this case are electric, gas or solid fuel (pellet) units.In case of frequent power interruptions, it is recommended to install combined boilers using several types of fuel.
As an example, a medium-power gas unit was selected, which is explained by the comparative cheapness of the energy carrier used in them and the efficiency of the heating method itself. The working temperature in the combustion chamber of such a sample is significantly lower than in other models.
Hood materials
When choosing a material for arranging the hood, they proceed from the possibilities and specific conditions of the work. Most often, for these purposes are selected:
- brick;
- ceramics;
- metal.
Brick is usually used for the manufacture of hoods in solid fuel boilers. Despite the fact that it is rather difficult to clean it, the service life of units with such a hood is quite long. This material is not suitable for gas units, since at low combustion temperatures, condensate will accumulate in the pipe.
Ceramic is much better suited for gas - it can withstand temperatures up to 650 ° C. But in this case, it is necessary to provide protection against the ignition of soot in the chimney, having foreseen a condensate drainage channel. As an option - insulation of the outlet channels with mineral wool.
Steel pipe is a good choice for solid fuel and gas heating systems. At relatively high temperatures with solid pellets, a hood made of heat-resistant metal with thicker walls (up to 1 mm) is selected, and when using gas, this indicator is taken to be 0.6 mm.
Selection of the type of exhaust duct with a fan

The next step is to select an exhaust duct with a fan that is suitable for the given conditions, guaranteeing the required performance. This indicator is determined by a simple calculation using a formula that takes into account the volume of the boiler room (let it be equal to 10 m³) and the need to renew air three times in it during the day. Multiplying these two figures, you get 30 m³ / hour - this is the minimum capacity of the required fan.
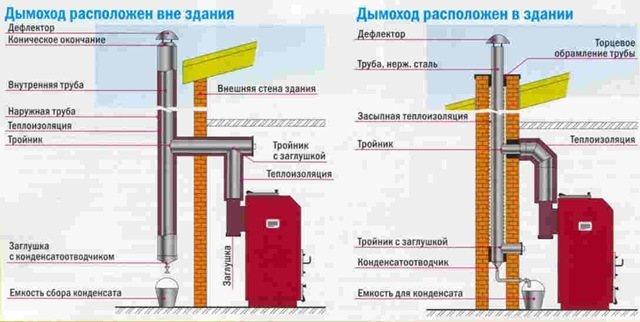
Coaxial flues are available in two different designs: horizontal and vertical. The first ones are traditionally mounted along the walls, and the second ones are laid in any acceptable place with an outlet through the ceiling to the attic and the roof.
When choosing a vertical chimney, you should be prepared for the fact that costs will increase, since it is longer and more difficult to install. It will also require a separate condenser collector. The disadvantages of horizontal design include the risk of freezing of condensate in the part brought out to the outside. In order to solve this problem without high costs, it is enough to insulate it with mineral wool or similar heat-insulating material - in case of not very severe frosts, this partially helps. To prevent the formation of ice at the end of the pipe, a lattice head is mounted.
For the correct installation of a horizontal chimney, it is important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- the outlet of the pipe is made approximately at a height of 2 meters from the ground;
- the distance from the outlet channel to the window located above it is at least 1 meter;
- when laying the pipe at an inclination of 3-12 degrees, it is not necessary to make a condensate collector;
- it is forbidden to bring the highway to an adjacent room;
- the distance from the outlet of the chimney to the nearby gas pipe must be 0.2 meters or more.
The classic configuration of the horizontal outlet includes the pipe itself, adapters of various types, as well as a set of decorative linings and ferrules with fastening bolts.
Gas boiler room ventilation standards according to SNiP
When carrying out the supply and exhaust system, you must strictly comply with all the requirements of building codes and regulations from 2.04. 05-91.
For gas-fired boilers, it is necessary to take into account three times the air exchange in 1 hour, and if such ventilation is not created naturally, then it is necessary to provide for a forced exhaust.
The air circulation pattern should be taken in accordance with Appendix. 11 SNiP:
- The gas boiler room must be equipped with ventilation, while the air duct outlet must be located on the ceiling.
- Air supply is provided through the ventilation duct or through the openings in the lower part of the doors.
- The flow rate is calculated according to the power of the boiler: for 1 kW of power, there must be at least 0.08m2 of air.
- Coming from an adjacent room: for 1 kW of power - over 0.3m2 of holes.
Other regulations on ventilation system equipment can be found in legal documents.


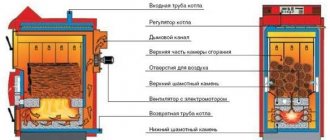
Solid fuel heating boilers - installation drawing


Content:
1. Features of operation of solid fuel boilers 2. Classification of solid fuel boilers 3. Single-circuit and double-circuit boilers 4. Traditional and gas generating principle of operation 5. Volatile and non-volatile option 6. Safety of solid fuel boilers
If there is no gas main in the village, when creating a heating network in a private house, a multifunctional solid fuel heat generator or an electric boiler is installed.
True, for the latter to work, a reliable power supply line will be required, since when the electricity is turned off, the heating device stops functioning, and constant network outages can lead to equipment breakdown. In this case, a solid fuel heating boiler is the best solution to the problem.

Types of ventilation for the operation of gas boilers
The ventilation system is a list of elements for the intake and removal of air, and it differs in the following ways:
- According to the principle of air exchange formation (natural and forced draft).
- By appointment. Exhaust, supply and combined ventilation.
- By design (channel and simple).
Let's consider in more detail the first two types of ventilation.


General information about boilers, their placement
A gas boiler is an equipment that allows you to heat and maintain water at a certain temperature level due to the thermal energy obtained as a result of gas combustion. The combustion process of gas is accompanied by the release of by-products that pose a significant threat to human health.
Their ingress into the body causes disturbances in the processes of human life. In large doses, compounds provoke the development of dangerous diseases. Do not forget about natural gas itself: it is explosive and requires special treatment when used.
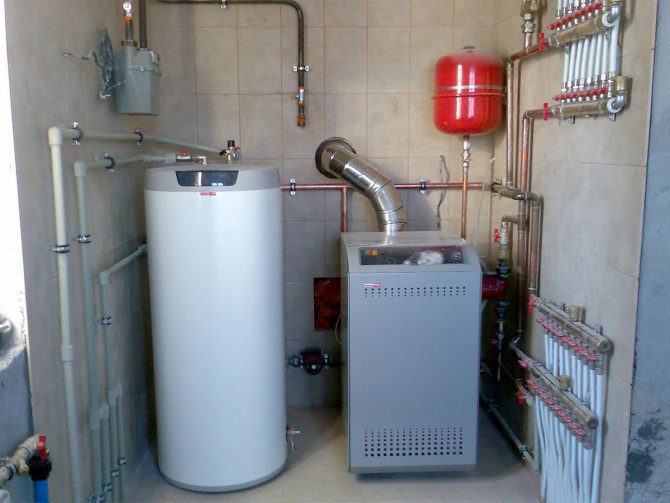
In private houses, various gas boilers are used, which have different requirements for air exchange. Placement requirements have been established for high-power floor-standing equipment. Such units can be installed in a separate special building, in an annex to the main house, in the attic, in the basement or in the basement.
Additional requirements are imposed on the facilities where the floor-standing gas boiler is located:
- The area is not less than 4 sq. m.
- The volume of the room is not less than 8 cubic meters. m.
- Ceiling height not less than 2.2 m.
- The width of the entrance opening is at least 80 cm.
- The presence of at least one window with direct air outlet with opening sashes for ventilation.
- The presence of an open air supply - a gap in a wall or window profile, through which oxygen is constantly supplied.
- Since the object is classified as explosive, the glazing area in it must exceed 0.05 sq. m. for 1 cubic meter. m. volume of the room.
The use of a basement and a plinth is allowed with restrictions, subject to a number of additional requirements. In such rooms, the equipment of the main and backup ventilation systems is mandatory, since.a malfunction of the air exchange structure will lead to an explosion hazard.
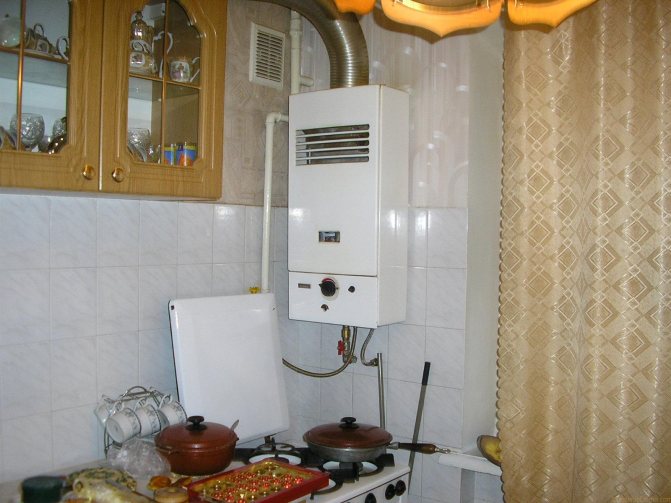
Most often, low power wall-mounted boilers are used. The average power of such heating units is 30 kW. They are provided with a productive and convenient internal combustion chamber. This equipment has less stringent placement requirements. Wall mounted boilers can be placed in a utility room, kitchen or bathroom.


Wall mounted gas boiler can be placed in the kitchen
- Delivery of the volumes of oxygen required for the direct combustion process. In case of insufficient supply of fresh air, combustion provokes the release of an excessive amount of hazardous compounds.
- Optimal conditions are created for the efficient operation of the equipment.
- Removal of combustion products and the gas itself from the room in the event of a malfunction of the equipment.
Classification of ventilation systems that are used in most private houses:
- By the principle of creating thrust: natural or forced.
- In the direction of movement: supply, exhaust, combined (coaxial).
- By design: channel or integral, without channels.
Factors affecting the parameters of the air exchange system in a room with a gas boiler:
- The power of the device, its functional features.
- Room area.
- Boiler load (frequency of use).
- The presence of windows, doors.
- Features of the climate of the area where the house is located (temperature, wind, precipitation, humidity, etc.).


There are several factors affecting the parameters of the air exchange system in a room with a gas boiler.
Natural ventilation in a gas boiler room
If there is a boiler in the house with a capacity of up to 30 kW, then it is enough to ensure the supply of air by equipping an exhaust hood at the bottom of the wall or door. A hole with a diameter of 10-15 cm can serve as such a source.
To create a ventilation duct for air flow you need:
- Install a pipe cut from any material (plastic, asbestos cement) into the hole.
- Attach a mosquito net on the outside of its end.
- It is advisable to install the inlet next to the firebox in the wall so that air can be sucked directly into the combustion chamber without creating dust in the room.
- The exhaust duct is mounted through the roof. It looks like a pipe of the same diameter, and at the same time it is equipped with a protecting insect net and an umbrella at the top to protect it from precipitation.
IT'S IMPORTANT TO KNOW! The diameters of the exhaust and supply ventilation pipes must be of the same size for optimal air exchange.
The door to the boiler room, if equipped with a grate in the lower part, can also serve as an exhaust element.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself: 5 silent modern hoods for the home - the criteria for the right choice


Your own heating engineer
Installing a solid fuel boiler with your own hands is quite within the power of any literate person, it is enough to know some of the features. It is better for a specialist to calculate the power of the boiler, the diameter of the pipes of the heating circuit and much more. It should also be decided whether the equipment will operate on a certain type of fuel or purchase a combined one, providing for loading with different types of fuel.
Before starting the installation, you should understand the technology and study the scheme.
This process is not complicated, not lengthy, but responsible. The installation of this solid fuel unit is carried out only with a clear knowledge of the technological process, otherwise poor heating operation is possible, expressed in excessive fuel consumption, insufficient heating of the room, or even the failure of a solid fuel boiler.
Before buying a device, you should calculate the value of the required power, based on the volume (not the area!) Of the heated room and the thermal conductivity of the walls (data are taken from the tables), and also decide what kind of automation should be supplied to the future boiler room, provided thatthat the adjustment will be automatic and not manual.
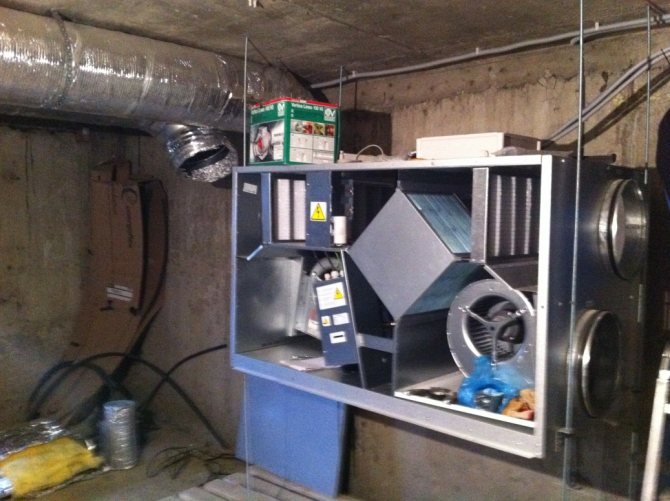
Forced ventilation
An artificial hood can be not only supply, but also combined, that is, supply and exhaust.
This process occurs when air is forced through the supply and exhaust pipes by fans - forcibly. For an hour, such a device pumps more than a dozen cubic meters of fresh air.
In modern ventilation units, there is control and regulation equipment that allows you to maintain not only the microclimate in the boiler room at the proper level, but also ensures the correct operation of the boiler.
Such ventilation systems are subdivided:
Monoblock installations. Devices of this type can be installed in any room.
Supply and exhaust systems. The intake and exhaust of air here is done by a forced method. Such equipment is usually installed in basements, mainly where high-performance gas boilers are used.
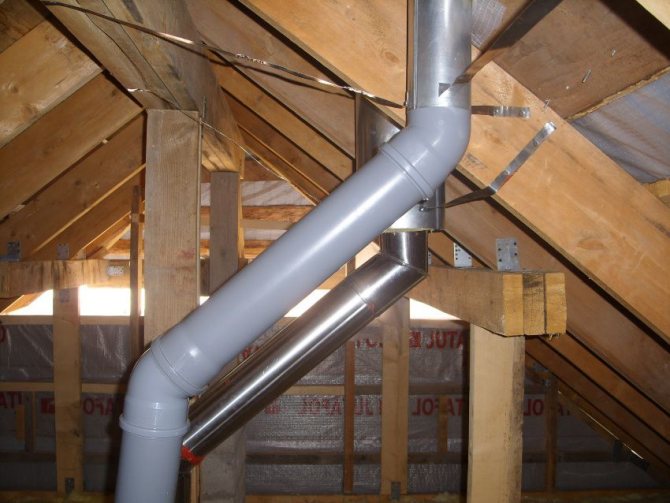
The best and safest type of forced ventilation is a boiler with a coaxial chimney. In this combined pipe, fresh air from the street is taken in along the outer gap, and exhaust carbon monoxide gases come out through the inner hole.
In addition, such ventilation increases the efficiency of the boiler, since already heated air is supplied to the room, due to the counter-emission of exhaust gas through the inner pipe.


Installation process
The chimney can be both internal (inside the house) and external (outside the house). Consider the installation process for each option.
Outside home
- Attach a horizontal section of the sandwich pipe that will pass through the wall to the boiler nozzle,
- isolate this area and the hole in the wall itself,
- attach a tee with a revision and install a plug,
- build up the pipe with subsequent links to the desired height. Brackets are used as fastening elements, with which the pipe is attached to the wall with a step of 2 m,
- attach a tapered tip to the top of the structure,
- strengthen the joints with clamps,
- paint the pipe surface with heat-resistant paint.
In the House
- mark the chimney exit points in ceilings and roofing,
- cut openings in structures,
- connect the boiler branch pipe with the adapter adapter,
- attach tee and revision,
- attach a sheet of steel and install the main bracket,
- build up the pipe to the required height,
- in the place of transition of floors, mount a protective structure (passage pipe) made of galvanized steel, in which you need to cut a hole slightly larger than the diameter of the chimney. Then the workpiece is put on the chimney and fixed to the walls of the opening in the ceiling,
- fix the chimney with wall brackets and strengthen the joints with clamps,
- install the protective cap on top of the pipe.
The outlet section of the ventilation duct above the roof should rise:
- above the roof ridge or parapet at least 0.5 m, if the chimney is at a distance of no more than 1.5 m from the parapet and the upper edge of the roof,
- above the ridge or parapet or be at their level, if the pipe is at a distance of 1.5 - 3 m from the ridge and parapet,
- be not lower than a conventional line drawn from the ridge at an angle of 10º - if the height of the weather vane is more than 3 m relative to the ridge,
- above a flat roof by at least 50 cm.
Watch the video on the chimney device:
Pros and cons of the two systems
Natural ventilation
You don't need any special skills to equip such a hood yourself, while it has a number of advantages:
- The absence of mechanisms makes such air exchange reliable and durable.
- There is no need to spend money on purchasing devices.
- Ease of use.
- Silence during operation.
At one time, such a hood fully met its requirements, but with the advent of new gas equipment, the view on this has changed.
At the same time, the following significant disadvantages were discovered:
- Dependence of the optimal air circulation on the season and climatic conditions.
- Inability to regulate the air flow.
- Penetration of foreign particles through the system.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with: Organization of ventilation of natural and forced type in the kitchen
And also with a decrease in air intake, there is a possibility of an increase in humidity in the room.
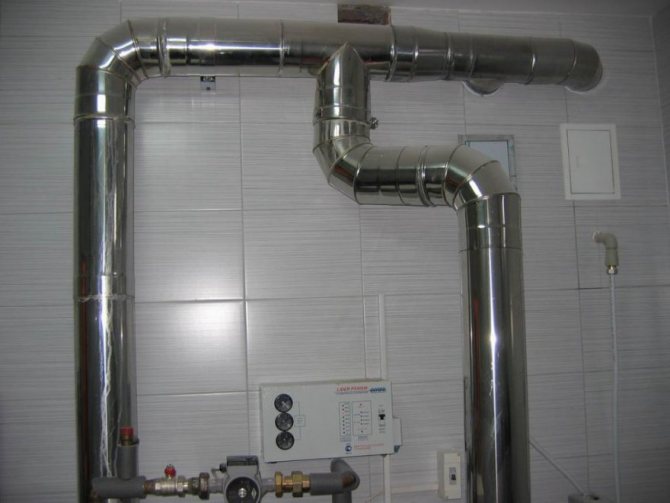


Artificial ventilation
Artificial hood is the best option when installing gas boilers, since:
- There is a possibility of self-regulation of the air supply.
- The importance of this ventilation in confined spaces.
- Nice microclimate in the room.
- The ability to regulate air exchange using the remote control.
- Independence from weather conditions.
If there is a boiler with a coaxial outlet in the house, then the built-in fan in it automatically creates a favorable atmosphere for human living.
The only drawback of such a system is the rather high cost of this installation.


Boiler dimensions in a private house: standards, standards, types
Architectural and construction work. General drawings (version of the closed smoke extraction system) (from TP 903-1-199) Album 5.14. Cotel. Architectural and construction work. Atypical products (from TP 903-1-199) Album 6.3. Subpropetrovsk setting.
Architectural and construction work. Atypical products (from TP 903-1-199) Album 9.10. DE-16 (10) -14GM Document Feeder. Appointment of the manufacturer of the control panel for automation and devices (from TP 903-1-199) Album 9.18 Water treatment device.
Manufacturer's task on control panels for automation and instrumentation (from TP 903-1-199) Album 11.3.Coteli. Connecting Compliance Mechanisms with Regulatory Authorities Album 11.5 Metal parts of ancillary equipment and instruments (from TP 903-1-199)
This is not useful Document approved by: Glavpromstroyproekt Gosstroy of the USSR, Decree no. 41 of 11/10/1983
Heat in the house - installing a solid fuel boiler
Among the owners of private houses, the most common today is the solid fuel heating system. Not everyone has the opportunity to connect gas, not everyone has enough funds to heat the house with an electric boiler. However, the installation of a solid fuel boiler is reliable and efficient enough to compete confidently with more modern home heating methods.
When connected to automation, these devices are quite competitive. In this regard, they can compete with them, if only long-burning boilers.
Ventilation system calculation
The performance of gas equipment and the safety of people depend on the correct installation of exhaust devices in the boiler room; therefore, one should not strive to do everything independently for the sake of economy.
ON A NOTE! When drawing up a project, it is necessary to bring the outlet of the supply pipe as close as possible to the fuel chamber for better air flow and, accordingly, for optimal fuel combustion.
When calculating the ventilation system, it is important to know the following parameters:
- Air speed.
- The volume of the room, taking into account the height of the ceiling.
- Air exchange in the room per unit of time.
The airspace volume is calculated according to the following formula V = L × S × H × n, where: V is the volume of air to be exchanged for 1 hour; L is the length of the room; S - width; H - height; n is the rate of air exchange.
For floor-standing gas boilers, the fan is chosen with a power reserve exceeding the usual load by 25-35%.
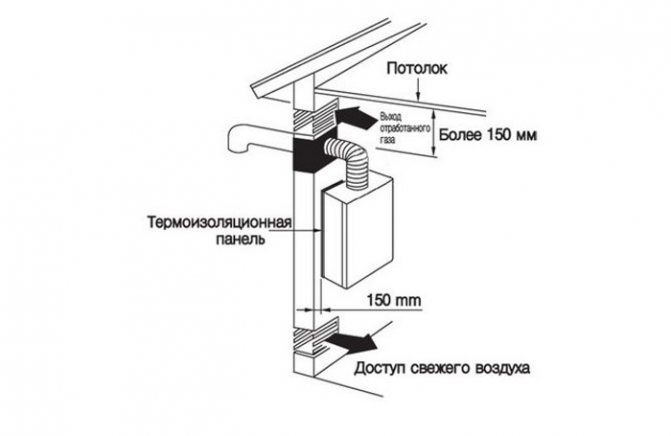

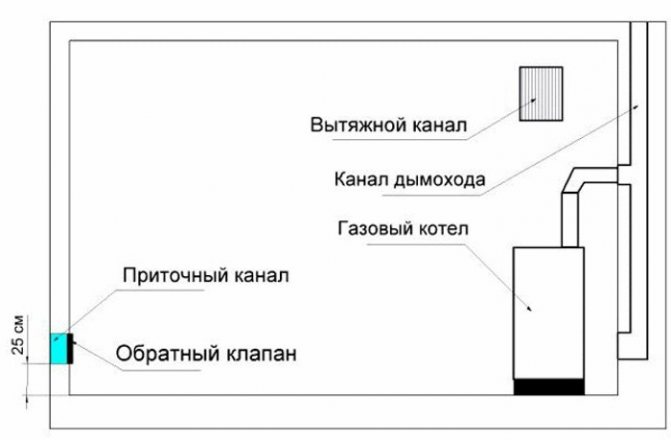
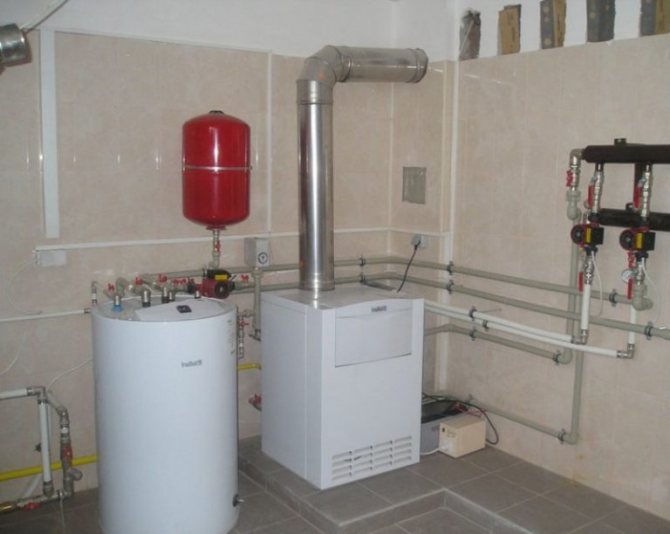
Ventilation system device
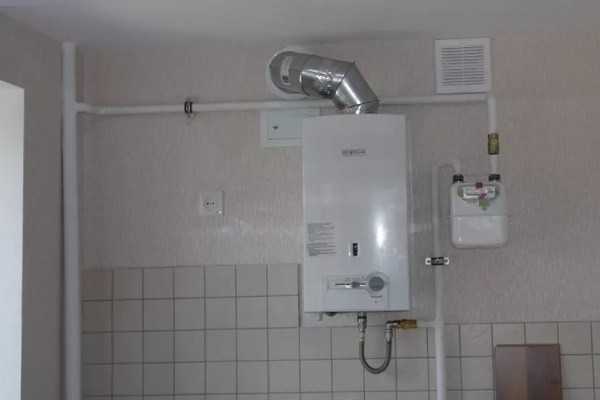


The ventilation duct should be located near the gas boiler
For a heating unit with a closed firebox, a coaxial chimney is optimal, which contains two insulated channels in one pipe. The inner tube is used to remove the combustion products, and oxygen enters the outer chamber.
When installing ventilation, follow the rules:
- no more than two types of gas equipment are connected to the chimney;
- the ventilation shaft is tightly insulated;
- the supply and discharge system is made of materials that do not burn;
- the cleansing channel is made 25 cm below the main one
- from the horizontal smoke exhaust pipe to the ceiling must be at least 20 cm;
- the hood outlet is insulated from the cold by heat-resistant materials.
For a wall-mounted boiler with an open firebox, separate air supply and smoke exhaust pipes are arranged, with the holes provided opposite each other. The system is equipped with a check valve to prevent the rod from overturning.