27.11.2014
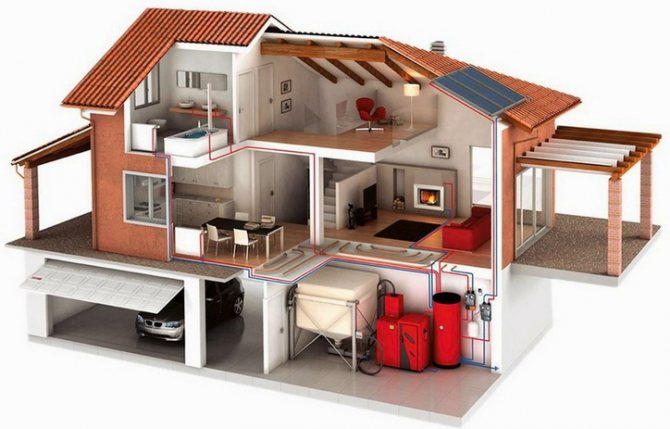
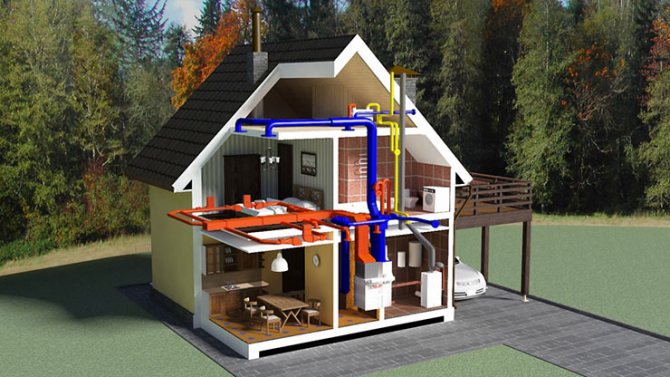
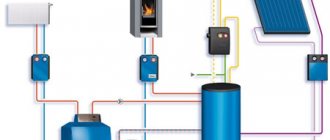
All kinds of communications play an important role in the life of any owner of a country house, but what really should work flawlessly is heating systems for the house. This is especially true for regions in the northern part of the country, where heating equipment must be of the highest quality in order to ensure optimal temperature conditions. But first you need to figure out what heating systems exist at all. The main parameter by which the efficiency of the systems is determined is the ability to provide a comfortable microclimate in the house.
- 1 The main types of heating systems
- 2 Water heating
- 3 Steam heating in the house
- 4 Air heating systems
- 5 Infrared
- 6 Dynamic heating
- 7 Heating boilers
The main types of heating systems
Houses and apartments are heated artificially in order to compensate for the heat loss that occurs due to a drop in outdoor temperatures. There is special equipment that effectively copes with this task. But what kind of equipment will eventually be selected for installation directly depends on how the thermal energy will be produced. In addition, the thermal insulation of the house itself is also important.
In this regard, home heating systems are divided into several categories:
- water heating systems
- steam
- air
- infrared
- dynamic heating.
Let's try to figure out each of the options.
Steam heating in the house
This method of heating a country house implies that water vapor will act as a coolant instead of a liquid. But it is characteristic that in Russia it is forbidden to install such systems in residential buildings or public facilities, which can be found in the relevant norms and requirements. The source of heat for such heating systems for the house can be both a reduction device and a conventional steam boiler.


The main advantages of steam systems:
- heat exchangers practically do not lose heat energy.
- all heating equipment is quite compact, moreover, it is relatively cheap.
- finally, the inertia is also relatively low, due to which the room is quickly heated.
But at the same time, there are disadvantages:
- it is quite difficult to install bends;
- if you examine all the planes of the elements with a thermometer, then they will demonstrate good performance.
- when the system is filled with coolant, this process is accompanied by a lot of noise.
- with such a system, the temperature cannot be raised / lowered smoothly.
Read about all the features of work and how to organize steam heating in the house.
Note! The described type of heating system is considered the least safe of all those given in the article. Moreover, system parts wear out at a very high rate, as they withstand critically high temperatures during operation.
Installation steps
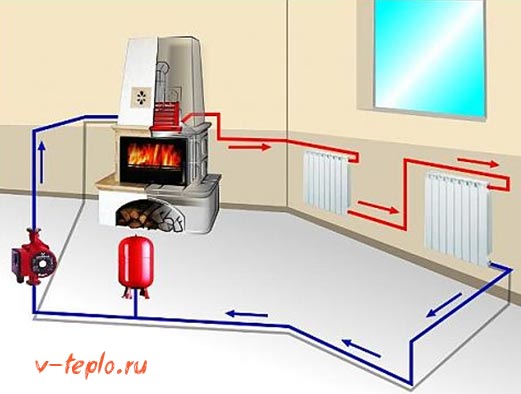
The assembly of the heating system according to this scheme is carried out in the usual manner. I.e:
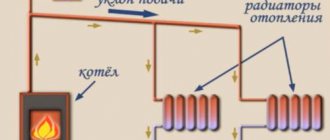
The boiler is being mounted. The height of the room where it will be installed should not be less than 2.5 m. In this case, the minimum allowable volume of the room is considered to be 8 m 3. The boiler is usually chosen on the basis that 10 m 2 of the room requires 1 kW of power.
Radiators are hung. The most popular type of this equipment is bimetallic batteries. Before hanging radiators, markings should be made. This heating equipment is usually attached to special brackets.
The highways themselves are being stretched. Most often, metal-plastic pipes are used to assemble heating systems, including associated ones. Their advantages include ease of installation, the ability to withstand even very high temperatures and durability.
A circulation pump is installed. This device is usually installed in the immediate vicinity of the boiler, on the return pipe. You need to embed it through a bypass with three taps. A filter must be installed in front of the circulation pump. This add-on will significantly extend its lifespan.
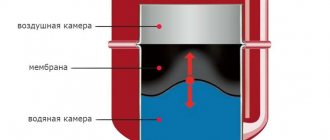
An expansion tank and a safety group are mounted. The first is connected to the return through a single pipe. Of course, a diaphragm expansion tank must be selected for the Tichelmann system. The safety group is usually supplied with the boiler.


Air heating systems
Today, air heating is an essential element in most storage facilities with significant heating volumes. With regards to the heat source, in this case there are only two options - a heat generator and a heater. Both devices are characterized by the fact that they permanently maintain a given temperature regime, using a minimum amount of energy. Such equipment is also called climatic.
Its main advantages:
- during the operation of devices, several times less fuel is required than in similar systems with water heating;
- they are also quite economical, since they provide for both heating in the cold season and cooling in the summer;
- during use, the air in the room is heated directly, in other words, there are no "intermediaries";
- air heating can last long enough, the minimum period for it is 20 years.
You can find out more about how such a system works here.
There were no significant drawbacks of this kind of systems.
Note! Such versatility as air heating is not found in any other system. It can even effectively cool the room if needed.
One-pipe system versus two-pipe system
The main distinguishing feature of the one-pipe design is one pipe to which the heater is connected. Radiators are connected in series. The coolant cools down in each of them and approaches the subsequent devices with a lower temperature. Thus, the last batteries in the chain are much colder than the first ones. The advantage of the system is the relatively low cost of components and installation. However, there are also significant disadvantages.
The first is the inability to regulate the temperature of the radiators. You can neither reduce nor increase heat transfer, as well as disconnect the battery from the system. However, when installing devices using a special jumper called a bypass, it will be possible to turn off the radiator if necessary. But the indirect heating of the room with the help of supply pipes and a riser will continue.
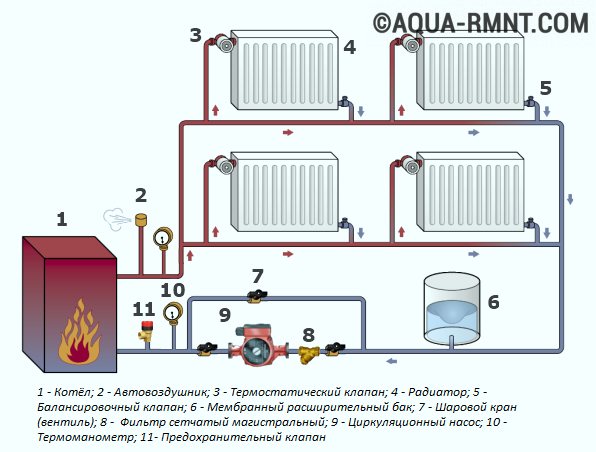

A single-pipe heating system does not imply the possibility of regulating the temperature of the coolant in the radiators, in addition, less heated water enters each subsequent heater in the chain
The second significant drawback is the temperature difference between series-connected heating devices. In order to level it as much as possible, you can choose radiators of different sizes. In this case, the smallest should be the first, and the area of all subsequent ones gradually increases. However, the appearance of the premises in which the system will be located may suffer from such a variety.
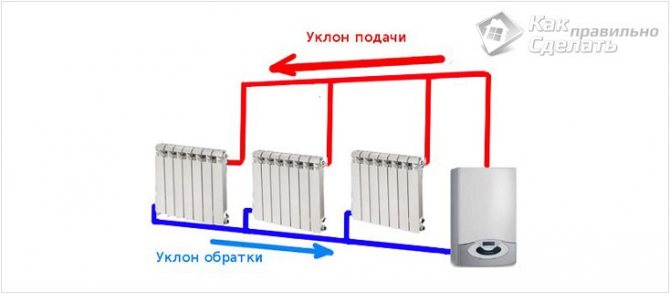
Two-pipe systems imply a supply and a discharge pipe to each radiator.Thus, the coolant cooled in the equipment is discharged into the boiler, and does not enter the next device. This allows water to be supplied to the radiators at approximately the same temperature. The system is devoid of the disadvantages of one-pipe designs. It can use pipes with a smaller diameter and connections of smaller sizes, which makes the structure more aesthetically pleasing and allows it to be used for hidden laying, for example, in a floor screed.
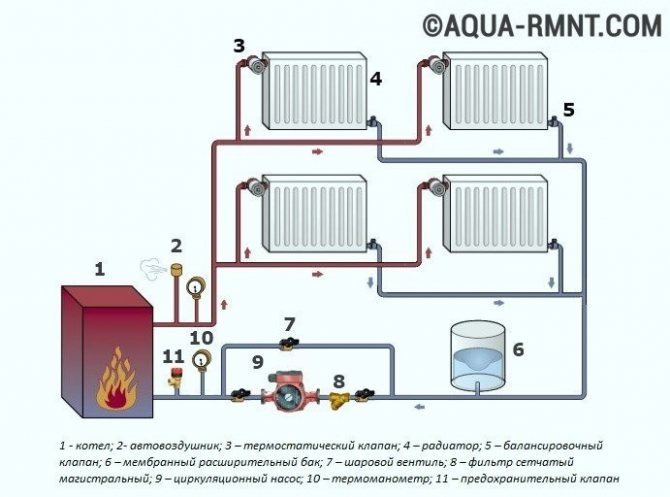

A distinctive feature of the two-pipe system: a supply and discharge line is suitable for each radiator, which allows you to maintain the same temperature of the coolant on the way to all devices
Parallel connection of two-pipe radiators is very convenient. When installed, a crane is mounted on each device, which makes it possible to regulate the temperature of the equipment. If necessary, it can be used to disconnect the battery from the system and carry out its replacement or repair. There are models of thermostatic regulators that allow you to automatically regulate the room temperature. The main disadvantage of two-pipe structures is the greater number of pipes required for the arrangement. This makes the system more expensive and more difficult to install.
Infrared
In this case, the room will be heated by means of special radiation. The infrared ray can serve as your main source of heat, as well as an auxiliary one. It is characteristic that such equipment is capable of heating even open spaces, which cannot be said about any other system.

This kind of heating systems for the home have their own advantages:
- they make it possible to save a lot (about 50 percent) of consumed electricity
- At the same time, the heat source does not work constantly, and often no more than 10-15 minutes per hour, effectively and evenly heating the room
- no combustion products are formed during operation
- finally, it does not "burn" oxygen and does not dry out the air.
You can get acquainted in detail with the features of installation and the principles of operation of infrared heating. in this article
Infrared heating is the most "natural", most natural heating. Judge for yourself: planet Earth is also heated in this way! Half of all the energy released by the sun is in the infrared range.
Classification according to the direction of movement of the coolant


Depending on the direction of movement of the supply and return coolant relative to each other, heating systems design the three most common schemes: dead-end, with a passing movement of the coolant and collector (beam).
Dead-end schemes for the movement of the coolant
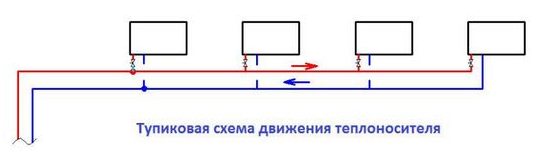

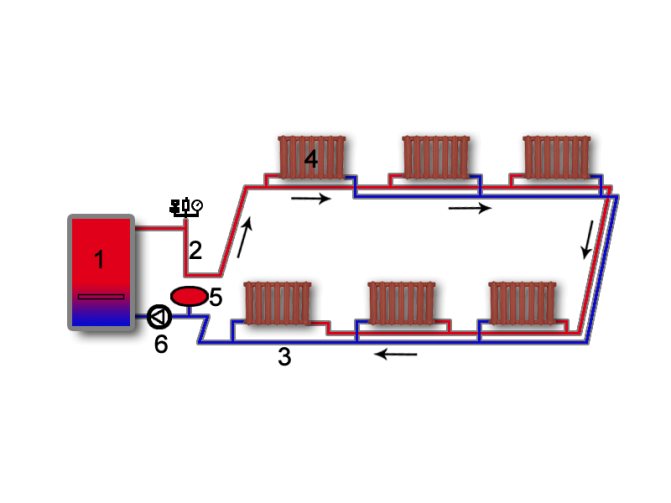
In dead-end (standard) heating systems, heat carriers move in counterflow, the most distant radiator branch from the boiler has greater resistance than the one that is closer. Therefore, a situation may arise when an uneven heating of the nearest radiators occurs. In order to avoid this, it is necessary to create additional resistance in the shorter circulating rings, that is, to install a balancing armature.
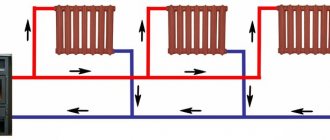
Accompanying schemes for the movement of the coolant
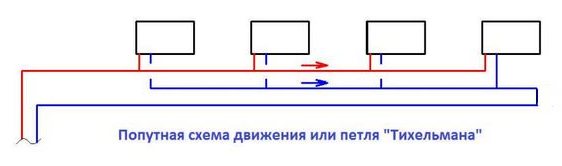

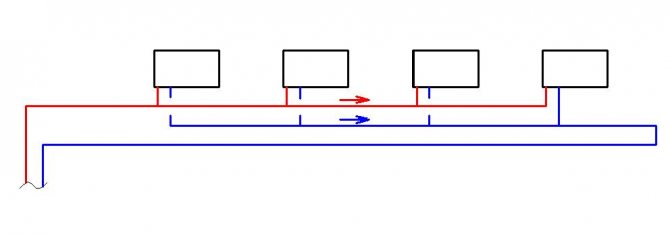
With the passing movement of the coolant in parallel in the supply and return pipes of the heating system, all circulation rings, that is, branches with radiators, are in the same conditions. That is, both pipelines and risers or radiators are hydraulically balanced with each other. However, such systems are the most metal-intensive in comparison with standard ones, and also require much longer pipelines to be laid. This is reflected, first of all, in the cost of the system and the cost of installation work. Therefore, associated schemes in housing construction are used most rarely.
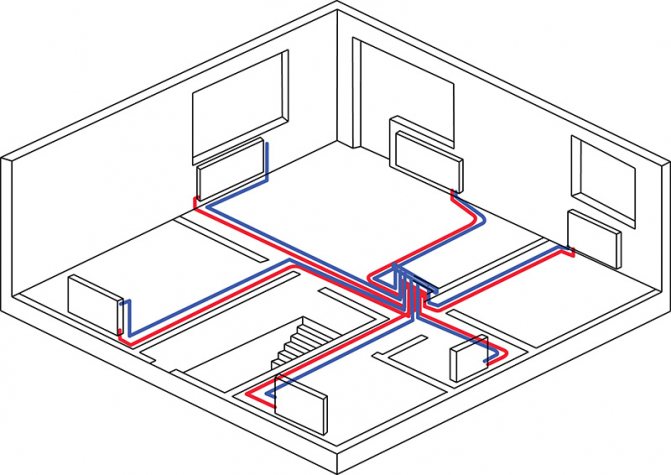
Collector heating circuits
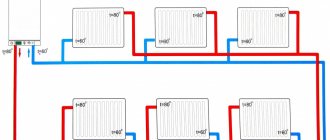
The ideal option for cottage and residential construction in general is the application collector circuit of the heating system.
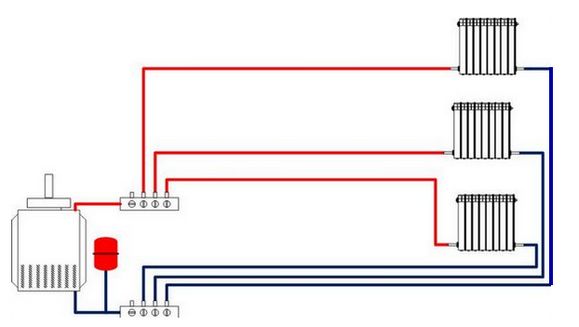

Such a system is a collector cabinet installed on the floor or in the boiler room, in which, in addition to shut-off and balancing valves, collectors with outputs are installed either to the radiator branch or to each heating device. Such a system is also hydraulically stable and easily amenable to regulation of the individual most distant branches or loaded in terms of thermal power. When planning the radial circuit of the heating system, each radiator can be connected to each outlet of the collector separately, and the pipelines can be laid in a hidden way. In this case, the section of the pipeline must be made of a single piece of pipe.
Dynamic heating
Progress does not stand still, but moves in many steps, heating technologies are constantly being improved. One of these innovative heating methods is dynamic. It lies in the fact that during operation, one half of the generated heat energy is transferred to the room, and the second is spent on the operation of the pump located between the external atmosphere and the house.

There is a small classification of heat engines, developed based on what kind of heat source is used.
- Open equipment requires the use of a coolant, moreover, a liquid, which would circulate through the pumping system.
- In closed geothermal devices, the basis is the thermal energy of the soil or groundwater. In this case, the location of the collector can be as follows:
- vertical, when the reservoir is launched into wells, the depth of which does not exceed 200 meters
- horizontal, when the collector is simply located lower than the level of soil freezing passes
- water, in which the collector is installed in any body of water.
An excellent review article on this topic is presented here.
Traditionally used heating schemes
- One-pipe. The circulation of the heat carrier is carried out through one pipe without the use of pumps. On the line, the radiator batteries are connected in series, from the very last through the pipe the cooled medium is returned to the boiler (“return”). The system is simple to implement and economical due to the need for fewer pipes. But the parallel movement of streams leads to a gradual cooling of the water, as a result, to the radiators located at the end of the series chain, the carrier arrives significantly cooled. This effect increases with an increase in the number of radiator sections. Therefore, in rooms located near the boiler, it will be excessively hot, and in remote rooms, it will be cold. To increase heat transfer, the number of sections in the batteries is increased, different pipe diameters are installed, additional control valves are installed, and each radiator is equipped with bypasses.
- Two-pipe. Each radiator battery is connected in parallel to the pipes for the direct supply of the hot coolant and the “return”. That is, each device is supplied with an individual outlet to the "return". With the simultaneous discharge of cooled water into the common circuit, the coolant returns to the boiler for heating. But at the same time, the heating of the heating devices also gradually decreases as they move away from the heat supply sources. The radiator located first in the network receives the hottest water and is the first to give the carrier to the “return”, and the one located at the end receives the coolant as the last one with a lowered heating temperature and also the last to give water to the return circuit. In practice, in the first appliance, the hot water circulation is the best, and in the last one it is the worst. It is worth noting the increased price of such systems in comparison with one-pipe systems.
Both schemes are justified for small areas, but ineffective with long networks.
An improved two-pipe heating scheme is Tichelman. When choosing a specific system, the determining factor is the availability of financial capabilities and the ability to provide the heating system with equipment that has the optimal required characteristics.