What distinguishes a convector from a radiator
The described devices are a type of heating devices. They can work independently or as elements of a heat supply system. The main difference between a convector and a radiator is in the design and principle of operation of the devices.
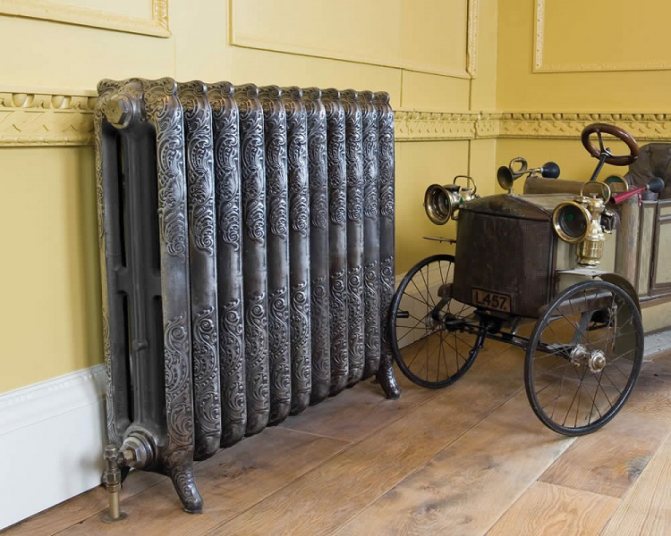
Radiator
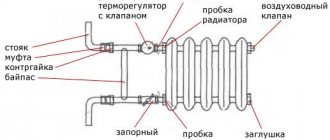
It is a unit with a sectional type metal casing. All free space in the sections is filled with coolant. Water, special mineral oil or antifreeze liquid are used as the heat carrier.
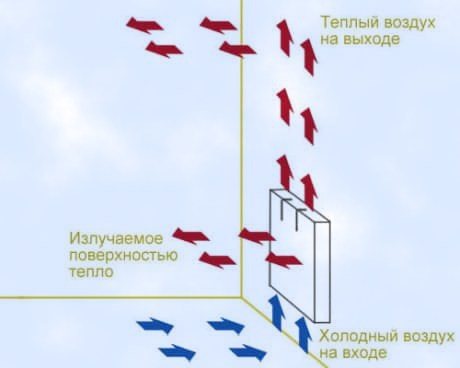
The principle of operation of the unit is based on the method of thermal radiation. Under the influence of a heat source, the heat carrier is heated. The heating element is such a source.
An increase in the temperature of the coolant leads to heating of the surface of the device body. A heated housing generates heat to the surrounding area. Heat radiation increases the heating level in the room.
The coolant temperature is monitored by a built-in heat sensor. Automation turns on and off the device when the set values are reached. The heating of the working fluid is controlled using a built-in thermostat.
Convector
To answer, what is the difference between a heating convector and a radiator, consider the principle of operation of the device.
The operation of the device is based on convection of air masses in a room. It is an installation with a panel-type metal casing. A heating element with a thermostat is located in the housing. The thermostat is used to regulate the heating temperature.
The housing has an open space at the bottom. Through it, a stream of cold air enters the housing. The heating element heats the cold air to a predetermined level. Heated air streams rush upward.
To accelerate and direct the warm air flow, special louvers in the device body are used.
Warm air masses displace cold air in the upper part of the room. The flow of cold air goes down. At the bottom, it enters the device housing again. The working cycle of air movement is repeated.
The set room temperature level is monitored by a thermal sensor. Sensor triggering leads to automatic switching on and off of the device. The set parameters are adjusted using a mechanical or electronic control unit.

Sooner or later, many apartment owners in which heating convectors are installed are faced with the fact that they stop heating.
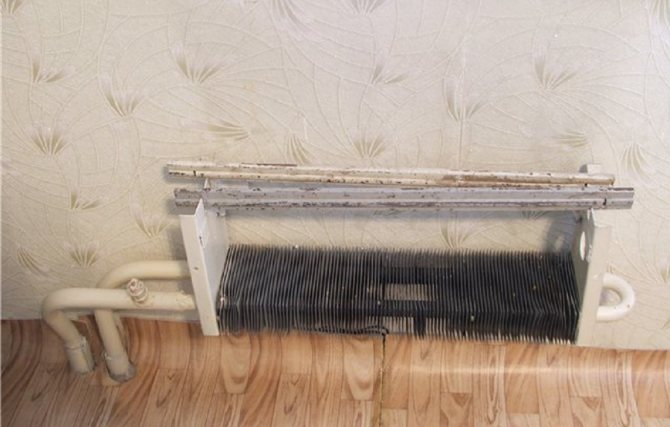


Why do convectors stop heating? A simple option is dust and debris accumulated between the plates. The air ceases to move freely through the convector plates, the heat transfer deteriorates. If the apartment is cold, and there is no way to replace the convector now, you can try to improve heat transfer by thoroughly vacuuming and cleaning the plates.
The second reason, the main one, is that the convector pipes are clogged with deposits. Sometimes they overgrow to complete obstruction. Only replacement will help here.
What to change the convector for? Bimetallic radiators are very fond of in Russia. In the nineties, inappropriate equipment was often used to repair worn-out district heating networks. Violations resulted in water hammer that could destroy the radiators. A high-quality bimetallic radiator is capable of withstanding enormous pressure, so they began to be massively installed, especially in high-rise buildings.
Now the housing sector has been put in order and there are no hydraulic shocks in heating systems.
Compulsory certification of heating devices has been introduced in Russia since 2020. State control has been established over the import and production of radiators. All radiators meet the requirements of GOST number 31311-2005 “Heating devices. General technical conditions ". It doesn't matter what and how the radiators are made, if they have a certificate, they can be installed in any heating systems, subject to the operating pressure. In the overwhelming majority of cases, you can choose those radiators that you like best. In some situations, a bimetallic radiator will not work and it is better to take an aluminum or steel tubular radiator. When replacing a convector, it is necessary to choose radiators with a minimum hydraulic resistance. The connection diagram for the new device must be used as close as possible to the existing one.
Why is it not always good to change a convector to a bimetallic radiator?
Convectors have low hydraulic resistance. Structurally, it is a pipe with heat-removing plates, through which the coolant flows freely. In addition, very often the convector is simply welded to the supply pipes, without valves and a transit bridge. A stream of coolant flows through the convector, which heats the entire staircase. You cannot overlap it. And even in such conditions, with a full flow, the convector pipe is overgrown with deposits. The more clogged convectors in the common riser, the colder it is in all apartments at the same time.
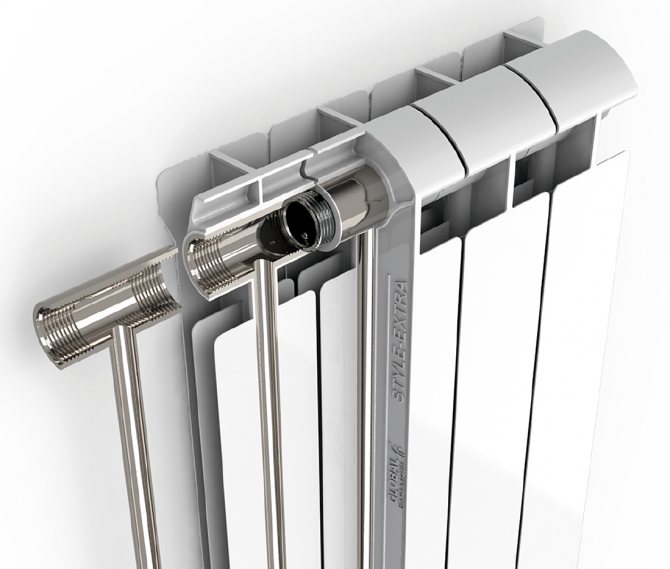


The bimetallic radiator consists of aluminum vertical sections, inside which thin steel tubes are pressed. The cross-section of these tubes is very small compared to the channels of aluminum radiators. Under normal conditions, the flow of water through the bimetallic radiator is sufficient for full heat transfer.
In heating systems with convectors, conditions are abnormal.
This is a situation known to all plumbers with the supply of the coolant from the bottom. For convectors, there is absolutely no difference where the hot water flows from, top to bottom or bottom to top. Therefore, the direction of the coolant flow in convector systems was determined only by the convenience of design and installation. Now there are many old houses in which the coolant is supplied from the bottom up. If a bimetallic radiator is installed in such a system, it becomes an obstacle to the free movement of hot water. The volume of water in the tubes is small. The water in them quickly cools down and tends to flow downward, which slows down the circulation. At the same time, the bimetallic radiator does not work well, everything does not warm up.
When installing bimetallic radiators with a coolant supply from below, you have to go for tricks.
Many installers mastered physics in grade 4 and remembered that the cooling water descends from top to bottom. Therefore, they often overlap the pipes so that the supply coming out from the bottom is connected to the upper inlet of the radiator. Here's an illustration:


There are two risers running through this apartment. Transit, supplying water to the upper floor for the entire entrance and a worker descending, all heating devices were connected to it.
The size of the stain on the wallpaper confirms that it was the convector that was installed. The convector pipes were probably very heavily clogged and practically did not heat up. This gave the welder the idea to crash into a transit riser. In the transit riser, on the left, water flows from bottom to top. Therefore, the welder had to overlap the pipes, connect the lower pipe to the upper inlet, and connect the upper pipe to the lower one. Without a doubt, the customer was delighted with the result, the radiator after installation heats up like a scalded one. But as a result, the hydraulic circuit of the heat supply of all apartments along this riser is disrupted, the radiator will slow down the normal movement of water. In addition, this radiator will act as a mud sump.If a convector connected to the descending riser with short supply pipes clogs in several years, imagine how this ring with a jumper on the ascending pipeline will be clogged.
What should have been done in this case? Just do not disturb the hydraulic circuit. Connect to the working, descending riser by cutting off the clogged inlets. Install a high-quality aluminum or bimetallic radiator. Both will work great and keep you warm for years to come. And this radiator will be clogged with deposits in a few years. Only from my point of view, a bimetallic radiator is not needed here. If we compare radiators of the same level, aluminum is cheaper and it has more heat dissipation.
The second favorite option for installers is the diagonal connection. With a diagonal connection, the radiator gives 3% more heat transfer than with a side connection. For many, these three percent have become a dogma that this is the only way to connect. In pursuit of that three percent, other factors often worsen and more can be lost as a result.
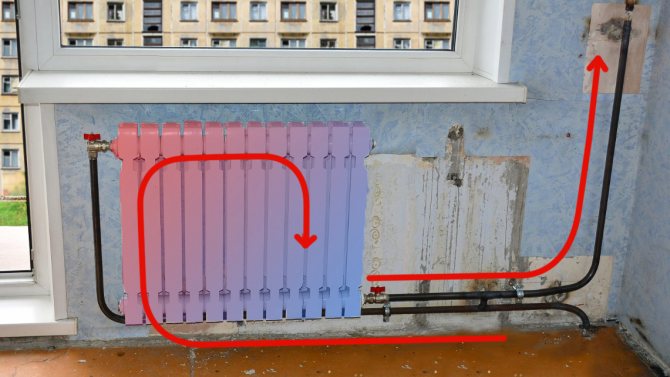

In the photo, a Chinese cast-iron radiator, the welder extended the supply pipe under the radiator to its far, upper corner. The problems are the same as with the overlap - too long lead. And two more angles of ninety degrees are added. All this slows down the flow rate. Contrary to popular belief, water flows slowly in central heating systems.
Despite the pressure in the system, the flow rate is very low. Thanks to the experiments of various creative personalities in a single entrance, circulation can completely stop. In any case, excellent conditions are created here for the sedimentation of sludge and sludge. In how many years will this pipe become completely silted up? It will take a much shorter period of time, the one during which the old replaceable convector has silted up.


Therefore, without taking into account the direction of supply from below, it would be better here not to violate the connection diagram and put an aluminum radiator with short, straight connections on the side. And everything will work fine for many years. We install aluminum radiators or tubular steel design radiators in ninety percent of cases. A high-quality radiator has a passport operating pressure of 16 atmospheres, a test pressure of 25 atmospheres. These values are not achievable in any heating system. Therefore, we install bimetallic radiators only at the request of the customer, in really high-rise buildings with a working pressure of 12 atmospheres and only when the coolant is supplied from above. We never twist monograms with overlaps and diagonals. And everything works fine, and it works for many years, because dirt does not settle or accumulate in short direct inlets. Also due to the fact that we mainly use copper pipes, the wall roughness of which is much less than that of black steel. So the choice for customers is now very wide, bimetallic radiators are not a sentence, in most cases you can install any radiators with a certificate. Let's summarize. When replacing a convector, it is better not to take risks and choose a heating device not in appearance, popularity and price, but in terms of hydraulic characteristics. Be sure to agree on the replacement with the Management Company. Always strive to install radiators only according to the classic scheme: piping to the radiator from the side, supply from above, return from below, without overlaps, diagonals and other plumbing perversions. Take care of your heating systems and a warm home for you!
You may also be interested in:
Buy high quality aluminum radiators.
Pipes used in the installation of radiators in central heating systems.
Services for the replacement and installation of radiators.
How to choose a heating radiator?
Advantages and disadvantages of convectors
The answer to the question of which is better - a convector or a radiator, allows you to get an analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of both types of systems.
The advantages of the devices include:
- Autonomous mode of operation.
- Low level of heating of the case surface (up to +70 ᵒС).
- Fast heating of cold air (1-1.5 minutes).
- Lack of coolant and pipelines.
- Possibility of combining devices into one network.
- Convenience of controlling one or several devices at the same time.
- Simplicity of construction and installation of the installation.
- Quiet and environmentally friendly.
- Explosion -, fire safety.
- Modern design.
The disadvantages are:
- A large amount of electricity used.
- The high cost of multifunctional installations.
- Low level of electrical safety.

Advantages and disadvantages of radiators
The advantages of these devices include:
- Ease of Management.
- Convenience of movement.
- Affordable price.
- Simplicity of care and maintenance.
The disadvantages are:
- High level of body surface heating (up to +100 100С… + 120 ᵒС).
- High fire hazard.
- Great weight.
The listed pros and cons will help buyers determine what is better to use in an apartment - a convector or a radiator.


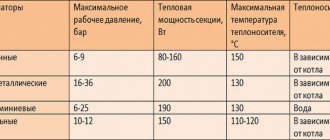
Technical characteristics and cost of heaters
The main characteristics and cost of heating radiators and convectors are shown in the table.
| Model name | Specifications | Producing country | Cost, rub. |
| Radiators | |||
| Ballu BOH / CL-05WRN 1000 | The number of modes - 3. The number of sections - 5. Power, kW - 1.0. Heating area, m2 - 15. Control - mechanical. There is a thermostat. Weight, kg - 4.2. | Russia | 1 990 |
| Vitek VT-1709 W | The number of modes - 3. The number of sections - 9. Power, kW - 2.0. Heating area, m2 - 20. Control - mechanical. There is a thermostat. Weight, kg - 6.5. Functions: * shutdown when overturning; * overheat protection. | China | 3 990 |
| De Longhi TRRS0920C | The number of modes - 3. The number of sections - 9. Power, kW - 2.0. Heating area, m2 - up to 24. Control - mechanical. There is a thermostat. Weight, kg - 12. Functions: * frost protection. | China | 8 990 |
| Convectors | |||
| Ballu BEC / EM-1000 | The number of modes - 2. Power, kW - 1.0. Heating area, m2 - up to 15. Control - mechanical. There is a thermostat. Weight, kg - 3.0. Functions: * shutdown when overturning; * overheat protection. | Russia | 1 990 |
| Electrolux ECH / B-1500 E | The number of modes - 5. Power, kW - 1.5. Heating area, m2 - up to 20. Control - electronic. There is a thermostat. Weight, kg - 3.0. Functions: * shutdown when overheating; * frost protection. | China | 5 790 |
| Bork R704 | The number of modes - 3. Power, kW - 1.0. Heating area, m2 - up to 20. Control - electronic. There is a thermostat. Weight, kg - 5.6. Functions: * touch screen; * automatic maintaining heating; * shutdown when overturning; * protection from children; * overheat protection; * remote control. | China | 12 890 |
Comparison of the tabular data shows a slight excess in the cost of convectors. This is due to the increase in the degree of their automation and the presence of a large number of useful functions.
The final assessment, which is better - convectors or heating radiators, will help to compare the features of the operation and maintenance of devices.
Features of the operation of radiators and convectors
Each of the considered types of installations has individual characteristics. Comfortable work with devices is determined by the number of useful functions.
Radiators
These heaters provide quick heating of rooms. The automatic regulator ensures the stability of the room temperature. The heat transfer fluids used have high thermal conductivity.
For ease of movement, many devices are equipped with casters. Transfer to another location is done using the built-in handle. For protection against overturning, side stops are used. For drying small items, a wall-mounted heated towel rail is used. On the front side of the control unit there is a place for the power cable.
Convectors
The devices have a convenient control system.The heart of this system is a mechanical or electronic thermostat.
The mechanical thermostat is easy to use. Manual units are of low cost. The main disadvantages are noisy operation and low temperature setting accuracy. The adjustment step of the mechanical thermostat does not exceed 5 ° C.
An electronic thermostat allows you to set the temperature with an accuracy of 0.1 ᵒС. Such devices have several operating modes. It is possible to change settings and program operating modes. Quiet operation allows the use of electrical appliances in bedrooms.
A large number of useful functions in the question of what is better for an apartment - a convector or a radiator, make an advantage in favor of devices of the first type. These devices have the following convenient features:
- frost protection;
- keypad lock;
- economy mode;
- remote control;
- Internet connection.
The function "Frost protection" allows you to maintain the temperature inside the room at the level of +5 ᵒС… + 7 С in autonomous mode. It is used in country houses and houses without central heating.

Water heating radiators
Radiators for water heating systems are built in about the same way as oil appliances. But they are heated not due to oil, but due to the coolant circulating through the system. They are equipment for creating permanent heating. Scope of application - centralized and autonomous heating systems. They are better than oil ones in that they do not consume electricity. And if they are powered by an economical gas boiler, then heating costs will be minimal.
Radiators for water heating are better than their oil counterparts for their increased reliability... And they are also better than convectors due to the large heating area. They also do not raise dust into the air and are easier to wet clean. Connected to a single heating system, they allow uniform regulation of the heating temperature in all rooms at once.


Water heating radiators are the most popular type of heaters used in our country.
Advantages of water radiators:
- These radiators have high heat dissipation;
- High environmental friendliness;
- Increased power of some models.
There are also several disadvantages:
- Convectors are better than radiators in that they are more compact. A striking example of this is miniature floor or baseboard models;
- Radiators are more expensive than convectors - therefore, the latter are slightly better in this regard;
- The radiator bodies are hot - in contrast to the same convectors.
The most significant drawback is the last one.
Safety first
The compared types of devices relate to high-risk heating devices. The devices are equipped with built-in overheating protection. When the maximum temperature is reached, the device switches off automatically.
Electrical devices have an increased risk of electric shock. To prevent injury, it is necessary to strictly comply with the requirements of fire and electrical safety.
Some models are used in rooms with high humidity. To protect against damage, the devices have a high degree of sealing.
Water convectors

The main distinguishing feature of water convectors is the need to supply pipes with a hot coolant to them.
Convectors can work not only with electricity, but also with the coolant coming from the heating system. The coolant is heated by boilers - electric, gas, liquid, solid fuel or universal. Due to their simple internal structure, they do not cause difficulties in operation and provide quick heating of the premises.
Water convectors are equipped with powerful heat exchangers.Modifications with steel and non-ferrous metal exchangers are presented to consumers' choice. The latter are much more expensive, but they are resistant to corrosion - both outside and inside.... Copper and aluminum are used as non-ferrous metals. The coolant flows through copper pipes, and the air is heated by aluminum fins.
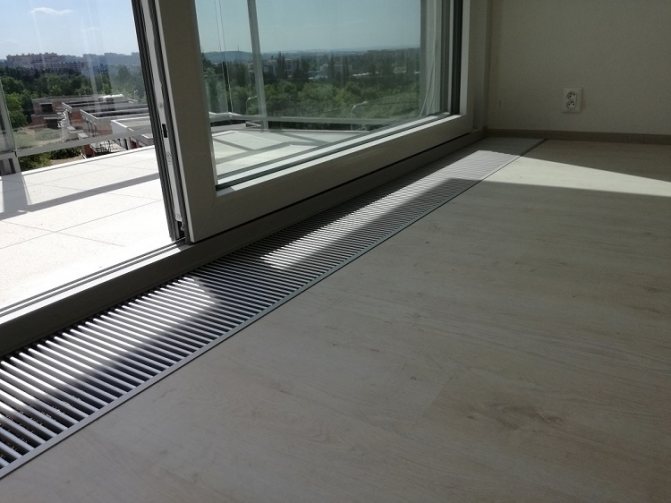
Convectors for hot water heating are available in several form factors:
- Wall mounted - these devices are mounted on the walls. It is best to install them under window openings;
- In the floor - most often placed under panoramic windows or windows with low sills that do not reach the floor;
- Built-in - for concealed installation in in-wall niches. It is best to purchase such convectors if you want to create an invisible heating system;
- In the trench floor - such convectors do the best at preventing condensation from settling on panoramic windows.


Floor models look great in front of panoramic windows or doors.
Let's talk about the advantages of water convectors:
- They do not need electricity - they are powered by a hot coolant;
- Heating systems are more economical - provided that they are not powered by electric boilers;
- Compactness and simplicity are undoubted advantages;
- High heating efficiency.
- It is better not to use convectors in rooms with high ceilings - in such conditions they are ineffective;
- Difficulty in installation - you need to lay pipes around the house;
- Susceptibility to corrosion and pressure fluctuations is something you have to put up with.
Compared to electric convectors, water convectors are better because heating systems based on them are more economical. The main thing is to power them from an economical heat source. And it's easier to manage such a system - just set the desired temperature on the heating boiler.