Appointment
A heat energy metering unit is being organized for the following purposes:
- Controlling the rational use of heat carrier and heat energy.
- Controlling thermal and hydraulic modes of heat consumption and heat supply systems.
- Documenting the parameters of the coolant: pressure, temperature and volume (mass).
- Implementation of mutual financial settlement between the consumer and the organization engaged in the supply of thermal energy.

Main elements
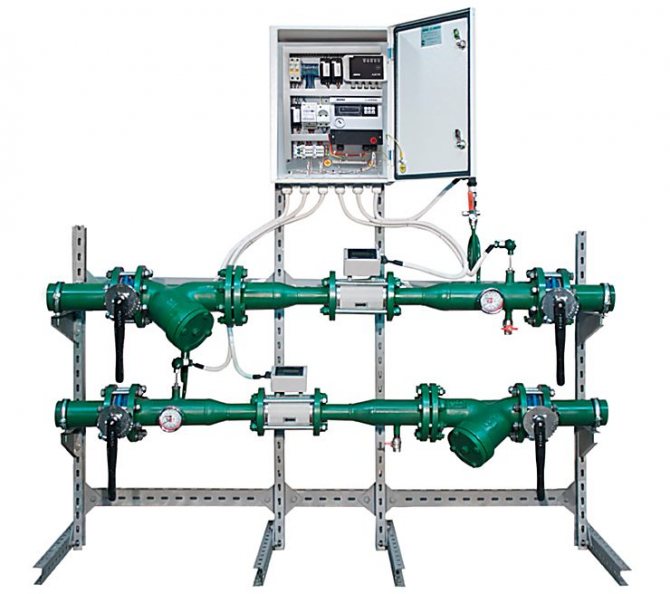
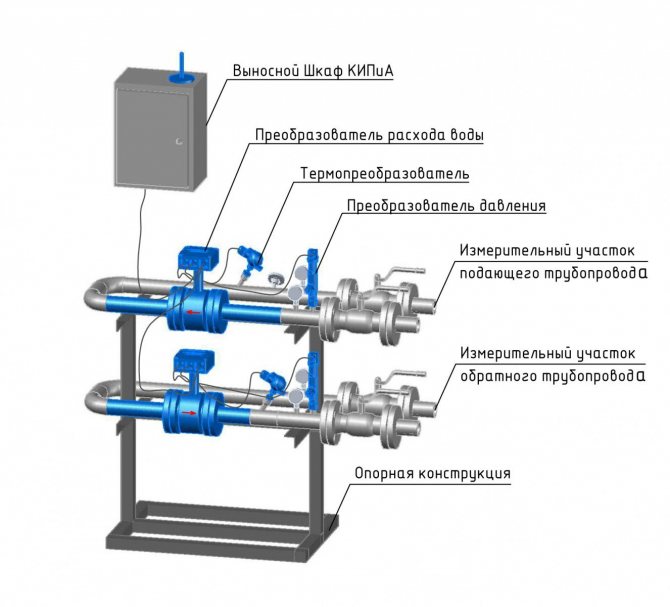
The heating unit consists of a set of devices and metering devices that ensure the performance of both one and several functions at the same time: storage, accumulation, measurement, display of information about the mass (volume), the amount of heat energy, pressure, temperature of the circulating liquid, as well as the operating time ...
As a rule, a heat meter acts as a meter, which includes a resistance thermocouple, a heat calculator and a primary flow transducer. Additionally, the heat meter can be equipped with filters and pressure sensors (depending on the model of the primary converter). Heat meters can use primary converters with the following measurement options: vortex, ultrasonic, electromagnetic and tachometric.
Device advantages
In addition to the fact that the installation of individual heat metering devices in an apartment allows you to pay depending on the readings, it undoubtedly has more positive aspects.


Heat meters for apartments
These characteristic advantages include:
- Private meter installations in a residential area allow energy consumption to be adjusted according to weather conditions. Mostly this is in demand in the spring and autumn periods, when the temperature outside can change every day.
- Using the device, you can establish malfunctions in the coolant line (air locks, blockage). This leads to an uneven heat supply, which, of course, will immediately reveal itself on the meter readings in the apartment.
- The installation of individual heat meters is also necessary because utilities calculate heating charges according to established standards, and not according to consumption. With the device, every month, heat metering in the apartment will be carried out according to the indications.
Thus, the benefits of installing individual heat metering devices in an apartment are obvious.
On a note. A heat meter installed on a hot water supply (hot water supply) will quickly justify its cost if the house has poor-quality heating. This is possible because in the case of meter readings below 40˚, the calculation is done as for cold water (according to Government Decree No. 354).
Meanwhile, the installation of such devices has a number of features, and therefore special attention should be paid to them.
Heat metering devices in the apartment
Individual products have a small flow section of the pipe, not exceeding 20 mm, while the calculation occurs in the range from 0.6 to 2.5 m 3 / h. This is allowed based on the flow rate of the coolant and the different temperatures of the water in the inlet and outlet pipes of the heating main.
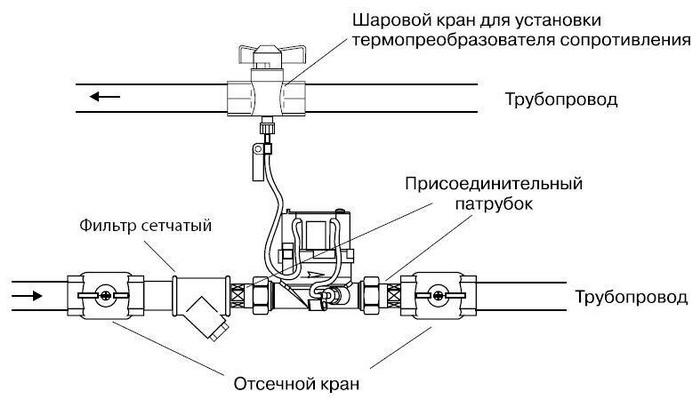

Heat meter connection diagram for apartments
It happens in this way: a meter and a heat meter are mounted on a liquid heating system device, in which operation is provided in pairs. Two temperature sensors branch off from the second device, one of them is attached to the inlet pipe, and the other to the outlet pipe.
As a result, the recording device collects the necessary readings of individual meters and, with the help of special transformations, displays the amount of consumed heat on the scale.
Heat meter
The heat meter is the main element of which the heat energy unit should consist. It is installed at the heat input to the heating system in close proximity to the boundary of the balance sheet of the heating network.

When installing a metering device remotely from a given border, heating networks add losses in addition to the meter readings (to account for the heat that is released by the surface of the pipelines in the section from the balance separation border to the heat meter).
The importance of accounting for consumed heat
Already from the introduction, we can conclude that any measures to reduce energy consumption should begin precisely with accounting for energy consumption. The scheme, according to which payment for heat is charged, until recently was the same in all countries of the post-Soviet space and was inherited from the USSR. The principle is simple: the supplier organization introduced an approved tariff per 1 m2 of premises, which includes all costs, delivery losses and profits of this enterprise.


Heat metering in an apartment building is needed in order to have an idea of the real heat consumption and to pay accordingly. Having a common building unit, you can safely proceed with the modernization of the building. The improvement in thermal performance will necessarily affect the heat consumption and will be taken into account by the devices. In addition, the introduction of the node will allow cutting off heating networks, for losses in which previously also had to be paid, they were taken into account in the tariff.
As a rule, the installation of metering devices provides financial savings for residents in the amount of 25 to 40%.
Heat meter functions
An instrument of any type must perform the following tasks:
1. Automatic measurement:
- Duration of work in the zone of errors.
- Operating time with the supplied supply voltage.
- Excessive pressure of the fluid circulating in the piping system.
- Water temperatures in pipelines of hot and cold water supply and heat supply systems.
- Coolant flow rate in hot water supply and heat supply pipelines.
2. Calculation:
- The consumed amount of heat.
- The volume of the coolant flowing through the pipelines.
- Thermal power consumption.
- The temperature difference between the circulating fluid in the supply and return pipelines (cold water supply pipelines).
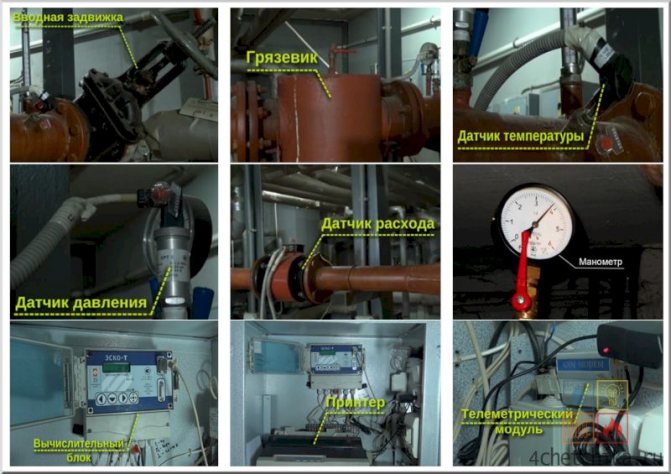
Thermal sensor
This device is mounted on the return pipeline together with shut-off valves and a flow meter. This arrangement allows not only to measure the temperature of the circulating fluid, but also its flow rate at the inlet and outlet.
Flow meters and temperature sensors are connected to heat meters, which allow calculating the consumed heat, storing and archiving data, registering parameters, as well as their visual display.
As a rule, the heat meter is housed in a separate cabinet with free access. In addition, additional elements can be installed in the cabinet: an uninterruptible power supply or a modem. Additional devices allow you to process and control data that is transmitted by the metering unit remotely.
Basic diagrams of heating systems
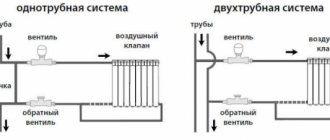
So, before considering the diagrams of heating units, it is necessary to consider what the diagrams of heating systems are. Among them, the most popular is the design of the upper distribution, in which the coolant flows through the main riser and is directed to the main pipeline of the upper distribution.In most cases, the main riser is located in the attic room, from where it branches into secondary risers and then is distributed over the heating elements. It is advisable to use a similar scheme in one-story buildings in order to save free space.
There are also diagrams of heating systems with lower wiring. In this case, the heating unit is located in the basement room, from where the main pipeline with warm water comes out. It is worth noting that, regardless of the type of scheme, it is recommended to also have an expansion tank in the attic of the building.
Heating unit diagrams
If we talk about schemes of heat points, it should be noted that the following types are the most common:
- Heating unit - a scheme with a parallel one-stage hot water connection. This scheme is the most common and simplest. In this case, the hot water supply is connected in parallel to the same network as the building's heating system. The coolant is supplied to the heater from the external network, then the cooled liquid flows in reverse order directly into the heat pipe. The main disadvantage of such a system, in comparison with other types, is the high consumption of network water, which is used to organize hot water supply.
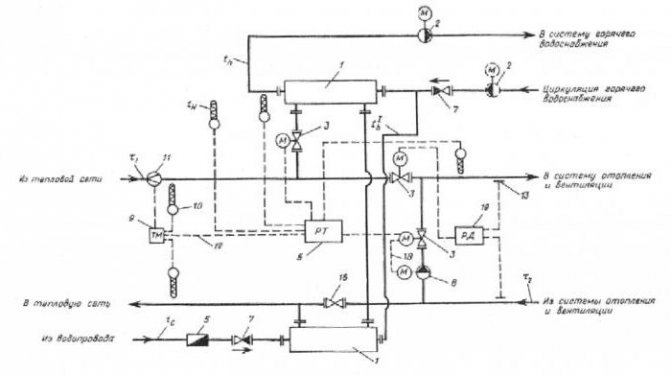

- Scheme of a substation with a sequential two-stage connection of hot water. This scheme can be divided into two stages. The first stage is responsible for the return pipe of the heating system, the second for the supply pipe. The main advantage that heating units connected according to this scheme have is the absence of a special supply of heating water, which significantly reduces its consumption. As for the disadvantages, this is the need to install an automatic control system to adjust and adjust the heat distribution. It is recommended to use such a connection if the ratio of the maximum heat consumption for heating and hot water supply is in the range from 0.2 to 1.
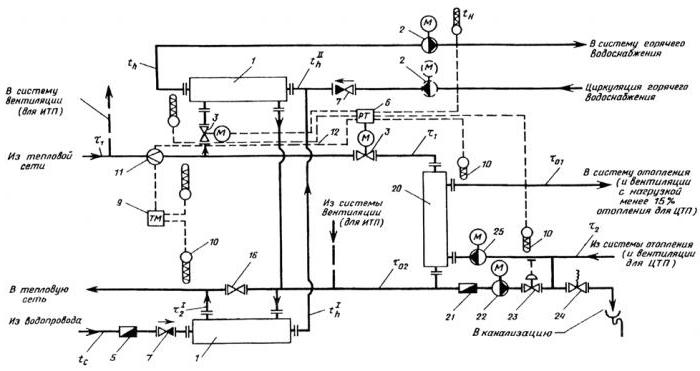

- Heating unit - a scheme with a mixed two-stage connection of a hot water heater. This is the most versatile and flexible connection scheme. It can be used not only for a normal temperature schedule, but also for an increased one. The main distinguishing feature is that the connection of the heat exchanger to the supply pipeline is carried out not in parallel, but in series. The further principle of the structure is similar to the second scheme of the heat point. Heating units connected according to the third scheme require additional consumption of heating water for the heating element.
Design features and principle of operation of heat meters of different types
According to the type of design and principle of operation, heat meters are:
- tachometric (or mechanical);
- ultrasonic;
- electromagnetic;
- vortex.
Mechanical heat meters
Structurally and according to the principle of operation, the simplest are mechanical devices, which are of the vane or turbine (rotary) type. They do not require the use of electricity, are reliable, do not present any difficulties in installation and subsequent maintenance. But they are demanding on the quality of the coolant, therefore they must be operated together with a filter that is installed before the device. When deposits appear on the impeller, the measurement accuracy becomes questionable. Of the important advantages, a low price should be indicated, but you should also pay attention to a short period of use: most often, after working out one intertesting period, the old device is simply replaced with a new one.
The principle of operation of the device is based on converting the translational motion of the coolant into rotational, produced by the impeller.Based on the number of revolutions, the necessary information about the amount of heat energy is read out.
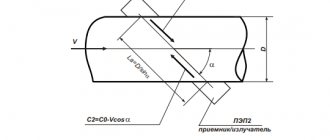
Ultrasonic devices for metering the consumption of thermal energy
The principle of operation of ultrasonic heat meters is based on measuring the amount of thermal energy using ultrasound: the transit time from the signal source to the receiver is determined. These two elements are installed on the pipe, but always opposite each other. Ultrasound in a liquid medium can propagate at different speeds, depending on the speed of movement of the coolant. Comparing these two values, the device determines the flow rate of the coolant. By design features, these metering devices can be: frequency, Doppler, time and correlation.
But when choosing this type of heat meters, which are characterized by high measurement accuracy, one should take into account the quality of the water in the pipe, which should not contain rust and other insoluble impurities. Otherwise, it will be very difficult to achieve high-quality measurements of heat energy consumption. The presence of a filter installed in front of the meter makes it possible to reduce the severity of the problem and obtain quite reliable data on consumption.
Operation of ultrasonic heat meters is allowed both with closed heating systems and with open ones.
Electromagnetic and vortex heat meters
The principle of operation of these devices is based on such a physical phenomenon as the ability of a liquid heat-transfer medium to be a source of the formation of electric waves in it. In terms of the accuracy of the measurements obtained, electromagnetic devices occupy a leading position, but can be used exclusively in systems with a horizontal coolant supply.


The principle of operation of vortex devices is based on the ability to form vortices in a liquid medium as a result of encountering an obstacle, and in this case, a counter plays its role. And the fixation of the frequency of formation and breakdown of vortices is fixed using a magnetic field or ultrasound. This type of device has a wider scope and can be mounted both on horizontal and vertical pipes. An important condition for the installation is the presence of long straight sections, while the total length of the system does not play a significant role, but the quality of the coolant, the flow rate, and the presence of air chambers significantly distort the measurements.
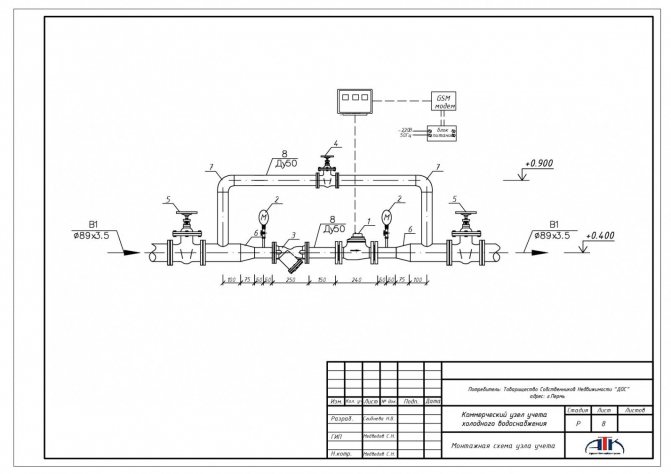
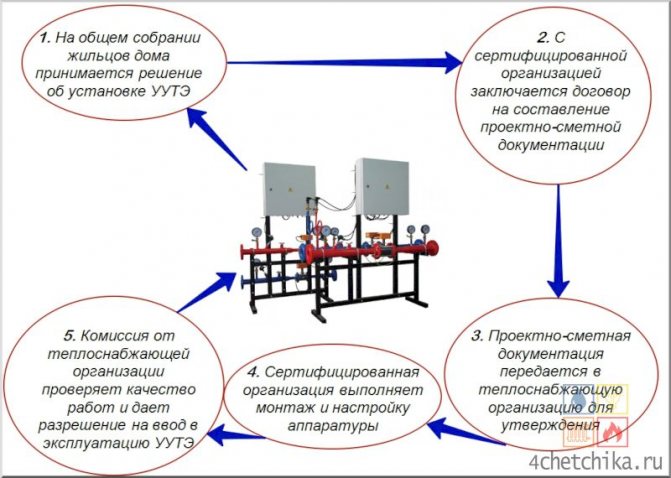
The order of installation of the metering unit
Before installing a heat metering unit, it is important to inspect the facility and develop project documentation. Specialists who are engaged in the design of heating systems, make all the necessary calculations, carry out the selection of instrumentation, equipment and a suitable heat meter.
After the development of design documentation, it is necessary to obtain approval from the organization that supplies heat. This is required by the current rules for accounting for heat energy and design standards.
Only after agreement, you can safely install heat metering units. Installation consists of inserting locking devices, modules into pipelines and electrical work. Electrical installation work is completed by connecting sensors, flow meters to the calculator and then starting the calculator to measure heat energy.


After that, the adjustment of the heat energy meter is carried out, which consists in checking the operability of the system and programming the calculator, and then the object is handed over to the agreeing parties for commercial accounting, which is carried out by a special commission represented by the heat supply company. It is worth noting that such a metering unit should function for some time, which for different organizations ranges from 72 hours to 7 days.
To combine several metering nodes into a single dispatching network, it will be necessary to organize remote recording and monitoring of information accounting from heat meters.
Installation features
Installation of a heat metering unit in an apartment building is divided into several main stages:
- Study and analysis of the object.
- Creation and approval of the project.
- Assembly and commissioning.
- Organization of monitoring.
- Providing a diagram of a heating unit of an apartment building to a heat supply organization and obtaining a permit for operation.
The cost of the procedure depends on the characteristics of the object and can vary significantly. If you need to replace the heat metering unit, the sequence of actions is approximately the same. The most crucial stage is the development of the project and the selection of equipment. Naturally, the installation of heat metering units should be carried out with maximum accuracy and precision. However, if the initial calculations turn out to be wrong, even high-quality expensive devices will not provide the required readings accuracy.


When a heating unit is installed in a private house, the matching scheme may differ slightly. In any case, going through the authorities on your own will require a lot of time. As a rule, the installation of heat metering units includes this service. Decide for yourself what is preferable for you - pay a little extra or save money through your own efforts. However, keep in mind that it is much easier for experienced representatives of a construction organization to obtain a permit than an individual.
Automation of heat metering units makes it possible to organize remote data collection from meters, which greatly simplifies object monitoring. UUTE maintenance should be trusted by professionals. Independence in this matter, as in the installation of heat metering units in Moscow, can lead to significant financial losses. If the equipment breakdown is not noticed in time, the repair can take a long time, and all this time you will overpay for unused heat. If you are interested in whether it is possible to install UUTE at the heating unit of your house and other questions on this topic, the answers to them can be obtained on our website.
Permit to use
When the heating unit is admitted to operation, the correspondence of the serial number of the metering device, which is indicated in its passport, and the measurement range of the set parameters of the heat meter to the range of measured readings, as well as the presence of seals and the quality of installation, is checked.
Operation of the heating unit is prohibited in the following situations:
- The presence of tie-ins into pipelines that are not provided for in the design documentation.
- The operation of the meter is beyond the accuracy standards.
- The presence of mechanical damage on the device and its elements.
- Breaking of the seals on the device.
- Unauthorized interference with the operation of the heating unit.
In accordance with the requirements of the "Rules for accounting for heat energy and heat carrier" (RD 34.09.102. Approved by the Ministry of Fuel and Energy of Russia on 12.04.97), each heat supply and heat consumption organization, regardless of the form of ownership, must keep records of heat energy and heat carrier consumption. For this purpose, heat sources (boiler houses and CHPPs) and heat consumers (heat points) are equipped with heat metering units.
Basic information about heat energy metering units.A heat metering unit is a set of instruments and devices that provides metering of heat energy, mass (volume) of the coolant, as well as control and registration of its parameters. The level of equipment of metering units for heat sources and consumers with measuring instruments depends on the heat supply scheme, type and value of heat load and is established by these Rules. The energy supplying organization (ESO) does not have the right to additionally require the consumer to install devices at the metering unit that are not provided for by the Rules. On the other hand, the consumer, in agreement with the ESS, can additionally install metering and control devices, if this does not violate the technology and accuracy of commercial metering.In this case, the readings of additional devices cannot be used in mutual settlements between the consumer and the ESP.
All work on the equipment of the metering unit must be performed by the organization. Licensed (permission) by Rostekhnadzor.
Metering devices perform one or several functions, such as: measuring, accumulating, storing, displaying information about the amount of thermal energy, the flow rate of the coolant, its pressure and temperature, as well as the operating time of the devices. Depending on the possibility of using information, devices are divided into indicating and recording. In the latter, the measured value is displayed on paper in digital or graphical form.
By the nature of the measured physical quantities, devices are subdivided into:
- manometers - devices for measuring pressure;
- thermometers - devices for measuring temperature;
- water meters - devices for measuring water flow;
- heat meters - devices for measuring the amount of heat.
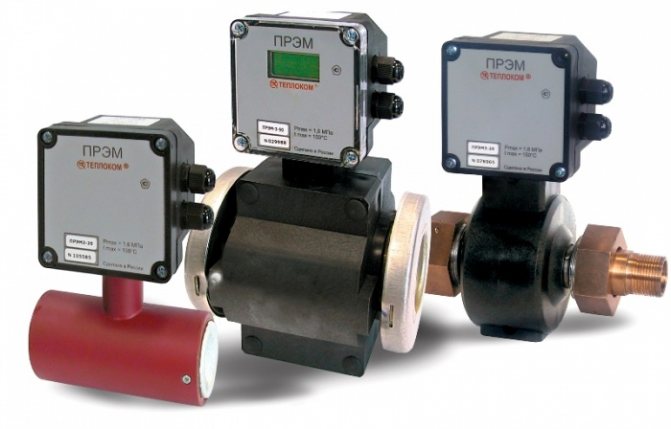
The most complex of the devices is the heat meter. It consists of two functionally independent parts: a heat meter and sensors for the flow rate of the coolant, its temperature and pressure. Having received data on the flow rate, temperature and water pressure, the calculator calculates the amount of heat.
As you know, the heat consumption is directly proportional to the product of the water consumption G by the difference in the enthalpies of the supply water in the supply line h1 and in the return line h2:
Q = G (h1 - h2)
The enthalpy of water characterizes the internal energy of 1 kg of water and is found as the product of the heat capacity of water C and its temperature t:
h = С × t
The heat capacity of water determines the amount of heat that must be supplied to 1 kg of water in order to change its temperature by 1 ° C in kJ / kg degrees or in kcal / kg degrees. Heat capacity, and hence enthalpy, depends on temperature and pressure. Therefore, to find it, the heat calculator must receive information from temperature and pressure sensors.
To measure the flow of water in heat meters, such methods are used as the method of alternating pressure on orifices, tachometric, electromagnetic, ultrasonic, vortex, etc. Therefore, heat meters are briefly called electromagnetic, ultrasonic, vortex, tachometric, etc.
The vast majority of heat meters measure the volumetric flow rate of water. To switch to mass flow, the calculator calculates the density of the water based on its temperature.
In general, heat meters calculate and record the following parameters:
- coolant flow rate in m3 / h (t / h);
- total volume (m3) and mass (t) of the coolant (cumulative total);
- total consumption of heat energy in Gcal (cumulative total);
- thermal power in Gcal;
- temperature of the coolant in the supply and return pipelines;
- temperature difference in pipelines;
- average hourly and daily values of the above parameters.
In addition, the heat meter provides data on the operating time in normal mode and in the event of a technical malfunction of the device. In the event of a malfunction in the measuring complex, a malfunction code and operating time are indicated in the presence of each abnormal malfunction.
The heat meter stores information about measurements, which can be output from the archive to a computer, printer, dispatcher console, etc. Viewing the archived data can be performed on the liquid crystal monitor of the device.
The device records parameters in the following ranges:
- the amount of heat - from 0 to 10 9 Gcal;
- mass or volume - from 0 to 10 9 t or m3;
- water consumption - from 0 to 10 6 m3 / h or t / h;
- water temperature - from 0 to 150 0С;
- the difference in water temperatures in the supply and return pipelines - from 2 to
150 0C;
- water pressure - from 0 to 2.5 MPa;
- time - from 0 to 10 9 hours.
The error in measuring the amount of heat, flow rate, temperature difference, water pressure and temperature does not exceed ± 2%. Time is measured with an accuracy of ± 0.02%
. Currently, heat meters are produced by many manufacturers (at least 45 companies), including St. Petersburg, "Logic", "Teplocom". , for example, produces heat meters of the ТСР type in the amount of 13 thousand pieces. in year. In St. Petersburg, at least 10,500 buildings are equipped with heat metering units. The use of metering units, as practice shows, allows you to save on heating bills by an average of 30%.
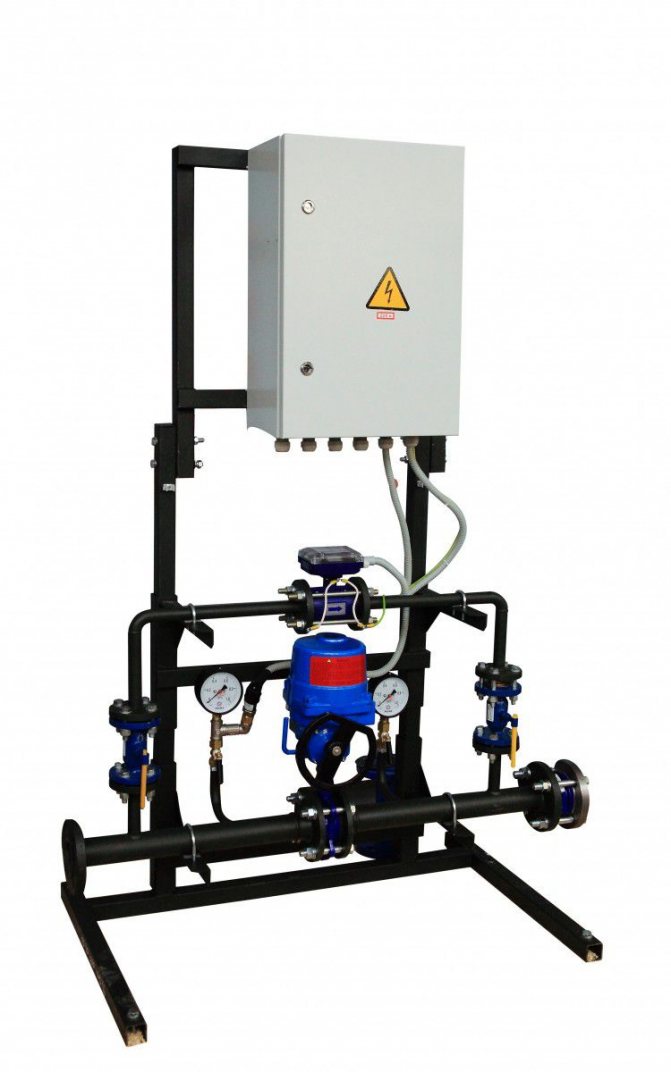
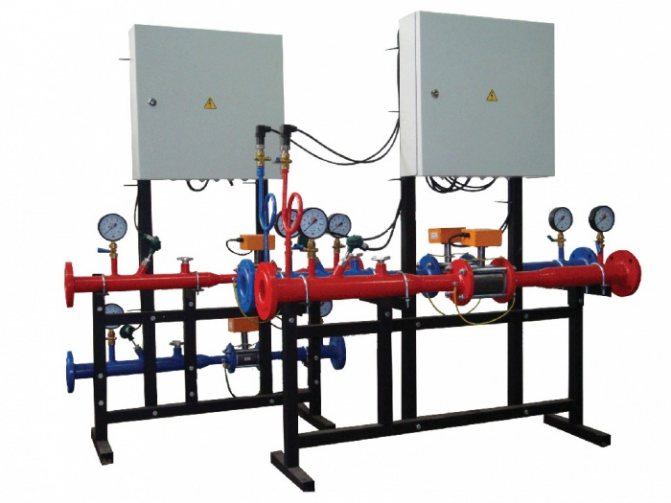
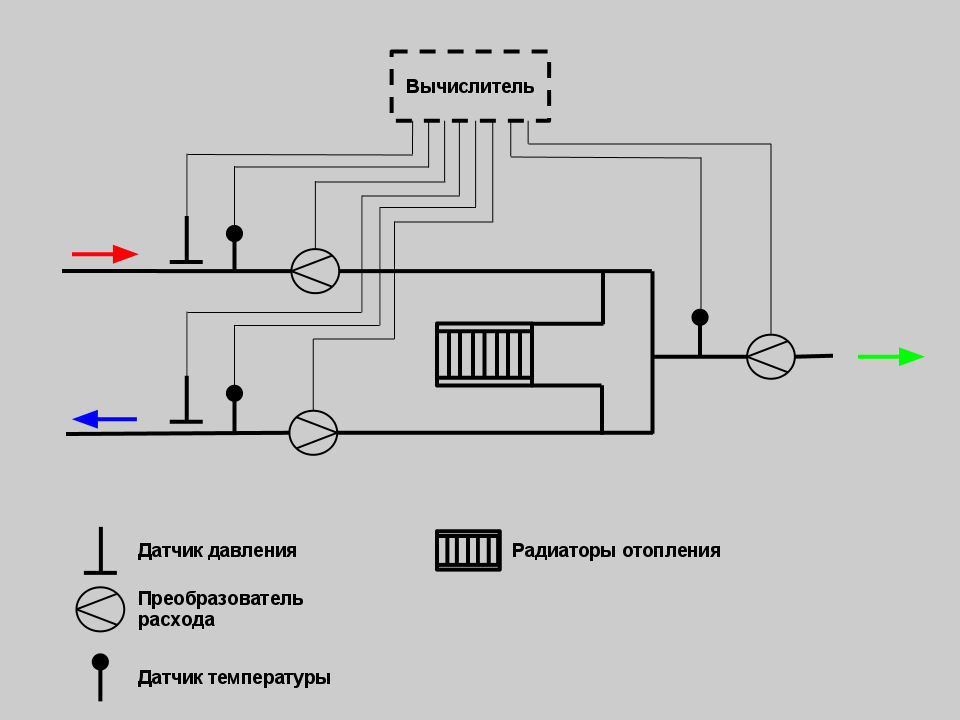
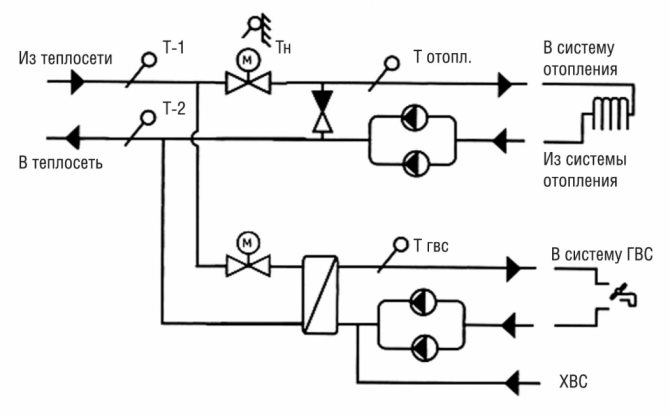
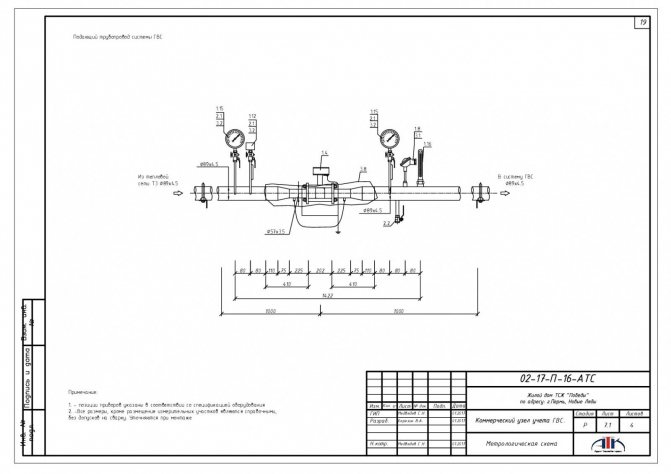
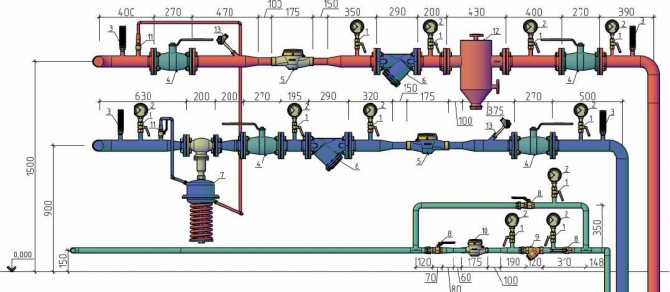
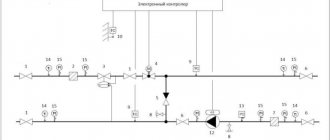
Examples of installation of heat metering units in a boiler room and heating points are shown in Fig. 1, 2 and 3.
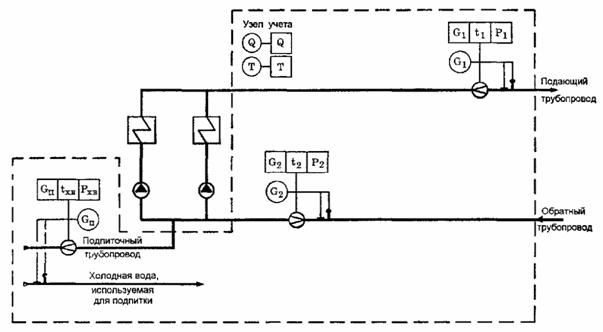

Fig. 1. Layout of points for measuring the flow rate of the coolant and its recorded parameters in the boiler room.
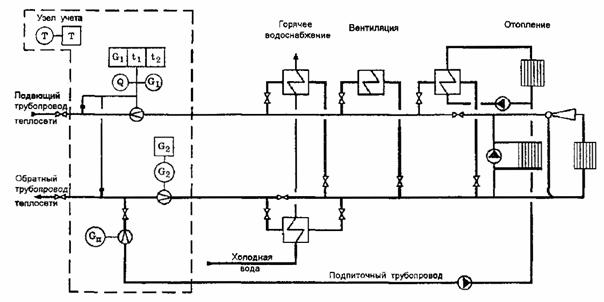

Fig. 2. Layout of points for measuring the flow rate of the coolant and its recorded parameters at the heat point of an open heat supply system
Fig. 3. Layout of points for measuring the flow rate of the coolant and its recorded parameters in a heating point with a closed heat supply system
User's approval for UUTE.The choice of devices for use at the metering unit of the consumer is carried out by the consumer in agreement with the ESS. In case of disagreement between them, the final decision is made by Rostechnadzor. Devices must be protected from unauthorized interference in their operation and be calibrated at intervals stipulated by the State Standard (for example, once every 4 years).
Admission to operation of UUTE is carried out by a representative of the ESP in the presence of a representative of the consumer, about which an Act is drawn up in 2 copies. The act is approved by the head of the ESO.
For the UUTE admission, the consumer representative submits the following documentation to the ESS:
- a schematic diagram of a heat point;
- project at UUTE, agreed with the ESO;
- passports for metering unit devices;
-documents on the verification of devices with a valid stamp by the state certifier;
-technological schemes of the metering unit, agreed with the State Standard, if the water flow is measured by the variable pressure method.
After receiving the Certificate of admission to operation, the representative of the ESP seals the UUTE devices.
Before each heating period, the readiness of the UUTE for operation is checked, about which an appropriate act is drawn up.
Operation of UUTE at the consumer.UUTE operation should be carried out in accordance with the technical documentation specified above. Responsibility for the operation of UUTE is borne by the person appointed by the head of the organization, who is in charge of this metering unit. Violation of the operating requirements set forth in the technical documentation is equivalent to the failure of the UUTE. In addition, UUTE is considered out of order in the following cases:
— unauthorized interference in its work;
— violation of seals on the equipment of the metering unit and electrical communication lines;
—mechanical damage to UUTE devices and elements;
— operation of any of the devices outside the established accuracy standards;
— upon expiration of the validity period of the State Verification of at least one of the devices of the metering unit;
— tie-ins into pipelines not provided for by the UUTE project.
The time of the metering unit exit is recorded in the log, which is immediately (within no more than one day) reported to the ESS. UUTE failure is documented in a protocol. After the metering unit is restored to its proper working capacity, it is admitted into operation by a representative of the ESS in the presence of a consumer's representative, about which a corresponding Act is drawn up.
The readings of the devices are recorded by the consumer on a daily basis at the same time in a special journal. Within the period established by the Agreement, the consumer submits copies of the journal to the ESS for calculating the consumed heat energy and coolant.
Periodic inspection of UUTE is carried out by representatives of the ESP and (or) Rostekhnadzor in the presence of a consumer representative.
Attachment 1
Security questions with answers
Notes:The brackets indicate:
1. PTE TE - rules of technical operation of thermal power plants
2. PTB - safety rules for the operation of heat-consuming power plants and heating networks of consumers.