Here you will find out:
- The essence of energy saving
- Ways to Improve Energy Efficiency at Home
- Infrared heating systems
- Induction electric boilers
- Thermal panels - energy saving heating
- Energy saving using monolithic quartz thermal electric heaters
- The use of solar energy
- Control system "Smart home"
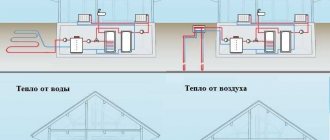
- Heat pumps of two types
- Heating with wood
- Heat recovery
More and more people are interested in energy-efficient heating systems. Energy saving methods are a significant nuance when choosing a heating system. The latest technology in this matter is infrared heating and induction boilers, solar heating and smart home systems.
The essence of energy saving
First, we want to reveal one little secret. You might be surprised, but any electric heaters are energy efficient. After all, what does this term mean for a device that releases thermal energy? It means that the energy contained in fuel or electricity is converted by a boiler or heater into heat as efficiently as possible, and the degree of this efficiency is characterized by the efficiency of the unit.

So, all electrical appliances for heating rooms have an efficiency of 98-99%, no heat source that burns different types of fuel can boast of such an indicator. Even in practice, the so-called energy-efficient electric heating systems generate 98-99 watts of heat, using up 100 watts of electricity. We repeat, this statement is true for any electric heaters - from cheap fan heaters to the most expensive infrared systems and boilers.
Comparative example. 1 kg of dry wood on average releases 4.8 kW of heat during combustion, but in reality we can only get 3.6 kW, since the boiler efficiency is 75%. An electric heater is much more efficient, having consumed 4.8 kW from the network, it will give 4.75 kW to the house.


A truly energy efficient heating system is a heat pump or solar panel. But there are no miracles here either, these devices simply take energy from the environment and transfer it into the house, practically without consuming electricity from the network, for which you need to pay. Another thing is that such installations are very expensive, and our goal is to consider, as an example, the available market innovations that are declared as energy saving. These include:
- infrared heating systems;
- induction energy-saving electric boilers for heating.
Types by design
Among other things, networks can be installed in buildings:
- one-pipe;
- two-pipe;
- collector.
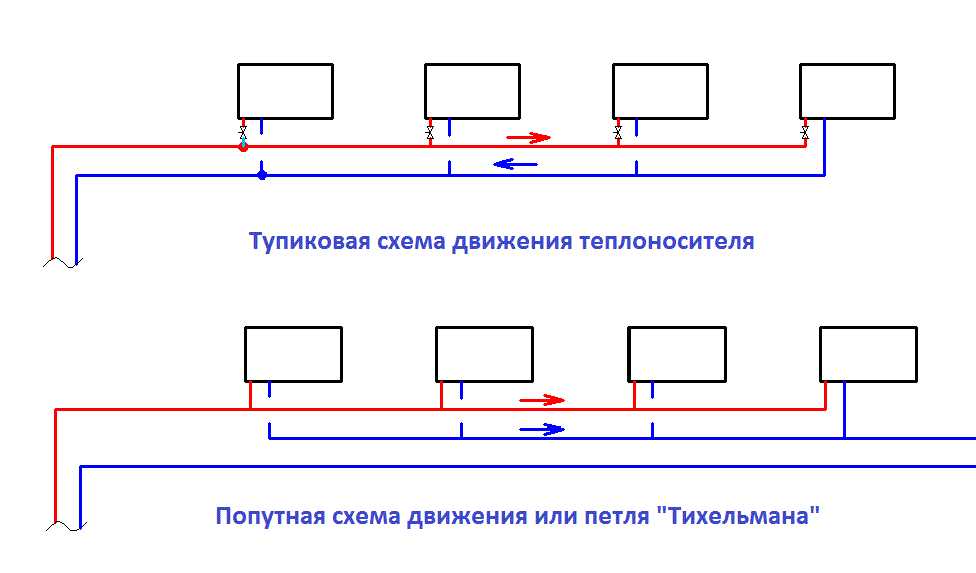
In this case, the classification of hot water heating systems is made according to the type of circuit wiring in the premises. In networks of the first type, the coolant is supplied from the boiler and returns to it through one looped line. Radiators in such communications are connected in series. The main disadvantage of this type of systems is the uneven heating of the premises. After all, the last batteries, when using such a scheme, heat up worse than those located closer to the boiler. To compensate for this disadvantage, when installing one-pipe systems, it is necessary to use special control and shut-off valves.
In two-pipe systems, water enters the heating circuit through one pipe and returns through the other. All radiators in networks of this type are heated to the same temperature.But such systems are more difficult to install than single-pipe systems. In addition, their assembly costs more.
Collector hot water heating systems are usually installed in houses above one floor. In this case, the main line from the boiler is fed first to the distribution manifold. Further, from such a collector, separate circuits are mounted for each radiator and other consumers.
Ways to Improve Energy Efficiency at Home
Various methods can be used to reduce the cost of energy used for heating:
- increasing the energy efficiency of the building;
- the use of the "Smart House" system, as well as other automation that allows you to minimize costs;
- reduction of electrical losses with the help of radiators and other devices;
- increasing the efficiency of heating boilers or furnaces;
- using environmentally friendly types of energy (firewood, solar panels).
For best results, you can use a combination of two or more options.
Even the most reliable and high-quality heating system will not bring much benefit if a large-scale heat loss occurs in the house, therefore, measures should be taken to prevent heat energy from leaking through cracks and open vents.
It is important to take simple but effective steps by covering floors, walls, doors, ceilings, and window frames with insulating material. In addition to thermal insulation according to regulatory requirements, additional insulation can be placed. This will further reduce heat loss, thereby increasing the energy efficiency of the building.


To carry out high-quality thermal insulation, you can call a specialist energy auditor. He will make a thermal imaging survey of the house, which will reveal the places of the most intense heat loss, the isolation of which must be carried out first.
As a rule, the greatest heat loss occurs through the walls, the ceiling of the attic, as well as the floor along the logs. These areas require high-quality thermal insulation. Shutters that close at night can be used to prevent heat leaks through the windows.
Types of equipment used
Thus, the classification of hot water heating systems can be made according to different criteria. But the equipment itself can be included in such networks in different ways. In most cases, when arranging heating systems in residential and industrial buildings, boilers are used as the main heating equipment. Such units, in turn, can be steam or water.
By the type of fuel used, the boilers are divided into:
- gas;
- liquid fuel;
- solid fuel.
Also, electrical units of this type can be installed in buildings.
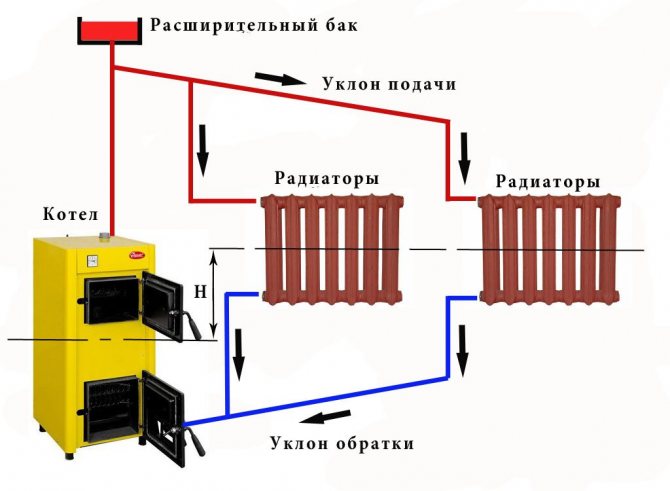
An expansion tank must be included in the design of any water heating system. As you know, water at temperature extremes can increase in volume. As a result, too much pressure builds up in the heating system line, which can lead to equipment damage and pipe rupture.
Expansion tanks are used to compensate for pressure in water heating systems. By the type of such equipment, networks of this type are classified into:
- open;
- closed.
In the first case, expansion tanks are usually installed at a considerable height from the boiler level. They are open devices.
In closed heating systems, sealed expansion tanks are used. Equipment of this type is installed next to the boiler. In both cases, the tanks are most often mounted on the return pipe, that is, on the line through which the already cooled coolant returns to the heating unit.
The classification of circulating pumps of heating systems is approximately as follows:
- equipment with a "dry" rotor;
- devices with a "wet" rotor.
The second type of pump is usually used for pumping small volumes of heat transfer fluids.The main advantage of such equipment is ease of installation and use.
Pumps with a "dry" rotor are characterized by high efficiency and undemanding to the quality of the coolant. But such equipment is quite noisy.
The classification of devices for heating systems can also be made according to the features of their design. In this regard, pumps are distinguished:
- cantilever, mounted on a foundation;
- block, equipped with air-cooled engines;
- inline, with nozzles located on a single axis.
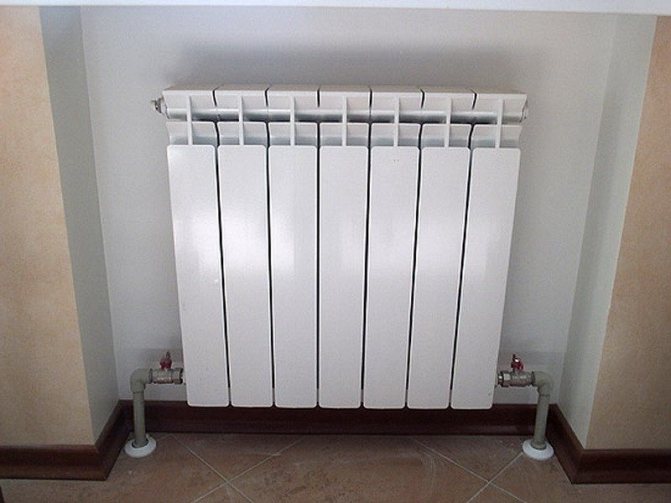
Radiators in heating systems can be used cast iron, aluminum or bimetallic.
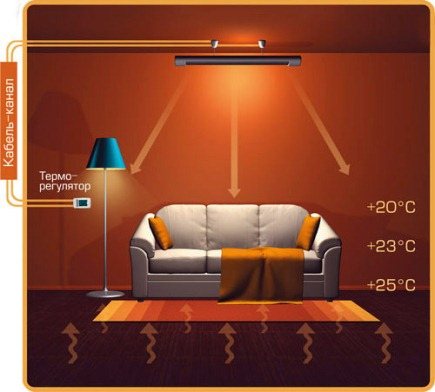
Infrared heating systems
The principle of operation of infrared heating devices of any design is to convert electricity into heat, giving the latter in the form of infrared radiation. With the help of this radiation, the device heats up all surfaces in the area of its action, and then the air in the room is warmed up from them. Unlike convective heat, such heat does not affect a person's well-being and in this regard is considered the best option.

For reference. The heat flux includes 2 components: radiant and convective. The first is infrared radiation emitted from heated surfaces. The second is direct air heating. All infrared heating systems made using energy-saving technology transmit 90% of the heat by radiation and only 10% is spent on heating the air. At the same time, the efficiency of the heaters is unchanged - 99%.
New products on the modern market, gaining more and more popularity, are 2 types of infrared systems:
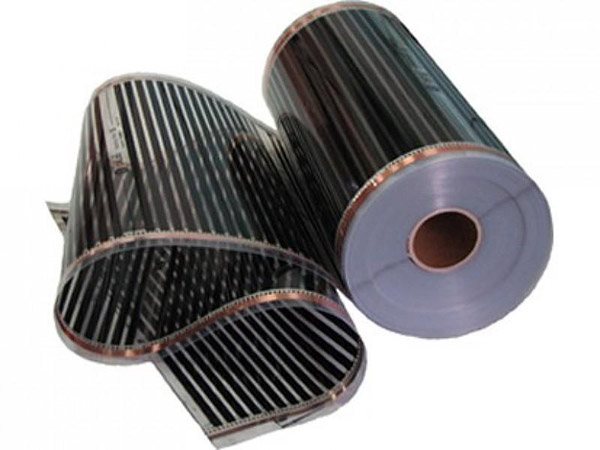
- long-wave ceiling heaters;
- film floor systems.
Unlike the usual UFO-type heaters, long-wavelength emitters do not glow, since their heating elements work according to a different principle. The aluminum plate is heated by a heating element attached to it to a temperature of no more than 600 ºС and gives out a directed stream of infrared radiation with a wavelength of up to 100 microns. The device with the plates is suspended from the ceiling and heats the surfaces located in the area of its action.


In fact, such energy-saving electric heating systems will give the room exactly as much heat as the energy consumed from the network. They will only do it in a different way, through radiation. A person can feel the heat flow only when they are directly under the heater.


Such systems, unlike convective ones, take a long time to raise the air temperature in a room. This is not surprising, because the transfer of heat does not go directly to air, but through intermediaries - floors, walls and other surfaces.
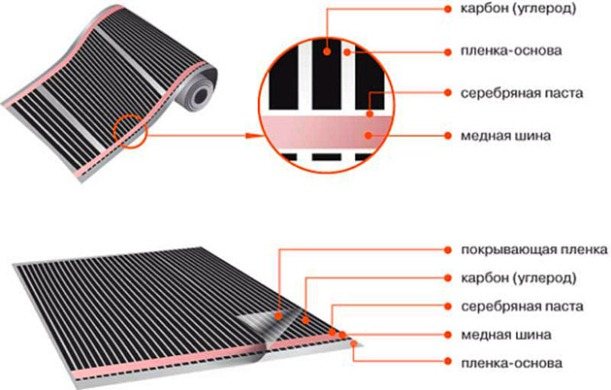

Intermediaries also use floor heating systems PLEN. These are 2 layers of a strong film with a carbon heating element between them, to reflect heat upwards, the bottom layer is covered with silver paste. The film is laid on the screed or between the joists under the floor covering made of laminate or other materials. This coating serves as an intermediary, the system first heats up the laminate, and from it the heat is transferred to the air in the room.


It turns out that the flooring converts infrared heat into convective heat - this also takes time. The so-called energy-saving heating of the house using film-heated floors has the same efficiency - 99%. What, then, is the real advantage of such systems? It lies in the uniformity of heating, while the equipment does not occupy the usable space of the room. And the installation in this case cannot be compared in complexity with a water heated floor or a radiator system.


About the heating system of a multi-storey building
House heating system. as a rule, it is one-pipe; the spill is either top or bottom.As for the return and supply, they can be placed in the basement, but it is possible that the return is in the basement, and the supply is located in the attic. The movement of water in the risers can be passing and go from top to bottom, or counter and go from bottom to top (in this regard, what was used for heating the house is important).
Heating system.
There are risers that are used with a counter coolant, they can also be associated. If the heating scheme of the house is exactly the same, then in any system there is a heated towel rail riser (in this case, the system can be either with an open water intake or with a closed one).
The number of sections and the size of the heating radiators are very important. Such parameters must be determined through calculations, as the water in the coolant cools down.
In this regard, there is one good advice: if there is a desire to replace the radiators with newer and more modern ones, then you should not use the services of friends, since you need to take into account the advancement and cooling of the coolant. In this case, it is recommended to use the services of a company serving the house, and do not throw out the jumpers, since the company is interested in their restoration.
Thus, it becomes clear that a multi-storey building is heated according to a fairly simple, but very effective system. Nevertheless, if there are any failures, then you should not do the repair yourself (especially if there is no appropriate preparation). In any case, it is imperative to call the masters from the service company, who, as a rule, eliminate all problems in the shortest possible time. The wizards use the following tools:
- pipe (gas) wrench;
- adjustable wrench;
- pipe bender;
- crimping pliers.
The comfort of residents in an apartment building depends on the correct planning and selection of the heating system. The difficulty of heating in a multi-storey building is to warm up each apartment in the building almost the same with a minimum difference in temperature. To understand how the heating systems of multi-storey buildings work, let's look at the example of a standard nine-story building with a central heating system.
With the help of valves, such a house is connected to the central heating system.
Immediately behind the valves, coarse filters, the so-called mud collectors, are installed. They capture large and medium fractions of dirt from the hot water supplied for home heating. After the mud collectors, more valves are installed, through which hot water is supplied for the needs of the residents of the house. It turns out that in an open heating system, water is heated for two purposes at once for heating and supplying hot water (hot water supply system for hot water supply). However, in order for the tenant of the house to safely use hot water, the valves are installed from the supply and return of the heating system of a multi-storey building.
Under normal conditions, the temperature of hot water supply to the heating system reaches 150 degrees. To make it possible to use hot water, it is served to residents after it has passed through the heating devices of all apartments and has given off heat. Hot water returned through the heating return will be no more than 60-70 degrees. If the temperature of hot water supplied to the heating system is low (this happens at the beginning of the heating season and with slight frosts), water is taken from the supply.
After the hot water supply, more valves are installed with the help of which it is possible to shut off the heating of the house, and in some cases a collector is installed.
Houses with more than five floors are equipped with a single-pipe heating system for a multi-storey building.
Only the supply of hot water to the heating system can differ. Feeding can be from the top (fed from the attic) or bottom pouring (fed from the basement).
Since the pressure of hot water in heating systems is quite high, it is possible to achieve practically the same level of heating for each apartment in the house. The disadvantage of such a heating system is that, if necessary, drain and fill the water in the system, air may remain in the heating system. A Mayevsky crane on radiators can help solve this problem. An alternative option for the central one can be individual heating of the apartment.
Induction electric boilers
This novelty appeared on the market relatively recently and aroused considerable interest, since it was advertised as another energy-saving installation. In reality, this water heater uses the law of electromagnetic induction, according to which a stationary steel bar placed inside a coil with a current flowing through it will heat up. There are no tricks here, the so-called energy-saving boiler operates with an efficiency of about 98-99%, like its other electrical "brothers".
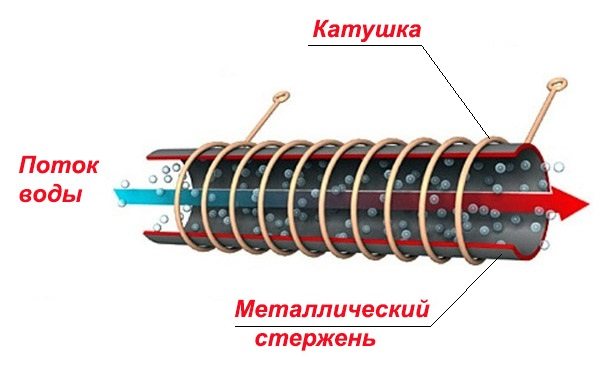

A clear advantage of the unit is that the coolant passing through it does not come into contact with important elements, but only with a metal rod. Therefore, the boiler is able to reliably serve for many years without any maintenance, except for periodic flushing. Other advantages of the induction apparatus are:
- small dimensions and weight, which is very important when placing a heat generator in a furnace room;
- rapid heating of the coolant.


Heat transfer method
The transfer of heat energy can be carried out in several ways.
Heat carrier
In this capacity, water or its mixtures with ethylene and propylene glycol is used, which freeze at lower temperatures. The high heat capacity of the coolants makes it possible to dispense with lines of a relatively small cross-section.
Air
Air heating means that a heat source heats directly the air entering the room. Air heating systems are often combined with ventilation. The main drawback of the solution, affecting its popularity, is the need to lay large air ducts: without prejudice to the finish, this can be done only at the construction stage.


Air ducts for supplying warm air will hide the suspended ceiling.
Steam
Heating systems with superheated steam with a temperature of 200-400 degrees are nowadays used exclusively at industrial facilities. They are convenient in that, due to the high temperature of the heating devices, they allow them to ensure their minimum dimensions at high values of thermal power. Lack of steam is a serious danger for the inhabitants of heated premises in case of accidents.
Infrared radiation
The so-called infrared heating devices transfer a significant part of the heat not to the air around them, but to directly surrounding objects and people through infrared radiation that lies outside the visible part of the spectrum.
The use of infrared emitters is economically justified primarily because it reduces the comfortable minimum temperature in the room. Due to the direct heating of the skin in open areas of the body, the zone of subjective comfort starts already from + 15-16C.
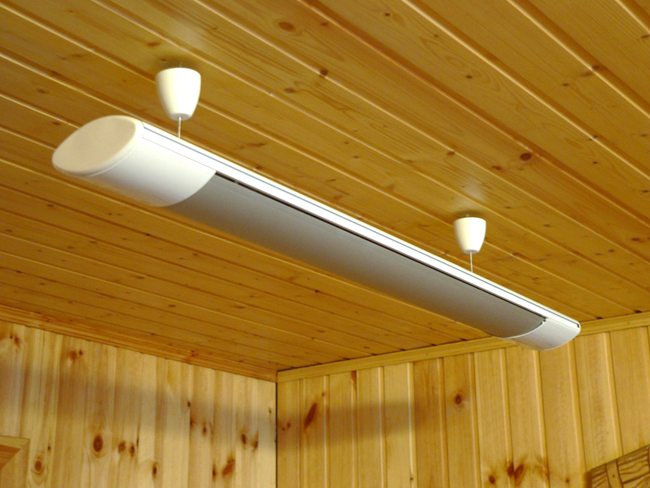


Ceiling infrared heater.
Thermal panels - energy saving heating
Among energy-saving heating systems, thermal panels are gaining special popularity. Their advantages are economical power consumption, functionality, ease of use. The heating element consumes 50 watts of electricity per 1 m², while traditional electric heating systems consume at least 100 watts per 1 m².
A special heat-accumulating coating is applied to the back of the energy-saving panel, due to which the surface heats up to 90 degrees and actively gives off heat.The room is heated by convection. The panels are absolutely reliable and safe. They can be installed in nurseries, playrooms, schools, hospitals, private homes, offices. They are adapted to power surges and are not afraid of water and dust.
An additional "bonus" is a stylish look. The devices fit into any design. Installation is not complicated; all the necessary fasteners are supplied with the panels. Already from the first minutes of turning on the device, you can feel warmth. In addition to the air, the walls are warming up. The only drawback is that the use of panels is unprofitable in the off-season, when you only need to slightly heat the room.
Air
On what grounds is it possible to classify a heating system of this type?
Natural and forced circulation
The heated air tends to rise due to the lower density of the relatively colder air masses. If the operation of air heating is based solely on natural convection, the heating element willy-nilly has to be placed below the heated rooms. In practice, forced air circulation, which is provided by low-power fans, is much more often used.
Recirculation
The simplest air heating scheme, which is easy to assemble with your own hands, is a boiler with an air heat exchanger, which takes cold air from the street and, after heating, supplies it to the living space. The exhaust air leaves the house through the exhaust ventilation.
The scheme is simple, but impractical: the heat loss in this case will be prohibitively large. The obvious solution is to use full or partial recirculation. Air is recirculated; it is much easier to heat it up to 50-60 degrees, normal for air heating, at an initial temperature of +20, and not -30C.
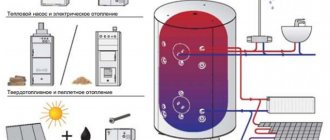
Energy saving using monolithic quartz thermal electric heaters
You can save energy if, for example, you use quartz heating electric heaters. Such efficient heating of a private house converts electrical energy into heat. The quartz sand contained in the heating elements retains heat for a long time after the power supply is turned off.
What are the advantages of quartz panels:
- Affordable price.
- Long enough service life.
- High efficiency.
- Relatively low power consumption.
- Convenience and ease of equipment installation.
- No oxygen burnout in the building.
- Fire and electrical safety.
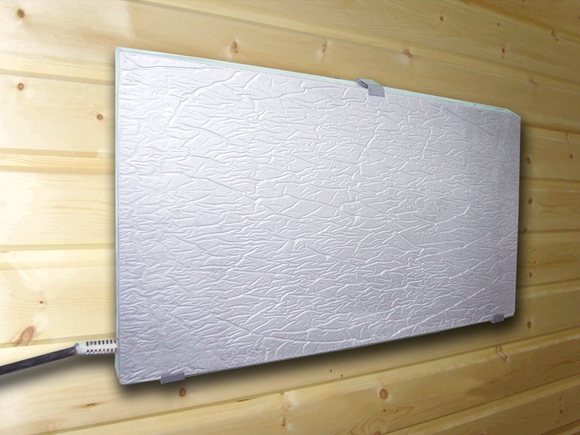


Monolithic quartz thermal electric heater
Energy-saving heating panels are made using a solution made using quartz sand, which provides good heat transfer and a long service life. Due to the presence of quartz sand, the heater retains heat well even when the power is cut off, and can heat up to 15 cubic meters of a building. The production of these panels began in 1997; every year they become more and more popular due to their energy saving. Many buildings, including schools, are switching to this energy saving in heating systems.
This heating system is made of modules connected in parallel, and how many there will be depends on the size of the room. Another plus is the possibility of automatic control.
What are water heating systems
Such networks are considered the best option for heating residential buildings. Both in private houses and in urban high-rise buildings, in the overwhelming majority of cases, it is water heating systems that are installed.
In industrial premises, such networks are also used quite often. The only thing is that they cannot be installed in buildings intended for the storage of chemicals such as:
- potassium;
- calcium carbide;
- sodium:
- lithium and some others.
That is, such heating networks are not collected where substances that can ignite on contact with water are stored or used in the production process.
Boilers are most often used as heating equipment in systems of this type. Water in networks of this type circulates through pipes, stretched through the premises. Heating radiators installed in rooms or workshops are directly responsible for heating the building.
The main advantage of water systems is that batteries and pipes do not heat up too much in this case. Consequently, the possibility of the occurrence of burns in case of accidental contact with them is excluded. Also, on batteries and highways of such networks, dust does not burn and does not sinter.
The use of solar energy
Solar heat is an environmentally friendly and efficient enough source for a variety of heating systems. Some modifications use electricity as an additional power supply, others operate only from solar cells. In some cases, additional equipment is not necessary - there is enough sunlight.
Modular air manifolds
Solar panels (collectors) are installed on the south side of the building at an angle so that they are heated by the sun's rays to the maximum. The system works in automatic mode: when the air temperature drops below the set point, the air is driven through the heating modules by means of fans. One air battery allows you to heat a room with an area of up to 40 m², respectively, a set of collectors is able to serve the whole house.
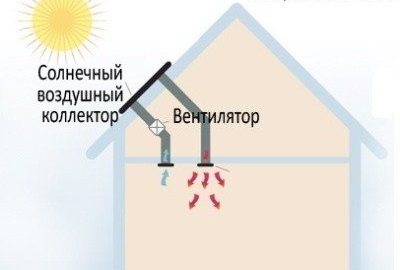

For the southern regions, solar air collectors of modular type are quite effective and inexpensive equipment for creating a heating system.
Solar modules are environmentally friendly and cost-effective, they can be conveniently used in conjunction with other heating systems as a backup energy source. The design of the devices is simple, so there are diy diagrams for assembling solar panels. Ready-made collectors are also affordable and pay off quickly. The only thing that needs to be done before purchasing them is to calculate the power of the equipment and the sizes of the modules.


In cottages and country houses, solar panels are installed for backup DC power supply of low power volts or AC loads of 220 Volts
Air-water collectors
Solar hot water systems are also suitable for any climate. The principle of operation of the system is simple: the water heated in the collectors flows through the pipes into the storage tank, and from it - throughout the house. The liquid is constantly circulated by the pump, so the process is continuous. Several solar collectors and two large reservoirs can provide heat to a summer house - provided there is enough sun, of course. High-temperature collectors allow you to install a "warm floor".
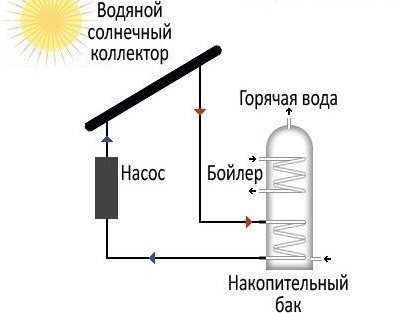

Solar hot water systems absolutely do not pollute the air and do not create noise, but their installation requires additional equipment: a pump, a pair of storage tanks, a boiler, a pipeline
The advantage of equipment operating on water collectors is environmental friendliness. Silence and clean air inside the house are just as important as heating and hot water. Before installing solar collectors, it is necessary to calculate how effective they will be in a particular case, because all the nuances are important for full operation: from the installation site to the expected power of the devices. One drawback should also be taken into account - in areas with a long summer period, an excess of heated water will appear, which will have to be drained into the ground.
Passive solar heating
No additional equipment is required for a passive solar heating device. The main conditions are three factors:
- perfect tightness and thermal insulation of the house;
- sunny, cloudless weather;
- optimal location of the house in relation to the sun.
One option suitable for such a system is a frame house with large glass windows facing south. The sun heats the house both from the outside and from the inside, as its heat is absorbed by the walls and floors.
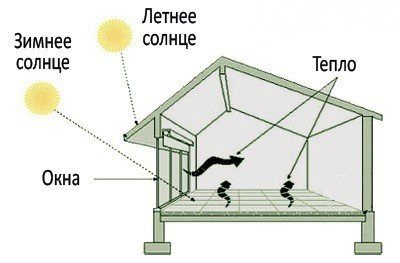

With the help of passive solar equipment, without the use of power supply and expensive pumps, you can save 60-80% of heating costs for a private house
Thanks to the passive system in sunny areas, heating costs are saved by over 80%. In the northern regions, this heating method is not effective, therefore it is used as an additional one.
All energy-saving heating systems have advantages over conventional ones, the main thing is to choose the most optimal, possibly combined, option that combines work efficiency and resource saving.
Classification
Heat supply systems are subdivided into:
- Centralized
- Local
(they are also called decentralized).
They can be water
and
steam.
The latter are not often used these days.
Local heating systems
Everything is simple here. In local systems, the heat source and its consumer are located in the same building or very close to each other. For example, a boiler is installed in a separate house. The water heated in this boiler is subsequently used to meet the needs of the house for heating and hot water.
Centralized heat supply systems
In a centralized heat supply system, either a boiler house serves as a source of heat, which generates heat for a group of consumers: a block, a city district, or even an entire city.
With such a system, heat is transported to consumers via main heating networks. From the main networks, the coolant is supplied to central heating points (CHP) or individual heating points (ITP). From the central heating station, heat is already supplied through the quarterly networks to the buildings and structures of consumers.
According to the method of connecting the heating system, heat supply systems are divided into:
Dependent systems - the heat carrier from the source of thermal energy (CHPP, boiler house) goes directly to the consumer. With such a system, the scheme does not provide for the presence of central or individual heating points. In simple terms, water from heating networks goes directly to the batteries.
Independent systems - in this system there are TSC and ITP. The coolant circulating through the heating networks heats the water in the heat exchanger (1st circuit - red and green lines). The water heated in the heat exchanger circulates already in the consumer heating system (circuit 2 - orange and blue lines).
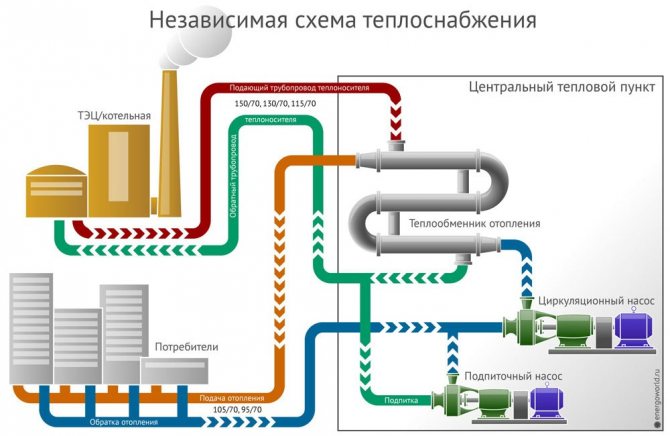

According to the method of connecting the hot water supply system, heat supply systems are divided into:
Closed. With such a system, the water from the water supply is heated by the heat carrier and supplied to the consumer. I wrote about it in the article.
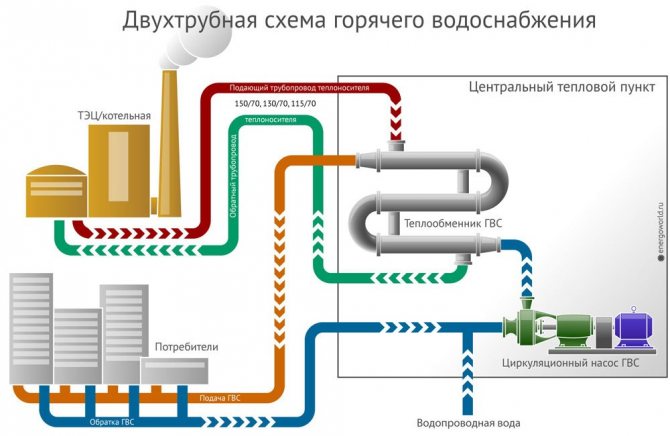

Open. In an open heat supply system, hot water is taken directly from the heating network. For example, in winter you use heating and hot water "from one pipe". For such a system, the drawing of a dependent heat supply system is valid.
Control system "Smart home"
Automatic devices of the “Smart House” complex are capable of making a huge contribution to saving energy sources used to generate heat.
The maximum level of efficiency can be achieved by choosing a system equipped with a number of additional functions, namely:
- weather-dependent control;
- indoor temperature sensor;
- the possibility of external control with the provided data exchange;
- the priority of the contours.
Let's consider all of the above benefits in more detail.
Weather-dependent temperature control in the house involves adjusting the heating level of the coolant depending on the outside temperature. If it's freezing outside, the water in the radiator will be slightly hotter than usual. At the same time, with warming, heating will be carried out less intensively.
The lack of such a function often leads to an excessive increase in the air temperature in the rooms. This not only leads to excessive consumption of energy resources, but also is not very comfortable for the inhabitants of the house.


Touchscreen control panels provide a choice of energy-saving options, allowing you to quickly and easily adjust the temperature in your home
Most of these devices have two modes: "summer" and "winter". When using the first, all heating circuits are turned off, while only devices intended for year-round use, for example, heating a pool, remain functional.
The room temperature sensor is needed not only to control the maintenance of the automatically set temperature. As a rule, this device is combined with a regulator, which allows, if necessary, to increase or decrease the heating.


An external temperature sensor is an indispensable part of most Smart Home control units. Such devices must be installed in the room, and if the heat supply is carried out floor by floor, then on each floor.
The thermostat can be programmed to reduce the temperature in rooms during certain hours, for example, when the inhabitants of the house leave for work, which leads to significant savings in heat costs.
Priority of heating circuits with simultaneous operation of different devices. So, when the boiler is turned on, the control unit disconnects the auxiliary circuits and other devices from the heat supply.
Due to this, the power of the boiler room is reduced, which allows to reduce fuel costs, as well as to evenly distribute the load for a given period of time.
The climate control system, linking the control of air conditioning, heating, power supply, ventilation into a single network, not only increases comfort in the house and minimizes the risk of emergency situations, but also saves energy.


Climate control drives that regulate all the functions of maintaining the temperature parameters in the room, as a rule, are hidden from view, for example, they are located in a manifold cabinet
External control - the ability to transfer data to smartphones allows owners to monitor the situation in order to quickly make adjustments if necessary. One of such solutions is a GSM module for a heating boiler.
In rooms with constant or long-term stay of people and in rooms where, according to production conditions, it is required to maintain positive temperatures during the cold season, a heating system is arranged.
Heating is called artificial heating of the premises of a building with compensation for heat losses to maintain the temperature in them at a given level, determined by the conditions of thermal comfort for the people in them and the requirements of the ongoing technological process. There are three types of heating: hot water, steam and air.
Heating systems include three main elements: a heat source (heat generator), heat lines (ducts or pipelines) and heating (heating) devices.
Heat is compressed in the heat generator, and the heat released during this is transferred to the heat carrier, i.e. environment that transfers heat from the generator to the heating devices. Heating devices transfer the heat received from the generator to the indoor air. The coolant moves along heat lines from the heat generator to the heating devices.
The heating system is one of the construction and technological installations of the building, which must meet the following basic requirements:
1) sanitary and hygienic - to provide the necessary internal temperatures, regulated by the relevant SNiP, without deteriorating the state of the air environment;
2) economic - to ensure the lowest reduced costs while reducing metal consumption;
3) construction - to provide for the placement of heating elements at the level with the architectural, planning and structural solutions of the building without violating the strength of the main structures during the installation and repair of heating systems.
4) assembly - to provide for the possibility of installation by industrial methods with the maximum use of standardized factory-made assemblies with a minimum number of standard sizes and limiting the use of individually manufactured assemblies and parts;
5) operational - characterized by simplicity and ease of management and repair, noiselessness and safety of operation;
6) aesthetic - to harmonize well with the interior decoration of the premises and not occupy unnecessary space.
In the practice of construction, various heating systems have been used, the choice of which is based on the use of certain features of the systems.
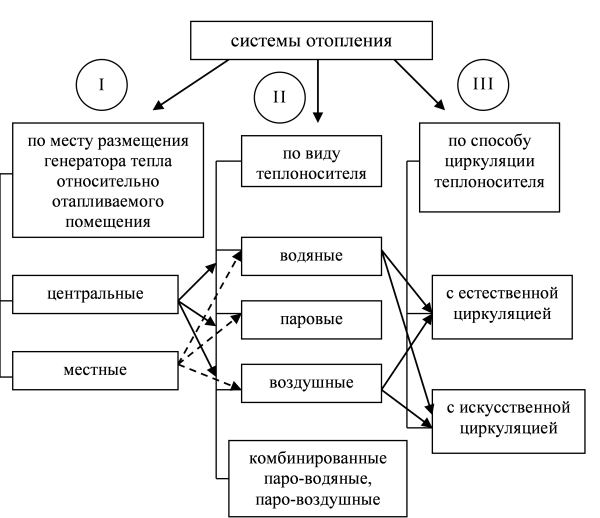
Heating systems are classified according to the following main features (Figure 5): by the type of heat carrier used; by the method of moving the coolant; at the location of the heat source.
By the type of heat carrier used
heating systems are divided into water, steam, air, fire-air.
By the method of moving the coolant
heating systems are divided into systems with natural (gravitational) motivation of the movement of the coolant and systems with forced motivation.
By the location of the heat source
heating systems are divided into central and local.
| Water heating systems | Forced | Central Local | Double-pipe Single-pipe |
| With a natural urge | Local | ||
| Steam heating systems | Low pressure High pressure | With gravity return of condensate With condensation tank and feed pump | |
| Stove heating | With non-heat-consuming furnaces With heat-consuming furnaces | ||
| Air heating | Combined with ventilation (direct flow) Recirculation | ||
| Electric heating | With intermediate heating agents (water, steam, air) With direct room heating |
Figure - 5 Classification of heating systems
In the local heating system
the heat generator, heating devices and heat-dissipating surfaces are structurally combined in one device. An example of local heating is a room stove. In it, the heat generator is the firebox, in which the fuel is burned, the smoke circulation serves as a heat conduit, heating the walls of the furnace and removing the combustion products from the furnace, and the air of the premises heats up when it comes into direct contact with the hot surfaces of the walls of the furnace. Local heating systems also include gas heating (when gas is burned in heaters located in a heated room) and electric, if electrical energy is converted into heat directly in the heaters themselves. The range of local heating systems is small and limited to one or two or three adjacent rooms.
Central heating systems
systems are called in which a heat generator (for example, a boiler) is located outside the heated premises, and the coolant is supplied to the places of consumption through pipelines.
In central heating systems, one heat generator, consisting of one boiler or a group of boilers, can heat not only an individual building, but also groups of buildings. A heating system that serves a whole group of buildings from one boiler house is called a district heating system.
Depending on the type of heat carrier, central heating systems are subdivided into water, steam, air and combined heating systems.
If a in the hot water heating system
circulation of water in pipelines and heating devices occurs under the influence of the difference in volumetric weights of cooled and heated water, then it is called
system with natural circulation.
In long-distance systems, it is economically impractical to use natural water circulation, as this would lead to the need to install pipes of too large diameters. Therefore, in these cases, they arrange water heating systems with artificial circulation of water using pumps (or pumping). These heating systems can use water with a temperature of up to 1000 C or high-temperature water (with a temperature of more than 1000 C) as a heat carrier.
In steam heating systems
steam from the boiler through pipelines enters the heating devices, where it condenses and, releasing the latent heat of vaporization, heats these devices. Condensate is returned to the boiler and again turns into steam.
Steam heating systems differ in the amount of initial pressure and are vacuum-steam
(with steam pressure up to 1 kgf / cm2), low pressure (from 1.0 to 1.7 kgf / cm2) and high pressure (more than 1.7 kgf / cm2). In steam heating systems, steam is moved by the pressure difference between the outlet of the boiler and in front of the heater.
Air heating system
depending on the type of primary coolant are subdivided into
water-air, steam-air, fire-air, electric-air and gas-air.
By the way the air moves, air systems can be with natural and mechanical impulse. In the second case, fans are used.
Combined heating system
is called a system in which either two different coolants are used, or one coolant, but with different parameters. It includes steam-water, water-water and all air heating systems.
Water and steam heating systems also differ in the way the main pipelines are wired (with upper, lower and middle wiring), by the way heating devices are connected to the risers (two-pipe and one-pipe), by the method of heat transfer from heating devices (convection and radiant) and by the type of heating devices (radiator, convector, panel, smooth pipes, etc.).
Requirements for heat carriers of heating systems.
The main requirements for heat carriers are the ability to accumulate heat, mobility and insignificant energy consumption for their movement. Hot water, steam and air used as a heat carrier most closely correspond to these requirements.
In addition, the temperature of the coolant (when exposed to heating devices) should not worsen the hygienic conditions of the room air.
Water, steam and air have different physical properties. Water is characterized by a high heat capacity, significant volumetric weight and high mobility, which makes it possible to transfer a significant amount of heat over long distances with a relatively small volume of water. When using hot water as a heat carrier, the surface temperature of heating devices (and, consequently, their heat transfer) can be regulated from one common center (for example, a boiler room), which allows more economical fuel consumption.
Table 2 - Properties of water vapor
| Pressure in kgf / cm2 | Tur temperature in C0 | Volume 1 Kg couple in m3 | Weight of 1 m3 of steam in Kg | Heat of vaporization 1 Kg couple in kcal | Total heat content 1 Kg couple in kcal |
| 99,1 | 1,722 | 0,5807 | 539,7 | 639,3 | |
| 1,2 | 104,2 | 1,4521 | 0,6887 | 539,5 | 641,3 |
| 1,6 | 112,7 | 1,1096 | 0,9013 | 531,2 | 644,7 |
| 119,6 | 0,9006 | 1,1104 | 526,8 | 647,2 | |
| 132,8 | 0,6163 | 1,6224 | |||
| 142,8 | 0,4708 | 2,1239 | 511,2 | 655,4 | |
| 0,382 | 2,6177 | 505,9 | 658,1 |
In steam heating, a large amount of heat released during condensation of steam, and a low volumetric weight of the latter, allow a significant amount of heat to be transferred over long distances with minimal energy consumption for moving the heat carrier. In addition, when using steam as a heat carrier, the number of heating devices is significantly reduced, since the temperature of the latter is much higher than with a heat carrier - hot water. The disadvantages of steam as a heat carrier include the impossibility of centrally regulating the heat transfer of heating devices, the high temperature on the surface of the latter and the possibility of burning organic dust on them, which worsens the sanitary and hygienic conditions of the heated premises. In addition, heat losses through steam and condensate pipelines significantly exceed heat losses through pipelines of water heating systems.
Air heating using heated air as a heat carrier, which has a relatively low temperature (500-700C), heat capacity and volumetric weight, consumes a lot of electricity to move large amounts of air. Its disadvantages can also be attributed to the noise that occurs during the operation of the fans.
For economic reasons, air heating is preferable to water and steam, since it does not require the installation of heating devices, the cost of which is about 60% of the cost of the entire heating system.
Heat pumps of two types
These designs are very popular. The device is considered the most efficient option for heating, since it is environmentally friendly. There is a type of heat pump called "mini-split". It has an outdoor unit and one or more indoor units that supply both hot and cold air. There are two types of models on sale:
- Air heat pumps. These are structures that have devices that, even at -20 degrees, take heat from the external air masses and distribute it throughout the house due to the installed air ducts.
- Ground source heat pumps. Devices with which you can use the energy of the soil. In the ground, they are laid horizontally in rings at a depth of 1.5 meters, no less (you should take into account the freezing of the soil). The pumps can be positioned vertically. For this, wells are drilled to a depth of 200 m.
Although they run on electricity, the devices are energy efficient. Considering the costs, their efficiency is very high (1: 3 for air, 1: 4 for geothermal structures).
In addition, the units are environmentally friendly and absolutely safe. Another advantage of heat pumps is reverse operation. They not only heat but also cool the air. The geothermal device can be combined with a water heater that will supply water up to +60 degrees.
Steam
A number of parameters that may differ for water heating are also applicable for steam:
- One- and two-pipe schemes can be found here;
- Layout can also be vertical or horizontal;
- The movement of steam and condensate is passing and dead-end.
Related article: Design and functioning features
But there are also characteristics that are relevant only for a couple.
- In vacuum-steam systems, the pressure is less than the atmosphere. In low pressure systems, it is no more than 1.7 kgf / cm2; anything beyond that is high blood pressure.
- Low pressure systems are not only closed, but also open (communicating with the atmosphere).
- Steam heating can be closed (with the return of condensate directly to the boiler) and open (condensate is collected in a separate container, from which it is then pumped into the boiler for reheating).
- In addition, the condensate lines can be dry (that is, not completely filled with water during heating operation) and wet.
Closed loop steam heating system.
Heating with wood
Since ancient times, wood has been widely used for heating houses: it is a renewable resource available to the population. It is not necessary to use full-fledged trees, you can also heat the room with wood waste: brushwood, twigs, shavings. For such fuel, there are wood-burning stoves - a prefabricated cast iron structure or welded steel. True, such devices have negative characteristics that hinder their widespread use:
- The most environmentally friendly heaters. When fuel is burned, toxic substances are emitted in large quantities.
- Preparation of firewood is required.
- Cleaning of burnt ash is required.
- Most fire hazardous heaters. If you do not know the technique of cleaning chimneys, a fire may occur.
- The room in which the stove is installed is heated, and in other rooms the air remains cool for a long time.
When choosing a wood-burning stove, you should pay attention to an effective modern model, which is equipped with a device - a catalytic converter. It burns unburned liquids and gases, thereby increasing the efficiency of the unit and reducing the emission of harmful substances.
Heat source
This role can be played by:
- Gas... Gas heating boilers supply the lowest price of heat energy. Where there are no gas pipelines, gas tanks or cylinders can be used instead.
But: in this case, the price of a kilowatt-hour of heat will increase significantly.
- coal and firewood... Solid fuel boilers for these energy sources are unified in most cases. Their main drawback is the limited autonomy of work: cleaning the ash pan and filling the fuel are required a couple of times a day.
But, boilers and gas generators of the upper combustion are capable of steam expanding the gap between the fillings.
- Pellets... Pellet boilers with dispensers and bunkers are allowed to achieve autonomy in a couple of days.
- Solarium... Here the autonomy is already calculated for seven days; the shortcomings can be attributed to the need and high noise of equipment in a bulky container for diesel fuel.
- Electricity... Along with direct heating devices, it is used by heat pumps that use electricity to pump heat from a relatively cold environment (air, water or soil) into a warmer room.
Here is a rough estimate of costs for various sources.
| Heat source | Price per kilowatt hour |
| Gas boiler (main line) | 0.7 p. |
| Solid fuel boiler (firewood) | 1.1 p. |
| Heat pump | 1.2 p. |
| Solid fuel boiler (coal) | 1.3 p. |
| Gas boiler (gas holder) | 1.8 p. |
| Gas boiler (cylinders) | 2.8 p. |
| Diesel boiler | 3.2 p. |
| Electricity (direct heating) | 3.6 p. |
Heat recovery
Using heat recovery will be a step towards creating an energy efficient private home, as well as a good way to save on utility bills. Heat recovery is the return of warm air through a ventilation system. When ventilating, we not only let in cold air, but also let out warm air, thus discrediting the central heating system and throwing money away.
With recuperation, not only the temperature regime is maintained, but the air is also cleaned. Every modern "passive" private house has a heat recovery system. The organization of recuperation is inexpensive, especially in comparison with the benefits that it brings. As statistics show, about 40% of the heat goes to the street when ventilated. But you have already paid for this warmth!
So, there are many different energy-saving heating systems and the main question is how to choose the most optimal one. To do this, you need to devote time and effort to its selection, purchase and installation.
Heat carrier

One of the classification schemes. Admittedly, it is far from complete.
If you do not go into small details, then there are three main types of coolant for heating systems:
- Water heating - in practice, this is not only water, but also various non-freezing liquids based on it, glycerin and oil. In most cases, it is possible to switch from one coolant of this type to another without any modification of the heating system.
- Use for heating couple imposes much more stringent requirements on the strength and heat resistance of pipes and heating devices. An obvious plus - superheated steam, due to its higher temperature, provides greater heating efficiency with the same size of the radiator or register. Minus - a great danger to the inhabitants of the premises in any accidents.
Please note: residential buildings are not heated by steam. In our time, steam heating is the lot of industrial premises, and mainly in enterprises with an outdated material and technical base.
- Finally, the premises can be fed heated air... For its transportation, insulated air ducts are used. As a rule, air heating is combined with a ventilation system.
Schematic diagram of an air heating boiler.
In this order, we will begin to consider the applied schemes.