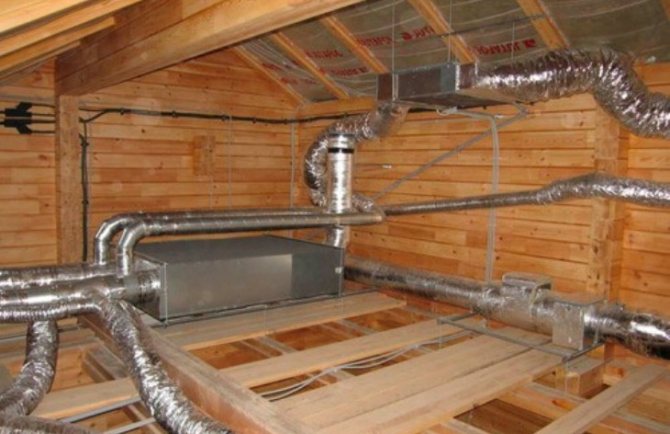
It is necessary to understand that, speaking about such a process as thermal insulation of air ducts, one must take into account the fact that these elements of the ventilation system are divided into household and industrial ones. The former are used in air extraction systems for residential and office buildings, the latter in industrial facilities or in buildings with an extensive ventilation network, where powerful fan units are used. For example, in the buildings of train stations, airports, shopping centers. Accordingly and the approach to thermal insulation in each case will be individual.
The benefits of insulating air ducts
To begin with, there are certain building codes according to which thermal insulation measures are carried out. They are determined SNiPom 2.04.14-88, in which it is clearly indicated where and how ventilation insulation should be carried out. This primarily applies to unheated premises and streets.
The thermal insulation of the ventilation system is carried out with one single purpose - not to reduce the service life of the air ducts.
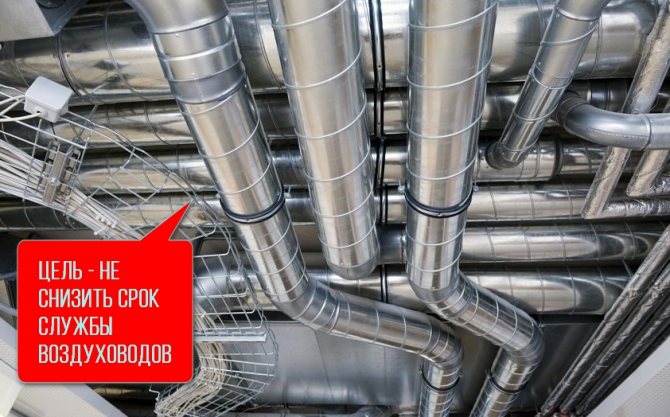

The thing is that the ventilation itself is the ventilation of the premises, in which the air inside the building moves at a speed of 1 m / s. And for this to happen, you need to install two holes (or more), into one of which fresh air from the street enters the inside of the structure, from the second the spent air is thrown out. So the whole structural part of the ventilation is a circuit for decoupling the air ducts operating on the hood, that is, warm air from the building will move along them.
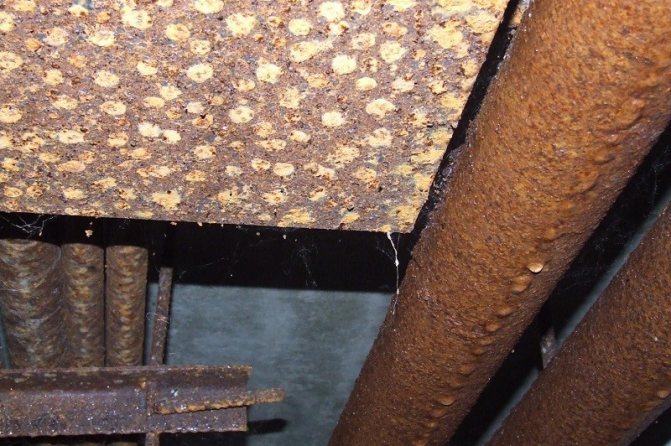
In unheated rooms or outdoors, warm air will begin to condense, forming moisture on the inner walls of sheet steel ducts. Metal corrosion occurs, which leads to a rapid failure of the entire system. The insulated air ducts prevent the contact of warm air with a cold environment, which means there is no condensation.

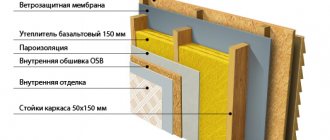
The SNiP rules clearly stipulate what kind of insulation and what thickness must be used in order to create all the conditions for high-quality and efficient operation of the ventilation system. And since the modern market offers a huge variety of thermal insulation materials, it is necessary to deal with them and determine the best insulation for ventilation pipes.
Thermal insulation functions. Why insulate air ducts
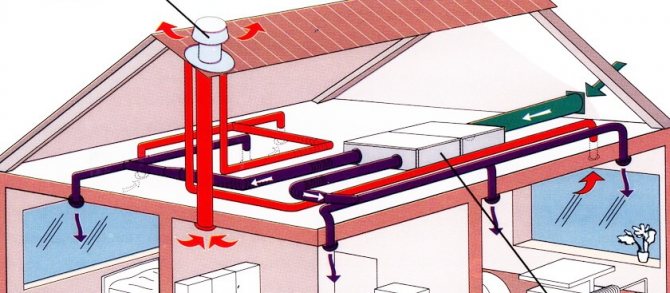
No modern building can do without an extensive network of air ducts for a wide variety of purposes. Air ducts are used in ventilation, air conditioning and heating systems (air heating, air exchange in the boiler room, smoke removal).
All of them are pipes in which air circulates. They differ only in the method of circulation, the air flow rate and the temperature of the pumped air. Regardless of whether the pipes carry cold or heat, the air ducts need to be insulated. An insulated air duct removes several problems at once: heat exchange, condensate, noise and vibration, fire protection. Fireproof, soundproof, heat-insulating - the used heaters can be both universal and highly specialized. The general principles for performing duct insulation are the same for most cases.
Thermal insulation and vapor barrier of air ducts to reduce heat transfer and heat loss
The task of ventilation, air conditioning and air heating systems is to bring air of a given temperature to the desired room. To reduce cold and heat losses in the duct, it is necessary to minimize heat exchange between the external environment and the air in the pipes. Ideally, this heat transfer should be zero.For these purposes, heat and vapor barrier are made throughout the air duct system. The materials used in thermal insulation must have four main properties:
1. low thermal conductivity; 2. low heat dissipation; 3. low vapor permeability; 4. low coefficient of moisture absorption.
Installation of thermal insulation of air ducts is carried out from the outside. It is necessary to lay the insulation so that there are no cold bridges.
Thermal insulation of air ducts to prevent condensation, corrosion, mold and mildew
Indoor and outdoor air masses have varying degrees of humidity. Combined with the temperature difference, this leads to the formation of unwanted condensation. Condensation, in turn, causes corrosion of the metal parts of the air ducts, leads to damage to the interior decoration of rooms and furniture, contributes to the emergence and spread of fungi and mold. This violates sanitary and hygienic standards and reduces the service life of the equipment. Therefore, thermal insulation of air ducts is a standard protective process, without which no construction can do today. The dew point can be both inside the duct and outside. To prevent the negative impact of moisture on the metal, it is necessary to calculate the optimal thickness of the insulation for thermal insulation of air ducts of all systems - air heating, ventilation, air conditioning.
How to insulate
To answer this question, it is necessary, as mentioned above, to divide ventilation systems into two categories. The first includes engineering networks in private homes, shops, restaurants and other consumer service points. That is, where the ventilation system itself is a small and not too branched pipe distribution. It works either according to the natural method of air removal, or forcibly with the help of fans. The second category is industrial ventilation networks. They only apply to the forced system.
Self-adhesive insulation for room air ducts
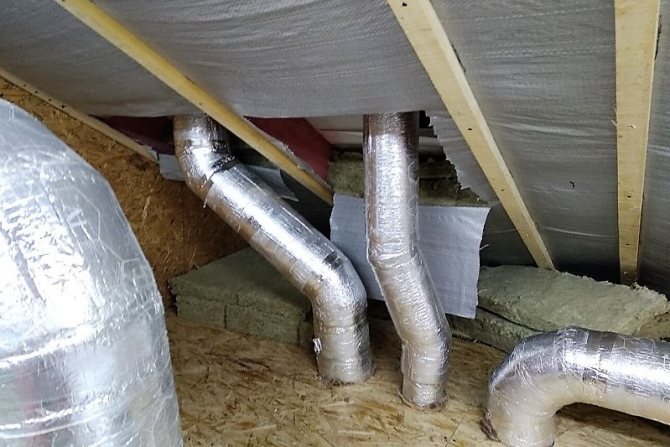
I would like to dwell separately on self-adhesive insulation for ventilation, as a very convenient option for doing work with your own hands. First of all, it is necessary to designate that this is "C" brand penofol. On the one hand, the foamed polyethylene is covered with foil, on the other with polyethylene film, on which the adhesive is applied. The latter is covered with another layer of film, which is removed before installation.


Self-adhesive heat-insulating material is simply cut to the required size, which must correspond to the perimeter of the duct, and then they close the pipe with it, pressing it with hands to its surface. The edges of the insulation are folded up to 5 cm and covered with foil tape.
Installation of thermal insulation
Consider several thermal insulation materials in terms of answering the question of how to insulate ventilation pipes in a private house. With penofol everything is clear, we will immediately make a reservation that this is the simplest option.
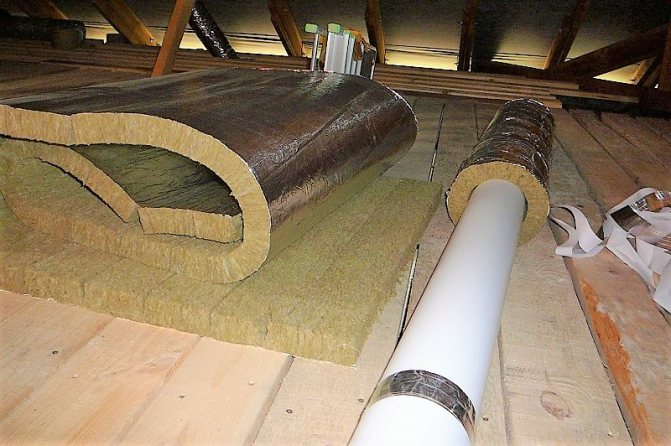
Mineral wool insulation
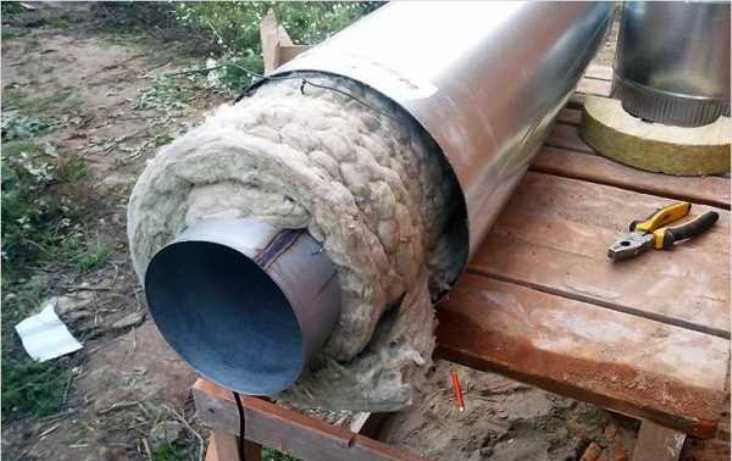
Insulation of a ventilation pipe with mineral wool requires the manufacturer to understand that this material is hygroscopic. Therefore, all work is carried out in the following order.
- All piping wrapped in a waterproofing membrane without gaps and gaps. Complete tightness of the coating.
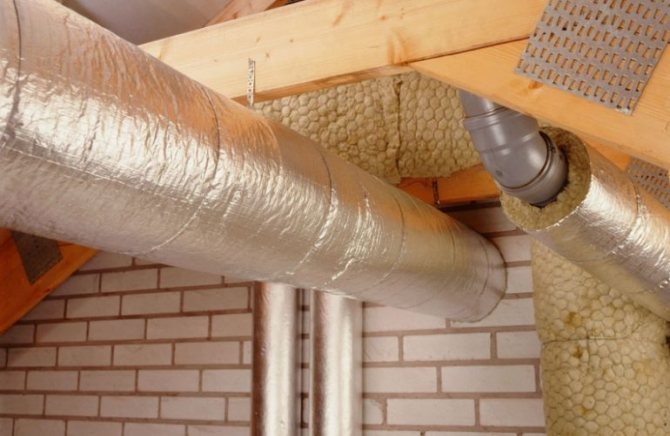
- Mineral wool is wound overlapping with respect to the strips to be laid. The thickness of the paving is determined by the above designated SNiP.
- Wrapped over another layer of waterproofing.
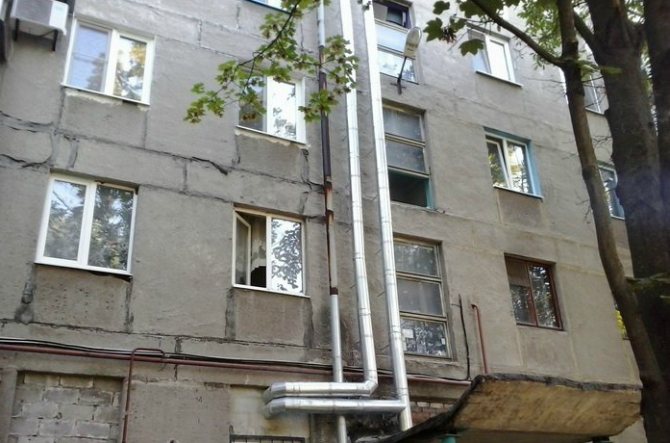
- If the air duct passes outside, then it is installed on top of the thermal insulation threshold boxbetter made of tin.
By the way, the installation of boxes is a prerequisite for assembling an outdoor area, which will provide not only protection of the system, but also effective air exchange inside the building.
If the ventilation pipe is not circular, but rectangular, then you can use mineral wool in mats to insulate it. They are cut to the required dimensions, they are laid over the pipe and pulled together with a clamp, tape or knitting wire. Waterproofing must be installed. Here it is important to tightly lay the pieces of cotton wool so that there are no gaps between them. The most inconvenient place is the outer corners of the ducts. After pulling together the main heat-insulating coating, they are filled with pieces of material cut from the mat to the required dimensions.
Why is it needed
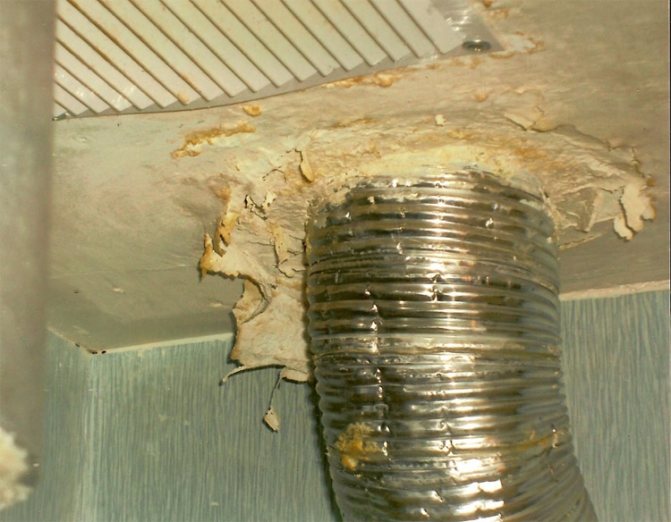
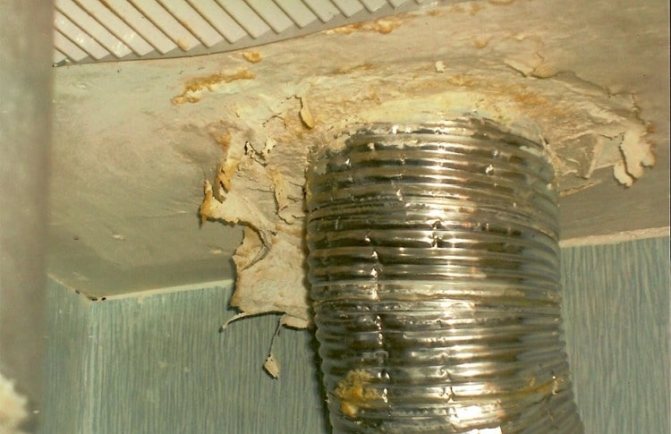
The key word is condensation. Without insulation, it will inevitably form on the inner surface of the ventilation duct and drain along the inner walls, flowing through leaking joints into the main walls and ceilings. The consequences are obvious: dampness of the walls and ceiling, the appearance of mold and their gradual destruction.
The effect of condensation on the ventilation duct itself depends on what material it is made of:
- Galvanizing can be damaged if the protective anti-corrosion layer is broken. Which, however, is inevitable when cutting a sheet.
- PVC and corrugated aluminum pipes tolerate contact with moisture without any consequences.
Another nuisance associated with moisture condensation is the gradual freezing of frost on the inner walls of the ventilation duct outside the warm room. For several weeks of operation in severe frosts, the pipe clearance can decrease from 100 - 150 millimeters to zero.
Where does the condensate come from?
There are two reasons for its appearance.
- Human life activity is associated with excessive air humidification. When washing dishes, preparing food, doing laundry, even just breathing, the atmosphere is saturated with water vapor.
- Meteorologists have long used the concept of relative humidity. The higher the air temperature, the more water vapor it can hold. 100% relative humidity is the maximum amount of water that can be vaporized in the air. However, if the temperature changes - and with the same amount of steam in the air, the relative humidity will change. With significant cooling, it can exceed 100%, after which the excess water will inevitably begin to condense on a surface with a low temperature. In our case, on the inner surface of the ventilation duct.


Consequences of moisture condensation in the ventilation duct.
A special case
In production, there is often a need for forced ventilation with a high air flow rate. In particular, for the removal of harmful volatile production products, sawdust, shavings, etc.
The noise of the air and what it carries can become a serious problem in some cases. In factory premises, ventilation insulation often pursues the goal not so much of combating condensation as of banal sound insulation. The methods, however, apply the same.
Warming with expanded polystyrene
Polyfoam or expanded polystyrene is a slab material, so they are insulated with a rectangular hood. The technology of thermal insulation of ventilation pipes is exactly the same as in the case of mineral wool mats. The only thing that can be noted is the optional laying of waterproofing layers, that is, they can not always be used. It all depends on the density of the material used, which varies between 40-75 kg / m³.
The denser the material, the higher its ability not to absorb moisture.


For example, for PPS-40 it is better to lay waterproofing, for PPS-60 it can no longer be used. And one more point regarding the insulation of ventilation pipes in the attic, as in an unheated room. This is a tight joint of insulation boards with filling of cracks and gaps with polyurethane foam.
Is it always necessary to insulate pipes in the attic
If the family has sons or daughters, it is worth making an effort to adapt this part of the house to the needs of the children. A tent house, a place for witchcraft - all this is an attic.It will be easier for a bachelor, bachelor, lover, a young family to do household chores, to take care of their well-being, if the attic is turned into a room with a minimum level of risk of injury. Dust, through cracks, moisture, open pipes interfere more than a low ceiling, poor lighting.
The attic can be a mystery room. It will be possible to revise the old photo album out of the box, sing your favorite song, turn on karaoke right here. Or he will become a room in which there is something frightening, just the thought of him will ruin the mood. The owner chooses what he should be. Hide the pipes, decorate them - the first thing to do in the attic. More precisely, the first thing to do is to take care of thermal insulation.
Any pipe will freeze in winter. By insulating all the pipelines available in this part of the house, you can achieve the following goals:
- will extend their service life;
- improve functionality;
- optimize the life support system in the house.
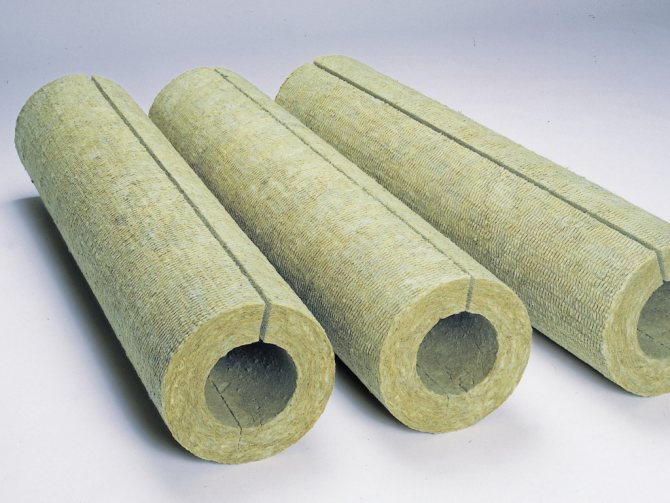
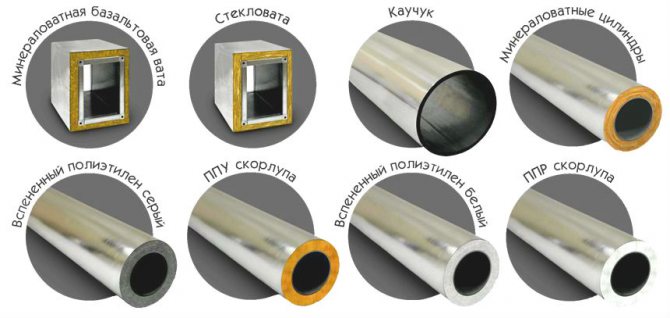
Heat insulating cylinders
Insulation of ventilation pipes can be carried out using special cylinders (shells), which are made of mineral wool, expanded polystyrene, polyurethane foam and polyethylene foam. They are used only for round pipes. They are selected by diameter and are of several varieties:
- One-piece with a longitudinal section;
- Consisting of two parts;
- Three;
- Four.


The type of cylinder is selected taking into account the diameter of the duct. The larger it is, the more parts the shell has. For example, a plastic pipe with a diameter of 110 mm, which is often used in the ventilation system of private houses, is closed with a cylinder in the first position. It is simply opened at the gap and put on the pipe, fastened with tape.
Insulated pipes for ventilation using this technology are a guarantee of their effective protection, plus ease of work. It should be added that the exit of the duct to the street, as well as the street area, can be insulated with cylinders. The only requirement is the installation of a protective box.


As for the price component of the insulation material, it should be noted that the cheapest shells here are made of mineral wool, polyethylene and polystyrene. The most expensive polyurethane foam. Manufacturers now offer this type of foam rubber material. Insulated ventilation pipes for them are the best, but very expensive option.
Insulation types
For insulation work on air ducts, any materials for this purpose can be used, which are used for walls, floors or ceilings. However, there are separate samples specially designed for this purpose.
Special heat insulator
For example, such a material is synthetic foam rubber, produced in the form of elastic flexible sheets. It perfectly keeps the given shape, serves for a quarter of a century, does not burn at all and has soundproofing properties.
When moisture gets in, the rubber does not rot, and its thermal conductivity reaches 0.036 W / m C.
Traditional materials
Traditional heaters include:
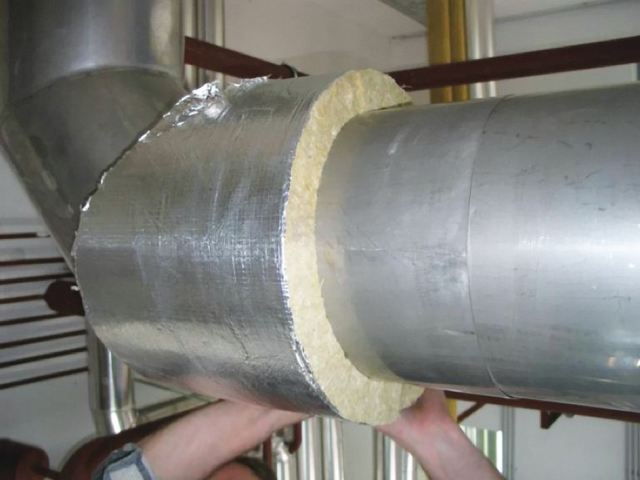


- mineral wool (0.035 - 0.045 W / mS, operation for at least 30 years);
- basalt fibers (0.030 - 0.048 W / mC, lasts about 50 years);
- glass wool (0.035 - 0.05 W / mS, without replacement up to 25 years);
- foamed polyethylene (0.04 W / mS, service life up to 80 years);
- polyurethane foam (0.02 - 0.03 W / mS).
Air valve
In modern practice, it is not uncommon to find an insulated air valve, when installed, no thermal insulation is required for the air duct system. This structure consists of a frame, a heating element and swivel blades. With its help, the supply of heated air is regulated. To some extent, the valve is a kind of insulation.
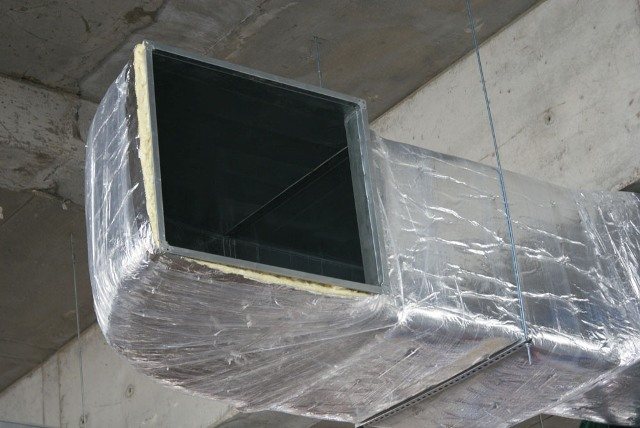


During drawing in, the air heats up, and the line between cold and hot air masses disappears.Each individual ventilation system requires its own valve, however, careful calculation will be required, without which it is impossible to choose the right device.
conclusions
So, when choosing insulation for ventilation pipes, it is necessary to take into account the shape and size of the latter. Do not forget about the simplicity of the work carried out if they are done by hand.
It is better to give preference to penofol than to mess with polystyrene foam plates, cutting and adjusting them to the size of the ducts.
Of course, the price of thermal insulation for ventilation will also play an important role. Therefore, it is recommended to choose the best option for the ratio of price and thermal conductivity. Let's go back to the thermal insulation of air ducts with penofol. For example, the thermal conductivity of mineral wool-penofol: 0.045-0.049 W / m K, that is, almost the same. The price of mineral wool-penofol for 1 m²: 1200-100 rubles. So much for the difference.