The service life of heaters, which heater to prefer
Many competent sources claim that the service life of mineral wool and polystyrene foam is 25 - 35 years. At the same time, the wall, which is insulated with these brick or concrete heaters, has been serving for more than 100 years. Therefore, the insulation of the wall during its service must be changed at least 3 times. Was the insulation chosen correctly, because of which it is necessary to overhaul the building in such a short time?
How long do inexpensive heaters last?
The main question is - where does the service life of cheap heaters of 30 years come from? Today, some manufacturers of mineral wool in the technical characteristics for individual brands of their products indicate that its service life is 50 years.
Moreover, this figure is not explained by anything, there is only a footnote stating that today there is no standard for determining the shelf life of heaters.
Scientific articles on artificial heaters indicate that heaters containing artificial organic substances can last no more than 35 years.
During this period, the destruction of organic matter, aging of the substance occurs, the insulation "cakes" or "dries up". The main thing is that as a result of this, the insulation loses its heat-saving ability by more than 1/3. Therefore, mineral wool insulation or expanded polystyrene must be completely changed within 35 years.

How is it in Europe?
Now in European countries, according to the legislation, an energy audit of each new house, including a private one, must be carried out after the completion of its construction. According to the results of which, energy consumption is issued to the building.
Proven energy savings have a very significant impact on property values in Europe.


Repeated energy audits should be carried out after 25-30 years, after a period equal to the service life of conventional heaters. Subsequent - after about the same period of time.
As a result, it becomes clear how much the building has lost its heat-saving properties, what enclosing structures and how much reduced the resistance to heat transfer, where it is necessary to change the insulation material or carry out other repairs.
Like we have
In our country, such studies are not mandatory, although they are recommended by the standards. As a result, in most cases, they are not carried out, and it is not possible to find out exactly the real service life of heaters by examining them after many years. It remains to use the data coming from abroad, according to which the indicated figures were taken.
An energy audit of new buildings and periodic inspections of the resistance to heat transfer of enclosing structures should preferably be carried out within the timeframes recommended by the standards. Then it will be possible to control changes in the insulation of the building, to carry out the necessary repairs in time.
When to change insulation
The exact answer when to change the insulation can only be given by a special examination of the heat-saving properties of the building (energy audit). But since over the past 20 - 25 years, when the use of insulation such as foam and mineral wool began, we did not carry out such surveys, it remains for subsequent checks only to compare the results obtained with theoretical calculated values. But there is no reliable statistics for the failure of heaters.
Accordingly, it is necessary to use the recommendations for replacing non-mineral heaters within the terms indicated above.
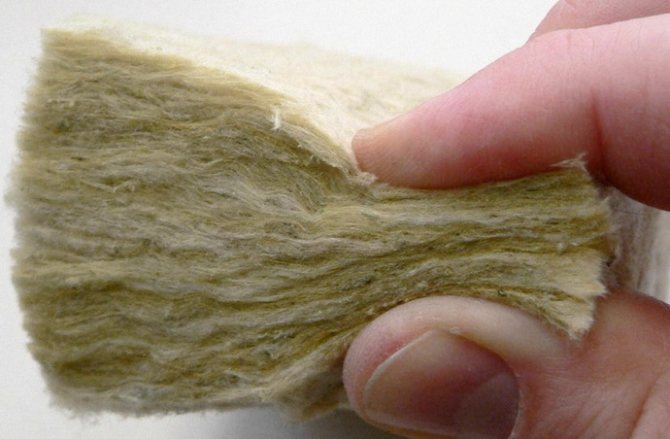


Experts agree that the service life of existing heaters with organic components is several times less than that of the enclosing structures that are insulated with them. The use of such heaters entails premature overhaul of buildings. How can you avoid this?
Dense mineral wool and aerated concrete with a long service life
There is consensus that denser mineral wool lasts longer. Partly because the quality of workmanship is provided by eminent manufacturers, and partly - in denser mineral wool there are fewer binder resins (all in all, mineral wool contains from 3 to 10% organic binders). More dense (more than 80 kg / m3) mineral wool samples last longer.
Aerated concrete made in autoclaves with a density of not much more than 100 kg / m3 is now a successful replacement for mineral wool. This material has a coefficient of thermal conductivity comparable to organic insulation - 0.5 - 0.8 m W / mS.
But most importantly, this is a completely mineral compound, which is essentially a foamed stone, therefore its service life (in the absence of excess moisture) is comparable to this indicator for heavy building materials - bricks, dense concrete.
The use of insulation without organic matter will save you from many problems in the future, especially when it comes to insulating multi-layer walls (how walls with clinker brick lining are insulated),
Low-density aerated concrete is a vapor-permeable insulation, its use is similar to the use of mineral wool.


Eternal foam glass
Another well-known insulation without organic matter is foam glass, the service life of which is more than a hundred years. This insulation has been used for a long time, (in particular in the secret arms sector), it has less heat-saving capabilities compared to effective insulation by about 1.5 times, it does not let water vapor through itself and does not accumulate water.
But its distribution is limited due to the increased price, although it is popular when insulating expensive houses.


Extruded polystyrene foam stands out among the foams for its predictable resistance to harmful factors and durability. It does not accumulate water, does not pass steam through itself (similar to foam glass), it has a denser structure and 2 times higher specific gravity compared to foam plastic (over 35 kg / m3).
But due to the higher price, it is used mainly in difficult conditions, in soils, for foundations, plinths, basements. In any case, among plastics, it is more recommended for use by the factor of "survivability" than other plastics.
As you can see, for the insulation of the building envelope, it is better to choose an insulation with a minimum of organic substances or without them at all.
The main characteristics of mineral wool
Before using mineral wool for insulation, many want to get to know this material better, so they are looking for a detailed description of it. Below is a list of the main characteristics of such wool, which will allow you to fully assess its operational properties.
Back to the table of contents
Heat insulating and sound-absorbing characteristics
Mineral wool properties table.
Mineral wool has a very low coefficient of thermal conductivity. It is within the following limits: 0.038-0.045 W / K × m. Due to this important property, only a 10 cm layer of mineral wool replaces brickwork 117 cm thick or a wall made of solid wood 25 cm.High thermal insulation of this material is achieved due to the presence of numerous air pores and channels in it, which make up about 95% from its total volume.
Another important distinguishing feature of mineral wool is the ability to restrain the penetration of sounds into the room. As a result, it is possible to create with the help of this material a comfortable atmosphere in the house, where unnecessary noise will not be present.If we talk about the exact sound insulation coefficient of mineral wool, then it is at around 0.95, while the maximum indicator is 1. Such an important characteristic is achieved due to the fact that a huge number of different fibers are located in such a material in a chaotic manner. They are excellent at absorbing sound waves.
Back to the table of contents
Non-flammability and vapor permeability of mineral wool
The most valuable advantage of this insulation is its high fire safety. It is non-flammable, so it will not spread fire or sustain a flame.
The structure of mineral wool and ecowool.
Mineral wool insulation can be done even in those buildings and rooms where it is planned to work at temperatures up to +1000 ° C.
Mineral wool has a high vapor permeability. The indicators of this material for this characteristic are within the following limits: 0.49-0.60 Mg / (m × h × Pa). This property is provided by the mineral wool due to its special structure, which allows it to "breathe".
This, in turn, makes it possible to provide the premises where it is used as a heater with a healthy internal microclimate. As a result, for these purposes it will not be necessary to use mechanical devices and spend money on their purchase.
Back to the table of contents
Naturalness and density
All the above-mentioned technical characteristics make mineral wool one of the best among the materials for insulation, but it is also chosen because it is natural and does not contain harmful chemical compounds. So, it is made from granites, tuffs, clays, limestones and basalts using special processing with the use of fire. Therefore, the use of mineral wool in country houses and apartments is ideal, since it will not harm the health of the residents.
Mineral wool has a high density. According to this characteristic, this material is divided into several types:
Types of mineral wool by density.
- 30-50 kg / m3 - mineral wool, represented by soft down, which is sold in bags or formed into rolls. This type of material is used to insulate horizontal planes in a room. Its compressibility reaches 50%.
- 75 kg / m3 - semi-rigid mineral wool, used for insulation of horizontal parts of buildings. The compressibility of the material is about 20%.
- 125 kg / m3 - mineral wool of medium hardness, excellent for protecting horizontal and vertical parts of the house. The compressibility of the material reaches 12%.
- 150-175 kg / m3 - hard mineral wool in slabs. It is designed for wall and roof insulation. The compressibility of the material is about 2%.
- 200 kg / m3 - mineral wool slabs with increased strength, which can be used under a load of up to 12 MPa.
It is important to consider that the high density of this material gives it the following additional important qualities:
- does not lose its original shape under its own weight;
- does not lend itself to deformation and compression;
- withstands additional loads.
Back to the table of contents
Structures of buildings and structures
Message from: Although manufacturers of mineral wool insulation indicate a service life of up to 50 years, the practice of using the material shows that in the event of a deviation from the technology of installing mineral wool, it will last for a few years. Under ideal conditions, subject to all installation requirements, the service life does not exceed 8 - 10 years. It is known that a year after the installation of mineral wool, thermal conductivity indicators deteriorate to 40%.
Familiar builders opened the socket with the minelite after 15 years of service. Instead of minelabs - dust. I have heard several other similar stories.How can the service life of the insulation be guaranteed for 50 years? How is this done, who knows? Some kind of calculation or test? Again, 50 years - under what operating conditions (temperature, humidity, frequency of blocking and freezing, etc.). Or they should write - 50 years for all climatic regions in the Russian Federation and 100% humidity. Immediately more questions arose.
Message from Aragorn: I understand that builders will not like it if designers will lay extruded polystyrene foam everywhere, as it is quite expensive. But only he has a service life of 50 years.
Extruded polystyrene is also not a panacea. Firefighters are categorically against him. Look at stone wool, basalt. They have a 50-year guarantee. Also not 100 years old, but already better than foam. Polyfoam is very toxic. And burns out in minutes. There are a lot of videos on the net with glowing expanded polystyrene facades. I recommend only non-combustible insulation to the architects I work with. And it is also important that it is vapor-tight. I think it's clear why. And regarding the short service life of the insulation, the penoplex generally has a 25-year warranty, at best. Despite this, only he is used in basement structures. Previously, there was not all this construction chemistry. There was expanded clay - insulation. Deprecated. There were 780mm brick walls outside, and there were more than a meter. Here is a long-liver brick. But. As for the legal component of this whole story, after a certain service life of the building, a major overhaul is carried out using effective materials already for the period when the overhaul is being carried out. This is all spelled out. So, most likely they will answer you, those to whom you contact with a claim regarding violation of consumer rights.
Message from: It is also important that it is vapor-tight. I think it's clear why.
Message from Engineer SV: I recommend only non-combustible insulation to the architects I work with. And it is also important that it is vapor-tight. I think it's clear why
.
Scope of application in questions and answers
Stone wool has a wide range of applications. Due to the naturalness of raw materials and its durability, stone wool materials are used both in private residential buildings and in high-rise buildings, for public buildings and industrial facilities. In the private sector, the most in demand are soft and hard slabs, as well as sandwich chimneys and protection of enclosing structures by means of stone wool when removing chimneys through walls.
Soft slabs are designed for warming and soundproofing unloaded flat and inclined surfaces: in frame houses in enclosing structures, in a roofing system between rafters, in interior partitions, in ceilings (between logs under a subfloor), in balconies and loggias. In those areas where minimum thermal conductivity is needed and rigidity is not required, since there is no load. If the task is not only to insulate, but also to isolate the room from noise, choose a material with a specific bias.
There are no special subtleties in the selection and installation of stone wool materials - usually the manufacturer indicates all the necessary information on the pack and on the website. And they are created in such a way that it is as simple and convenient as possible to work with them. For example, you can find material with a springy edge, as well as "double density" boards, which greatly simplify the installation process and ultimately save you money.
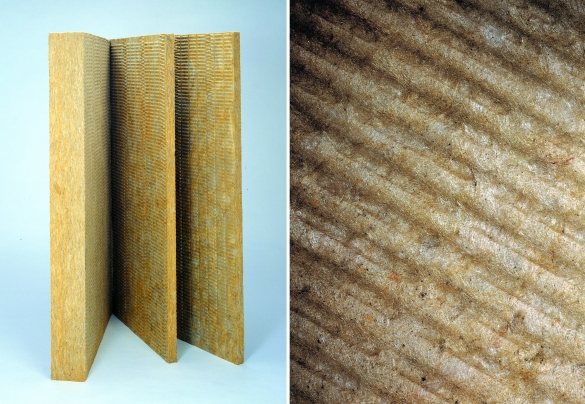


But sometimes questions still arise, the answers to which can be easily found on forumhouse.ru, in particular, on the branches led by representatives of manufacturers. Here are the most popular questions that are found on our forum.
Tell me what layer of stone wool is needed on a wooden floor for sound insulation. Is there a big difference between conventional insulation and acoustics.
As a rule, the interfloor floor is a frame made of wooden beams.According to the specialist, with such a structure, to ensure sound insulation, it is necessary to use a material certified as soundproof. Slabs are mounted in the frame, the optimal layer thickness is 100 mm, but the final choice also depends on the thickness of the beams. The thickness of the timber beams and the soundproofing boards must match. This solution can significantly reduce the level of airborne noise.
Plates of medium hardness are more often used for external insulation in systems of ventilated curtain facades and in well masonry between walls. To insulate rooms with high humidity, stone wool is also used in slabs; manufacturers have special series designed for a specific operating mode.
Rigid slabs are characterized by increased strength, they can withstand heavy loads (300 kg / m²) and are most often used for insulating floors under a "floating" screed. For wet facade systems, special rigid slabs are produced with a peel strength of at least 10 kPa, which makes it possible to apply a reinforcing and decorative layer directly to the material. It should be borne in mind that rigid plates, due to their higher density, have higher thermal conductivity, therefore, if it is not supposed to load the insulation, you should prefer the soft or semi-rigid version.
Not all structures are typical, often the distance between the elements of the subsystem does not correspond to the dimensions of the plates.
How to insulate the attic with spans of more than 580 mm, in my case at 720 mm? I mean, how to install cotton wool, can you insert it horizontally, not vertically, in order to reduce the amount of waste? Such a distance between the rafters is not my whim, this is how the company builds, and 720 mm is an average size, in fact there is not a single span, and the rafters are not installed in a vertical plane, that is, if the bottom is 680 mm, then from above maybe 740 mm.
In this case, it is necessary to use the horizontal installation of the slabs, but their thickness should be at least 100 mm, since such slabs will be less prone to deflection under strong compression.
Sometimes it is difficult for users to determine the insulation density.
What is the density of the material to insulate the facade for siding? The walls are brick.
Density is nothing more than specific gravity. The main aspect when choosing a material is the manufacturer's recommendations. Certain physical and mechanical characteristics are important. For example, the material for the frame must be elastic, and for the floor under the screed it must be rigid. For materials from different raw materials, stiffness and elasticity occur at different densities. Both raw materials and fiber size, as well as a number of other parameters, affect. For the installation of the heat-insulating layer into the frame without mechanical fastening, a light and elastic material is selected, it is easier to install and adheres closely to the structure. When choosing a denser material, it will be quite difficult to mount it into the frame without mechanical damage. Therefore, in conditions of economy, you need to choose not a dense material, but the one that is necessary in the design.
Service life of heaters: table, characteristics, description of advantages and disadvantages


Today in this article we will consider the current issue of the service life of heaters in the table. Typically houses, buildings and other structures are insulated for a long time, therefore materials are needed as reliably and of high quality as possible... Many people believe that various types of insulation do not last more than 30 years. Taking into account that the wall, which is insulated, costs about 100 years, we come to the conclusion that during this time the procedure must be done 2-3 times. If you calculate the cost of such an upgrade, then it may be far from pleasing.
What affects the life of the insulation?
As with everything, it is believed that the life of the insulation depends on its cost and quality. Manufacturers of the inexpensive substance claim that it can last at least 50 years. In practice, this figure is not confirmed by anything, therefore, in the footnotes, they write that today there is no standard operating time for heaters.
In addition, what matters is what the material is made of. Experts confirm that man-made fibers cannot be guaranteed for more than 35 years. During this time, they dry out and collapse. But most importantly, they lose half of their heat-saving properties. While natural fibers do not lose their original qualities and can serve for a longer period.
Regulatory guidelines require every home to undergo an energy audit after construction is completed. Such inspections should be carried out every 25 years in order to be able to assess the level of heat-saving properties at the moment. But since we are unable to find out the exact figures due to the verification, we use the data that come to us from Europe.
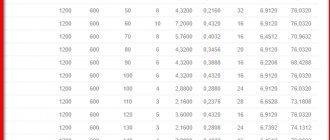
Comparative characteristics of the service life of heaters table
There are many types of insulation, but today we will consider in detail the most budgetary and reliable options. These include:
- Mineral wool.
- Basal cotton wool.
- Styrofoam.
The first type is called stone... It has a fairly high level of quality, since it is made from basalt stone. Its cost is much higher, but both the quality and the validity period meet expectations. According to statistics, mineral wool is used the most in construction. The service life is about 50 years. But this figure is still contested, and it has several nuances. At the moment, there are two types of mineral wool.
The service life of foam as insulation
Another commonly used insulation material is polystyrene foam. It is generally accepted that the shelf life of expanded polystyrene reaches several decades. Manufacturers give a guarantee for the durability of the material for 50 years. However, with the correct insulation procedure, this period can be doubled. This is one of the main reasons why it is so popular.


It should be borne in mind that there are several types of insulation made of foam:
- Polystyrene... A material that is made in the form of foam rubber. Suitable for protecting a room from the inside. It has very high performance characteristics.
- Polyvinyl chloride substances are very flexible. They have a very high resistance rate.
- Polyurethane foam... It is considered to be a hardy thermal insulation that will last quite a long time, quickly hardens, forming a very strong protection that can withstand many external influences.


Based on the above materials, we can conclude that the service life of the foam is very long and fully meets expectations.
What factors can affect the thermophysical properties of heaters over time?
Increase in humidity during the heating season
The thermophysical indicators of the heat-insulating layer are mainly influenced by the increase in its humidity during the period of the greatest moisture accumulation (heating period).
Geographic region of construction and humidity regime of operation
An increase in the thermal conductivity of mineral wool thermal insulation during moistening in comparison with thermal conductivity in a dry state is reflected in the thermal conductivity coefficients under operating conditions "A" and "B". Assignment to operating conditions "A" or "B" is determined by the geographical region of construction and the humidity regime of the room operation (dry, normal, wet).
Building structures in which the heat-insulating layer is most susceptible to moisture: a) facade heat-insulating composite systems (SFTK) and; b) three-layer walls, completely or partially, made of small-piece wall materials (layered masonry). These factors
affect the durability and heat-shielding properties of the building and the energy efficiency of the insulation used... Therefore, the term of effective operation of thermal insulation is understood as the operational period during which this material will not change its thermal performance, or will change within the permissible limits.
How is mineral wool made, its properties
Mineral wool is formed by melting rocks and passing them through the thinnest dies. The resulting fibers are immediately cooled at the exit from the furnace and wound onto spools. Electrical insulating woven materials are produced from stone fibers, but a certain part of them (usually rejection) is cut off the spools and ends up in beater machines, where cotton wool is produced.
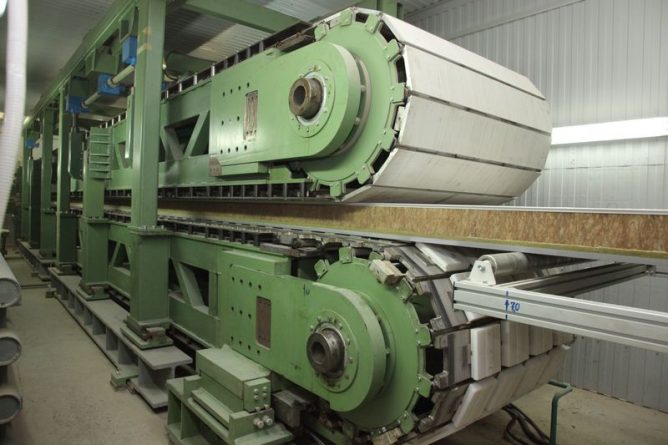


Then the resulting wool is fed under the presses, where canvases are formed, rolled into rolls (low density) and slabs (medium and high density mineral wool).
By its essence and chemical composition, fibrous wool remains the same stone (mining material), which is not afraid of dampness, mold, or any other fungi. This is a chemically neutral insulation that behaves calmly when the acid-base environment changes, does not react in any way to the appearance of, for example, rust. Mineral wool is not afraid of temperature changes, it is not prone to fires, it does not conduct electric current.
Where is mineral wool used?
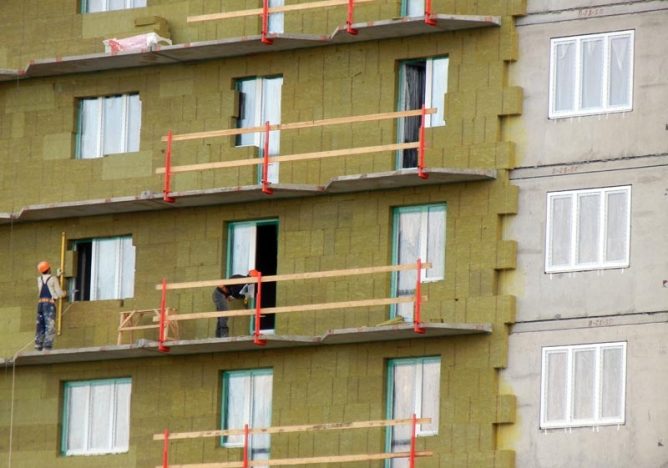
In general, mineral wool is an ideal insulation that is used for thermal insulation of pipelines of heating mains, water pipes, industrial boilers at thermal power plants.
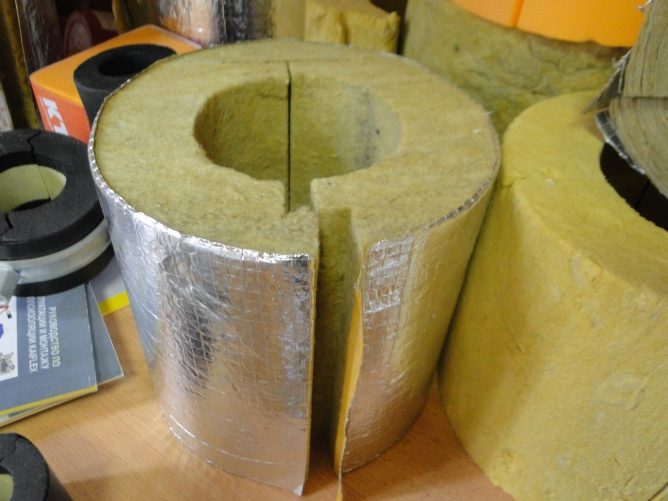


In recent decades, mineral wool is increasingly used to insulate walls in housing construction. With the correct implementation of all work on heat and vapor insulation, mineral wool insulation will retain heat for as many years as the walls stand. The manufacturer calls the service life of mineral wool insulation - 50 years. But in fact, with proper installation work, it will last much longer.
Density of mineral wool
The density index of mineral wool directly affects its thermal insulation properties and price. The more fibers there are in a cubic meter of material, the better it retains heat and is able to withstand heavy mechanical loads.
The density of different types of mineral wool and from different manufacturers varies in a fairly wide range - from 20 to 220 kg / m3. Therefore, when choosing mineral wool for wall insulation, you should clearly understand what it affects, which option is better suited for specific purposes.
Vapor permeability, sound absorption and thickness of the produced mineral wool slabs practically does not depend on its density. The difference, if there is, is insignificant.
Basically, the density of fibers in mineral wool affects:
- indicators of dynamic and static loads;
- resistance to "compression";
- preservation of the original form.
The denser the mineral wool, the longer it will last. But economic expediency dictates its own rules. Why overpay if the benefits are minimal.
Plus, for heavy material, it will be necessary to equip a more reliable and expensive frame.
Recommendations for the density of mineral wool for insulation of walls, floors, roofs:
- Up to 35 kg / m3 - only suitable for use on unloaded horizontal surfaces (for example, insulation of ceilings from the attic).
- Up to 75 kg / m3 - for interior partitions and ceiling from the inside.
- Up to 125 kg / m3 - insulation for facades (100 kg / m3 will be enough for a ventilated one, and 125 kg / m3 for a non-ventilated one).
- Up to 175 kg / m3 - material for supporting structures and intermediate floors.
- Up to 200-220 kg / m3 - an insulating layer on the floor under the concrete screed, for thermal insulation of attics and verandas.
What factors destroy mineral wool
In industrial facilities, even during major repairs, cotton wool cannot be replaced, because the material itself does not deteriorate as a whole, does not collapse or decompose. Breakdowns can occur when steam under pressure forms a hole in the pipe (fistula) and, breaking out, sweeps away the insulation. During the insulation work, the old insulation is not removed.


Mineral wool insulation is able to withstand a new operational period until the next major overhaul, so it is reused. The new material is applied where it has become smaller for various reasons. Only those sections of the insulating layer that, once opened, become clogged with dust, dirt and stone, are subject to replacement. Thus, the first enemy of mineral wool is dust and dirt.
The next enemy of this porous and breathable insulation is moisture in the absence of air. If water or condensate enters the thermal insulation layer, but does not have an outlet, it violates the thermal insulation properties. Vata stops breathing and keeps warm. Therefore, when installing thermal insulation, technological holes are provided through which air enters the thermal insulation layer and moisture is removed.


Minvata absorbs moisture well
Some manufacturers impregnate mineral wool with water-repellent substances, and this material is suitable for thermal insulation of the roof, exterior walls of the house.
Mechanical impact
From the above, the conclusion also suggests itself that the service life of mineral wool reduces mechanical impact from the outside. it
- fistulas in pipelines;
- wind that can sweep away loose casing on ground pipes;
- workers eliminating pipe leaks;
- rodents living underground and in homes.
Industrial thermal insulation is mainly subject to mechanical destruction.
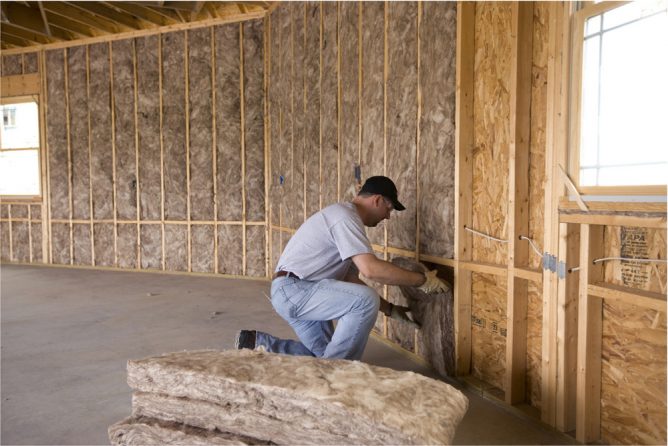


Rodents
No matter what the manufacturer says, practice shows that rodents arrange nests in almost all types of insulation. They are not even intimidated by the prickly and annoying glass wool. They gnaw through passages, arrange nests, thereby destroying the insulating layer.
Thus, in order to extend the service life of the thermal insulation layer, it is necessary first of all to comply with all the requirements for thermal and steam insulation at the stage of installation work, to eliminate factors that destroy thermal insulation.
Mineral wool thickness, requirements, manufacturers, catalogs
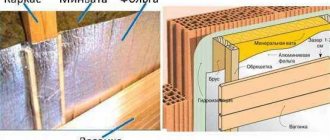
It is necessary to equip the frame and put insulation inside it, not forgetting about the hydro-vapor barrier. In more detail, it looks like this:
- A frame made of wooden blocks is made on the surface to be insulated. The distance between them is made a couple of centimeters less than the width of the roll or slab of mineral wool. So that she lies between them as tightly as possible. On inclined surfaces, for reliability, it can be additionally reinforced with "dowel-fungi" or glue. The bars can be replaced with drywall profiles.
- A vapor barrier is laid as the first layer. Then the mineral wool itself, and on top another waterproofing layer. When mounted outside, an option is acceptable when the first hydro-barrier is skipped. And mineral wool is glued to the walls with a polymer-cement composition. The option depends on the selected material and type of finish.
- The outer vapor barrier is attached to the frame. And on top of it another crate is stuffed to press down the mineral wool and the subsequent decorative finish. Or plastering is done.
Outcomes
Mineral wool allows you to quickly and independently make your home warm and cozy.
Moreover, such thermal insulation will serve for many years.The main thing is to thoughtfully approach the choice of mineral wool for wall insulation and correctly perform vapor barrier in order to minimize the effect of moisture on the material.
Stone wool as an effective insulation for the home
Mineral-based stone wool (aka ecowool) is presented in the form of insulation, which is in rather high demand in the building materials market.
Basalt insulation (stone wool)
Currently, there are a considerable number of manufacturers of this type of mineral wool, which is actively used as a reliable and effective insulation.
Before you buy mineral wool slabs and start using them, you should pay attention to the reviews and technical characteristics of this insulation.
Stone wool - from what, how, in what form
A universal heat-insulating material made from rocks, predominantly of the gabbro-basalt group (a product of volcanic eruptions), which is why stone wool is often called basalt. This group of rocks is characterized not only by strength, but also by a high melting point, which determines the choice of producers. The rock is melted at a temperature of more than one and a half thousand degrees, the finest fibers are drawn from the melt.
Stone wool has a layered structure, with a chaotic arrangement of fibers, which contributes to the formation of more air pores.
Derivatives of phenol-formaldehyde resin are most often used as a binder that transforms individual fibers into a single, elastic and durable web. These substances are considered the most stable and durable. As for safety, the additives are contained within the limits of the amount allowed by the standards, which makes them absolutely safe for both humans and the environment. This is confirmed by numerous studies and tests.
Andrey PetrovHead of the ROCKWOOL Design Center
This insulation is one of the few building materials with a positive ecological balance. That is, it helps to save more energy than was expended in its production, and theoretically can be subjected to endless recycling after the end of its service life.
Stone wool comes in several forms:
- Plates of various thicknesses and stiffness.
- Rolls.
- Specific products - insulation in the form of cylinders with seam or lock joints for pipelines and chimneys, laminated mats.