Heat dissipation is an important characteristic of radiators, which shows how much heat a given device gives off. There are many types of heating devices that have a certain heat transfer and parameters. Therefore, many people compare different types of batteries in terms of thermal characteristics and calculate which ones are the most efficient in heat transfer. In order to specifically solve this issue, it is necessary to carry out certain calculations of the power for various heating devices and compare each radiator in heat transfer. Because customers often have a problem with choosing the right radiator. It is this calculation and comparison that will help the buyer to easily solve this problem.
Heat dissipation of the radiator section

Thermal output is the main metric for radiators, but there are also a bunch of other metrics that are very important. Therefore, you should not choose a heating device, relying only on the heat flow. It is worth considering the conditions under which a certain radiator will produce the required heat flow, as well as how long it is able to work in the heating structure of the house. That is why, it would be more logical to look at the technical indicators of sectional types of heaters, namely:
- Bimetallic;
- Cast iron;
- Aluminum;
Let's carry out some kind of comparison of radiators, based on certain indicators, which are of great importance when choosing them:
- What thermal power does it have;
- What is the spaciousness;
- What test pressure withstands;
- What working pressure withstands;
- What is the mass.
Comment. It is not worth paying attention to the maximum heating level, because, in batteries of any type, it is very large, which allows you to use them in buildings for housing according to a certain property.
One of the most important indicators: working and test pressure, when choosing a suitable battery, applied to various heating systems. It is also worth remembering about water hammering, which is a frequent occurrence when the central network begins to carry out work activities. Because of this, not all types of heaters are suitable for central heating. It is most correct to compare heat transfer, taking into account the characteristics that show the reliability of the device. The mass and capacity of heating structures is important in private housing. Knowing what capacity a given radiator has, you can calculate the amount of water in the system and make an estimate of how much heat energy will be consumed to heat it. To find out how to attach to the outer wall, for example, made of a porous material or using the frame method, you need to know the weight of the device. To get acquainted with the main technical indicators, we made a special table with data from a popular manufacturer of bimetal and aluminum radiators from a company called RIFAR, plus the characteristics of MC-140 cast iron batteries.
In conclusion
The heat output of a radiator is understood as the amount of heat that it is capable of giving into the room under normal operating conditions. This is the most important parameter when choosing a heater for a home, the power calculation is relatively simple, so that everyone can choose the best option for themselves.
The video in this article shows a detailed example of calculating the required heat output of heaters for a home.
Did you like the article? Subscribe to our channel Yandex.Zen
Bimetallic radiators
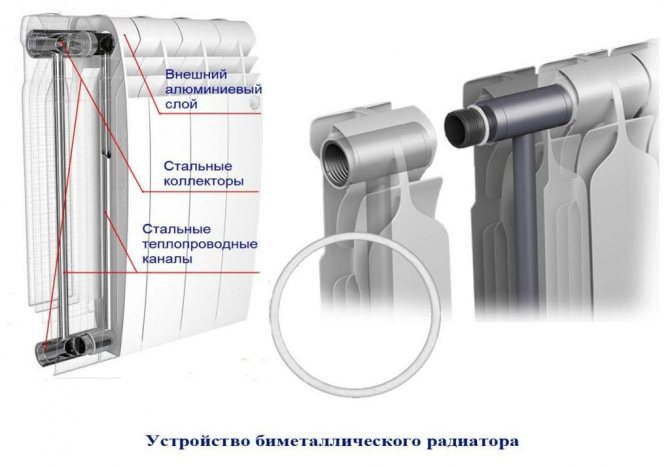

Based on the indicators of this table for comparing the heat transfer of various radiators, the type of bimetallic batteries is more powerful. Outside, they have a ribbed body made of aluminum, and inside a frame with high strength and metal pipes so that there is a coolant flow. Based on all indicators, these radiators are widely used in the heating network of a multi-storey building or in a private cottage. But the only drawback of bimetallic heaters is the high price.
Aluminum radiators
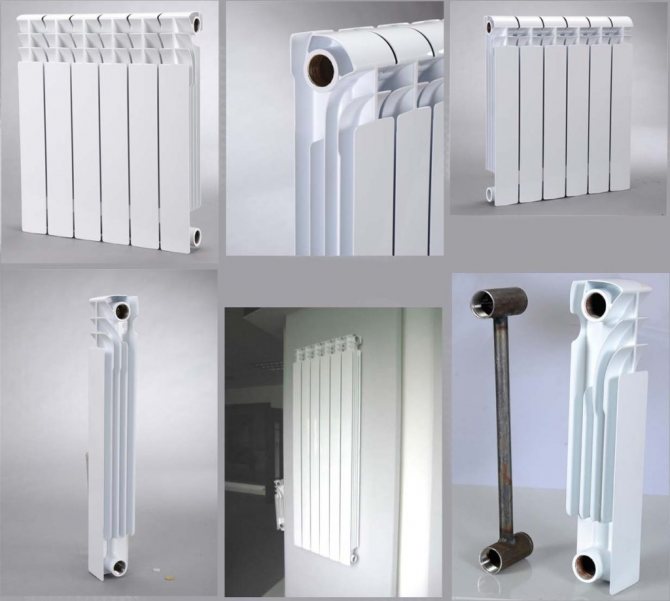


Aluminum batteries do not have the same heat dissipation as bimetallic batteries. But still, aluminum heaters have not gone far from bimetallic radiators in terms of parameters. They are used most often in separate systems, because they are not often able to withstand the required volume of working pressure. Yes, this type of heating devices is used for operation in the central network, but only taking into account certain factors. One such condition involves the installation of a special boiler room with a pipeline. Then, aluminum heaters can be operated in this system. Nevertheless, it is recommended to use them in separate systems in order to avoid unnecessary consequences. It is worth noting that aluminum heaters are cheaper than previous batteries, which is a certain advantage of this type.
Low temperature systems: heating the future
Ogint aluminum radiators have a 5-year warranty. →
The most important task in the development of technologies is to improve energy efficiency. To solve this problem in heating systems, the most effective way is to reduce the temperature of the coolant. That is why low-temperature heating is today a key trend in the development of modern heating technology.
A low-temperature heating system during operation consumes a much smaller amount of heat carrier compared to a traditional system. This provides significant savings. An additional plus is the reduction in the volume of harmful emissions into the atmosphere. In addition, operation with a "soft" temperature regime allows the use of alternative types of equipment - heat pumps or condensing boilers.
The main problem in the development of low-temperature heating for a long time remained that at low heating temperatures it was very difficult to create comfortable conditions in heated rooms. However, with the development of construction technologies allowing the construction of energy efficient buildings, this problem has been resolved. The use of modern building and heat-insulating materials makes it possible to significantly reduce the heat losses of buildings. Thanks to this, the low-temperature heating system can heat the house efficiently and efficiently. The achieved effect of saving the heat carrier significantly exceeds the additional costs that have to be borne for the thermal insulation of buildings.
Cast iron batteries
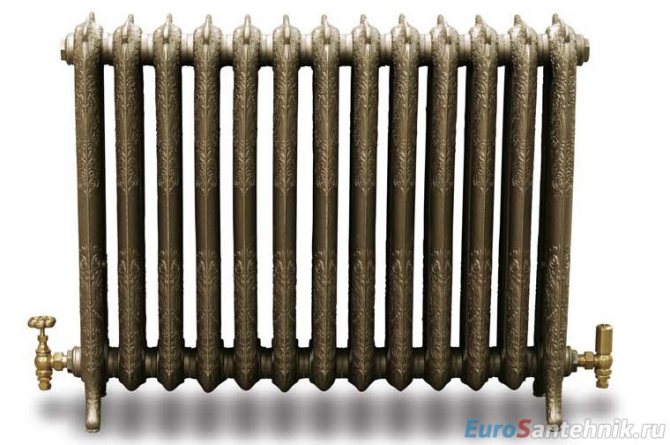


The cast-iron type of heaters has many differences from the previous, above-described radiators. The heat transfer of the type of radiator under consideration will be very low if the mass of the sections and their capacity are too large. At first glance, these devices seem completely useless in modern heating systems. But at the same time, the classic "accordions" MS-140 are still in high demand, since they are highly resistant to corrosion and can last a very long time. In fact, MC-140 can really last more than 50 years without any problems. Plus, it doesn't matter what the coolant is. Also, simple batteries made of cast iron material have the highest thermal inertia due to their enormous mass and spaciousness. This means that if you turn off the boiler, the radiator will still remain warm for a long time.But at the same time, cast iron heaters do not have strength at the proper operating pressure. Therefore, it is better not to use them for networks with high water pressure, as this can entail huge risks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Low Temperature Heating Systems

Low-temperature systems have a number of significant advantages:
- significant cost savings by reducing energy consumption;
- reducing the volume of harmful emissions into the atmosphere;
- improved comfort indicators. Due to the low heating of the radiators in the room, the air does not dry out and there are no strong convective currents that raise dust;
- safety. You cannot burn yourself with a radiator with a temperature of + 50 ... + 60 ° C, which cannot be said about a battery heated to + 80 ° C;
- reducing the load on the boiler, which increases the service life of the equipment;
- the possibility of using heat pumps, condensing boilers and other types of alternative equipment with a low temperature regime.
The disadvantages of this type of heating system are relative. So, a certain disadvantage can be called increased requirements for the used radiators... However, the use of Ogint Delta Plus batteries completely solves all the problems of choosing heating devices.
It should also be noted that in severe frosts, low-temperature systems cannot always cope with heating buildings. At the same time, the system can be transferred to work in a higher temperature mode without any special problems if necessary.
In general, low temperature heating systems are more efficient, economical and safer than traditional systems. Therefore, today we can confidently say that the future lies precisely with low-temperature heating.
Radiators for low temperature heating systems
Aluminum radiators
Steel batteries
The heat dissipation of steel radiators depends on several factors. Unlike other devices, steel ones are more often represented by monolithic solutions. Therefore, their heat transfer depends on:
- Device size (width, depth, height);
- Battery type (type 11, 22, 33);
- Finning degrees inside the device
Steel batteries are not suitable for heating in the central network, but have proven themselves ideally in private housing construction.
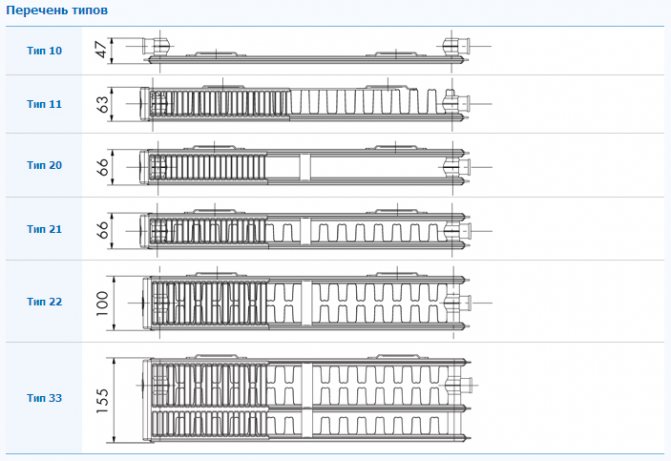

Types of steel radiators
To choose a suitable device for heat transfer, first determine the height of the device and the type of connection. Further, according to the manufacturer's table, select the device by length, considering type 11. If you found a suitable one in terms of power, then great. If not, then you start looking at type 22.
Calculation of heat output
To design a heating system, you need to know the heat load required for this process. Then already carry out calculations on the heat transfer of the radiator. Determining how much heat is consumed to heat a room can be quite simple. Taking into account the location, the amount of heat is taken for heating 1 m3 of the room, it is equal to 35 W / m3 for the side from the South of the room and 40 W / m3 for the north, respectively. We multiply the actual volume of the building by this amount and calculate the required amount of power.
Important! This method of calculating the power is increased, so the calculations should be taken into account here as a guideline.
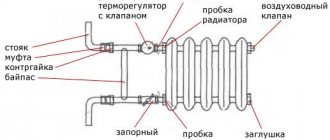
To calculate the heat transfer for bimetal or aluminum batteries, you need to proceed from their parameters, which are indicated in the manufacturer's documents. In accordance with the standards, they provide heat transfer from one single section of the heater at DT = 70. This clearly shows that a single section with the supply of a carrier temperature equal to 105 C from the return pipe of 70 C will give the specified heat flux. The temperature inside with all this is equal to 18 C.
Taking into account the data of the given table, it can be noted that the heat transfer of one single section of the radiator made of bimetal, which has a center-to-center dimension of 500 mm, is equal to 204 W. Although this happens when the temperature in the pipeline drops and is equal to 105 oС. Modern specialized structures do not have such a high temperature, which also reduces parallel and power. To calculate the actual heat flux, it is worth first calculating the DT indicator for these conditions using a special formula:
DT = (tpod + tobrk) / 2 - troom, where:
tpod - indicator of the temperature of the water from the supply pipeline;
tobrk - return flow temperature indicator;
troom is an indicator of the temperature from inside the room.
Then the heat transfer, which is indicated in the passport of the heating device, must be multiplied by the correction factor, taken taking into account the DT indicators from the table: (Table 2)
Thus, the heat output of heating devices for certain buildings is calculated, taking into account many different factors.
Selecting the exact number of bimetal battery sections
They come in several types, each of them has its own power. The minimum heat release reaches 120 W, the maximum is 190 W. When calculating the number of sections, you need to take into account the required heat consumption depending on the location of the house, as well as taking into account heat loss:
- Drafts that occur due to poorly executed window openings and window profiles, cracks in the walls.
- Waste heat along the path of the coolant from one battery to another.
- Corner location of the room.
- The number of windows in the room: the more there are, the more heat loss.
- Regular airing of rooms in winter also affects the number of sections.


For example, if you need to heat a room of 10 m2 located in a house located in the middle climatic zone, then you need to purchase a battery with 10 sections, the power of each of them should be equal to 120 W or its equivalent for 6 sections with a heat transfer of 190 W.
The best batteries for heat dissipation
Thanks to all the calculations and comparisons carried out, we can safely say that bimetallic radiators are still the best in heat transfer. But they are quite expensive, which is a big disadvantage for bimetallic batteries. Next, after them are aluminum batteries. Well, the last in terms of heat transfer are cast iron heaters, which should be used in certain installation conditions. If, nevertheless, to determine a more optimal option, which will not be entirely cheap, but not entirely expensive, and also very effective, then aluminum batteries will be an excellent solution. But again, you should always consider where you can use them and where you can't. Also, the cheapest, but proven option, remains cast-iron batteries, which can serve for many years, without problems, providing homes with heat, even if not in such quantities as other types can do.
Steel appliances can be classified as convector-type batteries. And in terms of heat transfer, they will be much faster than all of the above devices.
Application of radiators
Initially, only the so-called panel heating systems were considered as low-temperature ones, the most common representatives of which are underfloor heating systems. They are characterized by a significant heat exchange surface, which makes it possible to provide high-quality heating at a low temperature of the coolant.
Today, the development of production technologies has contributed to the fact that it became possible to use radiators for low-temperature heating. At the same time, batteries must meet increased energy efficiency requirements:
- high thermal conductivity of the metal;
- significant heat transfer surface area;
- maximum convective component.
TM Ogint offers energy-efficient aluminum radiators that fully meet the listed requirements and are ideal for completing low-temperature heating systems. Moreover, they are produced in full compliance with Russian standards and are fully adapted to domestic operating conditions.
So, the use of aluminum radiators of the Ogint Delta Plus model when creating low-temperature systems gives an important advantage over warm floors. Optimum indicators of economy and comfort are provided in cases where the heating system quickly reacts to changes in the outside temperature (when it rises, the coolant temperature decreases, and when it decreases, it increases). Modern automation used in boiler equipment provides all the possibilities for this. The disadvantage of underfloor heating is their inertia. Radiator systems are able to react to changes in external conditions almost instantly.