Among the numerous equipment that is involved in the operation of underfloor heating systems, you can find a small device that plays an important role in the control and regulation of the heating system. This is a servo drive, an electromechanical device, without which automatic temperature control for a warm water floor is not possible.
The device is based on an electrothermal reaction to a change in the heating temperature of the coolant in the main supply pipe and the subsequent mechanical action, which in the complex provides the opening or closing of the flow of hot water into the heating circuits. Servos or servomotors, officially in the language of professionals, the device is called an electrothermal servo drive, today they are present in almost all autonomous heating systems. New suburban residential buildings, cottages and summer cottages equipped with underfloor heating have underfloor heating, which is controlled by servo drives. It is the servo drive installed for the warm floor on the collector that performs the task of adjusting the coolant flow in the water floor heating system.
Existing types of servo drives today
Among the regulators that exist today, which have become widespread in everyday life, there are the following servos. All devices can be divided into several types. Each variety has a different principle of action and functionality. By the type of construction, the devices are of two types:
- closed;
- open.
By the names you can judge the principle of action. Closed servos are characterized by an open position when there is no power supply. The incoming signal activates the mechanical part, blocking the access of water to the system. For open view devices, the principle of operation is in reverse. In the normal state, the servo is closed, only with the arrival of a signal, the mechanical part is activated, opening the flow of water into the pipeline. It is up to you to judge which type is best suited for domestic use, evaluating the capabilities of your own heating system and the climatic conditions outside the window. Normally open servos are most often used in our country.
On a note: if the device fails, the coolant in the pipeline continues to circulate, leaving the floor warm for a certain time. This feature is especially relevant for country houses located in a cold climatic zone.
According to the method of power supply, servomotors are divided into devices that are powered by a constant current of 24V and devices that are connected to a conventional 220V AC power supply. Servo drives with 24V supply are equipped with inverters.
Often, consumers use another, rather rare type of device. We are talking about devices that are set in a normal position, depending on the technological requirements of the heating system. Such servos are called general purpose servos and can change functionality from normally open to normally closed and vice versa.
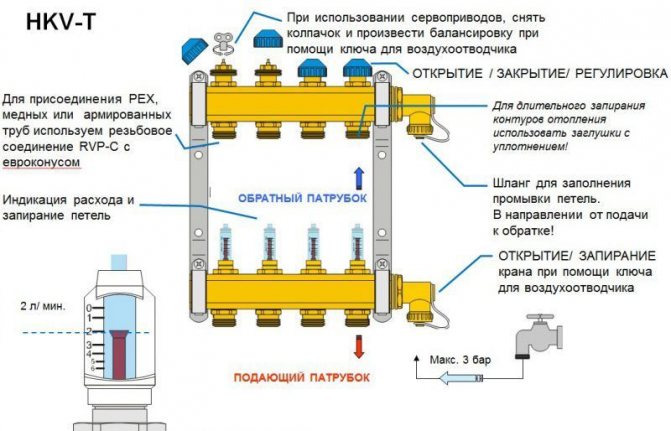
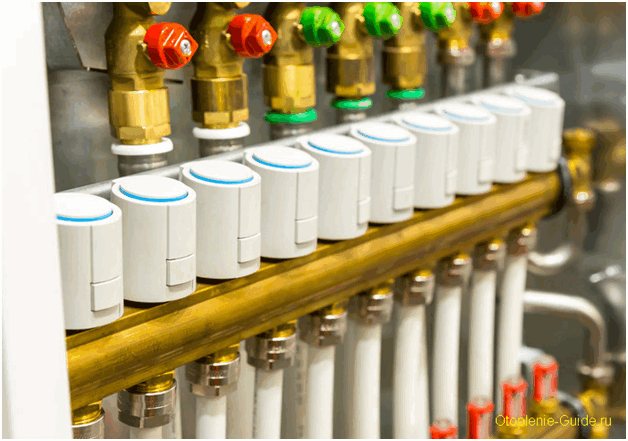
All three types of servomotors can be connected to the manifold. The only condition is the correct setting, balancing and operating conditions of the heating system.

Classification of devices by control method
Servo drive models on the market can be divided into 3 groups, depending on the control method:
- Mechanical... The main advantages are its low price and high reliability.No special knowledge is required from the user to operate it. This is a primitive device that regulates the flow of the coolant; constant monitoring is not needed. The disadvantages are the impossibility of programming and manual configuration - this can take a lot of time.
- Electronic... Such a servo has advanced functionality. The electronic display can display the operation of the system, the temperature, the presence or absence of breakdowns. The advantages are the convenience of regulating the temperature of the system and the ability to work in automatic mode. The downside is the high price.
- Remote controlled... Such servos allow you to make any settings, even ignoring the collector for the warm floor. The system is capable of working even in the absence of a person. It is desirable that the manifold assembly consists of elements from the same manufacturer. The downside is also the high price.


The actuators are installed on thermostatic valves mounted on the manifold or on free-standing valves. They necessarily have a shutdown mechanism and overheating protection.
Criteria for choosing the type of servo
In this section we will try to answer the question. What is the basis for the choice of devices of one type or another.
If you decide to equip your heating system "warm water floor" with servo drives, take into account the operating parameters of your heating. In what position should the valve be most of the time. In a situation when for you a warm floor is the main option for heating living quarters, when hot coolant constantly enters the pipeline, rely on a normally open servomotor. This type is ideal for a long heating season.
On a note: in case of interruptions in the electrical supply, the failure of the device will not stop the circulation of warm water in the heating water circuits. The warm floor will continue to be supplied with a coolant with prepared water.
For regions with warm climates, a normal closed servomotor is suitable. If you are not afraid of defrosting the heating circuit, and you periodically turn on the floor heating, this device will quite cope with its functions.
Important! The servo drive for underfloor heating with smooth adjustment has an electronic type regulator. Such devices more accurately respond to changes in the temperature of the coolant flow, smoothly moving the stem to the required position. The steplessly adjustable servomotors are designed for underfloor heating, in which it is often necessary to dose the volume of the incoming flow.
In most cases, such devices are not used in home heating systems with underfloor heating. Therefore, when purchasing, pay attention to whether or not the installation of an electronic regulator is required for the device. If the instructions say that such equipment is necessary, then you are dealing with an electronic servo drive. Let's say right away that it is impractical and unprofitable to use such a device at home.
Be sure to read: how to make a water floor from a gas boiler?
Scope of application
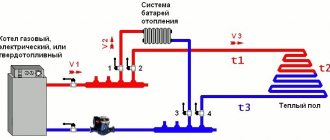
In the heating system, it can be installed in different places, for example, if it is necessary to regulate the flow of coolant into the heater, it is installed on the supply pipeline. But the servo drive of the heater damper will allow to regulate the air flow into the boiler furnace, that is, the heater power will be adjusted (see also the article “Modern Terem Heating - High Quality at an Affordable Price”).
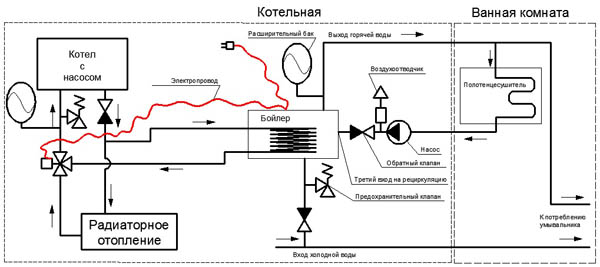

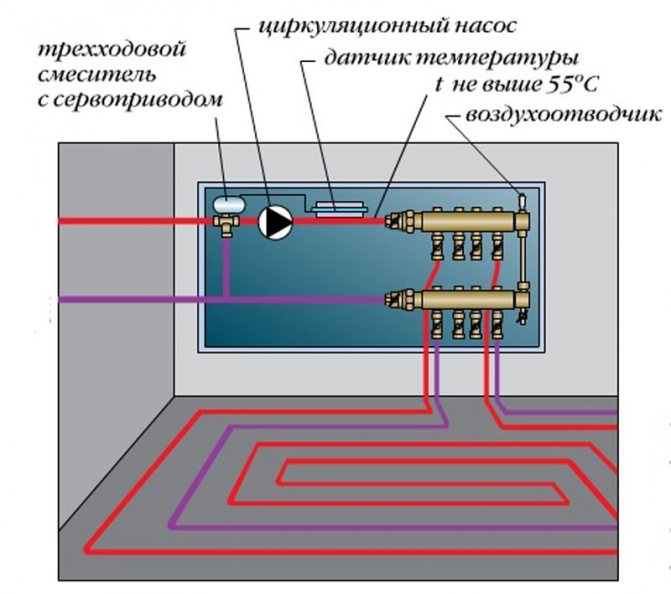
In the diagram, a three-way valve is installed on the return line
Room temperature control is most often done in two ways:
- using thermostats - the best option if heating radiators are used.In this case, regulators are installed in front of each battery and automatically regulate the flow of coolant into the radiator;
- by servo - most often used when it is necessary to adjust the temperature of underfloor heating.
Note! The actuators can be installed on the manifold header instead of the conventional thermal heads.
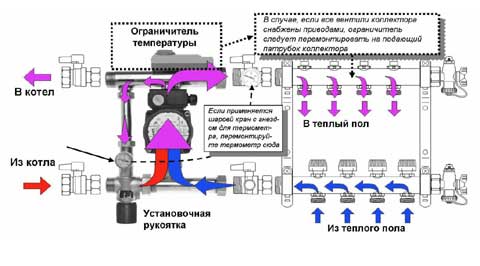

One of the options for connecting a warm floor
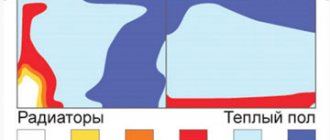
In the case of underfloor heating, it is especially important to keep the coolant not above a certain temperature. If, for example, you regulate the supply of the coolant using conventional thermostats, then when the system is started up, a situation may arise when hot water flows into the pipes. As a result, it will be simply uncomfortable to walk on the floor for a while, and part of the pipes may fail.
Installing a servo with a 3-way valve upstream of the manifold will avoid this. I usually do this, especially since the price of such a device is minimal.
The device and principle of operation of servomotors

The main working element of the servo is the bellows. Those. same part as for 3-way valve. Small in size, sealed cylinder with elastic body is filled with a substance that is sensitive to temperature. Depending on whether the temperature rises or falls, the volume of the substance changes accordingly. Figure - the diagram clearly demonstrates the structure of the servo motor, where the bellows occupies the main place.
The bellows is in close contact with the electrical heating element. Receiving a signal from the thermostat, the heating element is switched on from the mains and switched on in operation. Inside the bellows, the substance heats up and expands. Thus, the increased cylinder begins to press on the rod, changing its position and blocking the path of the coolant flow. Evaluating the work of the servo, we can conclude that the device is not equipped with any motors, there are no gears and transmission links in it. The usual working relationship is "heat and electricity". Hence the common name for devices, thermoelectric controllers.
In order for the valve to open again, the whole process is repeated only in the opposite direction. Lack of power will cause the heating element to stop working. Consequently, the substance inside the cylinder cools down, decreasing in volume. The pressure on the stem decreases, it rises, acting on the valve, and, therefore, hot water access to the system opens.
On a note: the substance placed inside the cylinder is toluene, which has high thermodynamic characteristics. A nichrome thread acts as an electric heating element.


Having familiarized yourself with the principle of operation of the device, it is important to remember that a certain time is required for the mechanical action of the valve. Despite the fact that when a signal from the thermostat is received, the heating element begins to heat the substance inside the cylinder. The time required for changes in the physical state of the fluid is 2-3 minutes, so the valve is not activated immediately.
For reference: when choosing a servo drive model, pay attention to the parameters of the heating element and the heating time of the liquid indicated in the passport of the device.
Unlike heating, liquid cooling is slower. The reverse process, i.e. it will take not 2-3 minutes to close the valve, but 10-15 minutes. In case of overheating, each servomotor should automatically shut down. For this, an emergency shutdown mechanism is provided in the design.
For example: the servo drives used in the work of the collector group are not all equipped with cylinders and cylinders with a substance. There are models in which thermoelements play this role, resembling a spring or a plate, which are heated under the action of the same heating element.Expanding, these parts act again on the stem, ultimately bringing the valve into working condition. You can determine in what position the valve is located by changing the appearance of the servo. The pull-out element signals the operation of the device. If this does not happen, then your appliance is not connected correctly or the heating system is working intermittently.
For reference: a servo motor that is hot to the touch means that in this case the device is closed and turned off. If the device is cool to the touch, therefore, the valve is open, the coolant circulates normally through the water circuits of the warm floor.
Review of popular models
Servo drives for water underfloor heating are produced by different manufacturers. Each model has its own characteristics.
VALTEC
VALTEC is a manufacturer of water and heat supply devices for the home. A group of Russian and Italian specialists is working together to create products. VALTEC manufactures the following actuators to control the operation of a floor-type heating system:
- TE3042.A. Refers to the group of normally open. Designed to control the valves of climate systems by commands that will be set by a thermostat, controller or manual switch. Device power - 2 W, conductor cross-section - 0.75 sq. mm. The connecting size is M30x1.5;
- TE3061.0. This is a normally closed electrothermal device. Designed for 3-way valves. The operation of the device is possible due to the thermal expansion of the liquid - toluene. Drive power - 2 W, conductor cross-section - 0.22 sq. mm;
- TE3041A.0. The device works due to the presence of a liquid in the body, which expands under the influence of temperature. Refers to the group of normally open. Connection to the valve takes place through an adapter that is included in the kit. Unit power - 1.8 W, conductor cross-section - 0.75 sq. mm.
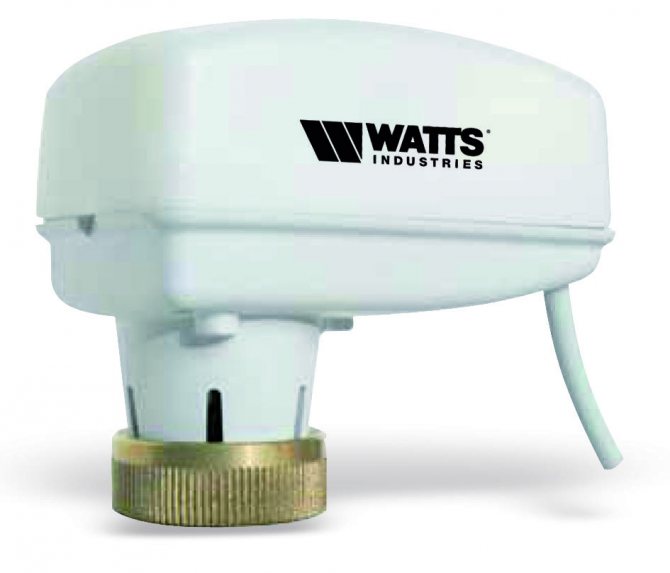
Watts
Watts is the world's leading manufacturer of heating technology in a variety of formats. Differs in high quality, affordable price and efficiency. Servos from Watts are models with an electromagnetic motor. Popular series:
- 22C. It is installed on the valve of the return pipeline and regulates the supply of heating agent to the underfloor heating system. The power is 2.5 watts. The 22C series includes normally open and closed devices, depending on the model. Protection class - IP44;
- 22CX. They belong to electrothermal devices to ensure the efficient operation of a water-heated floor. There are normally closed and open models. The power consumption in normal operation is 1.8 W. Operating fluid temperature in the system - + 110 ° С;
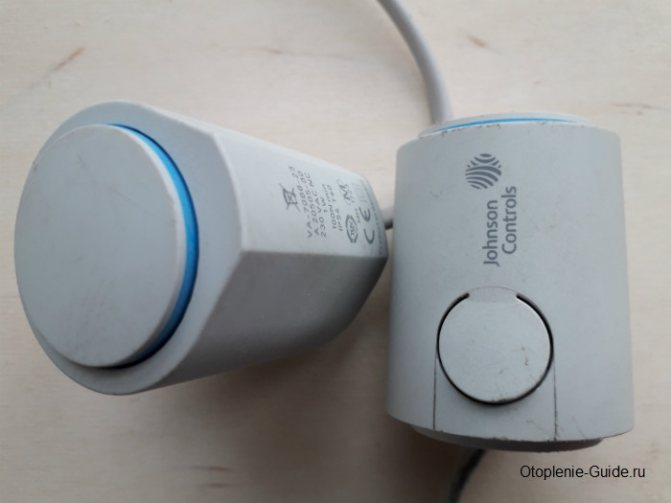
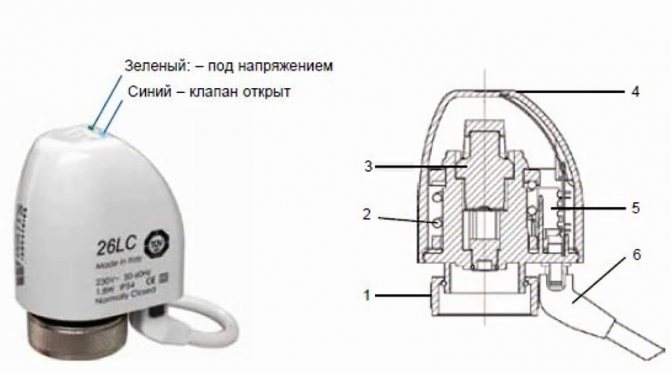
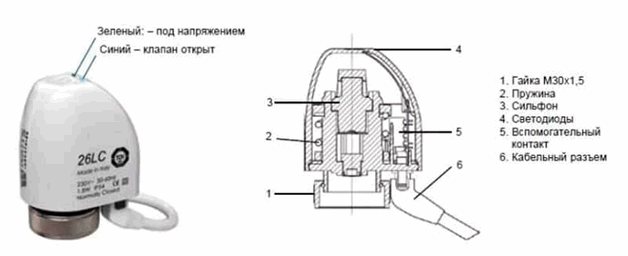
- 26LC. Electrothermal actuators for the collector. An LED indicator is placed on the body, which indicates its operating mode. If green lights up - the actuator is energized, blue - the device is open.
REHAU
Drives for adjusting the operation of a water-heated floor from a German manufacturer. They combine innovative developments and quality proven over the years. The most popular models from REHAU:
- UNI for 230, 24 V. The device is mounted on the valves of the manifold group using a special adapter. Refers to normally closed devices. Control over the operation of the drive is carried out through the indicator. Connecting cables with a cross section of 2x0.5 sq. mm;
- Actuator 230, 24 V. In the de-energized state, the valve is closed. To control the operation of the device, a light indicator is placed on the case.
LUXOR
The Italian company LUXOR specializes in the production of water shutoff valves and systems for regulating the temperature of the heating system for the home. The installed manifold group will include an SM 1347 drive.It is designed to regulate the temperature of the supplied heat carrier for a warm water floor. Main technical characteristics of the device:
- power supply - 24 V;
- operation of the device is provided by a stepper motor. Its control is electronic;
- there is LED indication on the case, which indicates the operating mode;
- installation takes place in an upright position - vertical or horizontal;
- maximum temperature in the system - + 100 ° С;
- cable 1.5 m long;
- storage temperature of the device - from 0 to + 50 ° С;
- the body is made of synthetic materials. Its color is gray;
- warranty availability - 2 years.
Regardless of the model chosen, the servo drive must be installed and operated in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations. They can be found in the instructions for the device. After the installation of the drive and all elements of the system, they begin to use them after complete testing.
Installing the servo. Features and nuances
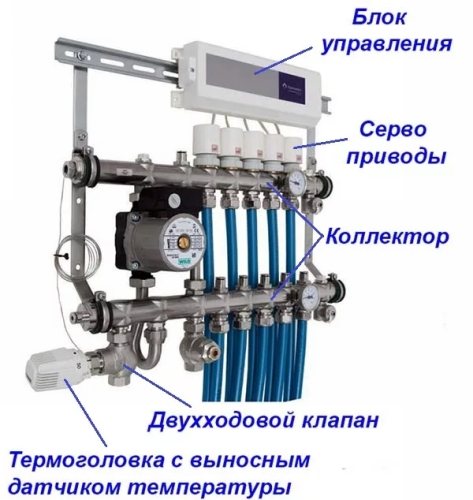
Before installing the servo drive, decide which type of thermostat the device will have to interact with. In cases where the thermostat controls the operation of one water circuit, both devices are directly connected with wires. When it comes to using a multi-zone thermostat, a device that serves several pipelines at once, the servo motors are connected as follows.
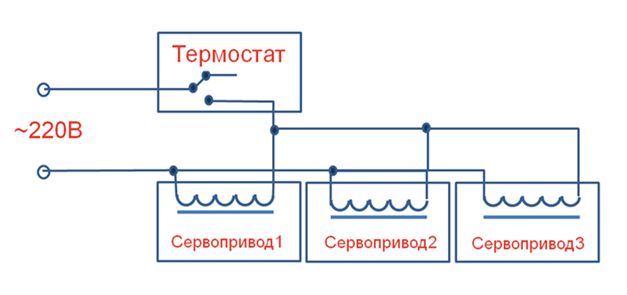

To correctly connect all the wires and terminals, a floor heating switch is used. The functions of this device include the connection and connection of devices for various purposes in a single circuit. In addition to the distribution and connecting function, the switch also plays the role of a fuse. In situations where all the shut-off valves of the water circuits are closed, the switch cuts off the power to the circulation pump.
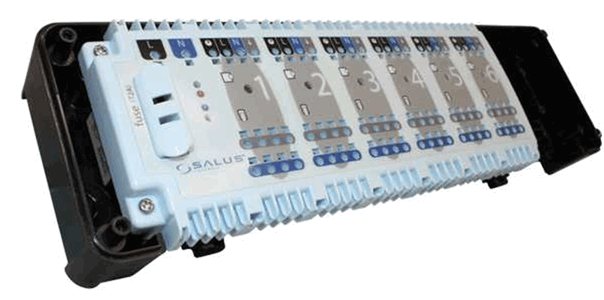

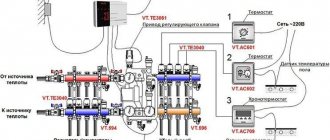
The switch is very convenient when heated floors are powered by an automated autonomous gas boiler. The figure shows how thermostats and servo drives are connected to a single control system.
Installation features
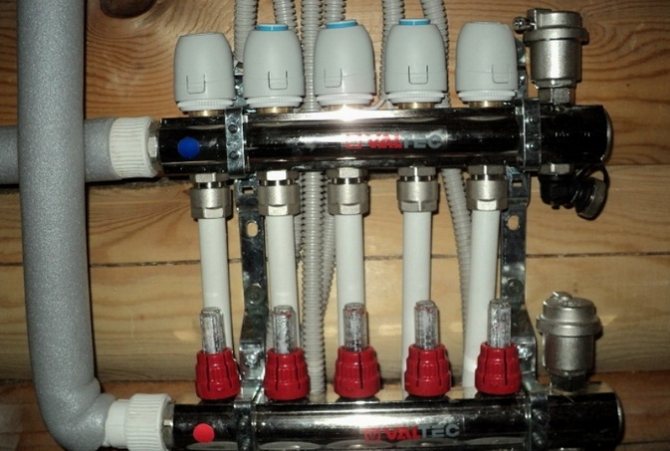
The underfloor heating electric drive is installed on the thermostatic valve of the collector.

Wiring diagram for one Watts 26LC electrothermal servo drive and a Watts milux room thermostat with an LCD display.
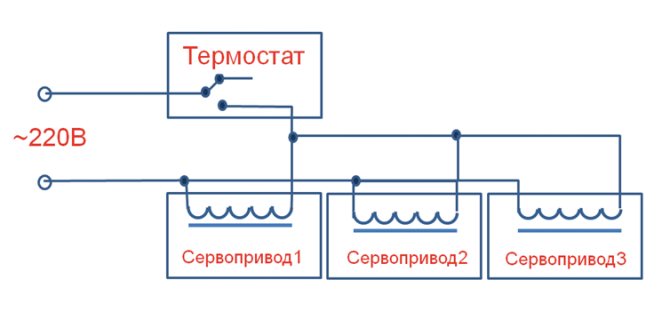

Connection of 2-3 actuators with one thermostat.
Servo mounting location, thermostatic valve to be mounted on the manifold.

Important! When the heating system is operating, underfloor heating from a solid fuel boiler, such a switch function as turning off the pump is fraught with stopping the heating device itself. Installing a bypass and a bypass valve will prevent you from stopping the pump and running the heater at idle.
Principle of operation
Due to the nichrome heating device, which is an electric current conductor, the toluene is expanded in the bellows. This is the work of the servo drive for underfloor heating.
The servo motor has a spring mechanism and a container with a special fluid, which expands when the temperature rises and affects the stem, which in turn extends and presses on the stem of the thermal valve. The valve closes automatically.
Due to the voltage, the liquid heats up and expands. This device does not have an electromagnetic motor.
The force used comes from the expansion of the liquid under the influence of temperature. This drive is a thermal drive.
Because of this, when voltage is applied to the servo, the valve closes only after a certain time, which was spent on heating the liquid. The occupied time is 1-3 minutes.
If there is no voltage, the servomotor will cool down and the valve will return to its original position. It takes a little longer for the device to cool down than it heats up.
There are servos for underfloor heating that do not have an expansion fluid.The principle of operation of these devices is to move the stem due to the heating of the compensating thermoelement (it is a plate / spring that changes its position when heated).
On top of the servomotor is a retractable mechanism required to detect the actuator tip in the thermostatic valve and displays the mode: On / Off.
The servo drive for the underfloor heating collector has an anti-overheating function and a mechanism that automatically cuts off the power. The device is installed on a manifold thermal valve or a separate thermal valve.


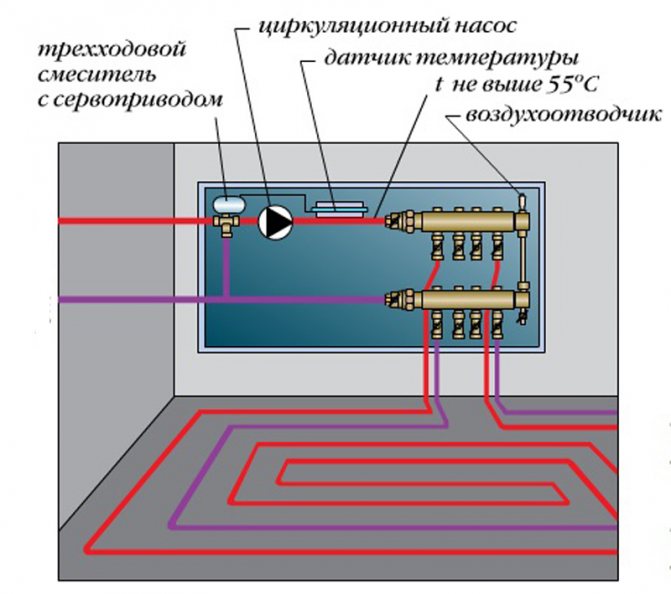
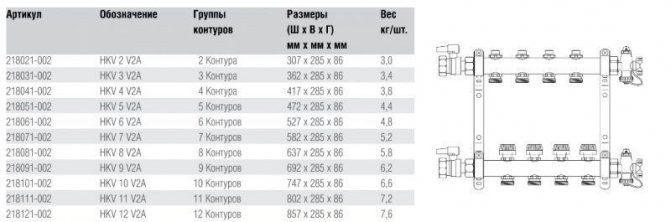
Servo-mounted manifold
conclusions
It should be noted that thanks to the advent of modern devices and devices, the control and adjustment of underfloor heating has become an ordinary and simple process. The design of many devices used for the operation of heating circuits is not particularly complicated. The principle of operation of many components and assemblies is also clear. This can be said with certainty about servos as well. Most of the devices are reliable, practical and easy to use. Thanks to the servomotors, it became possible to fully automate the underfloor heating control system, to make the conditions for using heating equipment simple and understandable.
Choosing a simpler option, you can get by with the installation of conventional control valves. Automatic regulators, temperature sensors and servo drives, a category of devices that work for your comfort and safety. Installing additional devices such as a switch and a bypass valve will make your heating system as efficient and safe as possible.
In this article, I will teach you how to use servos. And I will show the connection diagrams.
This servo is sometimes called: an electric actuator, a servo motor, a thermal actuator, etc.
Its official name electrothermal servo
( Easier:
Thermal actuator
). Servo motors are called drives with an electromagnetic motor.
There are servos for 3-way valves, information on this here:
Servo-assisted 3-way valve
Such a servo (thermal actuator
) can be used for both underfloor heating and radiator heating. Both for the manifold and for the thermostatic valve (valve). In this case, we will consider a connection for a warm floor and a connection for radiator regulation.
In this article, you will understand the rules for connecting such a servo drive and finally, close all questions on automatic heating control.
These servos are normally open and normally closed.
Normally open
- Open valve by default. That is, when there is no signal (voltage) to the servo, it is in the "Open valve" position. In this case, in the absence of voltage, the coolant passes through the open valve.
Normally closed
- Closed valve by default. That is, when there is no signal (voltage) to the servo, it is in the "Closed valve" position. In this case, in the absence of voltage, the coolant does not pass through the closed valve.
Universal, switchable thermal actuators
- such thermal actuators can be switched to one of two positions: Normally open and normally closed.
Servos can have different shapes:
When it comes to choosing an option
- open or closed type, then you need to understand the following:
If the valve is in the open position for a longer time, then the normally open mode is selected.
If the valve is in the closed position for a longer time, then the normally closed mode is selected.
In severe winter conditions, the normally open option is chosen. Particularly in Russia. In warm areas, you can choose a normally closed one. However, it all depends on many factors. The most common servo option is normally open.In addition, when the servo fails, there is no risk of freezing the room from the cold.
Servos for voltage are 220 volts, but there are also other voltages, for example, 24 volts. It is also possible that servos can accept direct current or alternating current. In most cases, this is 50 Hz alternating current.
For the servo to start closing or opening the valve, it needs a voltage signal. The usual signal to the servo is the usual power, which is indicated in the servo's passport. (220v / 24v).
How does a servo work?
Consider such a thermal drive. Manufacturer: Oventrop.
Inside there is such a mechanism:
Servo drive principle
The operating principle of the drive is based on the expansion of the liquid (toluene) in the bellows due to the passage of an electric current through the nichrome heating element.
The servo mechanism has a spring mechanism and a container in which a special fluid is placed, which expands under the influence of temperature and presses on the stem. The stem, extending, presses on the stem of the thermal valve and the valve closes. Under the influence of voltage, the liquid heats up, and the liquid expands. That is, this servo does not have an electromagnetic motor. The use of force is taken from the expanding fluid under the influence of temperature, therefore this servo is called a thermal actuator. Since the force of motion comes from the expansion of the liquid when it is heated.
Therefore, when voltage is applied to the servo, the actuator does not close the valve instantly, but after a certain time has elapsed, which takes the fluid to warm up. This is about 1-3 minutes depending on the manufacturer.
When there is no voltage in the thermal actuator, the valve comes to its original position when it cools down enough for this. It takes much longer for the servo to cool down than it heats up. Therefore, the opening time of the thermal actuator is from 5 to 15 minutes.
There are thermal actuators (servos) that do not have expansion fluid. In such servo drives, the movement of the stem is achieved by heating the compensating thermoelement. The thermoelement can be like a plate or a spring, which changes its position when heated. This can be seen in electric thermostats of electric stoves.
Heated servo on the left, cooled down on the right.
On top of the servo there is a retractable mechanism, it is needed in order to:
Firstly
, determine the seating of the servo in the thermal valve.
Secondly
, notifies about valve mode: On / Off.
That is, if it is lifted up, this indicates that the valve is closed. If it is down, the valve is open.
If this mechanism has standard dimensions in height, then you should be wary. This thermal actuator may not match the thermal valve or not be connected correctly. That is, the dimensions of the extended stem do not match the thermal valve.
The servos have overheating protection. There is a built-in power off mechanism.
This servo can be checked by touch, if it is hot - the valve is closed, if it is cold - the valve is open.
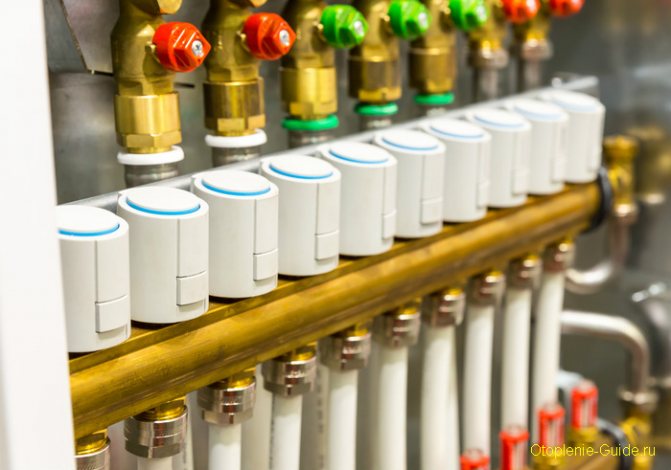
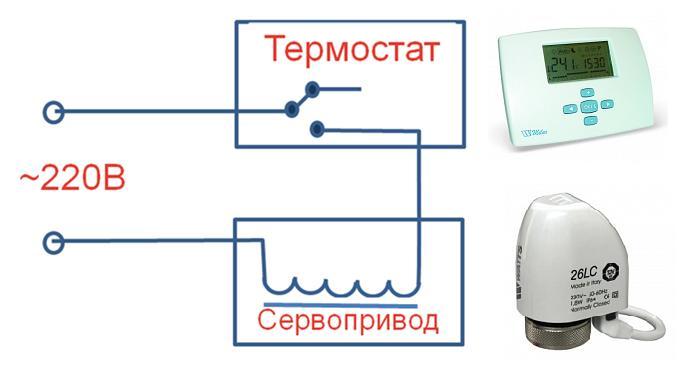
This servo is connected to a thermostatic manifold valve or it can be a separate thermostatic valve as shown in the picture:
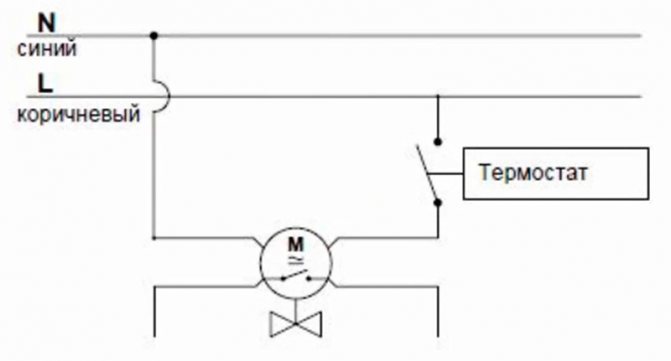
Electric circuit of the servo drive and thermostat for 220 volts.
You can also connect 2-3 servos with one thermostat.
Regarding the current and voltage, it is described below ... this text cannot be seen from here ...
The question is, is it worth keeping phase zero? Even if you confuse the phase with zero, this circuit will still work. But keep it in mind when you connect more complex electronic devices. Errors can occur in complex devices. In any case, see the certificates of the electrical device and observe the Phase and zero. Phase (L). Zero (N). Earth (PE).
There are thermo-actuators with smooth control! A special signal is required for these thermo-actuators! Such a servo drive may be called: DC Thermionic Drive. Usually it is with a voltage of 24 volts. Control signal from 0 to 10 volts. That is, there is a special electronic regulator for it. This electronic controller, depending on a special electronic temperature sensor, supplies the required voltage to the thermionic drive. Depending on the voltage, the thermionic actuator obtains the exact position of the stem, which presses against the thermostatic valve. This thermionic drive is suitable where it is necessary to pass the coolant in a metered dose for smooth regulation. It is not needed for a warm water floor!
Therefore, when you wake up to buy or order a servo drive, make sure that you do not accidentally purchase a thermionic servo drive. Since such a drive must be used in conjunction with an electronic regulator.
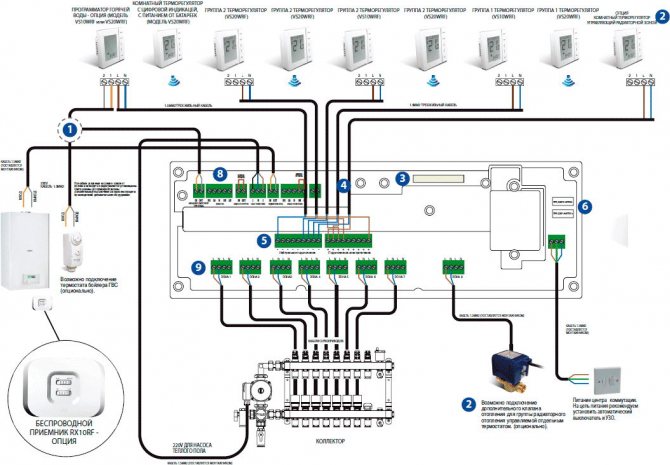
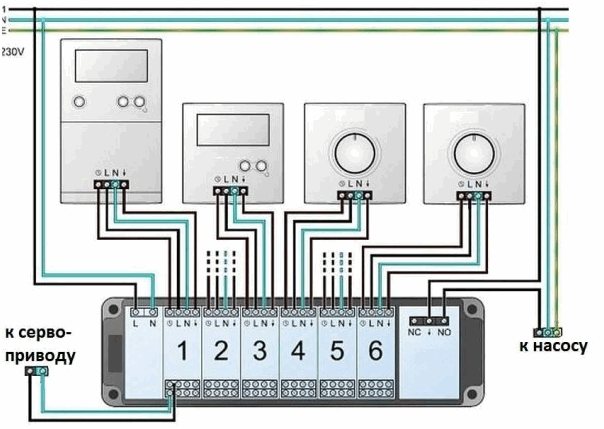
Between servo drive and thermostat can be connected Switching unit
which looks like this:
Switching unit
The switching blocks for switching thermostats and servo drives are called differently: a zone communicator, a commutator for mixing units, a terminal block for servo drives and pumping logic, just a communicator, and so on.
This communicator is used to transmit control signals (on / off) from room thermostats to servo drives of thermostatic valves that control the supply of coolant through the circuits.
In the absence of a request to supply the coolant to all connecting circuits, the switch relay gives a command to turn off the circulation pump of the mixing unit.
Switches are also classified by voltage and there are 220 volt switches.
That is, these switches can be useful in order to turn off the pump when all circuits are closed. There are switches with different software environments, which can be no less useful functionality for control systems, which you can learn from the manufacturer.
Some switches come with an electronic signal. Sold complete with thermostats that communicate information by means of a radio signal. These thermostats can be installed anywhere on the wall without laying cables. In general, they are very diverse in function ...
Wiring diagram of the servo, thermostat and commutator
For beginners, I recommend buying a 220 volt AC 50Hz servo. For those who live in Russia. That is, such a servo drive can be safely connected to a 220 volt power supply. In other countries, the mains voltages may change. When connected to the mains, the normally open valve will close.
I also recommend that you familiarize yourself with the power of the thermostats. To ensure that the voltage and current in the thermostat does not exceed those specified by the manufacturer. For example, I will say that there are no problems with overloads, take a thermostat with a voltage of 220 Volts and a current of up to 10 Amperes. And 220 volt servos have a current of about 0.3 amperes. So there should be no overcurrent with such a thermostat. Accordingly, the cross-sectional electrical wire can be 1-1.5 mm2.
It is better to make the electrical wire leading from the thermostat to the servo drive with three wires, since the working contacts of the thermostat have three connections. General, working and reverse signal. For the future, suddenly you need a return signal (opposite command) from the thermostat.
If you are not well versed in electricity, then I do not recommend taking switches at all. First, they are expensive. Secondly, the function to turn off the pump can be experienced. However, it's up to you.
When there is a possibility that all circuits will close, and the pump will operate at zero flow, in this case it is imperative to install a bypass valve, which gives flow when all circuits are closed.
Bypass valve.Purpose and setting.
Room thermostat. Room temperature controllers.
Electrical room thermostats are called thermostats.
Thermostat
Is an electrical temperature sensor that, through the selected temperature, gives a signal to the servo drive to close or open the valve. The thermostat has the ability to select the room temperature either mechanically (handle) or electronically (button).
The thermostat has one or two temperature sensors. The main temperature sensor is built into the device. It serves to obtain the air temperature. The other is considered a remote probe and is called an external immersion probe. A remote probe is needed in order to measure the temperature of the heated floor surface. It must be mounted inside a warm water floor, that is, in the concrete base of the warm floor. The external sensor is used to measure the temperature of the floor surface. This probe should be installed where the base of the floor will always be open. Also, it is not allowed to install the probe near windows and doors where a draft is possible. The probe must be installed between the flow and return pipes. The height of the sensor (probe) must not be lower than the middle of the concrete screed.
The sensor for determining the air temperature should be located at a distance of 0.8-1.5 meters from the floor. The closer the sensor is to the floor, the more heat it senses. The further, the less he feels the heat. This suggests that if the sensor is farther from the floor, then the temperature controller will be set more. If closer to the floor, then vice versa.
The sensor is installed only on internal walls. The inner wall is the wall behind which the heated room is located. Outer wall is a wall with no rooms behind it. The outside wall is cold. A sensor installed on an outer wall will deceive and give results that the room is cold.
Do not obstruct the wall (with cabinets, shelves, table, armchair, sofa) where the air temperature sensor is located. This wall must be free for natural air circulation through the temperature sensor. A wall near the front door is suitable for this. If the door is constantly open, then the sensor from the door must be installed at a distance of about 1 m from the door. Do not place equipment that generates heat near the air temperature sensor.
Make sure that there are no drafts near the air temperature sensor, such as ventilation. In theory, the ideal location for an air temperature sensor is in the center of the room to be heated, both in width, length and height.
Thermostat with two sensors
, can control two parameters at once: air temperature and floor temperature. This thermostat sets the cut-off thresholds for air temperature and floor temperature. If the temperature threshold of any of the two sensors is exceeded, then the servo drive is turned off.
Programmable thermostats
These thermostats are called chronothermostats. In them, you can set the operation of the servos by time and (or) by days.
Thermostats or switches with a wireless sensor.
The era of new technologies does not stand still and new inventions appear every decade. I can only say that such thermostats exist. The control panel of the thermostats can be installed anywhere, but the temperature sensor that determines the temperature can be where it is needed. The temperature sensor sends a command to the thermostat by means of a radio signal.
| Like |
| Share this |
| Comments (1) (+) [Read / Add] |
All about the country house Water supply Training course. Automatic water supply with your own hands. For Dummies. Malfunctions of the downhole automatic water supply system.Water supply wells Well repair? Find out if you need it! Where to drill a well - outside or inside? In what cases well cleaning does not make sense Why pumps get stuck in the wells and how to prevent it Laying the pipeline from the well to the house 100% Protection of the pump from dry running Heating Training course. Do-it-yourself water-heating floor. For Dummies. Warm water floor under a laminate Educational video course: On HYDRAULIC AND HEAT CALCULATIONS Water heating Types of heating Heating systems Heating equipment, heating batteries System of underfloor heating Personal article of underfloor heating Principle of operation and scheme of operation of underfloor heating Design and installation of underfloor heating materials for underfloor heating Water underfloor heating installation technology Underfloor heating system Installation step and methods of underfloor heating Types of water underfloor heating All about heat carriers Antifreeze or water? Types of heat carriers (antifreeze for heating) Antifreeze for heating How to properly dilute antifreeze for a heating system? Detection and consequences of coolant leaks How to choose the right heating boiler Heat pump Features of a heat pump Heat pump operating principle About heating radiators Ways of connecting radiators. Properties and parameters. How to calculate the number of radiator sections? Calculation of heat power and the number of radiators Types of radiators and their features Autonomous water supply Autonomous water supply scheme Well device Do-it-yourself well cleaning Plumber's experience Connecting a washing machine Useful materials Water pressure reducer Hydroaccumulator. Principle of operation, purpose and setting. Automatic air release valve Balancing valve Bypass valve Three-way valve Three-way valve with ESBE servo drive Thermostat to the radiator Servo drive is collector. Choice and rules of connection. Types of water filters. How to choose a water filter for water. Reverse osmosis Sump filter Check valve Safety valve Mixing unit. Principle of operation. Purpose and calculations. Calculation of the mixing unit CombiMix Hydrostrelka. Principle of operation, purpose and calculations. Accumulative indirect heating boiler. Principle of operation. Calculation of a plate heat exchanger Recommendations for the selection of PHE in the design of heat supply objects Contamination of heat exchangers Water heater for indirect water heating Magnetic filter - protection against scale Infrared heaters Radiators. Properties and types of heating devices. Types of pipes and their properties Indispensable plumbing tools Interesting stories A terrible tale about a black installer Water purification technologies How to choose a filter for water purification Thinking about sewage Sewage treatment facilities of a rural house Tips for plumbing How to evaluate the quality of your heating and plumbing system? Professional recommendations How to choose a pump for a well How to properly equip a well Water supply to a vegetable garden How to choose a water heater Example of equipment installation for a well Recommendations for a complete set and installation of submersible pumps What type of water supply accumulator to choose? The water cycle in the apartment, the drain pipe Bleeding air from the heating system Hydraulics and heating technology Introduction What is hydraulic calculation? Physical properties of liquids Hydrostatic pressure Let's talk about resistances to the passage of liquid in pipes Modes of fluid movement (laminar and turbulent) Hydraulic calculation for pressure loss or how to calculate pressure losses in a pipe Local hydraulic resistance Professional calculation of pipe diameter using formulas for water supply How to choose a pump according to technical parameters Professional calculation of water heating systems. Calculation of heat loss in the water circuit. Hydraulic losses in a corrugated pipe Heat engineering. Author's speech.Introduction Heat transfer processes T conductivity of materials and heat loss through the wall How do we lose heat with ordinary air? Heat radiation laws. Radiant warmth. Heat radiation laws. Page 2. Heat loss through the window Factors of heat loss at home Start your own business in the field of water supply and heating systems Question on the calculation of hydraulics Water heating constructor Diameter of pipelines, flow rate and flow rate of the coolant. We calculate the diameter of the pipe for heating Calculation of heat loss through the radiator Power of the heating radiator Calculation of the power of the radiators. Standards EN 442 and DIN 4704 Calculation of heat loss through building envelopes Find heat loss through the attic and find out the temperature in the attic Select a circulation pump for heating Transfer of heat energy through pipes Calculation of hydraulic resistance in the heating system Distribution of flow and heat through pipes. Absolute circuits. Calculation of a complex associated heating system Calculation of heating. Popular myth Calculation of heating of one branch along the length and CCM Calculation of heating. Selection of pump and diameters Calculation of heating. Two-pipe dead-end Heating calculation. One-pipe sequential Heating calculation. Double-pipe passing Calculation of natural circulation. Gravitational pressure Water hammer calculation How much heat is generated by pipes? We assemble a boiler room from A to Z ... Heating system calculation Online calculator Program for calculating Heat loss of a room Hydraulic calculation of pipelines History and capabilities of the program - introduction How to calculate one branch in the program Calculation of the CCM angle of the outlet Calculation of CCM of heating and water supply systems Branching of the pipeline - calculation How to calculate in the program one-pipe heating system How to calculate a two-pipe heating system in the program How to calculate the flow rate of a radiator in a heating system in the program Recalculating the power of radiators How to calculate a two-pipe associated heating system in the program. Tichelman loop Calculation of a hydraulic separator (hydraulic arrow) in the program Calculation of a combined circuit of heating and water supply systems Calculation of heat loss through enclosing structures Hydraulic losses in a corrugated pipe Hydraulic calculation in three-dimensional space Interface and control in the program Three laws / factors for the selection of diameters and pumps Calculation of water supply with self-priming pump Calculation of diameters from central water supply Calculation of water supply of a private house Calculation of a hydraulic arrow and a collector Calculation of a hydraulic arrow with many connections Calculation of two boilers in a heating system Calculation of a one-pipe heating system Calculation of a two-pipe heating system Calculation of a Tichelman loop Calculation of a two-pipe radial wiring Calculation of a two-pipe vertical heating system Calculation of a single-pipe vertical heating system Calculation of a warm water floor and mixing units Recirculation of hot water supply Balancing adjustment of radiators Calculation of heating with natural circulation Radial wiring of the heating system Tichelman loop - two-pipe associated Hydraulic calculation of two boilers with a hydraulic arrow Heating system (not Standard) - Another piping scheme Hydraulic calculation of multi-pipe hydraulic arrows Radiator mixed heating system - passing from dead ends Thermoregulation of heating systems Pipeline branching - calculation of a hydraulic pipeline branching Calculation of the pump for water supply Calculation of the contours of a warm water floor Hydraulic calculation of heating. One-pipe system Hydraulic calculation of heating. Two-pipe dead-end Budgetary version of a one-pipe heating system of a private house Calculation of a throttle washer What is a CCM? Calculation of the gravitational heating system Constructor of technical problems Pipe extension SNiP GOST requirements Requirements for the boiler room Question to the plumber Useful links plumber - Plumber - ANSWERS !!! Housing and communal problems Mountingworks: Projects, diagrams, drawings, photos, descriptions. If you are tired of reading, you can watch a useful video collection on water supply and heating systems