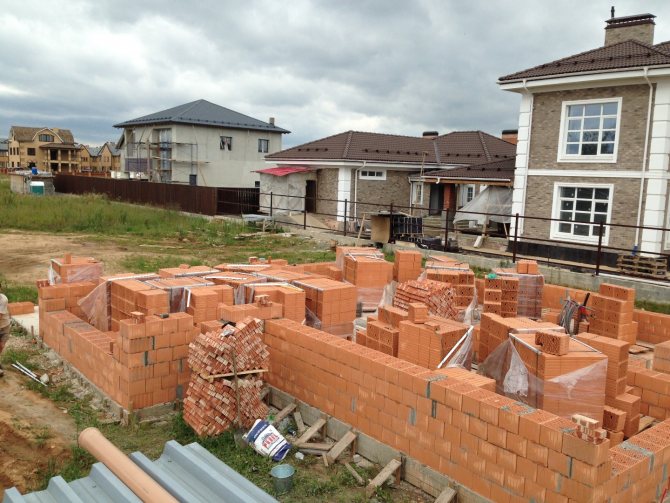
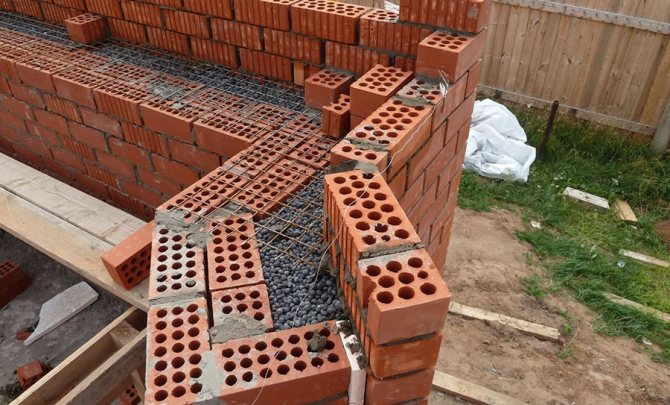
Brick building options include different types of masonry. The more and more popular is the well masonry of brick walls, which allows:
- save costs on expensive bricks;
- solve at the same time the issue of thermal insulation at home;
- reduce the weight load on the foundation of the building;
- reduce costs for external and internal finishing (without insulation).
The construction of multi-storey buildings by the method of well masonry in places with an increased humid climate is prohibited.
What is it?

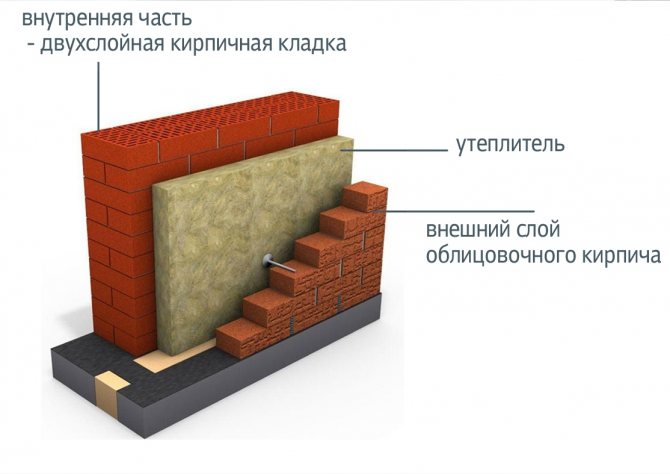
The masonry got its name from the cavities (wells) that are laid out in the process. When forming the walls, they are filled with heat-insulating materials, increasing the thermal stability of the structure. The thickness of the walls decreases, but thermal insulation, when properly installed, allows you to save not only during construction, but also on heating during the operation of the house. At the same time, two parallel walls are being conducted, which, according to different methods, in certain places connect the diaphragms - brick lintels. The lintels are a connecting link and take on the function of stiffeners.
Additionally, reinforced mesh or reinforcement is used to strengthen the structure. All metal parts must be coated with a durable anti-corrosion compound.
Well brick masonry allows you to combine and thereby significantly save on building materials. For example, expensive ceramic facing bricks are used for external walls, and white silicate bricks or gas silicate blocks are used for internal masonry.
Thermal insulation brick: concept and features


Many of us have had to deal with a situation when in the winter season it seems that the house is pierced by cold gusts of wind. In such a situation, heating systems are simply not able to cope with heating the home. And in the summer, we have to deal with the fact that in our houses and apartments during the day it continues to be very stuffy, despite the fact that the windows are simply wide open. This explains the increased attention to the material from which the house was built. Currently, the best material that is used in the construction of a house is considered to be heat-insulating brick. Insulating bricks are characterized by a low degree of thermal conductivity. This property guarantees the protection of the house in winter from the cold, while continuing to keep such precious warmth in the room. In addition, in the summer, this property helps to avoid overheating of the premises and provides an opportunity to enjoy the coolness in the room all summer long.
Types of insulating bricks We can talk about the existence of several types of heat-insulating bricks, which we will consider below: 1. Heat-efficient (hollow) brick Due to the fact that there are voids in the brick, a wall made of heat-efficient bricks can be almost twice as thin (in comparison with solid bricks), while guaranteeing excellent thermal insulation characteristics. When choosing a heat-efficient brick, one must not forget that the number of voids should be no more than 50% of the total volume of the brick. Otherwise, the reliability of the material is out of the question. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the fact that the thinner the slots of the voids, the better, since the thin slots of the voids are practically not exposed to contamination with the masonry mortar, while continuing to retain their inherent useful properties.Another factor that characterizes a heat-efficient brick is that the voids in the brick contribute to a decrease in its weight. In this regard, we can talk about a decrease in the total pressure of the wall on the foundation. 2. Porous (hollow) brick It differs from the heat-efficient (hollow) type of brick by its inherent porous structure. However, this type of brick has slots of voids. The porous structure of hollow bricks increases the inherent heat and sound insulation characteristics. Aerated hollow brick is often used not only as a material for masonry, but also for cladding. It must be remembered that when laying porous hollow bricks, it is necessary to pay special attention to the viscosity of the mortar that is used when laying it. This is due to the fact that the less often this solution is, the higher the likelihood of clogging the pores of the brick, which will reduce its inherent performance characteristics. In this regard, it is necessary to use only a thick mortar when laying this type of brick, which will help preserve the technical characteristics of porous hollow bricks. 3. Foam-diatomite brick Foam-diatomite heat-insulating bricks are usually used only in some industries or if there are specific requirements. Its use, for example, is advisable in the construction of smelting furnaces or boilers. 4. Cement-sand brick This type of heat-insulating brick is characterized by low thermal conductivity. This feature is explained by the fact that in its manufacture, in addition to cement and sand, quartz and carbonate sands (most often artificial) are used. It should be noted that such a composition is a factor that endows cement-sand bricks with increased efficiency: the price of cement-sand bricks is 2 and 3 times lower than silicate and ceramic bricks, respectively.
Pros and cons


In each type of work there are positive aspects and problematic points that turn into tasks, required solutions. Lightweight well masonry has its advantages:
- significant reduction in brick consumption (up to 20%);
- reduction of construction time;
- a large selection of heaters in the price range;
- reducing the load on the foundation;
- the wall with a small width has good thermal conductivity.
The quality of the work performed should always be monitored to avoid possible problems:
- In seismically active zones and on difficult soils, it is necessary to carefully calculate the distance between the diaphragms, since the walls have an inhomogeneous structure.
- After the lapse of time, it is not possible to add or replace the settled layer of thermal insulation.
- Temperature changes lead to the destruction or subsidence of low-quality insulation.
- Condensation on the walls is likely.
- Uninsulated metal reinforcement leads to the formation of cold bridges and loss of heat transfer.
Brick walls and their minimum thickness
There are no universal materials on the construction market that meet all the requirements in any area. For certain conditions, a certain wall thickness is suitable. Typical dimensions of the most common types of bricks are 250 * 120 * 65 mm, they are standard.
Recommended thickness of solid brick walls for residential buildings.
The thickness of the load-bearing brick wall is calculated, taking into account the standard parameters of a brick of 25 cm. Requirements for the choice of wall thickness are often determined by the loads on it, since the frame of any building is a system of load-bearing walls, which must be safe and reliable.
The load on load-bearing walls usually includes more than just their weight. It also includes the weight of other elements such as partitions, slabs, roofs, etc. The construction of buildings from materials requires additional supply.
The minimum size of the thickness of the bearing brick walls should be less than 1 brick with a standard thickness of 25 cm, which is necessary to ensure normal heat-saving qualities.
Back to the table of contents
Types of masonry
The main thing that characterizes well masonry is the voids that are filled with insulation, but the types of masonry play an important role in it.


Brickwork can be 2 bricks, 2.5 bricks, or modified. Each type of masonry has the right to be sold, depending on the purpose of the building and the climatic zone in which it is located. Since the main task of each type is to insulate the house, recently bricks with hollow cavities have been successfully used in well masonry. Air in the sealed space of a brick, laid in any type of masonry, also retains heat.
What is written in SNIP about this


The normative document regulating the arrangement of the reinforcing layer, namely SNiP 3.03.01-87 "Bearing and enclosing structures", has the following items:
- When reinforcing the masonry of external walls and columns, the thickness of the seam should be no more than 1.6 cm, and exceeds the sum of the diameters of the reinforcement at the intersection by at least 4 mm. For transverse installation in walls and walls, the mesh should consist of at least two rods in width. And it should protrude 2-3 mm beyond the outer edge of the wall.
- Partitions may not be reinforced if they are not fixed with temporary fasteners, and have a height of 1.5 m and a thickness of 9 cm.With a thickness of 12 cm, the height should not exceed 1.8 m.
- With longitudinal steel reinforcement bars are connected by welding. If it is not used, then the rods are ended with hooks and tied with wire. The rods overlap and each end must not be shorter than the sum of 20 diameters.
Calculations of the thickness, diameter and size of the mesh cells are determined from the standards given in SNiP II-22-81 "Stone and reinforced masonry structures".
Heaters
In the last century, in order to save money, the well laying of the house was carried out with filling with earth or clay with sawdust. This option did not justify itself due to the shrinkage of the earth layer, labor intensity and increased load on the foundation.
In Moscow and its region, as well as in Tatarstan, well masonry is prohibited for use in houses built at the expense of budgetary funds. And the point is not in the negative aspect of this method, but in the impossibility of controlling the quality of the installation of the insulation. Inspection of the commissioned objects on a thermal imager showed significant violations and heat loss.
In private buildings, the method is successfully applied, where the customer can directly participate in the construction process, or receive a step-by-step photo report of the work being carried out.
The cavities in the well masonry are filled with:
- jellied compounds (polystyrene concrete, penoizol, sawdust concrete);
- backfill insulation (expanded clay, mineral wool crumbs, foam glass gravel, ball foam);
- blocks of mineral wool (for vertical insulation) or foam of various thicknesses.
Since each layer of well masonry has different temperature conditions, installation and ventilation gaps play an important role. For example, mineral wool and foam insulation must be fixed with anchor reinforced spacers.
Experts advise to wrap mineral wool with polyethylene before installation and fix it with a ventilation gap. Before that, treat the inner part of the wall in the well itself with a primer.
In the upper and lower rows, for the movement of air flows, in order to avoid condensation on the walls, narrow vertical hoods are placed between the bricks.
Installation of a window and door in a three-layer wall
| The window or door is installed in the same plane with the insulation |
Placing a window and a door in the thickness of a three-layer wall should ensure minimal heat loss through the wall at the installation site.
In a three-layer wall, insulated from the outside, a window or door frame installed in the same plane with a layer of insulation at the border of the heat-insulating layer
- as it shown on the picture.
This arrangement of the window, door along the wall thickness will ensure minimal heat loss at the junction.
Watch the video tutorial on the topic: how to properly lay a three-layer wall of a house with brick cladding.
Arrangement technique


According to SNiP methods, when erecting three-layer walls with insulation made of mineral wool or foam, the inner wall is first removed, thermal insulation is attached to it, and then the outer part of the well is removed with the necessary ventilation gap, observing the location of the jumpers. At the same time, cotton wool is covered with a diffuse membrane for waterproofing.


On collapsible and highly heaving soils, the bearing and facing part of the well masonry of the structure is reinforced with monolithic belts of each floor level. This option excludes the possibility of cracking.
With the filling option:
- On the waterproofing layer of the foundation, 2-4 layers of dense brickwork are laid, at the corners starting from the butt sides. Each row is reinforced with a reinforced mesh.
- The base of the load-bearing and facing wall is formed with the necessary clearance for the selected heat-insulating material.
- Jumpers are laid out along the length of the wall after 60-120 cm. The gap from the lintel to the wall is from 2.5 cm, this excludes the formation of cold bridges in winter. Subsequently, since the lintels are located vertically to the entire height of the wall, the floor beams will be laid in place of their formation.
- Backfilling of walls with expanded clay or other thermal insulation is carried out no higher than 5-7 rows with tamping and filling with mortar.
- A reinforced mesh is installed on the poured solution to give rigidity to the structure, or in the process of laying between the layers in a checkerboard pattern, connect 2 walls with reinforcing bundles with bent edges and an anti-corrosion coating. Flexible ties are an alternative to reinforcement. They are made of fiberglass or basalt plastic, they do not corrode, they are sprayed with coarse sand for greater fixation and a built-in retainer for attaching the insulation to the wall.
- All corners of the building are fixed with reinforced mesh with anti-corrosion coating. Also, at the intersection of walls, external corners and in the belt in front of the roof, flexible ties are additionally installed. Under window and door openings, for any type of brickwork, 2-3 rows of a solid layer of brick are formed.
- The final 5-7 rows of the well masonry of the structure are laid out similarly to the initial rows with dense brickwork.
To reduce the load, in order to avoid wall delamination, the transverse seams are shifted by one quarter of the brick size, and the longitudinal seams are applied to 0.5 bricks. This ensures the solidity of the wall and the strength of the buildings.
The economical well masonry has many opponents. The main argument that they put forward is the impossibility of partial repair of the insulation of a house when it shrinks or deforms, but modern technologies make it possible to repair houses built more than 50 years ago. Thermal imagers see places where heat is lost, and foam insulation units fill the voids with high-quality insulation through small holes.
Well brickwork with insulation
The effectiveness of this method of insulation is much lower, but in some cases it is advisable. The advantages of mineral wool are: resistance to biological negativity, resistance to fire and low thermal conductivity. Insulation needs to be selected taking into account, firstly, its thermal conductivity: the higher the thermal conductivity, the better the insulation.Secondly, vapor permeability.
With a temperature difference, steam penetrates through the load-bearing wall, insulation and facing wall into the street. Each subsequent stage must have a higher vapor permeability than the previous one, otherwise the steam will linger in the insulation and condensate will form inside the structure, which will reduce the thermal insulation properties of the insulation by an order of magnitude, which cannot be repaired. Insulation made of glass wool, mineral wool or basalt wool has a higher vapor permeability than brick, and they are ideal for performing their functions.
The use of heat-efficient blocks in construction
Using heat blocks, you can build a reliable, durable and, most importantly, energy-saving building. Also, the use of heat blocks significantly increases the speed of wall construction, since now the construction of walls, their insulation and facade finishing are taking place simultaneously.
Due to the small width of the heat blocks and the presence of the tongue-and-groove system, the masonry is stronger and more reliable, which is also an important factor in construction. Another distinctive quality of heat blocks is their strength and resistance to stress.
For the formation and manufacture of the front side of the heat blocks, super-strong concrete is used, which is also impervious to moisture.
The main advantage of this concrete is that it does not need to be re-painted or renovated, and its cost, in comparison with similar products for the facade, is much lower.
In addition, modern technologies allow you to decorate the front part in different colors, which will make your home aesthetically pleasing.
What the front of a house built of heat-efficient blocks might look like:


Prices for heat blocks range from 6,000 to 8,000 rubles per cubic meter and depend on the manufacturer, exterior finish and filler composition.