ROOM MECHANICAL REGULATOR
A room mechanical thermostat is a device that regulates the operation of climatic equipment, maintaining the set temperature parameters of the room. It can be used both for heating and for cooling an apartment or house.
The main difference between room mechanical thermostats and thermostats of another type is that it is a separate, completely independent device, most often made in the form of an external wiring product, intended for indoor installation.
Simply put, a mechanical thermostat, depending on the set program, by turning on or off certain heating or cooling devices, maintains the required temperature in the room.
The main feature of the mechanical thermostat is the complete absence of electrical filling, i.e. no power is required for its operation, not even batteries.
How does a mechanical thermostat work, what exactly allows it to measure the temperature of the surrounding space and control electrical appliances?
OPERATING PRINCIPLE OF THE MECHANICAL THERMOSTAT
A mechanical thermostat is a device that perfectly reflects the principle - “Everything ingenious is simple!”. With all the difference in designs and components used, there is one single principle in the operation of mechanical thermostats, namely the ability of some materials and substances to change their mechanical properties depending on temperature.
As an everyday example, familiar to everyone, which would explain the principle of operation of a mechanical thermostat, we can cite an ordinary mercury thermometer, with which we measure body temperature.
The mercury contained inside the thermometer increases in volume with increasing temperature and enters the graduated capillary, thereby showing the exact temperature.
Roughly the same processes take place in a mechanical thermostat, the only difference is that a change in temperature to a certain level, which is indicated by us separately with a regulating wheel, starts certain processes, most often closes or breaks an electrical circuit, thereby turning on or off heating devices.
To make it clearer how it all works, let's look at the design of a standard room mechanical thermostat.
Mechanical thermostat device
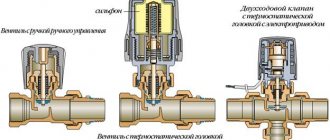
The main structural element of almost any room mechanical thermostat is a gas membrane. By the way, it is for this that they are often called membrane thermostats.
The special gas inside the membrane, when the temperature changes, changes its volume, thereby affecting the membrane walls. Which, when changing, trigger the mechanism for closing or opening the electrical circuit that feeds the heating or cooling system.
The choice of just such a device method for a room thermostat is due to the possibility of organizing a simple way to adjust its response temperature, as well as the fact that the device responds precisely to changes in the air temperature, and not the surface, which is most important in heating and cooling systems. Therefore, for example, for underfloor heating, it is more reasonable to use mechanical liquid thermostats with a remote sensor.
Adjustment of the response temperature for a membrane room thermostat is carried out using a control wheel with a scale, which is connected to the membrane mechanism.By turning the wheel, we bring the membrane walls closer or further away from the control mechanism, thereby changing the temperature at which the electrical circuit will close or open. In other words, if the triggering mechanism is closer to the membrane wall, then the gas located in it needs to slightly change the volume for it to trigger; accordingly, a lower temperature is needed and vice versa. This is how the adjusting wheel works.
Let's look at exactly how you can apply a mechanical thermostat to the heating system of a house or apartment.
The appearance and modernization of the device
One of the first thermostats is considered to be the emergence of a mercury device for maintaining an optimal temperature balance in an incubator for chickens, which was invented in 1620 by Mr. Cornelius Drebbel from Great Britain.
The thermostat has been actively used in the liquid cooling system of internal combustion engines since 1922, when the first and relatively powerful installations appeared with a large release of heat during operation. In the early stages, there were several unsuccessful attempts to use the device in the cooling system. Further, the design was improved, the engineers selected the optimal materials of manufacture and achieved such characteristics and reliability that the thermostat became a ubiquitous element in the liquid cooling system of an internal combustion engine.
We also recommend reading the article about the device of a centrifugal pump for a liquid cooling system of an internal combustion engine. From this article you can learn about the design features of the pump, its functions in the cooling system, the features of the operation and repair of the pump.
Two types of thermostats are used in car cooling systems. There are solutions with solid or liquid filling. The gel thermostat for an automotive liquid engine cooling system was invented by a Frenchman named Serge Vernier in 1963. The Vernet company specializes in the production of thermostats today, and the products of this brand enjoy a well-deserved reputation in the auto parts market for various car brands around the world.
Thermostat filler
The thermostat can have different types of filler at the heart of its design. We have already mentioned that there is a liquid filler and a solid one. The principle of operation and the structure of these solutions are practically the same. The differences lie only in the increased sealing of the liquid structure, as well as in the individual physical properties of the filler itself and its sensitivity to temperature fluctuations, depending on the composition.
Modern engines have received this type of device, which is based on a solid filler. Such a filler should be understood as the main thermoelement, which is initially in a solid physical state inside the thermostat.
Functions and location
After the engine reaches the optimum operating temperature, it becomes necessary to maintain this indicator within strict limits until the very moment the engine stops, and in some cases even for some time after the ICE stops working. The main task of the device is to control and distribute the flow of heated coolant inside the system to remove heat from the engine.
The thermostat can be located in different places, depending on the layout of the engine in the engine compartment, and the place of its installation directly depends on the model of the power unit. Also, the design features of the implementation of the cooling liquid system itself affect the installation site of the device. In most cases, the thermostat is located at the outlet of the coolant from the cylinder head. The second most common place for its installation is the inlet of a centrifugal coolant pump (pump).
Related article: What is included in the carburetor repair kit?
Using a mechanical thermostat in heating
Most often, room mechanical thermostats are used in heating houses, together with gas boilers. Manufacturers quite often in the design of boilers provide for a connection diagram through a mechanical thermostat. The device is installed in a break in the supply wire leading to the boiler and in the case when the air temperature in the room drops below the set threshold value, the circuit closes and the gas boiler starts up, starting to heat the room, maintaining the temperature of the coolant.
The basic diagrams for connecting a mechanical thermostat to heating or cooling are described in our article "Wiring diagram for a mechanical thermostat"
In exactly the same way, home thermostats are connected to any electric heaters in rooms, be they oil heaters, infrared heaters, or any other used for heating indoor air. Thus, the heating process becomes fully automated, requiring almost no human participation in its work, after adjustment.
There are a lot of possible options for using mechanical thermostats; it is simply irreplaceable in heating automation due to its unpretentiousness and reliability. And the simplicity of the design allows manufacturers to produce room mechanical thermostats at a much lower cost than electronic ones, which is an important part of their popularity with the consumer.
The main types and capabilities of thermostats
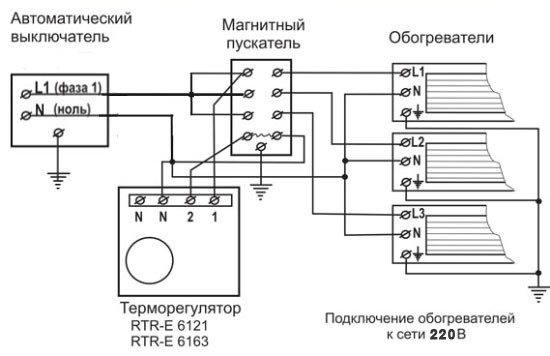
Thermostat connection diagram.
There are two main types of thermostats: gas-floor and liquid.
A gas-floor thermostat, in contrast to a liquid type, is more sensitive to changes in the temperature regime of the environment and has a longer service life - up to 20 years. Gas condensate is used as a heat-sensitive substance.
As for the liquid type, it has more accurate temperature indicators than the gas-floor one. In most cases, paraffin is used to fill it.
Also thermostats are:
- Analog room. Such a device allows you to continuously maintain the selected temperature regime. However, its technical capabilities are somewhat limited. Starting and stopping, as well as changing the operating parameters, occur only manually and completely exclude the programming of the system.
- Digital room. The installation of devices of this type expands the control capabilities, which reduces the load on the heating system. The digital thermostat changes and maintains the temperature according to a preset program. In addition to the simplest functions ("convenience" and "damping"), it allows you to adjust the mode and automatically switch up to 4 times a day.
- Thermostats for an additional "warm floor" system. A feature of the functioning of such a system is its independence from the air temperature, and the room is heated by other heating installations (convector, radiator, etc.). Therefore, the operation of the thermostat is provided by a sensor installed in the floor area.
Related article: Bathroom renovation: photo examples of renovation
Sometimes it is not possible or technically difficult to regulate the operation of the heating system in the usual way. Such a situation may arise during the reconstruction of objects or in the case of additional installation of heating devices. Therefore, the optimal control of the heat supply in this case is the installation of a thermostat with a wireless control method.
Selecting a mechanical thermostat (thermostat)
Currently, there are many manufacturers of mechanical thermostats, there are models and famous brands, but, most often, on sale you will find unfamiliar, unknown names.In my practice, I have used a large number of different mechanical thermostats and can advise the following:
- When choosing, be sure to pay attention to the maximum switching power. If it is written that the thermostat is 10 Amperes, it will be possible to connect a load of no more than 2.2-2.3 kW to it. Thermostats with more than 3.6 kW of connected power are rare. If you need to connect more power, you will have to use a contactor, according to the connection diagram, the link to which I gave a little higher.
— Of the inexpensive thermostats, I liked this one - BALLU BMT-1 - you can buy it here. By design, it is completely similar to that described in this article. It will work for you for exactly 3-5 years, and then it depends on the build quality of a particular model and operating conditions. For a summer residence, a garage - that's it!
If you need advice on choosing a model of a mechanical thermostat - write in the comments, I will try to help with advice!
Principle of operation
As mentioned above, the main task of the thermostat is to block the flow of antifreeze until the engine is properly warmed up.
Until its temperature reaches about 95 degrees, the thermostat will not allow the flow of coolant to the main elements of the system. How does he do it?
The inner filling of the thermostat contains an irreplaceable component - artificial wax. As the engine warms up, this wax begins to melt. In order to speed up this process, additional components such as copper, graphite and aluminum are added to it. During the melting process, the wax has the ability to expand, changing from a solid to a liquid state. This metamorphosis generates pressure, which pushes out a special pin, which, in turn, opens the way for antifreeze to the engine from the thermostat. When the motor stalls, the system cools down and everything happens the other way around - the wax hardens little by little, the pin returns to its place and then the valve again goes into a closed state. This is the whole principle of the thermostat.
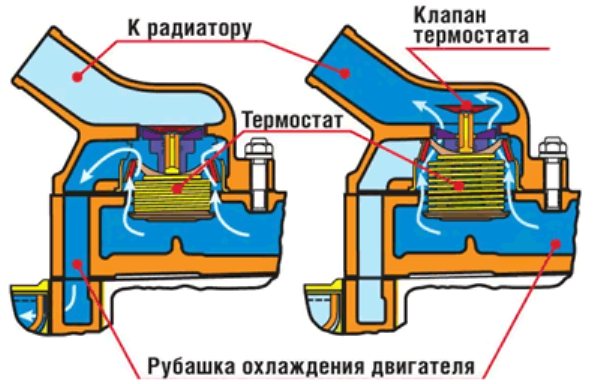

Small and large circle of coolant circulation through the thermostat
If you are interested in following this principle with your own eyes, then you can conduct the most simple experiment at home. For it, you just need to place the car thermostat in a pot of water, and then put it on a burning hotplate. You will be able to observe how as the water approaches the boiling point, the valve begins to open slightly and this clearly demonstrates the operation of the thermostat in the engine cooling system.
Of course, such an element cannot work smoothly and sometimes fails. As a result, all sorts of problems happen, and any conscientious motorist is better off knowing their list just in case.