Advantages and disadvantages of a one-pipe circuit
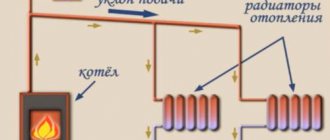
In such a system, one pipe is used to run the coolant. Several advantages of this type:
- Lower costs for the material used;
- Simplified and quick installation;
- Hydraulic stability;
- Simple wiring diagram;
- Less heating medium used, making it easier to drain the system.
The single-circuit heating design provides primary cost savings. The number of pipes, wiring, risers and lintels is much less than when arranging two-pipe heating.
Disadvantages of a one-pipe heating system:
- Large heat loss on the way to distant radiators. The latter, as a result, require a volumetric increase in order to achieve a comfortable room temperature. The reason for the decrease in their heating lies in the exchange of hot water with cold water in each heating device standing in the way;
- The inability to regulate the temperature of individual batteries. Decreasing feed in one leads to cooling of all subsequent ones;
- The need for a large head of water. The load on the pumps and the entire system as a whole increases. The appearance of leaks is more frequent, the circuit requires constant replenishment of the coolant.
Important! The single-circuit design is extremely sensitive to low temperatures. When the smallest section on the path of the coolant freezes, the entire heat supply is blocked. In this case, the detection of a frozen element is extremely difficult, and a delay in eliminating the problem leads to freezing of the entire circuit.
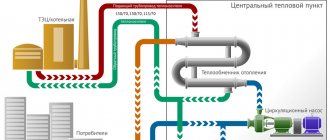
How the heating system works in an apartment building
The normal operation of heating an apartment building depends on compliance with the basic parameters of the equipment and the coolant - pressure, temperature, wiring diagram. According to the adopted standards, the main parameters must be observed within the following limits:
- For an apartment building with a height of no more than 5 floors, the pressure in the pipes should not exceed 2-4.0 Atm;
- For an apartment building with a height of 9 floors, the pressure in the pipes should not exceed 5-7 Atm;
- The range of temperature values for all heating schemes operating in residential premises is +18 0 C / + 22 0 C. The temperature in radiators on staircases and in technical rooms is + 15 0 C.
The choice of piping in a five-story or multi-story building depends on the number of floors, the total area of the building, and the heat output of the heating system, taking into account the quality or availability of thermal insulation of all surfaces. At the same time, the difference in pressure between the first and ninth floors should not be more than 10%.
One-pipe wiring
The most economical piping option is single-circuit. A single-pipe circuit works more efficiently in low-rise buildings and with a small heating area. As a water (and not steam) heating system, one-pipe wiring began to be used from the beginning of the 50s of the last century, in the so-called "Khrushchevs". The coolant in such a wiring flows through several risers to which apartments are connected, while the entrance for all risers is one, which makes the installation of the route simple and quick, but uneconomical due to heat losses at the end of the circuit.
Since the return line is physically absent, and its role is played by the working fluid supply pipe, this generates a number of negative aspects in the operation of the system:
- The room heats up unevenly, and the temperature in each individual room depends on the distance of the radiator to the point of intake of the working fluid. With this dependence, the temperature on the distant batteries will always be lower;
- Manual or automatic temperature control on heating devices is impossible, but in the "Leningrad" circuit it is possible to install bypasses, which allows you to connect or disconnect additional radiators;
- It is difficult to balance the one-pipe heating scheme, since this is possible only when shut-off valves and thermal valves are included in the circuit, which, when the parameters of the coolant change, can cause a failure of the entire heating system of a three-story or higher building.
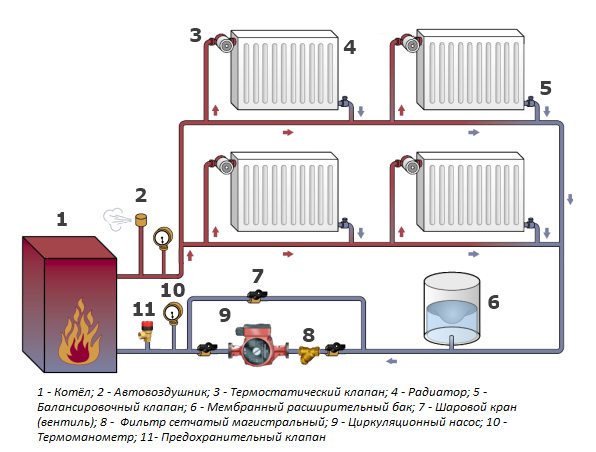
Advantages and disadvantages of a two-pipe system
H2_2
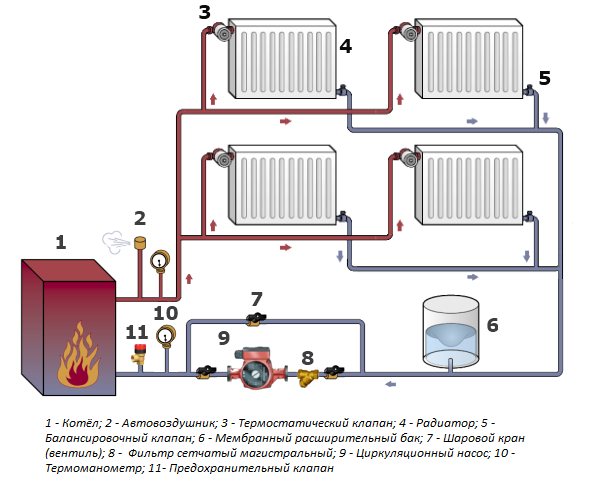

Comparison of heating systems is impossible without an overview of the two-pipe system. The design feature is the use of two different pipes for supplying hot water and draining cold water from radiators.
Heat losses along the path of the coolant are insignificant, which saves fuel. The dual-circuit circuit allows you to freely regulate the heating of each individual battery or turn them off.
The disadvantages of a two-pipe heating system are minor. The circuit diagram is more complex, requires more installation costs and more time. However, this pays off thanks to its good practical qualities.
Fact! The double-circuit design is not afraid of freezing of individual sections, and they do not block the rest of the heating devices involved in heat exchange. The affected areas are easy to detect by tactile method.
What are the types of heating systems for an apartment building
Depending on the installation of the heat generator or the location of the boiler room:
- An autonomous system in an apartment, where the heating boiler is installed in a separate room or in the kitchen. The costs of purchasing a boiler, radiators and related piping materials return quickly, since such an autonomous system can be adjusted based on your own considerations regarding the temperature regime in the house. In addition, the individual pipeline does not lose heat, but on the contrary, it helps to heat the premises, as it is laid through the apartment or around the house. An individual boiler does not need to be adapted for the reconstruction of centralized heating - once a heating scheme is drawn up and implemented, it will work for a lifetime. And, finally, an already working circuit can be supplemented with parallel or series-connected circuits, for example, a "warm floor";
- The option of individual heating, which is designed to service the entire apartment building or the whole residential complex, is a mini-boiler room. An example is the old boiler houses serving the quarter, or new complexes for one or more houses on different energy sources - from gas and electricity to solar panels and thermal springs;
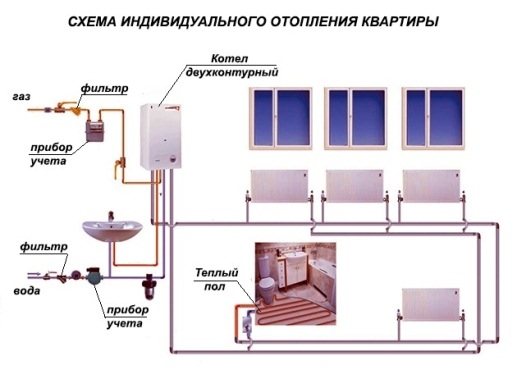

A centralized heating scheme in a multi-storey building is the most common working solution to the problem so far.

Heating schemes depending on the parameters of the working fluid:
- Heating on ordinary water, in the pipes of which the coolant is not heated above 65-70 0 C. This is a development from the field of low-potential systems, but most often old schemes work with the temperature of the working fluid reaching 80-105 0 C;
- Steam heating, where not hot water moves in pipes, but steam under pressure. Such systems are a thing of the past, and today they are practically not used in the delivery of heat and heating of any type of apartment buildings.

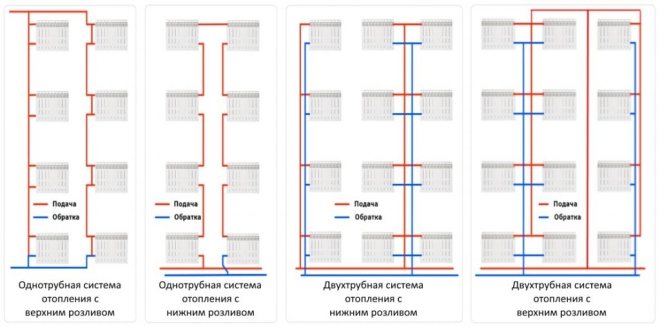
Based on the piping diagram:
- The most common is a one-pipe heating system for a multi-storey building, where both supply pipes and return pipes are one thread of the heating main. Such a scheme can still be found in "Khrushchev" and "Stalin" buildings, but in practice it has a big drawback: batteries or radiators connected in series in the circuit do not provide uniform heat transfer - each next heating device will be slightly colder, and the last radiator in the pipeline will be coldest. For at least approximately the same heat distribution throughout the rooms, each radiator following in the circuit must be equipped with a larger number of sections.In addition, in a one-pipe heating scheme in a five-story building, it is impossible to use radiators that do not correspond to the design parameters, and devices for regulating heat transfer - valves, etc. regulation;
- The Leningradka scheme is a more perfect solution, but according to the same one-pipe scheme. In this scheme, there is a bypass (pipe jumper) that can connect or disconnect additional heating devices, thereby regulating heat transfer in the room;
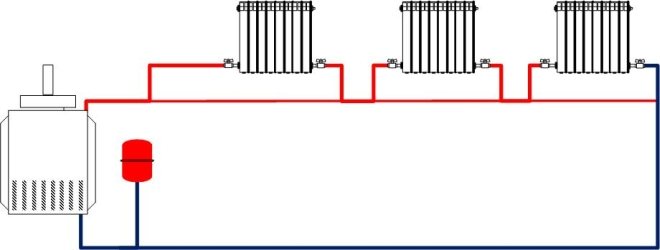

- A more advanced two-pipe heating system in an apartment building began its existence with the construction of buildings according to the project of the so-called "Brezhnevka" - a panel house. The supply and return flow in such a scheme work separately, so the temperature of the working fluid at the inputs and outputs of apartments in a 9-storey building is always the same, as in radiators or batteries. Another plus is the ability to install a regulating automatic or manual valve on each heating device;
- The beam (collector) scheme is the latest development for atypical housing. All heating devices are connected in parallel, and taking into account the fact that this is a closed OO system in an apartment building, the piping can be made hidden. When implementing the beam scheme, all adjusting devices can limit or increase the supply of heat in a metered manner.
Other types of heating circuits
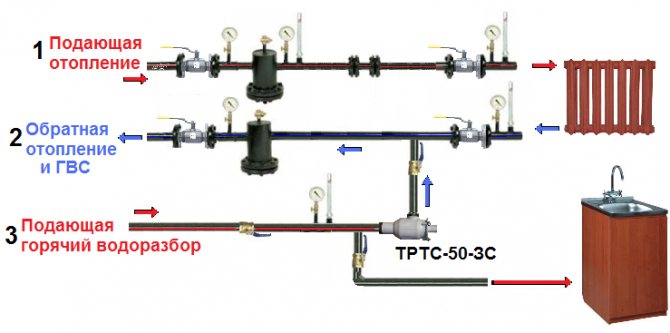

The three-pipe system consists of two supply pipes and one common one for collecting return water. Its advantages are that there is no need to use check valves, only one pump provides circulation. As a result, the three-pipe design is easy to operate, since the coolant is automatically consumed between the devices. The types of such circuits are more flexible than two-pipe ones, their advantages are in convenient regulation and automated heating of individual parts of the building. When choosing a double-circuit heating and having a sufficient budget, it makes sense to pay attention to the functionality of a three-pipe system.
A bifilar heating system is a cross between one- and two-pipe schemes. The entire circuit is divided into two identical parts with their own radiators, risers and branches. Both ends are connected in order by one pipe, first all the devices of the first, and then the second end. The water in the radiator compartments moves in opposite directions with different heats, thereby maintaining the same temperature throughout the system. According to this feature, the bifilar circuit refers to double-circuit heating, and according to a series connection with one pipe - to single-circuit, which is also convenient to use.
Open heating system operation
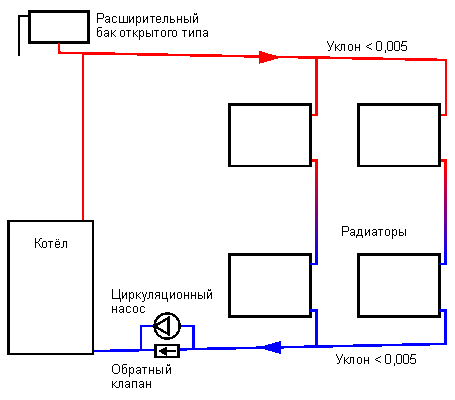

The choice of the heating system also depends on the other qualities of the circuit. When the question is raised, which heating system to choose, it is necessary to take into account the differences between an open and a closed heat supply circuit.
Open system design:
- Boiler. Solid fuel and gas boilers are used;
- Pipelines;
- Batteries;
- Expansion tank.
The heat carrier receives heat energy when the boiler is heated. The circulation process begins under the influence of the zonal pressure difference. The final and starting point is the fuel boiler. Due to the temperature expansion of water, the circuit requires the inclusion of an expansion tank, into which excess water will enter.
Significant disadvantages of an open design include energy loss and oxygen ingress into the circuit. These factors reduce the heat dissipation of the system. There is a risk of air pockets and corrosion on metal parts.
Advice! In an open plumbing system, you should not use any type of antifreeze as a coolant. Their tendency to evaporate will lead to a rapid quantitative loss through the expansion tank. In addition, their vapors negatively affect the health of residents.
Horizontal routing
This type is widely used for heating private one-story houses and apartments, which are equipped with an autonomous heating system. Horizontal wiring is easy to install and maintain. This scheme is mainly used in two-pipe and radiant heating systems, which makes it the most popular. The horizontal scheme allows you to connect heating devices in various variations, which significantly increases the heat transfer of the heating system - as a whole.
Horizontal heating distribution has three types:
Single pipe
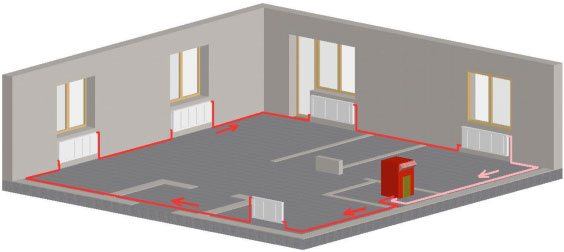

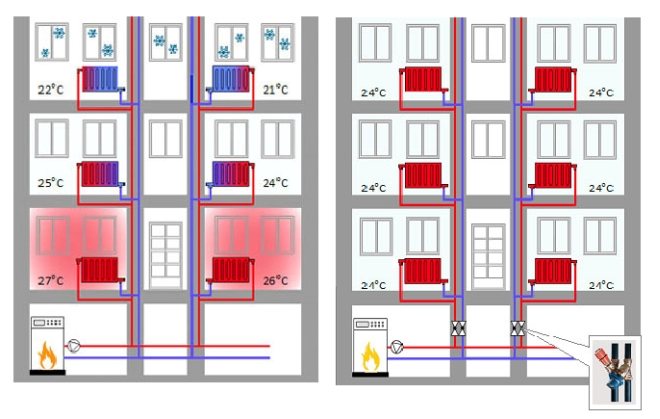
The heating system, which is built according to the one-pipe principle, is widely used in apartments in multi-storey buildings. The heated coolant in such a heating system first rises to the very last floor, and then descends along the descending line of the heating circuit. It is to this line that all heating devices are connected. There is a slight drawback to single-pipe wiring. The thing is that the upper floors of a high-rise building receive the greatest amount of heat, and the coolant reaches the very first floors after cooling down a little. Consequently, there will be excessive heating on the upper floors, and insufficient heating on the first floors.
One-pipe wiring of the horizontal heating system is also used in private cottages, which have 2-3 floors. In this case, the one-pipe scheme will work most correctly, since the coolant will not cool down, passing these three floors, and the temperature on all floors will be approximately the same. Also, a single-pipe wiring has a higher hydrodynamic resistance than a two-pipe wiring, and higher heat losses are observed in a single-pipe wiring.
One-pipe horizontal heating distribution also has some advantages. Such a scheme is easy to design. Also, a one-pipe circuit is much easier to install, and much less materials are used during the installation of such a circuit. Better circulation of the coolant is observed in one-pipe wiring, and in such systems, especially in private houses, antifreeze is often used as a coolant.
Two-pipe wiring
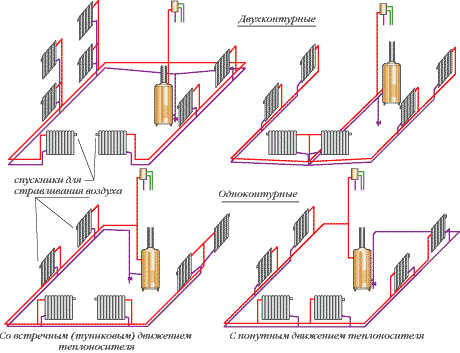

Horizontal wiring of the two-pipe type is increasingly used in multi-storey buildings. With the help of such a wiring, it becomes possible to install heat metering devices, which allows you to save on heating costs. The user gets the opportunity to pay for the amount of heat he received. Horizontal wiring in apartment buildings also allows:
- Disconnect one separate apartment from the heating system, which is convenient when carrying out repair work;
- Reduce heat consumption if the tenants of the apartment are absent for a long time;
- Design a heating system for a single apartment according to an individual project;
- Increase maintainability.
Also, the heating system with horizontal wiring of the two-pipe type, which is mounted in a multi-storey building, allows you to organize a "warm floor" system in the apartment. In a multi-storey building, the horizontal heating system is divided into zones - several floors for each zone.
In a horizontal two-pipe heating circuit, water or antifreeze circulates from the boiler to the heating devices. After the coolant gives up heat, it returns back to the heating boiler through the return line (return line). Thus, there are two lines in a two-pipe heating circuit - supply and return. Heating systems, which are built on a 2-pipe principle, are divided into two types:
- open;
- closed.
In open systems, the expansion tank is installed at the highest point of the heating circuit, and this tank is also open (connected to the atmosphere).Through such a tank, the heating circuit is also replenished.
In closed two-pipe heating systems of a horizontal scheme, membrane-type expansion tanks are used. This tank has two chambers. The first chamber is filled with compressed air, and the second chamber is connected to the heating circuit. Closed heating systems of a two-pipe design have no connection with the atmosphere, and the coolant in them is under pressure. Closed systems are good because, due to the lack of oxygen inside the circuit, corrosion processes occur much slower in them.
Two-pipe routing has many advantages. Such a wiring makes it possible to install heating radiators, the temperature in which can be controlled using manual or automatic valves. This convenient solution allows you to regulate the temperature in any room. Also, two-pipe wiring can be modernized, even after putting it into operation. Additional heating radiators or other devices can be added to such a wiring.
Two-pipe wiring of the horizontal heating circuit has small disadvantages:
- the scheme is more complex than one-pipe;
- higher cost;
- such a wiring is much more difficult to mount.
Beam layout
This wiring is also called "collector". Beam wiring is also a type of horizontal heating pipe installation scheme. The essence of the beam wiring is that all the heating devices of the heating circuit are connected to one common collector. Rather, there are two such collectors in the beam layout:
- Supply manifold.
- Return manifold.
Radiation wiring allows for a more differentiated regulation of the temperature inside the room, supplying heated water of different temperatures to each room. Also, such a horizontal wiring allows you to disconnect heating devices from the heating system, say, in non-residential rooms. Radiation wiring allows you to repair individual sections of the heating system, without completely draining the water from the system. This wiring is most often used for underfloor heating.
The beam scheme has many advantages, but it is also not without its disadvantages. Such horizontal wiring is difficult to install and more materials and valves are used during its installation. It is also advisable to hide the beam wiring in the walls, and install the collectors themselves in special cabinets or niches. Beam routing can be either horizontal or vertical. One-pipe and two-pipe heating circuit distribution can also be subdivided into these two types.
Pros and cons
Horizontal wiring of all types is the most effective, since in such a configuration of the heating system, it is possible to more flexibly adjust the temperature in all rooms - individually. Horizontal wiring also reduces gas consumption. The disadvantages of this wiring can be attributed only to its complexity and material consumption, but these small disadvantages are leveled by all the advantages of this type of wiring.
Closed heating system operation
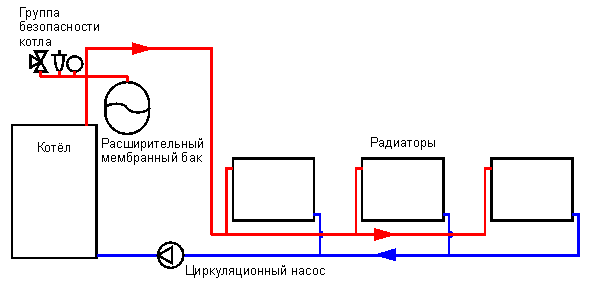

The closed structure does not have direct access to open air during operation. The role of the expansion tank is played by a membrane tank. Excess hot water gets into it, pushing through the rubber membrane. In this case, the nitrogen in the air chamber is compressed. The coolant is removed from the tank by a special pump.
The absence of oxygen contact with the circuit elements prolongs their service life. The heat carrier does not evaporate and does not require frequent recharge. The closed circuit allows the connection of additional heat supply sources with their integration into the overall system. The temperature is controlled by decreasing or adding the heat carrier.
A closed system requires constant access to electricity for the pumps to run smoothly.Despite this difference, it works more efficiently in smaller homes. Multi-storey buildings require a large number of membrane tanks and complex calculations.
Important! The closed design of the heat supply allows unauthorized air penetration through the deformation of the joints. Their tightness and the presence of airing must be checked regularly.
Heating system selection
If we compare heating systems for a specific object, then their merits are determined by the scale of the building. An open circuit leads to significant heat loss and the risk of oxygen saturation of the coolant, therefore, it is inconvenient for small private houses. The closed structure is optimal in such dwellings and has found wide application. However, in the event of prolonged power outages, its installation will lead to freezing of the premises.
In high-rise buildings, the advantages of closed-circuit heating are offset by the need to accommodate very large membrane tanks. In order for the closed circuit to be functional, they are replaced with special free-flow installations working in tandem with pumps - pressure regulators. The open design is easier to install in multi-storey buildings. The problem of airing is solved by using air vents.