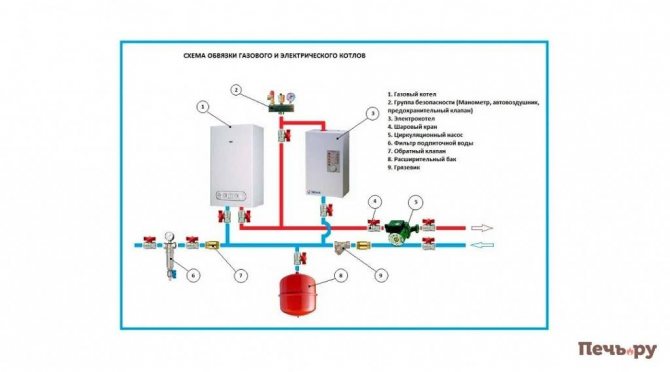
Ordinary water is often the heat carrier in the heating system of a private house. Although its use creates a certain problem - at a temperature of zero degrees, the liquid crystallizes, which can lead to mechanical damage to pipelines, radiators (batteries), and boiler equipment. To avoid such problems, "anti-freeze" is used - a special anti-freeze liquid for heating systems. In terms of properties, it is very similar to automobile antifreeze, although in some ways it is still different.
To use or not to use an antifreeze liquid as a heat carrier?
There is no GOST or standard that provides for the mandatory use of a coolant or prohibits its use. Sometimes there are projects of industrial systems that require the use of "water-glycol solutions", and if you turn to the manufacturers of heating equipment, they also do not have a single common solution - some prohibit altogether, others allow the use of certain brands of coolants. Which solution is correct?
The answer to this question can be obtained taking into account the combination of many factors: this is the model of the equipment, and the type of structure, the mode of its use, the material and insulation of the walls, the type of system, the region of location. But the most important factor is the degree of security of the system in unforeseen, emergency cases.
eddiki
I made myself a heating system for the first time in my life on metal-plastic, there are no leaks in the fittings. The argument in favor of antifreeze was brought by a specialist who started the boiler for me - antifreeze has its drawbacks, but the main thing is to preserve the system in case of any force majeure. According to him, a lot of CO died on the water for various reasons last winter. I have propylene glycol, -20, the system works, and I sleep peacefully when I am not at the dacha.
It's no secret that the main task of the coolant is to protect the system from defrosting and damage in case of unforeseen situations. And there are a lot of such situations when a house can remain without heating for a long time:
- long departure of the whole family, when there is no one to heat the house;
- seasonal use of a summer cottage or home;
- Finally, no one is immune from pipeline accidents or prolonged power outages, which have become common in the winter after freezing rains that cut power lines.
In such conditions, the use of an antifreeze liquid is an absolutely justified solution.

Types of low-freezing liquids
Non-freezing liquid for heating a house is the same antifreeze or antifreeze, no difference. More precisely, there is a difference, but it is more about the composition of the anti-freeze than the main properties. And their main property is not to turn into ice when the temperature drops, down to -60 degrees. In this case, the cooled composition thickens.
Propylene glycol is part of the eco-friendly anti-freeze
Any non-freezing liquid for heating, a warm house in particular, is made according to the same principle. Their composition:
- glycolic (alcohol) base;
- the main active ingredient;
- substances that prevent corrosion (inhibitors);
- substances responsible for the characteristics of the composition (additives).
So, it is already clear that non-freezing liquid for water heating is an alcoholic substance. Glycol by itself is not dangerous, but some additives can be very harmful to health. The following can act as an active component in anti-freeze:
- ethylene glycol;
- propylene glycol;
- glycerol.
The scope depends on the composition where the non-freezing liquid will be used for heating systems.User reviews agree that it is better to avoid ethylene in the composition of non-freezers.
Ethylene glycol liquid, in which ethylene glycol acts as an active substance, is strongly discouraged from using in homes of permanent residence. It is very toxic and causes burns when it gets on the skin. The ingestion of the composition into a person in the form of a liquid or gas leads to serious consequences, up to and including death.
Low-quality antifreeze and the well-known machine antifreeze, which is also sometimes poured into heating, are made on an ethylene basis. If there is even the slightest possibility of human contact with ethylene glycol, then it is better to refuse its use:
- evaporation from an open-type expansion tank;
- a leak;
- mixing into the DHW circuit in double-circuit boilers.
Do not use ethylene glycol antifreeze liquids for heating, where a double-circuit boiler acts as a heater.
Propylene glycol liquid for heating boilers, non-freezing, is completely non-toxic. This does not mean that you can drink it, but accidental contact with minimal doses on the skin or even inside will not lead to health complications. This anti-freeze can be used safely.
Glycerin antifreeze liquid has been poured into the heating system since the middle of the twentieth century and is still successfully used. Glycerin is, in general, a universal remedy. What is characteristic, unlike the above two types of non-freezing, glycerin does not dry the rubber, but, on the contrary, restores it, gives a second life. That is, it acts on it like a silicone lubricant, so there is no need to worry about the condition of the sealing gum.
The problem of heating the winter greenhouse has been solved, everything is quite simple.
If you want to know the principle of heating a greenhouse by Buleryan, click on the link
Which one to choose, how do they differ?
Serg3515
A lot has been written and rewritten on this topic, but I never saw a clear answer (and preferably from a user with experience). In this regard, if I may, questions. So, after all, what to fill? (what antifreeze liquid). Electric boiler, two-pipe system, metal-plastic pipes.
It can be very difficult for an uninitiated person to understand the abundance of offers and the range of prices.
The key factor in choosing a coolant is its base, i.e. basic chemical raw materials. The following are traditionally used as a basis:
- ethylene glycol is a toxic dihydric alcohol;
- propylene glycol is a non-toxic substance acceptable for use in the food industry.
The second selection criterion is the additives used in the coolant. Distinguish between organic additives (carboxylate) and inorganic. Additives affect the life and quality of the coolant. The coolant with organic additives has a longer service life, and during operation it more reliably protects the system from the effects of corrosion.
The third indicator is how the manufacturers of heating equipment relate to this product, in other words, is it permissible for a particular heat carrier to be used in a system where this type of equipment is used.
Rating of coolants in terms of a set of quality characteristics:
- Heat transfer fluid based on propylene glycol with organic additives and manufacturer approvals. Such a coolant provides the widest range of indicators: it is environmental friendliness with safety, and service life, and physical and chemical indicators, and versatility of use, from kindergarten to food production.
- Heat transfer fluid based on ethylene glycol with organic additives and manufacturer approvals. Such a coolant already has limitations in its application. You can determine its purpose: industrial facilities and systems, reliably isolated from human life.
- Heat transfer fluid based on propylene glycol with conventional inorganic additives. Although such a product has a shorter service life, it is harmless enough for the neighborhood with people and animals.
- Heat transfer fluid based on ethylene glycol with inorganic additives. Poisonous, short service life. Its use is often driven by the need to save money. If the system is well isolated from contact with human life, such a decision is quite logical.
P.S. Glycerin-based heat carrier. Glycerin is the simplest trihydric alcohol, which is a viscous transparent liquid, also used as a food additive. The product has a high density, kinematic and dynamic viscosity. Equipment manufacturers provide indicators several times lower than those present in a glycerin-based coolant. The product does not have operational and physical advantages, although it is quite easy to manufacture, therefore it is inexpensive. European manufacturers of chemical compositions are very negative about the use of glycerin as a base for antifreeze liquids.
Types of antifreeze compounds for heating systems
In modern heating systems, three main types of antifreeze are used, differing in chemical composition - these are heat carriers based on:
- ethylene glycol;
- propylene glycol;
- glycerin.
But, despite the difference in chemical compositions, they all share the feature of crystallizing at very low temperatures - from -40 to -75 ° C. In addition, their important operational advantage is that even after crossing the limit, they do not go into a solid state, but turn into a gel-like substance that is not capable of causing deformation processes in the elements of the system, since its volume does not undergo any changes. Of the general features, it should also be noted:
- increased viscosity and density;
- lower heat capacity;
- high penetrating power, due to which the destruction of seams and joints occurs;
- toxicity, although each species is significantly different in this parameter.
Ethylene glycol antifreeze
This type of anti-freeze is quite popular, but mainly due to the lowest price among antifreezes, they are easily recognizable by their characteristic red color, which warns of the toxicity of this drug. For heating systems, you can purchase both ready-to-fill compounds and concentrates, which should be prepared using distilled water. The maximum temperature at which the concentrate crystallizes is -65 ° C, and the final solution is -30 ° C. The term of use of such antifreeze is on average 5 years, after which it needs to be replaced.


During its operation, it is important to control the heating temperature of the coolant, since at high temperatures, close to the boiling point, the decay process begins, followed by precipitation, which becomes the main problem - it can clog the entire line. The liquid component of this decomposition has a high chemical aggressiveness and leads to the onset of the metal corrosion process. The situation is somewhat saved by the fact that these antifreeze compositions are used with special additives capable of counteracting the foaming of antifreeze in the system, which results in gas locks. But in the event that the decomposition process as a result of exposure to high temperatures was started, they completely lose their functions.
Ethylene glycol antifreezes can only be used if the boiler equipment has a function for precise temperature settings and the most reliable sealing of all joints and joints, since the leakage of antifreeze is dangerous due to its high toxicity.
Propylene glycol formulations
In terms of their main technical characteristics and parameters, they are the main competitor to ethylene glycol formulations, but unlike them, they are not toxic, which is usually evidenced by a special label on the Eco package. This antifreeze is ideal for boilers with two circuits, as accidental contact with water or mixing them does not pose a particular threat to human health, although this should be avoided.
Among the original characteristics, it should be noted that:
- higher density of matter and heat capacity of the composition;
- the presence of a lubricating effect inherent in this type of antifreeze, due to which the hydraulic pressure decreases, and therefore, due to the absence of additional resistance, the overall efficiency of the system working with this composition increases.
The advantage of using propylene glycol antifreezes is that they are more durable - on average, the operation of the system with them lasts about 10 years. The main disadvantage is the high price, in comparison with ethylene glycol compositions, the difference is approximately 2-3 times, depending on the manufacturer's brand.
Glycerin based antifreezes
If the heating in the house provides a glycerin-based fluid, then you do not need to worry about its toxicity, as well as about the integrity of the system.


These compounds are maximally loyal to its elements, including those with zinc spraying, do not corrode joints and seams. The temperature range is impressive too: from -30 to 100 ° C, but at the same time the price is lower than that of propylene glycol antifreezes. But this type of anti-freeze also has some disadvantages, as well as application features:
- density, the highest among all types of antifreeze, which does not have the most positive effect on the pipe system and pumping equipment, which are forced to withstand additional loads, the high viscosity of the composition has a similar effect on the service life of boilers;
- a sufficiently low heat capacity requires the installation of larger radiators in the premises;
- the lack of stability of the substance at high heating of the coolant, which is manifested by abundant foaming or even decomposition, as a result of which the decay products exhibit the qualities of carcinogens;
- if overheating occurs, then the coolant has no ability to recover and needs to be replaced.
Glycerin-based antifreezes were the first on the anti-freeze market and at the moment are not of particular interest to manufacturers, either of the formulations themselves or of heating equipment. There is no clear standardization of this substance, so there are frequent cases of its fakes, as well as replacing more expensive solutions based on propylene glycol with it. Therefore, if the choice fell on this type, its purchase should be made only from trusted sellers.
Dilute with water or not?
The origin of this issue is due to the fact that equipment manufacturers set the same requirements, worrying about the safest and most efficient operation. Buyers are sticking to their cost-saving line. And manufacturers of heat transfer fluids maneuver between the requirements of manufacturers, buyers and sales practices. As always - the truth is somewhere in between.
Manufacturers of non-freezing liquids, in general, offer coolants "-65C" or "-30C" on the market. Firstly, this is due to the formed demand, and secondly, such a coolant is guaranteed not to be frozen at the time of sale.
Equipment manufacturers have their own truth. So, the density of antifreeze liquid marked "-25C", generally recommended by equipment manufacturers for reasons of optimal fluidity, is 1.03 g / cm3, and for liquid "-30C" - 1.04 g / cm3.
The fact that the content of the main substance in the composition of the coolant will be several percent higher is not an “outrageous” deviation, but taking into account the fact that water can be added to the coolant either when feeding the circuit, or if the water is not completely drained from the system after flushing , The "reserve" of concentration is simply necessary.
On the other hand, dilution of the coolant "-30C" to "-25C" - and this value is 3-4% - will not bring tangible savings for the buyer, but at the same time will increase the risk of losing other necessary properties. But in the case when the buyer plans to use the concentrated coolant "-65C" and dilute it already - here the savings can already be up to 20%.
A matter of choice
The behavior of an antifreeze liquid in a heating system directly depends on how high-quality additives were added there, as well as on the operating conditions.
However, it should be noted that all anti-freezing compounds have 2 key positive characteristics:
- Anti-corrosion properties.
- Anti-foaming properties.
Without additives that ensure the availability of these indicators, the liquid turns out to be quite aggressive. The fact is that the air contained in the foam leads to disruption of the circulation process, the appearance of air pockets and the formation of water hammer.
It should be noted that all additives are equipped with a certain service life. After the time allotted to them, they disintegrate at the molecular level. When this happens, a precipitate forms and acid is released.
The service life of the anti-freeze can be as follows:
- Ethylene glycol based antifreeze has been functioning for 5 years.
- On propylene glycol for 5 years too.
- Non-freezing liquidmade on the basis of glycerin has been working for about 10 years.
It is worth noting that you should not heat up the heating system to too high temperatures. If this figure rises to 90 degrees, then the antifreeze will begin to disintegrate and lose its main positive characteristics.
Such an increase in temperature can occur involuntarily:
- Due to incorrect starting of the heating system after it has been idle for a long time.
- Due to improper assembly the entire heating system.
Additives have a direct impact on a number of characteristics of antifreeze heating fluid, including the following:
- viscosity;
- expansion under the influence of high temperature;
- density;
- thermal conductivity;
- fluidity;
It should be noted that the quality of the additives affects the level of all these characteristics. The thermal conductivity of this liquid is much lower than that of water, with the lowest thermal conductivity observed in glycerol agents. Due to the rather high viscosity index, the non-freezing liquid is much more difficult to circulate than water.
In order for the coolant to move normally along the circuit, it will be necessary to use a fairly powerful pump.
An increased flow rate can result in a large number of leaks. They can occur even where ordinary water will not seep.
Key areas of leakage can be:
- Pipe joints.
- Plotswhere various additional elements are connected.
- Directly in the heating boiler itself.
- Radiators, especially areas where sections are connected to each other.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lKKW_NrnUug
What is the service life, how do you know: when to replace?
The question is quite common.
Andreic
Connoisseurs, clarify the situation: contractors today said that antifreeze has a 5-7 year life. Then it loses its properties, begins to precipitate, as it were, and does not go through the heating system as it should be. Is it true or not?
For heat transfer fluids containing organic (carboxylate) additives, the service life is 10 seasons (10 years), for heat transfer fluids with "ordinary" silicate additives, this period is about 5 years (heating seasons). In order to control the quality, every year, after the end of the heating season, you can carry out a simple procedure - pour a small amount of the coolant into a transparent glass container. The obtained sample is visually inspected for the presence of mechanical and other impurities, color, transparency. If the coolant contains mechanical impurities (crumbs, grains of scale), it can be drained, filtered, flushed out and refilled. If there are traces of chemical changes (flakes, clots), it is necessary to contact a specialist.
In which systems can antifreeze be used?
There are a number of restrictions on the use of antifreeze:
- Non-freezing liquid, regardless of chemical composition, can only be used in a closed circuit. This means that there is constant pressure in the system, the circulation is constantly forced, due to the pump.
- Heat carriers are not used with electrolysis type electric boilers. The electrolysis type is when a coolant is used as an electrical conductor. The electrical conductivity of heat carriers is low, and this will lead to high energy costs.
- Non-freezing liquids must not be used in contact with galvanized surfaces (pipes).
Features of pouring antifreeze into the heating system
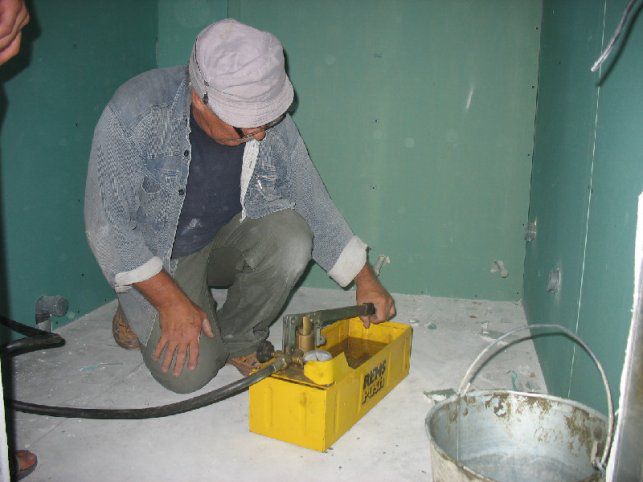


hand pump for pressure testing and filling heating with antifreeze
In order not to make an anti-freezing liquid for heating yourself and at the same time risk the performance of the entire system, it is necessary to purchase a ready-made composition. However, in addition to this, you should familiarize yourself with the filling technology.
If there is an old coolant in the system, it should be drained. In this case, it is recommended to check its condition. The degree of contamination will indicate the relevance of complex cleaning. It is performed before pouring antifreeze into the heating system. The subsequent stages of work consist in the implementation of the following points:
- If antifreeze was used before - a complete flushing of the system is mandatory. Otherwise, mixing of two different antifreeze fluids for furnace heating may lead to undesirable chemical reactions;
- Closed system... In it, the filling point should be lower than all other heating devices. With the help of pumping equipment, the heating system of a private house is filled with non-freezing liquid. It is important that the pressure in the pipes does not exceed 3 atm;
- Open system... For her, the use of antifreeze liquid for hot water heating is not recommended. Continuous contact with air can lead to a significant increase in foaming. Filling is done through the upper expansion tank;
- Heating testing... The temperature in the system rises gradually. At the same time, the tightness of all units is checked, as well as the absence of extraneous noise during the circulation of the coolant.
During operation, you will need to top up antifreeze liquid for heating yourself. Therefore, it is recommended to purchase it with a margin - 15-20% more from the calculated volume of the system.
You cannot make an anti-freeze liquid for heating yourself. Also, the use of automotive antifreezes is not recommended, since in most cases they are made on the basis of unsafe propylene glycol.
How to determine the required temperature, or is -30C a lot or a little?
Application practice shows that the temperature in a room that has not been heated for a long time and the ambient temperature are always different. The room will always be warmer - 10 degrees or more.Even if "outside the window" is minus 40, and the room is frozen to minus 30, the coolant will not turn into ice and, accordingly, will not burst pipes and radiators. In order for antifreeze marked -30C to freeze and damage the heating system, the temperature (in the house) must be below -50C, which in reality is quite difficult to imagine.
Rash98
For three seasons I have been using propylene glycol as antifreeze in a natural circulation system. Everything works perfectly. The batteries heat up after just 10 minutes. I use propylene glycol not concentrated, but diluted to the freezing point minus 30 degrees. S. Zalit once three years ago.
On the other hand, non-freezing liquids with a temperature of minus 10, 15 and even 20C should not be used for a number of reasons:
- Even in the central regions of Russia in winter, the temperature drops below the indicated values. In such conditions, hardly anyone will want to buy a product that has turned into a "snow porridge", despite the fact that after thawing, it will fully return its properties.
- At the slightest dilution (which is very likely, especially in double-circuit boilers, or after flushing the system), the coolant without a small temperature reserve will lose its necessary properties.
Heating system requirements
So, as already indicated, if it is planned to use antifreeze as a coolant, this should be taken into account at the design and installation stage, but it should also be borne in mind that these compositions are used exclusively in closed systems.
In addition, it must be borne in mind that:
- forced circulation will also be mandatory, since it will not work to ensure the required transport speed of the coolant due to its higher viscosity and density;
- will have to introduce a complete ban on the use of pipes and fittings made of zinc;
- special attention will have to be paid to all connections - it is not allowed to use tow and oil-based paint for this, since the aggressive environment of the composition will simply destroy them;
In the event that the heating system is planned to be operated with an anti-freeze coolant, then there are some requirements for boiler equipment - it must have a control system with which it will be possible to maintain the temperature level, since for some types of coolants in this group, the threshold of 65- 75 ° C is unacceptable. Attention should also be paid to the circular pump, especially if the system is being transferred from water to antifreeze: the power of the old one is simply not enough, even with the same circulating volume. You will also need an expansion tank with a large, approximately 1.5-2 times, volume. The diameter of the pipes will also have to be increased, as well as the installation of radiators with an increased volume.


In the event that the autonomous heating system is equipped with an electrode electric boiler, then the use of antifreeze should coincide with the recommendations of the equipment manufacturer. This is due to the fact that the heating of the coolant occurs due to the passage of alternating current through it, therefore the qualitative composition of the anti-freeze is very important - it must have the required density and provide the required electrical resistance.
Non-freezing mixtures, as a rule, are sold ready for filling into the system, but if for some reason, for example, antifreeze is designed for a maximum temperature of -40 ° C, and the maximum in winter rarely exceeds -20 ° C, in this case it can be diluted. but only with distilled water. But all the same, if there is a question about the use of antifreeze in the heating system, then even with mild winters, you should still focus on the indicator of -30 ° C.
When there was water in the system, everything was fine, the coolant was poured in - all connections flowed.
Arnau
It's time to decide how to fill the heating system in a country house: distilled water or antifreeze.
Against antifreeze, the main reason is that it corrodes the connections, leaks are possible and you need to frequently change the components.
Indeed, non-freezing liquids are more fluid than water. And the fluidity increases with increasing temperature. They do not contain chemical compounds that, forming calcium deposits, can clog micro-gaps. Even if the micro-gaps are clogged with something, the coolant additives "clean" the clogged formations and restore the flow. Therefore, it is necessary to pay more attention to the assembly of joints in the system where it is planned to use antifreeze. And, as mentioned earlier, before starting, it is imperative to carry out commissioning work, which includes pressure testing of the system.
Can antifreeze be used?


heat supply circuit with antifreeze instead of water
Antifreeze or antifreeze liquids are known to almost everyone. They are widely used in vehicle cooling systems in winter. In a car engine, antifreeze transfers excess heat from the engine, cooling it down. Moreover, even in the most severe frosts, it does not freeze. It is these properties - the ability to transfer heat even at the lowest temperatures and have led to the use of antifreeze for the construction of heating systems. It is especially important to use such a coolant in a system, part of the pipeline of which runs through an open area.
A good feature of "non-freezing" is that it provokes less corrosion on the inner surface of pipeline systems than ordinary water. Another undoubted advantage is the absence of suspended limestone solutions in non-freezing liquids - so you don't have to worry about possible scale formation.
There are several modifications of antifreeze fluids that can be used in heating systems. The choice of a specific type is made taking into account the climatic conditions and the configuration of the heating system of your home.
What is heating system flushing fluid and should it be flushed?
In addition to the heat carrier itself, when operating the heating system, you will also have to purchase a liquid intended for flushing with a pipeline and heating radiators.
Of course, as a last resort, you can rinse the inner surface of the pipes with ordinary tap water, but it is better to do this all the same with the help of special fluids, in which special chemical additives are introduced.


heating flushing
An alternative flushing option can be the use of water with a caustic soda solution added to it. Such a mixture is poured into the heating system and remains inside it for about an hour. The soda solution comes into contact with scale on the inner surface of the system and dissolves it. In addition, the baking soda solution will dissolve the corroded areas.
How to choose a liquid for a heating system?
- First of all, it is necessary to determine the operating parameters of the system. Here two extreme values will be important to you - the maximum temperature of the coolant when heating in the boiler and the minimum temperature of the ambient air.
- Next, you need to carefully study the technical characteristics of your heating system. Actually, the main attention should be paid to the characteristics of the heat exchanger in the boiler. Some manufacturers may not allow the use of anti-freeze fluids.
- And, finally, after determining the permissibility of using an anti-freezing liquid and its possible temperature parameters, proceed directly to the choice of the brand of liquid, focusing on its lowest toxicity. All the same, the heating system will be located in a residential area, and possible fluid leaks should not lead to poisoning.
Using alcohol as a heat carrier
No matter how blasphemous it may sound for a man's ear, it is allowed to use alcohol as a heat carrier. The alcohol does not freeze and can be used over a wide temperature range. Naturally, industrial alcohol is used in this capacity, which is a deadly poison for humans. However, many manufacturers of boilers and heat exchangers are critical of the use of fluids such as bischofite or ethylene glycol as a heat carrier.


bischofite
The disadvantage of using pure alcohol as a heat carrier is its high volatility - about five liters per year will evaporate through microscopic pores in the system.