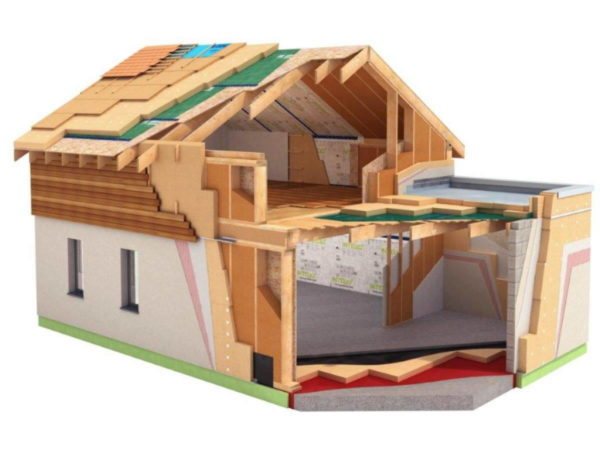
The specifics of the structure of the frame walls and the composition of their materials
Conventionally, the design diagram of any walls of frame houses can be represented as follows:
- Vertical racks
- Horizontal straps
- Insulation
- Finishing materials (external and internal)
As you can see in the photo above (on the right), the thickness of the walls can be very different, and in the following sections of the article we will consider what affects the determination of its dimensional parameters.
Several different technologies are offered in the construction of frame houses. Depending on their characteristics, various materials are purchased for a frame house. It should be noted that they are not selected taking into account only their aesthetic values and appearance.
This article discusses some information about the materials used in the construction of frame houses, their pros, cons and features of choice.
Frame-backfill structures have been used in construction for a long time. Previously, the walls were covered with improvised materials with thermal insulation properties. They used sawdust, slag, but such houses were less durable and comfortable. With the advent of new technologies, the situation has changed dramatically. Now such buildings have many advantages over squared houses.
Frame walls in such houses are distinguished by their strength, reliability, have a good percentage of heat transfer, and retain moisture.
Frame construction in our country has been known for a long time. For more than a century ago, frame-filling technologies were used for the construction of light buildings. For the construction of the walls of the house, boards were used, from which constructions were made in the form of boxes.
The box-walls were covered with improvised heat-insulating materials, most often sawdust and slag. Such buildings were less durable and comfortable than the same houses from a bar. But in recent years, many technologies have appeared that make frame construction so practical that it begins to displace the construction technology from timber for winter houses and summer cottages.

This is due to the appearance on the construction market of new materials with improved operational and technical characteristics and ideally suited for frame technologies. These are oriented strand boards (OSB), MDF, sandwich panels, etc. They have a number of positive qualities:
- Low weight, allowing the use of lightweight foundations as a load-bearing base.
- Ease of installation, as a result of which construction becomes less costly and quick.
- Durability. With the correct installation of frame walls, they can serve no less than walls from a bar.
- Affordable cost. The construction of a frame house will cost much less than the construction of a brick, timber or monolithic building.
OSB sheets or boards are attached to the frame, creating external and internal protective layers. The space between them is filled with heat-insulating materials.
The wall is a kind of layer cake
Layered cake
Advantages and disadvantages of mineral wool
Mineral insulation is successfully used both outside and inside buildings. It can be used to insulate both a residential building and an outbuilding. Sometimes mineral wool is even used for decorative purposes and decorates the facade of houses with it. What other advantages this material has will be discussed below:
- It can be used not only as thermal insulation, but also to suppress sound vibrations;
- There is mineral wool that does not burn;
- During contact with metal, the mineral wool does not rust;
- The material is resistant to high and low temperatures and does not deteriorate under their influence (some of its types);
- It is easy to saw and mount on the walls.


The material can be used not only as thermal insulation, but also to suppress sound vibrations.
Of course, mineral wool has its own small drawbacks:
- Steam does not pass well through the mineral wool. This can cause unwanted condensation to form. Therefore, it is better to attach a special film to the top of the insulation;
- Poor quality material can harm human health. However, if you buy it from trusted manufacturers and choose it correctly, there will be no health problems.
Before buying mineral wool, you need to know exactly in what kind of finish it will be used. Indeed, in each individual case, a specific type of this insulation should be used.


Steam does not pass well through the mineral wool.
Each type of mineral wool has its own strengths and weaknesses.
Glass wool
Glass wool has a number of advantages that affect the choice of the buyer, and therefore the popularity of the insulation remains quite high:
- budgetary cost;
- very good thermal insulation characteristics;
- versatility - you can insulate any element of the building structure and not only;
- well resists mold and mildew - quartz fiber is not the basis for the reproduction of microorganisms;
- environmental friendliness - the material is not allergenic and does not emit harmful substances when heated;
- convenient delivery from the point of sale to the place of work;
- fire safety - belongs to the class of non-combustible materials (“NG” is indicated on the packaging);
- tolerates high temperatures, in connection with which industrial furnaces are lined with glass wool to preserve heat, and chimneys, to prevent the fire of wooden structures;
- simple laying technology - the work can be performed by a home craftsman without experience in performing thermal insulation work;
- low specific weight, which practically does not create loads on the insulated structures.


The disadvantages include:
- high hygroscopicity, which in conditions of high humidity reduces the insulation effect to zero;
- relatively short service life - about 10 years. The manufacturer's statement about a long service life, more than 30 years, is not confirmed by practice - over time, shrinkage occurs even in a dry room;
- low resistance to alkalis - react and break down;
- sting - protection of the body and respiratory organs is required during work;
- attraction for rodents - they like to make moves and arrange nests, despite the taunt.
Slag
For slag, the pluses include:
- low price - the raw material is blast furnace waste, which metallurgists do not know what to do with (only about 10% is recycled);
- high thermal insulation capabilities, still inferior to other types of mineral wool;
- like fiberglass, easy installation;
- good sound absorption of airborne noise, but not shock and structural;
- long service life, but only in dry places;
- biological resistance to microorganisms (mold, fungus).
Disadvantages:
- weak resistance to water with high hygroscopicity, as a result of which sulfuric acid is formed in an environment with high humidity, which destroys the structure of the house;
- high fragility and prickly fiber, requiring protection of the body and respiratory tract with the help of overalls, gloves and a respirator;
- low resistance to vibration loads - settles, sharply increasing thermal conductivity;
- the presence of formaldehyde in volatile compounds;
- loss of properties during sudden temperature fluctuations - sits down.
The above disadvantages practically excluded the use of slag wool in housing construction.
Basalt wool
Thermal insulation material based on basalt fibers took the best properties of raw materials:
- durability - manufacturers give a guarantee for 25-30 years of service with a total service life of at least 50 years;
- the highest resistance to heat: withstands temperatures up to 1000oС;
- weak hygroscopicity - when you try to pass water through the mat, it will not get wet: only 0.095% of moisture is absorbed when soaked for 24 hours.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the insulation of the ceiling inside the bath


In addition, the insulation has a number of other advantages:
- low coefficient of thermal conductivity allows you to effectively insulate any structure at home;
- good airborne noise absorption due to the porous structure and random arrangement of fibers - up to 57 dB. However, little helps against impact and structure noises - the wrong structure of the material;
- not covered with mold and fungus - stone fibers are not the basis for the reproduction of microorganisms;
- it is not damaged, unlike glass wool, by rodents - because of the stiffer fibers, mice and rats do not arrange passages and nests in the insulation;
- versatility - can be used inside and outside the building, insulate a wooden, concrete, brick house or aerated concrete building;
- easy to transport and carry;
- simple insulation technique - work can be done on your own;
- resistance to chemical reagents;
- high elasticity, which allows you to keep the dimensions all the time of service;
- ecological purity - the available formaldehyde resin releases harmful and toxic substances when heated in such a small amount that the human body does not react in any way.
There is one more advantage that few people pay attention to: when insulating a facade or walls from the inside of an apartment (house), decorative plaster can be applied directly to this type of insulation.
Among the disadvantages:
- high price;
- the presence of connecting seams, which over time reduce the level of thermal protection - a relative minus, since it is far from the critical drop in properties (the problem partially arises only when the mats are rigidly fixed to the wall using glue or special dowels);
- in the process of work, unpleasant dust is released, from which it is necessary to protect the lungs with the help of personal protective equipment.
Requirements for thermal insulation material
The frames of houses built using the "Canadian" technology are assembled from OSB or wood. In order for the insulation not to cause damage to structures, it must have sufficient vapor permeability - at least 0.32 Mg.
Fibrous heat insulators - mineral wool materials - absolutely meet this requirement. Popular synthetic insulation materials, such as polystyrene and polymer-based analogs, cannot be used in wooden structures for two reasons:
- Firstly, due to the lack of elasticity, the heat insulator will not be able to adapt to temporary deformations of the wood (shrinkage, increase in volume). As a result, the formation of cracks and cold bridges.
- Secondly, polystyrene and its analogs do not allow the tree to "breathe". This leads to the accumulation of moisture, the appearance of mold and rotting of the structural elements.
When choosing how to insulate a frame house, in addition to vapor permeability, additional properties of a heat insulator should be taken into account. The following indicators are welcomed:
- fire safety;
- environmental friendliness;
- low thermal conductivity;
- shrinkage resistance;
- minimal water absorption.
Tips and tricks for wall insulation with mineral wool
Below will be presented tips from experienced craftsmen for wall insulation with mineral wool. They will help to carry out installation work on insulation with high quality:
- Before starting work, you must carefully read the step-by-step instructions for insulation;
- Do not forget about creating a vapor barrier after laying mineral wool inside the frame or when attaching it directly to the wall itself;
- It is important to wear protective equipment to protect your eyes, hands and respiratory tract from small particles of cotton wool;
- Make sure that there are no gaps between the battens and the slabs through which cold air and moisture can penetrate.
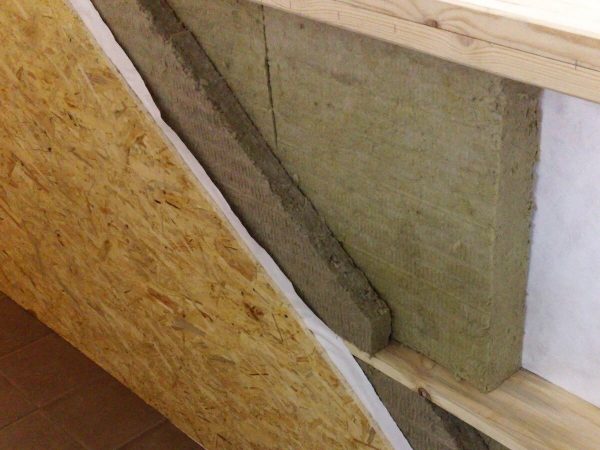


Make sure that there are no gaps between the battens and the slabs through which cold air and moisture can penetrate.
If you follow all these recommendations, anyone will be able to insulate walls with mineral wool without outside help.
Basic materials
When choosing a material for construction, an engineering calculation should be done well. There are several design options:
- Frame sheathing;
- Frame-panel board;
- Sip panels;
- Frame-backfill.
This method involves the use of boards for the construction of the frame. The structure is sheathed in addition to the timber. The thickness of the boards is 25 mm, the size of the chipboard boards ranges from 16-20 mm.
We offer you to familiarize yourself with: How to insulate the ceiling in a bath with your own hands
The inside of the walls is insulated. The thickness of the walls depends on the insulation. The finish and the distance between the boards are also taken into account.
The construction method has many advantages. Structures are erected quite simply and quickly. A small number of workers will be required, no special equipment will be needed.
The thickness of the walls is determined by the dimensions of the timber and the selected insulation material. On average, it is about 150 mm.
For construction, special panels are purchased, which are manufactured in factories. The thickness of one panel varies from 50 mm to 200 mm.
This is the most economical construction option. In this way, utility rooms are mainly erected, but they are also used for residential buildings. The walls of the structure are insulated with slag, sawdust, expanded clay or cellulose filler. The frame is sheathed with a croaker.
The thickness of the walls depends on the interior and exterior finishes, on average 150 mm.
Technology and methods of wall insulation
Insulation works outside and inside the building are carried out using different technologies.
Outside
There are several ways to insulate the facade:
- system "well";
- "Wet" method;
- ventilated facade.
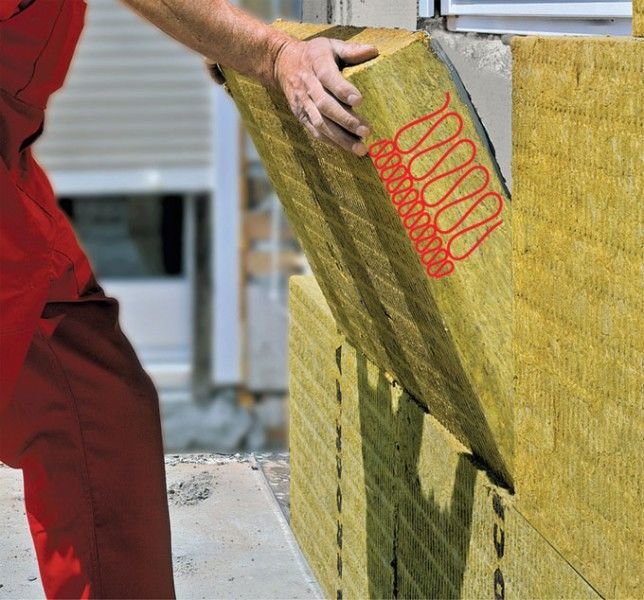
In the first method, the insulation slabs are placed inside the wall. In this case, the structure of the latter looks like this: a base wall made of bricks or foam blocks (inner part) - fiberglass or basalt wool - silicate brick (outer cladding).
The "wet" method involves fixing the insulation mats on glue with additional fixation with 5 special dowels and applying decorative plaster over the stone wool with a layer of 2-3 cm thick.
The ventilated facade method is used when insulating wooden houses from a bar and high-rise buildings when facing walls with slabs. Its essence is in stuffing the crate over the entire area of the walls and placing insulation sheets in the formed cells. The mats are fixed either with glue or plastic dowels with a wide head.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with What is the thickness of plywood for the floor on the logs
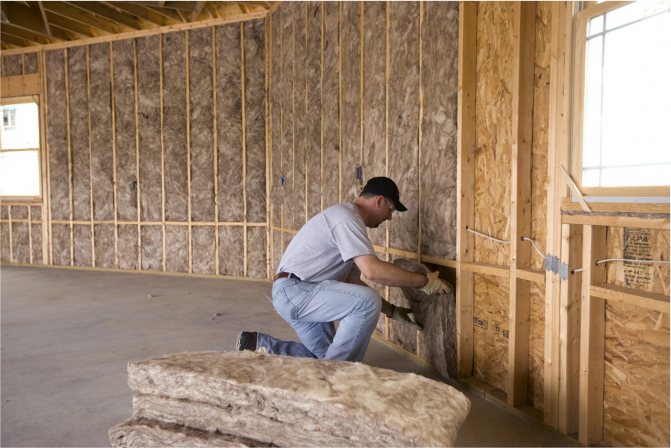
From within


To insulate the walls from the inside of the apartment, a frame is made of a metal profile or wooden slats. Mineral wool slabs are tightly driven between the edges of the sheathing and covered with plasterboard or plywood. Sometimes decorative plaster is applied, but in this case, the insulation is additionally attached to the wall with glue and plastic dowels.
Having chosen the desired thickness and other properties of mineral wool for wall insulation, it's time to move on to choosing the method of fastening. When it comes to outdoor work, there are three main methods to do this: a well system, a wet method and a ventilated facade.
The first point implies such a design: mineral wool is laid between bricks (or other building materials) inside the wall.A ventilated facade is an option for wooden houses, when a frame is erected around the perimeter of the building, and mineral wool is tightly packed inside it. Fastening the mineral wool to the wall is easy; this requires either plastic dowels or an adhesive.
As for the wet method, then according to it, the plates should be fixed directly to the surface of the wall, and not inside it. Let's consider this option in more detail.
Choosing the optimal insulation
Mineral wool heat insulators are the most acceptable option for insulating a frame house. Materials are made from different raw materials, which determine the basic characteristics and scope. The general advantages of all types of mineral wool include: light weight, fire safety, resistance to pests and the necessary vapor permeability.
The main disadvantage of fiber insulators is hygroscopicity. To preserve the properties of the insulation, mineral wool needs high-quality vapor and waterproofing.
The main component of the insulation is rocks of volcanic origin: basalite, diarite and basalt. Stone wool is a completely non-combustible material that can withstand temperatures of 1000 ° C. The heat insulator retains its physical properties for 40-50 years. The main advantages of basalt-based mineral wool:
- low thermal conductivity - 0.36-0.42 W / m * C;
- resistance to mechanical stress;
- good noise insulation characteristics;
- resistance to temperature fluctuations.
The composition of the insulation includes hydrophobic additives that provide quick moisture removal. Basalt heat insulator is produced in slabs, the density of the material is 35-50kg / cu. m. The disadvantage of stone wool in comparison with fiberglass counterparts is less elasticity and susceptibility to rodents.
The basic components of a heat insulator are glass breakage and sand. The addition of binders makes it possible to form rolls from the finest fiberglass. Approximate dimensions of mats: thickness - 100 mm, width - 1200 mm, length - 10 m.
It is equally important to calculate what density the insulation should be used. For thermal insulation of frame buildings, this parameter of glass wool should be at least 15-20 kg / cu. m.
Features of glass wool:
- high elasticity - the material easily assumes and quickly restores the given shape, which is very convenient during installation;
- vibration resistance;
- not susceptible to mold formation and unattractive to rodents.
Like rock wool, fiberglass is fire resistant. However, in comparison with the previous insulation, glass wool loses on several points:
- Unsafe material - installation is carried out in a respirator and protective clothing. The fibers are very fragile and a lot of "glass" dust is emitted during cutting.
- Shrinkage of the heat insulator - over time, the risk of cold bridges formation increases.
A new word in the segment of thermal insulation materials is ecowool. The material is 80% recycled paper. Additional components: boric acid and sodium tetraborate. Minor ingredients provide protection against microorganisms and reduce flammability.
Distinctive features of ecowool:
- Ecowool is a loose insulation, and therefore the technology of its application is fundamentally different from working with sheet mineral wool. To create a heat-insulating layer, special equipment is required - a pneumatic inflatable device.
- With poor-quality insulation of the walls of a frame house, there is a risk of ecowool shrinkage, which is fraught with the formation of non-insulated zones.
- The material is not recommended for use near open sources of fire, chimneys and chimneys. A protective layer of basalt foil-clad refractory mats or a fencing made of asbestos-cement slabs is required.
The main advantages of ecowool: environmental friendliness, the possibility of insulating hard-to-reach places and high soundproofing qualities.
This group is represented by mats and boards made of wood-fiber materials. The technical and operational characteristics of the insulation are at a fairly high level:
- good thermal insulation - thermal conductivity is comparable to that of mineral wool;
- preservation of the structure even when wet - the properties of the insulation do not change when moisture is absorbed in the amount of 20% of its own weight;
- high strength and excellent sound insulation - protection against impact and "air" noise;
- sufficient density and elasticity - the insulation is attached between the frame racks without additional clamps;
- environmental friendliness of the material and safety of installation work.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: How to knit a loofah for a bath with your own hands: simple and affordable ways
Wood-fiber insulation "breathes" and helps maintain a comfortable microclimate in the house. The disadvantages of a heat insulator include: high cost and flammability.
Types depending on the material of manufacture
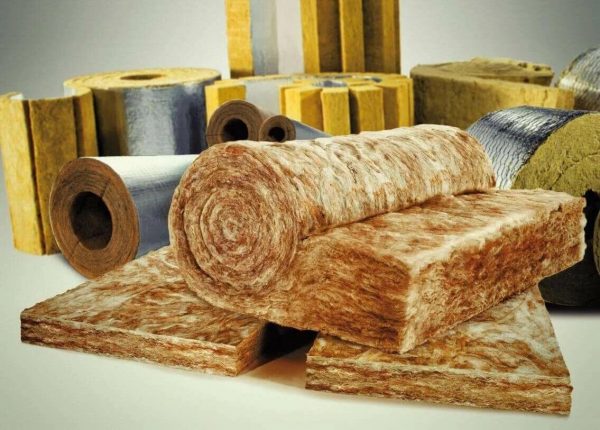
The 3 options for thermal insulation plates made of mineral wool are related to - glass wool, stone and slag wool.
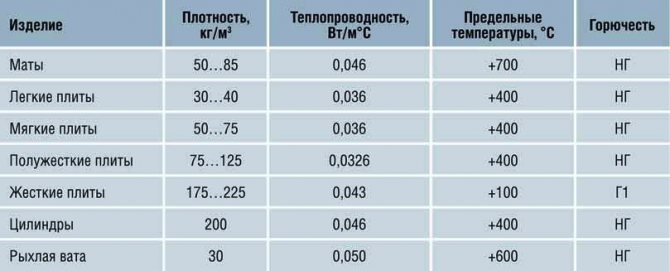

These varieties have a specific width of mineral wool, fiber length and technological parameters that establish their popularity for use in a particular area.
Slag
Slag wool is produced from electrode blast furnace slag, has a fiber size from 4 to 12 microns and a length of 16 mm. Thermal conductivity is 0.48 W / mK with increased hygroscopicity. Mineral wool dimensions - 500 × 1000X50 mm. This modification is hydrophobic and more than others has a predisposition to moisture, which does not make it possible to use it on external roofing insulation, and its low level of fire safety excludes its use in attic rooms.


Another disadvantage is that the fibers are rather brittle, and it is possible to work with such material only with gloves. Despite all this, given the good flexibility and uniform thickness, it is quite convenient to work with such a material. In addition, the slag is not heavy, even a decent amount of mats does not form a load on the roofing system. It has a very light structural structure, thermal conductivity 0.048 W / mK.


Due to its own texture, it has a high vapor permeability and hygroscopicity, and therefore, with this type, it is necessary to use waterproofing.
Glass wool
Glass wool - refers to budget building materials for thermal insulation. At the same time, it has a very good density and elasticity, with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.050 W / mK. It is made from the same consumable material as ordinary glass - sand, soda, dolomite and limestone. Fiber size up to 15 microns. The dimensions of the mineral wool insulation in the slabs are 1250X600X50 mm.
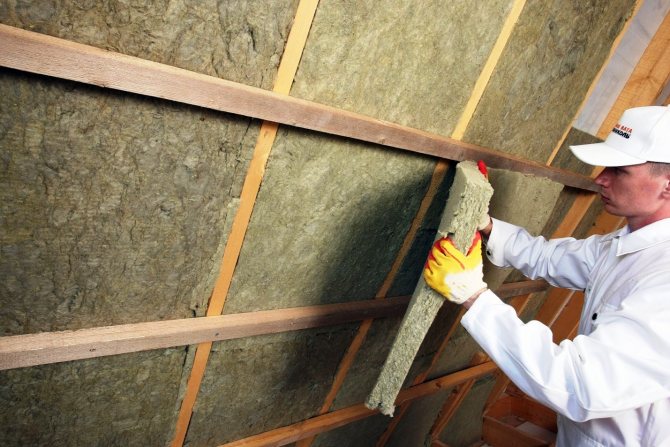


The permissible temperature regime is + 450C. The main advantage is the relatively low price. The disadvantages are low performance and a high risk for the respiratory organs of humans and the skin, which makes it necessary to quickly perform insulation work, with dense protection of the laid layer with surface material, while the employee must use special clothing, respirators and goggles when working.
Ventilation gap
The ability of the material to pass water vapor indicates the presence of ventilation. If its indicator is low, it becomes necessary to build a forced draft. Walls made from natural materials naturally let in steam. Artificials do not have this characteristic.
When only mineral wool is used as insulation, then such a building will pass moisture well. To protect the wall from external condensation, a membrane film is mounted from the street. It prevents steam from penetrating into the insulating material and brings it out well.
With a competent construction of the frame, mineral wool with a mandatory slot for ventilation is used as an insulating material. The gap prevents the formation of liquid on the cladding.
Dimensions and shape of mineral wool
Stone wool for wall insulation, like any other, is made in two formats - a roll and a slab.
Roll wadding is a long strip of material. The length is from 7 to 10 meters, and the width is a maximum of 120 cm. The thickness is 0.5 cm. These parameters make it easy to transport mineral wool and fix it to the wall. Cotton wool in rolls is usually sold of lower quality and, accordingly, at a lower cost.
Thermal insulation of walls with stone mineral wool in the form of slabs is even easier. Plates are designed specifically for flat vertical surfaces. Typically, each unit is 120 cm long and 100 cm wide. Thickness from 3 cm (for floor) to 10 cm (for roofs). It is very easy to install such slabs; you do not need to hire a professional for this.
DIY video instruction on thermal insulation
In most cases, mineral wool in the form of mats is used to insulate frame structures. Therefore, the subsequent instruction will be based on the work with this particular material.
First of all, you should understand the structure of the insulating cake, calculate the material and prepare the surface for laying. It doesn't matter which side to start work - from the outside or from the inside. Some people think that it is more convenient to perform thermal insulation from the side of the street. However, weather factors must be taken into account.
Standard structure of a thermal insulation cake with the sequence of layers from the inner cladding to the facade of the house:
- Interior decoration.
- OSB board.
- Vapor barrier.
- Insulation layer.
- Windproof membrane.
- Lathing made of bars for arranging the ventilation gap.
- OSB board.
- External cladding.
The recommended pitch of frame beams is 580-590 mm. This range is optimal when using standard 60 cm wide mineral wool mats. According to the standards, the thickness of the insulation for a temperate climate is 150 mm. To fill the space between the beams of 15 cm, it is advisable to use mineral wool of two standard sizes: 50 and 100 mm.
Surface preparation is reduced to cleaning from dust, removing protruding nails and blowing out the cracks with polyurethane foam between the frame elements. Before fixing the insulation, it is necessary to check the wooden structures for dampness, dry problem areas with a construction hairdryer.
First you need to prepare a base for laying insulation. From the inside of the house, this role will be performed by a vapor barrier film and OSB boards.
Procedure:
- Roll out a roll of insulating material and cut it to fit the walls of the house.
- Fix the vapor barrier canvases one by one to the vertical racks of the frame using a stapler. Installation rules: the insulating strips are directed perpendicular to the wooden beams, the minimum overlap is 10 cm.
- Check the tightness of the protective layer.
- Cut OSB boards with a jigsaw.
- Fix the panels to the frame, overlapping the vapor barrier foil.
In the future, OSB boards will serve as the basis for applying the finishing of the walls.
An important advantage of using mineral wool or wood fiber insulation is the ease of fastening with your own hands. Both heat insulators are resilient enough, so they do not need additional fixation. The slabs are inserted between the frame posts and are held in place due to the slight difference in dimensions.
So that the thermal insulation layer does not lose its effectiveness over time, it is necessary to follow certain rules for its installation:
- Laying is done in two layers, the slabs are staggered. The second row of mineral wool should overlap the joining seams of the first in the middle. This technique prevents the appearance of "cold bridges" that contribute to the accumulation of condensation and moisture.
- Insulation boards need protection from strong wind and precipitation. By analogy with the inner wall, the heat insulator is sheathed with a special hydro-windproof membrane.
The film insulation is fixed with a stapler. For a more secure attachment, you can use the counter-crate system.
Bars attached to the top of the wind barrier create the necessary air gap between the thermal insulation material and the exterior trim. Further insulation of the facade depends on the material of the finishing cladding.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Wood processing in the steam room
Under the block house and siding of various types, slabs of moisture-resistant OSB are nailed onto the crate, to which guide bars are attached. Artificial, natural stone or façade tiles are laid directly on oriented strand boards.
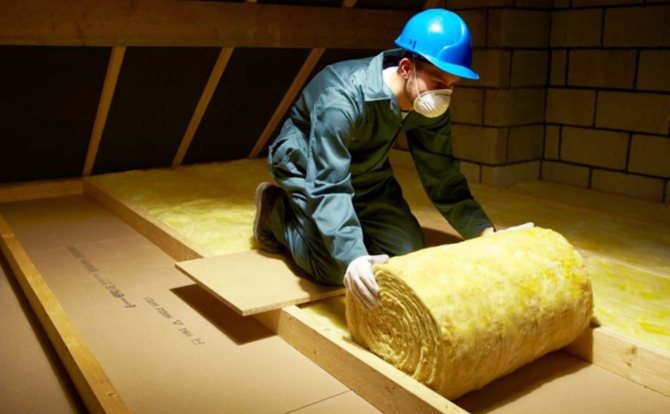
High-quality roof insulation is of great importance in preserving heat. Thought-out and competently executed thermal insulation of the roof of a frame house saves 25-30% of thermal energy. A popular option for insulation is the placement of mineral wool between the rafter legs. The roofing cake must be supplemented with a vapor barrier film and a diffusion membrane.
Let us describe in sequence how to properly insulate the roof:
- Pull a water-repellent diffusion film along the outer end of the rafters. Secure the membrane with a counter batten.
- Lay insulation on the inside of the rafter system. Thermal insulation is placed in two layers 100 mm thick, the installation scheme is a checkerboard layout.
- Cover the mineral wool with a vapor barrier film, observing the horizontal laying of the vapor barrier in the direction from bottom to top. The overlap of the film insulation is 5-10 cm.
- Sheathe the ceiling with OSB, plasterboard, plywood or clapboard. External roofing is carried out using counter battens. Sheathing beams are nailed onto the slats, creating a ventilation gap. OSB boards or roofing material (slate, corrugated board, metal or flexible tiles) are attached on top.
A lot of heat also goes through the base of the house - about 15-20% of the heat costs are on the floor. Alternatively, you can organize a water floor heating. However, it is easier and cheaper to insulate the base with mineral wool.
Work progress:
- Cover the sub-floor with roll-up waterproofing, observing an overlap of 5 cm.
- Fasten the canvases together with reinforcing tape, walking along the joining lines.
- Install a log system of boards on top of the waterproofing.
- Cut the insulation under the cells in the logs. The size of the heat insulator should exceed the distance between the boards by 1-2 cm - this gap is necessary for tight joining and eliminating gaps. Insulation thickness - at least 200 mm.
- Cover with a vapor barrier film, and lay plywood or a fine plank floor on top.
The described technology is suitable for insulation of interfloor or attic floors.
More information about the technology of home insulation is described in the video.
Varieties of mineral wool
If it is necessary that the cold does not penetrate into the house, and the heat does not come out, the dwelling is insulated with mineral wool. All of its types have fibers in their structure. They arise during the manufacture of this material. Certain minerals are cooled and the resulting composition is shaped into long filaments. It is for the raw materials that were used directly in the processing process that several varieties of mineral wool are distinguished:
- Stone - is made from the hardest minerals (basalt, porphyrite or granite) and is needed to insulate houses from the outside. This type of material has the highest strength and wear resistance.


This type of material has the highest strength and wear resistance. - Slag - the basis of such material is metallurgical waste. In terms of quality and efficiency, it is lower than stone mineral wool.After all, it is subject to changes in high and low temperatures. Such mineral wool is suitable for insulating summer cottages, summer kitchens and outbuildings;
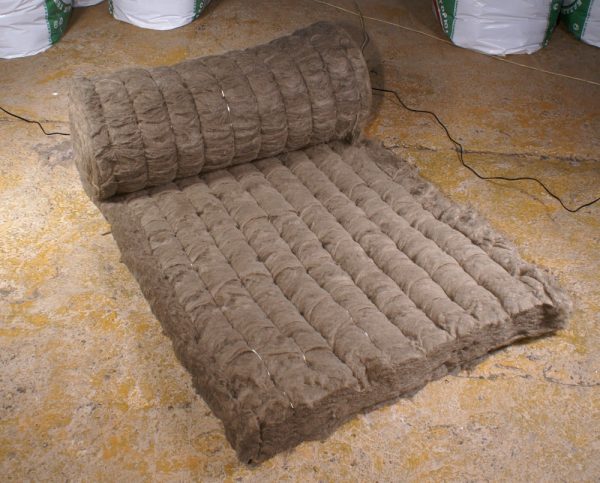


Such mineral wool is suitable for insulating summer cottages, summer kitchens and outbuildings. - Glass - the main component in it is incandescent glass. Dolomite, limestone and sodium bicarbonate are also added to it. Such material is not subject to combustion and can be used in those buildings where it is important.
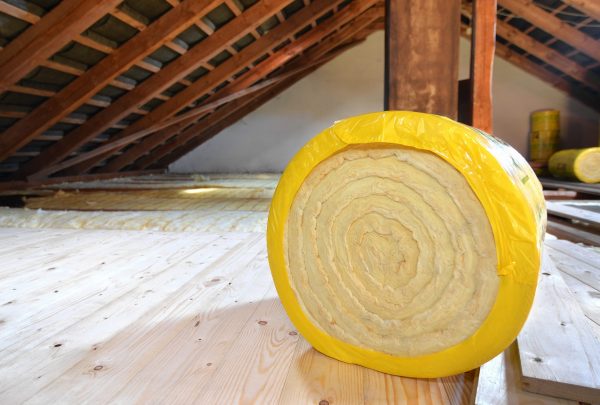


Such material is not subject to combustion and can be used in those buildings where it is important.
In its shape, the mineral wool can be rolled and made in the form of slabs. Roll wadding has the following dimensions:
- The length of the insulation for the walls is 6-9 meters;
- The width of the insulation is 100-120 centimeters;
- The thickness is one and a half centimeters.
Slab mineral wool is 120 centimeters long and 1 meter wide. Its thickness varies from 2.5 to 10 centimeters. Thicker material is used for roof insulation, while thinner material is used for floor and walls.
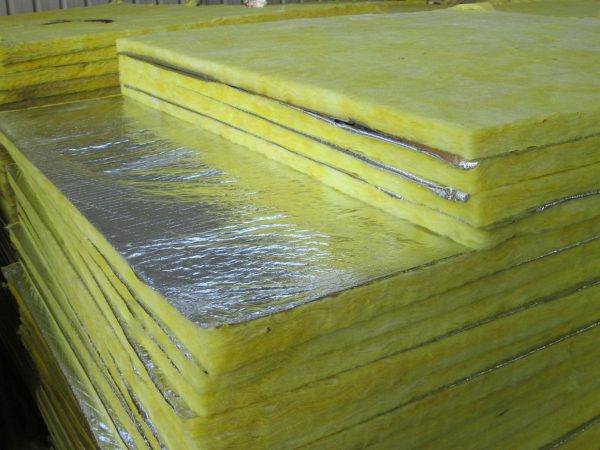


Thicker material is used for roof insulation, while thinner material is used for floor and walls.
Any type of this insulation has fibers. These fibers are formed during the cooling of the crushed minerals, which are then pulled into long thin threads. The material is classified based on the initial raw materials:
- Stone. Made from granite, basalt or porphyry. Wall insulation with basalt mineral wool is best suited for buildings that must be in perfect condition for many decades. This mineral wool has the highest strength.
- Slag. It is based on waste from the metallurgical industry. The quality of such a product is lower than that of the previous subspecies. Slag mineral wool for wall insulation does not tolerate sudden changes in temperature. Typically used as an inexpensive option for use in barns or summer buildings.
- Glass. It is made from molten glass to which limestone, dolomite and soda are added. The most resilient variant, it resists vibration well. Suitable for buildings where fire safety is especially important.
Insulation of walls from the inside with any mineral wool requires analysis - which option is suitable in a particular case. Having decided on the type of material, we move on to its form.
Recommended insulation thickness
The optimal thickness of the insulation depends on the region of residence and the selected material.
If you decide to use mineral wool, then for the southern regions this characteristic should be above 150 mm, in the northern regions of the country - at least 250 mm.
Using polystyrene, make calculations as follows: in the north of the country, the recommended thickness is 150 mm or more, and in the southern regions it should be more than 50 mm.
When calculating the thickness of the insulation material, additional characteristics should be taken into account. This is the material of the inner and outer sheathing, the windproof layer, the density of the joints. After all, the heat resistance of the walls directly depends on the quality of the work performed.
general information
Mineral wool is a fibrous material obtained from metal slags or molten rock.
Mineral wool for effective wall insulation has been used for more than a decade, but now manufacturers are producing much higher quality products than before. Reduced the harmfulness of the material to the environment and the human body, increased thermal insulation properties.
There are several subspecies of mineral wool for wall insulation, we will now consider them.
A variety of methods for using ecowool
The second most popular material for thermal insulation of frame buildings is ecowool. But here it is better not to experiment and entrust the work to professionals. Mechanized backfilling will ensure the required density and uniformity of laying. There are three methods of using ecowool:
- dry spray;
- wet application;
- glue method.
The dry method is applicable for horizontal surfaces, inclined closed cavities, filling intermediate floors and non-separable structures. The density of ecowool laying with this method is 45-65 kg / cubic meter. m depending on the slope.
Wet technology is suitable for vertical open walls. Ecowool flakes are moistened and applied to the surface under pressure. The density of the insulating layer is about 65 kg / cubic meter. m.
The glue method is similar to the previous one, but an adhesive component is added instead of water. The advantages of the technique: high adhesion of the insulation to the wall, elasticity of the material and low deformation after drying. The glue method is indispensable for thermal insulation of flows from below, the option is also suitable for processing walls.
The issue of house insulation must be considered even at the construction stage. It is more profitable from a financial point of view and more technically correct. Structural elements are insulated as the building is erected, and there is no need to overhaul the building after commissioning.
Tags: frame, wall, thickness, insulation
«Previous post
External wall insulation
The procedure for the wet method is as follows:
- Clean the surface, get rid of all indentations and irregularities.
- Fasten the basement cornice.
- Glue mineral wool with a special compound.
- For added security, secure it with dowels.
- Apply reinforcing mesh.
- Prime the surface thoroughly.
- Plaster it.
- Finally, paint it in any color you like.
If this option is not suitable and you are inclined towards classical insulation, then build a ventilated facade according to our instructions:
- Saturate the wall with antiseptic. If you notice rot, then it also needs to be treated with a special solution.
- Remove slopes and / or trims.
- Dry the walls for at least 24 hours.
- Lay a layer of membrane with high vapor permeability in such a way that the smooth side is in contact with the mineral wool. The membrane can be omitted if the wall is perfectly flat.
- Use self-tapping screws to fix wooden slats on the wall; their thickness should be equal to the thickness of the insulation, and the distance between them should be 2 cm less than the width of the mineral wool slab.
- In the resulting crate, lay the material itself for insulation.
- The next layer is a material for protection from wind and water. You can fix it with a stapler.
- To form a ventilated gap, counter battens are also nailed on top of the crate - the facing material should be at a distance of 6 cm from the insulation.
Finally, install new platbands and slopes (the old ones will not work because the walls have increased in thickness).















