Good time of the day, dear reader! Pipelines designed to supply water or heat to a room require high-quality protection against heat losses, mechanical stress and the negative effects of moisture, especially when it comes to their external sections. For these purposes, when assembling highways and wiring of private systems, galvanized pipe insulation is widely used, which effectively prevents the rapid deterioration of thermal insulation on the pipeline, freezing, the appearance of condensate and corrosion formations on its parts.
Why Isolation Is Needed at All
Galvanized steel insulation is a protective coating on the outer surfaces of pipes, which increases their resistance to corrosion, mechanical damage and harmful environmental influences.
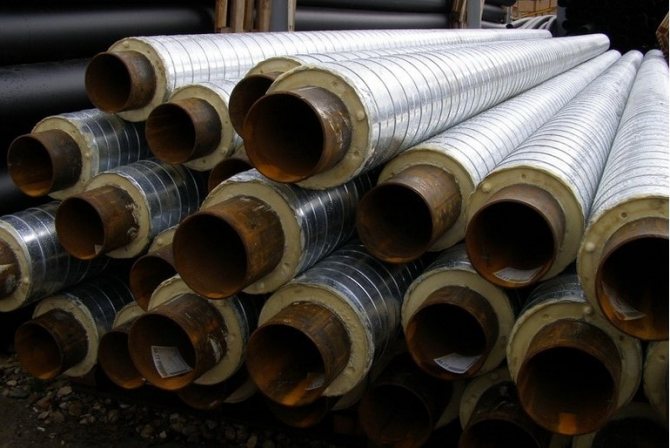

It also gives the structure a more aesthetic appearance, helps to increase the operating temperature range of the transported substance, reduce heat loss and fire hazard.
Covering Protective Layer and Package Contents
When insulating equipment, pipelines, tanks and air ducts located outdoors, all heat-insulating materials require the use of a cover layer of insulation. The only exceptions are those materials - which are already duplicated (more often glued to the cover layer).
You can watch an overview of galvanized windows in our video:
The need to use a cover layer is also indicated in legislative documents - in particular, the main guiding document for the design of pipeline insulation at the moment is SP 61.13330.2012 “Thermal insulation of equipment and pipelines”. This set of rules should be observed when designing thermal insulation of the outer surface of equipment, pipelines, gas ducts and air ducts located in buildings, structures and in the open air with a temperature of the substances contained in them from minus 180 to +600 ° C, including pipelines of heating networks at all laying methods.
Here are some terms and definitions:
- Covering layer: A structural element installed on the outer surface of thermal insulation to protect against mechanical damage and environmental influences;
- Vapor barrier layer: An element of the heat-insulating structure of equipment and pipelines with a temperature below the ambient temperature, which protects the heat-insulating layer from the penetration of water vapor into it due to the difference in partial vapor pressures at the cold surface and in the environment;
According to SP 61.13330.2012 p4.4., The structure of thermal insulation for surfaces with a positive temperature should include as mandatory elements:
- thermal insulation layer
- cover layer
- fastening elements.
Now there are many materials that can also combine these two qualities at the same time.
Despite the fact that the standards were issued back in the 70-80s, and often in the market you can hear "the regulatory framework is outdated" - we can proudly say that these recommendations were based on great engineering potential! The realities of those years were such that technologies did not allow making high-quality products and the engineering thought of real experienced scientists came into force. Even not with poor quality materials, with the help of suspensions, wires, support brackets, support rings and other "little things", it was possible to create a heat-insulating coating that could stand for ten years.
What materials are used
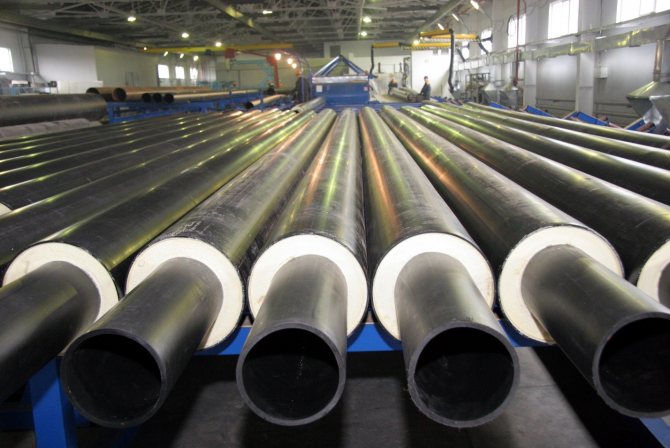
This type of insulation is made of galvanized sheet steel in the form of cylinders or shells of different diameters, from which you can choose the right option for any external pipeline.
Installation of galvanized protective shells is carried out on a previously fixed heat-insulating material:
- polyurethane foam. This insulator has a low coefficient of thermal conductivity, hygroscopicity, durability, good adhesion to steel and sheath material, and is applied by spraying. By agreement with the customer, pipes in polyurethane foam insulation (PPU) are equipped with an UEC system (operational remote control). It allows you to obtain real-time information about damage to the steel pipe and shell, the appearance of places of moisture in the heat-insulating layer, disturbances in the operation of the signal wire;
- PPU shell - products made of foamed polyurethane, made in the form of split cylinders, half-cylinders, prefabricated elements. They are fixed on the pipe along the screed;
- polymeric mineral foam. The material has a low coefficient of water absorption, retains heat well in the pipeline. The cost of foamed polymer mineral insulation (PPM) is lower than other options for heat insulators;
- extruded polyethylene. Insulation of pipes with extruded polyethylene is considered to be reinforced (VUS). It is applied at the factory, forms a completely waterproof layer, resistant to temperature extremes and the effects of various chemical compounds and aggressive environments;
- rubber - bituminous mastic. Performs the function of waterproofing metal pipes, without affecting the decrease in their thermal conductivity. The technology of insulation with rubber-bitumen mastic involves the application of several layers: a primer that increases the adhesion of metal surfaces, polymer-bitumen mastic and non-woven fabric for reinforcement. For wrapping the insulated pipe surface, a polymer film or galvanized coating is used.
Insulation of pipes with polyethylene
Has established itself as a material with high dielectric and strength properties. Has a sufficient level of adhesion to steel, which is important for reliable fixation. Today it is a priority option for protecting pipes from rusting. They are subdivided into reinforced (US) and highly reinforced (VUS).
Practice has shown that the best protection is provided by three-layer pipe insulation (GOSTs 9.602-2005 and 9.602-2016). Application is carried out by side extrusion technology. The procedure is preceded by shot blasting of the surface, then the pipes are covered with an adhesive composite (adhesive), and then with a heat-stabilized polyethylene composition.
The thickness of the pipe insulation is regulated by GOSTs, depending on the diameter, type and number of layers (the minimum value is indicated):
- 3-layer VUS pipe insulation:
- ⌀ 57–89 - 2.2 mm;
- ⌀ 102–259 - 2.5 mm;
- ⌀ 273–426 - 3 mm;
- from ⌀ 530–820 - 3.5 mm;
- 2-layer highly reinforced type:
- ⌀ 219–259 - 2 mm;
- ⌀ 259–426 - 2.2 mm;
- from ⌀ 530 - 2.5 mm;
- reinforced 2- and 3-layer:
- up to ⌀ 273 - 2 mm;
- ⌀ 273–530 - 2.2 mm;
- ⌀ 530–820 - 2.5 mm;
- from ⌀ 820 - 3 mm;
You can find out the prices for pipe insulation by calling the phone number indicated in the header of the site. We apply an anti-corrosion coating made of extruded polyethylene and offer used pipes with already applied VUS. Check with the experts for more information.
Purpose of galvanized protective covers
The galvanized casing is a cylindrical product with knurled drainage ribs. It is installed as a protective waterproofing shell on open pipelines with a heat-insulating layer of mineral wool or polyurethane foam shells coated with a waterproofing film.
Also, products are produced in which the outer shell is made of polyethylene.
Requirements, Properties and Specifications of the Coating
In case of open laying of pipelines to protect the thermal insulation of pipes, they are carried out by means of a spirally rolled sheath made of thin sheet galvanized steel of class 1 or 2 (GOST 14918-80), in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.0414-88.
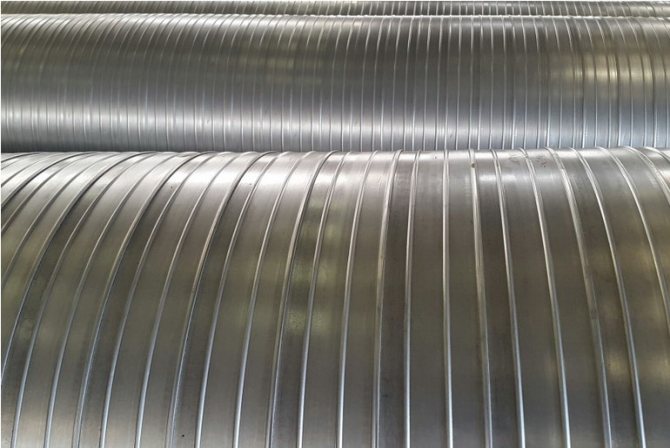


The surface of the shell, according to GOST, on the outside should be perfectly smooth or with insignificant longitudinal stripes and waviness that does not take the pipe wall thickness beyond the permissible limits, on the inside it should be rough. Both surfaces must be free of bubbles, cracks and foreign matter.
Main technical characteristics of products:
- wall thickness - 0.55 - 1.0 mm;
- range of outer diameters - from 100 to 1600 mm;
- the length of straight sections is 8-12 m for pipes with a diameter of less than 219 mm and 10-12 m for products with a diameter of 273 mm or more.
Galvanized insulation thickness
Tube-rolling materials with galvanized protection are manufactured in accordance with GOST 30732-2006. They are of high quality and can significantly reduce heat losses.
Video
The amount of thermal insulation is also carried out in accordance with standard regulations. She may be:
- standard;
- reinforced.
The required size of the coating is determined on the basis of the set technical assignment, while taking into account internal and external factors.
How much galvanized insulation is overlapped on a steel pipe is shown in the table provided.
| External volume of the pipe (cm) | Wall thickness (cm) | Nominal volume of galvanized protection | Minimum galvanized dimensions (cm) |
| 3,2 | 0,3 | 100; 125; 140 | 0,055 |
| 3,8 | 0,3 | 125;140 | 0,055 |
| 4,5 | 0,3 | 125; 140 | 0,055 |
| 5,7 | 0,3 | 140 | 0,055 |
| 7,6 | 0,3 | 160 | 0,055 |
| 8,9 | 0,4 | 180 | 0,06 |
| 10,8 | 0,4 | 200 | 0,06 |
| 13,3 | 0,4 | 225 | 0,06 |
| 15,9 | 0,45 | 250 | 0,07 |
| 21,9 | 0,6 | 315 | 0,07 |
| 27,3 | 0,7 | 400 | 0,08 |
| 32.5 | 0,7 | 450 | 0,08 |
| 42.6 | 0,7 | 560 | 0,1 |
| 53 | 0,7 | 675; 710 | 0,1 |
| 63 | 0,8 | 775; 800 | 0,1 |
| 72 | 0,8 | 875; 900 | 0,1 |
| 82 | 0,9 | 975; 1000 | 0,1 |
| 92 | 1 | 1075; 1100 | 0,1 |
| 102 | 1,1 | 1175; 1200 | 0,1 |
| 122 | 1,1 | 1375; 1400 | 0,1 |
| 142 | 1,2 | 1575; 1600 | 0,1 |
Sizes and dimensions of the casing, which are provided in the table, are made in strict accordance with the standard. It is also possible to manufacture external protection of a spiral-wound type with a large indicator of the wall size.


The length of the pipe, which is the shell, is arbitrary. It depends on the measured length of the steel assortment. Taking into account the zones without protection, this is from 150 to 210 mm.
On products of small diameters, the thickness of the protective layer can be from 32 to 45 mm, and on versions of medium and large dimensions, it is from 50 to 92.5 mm.
This casing is made according to GOST 14918-80 standards from steel strip in rolls. During the production, equipment is used, which is distinguished by high productivity. It guarantees a high level of precision when cutting workpieces and strong external and internal fastening seams when rolling.
Plasma cutting machines are used when cutting steel sheets and fittings. These units are equipped with self-diagnostic systems that allow cutting with an accuracy of 0.05 cm.
In the production of tubular products with galvanized insulation, small areas are left unprotected on both sides of the billets. They are needed to fasten parts to one another.
After bonding pipe-rolling materials, places without insulation must be insulated. For this, specially provided kits are used.
Video
The dimensions of galvanized steel pipes are also different. Their diameter varies from 14 to 137.5 cm. Experts distinguish them for safety, because they will not release substances that can be harmful to health.
The galvanized coating is used to protect the insulation layer on the trunk, stretched by the external method. In addition, it can be used in pipelines passing through through and semi-through channels.
Advantages and disadvantages of a protective coating
The advantages of galvanized casings include:
- light weight (galvanized steel sheets have a large area, and at the same time weigh little);
- simplicity and ease of installation on already assembled structures;
- complete readiness for installation;
- possession of high strength;
- durability;
- compliance with all fire safety and building codes;
- compactness and ease of transportation;
- aesthetic appearance;
- the possibility of using both outside and inside the premises.
The disadvantage is the need for periodic inspections during operation to detect damage, followed by replacement of the unusable part with a new product of the same size.
Why and what to protect the pipeline
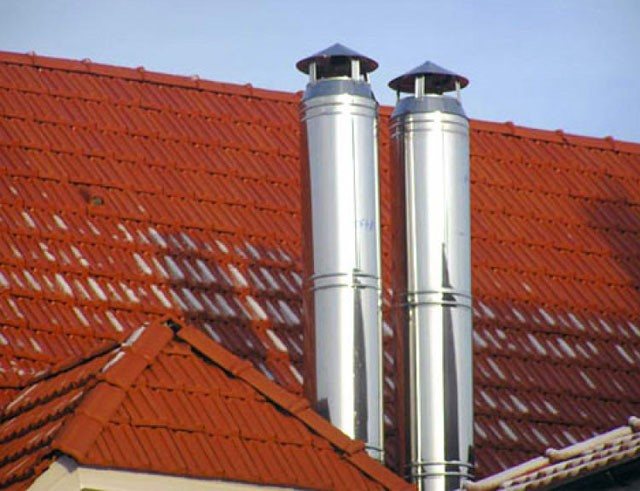


Galvanized insulation protects pipes from atmospheric influences
Pipes are made from iron, metal alloys, plastic, metal-plastic. All of them have their own "life" and wear out during operation under the influence of the environment in which they are located (precipitation, sun, temperature, air humidity, soil or water pressure). In addition, the wear of the line occurs from the inside under the influence of the transported substances. Therefore, in order to extend the time of their operation, protection is simply necessary.
Metal pipes are strong, reliable, but not protected from corrosion, corroding the pipe from the outside. If insulation is not done, then in the near future their walls will lose their strength and in the near future will require replacement.


In the absence of insulation, pipes quickly become rusty
Corrosion occurs when:
- High air humidity, rain, snow. With direct contact, the iron rusts, the pipe walls become thinner and destroyed.
- Exposure to chemicals. The metal also rusts, which leads to the destruction of pipes - typical for chemical production.
- Wandering current. Electric current destroys metal lines in the ground.
- Low air temperature. Frost leads to a decrease in the temperature of the passing liquid or its freezing (water, fuel oil, oil, diesel fuel, etc.) As a result, condensation appears on the surface of the pipes.
All of the above types of disastrous phenomena, destroying the transport main of the pipeline, cause losses associated with the repair and loss of transported products.
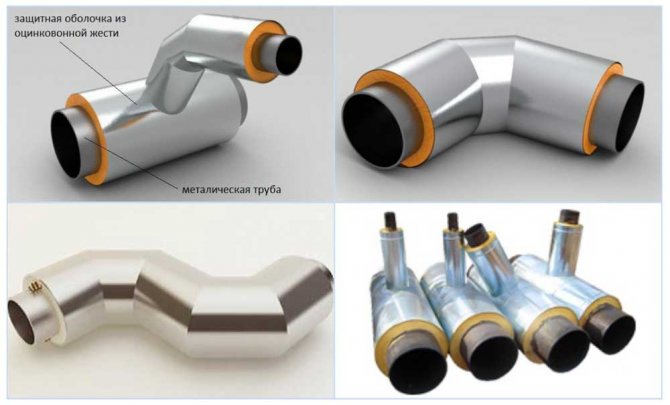
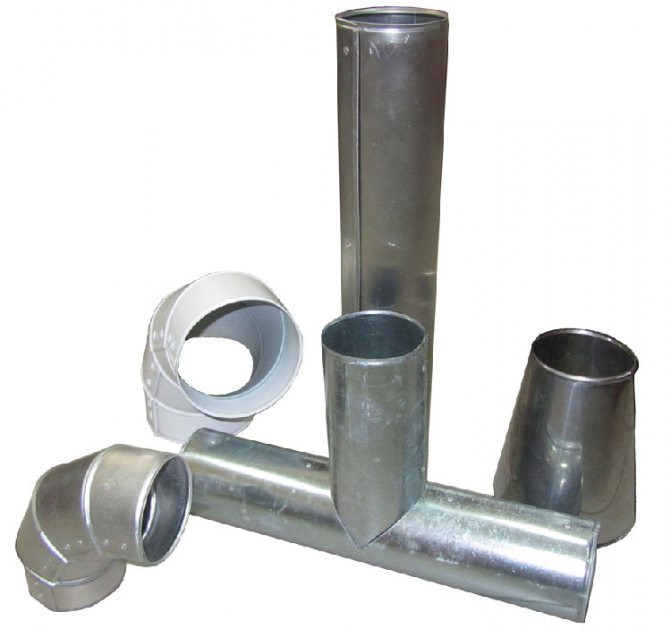
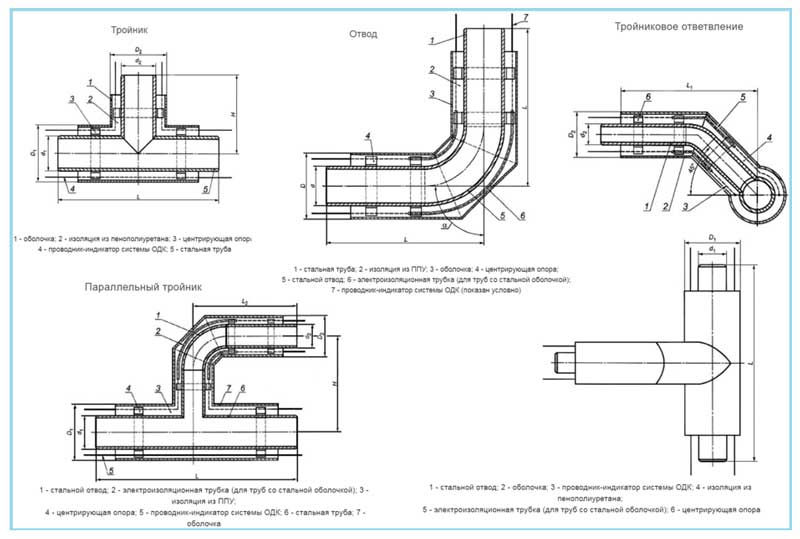
Structures and types of fittings
Utilities networks have a complex spatial configuration, include shut-off - control and control - measuring valves. Therefore, to insulate such structures, not only straight sections are needed, but also various shaped elements: tees, bends, transitions, plugs, etc.
Straight section
It is a ready-to-install product in the form of an open cylinder. It is mounted with an overlap with other segments, fastened with locks - latches, screws or rivets.


The main standard sizes of straight sections of shells:
- length - from 470 mm to 1000 mm;
- outer diameter - from 60 mm to 500 mm (in 10 mm increments), from 90 mm to 1000 mm (in 10 mm increments);
- holes for fasteners - 4-6 pcs. with a diameter of 2.7 mm for self-tapping screws or in the amount of 3-6 pcs. with a diameter of 3.2 mm for rivets or latches.
Diversion
Elbows - parts made of galvanized steel 0.55 thick; 0.7; 1.0 mm with a bend radius of 90 or 45 degrees. They are used in places where the pipeline changes direction to protect the thermal insulation of shaped elements.
Tee
Tees protect the branch points of the pipe network. Available in several versions:
- round T-shaped 90 degrees;
- straight with the same length of pipes;
- with a shortened shoulder length at 30 and 45 degrees.
They are installed in the same way as straight-line products with an overlap, fastened to self-tapping screws for metal (such as bugs) or rivets.
End cap / transition
End caps - designed to protect the heat-insulating layer at the end of pipelines. Consist of two parts with zig-holes, fixing holes and self-tapping screws.
A transition is a straight, concentric or eccentric shell section, ready for installation. It has one longitudinal and two transverse ridge, holes for fasteners and the required number of self-tapping screws.It protects fittings installed at the junction of pipes of different diameters or made of different materials.
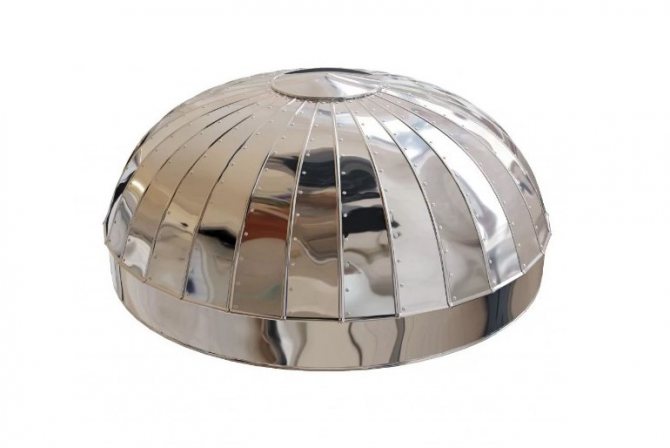
Zeppelins
Zeppelins are circular shaped pieces made up of segments (petals).
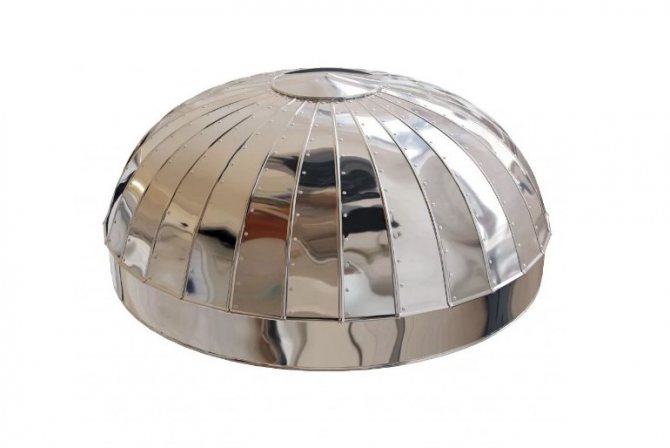


Ridges and holes for rivets (self-tapping screws) are provided along the edge of each segment. Zeppelins are used to insulate the ends of tanks and tanks.
Shells for valves and flanges
They are made in the form of a detachable box with the necessary zigs and special locks - latches, for rigid and reliable fixation of parts of the product. They serve as protection of the heat-insulating layer from the negative impact of the environment at the locations of shut-off devices, various instrumentation, flange connections of the pipeline system.
Cones
Tapered casings are a type of galvanized coating of a tapered shape with longitudinal and transverse ridges. They perform the function of protecting the thermal insulation layer on the end surfaces of tanks, on chimney pipes and ventilation outlets from the street side.
Sidebars
A shell for a tie-in is a straight line segment with longitudinal and transverse ridges and a curved abutment for mating with the main insulation element, holes for fasteners and the required number of self-tapping screws. It is used to protect the insulation layer at the points of abutment (branching) of lines from the main pipeline.
Installation of grounding and neutral protective conductors.
Earthing conductors are laid horizontally and vertically or parallel to inclined building structures. In dry rooms, grounding conductors are laid directly on concrete and brick foundations with fastening of the strips with dowel-nails (Figure 3.3, a), and in damp, especially damp rooms and rooms with corrosive vapors - on pads (Figure 3.3, b) or supports (holders) at a distance of at least 10 mm from the base (Fig. 3.3, c, d). The conductors are fixed at distances of 600-1000 mm on straight sections, 100 mm at turns from the tops of the corners, 100 mm from the branch points, 400-600 mm from the floor level of the premises and at least 50 mm from the bottom surface of the removable channel ceilings. The connection of grounding conductors and their connection to the metal structures of buildings is performed by overlapping welding, with the exception of detachable places intended for measurements. When connecting conductors, the length of the overlap for welding is taken equal to the width of the strip with a rectangular cross section and six diameters with a circular cross section. Grounding conductors to the frames of machines and devices are connected under the grounding bolt on their bodies. If machines are installed on skids, they are grounded by connecting the skids to an earth conductor. Openly laid grounding and zero protective conductors have a distinctive color - on a green background they paint a yellow stripe along the conductor.
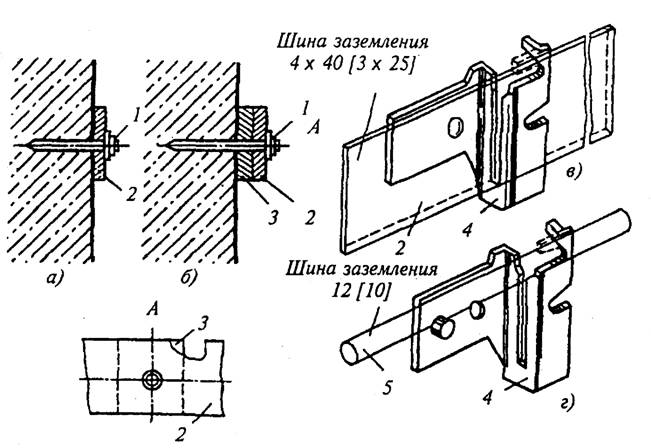

Types of fastening of grounding conductors: a - to the wall; b - lined; c, d - on holders for strip and round steel; U - dowel; 2 - strip; 3 - lining; 4 - holder; 5 - round steel The places intended for connecting inventory portable earthing switches are not painted.
Installation technology for lightning protection devices for buildings and structures. Lightning protection devices (lightning rods) consist of lightning receivers that directly perceive a lightning strike, down conductors and ground electrodes. For the installation of lightning rods, rods made of round, strip, angle, tubular steel with a cross section of at least 100 mm2, a length of at least 200 mm are installed vertically, fixing them on a support or directly on the protected building or structure; cable - made of galvanized multi-wire steel cable of at least 35 mm2 (diameter about 7 mm), reinforced on supports above the protected buildings or structures; lightning protection mesh - made of steel wire with a diameter of 6 mm is laid directly on the non-metallic roof of the building or under a fireproof insulation. Depending on the category of the building for the lightning protection device, the grids are used with 6 x 6 cells; 3 x 12; 12 x 12; 6 x 24 m. A metal roof and other metal parts towering over a building (structure) can also serve as a lightning rod.The designs of down conductors and ground electrodes in lightning protection devices are similar to those of grounding conductors and ground electrodes in protective grounding devices for electrical installations, therefore, the requirements for their arrangement and laying, as well as the methods of installation work, are similar to those described above.
To protect underground metal structures from corrosion caused by stray currents, polarized drainage is used. The protection ensures the removal of stray currents from underground metal structures through a drainage device into the rail network or negative bus of the traction substation. Polarized electrical drainage UEDZ-2 is used if the potential of an underground metal structure in relation to the rail network or to the ground is positive or alternating and when the potential difference "underground structure rail" is greater than the potential difference "underground structure - ground". UEDZ-2 is installed on the wall of a building, on a pole, on metal supports or on a special rack at a height of 1-1.5 m from the ground. The drainage must be accessible at any time of the year. The drain cables are routed through the holes in the bottom of the enclosure.
The cable going to the protected metal structure is connected to the terminal with the (-) sign. The drainage cable is laid in the ground to a depth of 0.5-0.7 m, in accordance with standard documentation, series 5.905-6 "Units and details of electrical protection of underground engineering networks from corrosion."
approximate cost
The approximate cost of straight sections of galvanized steel enclosures is shown in the table.
| Outside diameter | Price per piece, in rubles |
| Ø 100 | 180 |
| Ø 125 | 230 |
| Ø 160 | 300 |
| Ø 200 | 370 |
| Ø 250 | 460 |
| Ø 315 | 565 |
| Ø 400 | 880 |
| Ø 450 | 992 |
| Ø 500 | 1110 |
| Ø 560 | 1225 |
| Ø 630 | 1378 |
| Ø 710 | 1686 |
| Ø 800 | 2058 |
| Ø 1000 | 2572 |
| Ø 1250 | 3200 |
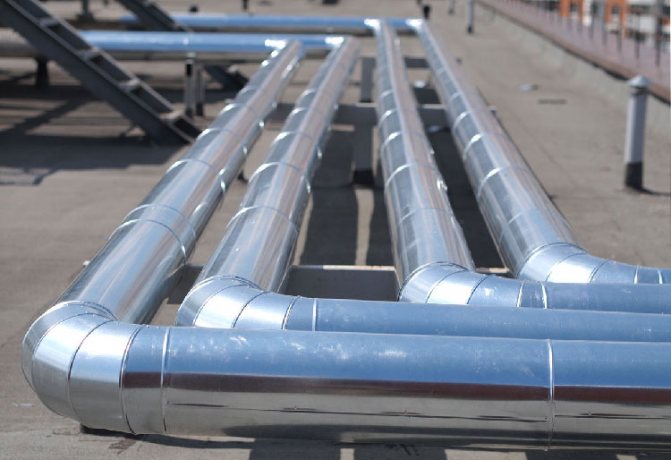
Scope of application and installation features
Galvanized steel casings have high performance characteristics and an affordable price, therefore they are widely used in:
- hot and cold water supply systems
- sewer mains;
- oil and gas pipelines;
- thermal lines laid underground, in trenches, by ground method;
- ventilation systems;
- arrangement of stoves, fireplaces (insulation of chimneys);
- fire-fighting water supply systems;
- systems of supply and discharge pipelines with circulating process fluid;
- to protect the open working bodies of machines and mechanisms.
The process of installing a galvanized shell is quite simple, does not require the use of special technological equipment and is easy to do with your own hands.
Non-professionals can use the following step-by-step instructions for isolating a separate section in an already operating highway:
- clean the surface of the required section of the pipeline from dirt;
- degrease it white - with alcohol or solvent;
- apply a bituminous primer to the surface of the working pipes;
- remove moistened parts of polyurethane foam insulation at the ends of adjacent pipe sections;
- heat up the protective shell at the junction to a temperature of about 80 ° C - a special adhesive tape (bitumen-rubber MBR) is laid on this place;
- fix the protective galvanized shell at the junction, securing the product with special clamps or cuffs;
- drill several holes for pouring polyurethane foam;
- mix the foaming agent and pour it into the prepared holes;
- seal the holes with Abris sealing tape.
The main condition is that the installation must be carried out at an ambient temperature of at least + 20 ° C and in dry weather.
In rainy weather, the network should be laid under a canopy or in another type of shelter, otherwise moisture may penetrate in the form of condensation or precipitation into the inner layer of insulation.
General information about the material
The quality of the coating is distinguished by high protective properties, therefore, insulation takes first place among other types of material.
With the help of the material, insulation work is performed in the following areas:
1. in the gas industry, to insulate underground pipelines with an operating pressure not exceeding five and a half milliamperes.
2. oil industry and water supply.
3.Apply for laying sewers.
Attention! The highly reinforced insulation method plays the role of increased protection against corrosive deposits, the material is made according to all state standards, and also has a higher reliability in comparison with similar analogs.
Bare pipe rolls are laid in a specialized polyethylene material in order to improve the adhesive properties of the insulation in relation to the pipe surface. The procedure creates a protective function of pipes from the influence of mechanical type and water.


The wear resistance of the coating exceeds 30 years, just as long as the pipeline networks do not require repair measures with the replacement of products.
The liquid distilled through pipes can have a temperature regime of minus forty degrees, a maximum of eighty degrees above zero, the optimal pressure is from two and a half to five and a half milliamperes.
The methods used by the VUS. The upgraded material solves the problem of corrosion, which is always acute during the installation of pipeline systems. Steel is constantly exposed to air and water, which negatively affect the quality of the coating. Underground utilities are affected by groundwater, which is distinguished by the content of corrosive substances.
The main methods of VUS include:
1. bitumen or bitumen-rubber mastics are common pipe processing options. Reinforcing and protective material is laid on top of the mastic. Anti-corrosion insulation is applied in two layers to pipeline products, equal to 3 millimeters, Kraft paper is applied in another layer.
2. This method involves the application of mastic in four layers. A roll reinforcing layer is placed between the second and third layer of the coating. The protective material is based on kraft paper.
3. The third method involves the application of a larger reinforced coating, which has 6 interlayers with two layers of reinforcement. Layers for protection are laid in 9 millimeters.