Published by lpunity in 12.11.2018
Any buildings and apartments that are connected to the district heating network use heat to organize and maintain the optimal temperature for consumers. The device that organizes the control of the amount of energy is called a heat meter. Such a device must meet the requirements for heat metering units in accordance with the contract concluded with representatives of the heating network. It can also monitor readings and parameters during the operation of heat carriers (water and steam circulating in heating devices) at consumers.
Rules for the organization of commercial metering of heat energy
When using a heat meter under a contract, the consumer pays only for the amount of heat produced. This device is needed to organize the savings in the amount of heat consumed and reduce fuel consumption in accordance with the signed contract after the adoption of the act. Technical metering of heat energy is a necessary organization in a modern building to control the equipment of power grids.
The requirements for commercial heat metering units say that these are devices for organizing the measurement of temperature and volume of heat energy. According to the rules, they consist of a flow meter, temperature sensors at the inlet and outlet, and an electronic calculator. Taking into account the information on the mass of the flow, the consumer can determine the volume of water and steam that the equipment produces by the meter.
To organize measurements of parameters, consumers can use the following formula: the produced mass of heat is equal to the volume of heat supplied through the flow meter multiplied by the difference in temperature in the supply and return pipelines. This indicator is multiplied by the heat transfer coefficient, which characterizes the parameters of the equipment according to the operating contract.

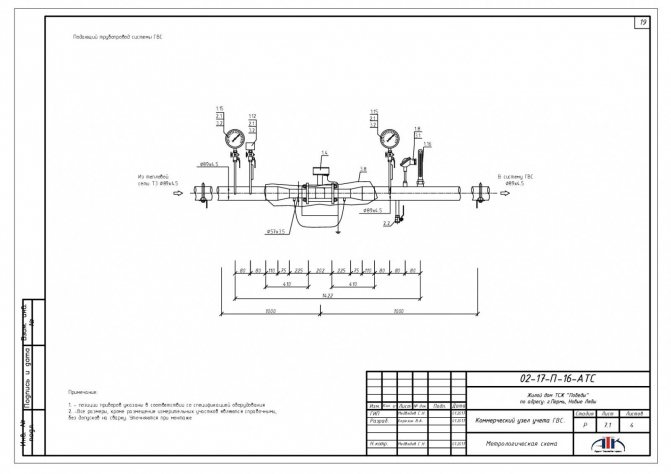
The current technical conditions and the passport of the heat metering unit determine the installation rules. For example, a heat meter must be included in the register of measuring instruments, like any other metrological device.
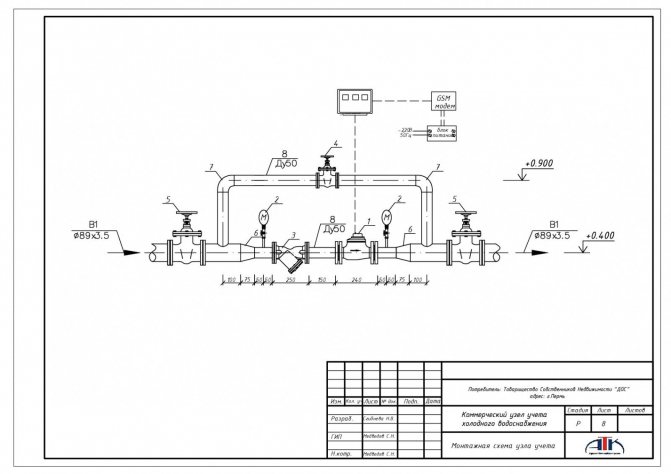
In accordance with the technical specifications for the organization of the installation of heat energy meters, they are mounted on straight sections of the system, and temperature sensors - on pipelines with a diameter of at least 70 mm with the inclusion of additional fittings (filters, ball valves, measuring manometers and thermometers). The work is performed by representatives of the heating network.
This set of equipment for the heat supply system, according to the rules of the organization, is called a commercial metering unit. Requirements for work on its installation are regulated in Article 19 (Organization of commercial metering of heat energy, heat carrier Federal Law "On Heat Supply").
TECHNICAL ACCOUNTING OF HEAT.
Tweet
TECHNICAL ACCOUNTING OF HEAT.
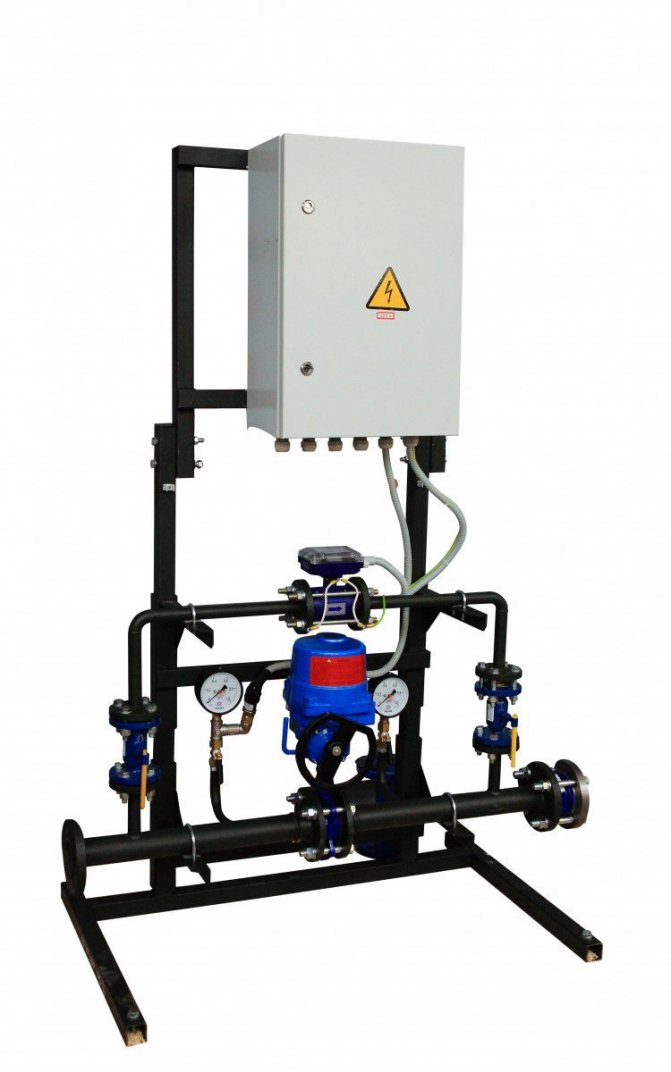
System technical heat metering allows you to calculate the amount of supplied and consumed heat and keep track of the flow rate of the coolant.
Systems technical heat metering especially relevant for enterprises producing and consuming thermal energy. CHP and boiler houses - the main heat producers are faced with the need to account for heat energy production and determine the mass of the heat carrier, for internal assessment of technical and economic indicators and for the supply of heat energy to specific consumers.
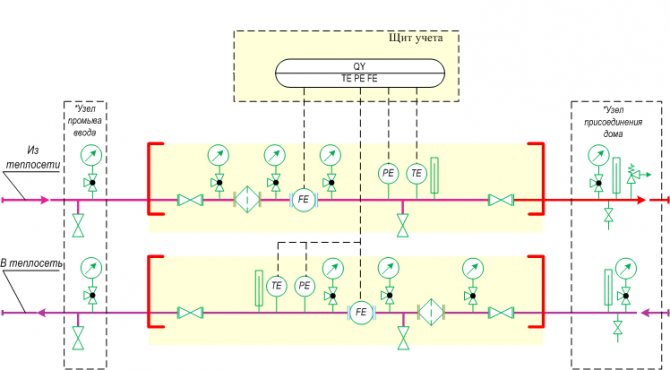
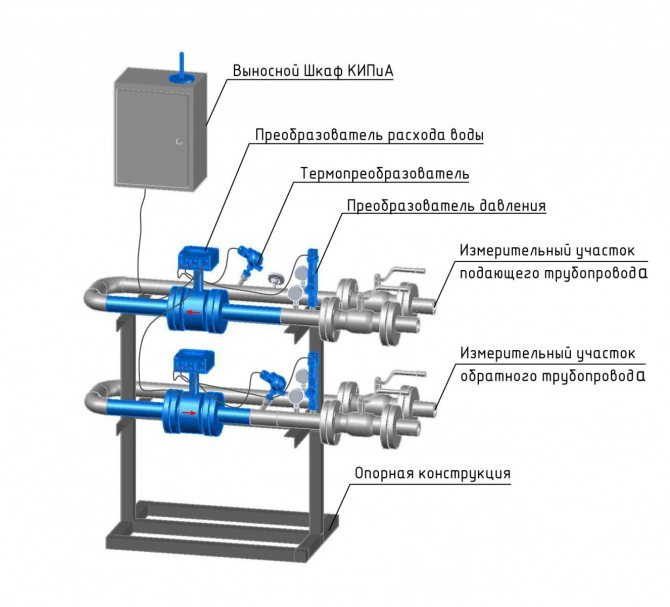
Fig. 1. Heat metering system equipment.
Systems technical heat metering are designed to provide:
- reliability and legitimacy of accounting and control of heat and coolant parameters;
- formation of technical operational accounting information on the volume of heat consumption and the parameters of the coolant;
- formation of an accounting database for the purpose of further statistical analysis.
Technical accounting of heat implies the determination of the following basic parameters:
- the amount of heat energy consumed by the consumer every hour on an accrual basis;
- the value of the volume of the coolant for each pipeline for each hour with a cumulative total;
- average hourly and average daily temperature of the heat carrier for each pipeline.
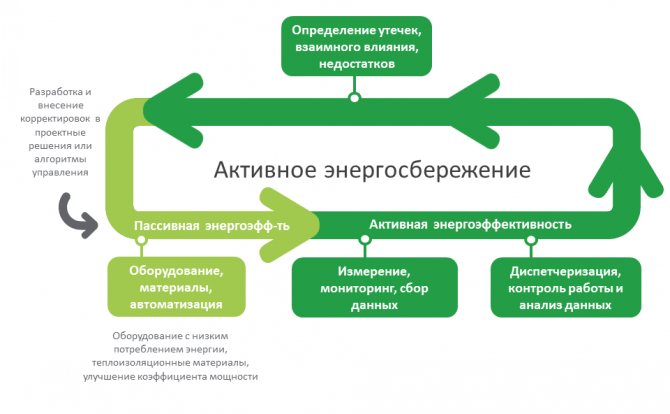
Technical accounting systems for heat, as a rule, are formed from unified technical means of measurement, devices, elements and in the aggregate is an information system, if necessary, widely spaced across the territory, divided into the following levels:
- Measuring. Consists of sensors of primary information. Serves to measure the temperature of the outside air and the parameters of the heat carrier: flow; temperature; pressure.
- Data collection and transmission devices.
- Data collection server.
- Database storage.
All main technical measuring instruments are registered in the State Register.
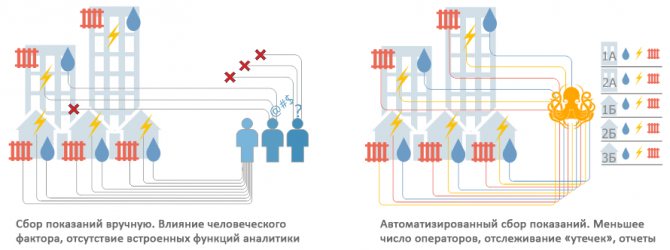
Thus, using the system technical heat metering companies that are engaged in the technical operation of heat points and heating systems, in practice, develop and implement algorithms that reduce heat energy consumption and reduce losses without reducing the quality of services. It is advisable to perform alignment technical heat metering with technical accounting for water.
Share on social media networks
РќСЂР ° вится
Installation of measuring equipment
According to the rules for installing heat metering devices, there are two ways to install measuring devices:
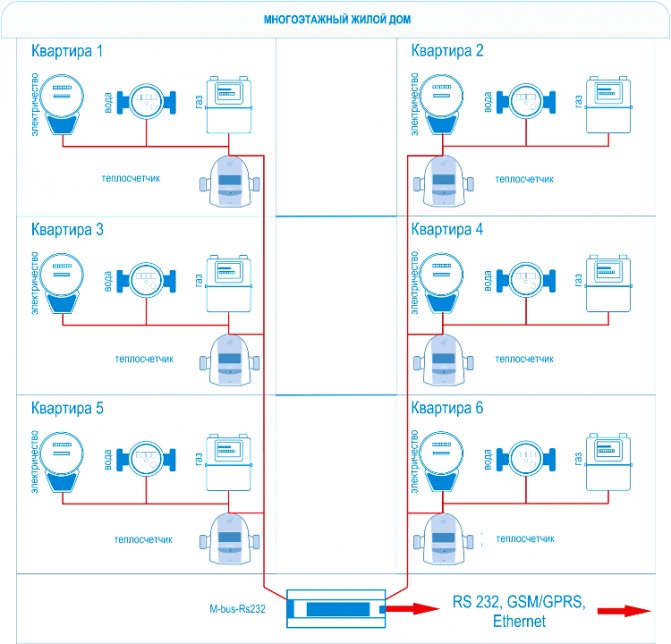
- Measurement of temperature and energy mass requires the organization of heat meters on each heat carrier. To get the total consumption of heat mass for an apartment, the consumer needs to add data on all equipment in the reporting period.
- The organization of one metering device for heat consumption in the riser and temperature sensors is carried out on each heat carrier at consumers. In this case, the amount of work on reprogramming is determined by representatives of the heating network. They also add data for each pipeline to get the total consumption by consumers.
Only one-pipe horizontal systems allow measurement with one heat meter. However, such devices are equipped only in industrial and industrial buildings. Therefore, an effective solution to the problem, which does not require significant investment and reconstruction of the premises, is the installation of commercial temperature measuring devices.


The cost of installing an apartment heat meter
Our company is also engaged in verification, repair, dismantling and installation of general house heat meters and calculators, flow meters, thermal converters and commissioning. VIST, KM-5, MAGIKA, Malachite-TS8, Malachite-RS8, SKM-1, TEM-05M, TEM-104 with PRP, TEM-106 with PRP, SA-94, SENSUS Polikom M, VZLET, VKT-5, VKT-7, MKTS, ST-10, TEROSS, TMK, TEM-104, TEM-106, ESCO, MT200DS, MULTIKAL, VTE-1.
Verification of an apartment heat meter in the laboratory - 2,018 rubles
SANEXT - 14,000 rubles
MARS - 14,000 rubles
Replacing an apartment heat meter with a new one - 6,000 rubles
The package includes:
- Heat meter with immersion sleeve, diameter 15 mm .;
- Ball valve - 3 pcs.;
- A package of documents;
- Installation;
- Sealing.
Additional accessories for a non-standard situation or with a diameter of 20 mm. are paid additionally.
Installation of a heat meter is possible only after being inspected by a specialist.
The heat meter is installed on the heating radiator in the apartment, depending on the structure of the central heating system itself.There are two types of central heating: vertical and horizontal. With a vertical system (pipes, or a pipe coming out of the ceiling and going into the floor), a heat meter is installed on each radiator in each room. Saving utility services up to 70%, with horizontal wiring (pipes enter the apartment from the wall and run parallel to the floor from room to room), the meter is installed alone for the entire apartment.
For apartment heat metering, heat meters KARAT-Compact, eif, MARS, DIO-99, MINOL, TEHEM, DANFOS, PULS, B METERS Hydrocal, Elster, VALTEC can be used.
The KARAT-Compact heat meter is a small-sized device designed for heat metering in apartments and cottages. This heat meter stands out for its modern design and low price. The successful original design of the heat meter provides ease of installation and ease of maintenance, compact dimensions - trouble-free integration in tight spaces.
The flow path (EAS element) is permanently installed in the pipeline, the measuring unit is screwed into it.
Additionally, the liquid end (EAS element) is equipped with a shut-off cover. This design allows during operation to remove the measuring unit for maintenance and verification without stopping the heat supply system. At the stage of installing the heat meter, the closing cover makes it possible to install the measuring unit after the end of the plumbing work.
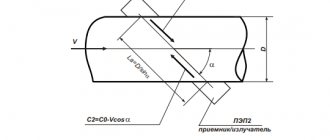
Features in the design of the measuring part of the heat meter are the basis for high accuracy and stability of measurement over many years. The coaxial flow transducer in a multi-jet dry-running design is equipped with a large number of inlet and outlet channels. Their positioning to optimize water flow reduces axle load, which increases service life and provides high sensitivity. This design minimizes pressure loss and eliminates the need for straight up and downstream runs. The absence of a magnetic coupling in the design excludes the possibility of outside interference in the operation of the device using a magnet.
With its small size, the KARAT-Compact heat meter has all the functions necessary for this class of devices.
There are several options for KARAT-Compact heat meters.
Heat meters KARAT-Compact are manufactured in two versions:
| Name | Execution | Pipeline |
| KARAT-Compact-MB | Monoblock | Feed or reverse * |
| KARAT-Compact-SP | With a remote calculator (up to 60 cm) | Feed or reverse * |
Heat meters are subdivided according to nominal flow rates of 0.6; 1.5; 2.5 m3 / hour and the diameter of the pipeline DN15, DN20
Summary table. Executions and modifications of KARAT-Compact heat meters
KARAT-Compact-MB for installation in the return pipeline:
| Du, mm | 15 | 15 | 20 |
| Rated consumption, m 3 / hour | 0.6 | 1.5 | 2.5 |
KARAT-Compact-MB for installation in the supply pipeline:
| Du, mm | 15 | 15 | 20 |
| Rated consumption, m 3 / hour | 0.6 | 1.5 | 2.5 |
KARAT-Compact-SP for installation in the return pipeline:
| Du, mm | 15 | 15 | 20 |
| Rated consumption, m 3 / hour | 0.6 | 1.5 | 2.5 |
KARAT-Compact-SP for installation in the supply pipeline:
| Du, mm | 15 | 15 | 20 |
| Rated consumption, m 3 / hour | 0.6 | 1.5 | 2.5 |
Example: Installation of the KARAT-Compact heat meter in the return pipeline:
| The thermocouple is installed in the tee | The thermal converter is installed in a special ball valve with a hole for the thermal converter |
Design and principle of operation
The main task of heat metering devices is to determine the temperature and take into account the flow rate of the coolant. In connection with the tasks set, the device has a relatively complex design and, as a rule, includes the following main blocks:
- temperature sensors installed on the supply line and in the return pipe;
- coolant flow sensor;
- pressure transducer;
- calculator;
- display.
Since heat meters equipped with the ability to transfer readings to an automated control and accounting system are becoming more and more popular, batteries and electronic units can be included in such a device to carry out calculations, store data and automatically transfer them.
The design can be complicated by adding additional blocks to expand the functionality of the device, which can additionally
- measure the running time;
- calculate and store the average temperature conditions for a certain period of time;
- measure the consumed energy for a specific time interval, etc.
The principle of operation of the heat meter is based on the calculation of heat. Calculations are carried out in the device itself, equipped with a calculator. The readings of temperature sensors and a coolant flow sensor are taken as a basis. Further, in the calculator, the calculation takes place according to the formula, which is the product of the readings of the water flow rate by the difference between the readings of the temperature sensors. The obtained value is written into the archive and displayed on the display.