Thermal insulation of pipelines: ways to solve the problem
It is possible to provide effective protection for piping systems from environmental factors, mainly from the outside temperature, if the following measures are taken:
- creation of a heating system using heating cables. This method involves performing work on fixing heating elements on top of household pipelines or setting up a device inside the collector. Heating elements work from the electrical network. Please note that when continuous heating of pipelines is performed, then self-regulating wires are used, which are switched on and off automatically. The use of such heating systems excludes situations of overheating of structures;
- laying of pipelines below the level of soil freezing. This option of their placement eliminates the contact of networks with sources of cold;
- the use of closed underground boats. The air space is isolated, so the air around the pipes cools slowly. And this allows you to exclude freezing of the coolant or other contents of the pipes;
- creation of a circuit of heat-insulating materials to ensure high thermal protection of pipelines. This is the most common type of pipeline protection.
Since the latter method is most often used, it makes sense to talk about it in more detail.
Isolation and SNiPs
SNiPs are types of regulatory documents. In production, they are widely used. Thanks to the use of SNiPs, it is possible to perform thermal insulation in accordance with all norms regarding density. An indicator such as the coefficient of thermal conductivity for various types is also taken into account.
Video
For example, some SNiP requirements apply to surfaces that have a temperature of no more than 12 degrees. In this case, the presence of a vapor barrier layer becomes a mandatory requirement.
The calculation is carried out according to a special procedure with surfaces that do not have a specific temperature regime. And that change specifications too quickly.
Standards for thermal insulation of pipelines
Requirements for thermal insulation of equipment pipelines are formulated in SNiP. The regulatory documents contain detailed information about the materials,
which can be used for thermal insulation of pipelines, and besides this methods of work. In addition, in the regulatory documents
standards for thermal insulation contours are indicated, which are often used to insulate pipelines.
The SNiP contains the following recommendations for thermal insulation of pipelines:
- regardless of what temperature the coolant has, any pipeline system must be insulated;
- both ready-made and prefabricated structures can be used to create a heat-insulating layer;
- corrosion protection must be provided for the metal parts of the pipelines.
It is desirable to use a multilayer loop structure for pipe insulation. It must include the following layers:
- insulation;
- vapor barrier;
- protection made of dense polymer, non-woven fabric or metal.
In some cases reinforcement can be built, which eliminates the crushing of materials, and in addition, prevents deformation of the pipes.
It should be noted that most of the requirements contained in regulatory documents relate to the isolation of high-capacity main pipelines.But even in the case of installing household systems, it will be useful to get acquainted with them and take them into account when installing water supply systems for sewerage on our own.
"Isolation of heating networks"
INSULATION OF THERMAL NETWORKS
Currently, mineral wool, polyurethane foam (PPU), polyethylene foam and other foamed polymeric thermal insulation materials and piece products made of lightweight concrete are most often used to insulate heating networks. Mineral wool insulation has low thermal conductivity in a dry state. But due to violations of the conditions of transportation, storage at the construction site, installation in conditions of high humidity, inaccurate fastening, damage to the vapor barrier film, mineral wool loses its heat-shielding properties, deforms, settles, which leads to the need to repair and replace the heat-insulating material. In addition, none of the mineral wool, including basalt wool, are suitable for insulating pipes with a coolant temperature above 250 ° C, since the impregnating composition decomposes. The applied polyurethane foam insulation is generally suitable at a coolant temperature of up to 150 ° C. If the waterproofing is damaged and water gets in, the PU foam decomposes. Single piece heat-insulating materials, capable of providing reliable thermal protection of pipelines for a long time and possessing the necessary heat resistance, are made in the form of shells from perlite concrete, foam glass and other inorganic materials, have a fairly high cost and require factory production. The cheaper heat-insulating materials include non-autoclaved monolithic foam concrete of natural hardening
- a kind of lightweight aerated concrete, obtained as a result of hardening a solution consisting of cement, water and a surfactant, or simply - foam. The foam provides the necessary air content in the solution and its uniform distribution throughout the mass in the form of small closed cells, which gives the material thermal insulation properties and moisture resistance. Foam concrete has high adhesion to metal and reliably protects the metal from external corrosion. The coefficient of linear expansion of foam concrete is comparable to the coefficient of linear expansion of a steel pipe. Foam concrete can be used for thermal insulation of pipelines, equipment, gas ducts and air ducts located both in buildings and in the open air in non-passable channels and for channelless laying with a coolant temperature from minus 150 ° С to plus 600 ° С, including pipelines of heating networks for new construction and renovation work.
If the waterproofing is damaged, foam concrete can collect up to 22-25% of water, which subsequently evaporates. At the same time, foam concrete, due to the hydration reaction, becomes stronger and retains its heat-shielding properties.
The technology of monolithic non-autoclave foam concrete involves the use of mobile complexes that allow the production of heat-insulating foam concrete with an average density of 150 - 200 kg / m3 directly on site, pouring it into the annular space, followed by hardening in natural conditions and the formation of a durable, heat-resistant heat-insulating layer on the pipeline surface. The installation for the production of foam concrete consists of: a low-speed, excluding foam breaking, a cyclic mixer, a foam generator for the production of foam, a compressor and a gerotor pump, which ensures a smooth supply of foam concrete with minimal destruction of air bubbles.
Work can be performed in winter at temperatures as low as -15 ° C. In this case, it is necessary to ensure a positive temperature of the foam concrete during the first 4-5 hours. This is achieved by using hot water when mixing and insulating the pouring point.
The cost of insulation of pipes with monolithic foam concrete is much less than insulation with mineral wool or polyurethane foam.
Work technology
Pipeline sections are cleaned of rust, dust, dirt, oil stains and insulation residues during repair work (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Pipeline section
The estimated thickness of the foam concrete layer is created using centralizers (Fig. 2) made of polymeric materials (at a coolant temperature not higher than 120 ° C) or galvanized steel, installed on insulated pipes at the rate of 1 centralizer per 1 casing (shell).
Fig. 2 Centralizer
Centralizers-plugs are installed at the initial and final sections of the pipeline (Fig. 3). In addition, plugs are installed along the length of the pipeline so that the volume of the limited area corresponds to the volume of the mixer.
Fig. 3 Centralizer-blank
A casing (shell) made of galvanized steel or aluminum is installed on the centralizers using self-tapping screws so that the filling hole is located at the top, strictly in the center of the pipe (Fig. 4). The filling holes, in the future, are sealed with a waterproofing, but vapor-permeable material, in order to remove excess moisture from the foam concrete.
Fig. 4 Metal casing (shell) with filling holes.
Pouring of foam concrete is carried out in 2 stages. Initially, a small volume of the area bounded by plugs is filled to control the possible flow of the foam concrete mixture at the joints of the casing with fixed supports. The leaks are sealed with polyurethane foam. Control of the filling of the space between the pipeline and the metal casing (shell) is carried out visually through the filling holes. The vertical sections of the pipeline are filled in the same way (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5 Vertical section, prepared for pouring foam concrete.
Filling on an operating pipeline must be done at a coolant temperature of no more than 60 ° C. If the temperature is higher than 60 ° C, it is necessary to lower the temperature to the specified temperature for the curing time of the foam concrete (12-24 hours).
The thickness of the foam concrete layer depends on the temperature of the coolant, the temperature zone (for external pipelines) and the diameter of the insulated pipeline. Considering that the unit of measurement of pipeline insulation in rates and prices is 1 m3 of insulation, and calculations often operate with the diameter of the pipeline and its length, below is a table of ratios of 1 m3 of insulation with the length of the pipeline to be insulated. The table is designed for insulation of external pipelines in the III temperature zone with foam concrete with a density of 200 kg / m3 at 4 temperatures of the coolant.
| Insulated pipeline diameter, mm | Length of the pipeline (linear meters), insulated with 1 m3 of monolithic foam concrete D 200 at a coolant temperature: | |||
| Up to 120 ° С | 200 ° C | 300 ° C | 400 ° C | |
| 50 | 84,838 | 54,601 | 39,03 | 27,723 |
| 65 | 58,576 | 41,435 | 28,552 | 20,952 |
| 80 | 44,590 | 31,308 | 21,101 | 15,459 |
| 100 | 34,266 | 23,809 | 16,165 | 11,684 |
| 125 | 26,849 | 18,762 | 12,829 | 9,388 |
| 150 | 22,439 | 15,943 | 11,135 | 8,277 |
| 200 | 17,316 | 12,202 | 8,487 | 6,304 |
| 250 | 13,854 | 10,052 | 7,017 | 5,212 |
| 300 | 11,457 | 8,487 | 5,897 | 4,477 |
| 350 | 10,099 | 7,345 | 5,104 | 3,871 |
| 400 | 8,739 | 6,294 | 4,451 | 3,363 |
| 450 | 7,699 | 5,591 | 3,960 | 2,999 |
| 500 | 6,848 | 4,957 | 3,493 | 2,658 |
| 600 | 5,610 | 4,078 | 2,888 | 2,215 |
| 700 | 4,672 | 3,398 | 2,422 | 1,854 |
| 800 | 4,045 | 2,940 | 2,112 | 1,612 |
| 900 | 3,55 | 2,578 | 1,851 | 1,439 |
| 1000 | 3,17 | 2,327 | 1,68 | 1,304 |
| 1400 | 2,19 | 1,601 | 1,193 | 0,927 |
Magazine "Pricing and Estimated Rationing in Construction", November 2009 No. 11
Materials for thermal insulation of pipelines
At the moment, the market offers a large selection of materials that can be used to insulate pipelines. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages, as well as application features. To choose the right heat insulator, you need to know all this.
Polymer heaters
When the task is to create an effective system for thermal insulation of pipelines, most often attention is paid to foamed polymers. A large assortment allows you to choose the right material, thanks to which you can provide effective protection from the external environment and eliminate heat loss.
If we talk in more detail about polymeric materials, then the following can be distinguished from those available on the market.
Polyethylene foam.
The main characteristic of the material is its low density. Moreover, it is porous and has a high mechanical strength. This insulation is used to make cut cylinders. Their installation can be performed even by people far from the sphere of thermal insulation of pipelines. However, this material has one drawback: structures made of polyethylene foam, have fast wear and in addition to this, they have poor thermal stability.
If polyethylene foam cylinders are chosen for thermal insulation of pipelines, then special attention should be paid to their diameter. It must match the collector diameter. Considering this rule, when choosing a design for insulation, it is possible to exclude spontaneous removal of covers from polyethylene foam.
Expanded polystyrene.
The main feature of this material is elasticity. It is also characterized by high strength indicators. Protective products for thermal insulation of pipelines made of this material are produced in the form of segments, which by their appearance resemble a shell. Special locks are used to connect parts. They have spikes and grooves, thanks to which the quick installation of these products is ensured. The use of a polystyrene foam shell with technical locks excludes the occurrence of "cold bridges" after installation. In addition, there is no need for additional fasteners during installation.
Polyurethane foam.
This material is used mainly for pre-installed thermal insulation of heating network pipelines. However, it can also be used to insulate household piping systems. This the material is produced in the form of foam or shell, which consists of two or four segments. Spray insulation provides reliable thermal insulation with a high degree of tightness. The use of such insulation is most suitable for communication systems with complex configurations.
Using polyurethane foam in the form of foam for thermal insulation of pipelines of heating networks, it is necessary to know that it is destroyed under the influence of ultraviolet rays. Therefore, in order for the insulating layer to serve for a long time, it is necessary to ensure its protection. For this, a layer of paint is applied over the foam or a nonwoven fabric with good permeability is laid.
Fibrous materials
Heaters of this type are mainly represented by mineral wool and its varieties. At present they are the most popular among consumers as a heater. Materials of this type are in good demand as well as polymeric materials.
Thermal insulation made with fiber insulation has certain advantages. These include the following:
- insignificant coefficient of thermal conductivity;
- the resistance of the heat-insulating material to the effects of aggressive substances such as acids, alkalis, oil;
- the material is able to maintain a given shape without an additional frame;
- the cost of the insulation is quite acceptable and affordable for most consumers.
Please note that during work on thermal insulation of pipelines with such materials shrinkage of the fiber must be avoided when laying insulation. It is also important to protect the material from moisture.
Products made of polymer and mineral wool insulation for thermal insulation in some cases can be covered with aluminum or steel foil. The use of such screens will reduce heat dissipation.
Stages of thermal insulation of heating pipes
Mineral wool
Processes for warming the heating pipeline with mineral wool must be carried out with gloves on.
- First of all, the material is cut in accordance with the required dimensions.
- Winding on the pipe is carried out, while it is not necessary to tighten it too much.
- At intervals, they should stop, fixing with electrical tape, wire or solid rope.
- Having finished covering the pipeline with mineral wool, it is necessary to prepare a protective sheathing, which is made of roofing material or corrugated foil, which is pre-cut into pieces.
- Having installed a shell made of foil or roofing material, it is secured with plastic ties or ropes.
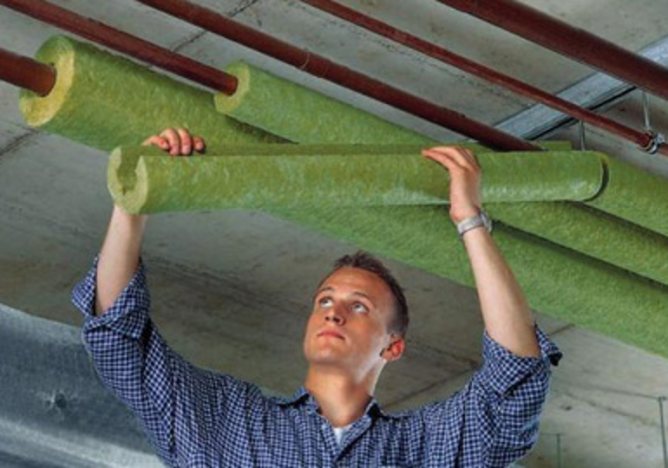

Polyurethane foam shell
With a small diameter, you can use a cylindrical or semi-cylindrical shell shape.
- Heat-insulating material is put on the pipeline.
- It is fixed with glue, tape, wire or self-adhesive tape.


If the pipe has a large diameter, then it is necessary to pick up the shell, which consists of several parts. This type of material is fixed according to the groove-thorn principle.
Having made high-quality insulation of heating networks, it will be possible to save a significant amount of heat inside the room. Therefore, the choice of insulation should be approached responsibly, having weighed all the advantages of thermal insulation building materials available on the market before making a purchase.
Multilayer structures for pipeline protection
Often, pipe-in-pipe insulation is used to insulate pipelines. Using this diagram, a heat shield is installed. The main task of the specialists installing such a circuit is to correctly connect all the parts into a single structure.
Upon completion of the work, a structure is obtained that looks like this:
- a pipe made of metal or polymer material acts as the basis of the heat-shielding circuit. She is the supporting element of the entire device;
- heat-insulating layers of the structure are made of foamed polyurethane foam. The application of the material is carried out according to the pouring technology, a specially created formwork is filled with the molten mass;
- protective cover. Galvanized steel or polyethylene pipes are used for its manufacture. The former are used for laying networks in an open space. The latter are used in cases where pipeline systems are laid in the ground using channelless technology. In addition, often when creating this type of protective casing in a heater based on polyurethane foam copper conductors are laid, the main purpose of which is to remotely monitor the state of the pipeline, including the integrity of the thermal insulation layer;
- if the pipes are delivered to the installation site assembled, then the welding method is used to connect them. Specialists use special heat-shrink sleeves to assemble the heat-shielding circuit. Or overhead couplings can be used, made on the basis of mineral wool, which are covered with a layer of foil.
Insulation materials analysis
Polymer heaters
When choosing materials to protect pipelines from heat loss, first of all, they turn to foamed polymers. With their assortment, you can choose a heater that will help solve the problem.
At the top of the list are the following insulation compounds:
- Polyethylene foam. The material is characterized by low density, porosity and low mechanical strength. Cylinders with a slit are made from it, which can be mounted even by non-professionals. The disadvantages of pipe insulation are considered to be rapid wear and poor heat resistance.
Note! The diameter of the cylinders must match the diameter of the manifold. In this case, after mounting the covers, they cannot be removed spontaneously.
- Expanded polystyrene. Insulation is characterized by low elasticity and significant strength. Produced in shell-like segments.The details are connected by means of locks with spikes and grooves, as a result of which "cold bridges" are eliminated and additional fasteners can be dispensed with.
- Polyurethane foam. It is used for pre-installed thermal insulation, although it can also be used in everyday life. It is produced in the form of foam or "shell", consisting of two or four segments. The spraying method provides reliable hermetic thermal insulation of communications with complex configurations.
Important! To protect the polyurethane foam from UV damage, it is coated with paint or non-woven fabric with good permeability.


Tubular polyethylene insulation
Fibrous materials
Heaters based on mineral wool or its derivatives are no less popular (and sometimes more) than polymeric materials.
Fiber insulation has the following advantages:
- low coefficient of thermal conductivity;
- resistance to acids, oils, alkalis and other external factors (heating, cooling);
- the ability to maintain a given shape without the help of an additional frame;
- moderate cost.
Note! When thermal insulation of equipment and pipelines with such materials, make sure that the fiber is not compressed or exposed to moisture.


Foil-coated mineral wool cylinders
Cases made of polymer and mineral wool insulation are sometimes covered with steel or aluminum foil. This heat shield reduces heat dissipation and reflects infrared radiation.
Multilayer structures
Thermal insulation according to the pipe-in-pipe method is done with the help of an already installed heat-shielding casing. The task of the installer in this case is to correctly connect the parts into a single structure. In the end, it looks like this:
- The base is in the form of a metal or polymer pipe. It is considered the supporting element of the entire device.
- Foamed polyurethane (PPU) thermal insulation layer. It is applied using the pouring technology, when a special formwork is filled with molten mass.
- Protective cover. Made of galvanized steel or polyethylene pipes. The first are intended for laying networks in open space, and the second - in the ground using channelless technology.
- In addition, copper conductors are often laid in polyurethane foam insulation, designed for remote control over the state of the pipeline, including the integrity of the thermal insulation.
Pipes that arrive at the installation site already assembled are connected by welding. For the assembly of heat-shielding circuits, special heat-shrinkable sleeves or overhead sleeves made of mineral wool, covered with a layer of foil, are used.


Multilayer construction with external galvanized steel coating
Diy thermal insulation device for pipelines
There are a number of factors on which the technology of creating a heat-insulating layer on pipelines can depend. One of the most important is how the collector is laid - from the outside or its installation is carried out in the ground.
Insulation of underground networks
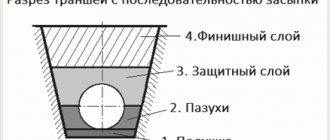
To solve the problem of ensuring thermal protection of buried communications, insulation work is carried out in the following order:
- first, sewer trays are laid at the bottom of the trench;
- after that, pipes are laid on top of them, after which they begin to seal the connections between them;
- then jackets are put on the pipes, and then the structure is wrapped with a vapor-proof fiberglass. Clamps made of polymer materials are used to fix the materials;
- then the tray is closed with a lid, after which it is covered with soil. Into the gap between him and the trench sand-clay laying is in progress mixtures followed by careful compaction;
- if there are no trays, then the pipes are laid on compacted soil with sand and gravel mixture.
Thermal insulation device on our own
The technology for thermal insulation of equipment and pipelines depends on whether the collector is laid outside or mounted in the ground.
Insulation of underground networks
Installation and thermal protection of buried domestic networks are carried out in the following order:
- Place sewer trays at the bottom of the trench.
- Lay the pipes and carefully seal the joints.
- Put on heat-insulating casings and wrap the structure with vapor-proof glass cloth. Use special polymer clamps for fixing.
- Place the lid on the tray and cover it with soil. Place a sand-clay mixture in the gap between the tray and the trench and compact it thoroughly.
- In the absence of a tray, the pipes are laid on compacted soil covered with sand and gravel mixture.


Thermal insulation of pipes with laying in a tray
Thermal protection of the external pipeline
According to SNiP, thermal insulation of pipelines located on the surface of the earth is carried out as follows:
- Remove rust from all parts.
- Treat the pipes with an anti-corrosion compound.
- Install a polymer "shell" or wrap the pipe with a roll of mineral wool insulation.
On a note! You can cover the structure with a layer of polyurethane foam or apply several layers of thermal insulation paint.
- Wrap the pipe as in the previous version. In addition to fiberglass, a foil film with polymer reinforcement is also used.
- Secure the structure with steel or plastic straps.
Compliance with the requirements for thermal insulation of pipelines is a guarantee that you will do it correctly. This means that the temperature of hot water will remain on the way from the boiler room to the house, and cold water will not freeze even in severe frosts.
INTRODUCTION
These building codes and regulations have been developed taking into account modern trends in the design of industrial thermal insulation and the recommendations of international organizations for standardization and regulation.
The regulatory document contains requirements for heat-insulating structures, products and materials that are part of structures, norms for the density of heat flux from insulated surfaces of equipment and pipelines with positive and negative temperatures when they are located outdoors, indoors, non-passable channels and with channelless laying. The document provides rules for determining the volume and thickness of compacted fibrous thermal insulation materials, depending on the compaction coefficient.
These standards were developed by: Cand. tech. sciences B.M. Shoikhet
(work manager),
L.IN. Stavritskaya
, Cand. tech. sciences
V.G. Petrov-Denisov
(JSC "Engineering company for heat engineering construction JSC" Teploproekt "),
V.A. Glukharev
(Gosstroy of Russia);
L.S. Vasilieva
(FSUE CNS).
The work was attended by: Cand. tech. sciences E.G. Ovcharenko
,
B.C. Zholudov
(Union "Concern STEPS");
A.S. Melech
(JSC "Holding"); Cand. tech. sciences
Ya.A. Kovyliansky
,
A.I. Korotkov
, Cand. tech. sciences
G.Kh. Havemerkin
(JSC VNIPIEnergoprom);
V.N. Yakunichev
(SPKB branch of JSC ""); Cand. tech. sciences
BUT
.
IN
.
Sladkov
(State Unitary Enterprise "Research Institute Mosstroy").
SNiP 41-03-2003
BUILDING STANDARDS AND RULES OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
THERMAL INSULATION OF EQUIPMENT AND PIPELINES
DESIGNING OF THERMAL INSULATION OF EQUIPMENT AND PIPE LINES
Date of introduction 2003-11-01