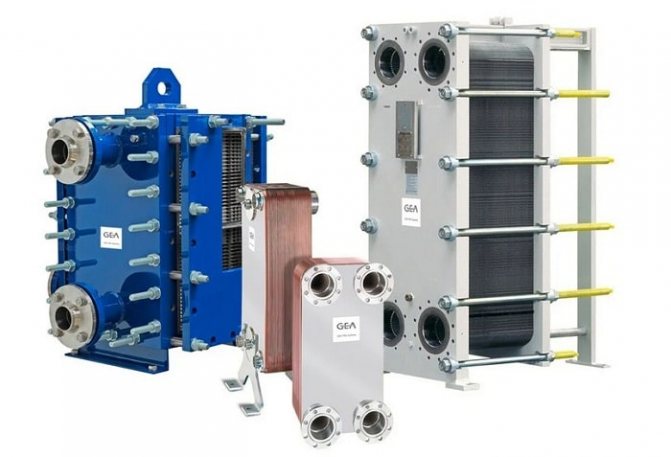
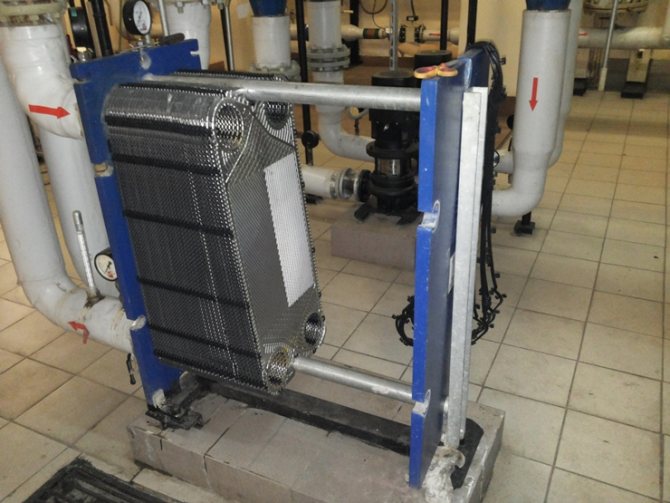
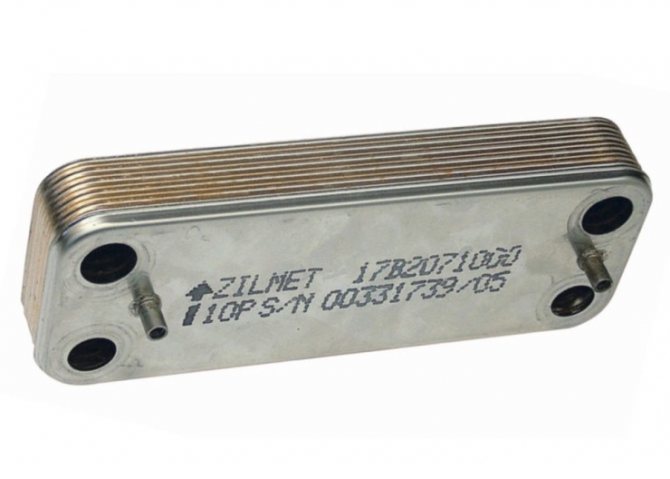
- Applications
Reliable, safe and easy-to-maintain plate heat exchangers are replacing the outdated shell-and-tube units. They better cope with the transfer of energy from the primary to the secondary circuit and withstand pressure fluctuations perfectly. The devices are much smaller and faster.
In this article, we will take a closer look at the design of the plate heat exchanger, the principle of operation of the equipment, the scope and features of the operation of these high-performance units.
Device and principle of operation
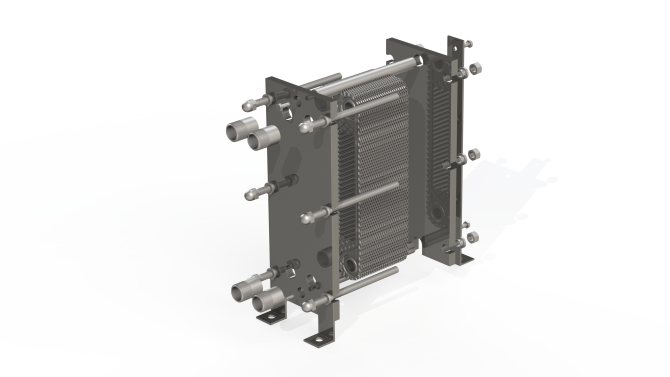
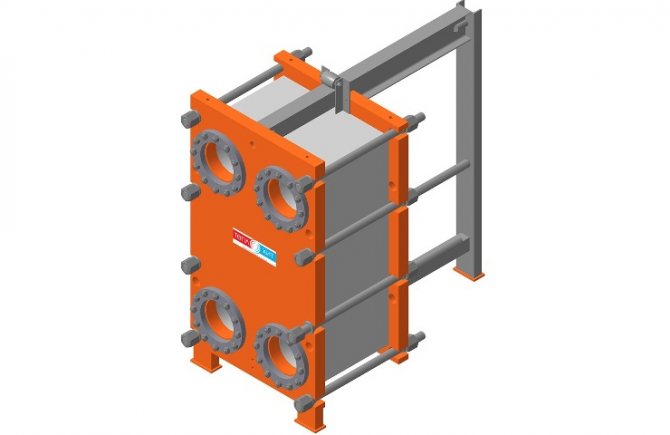
Gasketed plate heat exchanger design includes:
- a stationary front plate on which the inlet and outlet pipes are mounted;
- fixed pressure plate;
- movable pressure plate;
- package of heat transfer plates;
- seals made of heat-resistant and resistant to aggressive media material;
- upper supporting base;
- bottom guide base;
- bed;
- set of tie bolts;
- A set of support legs.
This arrangement of the unit ensures the maximum intensity of heat exchange between the working media and the compact dimensions of the device.
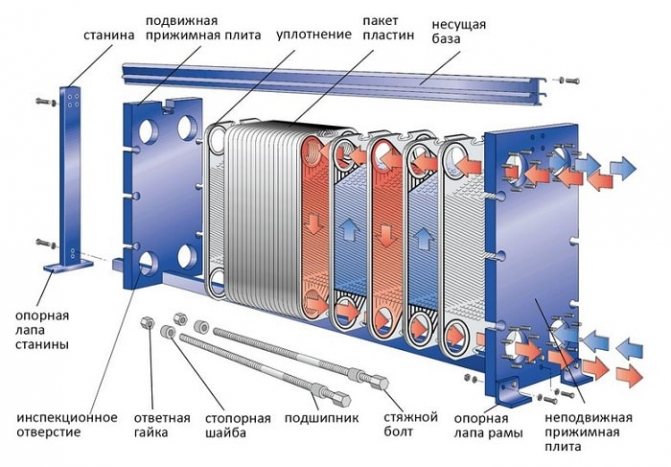
Gasketed plate heat exchanger design
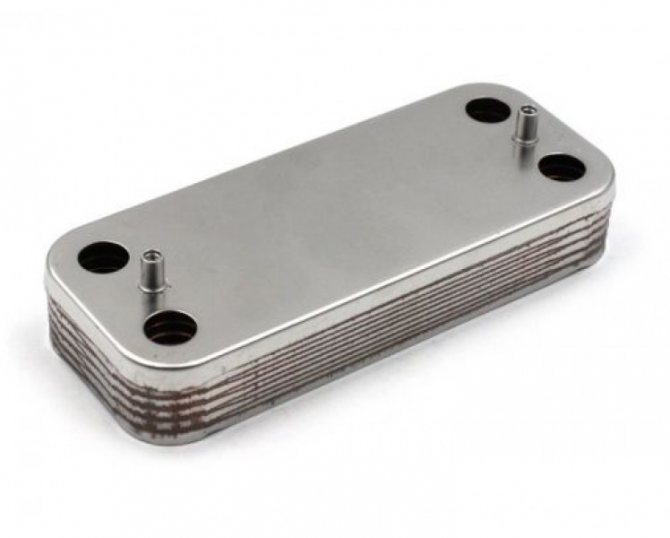
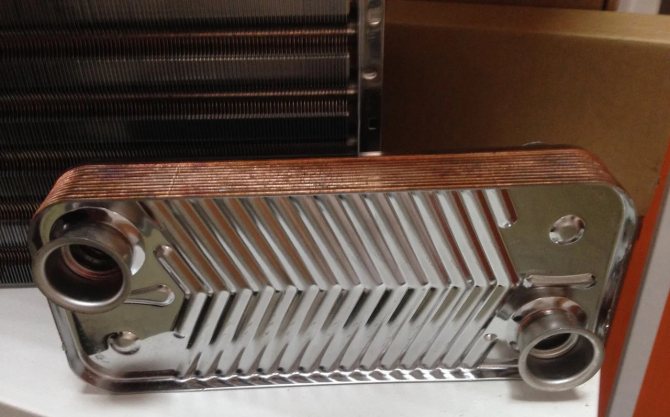
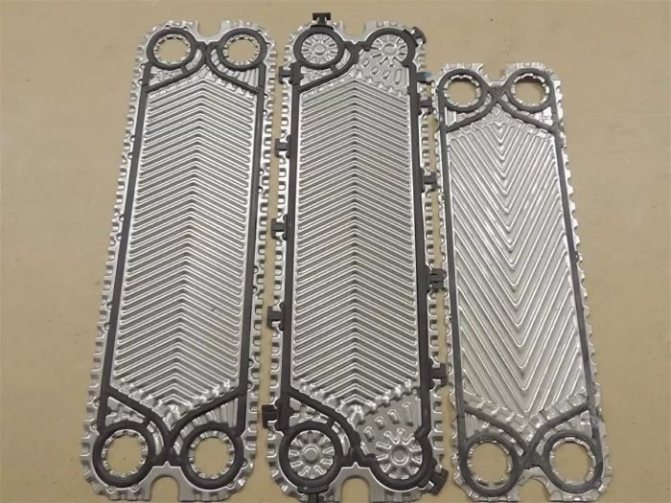
Most often, heat exchange plates are made by cold stamping from stainless steel with a thickness of 0.5 to 1 mm, however, when using chemically active compounds as a working medium, titanium or nickel plates can be used.
All plates included in the working set have the same shape and are installed sequentially, in a mirror image. This technique of installing heat transfer plates provides not only the formation of slotted channels, but also the alternation of the primary and secondary circuits.
Each plate has 4 holes, two of which ensure the circulation of the primary working medium, and the other two are insulated with additional contour gaskets, excluding the possibility of mixing the working media. The tightness of the connection of the plates is ensured by special contour gaskets made of a material that is heat-resistant and resistant to the effects of active chemical compounds. The gaskets are installed in the profile grooves and fixed with a clip lock.
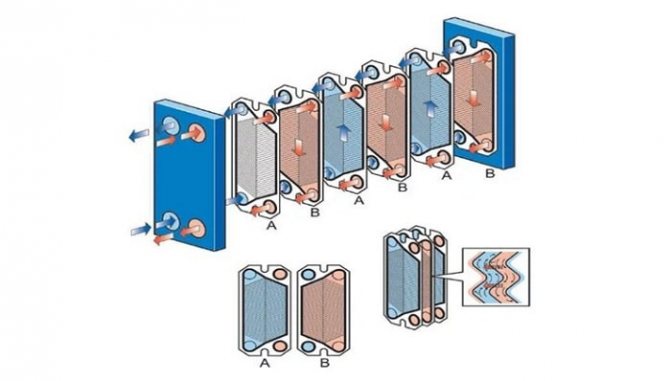

The principle of operation of the plate heat exchanger
Evaluation of the effectiveness of any plate maintenance is carried out according to the following criteria:
- power;
- the maximum temperature of the working environment;
- bandwidth;
- hydraulic resistance.
Based on these parameters, the required heat exchanger model is selected. In gasketed plate heat exchangers, it is possible to adjust the throughput and hydraulic resistance by changing the number and type of plate elements.
The intensity of heat exchange is due to the flow regime of the working medium:
- with a laminar flow of the coolant, the intensity of heat transfer is minimal;
- the transient mode is characterized by an increase in the intensity of heat transfer due to the appearance of vortices in the working environment;
- the maximum intensity of heat transfer is achieved with turbulent movement of the coolant.
The performance of the plate heat exchanger is calculated for a turbulent flow of the working medium.
Depending on the location of the grooves, there are three types of heat transfer plates:
- from "Soft"
channels (grooves are located at an angle of 600). Such plates are characterized by insignificant turbulence and low intensity of heat transfer, however, “soft” plates have minimal hydraulic resistance; - with "Average"
channels (corrugation angle from 60 to 300). The plates are transitional and differ in average turbulence and heat transfer rates; - from "Tough"
channels (corrugation angle 300). Such plates are characterized by maximum turbulence, intense heat transfer and a significant increase in hydraulic resistance.
To increase the efficiency of heat exchange, the movement of the primary and secondary working medium is carried out in the opposite direction. The process of heat exchange between the primary and secondary working media is as follows:
- The coolant is supplied to the inlet pipes of the heat exchanger;
- When working media move along the corresponding circuits formed from heat exchange plate elements, intense heat transfer occurs from the heated medium being heated;
- Through the outlet pipes of the heat exchanger, the heated coolant is directed to its intended purpose (to heating, ventilation, water supply systems), and the cooled coolant again enters the working area of the heat generator.
The principle of operation of the plate heat exchanger
To ensure efficient operation of the system, complete tightness of the heat exchange channels is required, which is provided by gaskets.
Heat exchanger classification
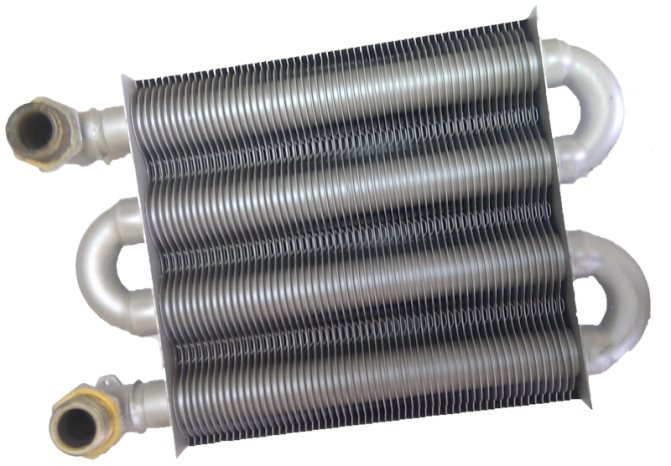


Primary heat exchanger for a heating circuit in the form of a coil with plates
Gas boilers can perform several functions. The main one is home heating. However, dual-circuit models also heat water for various domestic needs, from washing dishes to bathing. On this basis, heat exchangers are distinguished.
Primary
Serves the heating system. It is a pipe with a rather large diameter, bent in the form of a coil in one plane. To increase the working surface of the device, plates of different sizes are also placed here.
The primary heat exchanger is subjected to the highest loads. From the outside, combustion products act on it - soot, dirt, acid anhydrides, from the inside - salts dissolved in the coolant. To reduce wear, the part is coated with paint and treated with anti-corrosion compounds.
The best option is a stainless steel or copper heat exchanger, as it is not susceptible to rusting and is not afraid of salt deposits.
Secondary


Secondary heat exchanger for DHW
Such a heat exchanger heats the hot water supply liquid. Its heating temperature is lower, but it is not worth heating water for domestic needs above +60 C. Most often it is a plate structure: it is assembled from many plates with extruded passages through which tap water circulates. Multi-pass models are more effective, since within one plate the liquid changes direction several times, that is, it stays in it longer and warms up better. It is made from steel, copper, aluminum.
Bithermal
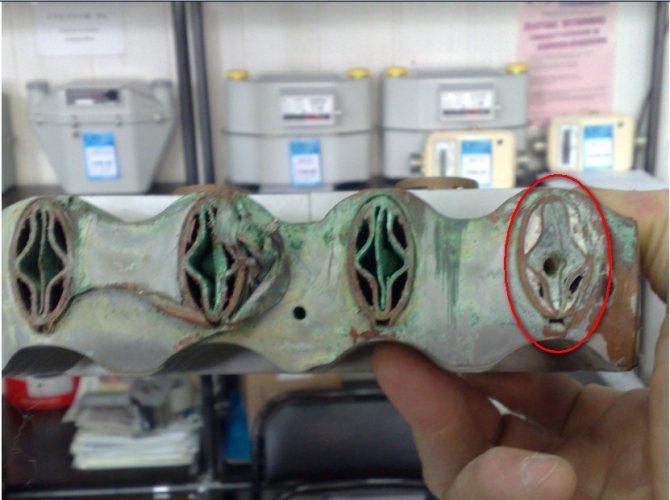


In case of clogging, bithermic heat exchangers must be replaced with new ones.
Represents 2 pipes inserted into each other. The coolant moves along the inside, and water for hot water supply moves along the outside. The heating fluid is heated in the combustion chamber and partially gives off heat to the domestic water.
The design is much cheaper. But although the water heats up faster here, its volume is limited. In addition, the bithermal heat exchanger is very sensitive to water quality and gets dirty much faster. Cleaning the device is not enough.To prevent quick clogging and failure, it is necessary to install water filters at the inlet.
It is not possible to clean the combined heat exchanger as a normal separate one. In case of large deposits of salt or clogging, the element will have to be replaced.
Requirements for gaskets
To ensure complete tightness of the profile channels and prevent leakage of working fluids, the sealing gaskets must have the necessary temperature resistance and sufficient resistance to the effects of an aggressive working environment.


The following types of gaskets are used in modern plate heat exchangers:
- ethylene propylene (EPDM). They are used when working with hot water and steam in the temperature range from -35 to + 1600С, unsuitable for fatty and oily media;
- NITRIL gaskets (NBR) are used to work with oily working media, the temperature of which does not exceed 1350C;
- VITOR gaskets are designed to work with aggressive media at temperatures no more than 1800C.
The graphs show the dependence of the service life of the seals on the operating conditions:
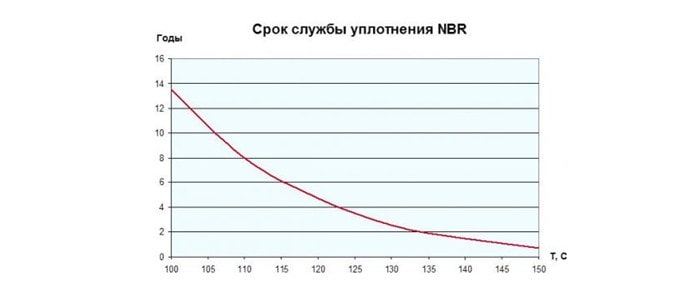

There are two ways to fix the gaskets:
- on glue;
- with a clip.
The first method, due to the laboriousness and duration of installation, is rarely used, in addition, when using glue, the maintenance of the unit and the replacement of seals are significantly complicated.
The clip lock provides quick installation of plates and easy replacement of broken seals.
Characteristics and calculation
Plates and gaskets as the main parts of heat exchangers are made from materials of different characteristics and characteristics. When choosing in favor of a certain product, its purpose and scope of application play the main role.
If we consider heating systems and hot water supply, then in this area, plates made of stainless steel and plastic seals made of special NBR or EPDM rubber are most often used. The presence of stainless steel plates makes it possible to work with a heat carrier heated to 120 degrees, in the other case, the heat exchanger can heat the liquid up to 180 ° C.


Spacers are located between the sealing plates
When using heat exchangers in the industrial field and connecting them to technological processes with the action of oils, acids, fats, alkalis and other aggressive media, plates are used that are made of titanium, bronze and other metals. In these cases, the installation of asbestos or fluoroelastomer gaskets is required.
The choice of the heat exchanger is carried out taking into account the calculations that are made using special software.
During calculations, it is necessary to take into account:
- flow rate of the heated liquid;
- initial temperature of the heat carrier;
- heating agent costs;
- required heating temperature.
Heated water up to 90-120 ° C or steam with temperatures up to 170 ° C can be used as the heating medium that flows through the heat exchanger. The type of heat carrier is selected taking into account the type of boiler equipment used. The dimensions and number of plates are selected so that a heat carrier is obtained with a temperature that meets the current standards - no higher than 65 ° C.

The heat exchanger can be made of different types of metal
It must be said that the main technical characteristics, which are also considered the main advantages, are the compact dimensions of the equipment and the ability to provide a fairly significant consumption.
The range of exchange areas and probable costs of the devices is quite high.The smallest of them, for example, from the company Alfa Laval, have a surface size of up to 1 m² and at the same time ensure the passage of a heating medium amount up to 0.3 m³ / hour. The most oversized devices have a size of about 2500 m² and a flow rate that exceeds 4000 m³ / hour.
Specifications
Generally, the technical characteristics of a plate heat exchanger are determined by the number of plates and the way they are connected. Below are the technical characteristics of gasketed, brazed, semi-welded and welded plate heat exchangers:
| Working parameters | Units | Collapsible | Brazed | Semi-welded | Welded |
| Efficiency | % | 95 | 90 | 85 | 85 |
| Maximum working medium temperature | 0C | 200 | 220 | 350 | 900 |
| Maximum pressure of the working medium | bar | 25 | 25 | 55 | 100 |
| Maximum power | MW | 75 | 5 | 75 | 100 |
| Average period of operation | years | 20 | 20 | 10 — 15 | 10 — 15 |
Based on the parameters given in the table, the required heat exchanger model is determined. In addition to these characteristics, one should take into account the fact that semi-welded and welded heat exchangers are more adapted to work with aggressive working media.
Heat exchangers made of steel
The steel heat exchanger is technologically the easiest to manufacture. Hence the low cost of such boilers, and hence their availability.
Steel, as a material, has good ductility, and therefore, under the influence of temperatures, a heat exchanger made of steel is less susceptible to thermal deformation.
At the same time, steel is susceptible to corrosion, which means that the service life of a boiler with a steel heat exchanger is relatively shorter. And the weight of such boilers is large, but the efficiency is not the best.
What is a heat exchanger in a heating system for?
Explaining the presence of a heat exchanger in a heating system is quite simple. Most heat supply systems in our country are designed in such a way that the temperature of the coolant is regulated in the boiler room and the heated working medium is supplied directly to the radiators installed in the apartment.


In the presence of a heat exchanger, the working medium from the boiler room is dispensed with clearly defined parameters, for example, 1000C. Getting into the primary circuit, the heated coolant does not enter the heating devices, but heats the secondary working medium, which enters the radiators.
The advantage of such a scheme is that the temperature of the coolant is regulated at intermediate individual thermal stations, from where it is supplied to consumers.
Difference between primary and secondary heat exchanger in a gas boiler
A heat exchanger for a gas boiler can be called one of the most significant units. This part performs a number of functions that directly affect the functioning of the equipment. More information about the operation of heat exchangers in Viessmann gas boilers can be found here: https://zakservice.com/g76389313-teploobmenniki-viessmann. You can also buy them there. And in this article we will talk about the types of heat exchangers and their differences.
To begin with, we note that the heat exchanger is responsible for transferring the energy obtained from the combustion of fuel (gas) to water, which is subsequently heated. There are 2 types of heat exchangers:
- Primary. Energy is transferred from the fuel directly to the coolant.
- Secondary. Energy transfer is carried out from liquid to heat carrier.
Let's talk about the features of each of these types separately.
Primary boiler heat exchanger


Such a device has the appearance of a large pipe, which is bent in the form of a "snake". By the type of action, it directly interacts with water. Because of this feature, it is customary to make such products from stainless metals, including steel and copper. Plates are located in the plane of the pipe. Paint is used to protect the part from corrosion.
The heat exchanger capacity is directly proportional to the size. In this case, the unit can be damaged by all sorts of external factors or the deposition of salts inside the pipes.The latter cause difficulties in the circulation of water. It is because of this feature that regular cleaning and rinsing is required. It is also recommended to additionally install filters for the heat exchanger, which extend its service life.
Secondary boiler heat exchanger


The type of heat exchanger under consideration is also called "Hot type"... Such products have interconnected plates. The most demanded material for their manufacture is stainless steel. It can provide sufficient heating even with a strong flow of heating medium. This can be achieved due to the high conductivity of the metal, as well as the large contact area with the carrier. The power in this case depends on the dimensions of the plates.
Modern heat exchangers for boilers are quite economical. At the same time, such products sometimes fail. In this case, a replacement is required. We recommend that you trust this procedure exclusively to professionals. Also, you should choose only high-quality products, which will guarantee a long service life of your heating equipment.
Did you like the article? Rate and share with your friends!
5 0
Advantages and disadvantages
The widespread use of plate heat exchangers is due to the following advantages:
- compact dimensions. Due to the use of plates, the heat exchange area is significantly increased, which reduces the overall dimensions of the structure;
- ease of installation, operation and maintenance. The modular design of the unit makes it easy to disassemble and wash the elements requiring cleaning;
- high efficiency. The productivity of the PHE is from 85 to 90%;
- affordable cost. Shell-and-tube, spiral and block installations, with similar technical characteristics, are much more expensive.
The disadvantages of the plate design can be considered:
- the need for grounding. Under the influence of stray currents, fistulas and other defects can form in thin stamped plates;
- the need to use quality working environments. Since the cross-section of the working channels is small, the use of hard water or poor-quality heat carrier can lead to blockages, which reduces the rate of heat transfer.
Plate heat exchanger piping diagrams
There are several ways to connect the PHE to the heating system. The simplest is considered to be parallel connection with a control valve, the schematic diagram of which is shown below:
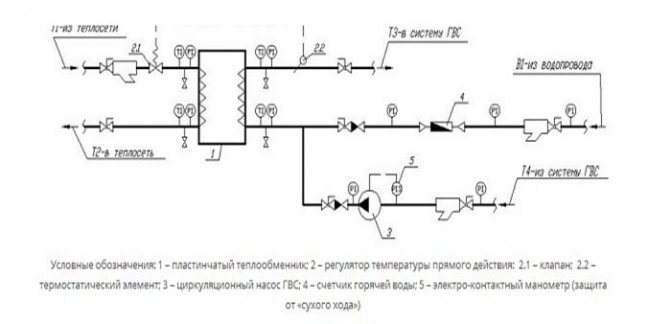

Parallel connection diagram of PHE
The disadvantages of such a connection include an increased load on the heating circuit and a low efficiency of water heating with a significant temperature difference.
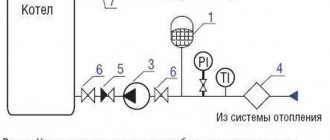
Parallel connection of two heat exchangers in a two-stage scheme will provide more efficient and reliable operation of the system:
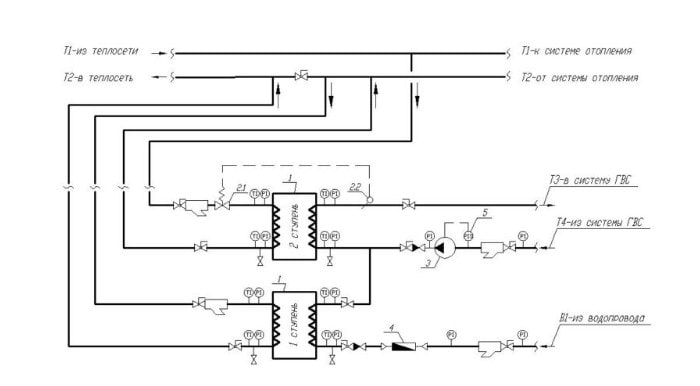

Two-stage parallel connection diagram
1 - plate heat exchanger; 2 - temperature regulator; 2.1 - valve; 2.2 - thermostat; 3 - circulation pump; 4 - hot water consumption meter; 5 - manometer.
The heating medium for the first stage is the return circuit of the heating system, and cold water is used as the medium to be heated. In the second circuit, the heating medium is the heat carrier from the direct line of the heating system, and the preheated heat carrier from the first stage is used as the heated medium.
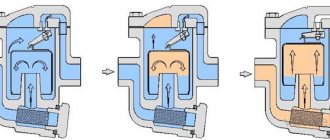
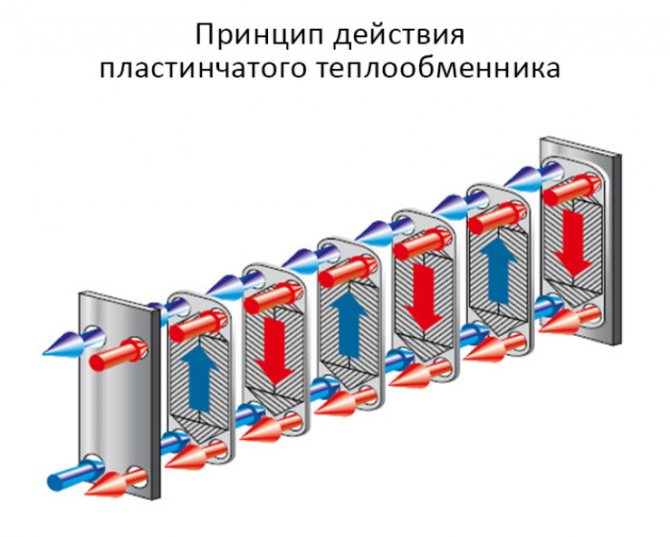
The principle of operation of the high-speed plate heat exchanger
The principle of operation of a plate heat exchanger is as follows. The space between the plates is filled with alternately heated medium and coolant. The sequence is regulated by the gaskets. In one section, they open the way for the coolant, and in the other, for the heated medium.
During the operation of the high-speed plate heat exchanger, an intensive transfer of energy occurs in all sections, except for the first and the last. Liquids move towards each other. The heating medium is supplied from the top, and the cold medium is supplied from the bottom. Visually, the principle of operation of a plate heat exchanger is presented in the diagram below.
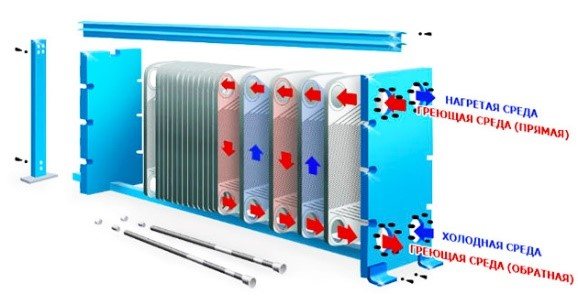

As you can see, everything is pretty simple. The more plates the better. According to this principle, the efficiency of plate heat exchangers is increased.
User's manual
Each factory-made plate heat exchanger must be accompanied by a detailed operating manual containing all the necessary information. Below are some basic provisions for all types of VET.
Installation of PHE
- The location of the unit must provide free access to the main components for maintenance.
- The fastening of the supply and discharge lines must be rigid and tight.
- The heat exchanger should be installed on a strictly horizontal concrete or metal base with sufficient bearing capacity.
Commissioning works
- Before starting the unit, it is necessary to check its tightness according to the recommendations given in the technical data sheet of the product.
- At the initial start-up of the installation, the temperature rise rate should not exceed 250C / h, and the pressure in the system should not exceed 10 MPa / min.
- The procedure and scope of commissioning work must clearly correspond to the list given in the unit's passport.
Operation of the unit
- In the process of using the PHE, the temperature and pressure of the working medium must not be exceeded. Overheating or increased pressure can lead to serious damage or complete failure of the unit.
- To ensure intensive heat exchange between the working media and increase the efficiency of the installation, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of cleaning the working media from mechanical impurities and harmful chemical compounds.
- Significantly extending the service life of the device and increasing its productivity will allow regular maintenance and timely replacement of damaged elements.
Classification of plate heat exchangers according to the principle of operation and design
According to the principle of operation, plate heat exchangers are divided into three categories.
- One-pass designs. The coolant circulates in the same direction throughout the entire area of the system. The basis of the principle of operation of the equipment is the counterflow of liquids.
- Multi-pass units. They are used in cases where the difference between the temperatures of the liquids is not too high. The heat carrier and the heated medium move in different directions.
- Double-circuit equipment. It is considered the most effective. Such heat exchangers consist of two independent circuits located on both sides of the product. By adjusting the power of the sections properly, you will quickly achieve the desired results.

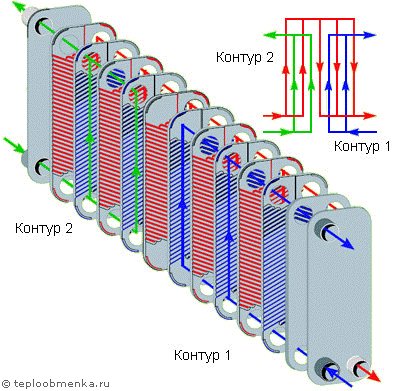
Manufacturers produce gasketed and brazed plate heat exchangers.
- Products of the first group are more popular. Such units are used in industry and hot water systems. Collapsible models are easy to maintain and repair. The power of the equipment is regulated.
- In brazed heat exchangers, the plates are rigidly interconnected and placed in a non-separable body.


There are no rubber pads. Such models are most often used for heating or cooling water in private homes.
Plate heat exchanger flushing
The functionality and performance of the unit largely depends on high-quality and timely flushing. The frequency of flushing is determined by the intensity of work and the characteristics of technological processes.


Treatment methodology
Scale formation in heat exchange channels is the most common type of PHE contamination, leading to a decrease in the intensity of heat exchange and a decrease in the overall efficiency of the installation. Descaling is carried out using a chemical rinse. If besides scale there are other types of contamination, it is necessary to mechanically clean the heat exchanger plates.
Chemical washing
The method is used for cleaning all types of PHE, and is effective when there is little contamination of the working area of the heat exchanger. For chemical cleaning, disassembly of the unit is not required, which significantly reduces the time of work. In addition, no other methods are used to clean brazed and welded heat exchangers.
Chemical flushing of heat exchange equipment is carried out in the following sequence:
- a special cleaning solution is introduced into the working area of the heat exchanger, where, under the influence of chemically active reagents, intensive destruction of scale and other deposits occurs;
- ensuring the circulation of the detergent through the primary and secondary circuits of the TO;
- flushing of heat exchange channels with water;
- draining cleaning agents from the heat exchanger.
During the chemical cleaning process, special attention should be paid to the final flushing of the unit, since the chemically active components of the detergents can destroy the seals.
The most common types of contamination and cleaning methods
Depending on the operating media used, temperature conditions and pressure in the system, the nature of the contamination can be different, therefore, for effective cleaning, it is necessary to choose the right detergent:
- descaling and metal deposits using solutions of phosphoric, nitric or citric acid;
- inhibited mineral acid is suitable for removing iron oxide;
- organic deposits are intensively destroyed by sodium hydroxide, and mineral deposits by nitric acid;
- grease contamination is removed using special organic solvents.
Since the thickness of the heat transfer plates is only 0.4 - 1 mm, special attention should be paid to the concentration of active elements in the detergent composition. Exceeding the permissible concentration of aggressive components can lead to destruction of the plates and gaskets.
The widespread use of plate heat exchangers in various sectors of modern industry and utilities is due to their high performance, compact dimensions, ease of installation and maintenance. Another advantage of the PHE is the optimal price / quality ratio.
Principle of operation
If we consider how a plate heat exchanger works, then its principle of operation cannot be called very simple. The plates are turned to each other at an angle of 180 degrees. Most often, one package contains two pairs of plates, which create 2 collector circuits: the inlet and outlet of the heat carrier. Moreover, it must be borne in mind that the steam that is on the edge is not involved during heat exchange.
Today, several different types of heat exchangers are manufactured, which, depending on the mechanism of operation and design, are divided into:
- two-way;
- multi-circuit;
- single-circuit.
The principle of operation of a single-circuit apparatus is as follows. The circulation of the coolant in the device along the entire circuit is carried out permanently in one direction. In addition, a counterflow of heat carriers is also produced.
Multi-circuit devices are used only during a slight difference between the return temperature and the incoming heat carrier temperature. In this case, the movement of water is carried out in different directions.
More about the plate heat exchanger:
Two-way devices have two independent circuits.With the condition of constant adjustment of the heat supply, the use of these devices is most expedient.