Breakdown signs
If the room does not warm up enough in winter, then it is felt immediately. The lack of heating is manifested not only by the discomfort of the residents. The walls are covered with mold and mildew, the rooms smell damp, and there is a strange noise in the pipes.
Problems can be accompanied by some signs
:
heat is supplied unevenly throughout the room;
If several of these signs have arisen, then it is necessary to identify the cause of the breakdown and eliminate it. Otherwise, the system will function even worse.
Causes of malfunctions
Most residents of private houses and apartments do not consider it necessary to understand the engineering design of the heating system. They assign the solution of all problems arising with the central structure to the employees of the corresponding services. Although it is really better to entrust the repair to qualified specialists, you need to learn how to deal with minor breakdowns on your own, because sometimes they can be fixed at home.
Such knowledge is indispensable for the owners of private houses and cottages, where the entire system is under the control of one person. The owner should know at least the general design of the equipment and be able to identify minor problems.
The main reasons why there is no circulation in the heating system
:
- incorrect design;
- inconsistency of equipment with design requirements;
- imbalance due to unauthorized connections;
- poor quality installation;
- education;
- improper installation of radiators;
- damage to pipelines;
- violation of tightness in seams and joints.
Each reason must be considered separately, because it is accompanied by different consequences.
Erroneous design
Before installing the system, the master or the owner of the house himself draws up an engineering project. All calculations and measurements must be carried out very carefully, since the slightest mistake can lead to interruptions in the operation of the equipment. This takes into account the layout of the house, its area, the number of radiators, the climatic conditions of the region, the presence or absence of other heating systems and heaters.
You can't skimp on a quality project. Otherwise, when starting up the equipment, several batteries may not be connected or water will flow out of the pipelines. Then you will have to turn off the entire system and construct it again, again carrying out calculations and creating drawings and diagrams.
Experts who should be entrusted with this painstaking and hard work, take into account all the factors affecting the normal functioning and reliability of heating units. Be sure to plan the slope of the vertical and horizontal sections of the pipeline. The technical parameters of the equipment itself can be found in the documents attached to it. The optimal boiler performance should be at least 1 kW for every 10 square meters of floor space with 3 m high ceilings.
Natural circulation heating system without pump and electricity
Heating schemes for wooden residential buildings
It should be noted that the heating scheme in a wooden house is not simple. Electric, air and oven options can of course be used.But most users opt for water heating systems.
A house made of wood has a high heat capacity, so more heat energy is needed to warm it up.
In addition, the heating scheme for a private house assumes that it is necessary to constantly maintain the room temperature of the water. This is necessary so that the room does not get damp. With such a heating device, the system consists of a heat-heating boiler, mains and heating units. The structure must be equipped with ball valves and thermostats. Of course, an artificial heating system can also be used to heat a wooden house, but a heating scheme without a pump is still more common. We have already written in more detail about the heating system with pump circulation here.
Heating scheme for a two-story residential building
A heating system with natural circulation of a two-story house is being implemented in two-pipe and one-pipe systems. They have the same principle - a pipe rises from the boiler up to the maximum height, and then the coolant is distributed over the heating structures. The difference is as follows: in a two-pipe heating system, water that has already cooled down is collected in another pipe, which is fed to the return flow inlet of the heat boiler. As for the one-pipe system, a pipeline from the outlet of the last battery goes to the boiler return flow inlet. A two-pipe heating system with natural circulation is the most suitable option for houses with two floors.
The two-pipe system differs from a single-pipe system only in the procedure for connecting heating elements. It is recommended to install a regulating tank in front of each battery. To ensure normal circulation of water in a two-story house, there is always enough distance between the center of the heat boiler and the upper point of the supply pipeline. Therefore, a storage tank for heating can be equipped not in the attic of the room, but on the second floor.
Heating scheme for a one-story residential building
A one-pipe heating scheme with natural circulation of a one-story house is most suitable for such structures. Such a system consists of one pipe and includes a boiler for heating, piping, wiring and an expansion tank. The scheme of such a system is simple. Therefore, its installation can be done with your own hands. A pipe is run along the perimeter of the dwelling. It is necessary to choose pipes of large diameter - not less than DU32.
The pipe is mounted inside the dwelling. On the supply side, the wiring must be higher than where the return flow returns to the heating boiler. Radiators or convectors are cut into the loop. For this, pipes with a smaller diameter are used. It is advisable to install chokes and valves on the connections. Also, an air vent will be useful. Such a scheme allows you to heat a room without using auxiliary fittings.
In the private sector, a horizontal heating system is widely used, which is classified into dead-end and associated water flow systems. In a dead-end system, each of the batteries is located farther from the boiler. Such a system can be easily unbalanced. Therefore, it takes a very long time to set it up. It should be noted that the associated heating system, the scheme of which assumes a greater flow rate of pipes compared to a dead-end one, is used mainly in simple heat supply systems.
When choosing a passing system, one must take into account that the circulating rings must be the same.
All radiators in the system work as one. Today, flexible hoses are very often used to heat the house. They are used to connect heaters to the heating system.
Low-quality equipment
Due to the wide range of heating boilers and the variety of models, manufacturing firms, the buyer can easily make a mistake when choosing a suitable unit. Therefore, it is necessary to focus on the approved project. All parts and elements of equipment must comply with its requirements.
It is according to the plan that a certain type of radiator is acquired with a suitable number of sections in them. Shut-off valves, adjusting elements and connecting assemblies must be mutually compatible.
Most often, problems arise due to insufficient circulation of the coolant through the pipes
... Special pumps can enhance the movement of water, but they must be chosen carefully, otherwise the devices will become a source of hum and noise. Additionally, old iron pipes are replaced with modern metal-plastic or polypropylene products. This will avoid some problems in certain heating systems.
Plastic pipelines are easy to install and connect to the boiler, but it is better to entrust this work to the master. After all, not all types of plastic are suitable for use in heating equipment, some models do not withstand high temperatures and burst under their influence.
Unbalance and installation
Another reason why water does not circulate in the heating system is an incorrectly carried out imbalance during the repair or redevelopment of the apartment. This is influenced by the uncontrolled installation of new radiators and underfloor heating.
The batteries on some floors continue to function normally, on others they will remain cold, since they do not receive the coolant. Although the foremen can easily balance the distribution of water across all risers, the system will not work in several apartments.
If some residents removed the thermostats when replacing heating equipment, then the heat will not flow into the dwellings of their neighbors. To eliminate this problem, it is necessary to remove thermostats in all apartments. You can increase the heat supply if you follow the example and also replace all the radiators. Bimetallic or aluminum batteries will harmoniously fit into modern heating systems. You must first obtain permission to replace devices, since you cannot do this on your own.
In a private house, the batteries located closer to the boiler heat up the most. To restore the balance, you need to turn off the adjustment taps and restrict the access of the coolant to the nearby radiators. But sometimes the new battery does not heat up either. If the entire system was working properly before installing it, then the problem is incorrect installation. When welding several polypropylene pipes, the master overheated the product, due to which its inner diameter decreased. The specialist must redo all the work free of charge. All structural elements must be securely and efficiently fastened.
Why do the batteries in a private house not warm up well?
Just as in the case of a high-rise building, there may be several reasons for the poor performance of heating batteries in a private house.
Reason 1: problems in the hydraulics of the heating system
The most common reason batteries stay cold is due to the hydraulics in the heating system. In this case, one of the heating branches is working properly, and the other is intermittent. This is typical for a new heating system or when adding radiators to an existing one. If the hydraulics are incorrectly calculated, and in particular the diameters and lengths of the pipes, some of the batteries may simply not heat up. The hydraulics can be adjusted using special cranes.
Reason 2: one-pipe heating system
Many private houses have one-pipe heating systems. In such a system, batteries that are often remote from the boiler heat up much worse than those close to them. This does not mean that there are problems, this is a feature of the operation of a one-pipe system.The only solution here may be only to replace the system with a two-pipe one.
Reason 3: boiler malfunction
The batteries may not warm up due to malfunctions in the operation of boilers with built-in automation, pumps and sensors, which is a typical problem for autonomous heating systems. In this case, it is necessary to contact directly a specialist working with such equipment.
Air congestion
Cold batteries are usually caused by air, which prevents water from flowing freely.
An airlock is formed for several reasons.
:
Oxygen bubbles accumulate in one of the batteries or at the top of the heating system. Because of this, the bottom of the radiators will be hot and the other half will be cold. And also when the equipment is operating, gurgling sounds occur. In multi-storey buildings in the uppermost apartments, the boilers stop working completely.
In older apartment buildings, many pipes have long since expired. Therefore they can cause accidents and lower heat levels
... Microelements contained in the coolant are deposited inside the pipelines. They make it difficult for the water to circulate normally. The correct solution would be to replace products, but this is not always possible.
Scale layers form on the inner surface of the boiler, this reduces the pressure in the system. This problem is caused by the use of hard water saturated with minerals and salts. Special reagents must be added to the equipment, which soften the quality of the coolant.
Leakage occurs when pipes are corroded or improperly connected. If it is in a visible area, then it is easy to seal the hole with sealants. It is more difficult to deal with a problem hidden in a wall or floor. In this case, you will have to cut off the entire branch, fix the problem and mount a new section. In addition to sealants, you can use special parts for clamping the pipeline, corresponding to it in diameter. If it is not possible to purchase such devices, then it is enough to make a clamp. The leak is covered with a piece of soft rubber and tightly secured with wire.
If a leak is detected on the radiator or its junction with the pipe, the hole is wrapped with a strip of fabric, having previously soaked it in moisture-resistant construction glue. Cold welding is sometimes used. To avoid such problems, the entire system is inspected for damage before the start of the heating season. It is imperative to start the boiler and check the quality and reliability of its operation.
There is often no circulation in the heating system. What to do in this case is up to the owner of the house. It is advisable to call a specialist who will quickly and efficiently carry out all the repair work. You need to take preventive measures on your own to keep the equipment in working mode.
In water heating systems, a problem often occurs that leads to a deterioration in the circulation of water inside the circuit. The problem has a specific name - airing in the heating system. Uninterrupted operation of water heating is based on the principles of hot water (heat carrier) circulation inside the circuit and heat transfer through radiators that heat the premises. Air in the system leads to the appearance of air locks and, as a result, to ineffective functioning of the entire system due to a decrease in heat transfer.
To start solving the problem, it is necessary to establish the reasons for the appearance of air: natural or artificial. The natural reason is the airing of the system due to the property of heated water to release air. The higher the temperature of the coolant, the more air bubbles are released. According to physical laws, the accumulation of bubbles occurs in the upper part of the circuit, as air is lighter than water. The rest of the reasons are considered artificial. It is difficult to give a complete list, but the main reasons are considered to be the following:
- insufficient pressure in the system;
- errors in the installation of the heating circuit (for example, incorrect pipe slope);
- errors when starting the system into operation (for example, too fast filling of the circuit with water);
- high concentration of air in the water used;
- incorrect operation of locking equipment (possibly loose connections of individual elements);
- blockage of pipelines;
- the consequences of repair and maintenance work;
- corrosion on metal surfaces of circuit elements;
- incorrect operation of air vents or their absence.
Stabilization of pressure in the heating system
The expansion of water as a result of heating is a natural process. In this indicator, the pressure can exceed the critical value, which is unacceptable from the point of view of heating operation. In order to stabilize and reduce pressure on the inner surfaces of pipes and radiators, it is necessary to install several heating elements. It will be much easier and more efficient to adjust the heating system in a private house with their help.
Expansion tank adjustment
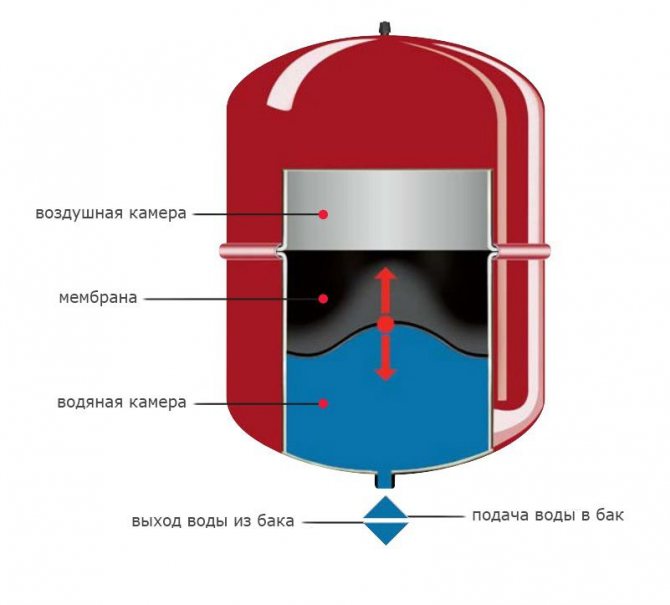
It is a steel tank divided into two chambers. One of them is filled with water from the system, and air is injected into the second. The air pressure value is equal to the normal one in the heating pipes. If this parameter is exceeded, the elastic membrane increases the volume of the water chamber, thereby compensating for the thermal expansion of the water.
Before adjusting the differential pressure in the heating system, check the condition and setting of the expansion vessel. You can adjust the pressure in the heating system by purchasing a tank model with the ability to change it in the air chamber. As an additional measure, install a pressure gauge to visually check this value.
However, with a significant jump in pressure, this measure will not be enough. In this way, the differential pressure in the heating system can be adjusted if it does not exceed a critical value. Therefore, it is recommended to install additional devices.
How to adjust a security group
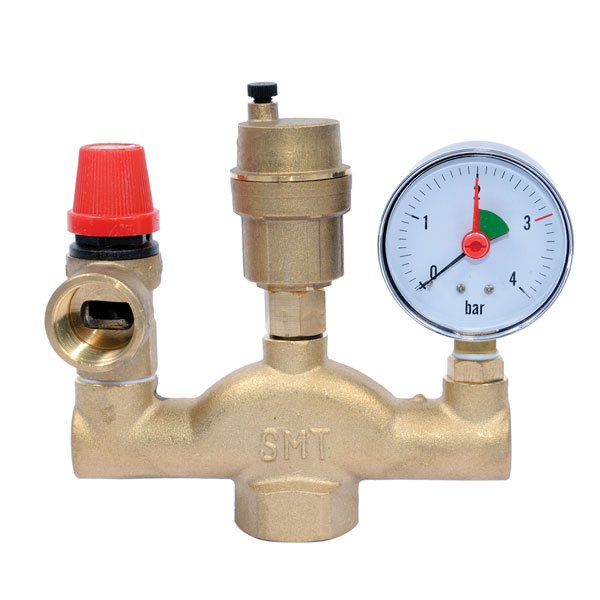


This group of devices includes the following elements:
- Pressure gauge
... Designed for visual control of the heating system; - Air vent
... If the water temperature exceeds 100 degrees, excess steam acts on the valve seat of the device, releasing air from the pipes outside; - Safety valve
... It works in the same way as a water drain, but it is needed to drain the excess coolant from the pipes.
How to adjust a heating radiator using this unit? Alas, it is designed to prevent emergencies in the entire system. Batteries need a different device.
Mayevsky crane
Structurally, it is similar to a safety valve. A special feature is its small size and the ability to mount on a radiator pipe with a small diameter.
In order to properly adjust the heating batteries, you need to know in what cases the Mayevsky crane is used:
- Elimination of air congestion in radiators. By opening the valve, air is released until the coolant flows;
- Setting the parameters of the critical pressure value. In the event of an emergency expansion of water, the valve opens and the pressure in the radiator stabilizes.

The latter function is optional and is often not used. This task is best done by the security team. Correct regulation of heating in the house should include all of the above elements.
Consequences of airborne
Violation of heat transfer due to air congestion is unpleasant for residents who pay for heating, but in fact receive an underestimated indoor temperature. But this is not the only negative, there are other negative consequences:
- noise and vibration during the circulation of water, which in the worst case is fraught with the destruction of integrity at the junctions of the circuit elements;
- defrosting the system if there is no water circulation in several radiators;
- excessive fuel consumption in order to increase heat transfer;
- destruction of internal metal parts under the influence of air (due to corrosion).
The totality of all the consequences affects the working capabilities and the overall operational life of both individual elements and the entire heating system.
Airing out
Ventilation can occur when the system is filled with a coolant and during operation. Situations are resolved in different ways, but it all comes down to bleeding air using valves and taps built into the system.
The filling of a closed system with forced circulation must take place in a specific sequence in order to avoid the formation of air pockets. The supply of cold water is carried out from the bottom up, the taps for air exhaust are left open, only those that are installed for draining the water are closed. Rising, the coolant squeezes out the air through the open valves and taps. As the water begins to run through the tap, it is closed. So gradually, necessarily smoothly, fill the system with water. The pump is started when the circuit is completely filled with coolant.
Manual or automatic air vents and air separators are used for air release. It is clear that the installation of manual air vents implies the discharge of air by the service personnel or the tenant of the apartment (house). Such air vents are found in ordinary residential buildings in the premises of the upper floors or on technical floors. Mayevsky's crane is known to many residents of old high-rise buildings, which each heating season independently discharge the accumulated air. In new homes, the practice is to install a manual drain valve on the technical floors.
The automatic air venting system works in isolation from human input. The principle of operation of automatic air vents is the same. In the air vent housing there is a float on which water enters. The float presses on the spring-loaded stem, opening access to the outside. The body is gradually filled with coolant, the float presses on the stem and closes the outlet. In order for the air vent to work properly, periodically check the cleanliness of the needle and the suitability of the O-ring for further operation.
The need for separators arises when operating large heating systems, where manual discharge is problematic. The separator copes with the removal of air dissolved in water. It converts air into bubbles and flushes them out of the system. In parallel, the separator (depending on the model) can capture impurities that are present in the coolant (sludge).
All air vents are mounted at critical points - at pipe bends and at the top points of the circuit.
One of the simplest is the natural circulation heating system. However, this simplicity in the absence of proper experience with such systems can "get out sideways" during operation.
Heating with natural circulation was widespread a decade ago in small country houses and some apartments with individual heating. Now the market is "conquered" by systems with forced circulation of the coolant, thanks to the opportunities that they provide.
But let's talk about water heating with natural circulation.
How the system works
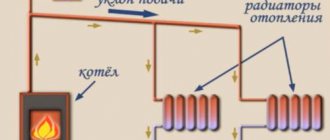
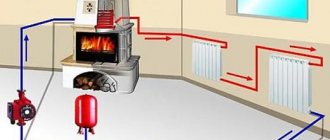
Water, heating up in the boiler, rises up the central riser and through the supply pipeline enters the heating radiators (heating devices), where it gives off part of its heat. Further, the already cooled water through the return pipeline again enters the boiler and heats up again. Then the cycle is repeated, providing a comfortable temperature in the heated room.
To ensure the natural circulation of the coolant (usually water) in the system, the horizontal parts of the pipeline are mounted with a slope of at least 1 cm per linear meter of the length of the horizontal section of the heating system.
Hot water, due to a decrease in its density when heated, rises up the central riser, squeezed out by cold water returning to the boiler. Further, it spreads by gravity along the supply pipeline to the heating radiators. After "staying" in them, the water also flows back into the boiler by gravity, again squeezing up the water already heated in the boiler.
The air that has entered the system with the coolant can create an air lock in the heating radiators, but often in such heating systems with natural circulation, air bubbles, due to the slopes of the pipeline, "travel" upward and exit into an open-type expansion tank (a tank in contact with atmospheric air ).
The expansion tank is designed to maintain constant pressure in the heating system, due to the fact that it is filled with the volume of the coolant that has increased during heating, which then "gives" back to the system when the temperature of the liquid drops.
We draw conclusions!
So! The rise of water in the system (riser to the supply pipe) is carried out due to the difference between the densities of the heated and cooled liquid. The movement (circulation) is also supported by gravitational pressure (return pipe).
When the coolant moves through a pipeline in a heating system with natural circulation, resistance forces act on the liquid:
- friction of the liquid against the pipe walls (large diameter pipes are used to reduce);
- changing the direction of movement of the liquid on bends, branches, channels of heating devices (radiators).
Natural circulation heating - operating principle
The coolant (water) heated in the boiler flows through the supply pipeline, and then through the riser to the radiator batteries, which are given heat.
After that, the water is returned through the return pipelines to the boiler, where it is again heated to the required temperature. The cycle is repeated many times.
Water heating with natural circulation requires horizontal piping with a slight slope facing the direction of the flow of the water stream.
The heated water, rising up the risers due to thermal expansion, is squeezed out by the colder water flow emanating from the return. After that, the heated water spreads by gravity along the horizontal outlets, and the cooled water (in the same way) enters the boiler.
The inclination of the pipes facilitates the diversion of air bubbles to the expansion tank, since the gas is lighter than water - it rushes upward, and the inclined pipes help it not to linger and flow into the expander, and then into the atmosphere.
The expansion tank leaves the pressure in the entire system constant, it serves to accept the volume of water that increases with heating, and after cooling it again gives it back to the pipeline.
A natural circulation heating circuit causes the water to rise by expansion when heated or by gravity.

Natural circulation heating circuit. Click to enlarge.
Circulation occurs due to the density difference between the heated water, which rises up the supply riser, and the chilled water descending through the return riser.
The gravitational pressure is spent on the transfer of the coolant, as well as on overcoming the resistance in the pipeline network. These resistances are caused by the special friction of the water flow against the pipe walls, as well as the presence of local resistances in the system itself.
Such local resistances include turns and branches of pipes, fittings, as well as the heating devices themselves.The gravitational pressure will depend on how much internal resistance will arise in the pipelines. To reduce friction, pipes with an increased diameter are used.
Basic physical parameters of a natural circulation heating system
The circulating pressure Pc is a physical quantity determined by the difference in the heights of the centers of the boiler and the lowest heating device (radiator).
The greater the difference in heights (h) and the difference in the densities of heated (ρ g) and cooled (ρ o) liquids in the system, the more qualitative and stable the circulation of the coolant will be.
P c = h (ρ about -ρ g) = m (kg / m 3 -kg / m 3) = kg / m 2 = mm.w.st.
Let's "look for" the reason for the appearance of the circulating pressure in the heating system with natural circulation in the "wilds" of the laws of physics.
If we assume that the temperature of the coolant in the heating system "makes a jump" between the centers of the devices (boiler and radiators), that is, the upper part of the system contains hotter water than the lower part of the system.
Density (ρ g) (ρ g).
We cut off (mentally) the upper part on the contour diagram and ... What do we see? A familiar picture from school - two communicating vessels at different levels. And this will lead to the fact that the liquid from a higher point, due to the action of gravitational force, will flow to a lower one.
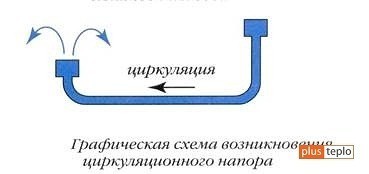

Due to the fact that the heating system is a closed loop, the water does not splash out, but simply strives to equalize its level, which leads to pushing the heated water up and to its further "independent gravitational" path through the heating system.
The conclusion is this! The fundamental indicator of the circulating pressure is the difference between the installation heights of the boiler and the last (lower) one in the radiator system. Therefore, in heating systems of private houses, boilers are, if possible, located in basements, observing the maximum height of 3 m.
In apartment versions, boilers are trying to "deepen" to the floor slab, respectively, "fireproofing" the "nest" of the boiler landing on the floor.
According to the formula given above, the difference in the densities of cold and hot water in the system also has a significant effect on the circulating head.
A heating system with natural circulation is a self-regulating system, that is, for example, when the heating temperature of the heating medium naturally rises (see the formula), the circulating head and, accordingly, the water consumption increase.
At low temperatures in a heated room, the difference in water density is large and the circulating pressure is large enough. When the room warms up, the coolant no longer cools so much in the radiators, and the difference in the densities of the heated and cooled coolant decreases. Accordingly, the circulating pressure also decreases, reducing the "flow rate" of water.
Has the indoor air cooled down? For example, someone opened the doors to the street. The density difference increased again, increasing the water pressure.
Pressure, water velocity and return temperature in the heating system
Basically, the requirements for heating systems imply dividing the specifics of heating operation into two types:
- independent, here the heat source is located directly in the room - it is used in an individual house or in high-rise buildings of an elite type;
- dependent, where a network of pipelines is connected to the heating complex - is used in most houses of the urban massif and urban-type settlements.
According to the specifics of the circulation of the heat carrier, water is mainly used, where the speed of the water in the heating system directly affects the temperature in the radiators. The circulation is divided into natural (according to the principle of gravity) and forced (heating system with a pump). By distribution, it is customary to distinguish between a heating system with lower and upper piping.
Temperature
Despite the wide selection of provided heating systems, the options for heat supply and return are quite few. The maximum temperature in the heating system must also be set according to the rules in order to avoid further malfunctions.
Radiators are connected to the heating system in one of three ways: bottom, side or diagonal.
Also, the bottom connection is also called differently: "Leningrad", saddle. According to this scheme, the return and supply are installed in the lower part of the battery. In most cases, it is used when pipes are laid under a baseboard or under the floor surface. The return temperature in the heating system must not differ from the supply temperature.
Water speed
If there are few sections, heat transfer will be extremely ineffective compared to other schemes - the speed of water in the heating system decreases, which leads to heat loss.
Side heating is the most popular type of connecting radiator batteries to heating. Water is supplied as a heat carrier in the upper part, and the return pipe is connected from the bottom so that the return temperature in the heating system is considered equivalent.
To avoid a decrease in the efficiency of this type of connection with an increase in radiator sections, it is recommended to install an injection pipe.
Pressure
The diagonal type of connection is also called the lateral cross-circuit, because the water supply is connected on top of the radiator, and the return is organized at the bottom of the opposite side. It is advisable to use it when connecting a significant number of sections - with a small amount, the pressure in the heating system rises sharply, which can lead to undesirable results, that is, heat transfer can be halved.
In order to finally dwell on one of the options for connecting radiator batteries, it is necessary to be guided by the method of organizing the return. It can be of the following types: one-pipe, two-pipe and hybrid.
The option that is worth stopping at will directly depend on a combination of factors. It is necessary to take into account the number of storeys of the building where the heating is connected, the requirements for the price equivalent of the heating system, what type of circulation is used in the coolant, the parameters of the radiator batteries, their dimensions and much more.
Most often, they stop their choice on a single-pipe wiring diagram for heating pipes.
As practice shows, such a scheme is used precisely in modern high-rise buildings.
Such a system has a number of characteristics: they are of low cost, they are quite easy to install, the coolant (hot water) is supplied from above when choosing a vertical heating system.
Also, radiators are connected to the heating system in a sequential type, and this, in turn, does not require a separate riser for organizing the return. In other words, water, having passed the first radiator, flows into the next one, then into the third, and so on.
However, there is no way to regulate the uniform heating of radiator batteries and its intensity; they constantly record a high pressure of the coolant. The further the radiator is installed from the boiler, the more the heat transfer decreases.
There is also another wiring method - a 2-pipe scheme, that is, a heating system with a return flow. It is most often used in luxury housing or in an individual home.
Here is a pair of closed circuits, one of them is intended for supplying water to parallel-connected batteries, and the second for draining it.
Hybrid wiring combines the above two schemes. This can be a collector diagram, where an individual routing branch is organized at each level.
Disadvantages and advantages of natural circulation heating systems
Disadvantages with natural circulation include:
- Small circulating pressure, which determines the limited use of such heating systems - a small horizontal radius of action (up to 30 m).
- Large inertness of the heating system due to the large volume of coolant in the system and low circulation pressure.
- The likelihood of water freezing in, which is usually in a cold (unheated) attic.
The main advantage of such systems is the non-volatility of solid fuel boilers. That is, such systems can be used in homes where there is no power supply. The high inertness of the system due to the sufficiently large volume of the coolant in the system can play both a positive (a kind of heat accumulator with an “extinguished” boiler) and a negative role - a significant time change in the temperature of the system, especially at the start-up stage.
Types of heating schemes with natural circulation
Which natural circulation heating system will you choose? Hopefully correct!
The heating system must ensure uniform heating of all rooms. If the temperature in radiators or risers drops, then often the reason for this is a violation of circulation. For the efficient operation of the heating network and comfortable climatic conditions in the housing, there must be free circulation of the coolant along the highway. You should worry about this even at the design stage. Why there is no circulation of the coolant in the riser and the main and what needs to be done, you should know thoroughly in order to quickly eliminate this problem in the future.
The circulation of water in the system is disrupted due to complete or partial clogging in the riser or in the piping to the heating device, airing the mains, freezing the network, errors when laying pipes. Also, this is caused by the misalignment of the central heating system and the appearance of coolant leaks.
Poor pump performance
The purpose of the pump is to maintain the required water pressure in the heating circuit. A well-functioning pump must meet the following requirements:
- A necessary indicator of work productivity;
- Pressure;
- Appliance pressure;
- Compliance with the type of fluid;
- Compliance with the pipe diameter;
- The dimensions of the device are in accordance with the line length.
What to consider when choosing a pump


The pump must be able to handle its load. But it is imperative to consider whether it will work constantly or will only turn on to feed the heating system and adjust the pressure. This should be taken into account when choosing the pump power. For a pump that runs continuously, it is important to consider the energy consumption figure.
If you choose the wrong pump, it will not "push" the coolant well, and as a result, the battery heats up unevenly, and the pump itself may burn out from overheating. Poor water circulation will also be noted if the diameter of the accessories for connecting to the system is incorrectly selected.
When the pump is selected correctly, the heating system functions reliably and fully, and the movement of water is unimpeded.
If you have difficulties with choosing a pump, it is better to contact a specialist, they will help you choose the right device for a specific heating system.
Incorrectly selected pipe diameter
This is also one of the common reasons for poor water circulation in the heating main. It is necessary to choose the diameter of the pipes at the design stage.
First of all, it is necessary to take into account that different heating systems have their own rules according to which pipes are selected.
If the heating network is supplied to the central heating main, then the diameter of the pipes is chosen in the same way as for the apartment heating system. For autonomous heating, such diameters may differ.It all depends on whether there is a circulation pump in the system or the work will be carried out due to the natural circulation of water.
Also, the choice is influenced by:
- Pipe production material;
- Type of coolant used;
- Specific features of the heating mains wiring;
- Planned pressure in the system;
- The speed of movement of water along the highway.
Important! When calculating the diameter, the type of pipes must be taken into account, because the measurement system differs based on the material of manufacture. Steel and cast iron products are labeled taking into account the inner diameter, and copper materials along the outer section. This must be taken into account when planning a pipeline, where several different materials are combined in the pipeline.
Clogged system
As already noted, if there is no water circulation in the riser and the heating system, then the problem may be in the debris accumulated in the system. A coarse filter will help get rid of it.
Dirt that has entered the pipes is easier to remove by trapping it in the filter. First of all, this filter protects the pump. It is also recommended to install a filter at the boiler inlet. Such a water filter should be installed in front of every plumbing device. When installing the device, pay attention to the filter housing. It has an arrow that indicates which side to install the filter, depending on the direction of movement of the coolant.
The filter should be cleaned regularly. To do this, turn off the water, unscrew the plug, take out the mesh, rinse it, put it back in place and screw the plug back, after which you can open the taps.
Advice! To prevent clogging of the pipeline, during installation, it is necessary to control so that there is no debris in the pipes; for this, the ends are covered in the pipes. It is also necessary to check the radiators, as new products may contain factory shavings or other debris.
Airiness of the heating system
If the installation of the line is carried out in violation of the rules, then air locks are formed. They block the movement of water. To quickly solve such a problem, air vents or a Mayevsky crane are installed. For the central system, where a lot of air accumulates, automatic Mayevsky cranes are used. The air is quickly removed and the movement of the coolant through the network is restored.
These devices not only improve the circulation of the coolant through the central heating main, but also reduce heating costs.
Check valves
Often, for normal circulation in the network, some pumps become few, then check valves are installed. In this case, each circuit can work independently of the others. Even in a radiator branched system with several circuits, where there are several pumps, it is better to install check valves. It is not worth saving on their installation.
The absence of these mechanisms leads to the fact that the movement of water in the system slows down. This happens in those situations when a network with several circuits is laid. In order for warm water to flow along such a circuit where the pump operates, and its movement occurs in the desired direction, check valves are used. These elements are not always put, but only in those situations when there are no other technical solutions. Everything is explained by the fact that these elements create high hydraulic resistance, depending on the design. Therefore, there are limitations for installing these valves in natural circulation systems, and the reason for the limitations is the low water pressure in the line.
The actuator in the product is a spring that closes the shutter when the normal operating conditions of the heating network change. For systems with different operating parameters, products are selected with the appropriate elasticity and massiveness of the spring.Valves are a very important element, they ensure trouble-free operation of the central heating system, increase the efficiency of all equipment and improve circulation.
System leaks
If the system does not have good water circulation, there may be a leak in some areas. As a result of a leak, the network does not work correctly, the water movement is bad and the boiler malfunctions.
The first thing to do is to find the "weak" spots. Leaks occur in places where the connections are loosened due to corrosion damage, or poor installation of the system becomes the cause. If the network is openly mounted, then checking is not difficult. All such damage is quickly and easily identified. And to inspect a closed highway, you will have to call a specialist.
If a problem area is found, then it is necessary:
- Tighten loose connections and wind up with sealing tape or tow;
- Replace worn-out nodes;
- Cut and replace damaged pipe sections.
If there is no circulation of the coolant in the heating system, then there is nothing to say about any comfortable living in the house in winter. Because no matter how hot the boiler is, the radiators will still be cold. However, you need to think about this not when the system “worked, worked and suddenly stopped,” but even at the design stage, that is, now. In this article, we will deal with the problems leading to poor circulation of the coolant.
Why is there no circulation in the heating battery
The battery is connected on one side: supply from above, return from below. On the other side, on top, is the Mayevsky crane. The supply to the battery is hot, there is no circulation, because the temperature gradually decreases along the upper part of the battery, and the bottom is completely cold. As soon as I drain the water through the Mayevsky tap, the return line warms up quickly and strongly. I close the tap - the return line cools down just as quickly. Those. it turns out that circulation appears when you open the tap on the other side from the top. How can this be? I have access only to short sections of supply and return (10 centimeters), everything else is sewn up with boxes.
A breakdown in the heating system, imperfections, flaws, everything leads to cold radiators. If there is no circulation of the coolant, then the cause must be determined. Most often, the answer to why the heating does not work is on the surface, it is obvious.
Let us analyze in order the main causes of heating malfunctions, why water does not circulate through the pipes, and what needs to be done first.
Let's start with the simplest and most obvious reasons.
Clogged, clogged.
Each heating system must have a coarse filter. A completely small device with a fine mesh and a sump (installed downwards! At least to the side) saves equipment, pumps, a boiler from contamination of the coolant that will be present in any system. Shavings, thread scraps, rust, water sludge…. everything is trapped by the mesh in the filter.
The sump must be periodically untwisted, the mesh must be cleaned.
If circulation is disturbed in the heating system of a private house, then the first step is to check the filter, which should be installed on the return line in front of the boiler.
Air in the system, airing
Bleeding can occur in any closed-circuit piping arrangement where no venting measures have been taken. Air is always present in the coolant, including in a dissolved state, is released during pressure drops, and accumulates at the highest points. Including in the boiler.
Automatic air vents are installed at characteristic, highest points of the system, as well as on collectors and on special separators - the normal circuit is equipped with a special air trapping device, in which air bubbles are released from the coolant.
In addition, Mayevsky's taps (manual air vents) should be on each radiator, as well as possibly in other elevated places.
Check airflow, bleed air, install air vents - the usual procedure if circulation stops and the batteries are cold.
The circulation pump does not work
In private houses, the reason for the termination of the heating system is the breakdown of electrical equipment that controlled the movement of the coolant through the pipes.
If the heating suddenly stops working, then you need to check the performance of the circulation pump near the solid fuel boiler or the pump in the automated boiler. In addition, the same unit can be installed in each circuit, which must work properly.
Bad polypropylene pipes
Often, the consumer (customer) believes that polypropylene pipes are absolutely reliable and cannot cause problems with heating, cool batteries.
But polypropylene is much more insidious than old steel or metal-plastic pipelines. Each place of soldering (welding) is a potential increased resistance in the system or the reason for the cessation of circulation (weakened movement of water through the batteries), due to fusion of the material inside.
It is impossible to control the quality of the connections from the outside, all that remains is to cut out pieces, re-solder, redo the polypropylene pipes again.
The malfunctioning of a polypropylene system is a real problem for the home installer. Good professionals don't take this material at all.
Bad project
It is not uncommon for bad circulation where there is bad design. Typically, the batteries are not turned on correctly, according to some sequential scheme, where the last battery in the circuit receives much less coolant.
Another bad project is one-pipe circuits, where it is also difficult to establish the necessary circulation of the coolant through each battery.
If the radiators do not heat up evenly, there is poor circulation of the coolant on individual heating devices, first of all it is necessary to consider how the connection corresponds to the classic schemes - shoulder, passing, radial. It is necessary to bring home heating to the usual design standards, and then expect good circulation from it and the same heating of radiators.
Reasons for poor coolant circulation
There may be no circulation of the coolant in the heating system for the following reasons:
- insufficient power of the circulation pump (or pumps, if there are more than one). For this reason, the coolant simply does not reach the radiators farthest from the boiler, so they are cold (or slightly warm, which is why it is still not easier). There are several articles and videos in the section on heating calculations on how to choose the power of the circulation pump;
- check valves not installed. Usually their absence is "painful" for complex systems with several circuits. Check valves are used to ensure that the coolant moves along the desired contour and in the right direction (for more details, read on);
- system pollution. It happens that the pipes are clogged along the entire diameter - what kind of circulation is there! It is treated in only one way: by replacing the pipes. This is exactly the case when prevention is the best treatment. And "prevention" should be carried out even at the stage of installation of the pipeline and radiators. First, make sure that no debris gets inside the pipes. To do this, first making sure that there is nothing inside, we close the ends of the pipes with something before installation. For example, it is convenient to use simple plastic bags. Secondly, there may be debris in the radiators. Even new ones! So we check and get rid of;
- the pipe diameter is too small. Small diameter of pipes - large hydraulic resistance - the pump is not able to "push" the coolant along the entire pipeline - there is no circulation in the heating system (well, or it is so bad that it doesn't matter if it doesn't exist).Again, at the design stage, it is necessary to calculate the hydraulic resistance;
- accumulation of air in the system (airing). Air, of course, is not debris, but air locks will also prevent the coolant from circulating freely. Air jams may appear due to violations of the rules for installing the heating system. Getting rid of air is simple - install an automatic air vent at the highest point of the system and Mayevsky taps on the radiators.
Why the batteries are cold, and the riser is hot, experts explain
Do not warm your hands on cold batteries.
There can be a lot of reasons why the supply pipe is hot and the radiator is cold. Specialists for general development name only the main ones:
- the central tap on the heat supplying line is closed or the return line is closed;
- insufficient coolant flow;
- airing a system or a concrete riser, a radiator;
- the heating system is not balanced;
- pollution in the heating circuit;
- reducing the cross-section of the pipe supplying the coolant.
If the riser is warm in the apartment, and the battery is cold, you must contact the organization responsible for the heat supply of the house. Its specialists are obliged to eliminate any malfunction free of charge and within 24 hours.
However, the following actions of the residents of the house will help the craftsmen who have come to the call to quickly eliminate the malfunction of the heating circuit:
- it is necessary to install the pipe hot, and the radiator is cold only in one apartment, or this problem affects the entire riser. Perhaps the heating wiring of the entire entrance is faulty;
- it does not bother to go around all the entrances and see if the heating elements are hot there;
- you can go down to the basement and examine the pipes for breakdown. Even drip leakage leads to a drop in system pressure. This adversely affects her work.
All information received should be passed on to specialists. However, there are situations when the organization dealing with the heating of the house refuses to repair the wiring. In this case, residents need to contact the regulatory authorities with a complaint about poor quality services. They also read: "Where to go if the batteries are not heated?"
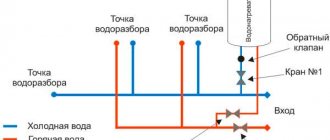
How to choose antifreeze in the heating system of the house so as not to get poisoned later if it is mixed into the DHW circuit?
Everything you need to know about filling the heating system with antifreeze can be found here.
Contour cleaner.
If the batteries are not heated up the riser. If the riser is cold, the battery is cold - this is a sure sign that the main line through which the coolant flows is blocked. In confirmation of this, it is necessary to walk through the neighboring apartments. They should warm up well. In this case, only a plumber can fix the breakdown, who will have on his hands the drawings for the wiring of the heating of the house.
The next state of affairs, when the pipe is hot and the battery is cold, indicates a blockage in the system or the presence of an air lock. They prevent the penetration of the coolant into the heating element. From this, the latter does not warm up. Clogs are removed only if the radiator is completely disassembled and air under pressure is forced through it. This can only be done by a specialist who has the necessary tools and equipment.
It is easy to eliminate the airlock that interferes with the full circulation of the coolant in the system. For this, each radiator is equipped with a Mayevsky crane. It is enough to open it and drain some hot water. Along with it, unnecessary air will come out. They also read: "What to do if the batteries are not heated?"
The main thing you need to know about electric heating boilers is how to choose, connect and operate.
All the nuances that you may encounter when installing an electric boiler in a heating system are described at this link.
If the radiators do not heat up all over the entrance.When the radiator is cold and the riser is hot, attention must be paid to the pressure in the circuit. With insufficient pressure, the coolant cannot pass through all the radiators in the circuit. As a result, the batteries lower their temperature as they move away from the heat-carrying line. Residents of the house cannot independently increase the pressure in the system, and therefore it is recommended to seek professional help. More specifically, call the organization that is responsible for the heat supply of the building.
Supply and return can be mixed up.
Residents of a new house, when starting the heating system for the first time, can observe the following situation when the battery is cold and the return is hot. Here it is appropriate to assume that mistakes were made during the installation of the heating elements. In this case, the pipes supplying the coolant and the return flow of the circuit are reversed. If we are talking about an individual heating circuit, then it is worth taking a closer look at the circulation pump. It may have been installed incorrectly.
When asked why there is a cold return in the batteries, experts unequivocally point to an incorrectly designed heating system. In some cases, it is appropriate to talk about a small flow rate of the coolant.
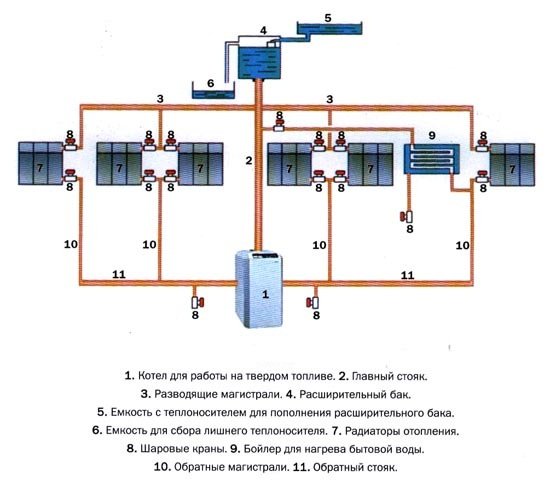
Heating medium circulation in a combined (branched) heating system
Let's start analyzing the circulation of the coolant from a complex system - then you will figure it out with simple schemes without problems.
Here is a diagram of such a heating system:
It has three contours:
1) boiler - radiators - boiler;
2) boiler - collector - water underfloor heating - boiler;
3) boiler - indirect heating boiler - boiler.
Firstly, it is imperative to have circulation pumps (H) for each circuit. But this is not enough.
In order for the system to work as we want it: the boiler is separate, the radiators are separate, check valves (K) are needed:
Without check valves, for example, we turned on the boiler, however, the radiators "for no reason, no reason" began to warm up (and it's summer outside, we just needed hot water in the mains). Cause? The coolant went not only to the boiler circuit, which we need now, but also to the radiator circuits. And all because we saved on non-return valves, which would not let the coolant go where it is not needed, but would allow each circuit to work independently of the others.
Even if we have a system without boilers and not a combined one (radiators + water heated floor), but “only” branched with several pumps, then we put check valves on each branch, the price of which is definitely less than the alteration of the system.
What is the return flow in the heating system?
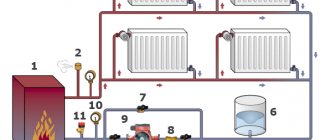
The return is coolantlocated inside the heating system. In the course of work, he passes through all heating devices and gives them warmth. Then, already cooled, the coolant returns to the boiler againwhere it heats up and starts a new cycle.
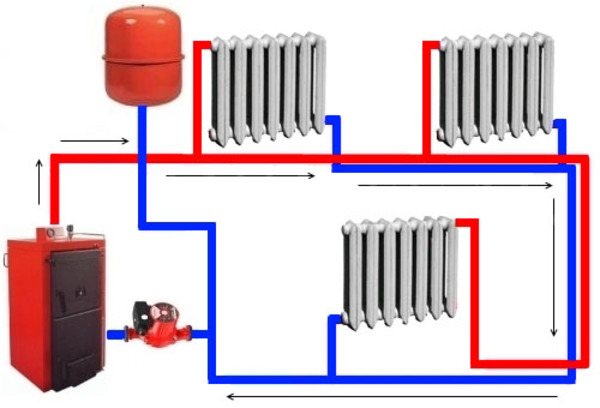

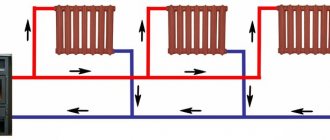
Photo 1. Heating scheme with a circulation pump and an expansion tank. The arrows show the movement of the coolant.
It acts as a coolant as an ordinary waterand antifreeze... It starts up either naturally (under the influence of gravity), or forcibly (using a pump).