Duct requirements
The main task of the ventilation pipe is to ensure the passage of the required amount of gases without seeping into the surrounding space with minimal loss of initial pressure and over a long period of operation. To ensure the fulfillment of the stated conditions, there are requirements for the duct arrangement.

Pipe and ventilation structures must comply with the following indicators:
- free movement of air masses at the design speed of the project;
- tightness of the stave and connections to maintain a stable thrust and avoid mixing of oncoming flows;
- noiselessness - aerodynamic sound should not exceed the sanitary standard of 25-35 dB;
- resistance to high air humidity and corrosive gases contained in the removed stream;
- fire safety - pipe fittings and straight sections are made of non-combustible materials;
- compactness and light weight - the system should not clutter up free space and require complex fastening to the supporting surface.
Smoothness of channels, thermal insulation qualities, ease of assembly and combination with the overall design of the room have a positive effect on the properties of air ducts. The stiffness of the roof exhaust pipes is important as they are subject to wind loads.
Plastic
Recently, plastic air ducts have begun to be used quite widely, and the point is that this product has a lot of advantages. High performance is provided by unique tightness, excellent resistance to aggressive media and active substances, as well as strength.
The plastic from which the air duct structures are made does not lose its properties when exposed to ultraviolet rays, withstands a wide temperature range from 0 C to +85 C, and is environmentally friendly. The plastic air duct is easy and quick to install; it can be cleaned and disinfected as needed.
Varieties and characteristics of ventilation pipes
Domestic air ducts are often made of plastic or metal. But there are much more options: traditional brick and asbestos-cement, ceramic and sandwich pipes, fabric from technical textiles. The characteristics of some species are worth considering in more detail.
Metal hoods
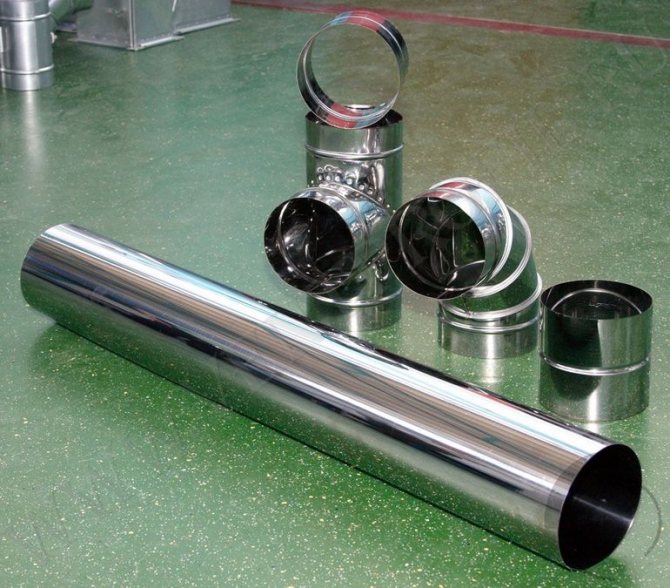
They have a number of advantages: strength and long service life, smooth inner surface, on which soot and dust deposits do not accumulate, immunity to high temperatures and corrosive effects of transported gases. They are made of different alloys - black steel, galvanized and stainless steel. The usual thickness of products is 0.5-1.2 mm, the maximum is 5.
Recommended: Photocatalytic Air Purifier


Sheet aluminum is rarely used, more often foil is used. Straight sections of air ducts with a diameter of up to 50 cm and a wall of 0.55 mm are made of tin, and for large sections, the thickness is taken as 0.7 and more millimeters.
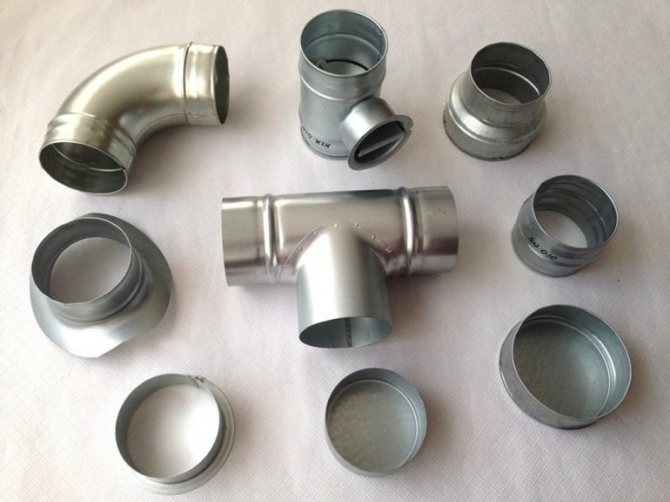


Each of the subspecies of metal ventilation pipes has its own characteristics:
- Welded black steel air ducts are installed in smoke exhaust systems with a possible temperature jump. The section can be round or rectangular with dimensions Ø10-160 cm, square 100 x 100 mm and above. Wall thickness - 1-2 mm, section length - 1.25-2.5 m, flange connection. All fittings and straight-line ones are covered with anti-corrosion primer GF-021.Automatic electric arc welding guarantees airtightness of the seam.
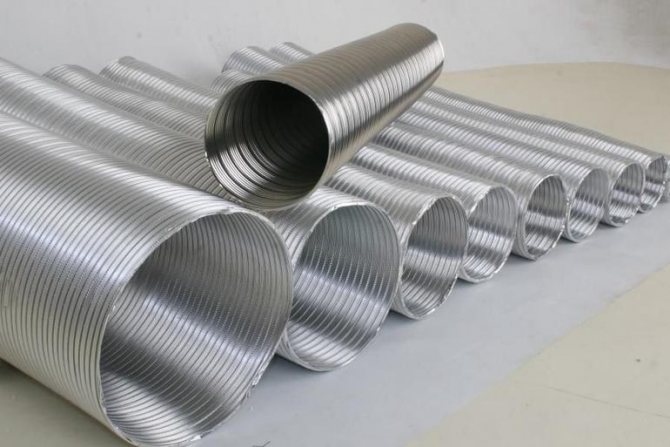
- Galvanized pipes, in comparison with previous products, have better protection against the corrosive effects of transported gas mixtures and are not afraid of contact with moisture. Round air ducts are made straight-seam or spiral-wound. For the rest of the parameters, the characteristics coincide with those of ferrous iron pipes.
- Stainless steel hoods are used to provide an object with an aesthetic appearance, hygienic properties and to move highly toxic and corrosive gas environments. In the manufacture, they use the techniques already mentioned, as well as the technology for the production of corrugated sleeves from multilayer foil with a size of 0.12−1.0 mm. In addition to flange connections, it is possible to join sections into a socket, lock fastening and welding with a special thermal gun. Compared to other metal air ducts, stainless ones are tougher and can withstand high temperatures - up to 900 ° C.
All steel chimneys have a long service life and high strength. They operate at temperatures ≥140 degrees and rarely clog due to their perfectly smooth surface.
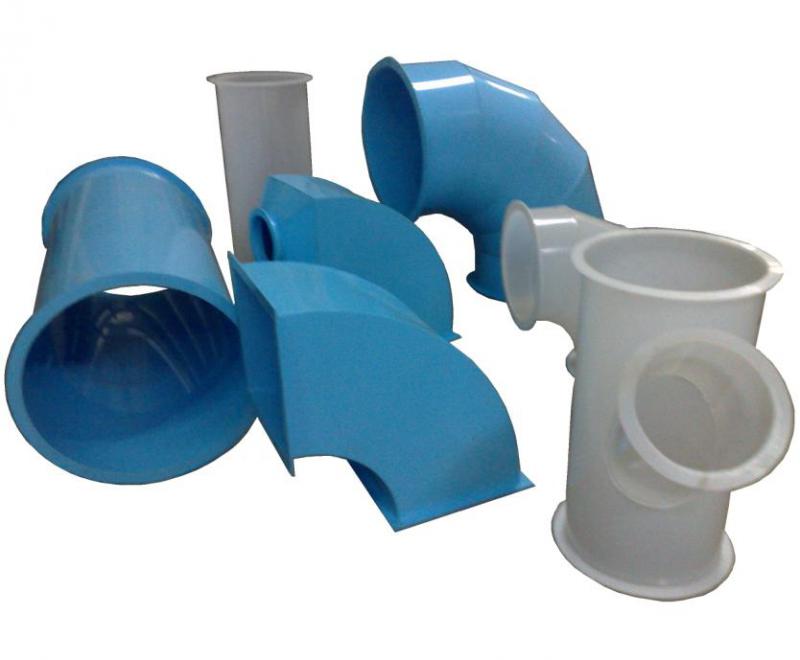
Plastic ducts
These pipelines are only a partial alternative to metal air ducts (the use of plastics in the hoods of heating devices is prohibited).


Polymer pipes are made of round, rectangular and oval sections and the following materials are used:
- PP - propylene: does not react to organics, acids and alkaline solutions;
- HDPE or HDPE - pliable polyethylene with ordinary properties;
- PVDF is a fluoroplastic resistant to all acids and designed to work under negative (from -40º) and hot (up to + 140ºC) temperatures;
- PVC - heat-resistant smooth vinyl pipes, can be rigid or in the form of a flexible corrugation, withstand up to 80 ° C and are not afraid of ultraviolet rays.
The sections are connected to each other by means of a socket, and are attached to the fans and heaters using flanges. Air duct cross-sections are standard, round diameters vary in the range of 100-1250 mm.
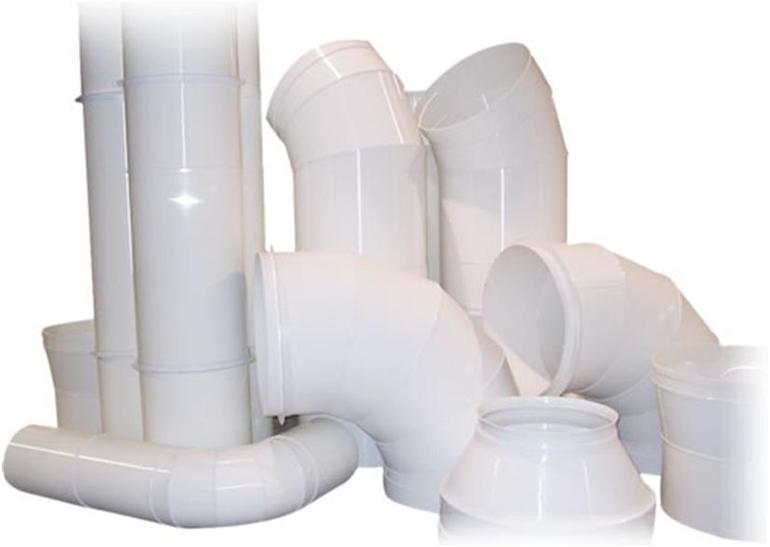


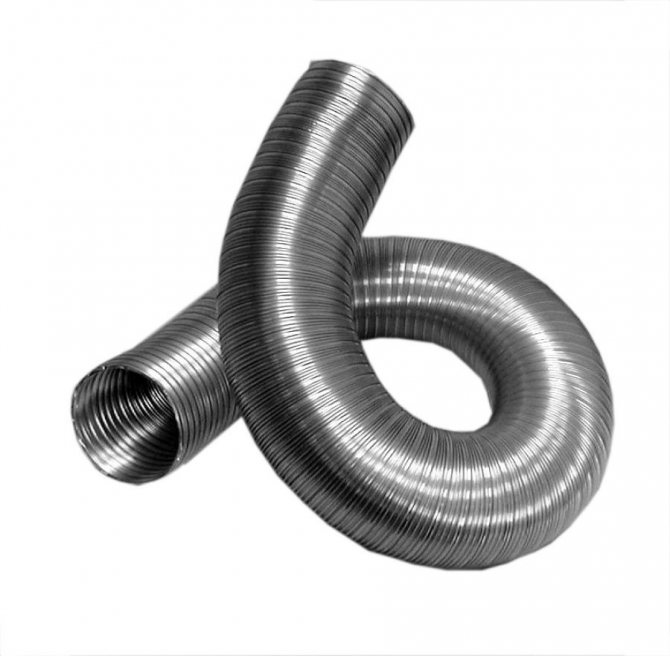
Polymer hoods have many advantages over metal sections: they can be cut with an ordinary hacksaw, and joined by heating the ends. Light weight, no seams and smooth surface - all these properties allow you to choose lower power fans. Noise from air movement inside the plastic duct is audible. The length of the lashes is 3-12 m.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with: Varieties and rules for choosing a recirculation hood
Combined sandwich pipe system
This design is a smaller diameter pipe inserted into a larger channel. The space between them is filled with a heat-insulating layer - non-combustible basalt wool. Both casings are made of stainless steel. Cheaper options - the outer pipe is galvanized, the inner one is made of black iron. Other combinations of metals are possible.
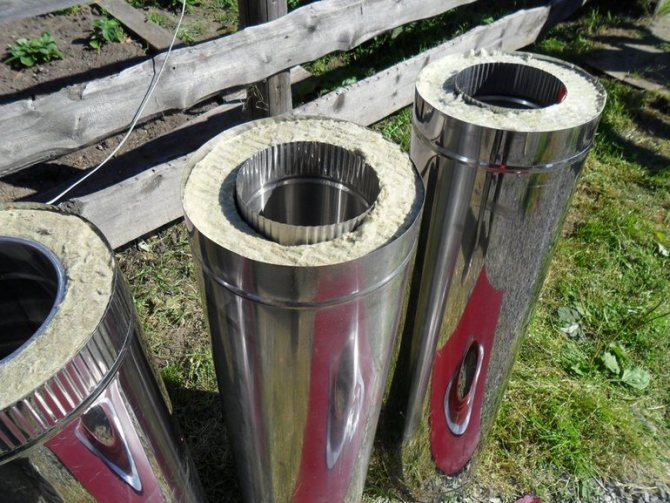


Insulated air ducts are installed to extract flue gases from a stove, fireplace or heating boiler. The device has a high degree of fire safety.
Advantages of sandwich pipes:
- the versatility of the design allows for installation inside and outside the building;
- ease of assembly - even an inexperienced craftsman can install a chimney from a sandwich section;
- the smoothness of the surface and the insulating layer eliminate the possibility of condensation and accumulation of soot inside the pipe;
- the lightness of the structure allows to ensure its stability without the construction of an additional foundation, which speeds up installation and reduces costs;
- an attractive look that can beautify the design of a building or a particular room.
The connection of the duct sections is carried out by the socket method.There are two disadvantages of sandwich pipes: high cost and relatively short service life - up to 15 years.
Welding methods


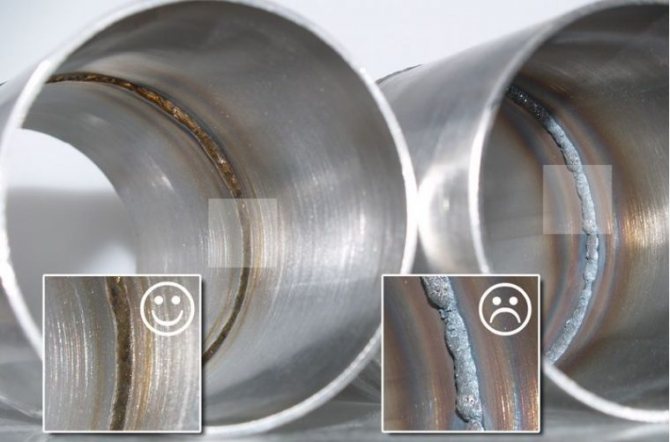
The welded method of connecting the duct is considered the most reliable
The craftsmen do not often have to connect the air ducts to each other using welding, since the process is expensive. This method is used if special requirements are imposed on the tightness of the structure. The welding process can be manual or mechanized.
Manual
Electric arc welding is used if the material thickness is more than 1.5 mm. Gas equipment is necessary if the metal is 0.8 mm thick. The second method is rarely used.
Mechanized
The mechanized welding method can be semi-automatic or automatic. It is used in businesses.
Selecting the required parameters
When determining the route and performing the air pipeline, it is necessary to solve a complex problem of the optimal combination of many factors. The main positions are rigid or flexible ducts, round or rectangular and of what diameter.


More about these areas:
- The duct is chosen according to the degree of compliance depending on the operating conditions and the complexity of the route. In a rigid mesh, corner connectors are used to change directions. Flexible sleeves provide a hassle-free fit over any vector. There is also a combined option, when a corrugated pipe is joined to a rigid straight section. It should be borne in mind that the corrugated walls reduce the speed of the air stream.
- The cross-sectional shape is determined by the throughput: the round configuration allows more air to flow with less resistance. In rectangular profiles, part of the corner area remains unused, which makes it necessary to accept a larger standard size of the duct. But flat pipes are easy to hide behind furniture or ceiling panels. The best option is an oval cross-section, which combines the advantages of a round and rectangular duct ends (high permeability and design characteristics).
- The dimensions of the ventilation duct for household ventilation systems are most often taken as Ø100 mm, which corresponds to a flat 55 x 110. Outlets of fans, grilles and kitchen hoods are made for this size.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with: Adjustable ventilation grilles
From a technical point of view, a length of 3 m is considered normal for household air ducts. An increase in the air path leads to a decrease in its throughput, since each additional meter eats up 10% of the productivity.
Local and general ventilation of residential and industrial premises
According to the service area, the types of ventilation are divided into two classes: local and general ventilation. If the maximum concentration of harmful emissions falls on well-defined areas of the room, then local ventilation is used. It is necessary to remove contaminants from the area of a specific workplace, and does not allow the exhaust air to spread to the rest of the territory. In domestic conditions, the most striking example of this type of mechanical ventilation is a kitchen hood. This type is called local exhaust ventilation. In production shops, this problem is solved with the help of local suction. Pollution is removed according to the principle of natural movement - hot harmful vapors are removed upward, and cold harmful gases become heavy and sink down. Local supply ventilation is used in the form of air showers, air oases and air curtains.
An example of mechanical local ventilation is a cooker hood
If a not well-defined area needs cleaning, the local system will be ineffective. In this case, general ventilation is used.It serves the entire premises or a significant part of it. A general exhaust system removes heat, gases, moisture, dust, liquid vapors and odors from buildings. The most basic type of such a system is a fan with an electric motor. It is installed in a window or doorway. A more complicated option is the use of fans with an exhaust air duct.
The general exchange supply system supplies clean air and distributes it throughout the entire volume of the room. A feature of the general exchange supply system can be called its ability to compensate for the lack of heat. To do this, the supply air is heated before being supplied. Most often, an equal amount of air is removed from the room and supplied. There are times when more is extracted, and the lack is compensated for by the overflow of air from neighboring rooms.
Scheme of arrangement in the office of general ventilation
Installation of ventilation pipelines
A preliminary ventilation design is developed, the parameters of the future system are calculated by the amount of air and the speed of its movement in the channels. The specifics of equipment and component parts are determined, purchases are carried out. Installation of ventilation pipes is carried out after marking the route and in accordance with the rules of SP 60.13330 and 73.13330.2012 concerning ventilation and air conditioning.


When assembling pipelines, the following points must be observed:
- stretch the corrugated sleeves completely;
- avoid sagging, since otherwise the pressure in the ventilation system is lost;
- be sure to ground the air ducts to avoid the build-up of static charges;
- install only rigid pipes if the vertical distance is more than 2 floors (this requirement applies to basements, concrete structures and the places where air ducts meet the ground);
- lay the radius when turning ≥2Ø of the pipe;
- use special metal adapters and sleeves in passages through walls.
During work, care must be taken, and in case of accidental damage, the section must be replaced. The air ducts are fastened to the walls and ceiling. At the same time, the parallelism of the centerline of the pipes with respect to the bearing surface is maintained. Compliance with the rules of installation and operation of the ventilation system will provide a comfortable microclimate in any room.
Connection types
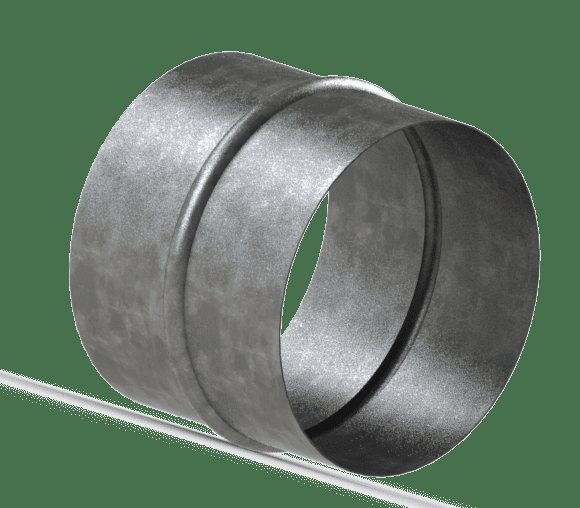


Duct nipple connection
The connection of ventilation pipes to each other is carried out by a welded or flanged method. In addition, the elements can be fixed with a bandage, nipple or sleeve.
Welded
It is possible to connect fragments of the air duct by welding if they are metal, while the thickness of their walls exceeds 1.5 cm. This method is most often used in industrial premises in which harmful gases accumulate. In this case, the seams should be as tight as possible. For galvanized materials, highly professional welding is required to avoid corrosion in the seam area.
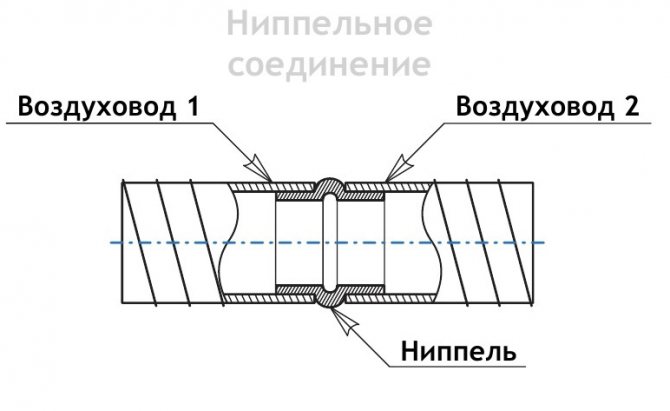
Nipple
A nipple is a part of a pipe with a raised rib in the middle. It is inserted into the main structure. The same rib is used for fixation. Another section of the duct is put on the product. The joint is sealed with metallized tape.
The nipple connection is carried out using a sleeve. Its diameter is larger than the main pipe. The coupling can combine 2 structural fragments. The rib in this case is on the inner surface of the element. This method is used to connect round ducts.
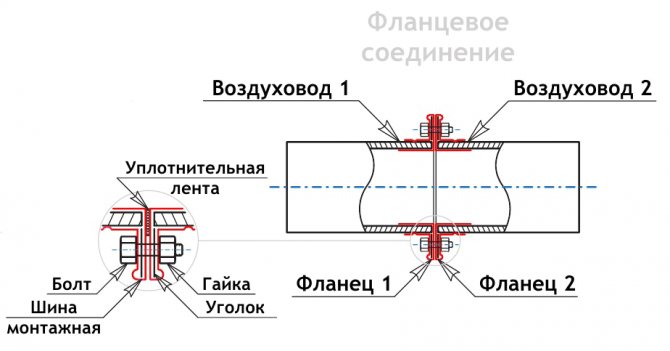
Flanged
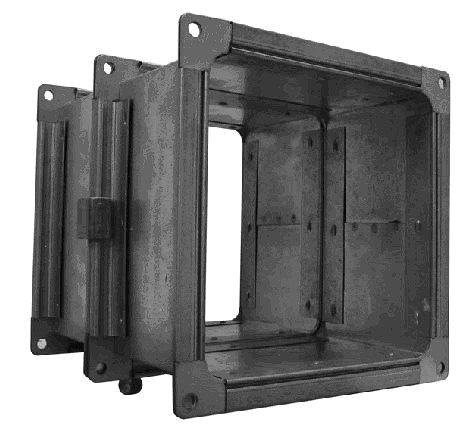


Flange for joining two parts of the duct
According to GOST, pipes can be connected using the flange method. For fastening parts, spot or solid welding is used. The flanges are fixed between themselves with nuts and bolts, as well as rivets. To ensure reliable sealing of the weld, it must be painted over.A sealing gasket is placed between the steel elements. Although efficient, flanged duct connections are labor intensive and expensive.
Bandage
The bandage method of joining the structure is in demand at chemical industry enterprises. It provides high reliability of the joint, but the manufacturing process itself is expensive, therefore it is unpopular for domestic use. The bandage is attached over the connecting seam. Before this, the ends require flanging. The bandage space is filled with a chemically inert sealant. This method is used to connect plastic ducts to each other.