Fresh, safe air for people is a basic factor that determines overall well-being and health. In industrial and warehouse complexes, the quality of aeration also cannot be treated superficially: it allows you to maintain the temperature and humidity regime necessary for equipment or goods, removes caustic fumes and dust from the premises. Therefore, the regulatory authorities strictly monitor that during the construction, use of buildings for any purpose, the basic requirements for ventilation systems, as well as specific provisions for the facility, are observed.
Air exchange complexes are generally subdivided into comfortable and technological. The former must comply with the sanitary and hygienic component of the requirements. The latter, in addition, are checked according to the conditions determined by the technology of the industrial facility.

For individual ventilation elements, specific positions are formed. Basic principles:
- for exhaust systems - maintaining an acceptable level of concentration of harmful substances in the air that enters the premises and removing contaminated masses;
- for local sources of supply ventilation - effective capture with the subsequent removal of industrial hazards (gas, corrosive vapors, etc.) and household hazards.
Classification of requirements
The norms that define the "reference" indicators and rules for organizing air exchange are developed at the national level. In general, they can be divided into general GOSTs, regulating provisions for ventilation, and SNiPs, which control individual parts of the sanitary component. For industries, facilities with an increased risk of fires (warehouses with fuels and lubricants, paint) or with specific conditions of detention (pharmacies, hospitals, chemical plants), separate instructions are being developed.
Requirements for ventilation systems are formed depending on their features. The basic function of any installation is to create an air environment that would satisfy all standards and solve problems:
- removal of waste masses with harmful impurities and excess heat;
- implementation of the influx of fresh, corresponding to SNiP.
Requirements for the installation of ventilation and indicators for its further operation can be classified in separate areas:
- sanitary and hygienic - ensuring the comfort of people in the room and monitoring safety for their health;
- operational - compliance with the simplicity and ease of maintenance, availability for repair, minimizing the need for it;
- architectural, installation - fire safety, vibration and sound insulation of equipment and structural elements, minimization of time and effort for installation and commissioning;
- economic - reducing (as far as possible and justified from the point of view of common sense) the cost of installing systems and their use.


Operational Requirements
The fulfillment of these requirements should facilitate the operation of the system after the start of its operation:
- Ensuring a sufficiently accurate maintenance of air parameters (especially important in precision air conditioning to maintain technological parameters)
- Minimal need for repair and maintenance, their simplicity and convenience
- Equipment that requires maintenance should be installed in a minimum number of technical rooms.
- Small inertia of the system. Switching from cooling to heating mode and vice versa should be done as quickly as possible.
- When one of the air conditioners stops, the other must continue to work, providing at least 50% of the required air exchange (interlocking of systems).
Rules for users
Personnel and private users of ventilation systems are not allowed:
- violate the integrity of the complex, air outlet and connecting elements;
- connect gas appliances to the system;
- disconnect or remove the fire-retarding and ventilation devices provided by the project;
- close openings, ventilation grilles, exhaust ducts;
- burn out the accumulated deposits yourself, and so on.
The requirements for the ventilation system of industrial premises are formulated taking into account the development of a procedure for personnel. Workers who maintain production facilities must act in accordance with the instructions and ensure:
- observance of the terms of cleaning of valves and branches;
- disconnecting the repaired parts of the system from the rest;
- the required frequency with which the efficiency of the ventilation systems is checked and their prevention;
- shutdown of ventilation in case of fire notifications;
- control over the serviceability of the fans - there should be no deflections or breaks on the blades, the wheels should be balanced and their smooth running should be monitored, the grounding devices should be checked regularly.


Construction and installation requirements
When organizing ventilation in residential premises, construction and installation norms and rules are important. They determine what is the minimum area required for this or that equipment, recommend the most simple and effective installation of air ducts, ensuring the minimum time and labor costs. Compliance with building codes ensures the fire safety of the building and prevents the spread of smoke and fire through the ductwork. According to building codes, vibration isolation and sound insulation are carried out, if they do not meet the standards, it will be unsafe to be in such a building. Compliance with the design standards of the room is also important: ventilation structures and elements must be tied to the overall design of the room at the project stage.
Key points of requirements
Among all the restrictions, the sanitary direction is especially important, as well as the fire safety requirements for ventilation systems. Failure to comply with them can lead to extremely sad consequences, and compliance with the established parameters is strictly monitored.
Sanitary and hygienic requirements for ventilation systems are put forward by the relevant authorities, and the inspection controls that:
- the volume of the inflow masses exceeded the drawn ones by 10-15%;
- air was supplied to the points with the least pollution, and was removed primarily from the places with the greatest;
- overheating or hypothermia of people in the premises did not occur;
- the level of noise, vibration was not more than permissible;
- microclimate indicators (humidity, speed of movement of air masses, temperature) were at the level of norms.
The ventilation requirements for warehouses, industrial production and household facilities take into account the conditions in which the level of compliance with fire safety is maintained. To do this, the valves are serviced, the system is cleaned of dust, dirt, accumulated deposits that can ignite, and the fasteners are checked. To prevent the ventilation system from causing an avalanche-like spread of fire, it must be properly installed and operated.
Sanitary Requirements
The air comfort of people in a room depends on several parameters that can be controlled by ventilation and air conditioning systems. The microclimate is characterized by:
- Air temperature
- Relative humidity
- Air speed (mobility).
For various types of premises (residential, public, industrial), there are standards and rules (SNiPs, sanitary standards) that establish the optimal and permissible air parameters.
Optimal (recommended) parameters - these are the most favorable conditions for the best human well-being. If a person is in a room with optimal air parameters, he feels thermal comfort and has high efficiency.
Valid (required) parameters microclimate are set for those cases when the optimal parameters for some reason are not observed (for technical or economic reasons). If a person is in a room with acceptable microclimate parameters, he may feel temporary discomfort and decreased performance. However, there should be no deterioration in health.
In addition, sanitary standards regulate:
- Air purity (pollution in the air of the working area should not exceed the MPC)
- Maximum permissible noise level
- Minimum consumption of fresh air per person.
For a number of technological processes, it is necessary to precisely maintain certain air parameters (temperature, humidity, purification). The air conditioning and ventilation system must cope with their implementation.
If the quantity and quality of products in production depends on the accuracy of the technology mode, and not on the productivity of employees, then in such a room it is necessary to maintain the air parameters that are optimal for the production process. If productivity is determined primarily by the people working indoors, then the focus should be on the comfort of the staff.
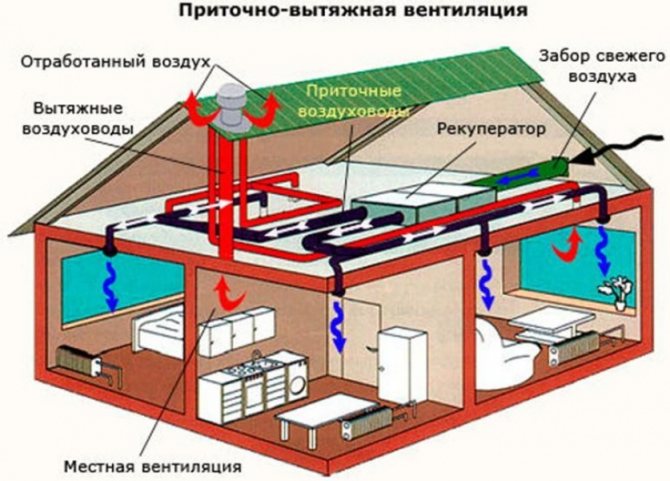
Fresh air (possibly purified) must be supplied to the room - naturally or mechanically. Contaminated air must be removed from the room. In industrial premises, this is done by local or general exhaust hood, and in residential premises, as a rule, due to natural exhaust.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
How the ventilation systems are installed can be found in the following video:
It is impossible to ignore the rules of fire safety or SanPiN, despite the high cost or inconvenience of their implementation. The number of technical solutions for ventilation of public buildings is quite considerable.
For each project, you need to select and look for the way to implement the ventilation system, which will be suitable for the stated requirements. But, if there is not enough experience in this area, it is better to turn to specialists who will help you correctly design and equip the ventilation system.
Please ask your questions on the topic of the article, share your experience and valuable advice on arranging ventilation. The communication block is located below.
Requirements for air ducts of ventilation systems. Requirements for ventilation systems
When designing ventilation systems, basic requirements are imposed on them:
1) Sanitary and hygienic requirements:
ventilation should ensure the air condition in the premises that meets the requirements of sanitary standards. The premises must maintain the established values of temperature, humidity, concentration of harmful substances. Particular attention should be paid to the dustiness of the air.
Imagine for a moment that, thanks to efficient energy conservation, another chimney is smoking. This leads to a decrease in harmful emissions, the trade of which is interesting. More importantly, our children breathe cleaner. We care about the environment we will have tomorrow. We care about the climate, which has already begun to punish us for our ruthlessness in the last century.
In this line of thought, there is reasonable energy saving. Financially beneficial healthy environmentally friendly.... There are many options for implementing an energy-efficient ventilation system. Indoor air cleanliness and the problems caused by long-term exposure to polluted rooms are among those that have been harsh in recent times. Air pollution in workplaces today is not only a health problem, but also an important factor that negatively affects productivity.
2) Technological requirements
consist in the fact that ventilation should ensure the air condition in the premises that meets the requirements of the ongoing technological process. Many technological processes, especially those related to the processing of hygroscopic materials, are very sensitive to the temperature and humidity of the internal air (light industry enterprises: textile, spinning and knitwear factories, printing enterprises, etc. and the food industry. In this case, internal parameters are assigned based on the requirements it is the technological process, and not the comfortable feeling of people.In many cases, to ensure the required parameters, it is necessary to use air conditioning systems, not ventilation systems.
For this reason, in the countries of the European Union, ventilation is one of the main building systems in public and administrative buildings. The picture in our country is completely different: the presence of a ventilation unit is a chimera, even for a significant part of newly built buildings in the public sector. Because the main problem is not the availability of sufficiently effective technical solutions to the problem of poor air quality in work and living quarters. The problem lies in the significant investment scale required for the design, construction and maintenance of a modern ventilation system.
3) Energy requirements:
ventilation systems must perform the functions assigned to them with a minimum consumption of heat and electrical energy. The fulfillment of this requirement is ensured by the introduction of modern methods of designing equipment and modern technologies for its manufacture, the correct choice of the size of equipment and ventilation ducts, the use of more efficient and economical equipment, the use of secondary energy resources (primarily the use of the heat of the removed ventilation air), the use of modern digital automatic systems. regulation (SAR).
In addition, the traditional purpose of ventilation - to replace polluted indoor air with fresh air from outside - has expanded in recent years in the direction of. Maximum limitation of pollutants. Into the fresh air flow into the interior spaces. The main function of modern ventilation is to release polluted air into the atmosphere only after proper cleaning. Therefore, as an important element of ventilation systems, systems are increasingly being introduced, not only filtering the incoming fresh air into the premises, but also capturing pollutants in the air stream leaving work or residential areas.
4) Economic requirements
: the cost of the ventilation system and its operating costs should be as low as possible. Unfortunately, this requirement is the most difficult to meet.
5) Design and technological requirements:
the design of the ventilation system should provide modern efficient methods of their production. Elements of ventilation systems must be manufactured at the current, already achieved level of production technology, with an appropriate degree of accuracy and appropriate quality.
In principle, sources of air pollution in buildings are divided into two main groups - mechanical and thermal. In the industrial field, sources of mechanical pollution are mainly generated by the processes of production of dust, water vapor, harmful gases and other substances that spread in the air. Thermal pollution is a secondary process that accompanies the operation of a wide range of production facilities and technological processes. In the public sector, pollutants include mold, detergents, cigarette smoke, office cars, etc.
6) Operational requirements
: the operation of the ventilation system should be minimally labor intensive. This is achieved primarily by increasing the service life of the equipment, which eliminates the need for frequent maintenance or repair. Access to serviced items of equipment should be as easy as possible. In large installations, wet cleaning of the interior surface is allowed.
One of the main arguments against the construction of ventilation systems is theirs. An important trend in the development of the modern world is the reduction of energy consumption on a global scale. It is said that a technical mismatch between energy consumption and the efficiency of modern ventilation systems has already been found.
In the regulatory framework of a number of European countries, provisions are made to promote the creation of energy-efficient ventilation systems not only in the public and industrial sectors, but also in the household. Another reason for the relatively limited utilization of the opportunities provided by good ventilation is the relatively difficult derivation of a poorly designed and poorly functioning ventilation system. Even in cases where indoor air quality is of paramount importance to the investor of a new building, limited information about the types of modern ventilation systems, both performance and functionality, makes them difficult to design.
7) Fire safety requirements:
the possibility of fire during operation of the ventilation system must be excluded. This is achieved by using special protective shut-off devices on air heaters and motors of fans, pumps and compressors. In addition, if the ventilation systems are serviced by a fire or explosive room, the equipment used must be explosion-proof. If necessary, special fire-retardant valves are installed on the ventilation ducts. The air ducts and the structure of the equipment enclosures must have the required degree of fire resistance, which is achieved by using non-combustible materials for air ducts, thermal insulation, and sealing materials.
On the other hand, the construction of highly efficient ventilation systems is associated with significant investments. However, the funds to buy and maintain them in public and business buildings are viewed primarily as an expense rather than an investment to preserve the health of the people who spend time in the building.
For this reason, it is a mandatory requirement for modern ventilation systems. Technically and cost effective. It is extremely important to achieve a high efficiency of the ventilation system in order to adapt it to the specific characteristics of the building - its purpose, features of the structure of the building, the number of people in it, the geographical location of the building, climatic features of the region, and much more. Consequently, the efficiency of the ventilation system is still highly dependent on the design stage of the building.


: the operation of the ventilation system must not adversely affect the environment.For the construction of plastic parts, synthetic materials are selected that do not contain and do not emit harmful substances. The air discharged into the atmosphere is cleaned to avoid pollution. Reducing energy consumption reduces thermal pollution of the environment.
The efficiency of a ventilation system depends on three main characteristics: suitability for the application, reliable operation and low energy consumption. From a technical point of view, ventilation is adapted to the specifics of the application when it is designed and implemented in accordance with the requirements for its functionality and the characteristics of the building. Reliability of operation is a function that, in relation to ventilation systems, means maintaining the optimal operating parameters of the selected technical solution for a long period of time.
9) Architectural and construction requirements:
individual elements of the ventilation system located inside the premises (air distributors, grilles, air ducts) must not violate their internal interior. Ventilation system equipment is located on auxiliary sites and specially designated technical rooms.
Given the steadily rising prices of primary energy sources, low energy consumption plays a decisive role in determining the feasibility of investing in a ventilation system. In accordance with the general trends in the development of technology, it is believed that to meet the three main criteria of a modern ventilation system, namely.
Reliability, low energy consumption. And taking into account the specifics of the application, the technical solution should be as simple as the constructive implementation. However, in a number of countries, requirements are also imposed on the technological level of ventilation systems, and not only on its technical and economic efficiency. An important role in meeting the performance criteria is the process of installing and maintaining the system. A properly designed and executed ventilation system maintains higher air flow rates while maintaining or even reducing energy consumption compared to legacy technical solutions.
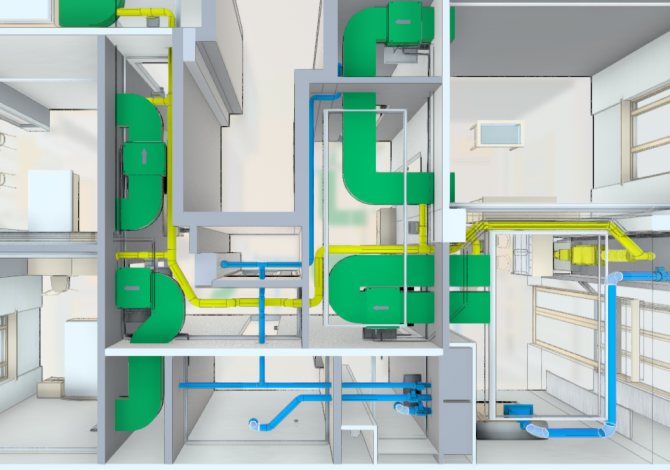
Premises for ventilation chambers and equipment should be located in places far from the main premises (to reduce the noise level), but so that it is not difficult to lay air ducts in ventilated areas. It is advisable to have several ventilation chambers at different ends of a large building in order to avoid laying long ducts. When laying air ducts along corridors, it is advisable to have a headroom in order to locate the air ducts behind false ceilings. An effective means of simplifying the routing of air ducts in multi-storey buildings is the device of a special technical floor at the top of the building, on which both supply and exhaust equipment can be easily placed.
Improved airflow control and heat utilization are important technical trends in ventilation systems. In the area of energy efficiency, a number of legal documents have been introduced in Bulgaria. Mainly due to the ever-increasing prices of primary energy sources, more and more buildings are thermally - and waterproofed, to a large extent.
Through walls, doors and windows. Unfortunately, the result of this process is a sharp deterioration in indoor climatic parameters, which reflects a constant increase in the number of allergic diseases. The reason for the deteriorating air quality and indoor humidity problems is that the use of ventilation lags behind the insulation process of buildings.
10) Construction and installation requirements:
the design of ventilation systems should provide for technological methods of installation of air ducts and equipment at the facility, ensuring the proper quality of the system assembly. Particular attention should be paid to sealing the seals when connecting duct links and connecting equipment items.
Modern high-tech ventilation systems with forced ventilation. From outdated technical solutions, but only as an initial investment. Considering the investment required to purchase a ventilation system in the long run, it often turns out that the handle of the financial resources required to operate, maintain and maintain a plant throughout its life is much higher. Ongoing heating and ventilation costs represent a significant portion of building maintenance costs.
Therefore, it is economically more profitable to purchase larger, but less energy-intensive ventilation systems that use the heat generated to the outside. The indisputable fact is that natural ventilation, in which clean air enters convection workplaces, requires lower capital and system costs than with forced ventilation. On the question of what kind of ventilation scheme.
Fasteners to structures must not damage them, they must be unified. Heavy equipment must have a frame or frame with holes for slinging. Oversized equipment should be dismountable as possible to facilitate transportation and delivery of ventilation chambers to the premises.
AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMS (SCR)
Natural or forced. Is more energy efficient, there are conflicting views. A number of experts argue that due to the heat loss associated with the leakage of warm air from the room into the atmosphere, these systems actually consume significant energy. Instead of using heat to be used for heating, it is practically dissipated in the space around the building. Another group of experts supports the idea that for applications where air is not supplied to the room and selective ventilation of some areas of the workspace is not required, it is more economical to use natural ventilation systems.
They are aimed at ensuring the air exchange necessary to comply with the requirements of sanitary standards. This applies to temperature and humidity parameters, as well as the permissible level of components harmful to human health. The most critical parameter is the content of dust in the air - many ventilation systems operate without filtration, the condition of the ventilation chambers and ducts does not meet the proper requirements. They provide for mandatory filtration of the supply air entering the interior. It is possible to carry out wet cleaning of the walls of the supply units thanks to their special coatings. New generation filters not only clean the incoming air from dust and bacteria, but also ozonize it and give it a pleasant smell.
For explanatory reasons, the world's leading manufacturers unite around the assertion that modern systems with automatic flow control and exhaust air flow using rational thermal energy are the most energy efficient.
Depending on the principle of operation, ventilation systems are of two main types - with natural and forced ventilation. Natural draft ventilation, also known as natural ventilation, is the most widely used ventilation principle so far. It is based on the fact that polluted air is warmer and rises up, leaving the room through special channels due to its lower density than cold air.This creates low pressure conditions in the building that force fresh air from outside through valves, ventilation windows and other leaks in the room such as openings in the bottom of doors, access holes, poorly sealed windows, etc.
Technology requirements
They are aimed at maintaining the compliance of the air composition in the industrial area with the requirements of the production technology. Some technological processes, in particular work with hygroscopic materials, require a special temperature and humidity regime. To determine the parameters of the ventilation system, it is not the comfort of the personnel that is of primary importance, but the production necessity. As a rule, it is necessary to be guided not by the rules for laying the ventilation system, but by general standards.
Forced ventilation systems, in turn, are also of two types - with a suction fan and so on. balanced ventilation systems that include a suction and discharge fan. Among the recommendations for the development of balanced ventilation solutions are the installation of systems with heat recovery systems and even the recovery of heat generated from the outside. For forced ventilation systems, in the most common case, polluted air from work and living quarters is discharged into the atmosphere using a suction fan.
Energy Saving Requirements
The essence of these points is that all the basic functions of the ventilation system should be performed with the least consumption of electricity and heat. This should be facilitated by modern methods of manufacturing ventilation equipment, the optimal selection of its parameters, the use of modern efficient technologies, including recuperation (secondary use of thermal energy of the displaced air), the installation of automatic parameter control (ACS). The use of these modern tools improves the functioning of ventilation equipment in one mode or another and allows efficient control of systems of any complexity with the lowest energy consumption.
The development of streamlined shapes of ventilation equipment also contributes to a strong decrease in the aerodynamic resistance of the ventilation system components, to optimize the energy parameters of ventilation and pumping equipment. The following measures will significantly reduce the energy consumption of the ventilation system:
- The use of electric motors with an external rotor;
- The use of inverter converters to control the rotation speed of fan and pump wheels;
- Application of bearings of modern designs;
- Use of high quality thermal insulation materials.
Requirements for the economic part
It should be expressed in the desire to minimize the financial costs of the ventilation system itself and operating costs, otherwise the customer may refuse it. This requirement is very difficult to fulfill - the price of high-quality ventilation equipment is high, the cost of using heat and electricity is constantly increasing. This leads to the inaccessibility of ventilation systems for a low-income customer.
Therefore, he often buys low quality equipment based solely on the price factor. In addition, the ventilation system is often formally created in order to be accepted by the fire and sanitary inspection services, which give permission for the further activities of the organization. The prospect of a ventilation system functioning for such a customer, as a rule, does not bother at all. As a result, the air condition does not even come close to meeting the minimum requirements. It is worth saying that the purchase price of the ventilation system itself and the cost of operating costs refer to different items within the accounting department of any enterprise. Costs per 1 year are calculated using a simple formula:
P = K / T + E
where
TO
- the capital cost of the system,
T + E
- the annual cost of heat and electricity costs.
Requirements for design and technological parameters
They boil down to providing the most efficient methods of manufacturing ventilation system components. Their design must comply with the standards of modern technological processes. The manufacture of ventilation system components must take into account and put into practice all modern technological solutions. This, in particular, concerns ensuring the quality of finished products and the accuracy of compliance with the parameters.
In modern production facilities, ventilation system components are manufactured on automated lines and CNC machines. It is this level of production that can give finished products the necessary reliability for further use. Technological processes are now as standardized as possible, the human factor is minimized.
Modern designs and technologies minimize expensive and time-consuming operations (eg assembly of screw connections). Almost all products that do not bear the key load are made of plastic. If possible, products are stamped. Even intricate decorative designs are made with automatic lines. This not only reduces the cost of production, but also increases the durability of this coating.
Performance requirements
They come down to minimizing the cost of operating the ventilation system, to reducing the corresponding labor costs. To do this, it is necessary to increase the service life of the ventilation equipment so that there is no need for frequent maintenance or repairs. For example, new generation bearings do not require permanent lubrication. Parts and mechanisms of the ventilation system should be as accessible as possible. For this purpose, doors and hatches are provided. Filters and heaters should also be located so that they can be easily serviced (slide-out models exist). In some cases, it is necessary to illuminate the elements of the ventilation system in order to visually monitor the condition of the ventilation equipment and carry out wet cleaning of surfaces.
Maintenance and repair of ventilation systems should only be carried out by trained and qualified personnel.
Fire protection requirements
Fire safety requirements are aimed at eliminating the likelihood of a fire hazardous situation during the operation of the ventilation system. To do this, automation devices are built into the system that turn off the operation of the equipment if there is a danger of fire. If the ventilation system operates at an explosion or fire hazardous facility, it is necessary to use explosion-proof equipment options (most manufacturers have them). There are fire dampers and should be installed if there is a risk of fire. The materials used in the ventilation system must also be non-flammable in such situations.
Environmental safety requirements
These requirements are aimed at preserving the environment. With regard to ventilation systems, it is necessary to abandon the use of freon-containing refrigerants that destroy the ozone layer of the Earth. The plastic components of the ventilation system must not contain components harmful to people. In addition, air and gases emitted during operation of the ventilation system must be cleaned with an effective filtration system. Reducing energy consumption is also one of the measures aimed at reducing environmental pollution.
Requirements for the architectural and construction part
Aimed at ensuring compliance of the ventilation system components with the interiors of premises and the appearance of buildings and their structures. The routing of the duct system and the location of ventilation equipment must not conflict with the architectural and structural requirements of the building.The total volume of the ventilation system should be minimized as much as possible, separate rooms (ventilation chambers) should be allocated for the main equipment.
The air duct arrangement system must take into account the location of the main building structures, especially the load-bearing elements, and in no way contribute to their destruction.
Installation of ventilation ducts through the roof waterproofing system should in no case violate the integrity of this system.
At the stages of architectural solutions and design, it is necessary to take into account the parameters and location of the main ventilation equipment, the dimensions of the section of the air ducts and the scheme of their laying. In rooms with a large area, it makes sense to mount several ventilation chambers in order to avoid laying long duct segments. In the corridors of buildings, it is advisable to place suspended ceilings at a distance of 30-50 cm from the main ceilings so that the air ducts can be placed in the resulting niche. When installing vertical sections of the ventilation system highways, you need to use special shafts or close the ventilation boxes with sheathing materials (usually from plasterboard).
Construction and installation requirements
Aimed at ensuring the reliability of the assembly of the structure, the quality of the installed ventilation system. The main emphasis should be placed on ensuring the tightness of all joints of the air duct segments, the quality of the seal. Fasteners in no case should spoil the material, their parameters should be clearly spelled out in the design and as-built documentation. In the work, you need to use a specialized (suitable for this type of work) tool. Heavy and oversized equipment must be moved and installed using special systems designed for this (special vehicles, slinging materials, special frames and frames).
Companies focused on modern production offer various advanced technological solutions, accompanying their equipment with detailed instructions. There are technical means for precisely maintaining horizontal and vertical alignment. In order to speed up the assembly, bolted connections are replaced by latch connections. If it is possible to use flexible air ducts for connecting ventilation equipment, this option is used. This allows minor dimensional variations to be compensated. In addition to gaskets, fast-setting sealants are sometimes used. Time-consuming flange joints are giving way to easy-to-assemble nipple joints, especially in suction areas where quick dismantling is required.
What documents regulate air exchange?
The main document, which describes the parameters and requirements for air exchange - SP 60.13330.2012 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning, many of which, by the way, are included in the list of mandatory ones, according to PP No. 1521.


Microclimate parameters are established in the current regulatory documents - sanitary standards and GOSTs. They help to avoid violations at the stage of ventilation design and achieve justice in case of violation of the rights to high-quality air exchange.
It describes the basic requirements for ventilation and air conditioning of buildings, including norms, fire safety arrangements and mandatory schemes with calculations.
The same document refers to:
- SP 118.13330.2012 Public buildings and structures.
- SP 44.13330.2011 Administrative and domestic buildings.
- SP 56.13330.2011 Industrial buildings.
- SP 7.13130.2013 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning. Fire safety requirements.
- SP 158.13330.2014 Buildings and premises of medical organizations.
- GOST 12.1.005-88 General sanitary and hygienic requirements for the air in the working area.
- GOST R 52539-2006 Air purity in hospitals.
- SanPiN 2.2.4.548-96 Hygienic requirements for the microclimate of industrial premises.
- SanPiN 2.1.2.2645-10 Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for living conditions in residential buildings and premises.
In all these documents, you can find answers to almost any questions related to air exchange in a particular building and room.
There is a lot of information, and for ordinary people most of it is superfluous, so we tried to highlight the most basic for you on some points.
Category No. 1 - residential buildings
At the design stage for residential buildings, as a rule, an exhaust ventilation system of a natural type is provided in apartments. It is installed in the form of channels in kitchens, bathrooms (toilets, as well as bathrooms).
However, if there is no end-to-end ventilation, as in some large apartments, the hood can also be installed through living rooms.


Mechanical forced systems help to achieve the required air exchange parameters in cases where the natural ventilation system cannot cope
The inflow is carried out due to the usual ventilation through doorways with an external exit and vents.
However, there are exceptions. For example, if the temperatures of a cold five-day period in a particular region can systematically reach -40 degrees, the engineer of a contractor building a 3-story building (or higher) often provides for a mechanical flow of air with heating.
But for the inhabitants of the IV climatic zone, air conditioners or other devices are required to help cool the air.
With air heating, air is supplied through its channels.
It is not uncommon to ask a question on the forum regarding the combination of ventilation ducts. In residential buildings, it is allowed to combine horizontal air ducts of a bathroom with a toilet or kitchen and vertical channels of a bathroom, toilet and utility blocks.
Stairways are ventilated both naturally and with the help of ventilation ducts, if there are no windows with vents.
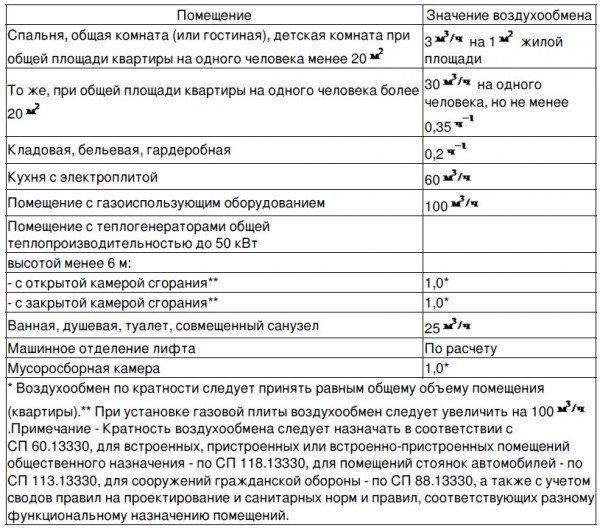

Air exchange rates in residential premises of buildings of the corresponding purpose are calculated according to SP 54.13330.2016 Residential apartment buildings
As you can see, the calculated parameters of optimal air exchange are contained in SP 54.13330.2016. The operational responsibility for the maintenance of residential buildings lies with the homeowners and engineers of the MC in the MKD.
Category №2 - administrative buildings
In buildings of this type, which are not located in climatic zone 4, supply and exhaust ventilation is used. Air conditioning at the expense of the budget is allowed with economic and technical justification.


The installed equipment in any building should be regularly checked, in accordance with established standards, it is imperative to clean it, as well as other maintenance
As for the inflow, the channels are individual for conference rooms and catering places. For the rest of the premises, a single system is most often designed.
Exhausting is carried out in a natural way, except for the following rooms where mechanical induction is applied:
- bathrooms;
- smoking rooms;
- rooms over 35 sq. m of area (due to an individual channel);
- film projection;
- fume hoods.
And also, natural draft is typical for any administrative building, with the exception of buildings more than 3 floors, with the number of employees exceeding 300 people.
According to the norms of air exchange of the inflow, the amount of normalized air depends on the purpose of the room. All norms are contained in SP 44.13330.2011 clause 7.2.
Category №3 - educational institutions
In establishments of this purpose, you are likely to come across a supply and exhaust system.
With the number of students up to 200 people, forced ventilation with natural motivation is used, more than 200 - always with a mechanical, but natural exhaust structure with a single air exchange from the offices through corridors, bathrooms and windows.
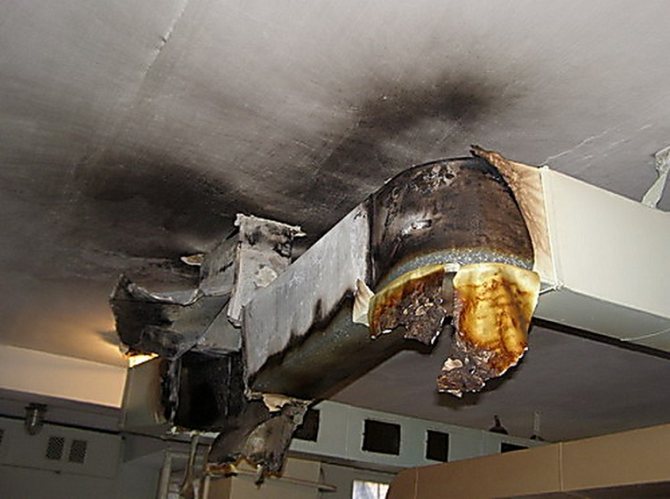


One of the most common causes of fire in engineering structures is ignition and flame propagation through ventilation compartments for a number of reasons. Therefore, in schools and educational institutions, the strictest requirements are imposed on ventilation.
If air heating is used in combination with ventilation, it is imperative to equip automatic regulation and control, while the supplied air temperature should not be higher than 40 degrees.
Separate ventilation systems should go out of classrooms, a gym, a dining room, preparatory rooms with exhaust units, a first-aid post and a bathroom.
Air exchange rates in various premises of educational institutions are spelled out in SP 118.13330.2012.
Category №4 - medical institutions
We include hospitals, pharmacies, clinics, and first-aid posts to medical institutions. A supply and exhaust system is also being designed here, however, with a mechanical impulse and some peculiarities.
In particular, for example, in hospitals there is a ban on the recirculation of air masses, which is natural, taking into account the requirements for fresh air and possible bacterial contamination.


In infectious compartments, it is necessary to arrange exhaust ducts from each box and from each section with a natural urge, and a supply duct with a mechanical feed and a natural corridor
Particularly stringent requirements for the quality of air exchange and the need to equip individual systems according to which rooms should be installed ventilation and air conditioning in the hospital.
That is to:
- generic;
- wards for newborns and nursing newborns;
- operational, postoperative (air mobility no more than 0.15 m / s, relative humidity 55-60%);
- resuscitation;
- intensive care boxes;
- premises for burn patients;
- X-ray departments;
- laboratories;
- bathrooms;
- pharmacy points;
- By the way, supply air with additional filter cleaning is supplied to these rooms.
If there are no infectious patients in the wards or rooms and a single mode is in effect, then ventilation systems can be combined.
It should be noted that from an engineering point of view, in hospitals, the most difficult engineering separation of ventilation of different rooms.
The normative values of the air exchange rate in medical organizations are fixed in SP 158.13330.2014, as well as in the "Instructional and methodological guidelines for organizing air exchange in ward departments and operating units of hospitals" and "Instructional and methodological guidelines on hygienic issues in the design and operation of infectious diseases hospitals and departments" ...
Category 5 - retail buildings
You must have noticed that many stores have musty air and mixed aromas. Of course, this should not be or is allowed, but at a minimum.
Stores are equipped with air conditioning or mechanical ventilation.


Before designing ventilation, the calculation of the possible number of guests + service personnel is carried out. Depending on the type of outlet, for each visitor there should be from 2.5 sq. m up to 3.5 sq. m area. And from here the rates of air exchange are already calculated
For separate halls of household and food trade, ventilation and air conditioning systems are separated.
In the storerooms, a natural exhaust hood is provided, also separate, but, in principle, it is possible to combine mechanical schemes with utility rooms, provided that fire-retardant valves are installed.
Of the features, we note that if sales areas are part of a residential or office center and are located on the ground floor, they must have independent ventilation and air conditioning systems from the common building.
As for the air-thermal curtains, they must be installed in the vestibules of shops with an area of 150 sq. m and markets ranging from 600 sq. m, if the temperature during the cold period drops below 15 degrees in a particular region.
It is possible to recirculate air, but not in rooms with chemical and synthetic agents, as well as flammable substances. However, the supplied outside air must be at least 20 cubic meters. m per hour for each visitor.