Home / Electric boilers
Back to
Published: 31.05.2019
Reading time: 4 minutes
0
913
The compact electrode electric boiler provides warmth in the room and makes it possible to remotely regulate the temperature. Its small size allows it to be installed in an existing heating system.
- 1 How an electrode boiler works
- 2 How it works
- 3 Is it possible to save with an electrode boiler
- 4 Review of the best models of electric electrode boilers
The principle of operation of electrode boilers
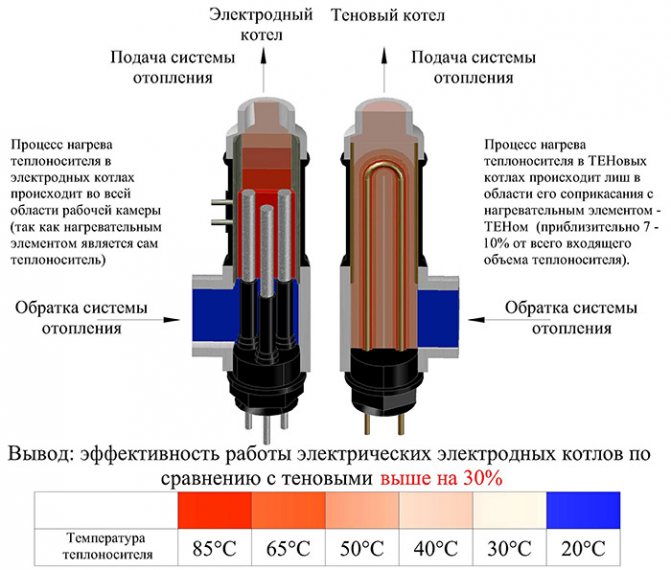
When describing the advantages of electrode boilers, the main emphasis is on the absence of intermediaries in the transfer of energy from the electrical network to the coolant. The main argument on which the marketing strategy for the promotion of electrode water heaters is bet is the direct heating of the liquid under the action of an electric current, which occurs due to its high resistivity.
When using this kind of equipment, the influence on the heat transfer of the scale crust formed on the surface of traditional tubular heating elements is excluded. The low inertia of the system is also considered an obvious advantage: the coolant begins to heat up immediately after the voltage is applied to the electrodes, while when using resistive heaters, it takes some time to heat the coil itself and its dielectric insulation.
The device of the electrode boiler: 1 - terminals for connecting to the network; 2 - sealant and insulation of electrodes; 3 - supply of cooled heat carrier; 4 - block of electrodes; 5 - coolant; 6 - boiler drum; 7 - insulating layer; 8 - outlet of the heated coolant
However, not everything is so rosy. First of all, it is doubtful that the entire coolant is under the influence of a dangerously high potential difference. In particular, with a zero break, all metal parts of the heating system become fatal to humans, and breakdowns are also possible if the neutral is not properly grounded.
It is worth mentioning the fact that not all fluids have a resistivity high enough to convert all applied power to generate electricity. A certain part of the current load does not encounter resistance and therefore flows freely into the ground. Against this background, statements that electrode boilers have an efficiency higher than 100% evoke a condescending smile from people who are well acquainted with the technical part of the issue.
The mechanism of the water heating system
For further understanding of the article, it is necessary to understand the structure and mechanism of operation of the ion electrode boiler. The principle of operation is very simple to understand - the heat carrier (water must contain the required amount of salt, if the percentage of salt exceeds the norm, then the product is diluted with distilled water) follows into the vessel in which the electrode is installed. If someone has a question, after reading the word "electrode", then we will explain: an electrode is a metal rod that is fixed to either side of the vessel. A phase is connected to the electrode, and a neutral conductor to the front side of the mechanism.
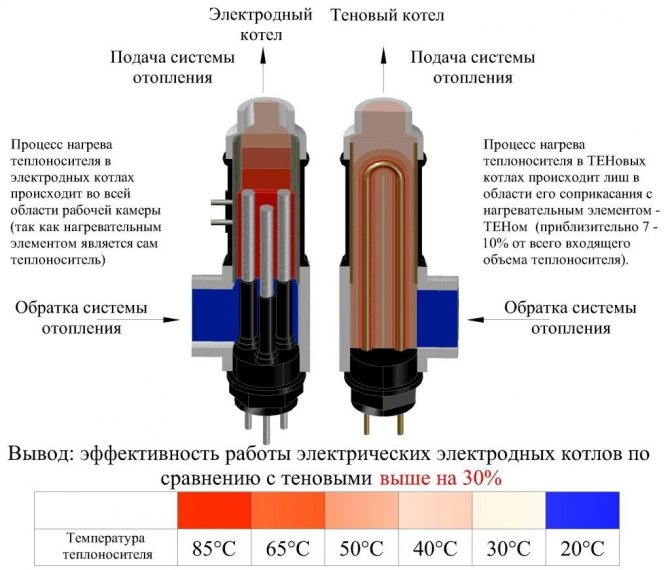
If you connect the water heating system to a network of two hundred and twenty Volts with a frequency of fifty Hz, then the device activates a chaotic process of movement from the anode to the cathode. This process helps to achieve the main goal - water heating. Many masters are used to calling such devices not electrode, but ionic - this is due to the peculiarities of the heating boiler operation.If the principle of operation of ion boilers is very simple to understand, then the efficiency of the system shows very high rates - 96-99 percent.
The electrode boiler contributes to the fact that it is possible to save up to forty percent of electricity compared to chimney boilers. The principle of operation makes it possible not to use chimneys, since the ion boiler does not produce combustion products.
Coolant requirements
In addition to natural losses when heating a liquid, electrode boilers have another nasty property. In the process of passing an electric current through water, the phenomenon of electrolysis is observed - the separation of the H2O molecule into gaseous components. This, among other things, further reduces the energy efficiency of the boiler, because in this case, electricity is consumed not for heating, but for electrolysis. However, the most obvious consequence of this effect is the formation of gas locks in pipes and radiators.
For these reasons, the heating medium for heating systems on electrode boilers must be selected with the greatest care. In order to reduce the conductivity of the coolant (increase the resistivity), the content of dissolved ions in the liquid used should be normalized. Basically, distilled water is used, to which electrolyte is mixed in the proportion recommended by the manufacturer, again, factory production.
The situation is more complicated if an antifreeze liquid must be used as a heat carrier. In this case, the system must be filled with a special antifreeze that cannot be diluted with water. With a significant displacement, refueling the system can cost a pretty penny, but this does not take into account the issue of the durability of the coolant. In the presence of metal parts in the system, the concentration of ions in the liquid increases over time, while effective methods for regenerating the coolant for electrode boilers have not yet been invented. But periodically at least part of the coolant will have to be drained, because each boiler requires cleaning the electrodes from plaque, and the system itself needs to be flushed.
Consequences of electrolysis and direct current action
The splitting of water into oxygen and hydrogen leads to the formation of air locks, which impede the normal circulation of the liquid. However, this is far from the main negative effect. In particular, during real operating experience, manifestations of electrochemical corrosion of aluminum radiators were found.
In the presence of cast-iron batteries in the heating system, the initial qualities of the coolant decrease, mainly due to the washing out of impurities from the open pores of the cast sections. Because of this, those wishing to use electrode boilers in such conditions have no choice but to replace the radiators or thoroughly flush the entire system.
The very fact that the coolant in the system is energized obliges to carefully provide grounding for each metal element of the system. If a clamp with a sufficiently low resistance can still be applied to a steel pipe, then high-quality grounding of a cast-iron radiator connected by a system of plastic pipes seems to be a very difficult task. So far, we can conclude that any heating system in which an electrode boiler is used requires a strictly individual approach.
How to do it yourself
First, you need to decide on the type of electrode boiler - single-circuit for heating or double-circuit for hot water supply. In the second case, the boiler drum is installed inside a tank with tap water.
Materials and tools for the manufacture of an electrode boiler
Most of the blanks that are suitable for the size can be found by rummaging in the garage, and the missing parts can be bought in the store. A complex tool is also not required.To assemble a standard boiler with a capacity of up to 10 kW, you need the following:
- A welding machine, preferably a modern inverter one, is easier to handle with this, and the quality of the seams will turn out to be very decent;
- Bulgarian;
- Drill;
- A piece of steel pipe 20-30 cm long and 8-10 cm in diameter, it will serve as a body;
- Metal rod 1–2 cm in diameter and 10–15 cm long for the central electrode;
- An iron tee with a diameter of the boiler body for attaching the electrode and supply pipes (ready-made ones are sold in plumbing stores);
- Coupling with an adapter for a standard pipe thread and a suitable diameter to the body;
- Electrode insulator made of a suitable bimetallic plug or PTFE seal;
- Contacts for zero phase and grounding from suitable bolts and nuts for M6 or M8;
- Sealant or special sealing tape;
- Corner for the manufacture of fastening the boiler drum to the wall or floor.
Manufacturing technology
We work in the following sequence:
- The finished body workpiece is cut to size and the sharp edges are cleaned. A ready-made tee is installed at one end and the connection is carefully welded. A sleeve or a standard threaded flange for the sleeve is welded to the opposite side. In this case, the connection is additionally sealed. It is allowed to cut a thread on a pipe for a tee and a coupling. The coolant will enter the boiler through a tee, and then, after heating, into the heating system through a coupling with a tap.
- We weld a terminal from a suitable bolt to the electrode in advance. In the insulator we drill a hole for the electrode. The electrode itself and the insulator are the most critical units in the boiler. All connections must be made carefully and seated on a sealant to avoid leaks.


The process of making an electrode boiler does not cause any particular difficulties.
It is important! The place where the phase is connected to the electrode must be carefully insulated or covered with a protective cover to avoid accidental electric shock:
- We weld two bolts to the body - one for connecting the ground, the second for supplying the zero phase. Grounding is mandatory from a copper wire with a cross section of at least 4 mm2.
- We clean it from rust and paint it with heat-resistant paint.
- We make the boiler fasteners from the corners and place it in the right place. We close it with a decorative screen and connect to the network.
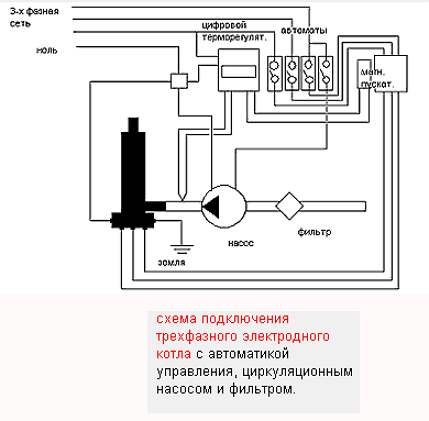

Electrode boiler connection diagram
Before the final installation of the assembled boiler, test it for leaks. To do this, pour kerosene or a similar liquid with high fluidity into it. You can also check the tightness by applying soapy water to the joints and welds, and supply air to the inside of the housing under a pressure of 3 atm., For example, from a car pump. Then the boiler is washed with special compounds that remove scale and rust inside.
Installation of a homemade boiler in the heating system
The operation of an electrode boiler differs from an induction or heating element, so its operation will require its own connection diagram. In the process of passing current through the coolant, electrolysis gas (hydrogen) is released, which impairs the performance of the system. To remove it, a special safety valve is cut into the upper part of the system, bleeding off excess pressure in the system.
You will also need:
- Expansion tank;
- Pressure gauge;
- Automatic air relief valve;
- Shut-off valves.
Installation of an ion boiler of any type is possible only in a vertical position, and the outlet pipe must be taken from a metal with a length of up to 1.5 m. The rest of the wiring is made of composite or any other pipes.


DIY electrode boiler
The operating temperature of the coolant in a sealed system reaches 120 degrees, therefore, protective covers are required. The advantage of a sealed circuit is that rust and scale do not form on the pipe walls for a long time.
The power of the electrode boiler can be adjusted by changing the concentration of dissolved salts in the coolant. To obtain optimal fluid resistance, the following method is used:
- We take distilled water or rain (snow);
- You will need a container, an ammeter, a large water syringe or measuring cup, baking soda;
- According to Ohm's law, we calculate the current in the circuit (for a 4 kW boiler at a voltage of 220 V, the current will be 18A);
- We dilute soda in a container in a ratio of 1 to 10 and pour it into the system through an expansion tank;
- We connect the ammeter to the terminals of the boiler and look at the readings on the switched on and warmed up boiler;
- Add water until the desired current value appears.
It must be remembered that the process of changing the concentration of the coolant occurs gradually, so it is worth waiting for the final establishment of the current at 16-17 Amperes. In further operation, you should regularly check the value of the current in the system, and, if necessary, adjust the density of the liquid by adding soda or water.
It is important! A low concentration of electrolyte reduces the efficiency of the boiler and leads to increased gas production.
Choosing a radiator to work with an electrode boiler
Due to the characteristics of the heat carrier with a large amount of dissolved salts, not all radiators are suitable for operation in the heating circuit. For this type of heating devices, the use of aluminum or bimetallic structures is allowed. They keep well heating over 100 degrees and high pressure, and the inner surface remains clean even after several years of operation.


Aluminum and bimetallic radiators retain heat well
It is important! The volume and number of sections are selected based on the following rule: for 1 kW of installed power, there should be 8-10 liters of heat transfer fluid. An excessive amount of liquid will not improve heating in the house, but the cost of heating it will be higher.
Information about the volume of radiator sections is indicated on the package, and the volume of liquid circulating through the pipes is found by the formula: V = S * L (m3 or liters), where V is the total volume, S is the cross-sectional area of the pipe, L is the total length of all pipes of the heating system.
Electrode boilers of small and medium power have proven themselves well for heating rooms up to 100 m2. At the same time, they can operate from a public 220 V network, and the maximum current strength does not exceed 20 A. Such devices are ideal for heating a country house or garage. A self-made boiler and coolant will bring significant savings, and in terms of their performance they will not be inferior to branded products.
Outstanding efficiency myths
When studying the advertising materials of electrode boilers, one gets the impression that consumers are considered deaf ignoramuses. Allegedly "ionic" boilers extract heat literally from nowhere, giving out thermal energy in the amount of 120-150% of the applied electrical power. At the same time, the laws of physics and, in particular, heat engineering are ignored in every possible way.
Statements that the electrode boiler is capable of mythically multiplying the energy put into it are absolutely groundless. Fortunately, today this trend in advertising campaigns has begun to decline, but its initial development can be attributed to the active spread of thermal equipment operating at the expense of heat pumps with a positive COP coefficient.
Even claims that 100% of electricity is converted into heat is an outright deception. Losses during formation still cannot be avoided, even when heating the coolant due to its own electrical resistance, because at least 2-3% will be spent on heating the supply wiring, the same amount will drain into the grounding system due to a decrease in the energy of charge carriers due to insufficient chemical purity liquid in the system or due to the formation of plaque on the electrodes. Conclusion: electrode boilers are capable of demonstrating a conversion coefficient close to 100% only under conditions of a demonstration stand, which, as you know, are far from real.
Feasibility of use
For all their shortcomings, electrode boilers do not just have the right to life, they occupy their own niche, where they solve a certain range of problems. Basically, their use is reduced to heating small areas, where the cyclical mode of operation is especially important. Due to the low inertia, the heating systems on electrode boilers are instantly put into operation, which means that heating can be carried out in a strictly defined period of time.
In addition, one cannot fail to mention the small dimensions of the electrode boilers. They represent, in fact, a small flask that can be easily integrated into a compact technical niche. If you need to heat a small space and there is no way to equip a separate boiler room, this kind of boilers will come in handy.
However, it should be remembered that this class of equipment works best in closed-type systems with a small displacement. Electrode boilers can be used in combination with underfloor heating systems, and when heated with radiators. However, we repeat, it is necessary to properly prepare the coolant and use advanced electronic thermal control circuits.
Electrode boiler connection diagram: 1 - ball valve; 2 - filter; 3 - circulation pump; 4 - drain valve; 5 - electrode boiler; 6 - security group; 7 - expansion tank; 8 - heating radiators; 9 - three-way valve with a servo drive; 10 - circulation pump; 11 - underfloor heating contour; 12 - underfloor heating control unit; 13 - electrode boiler control unit; 14 - digital thermostat; 15 - contactor; 16 - automatic protection
Connection diagram to the heating network
For normal operation, you will need to install a circulation pump, an expansion tank, a special filter and an automation unit. Most often, 3 typical schemes for connecting an electric boiler to the heating circuit are used.
Standard or sequential
The most common schematic diagram, in which the coolant is supplied from top to bottom using a pump. Allows you to connect a large number of heating radiators.
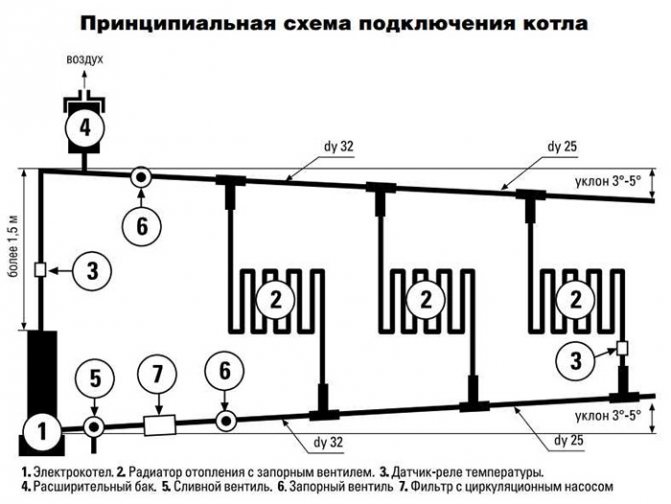

The schematic diagram of the boiler connection is the most common
Parallel circuit
Well suited for small rooms with 1-2 battery sections. Liquid circulation in such a circuit is possible by gravity due to convection. A second boiler or central heating can also be connected.
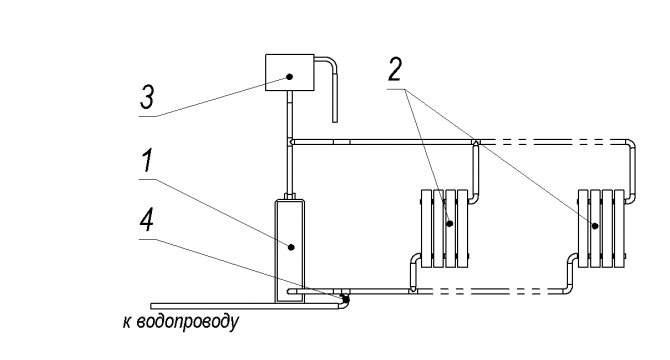

1 - boiler, 2 - heating system radiators, 3 - expansion tank; 4 - valve for filling / replenishing the system from the water supply
Underfloor heating connection
In houses with central or gas heating, low-power electrode boilers are used for floor heating. Such a floor retains heat longer and makes the indoor climate softer than when using infrared heaters.
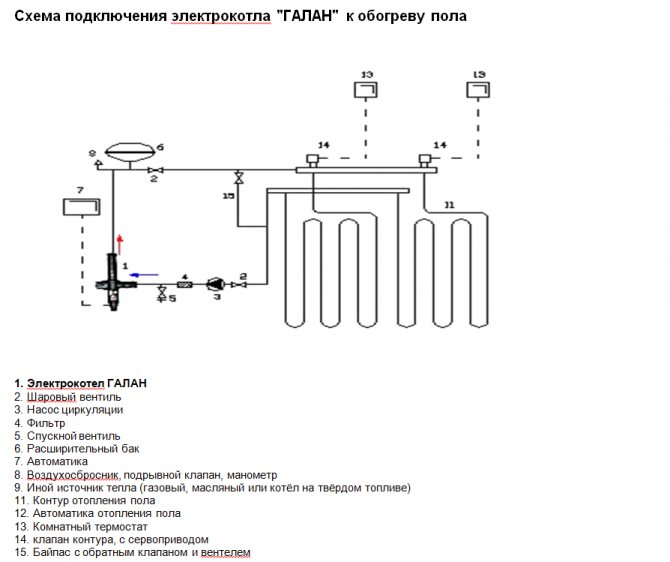

You can connect the underfloor heating to the boiler yourself
Heating water in the hot water supply system involves the use of special 2-circuit boilers, which can also be connected to a common heating system.
Before starting work on the drawing, it is necessary to indicate the number of circuits, the location of the heating radiators and the total number of pipes, the location of the pumps and filters. Provide taps for draining water and filling fluid into the circuit.
Maintenance of the heating system on electrode boilers
During operation, electrode boilers do not cause any particular problems. They are compact, quiet, and require a minimum of protective devices in the electrical and hydraulic piping. Nevertheless, periodic revision and maintenance of such equipment will still have to be carried out.
The boiler electrodes generally require attention. The claims about the absence of scale formation are not groundless, but as a result of electrolysis, at least one of the electrodes forms a hard crust of insoluble plaque. It must be mechanically cleaned at least once a year.In addition, the density and chemical composition of the coolant should be monitored: for different systems, the methods for determining its suitability may differ.
Do not forget about electrical safety. The grounding of the heating system must be of high quality, at least once every two years it is necessary to check the operating parameters of the circuit of the main grounding conductors and the resistance of external connecting elements. Without proper attention in this matter, electrode boilers turn into potentially life-threatening devices.
rmnt.ru
Advantages and disadvantages
Pros:
- Efficiency due to the principle of operation and a minimum of details, approaching 95-98%.
- High efficiency, due to the low energy consumption for heating and maintaining the temperature of the coolant up to 75 degrees.
- Extremely low chance of an emergency, which the automation could not prevent, water is a continuation of the electrical circuit, therefore, even if a pipe breaks through and a coolant leaks, the circuit will open itself and immediately stop heating.
- Small time reaction of the heating circuit to changes in settings, very fast warming up to the required temperature.
- Resistant to sudden power surges, which can only lead to a temporary drop in the power of the device, but will not turn it off at all.
- Easy to install.
- Minimum dimensions and weight in comparison with similar devices of other types, allow them to be used in a limited space of a private house or summer cottage.
- Ease of operation.
- Environmental friendliness.
Minuses:
- Increased requirements for the quality of the water in the circuit, since the formation of scale or an insufficient amount of salt in it can significantly reduce its conductivity, and hence the power of the entire heating system.
- As food uses only alternating current from the mains, since direct current causes electrolysis of water, which means that in case of power outages it will not work, since it cannot be powered from the battery.
- Electrical safety standards without fail require grounding, since in case of insulation breakdown, the chance of getting an electric shock is much higher than that of heating devices.
- Heating the coolant to a temperature of more than 75 degrees negatively affects its efficiency, and in this case, it begins to consume excessive electricity.
- Air trapped in the electrode chamber, can serve as a catalyst for corrosive processes in it, significantly reducing the life of the equipment.
- Water from a single-circuit system unsuitable for home use, as it is saturated with free ions.
- For technically correct operation some knowledge of electrical engineering is required to help determine and control the optimal value of the electrical conductivity of the water in the circuit during its operation.