In what cases is it compiled
The act is required for:
- Commissioning of new equipment. The act will be a confirmation that each element is in its place, the installation was carried out responsibly, the system is working.
- The onset of the heating season. After a summer break in operation, the pipes could fail. After checking their capacity, an act is drawn up.
- Already carried out repair work.
- The emergence of docked emergency situations on the pipeline. Thus, specialists identify the amount of work required, weak points of the existing heating network.
For the smooth operation of the heating system, preventive control checks are necessary, reliable information about the high-quality functioning of the system at startup.
Types of repairs

Heating system repair - a large amount of work associated with costs and inconveniences
The specifics of repairing a heating system in a private and apartment building differs in many ways. First of all, these are the size of the structure and ownership. Then the number of auxiliary and control devices is taken into account. The owner of a summer cottage or a country mansion can stop the system at any time and perform routine maintenance with his own hands, regardless of deadlines. If it is required to repair heating in an apartment in a high-rise building, these actions must be coordinated with the board and the management company. Moreover, in most cases only specialists can carry out system maintenance.
Planned repair
Scheduled work on the heating system is carried out in accordance with the schedule. The document is developed taking into account the material from which the communications are assembled, the chemical composition and purity of the coolant, the intensity of the system's operation. Depending on the available factors, scheduled repairs are carried out at intervals of 10-20 years.
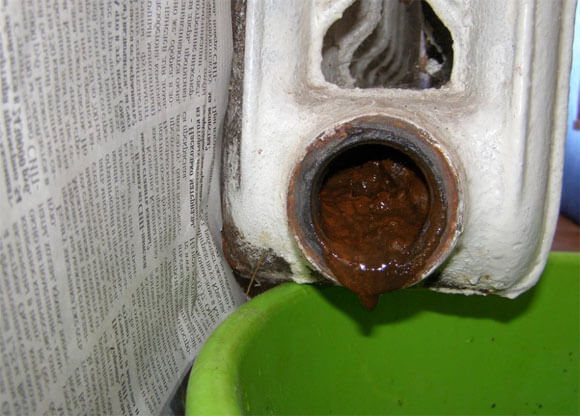


It is better to flush radiators during the warm season, when the system is not working.
This activity may include the following works:
- minor repairs of electric heating boilers;
- restoration of cast iron batteries;
- elimination of leaks;
- replacement of gaskets, couplings, taps and valves;
- flushing pipes;
- cleaning of radiators.
Regular procedures are carried out after the end of the heating season so as not to cause discomfort to the residents of the building. In cold weather, the system can be stopped only in the event of massive malfunctions or the appearance of prerequisites for emergency situations.
Scheduled repairs can be carried out by the staff of the house management plumbers, but the testing and commissioning work is carried out by the specialists of the energy company.
Major overhaul
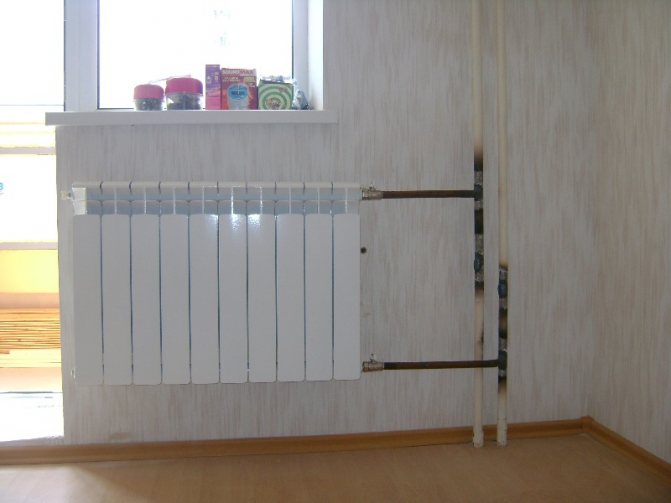


Replacing old radiators with new ones involves laying new pipes and recalculating the entire system
Major repairs are carried out as needed, sometimes 40-50 years after the building was put into operation. The frequency is determined by the degree of wear and tear of heating devices, equipment and communications. This event involves a partial or complete replacement of contour parts, in some cases with a change in the design wiring diagram.
In the process, heating batteries are being repaired or modern productive products are being installed.
In addition, the following parts of the system can be replaced:
- common risers;
- separate emergency sections;
- valves;
- control sensors;
- centrifugal pumps;
- expansion tanks.
Repair of electric boilers is carried out if there is a deterioration in the heating of the premises. The products have a complex structure, so it is advisable to invite specialists to restore them.
The essence and types of crimping
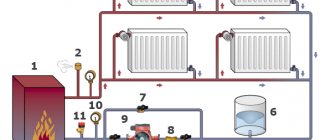
Nowadays, heating is most often carried out by the "water circuit" system. In this case, the heated water circulates through the labors, imparting its thermal energy to the premises. Leaks are unacceptable, the pipeline must be completely sealed for normal operation. Pressing, on the other hand, deliberately creates a volume in the pipe that is greater than normal.
When this is done with air, it is called pneumatic pressing.
When using water, then hydro-pressing. The latter method is considered safer and therefore more popular. For this reason, an example of hydraulic pressing is given as a blank.
When testing, it is recommended not to exceed the pressure inside the pipe by more than 15 MPa. When it comes to raising pressure with water, then there are limitations. The maximum possible pressure should not exceed the normal operating pressure by more than 30%.
In multi-storey buildings, they resort to pneumatic pressing if the pipes are very old and there is a possibility of flooding. But then a level of risk arises and all residents must be notified of the tests being carried out.
The work process is simple, but multi-stage. The algorithm looks like this:
- The necessary materials and equipment are being prepared.
- Draining the liquid that was in the heating system earlier.
- Uploading a new one.
- Create the highest possible test pressure.
- Taking control measurements after 10 minutes.
- Flushing, adjusting the heating system to normal pressure values inside.
- Documentary registration of the work performed, the formation of reports and acts.
But this is how the list of procedures looks only if there are no "thin spots" in the heating system and, accordingly, the tightness in it is not violated. If the pressure drops quickly, does not hold, then the system needs repair work. In such a situation, the specialist performs the necessary actions (pipe replacement, sealing of connections, cleaning, etc.), and then starts pressure testing from the very beginning. Only a heating system that has passed the test is approved for the heating season.
An important nuance! Pressure testing should be carried out after cleaning and flushing the pipes. Otherwise, salt and other deposits inside them can mask possible external damage and breakouts.
If there are deposits of the order of 1 cm on the inner surface, then this reduces the overall heat transfer and efficiency by 15 percent or more of the total indicators. For documentary confirmation of cleaning, a special act is also drawn up.
Operating instructions for heating and hot water supply systems
"APPROVED"
______________________
______________________
________________________
"_____" ___________ 200
INSTRUCTIONS
on the operation of heating and hot water supply systems
1.
Technical requirements for heating and hot water supply systems.
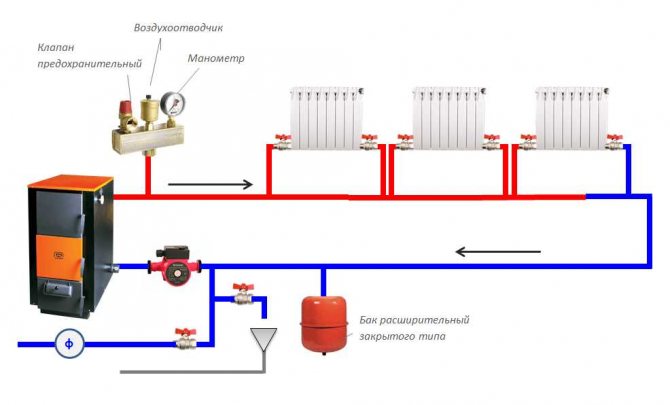
Heating devices must have devices for regulating heat transfer. In residential and public buildings, heating devices are usually equipped with automatic thermostats.
Free access to heating devices must be provided. Installed decorative screens (grilles) should not reduce the heat transfer of devices, impede access to control devices and cleaning devices.
The fittings should be installed in places accessible for service and repair. Heating pipelines are made of materials approved for use in construction
The pipelines laid in basements and other unheated premises are equipped with thermal insulation.
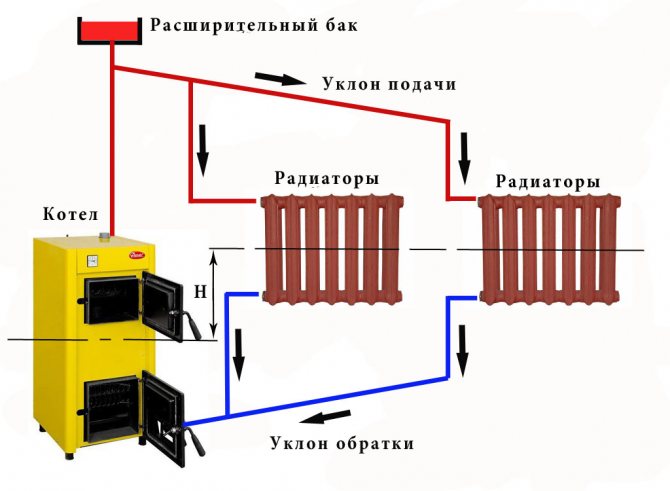
Slopes of water, steam and condensate pipelines should be taken at least 0.002. The system must be designed to be completely drained and filled.
Removal of air from heating systems with coolant water should be provided at the upper points.
2. Operation of heating and hot water supply systems.
When operating the heating system, it must be ensured:
- uniform heating of all heating devices;
- filling of the upper points of the system;
- the pressure in the heating system should not exceed the permissible for heating devices;
- the mixing ratio at the elevator unit of the water system is not less than the calculated one;
The maximum surface temperature of heating devices must correspond to the purpose of the heated room and to the established sanitary norms and rules.
During the operation of heating systems, you should:
- inspect the elements of systems hidden from constant observation (distribution pipelines in attics, basements and canals), at least once a month;
- inspect the most critical elements of the system (pumps, valves, instrumentation and automatic devices) at least once a week;
- periodically remove air from the heating system according to the operating instructions;
- clean the outer surface of heating devices from dust and dirt at least once a week;
- conduct daily monitoring of the parameters of the coolant (pressure, temperature, flow rate), the heating of heating devices and the temperature inside the premises at control points with an entry in the operational log, as well as the insulation of heated premises (condition of transoms, windows, doors, gates, enclosing structures and etc.);
- check the serviceability of the shut-off and control valves in accordance with the approved repair schedule, and remove the valves for their internal inspection and repair - at least once every 3 years, check the tightness of the closure and change the stuffing box seals of the control valves on heating devices - at least once every year;
- check 2 times a month by closing to failure with subsequent opening of the regulating bodies of valves and valves;
- replace the sealing gaskets of the flange connections - at least once every five years.
Before the heating system is put into operation after installation, repair and reconstruction, before the start of the heating season, its thermal test is carried out for the uniformity of heating of heating devices. Tests are carried out at a positive outside air temperature and a coolant temperature of at least 50 degrees. C. At negative outside temperatures, it is necessary to provide heating of the premises where the heating system is installed by other sources of energy.
The start-up of drained systems at a negative outside air temperature must be carried out only at a positive temperature of the surfaces of pipelines and heating devices of the system, providing it with other sources of energy.
The systems must be adjusted after all the developed measures have been completed and the identified deficiencies have been eliminated.
In the process of adjusting the prepared water system, the diameters of the nozzles of the elevators and throttling diaphragms are corrected, as well as the adjustment of automatic regulators based on the measurement of the water temperature in the supply and return pipelines, which determine the actual operating mode of the system being adjusted or a separate heat sink; in steam systems - adjustment of pressure regulators, installation of throttling devices designed to extinguish excess pressure.
The test results are documented in an act and entered in the passport of the system and building.
All the upper points of the distribution pipelines are equipped with air outlet fittings, and the lower ones - with fittings for draining water or draining condensate.
Get full text
Tutors
Unified State Exam
Diploma
The pipelines are made with slopes to exclude the formation of air pockets and the accumulation of condensate.
Flushing of systems is carried out annually after the end of the heating period, as well as after installation, overhaul, routine repairs with replacement of pipes (in open systems, systems must also be disinfected before commissioning).
The systems are flushed with water in quantities exceeding the design flow rate of the heating agent by 3 - 5 times, annually after the heating period, while complete clarification of the water is achieved. When carrying out hydropneumatic flushing, the flow rate of the water-air mixture should not exceed 3 - 5 times the design flow rate of the coolant.
To flush the systems, tap or industrial water is used. In open heat supply systems, the final flushing after disinfection is carried out with water that meets the requirements of the current standard for drinking water, until the indicators of the discharged water reach those required by sanitary standards for drinking water; for condensate pipelines, the quality of the discharged water must meet the requirements depending on the scheme for using condensate.
Connection of systems that have not been flushed, and in open systems - flushing and disinfection is not allowed.
To protect against internal corrosion, systems must be constantly filled with deaerated, chemically purified water or condensate.
Tests for the strength and density of the equipment of the systems are carried out annually after the end of the heating season to identify defects, as well as before the start of the heating period after the end of the repair.
9 Tests for strength and density of water systems are carried out with test pressure, but not lower:
- elevator units, water heaters for heating systems, hot water supply - 1 MPa (10kgf / cm2);
- heating systems with cast iron heating devices, steel stamped radiators - 0.6 MPa (6 kgf / cm2), panel and convector heating systems - with a pressure of 1 MPa (10 kgf / cm2);
- hot water supply systems - with a pressure equal to the working pressure in the system, plus 0.5 MPa (5 kgf / cm2), but not more than 1 MPa (10 kgf / cm2);
- for heaters of heating and ventilation systems - depending on the operating pressure set by the manufacturer's specifications.
The strength and density test is carried out in the following order:
- the heat consumption system is filled with water with a temperature not exceeding 45 degrees. C, air is completely removed through the air vent devices at the upper points;
- the pressure is brought to the working pressure and maintained for the time required for a thorough inspection of all welded and flanged joints, fittings, equipment, etc., but not less than 10 minutes;
- the pressure is brought up to the test pressure, if within 10 min. no defects are detected (for plastic pipes, the time for raising the pressure to the test one should be at least 30 minutes).
The strength and tightness tests of the systems are carried out separately.
Systems are considered to have passed the tests if, during the tests:
- no "sweating" of welded seams or leaks from heating devices, pipelines, fittings and other equipment were found;
Get full text
- when testing for strength and density of water and steam systems of heat consumption for 5 minutes. the pressure drop did not exceed 0.02 MPa (0.2 kgf / cm2);
- when tested for strength and density of panel heating systems, the pressure drop within 15 minutes. did not exceed 0.01 MPa (0.1 kgf / cm2);
- when testing the strength and density of hot water supply systems, the pressure drop within 10 minutes. did not exceed 0.05 MPa (0.5 kgf / cm2); plastic pipelines: with a pressure drop of no more than 0.06 MPa (0.6 kgf / cm2) for 30 minutes. and with a further drop within 2 hours by no more than 0.02 MPa (0.2 kgf / cm2).
The test results are documented by an act of strength and density tests
If the test results for strength and density do not meet the specified conditions, it is necessary to identify and repair the leaks, and then re-test the system.
When testing for strength and density, spring pressure gauges of an accuracy class of at least 1.5 are used, with a body diameter of at least 160 mm, a scale for a nominal pressure of about 4/3 of the measured pressure, with a scale of 0.01 MPa (0.1 kgf / cm2), verified and sealed by the sovereign.
Faults detected during operation are eliminated immediately or, depending on the nature of the malfunction, during the period of current or major repairs.
Routine repair of heat consumption systems is carried out at least once a year, as a rule, in the summer period, and ends no later than 15 days before the start of the heating season.
In winter, at negative outdoor temperatures, in the event that water circulation in the systems stops, the systems are completely drained to prevent defrosting.
Drainage is carried out at the written order of the technical manager in accordance with the operating instructions drawn up for local conditions.
When operating a hot water supply system, it is necessary:
- ensure the quality of hot water supplied for household and drinking needs in accordance with the established requirements;
- to maintain the temperature of hot water at the points of water intake for centralized hot water supply systems: at least 60 degrees. C - in open heat supply systems, not lower than 50 degrees. C - in closed heat supply systems and not higher than 75 degrees. C - for both systems;
- ensure the consumption of hot water in accordance with the established norms.
During the operation of hot water supply systems, you should:
- monitor the health of equipment, pipelines, fittings, instrumentation and automation, eliminate malfunctions and water leaks;
- monitor the parameters of the coolant and its quality in the hot water supply system.
The instruction was developed by ______________________________________________________