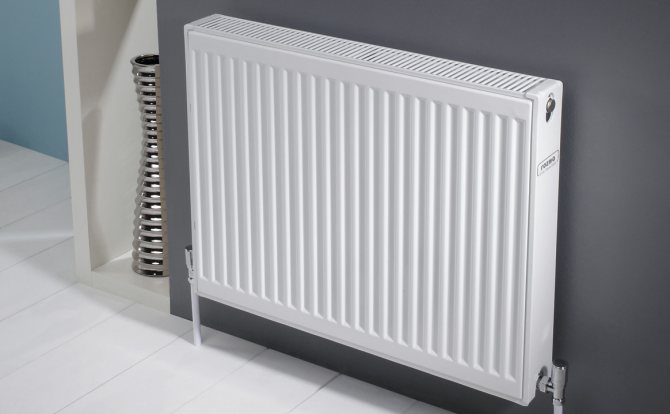
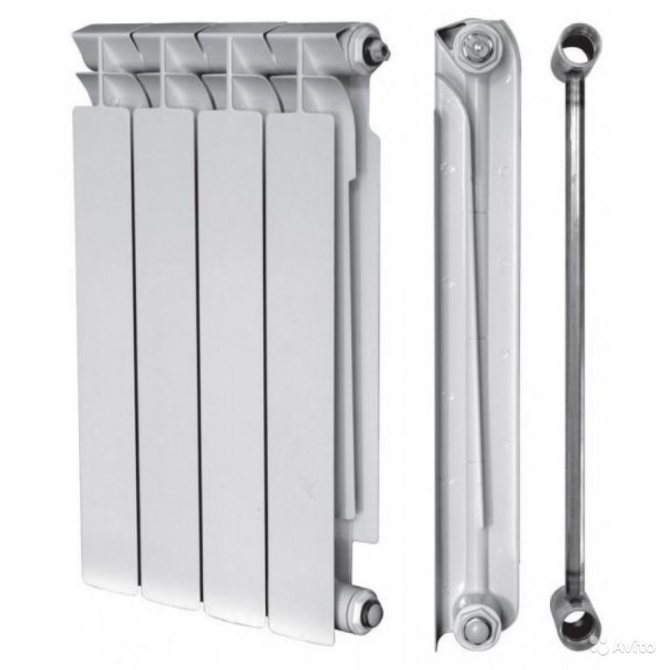
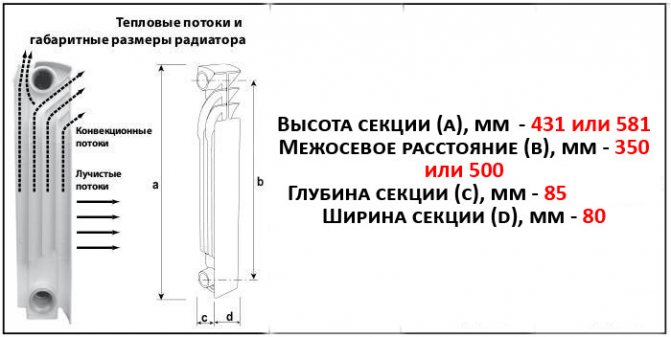
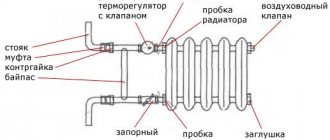
The key task of any radiator is efficient room heating. For this reason one of the main parameters, which you need to be guided by when choosing, - power (heat transfer) of a bimetallic radiator.
For each model of the device, the value is different, since it is determined depending on the volume (capacity) of the sections and their number. Knowing the power of 1 section of a bimetallic radiator, you can correctly calculate the optimal dimensions of the device for a particular room.
MC 90 - 500
A less common radiator, but cheaper than the previous model. The width of one section is 90 mm (more compact), the height is the same 500 mm, hence the name. Less efficient than MC 140, the power of one section of such a radiator is about 140 W of thermal energy.
Cast iron radiator 110 mm wide and 500 mm high between pipes. Relatively rare, it was not staged very often. Power of one section, about - 150 W
A relatively new development, a modified form. The radiator has a section width of 100 mm and a height (between the supply pipes 500 mm). Thermal power of one section - 135 - 140 W.
It is not rare now that you can see modern cast-iron radiators, produced by both import companies and our domestic ones. In appearance they are somewhat similar to aluminum radiators. The power of 1 section of such a radiator ranges from 150 to 220 W, much depends on the size of the radiator.
And that's all, I think I gave you the layout of the usual cast-iron radiators. Of course, the power can jump a little from manufacturer to manufacturer, but approximately the power is kept within these limits.
Heating radiator models and locations are selected at the stage of planning a house or apartment. The owners of private houses have to make this choice on their own. Unfortunately, for the majority of apartment residents, this issue is resolved by developers. It is much more difficult to heat a panel apartment. Heat transfer from cast iron radiators plays an important role
in the choice of such devices. What type of device should you choose: aluminum, bimetallic or cast iron?
It is not surprising that when choosing, rarely anyone is guided by effective indicators of devices and economic characteristics. Choosing the most affordable device from a price point of view is not very correct. To begin with, it is recommended to pay attention to such an indicator as the heat transfer of heating radiators.
This will depend on the type and quality of the material used in the manufacture of the radiators. The main varieties are:
- cast iron;
- bimetal;
- made of aluminum;
- of steel.
Each of the materials has some disadvantages and a number of features, therefore, to make a decision, you will need to consider the main indicators in more detail.
Made of steel
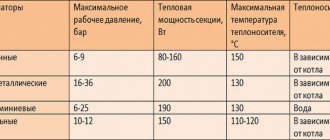
They function perfectly in combination with an autonomous heating device, which is designed to heat a substantial area. The choice of steel heating radiators is not considered an excellent option, since they are not able to withstand significant pressure. Extremely resistant to corrosion, light and satisfactory heat transfer performance. Having an insignificant flow area, they rarely clog. But the working pressure is considered to be 7.5-8 kg / cm 2, while the resistance to possible water hammer is only 13 kg / cm 2. The heat transfer of the section is 150 watts.
Jpg "alt =" steel radiator "width =" 401 ″ height = "355 ″>
Steel
Made of bimetal
They are devoid of the disadvantages that are found in aluminum and cast iron products. The presence of a steel core is a characteristic feature, which made it possible to achieve colossal pressure resistance of 16 - 100 kg / cm 2. The heat transfer of bimetallic radiators is 130 - 200 W, which is close to aluminum in terms of performance. They have a small cross-section, so over time, there are no problems with pollution. The significant disadvantages can be safely attributed to the prohibitively high cost of products.
Jpg "alt =" bimetal radiator "width =" 475 ″ height = "426 ″>
Bimetallic
Made of aluminum
Such devices have many advantages. They have excellent external characteristics, moreover, they do not require special maintenance. They are strong enough, which allows you not to fear water hammer, as is the case with cast iron products. The working pressure is considered to be 12 - 16 kg / cm 2, depending on the model used. The features also include the flow area, which is equal to or less than the diameter of the risers. This allows the coolant to circulate inside the device at a tremendous speed, which makes it impossible for sediment deposition on the surface of the material. Most people mistakenly believe that too small a cross section will inevitably lead to a low heat transfer rate.
Jpg "alt =" Aluminum radiator "width =" 564 "height =" 423 "srcset =" "data-srcset =" https://tepliepol.ru/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/aluminiy..jpg 360w , https://tepliepol.ru/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/aluminiy-80Ч60.jpg 80w "sizes =" (max-width: 564px) 100vw, 564px ">
Aluminum
This opinion is erroneous, if only because the level of heat transfer from aluminum is much higher than, for example, that of cast iron. The cross section is compensated by the ribbing area. Heat dissipation of aluminum radiators depends on various factors, including the model used and can be 137 - 210 W. Contrary to the above characteristics, it is not recommended to use this type of equipment in apartments, since the products are not able to withstand sudden temperature changes and pressure surges inside the system (during the run of all devices). The material of an aluminum radiator deteriorates very quickly and cannot be recovered later, as in the case of using another material.
Made of cast iron
The need for regular and very careful maintenance. The high inertness rate is almost the main advantage of cast iron heating radiators. The heat dissipation level is also good. Such products do not heat up quickly, while they also give off heat for a long time. The heat transfer of one section of a cast-iron radiator is equal to 80 - 160 W. But there are a lot of shortcomings here, and the following are considered to be the main ones:
- Perceptible weight of the structure.
- Almost complete lack of ability to resist water hammer (9 kg / cm 2).
- A noticeable difference between the cross-section of the battery and the risers. This leads to a slow circulation of the coolant and a fairly rapid pollution.
.jpg "alt =" Heat dissipation of heating radiators in the table "width =" 611 ″ height = "315 ″>
Power of 1 section of bimetallic heating radiators
The main task of any radiator is to heat the room. For these reasons, heat dissipation is the main parameter that should be considered when purchasing. For each model of heating devices, the heat transfer values are different, including for bimetal. This parameter is influenced by the volume and number of sections.
So, what is the power of 1 section of bimetallic heating radiators? Knowing the value, you can correctly calculate the required size of the device.
What is heat dissipation
Bimetal heating radiator
The definition of heat transfer is reduced to a couple of simple words - this is the amount of heat generated by a radiator over a certain period of time.Radiator power, heat power, heat flux - the designation of one concept and is measured in watts. For 1 section of a bimetallic radiator, this number is 200 watts.
Heat transfer table for heating radiators
In some documents, there are heat transfer values calculated in calories per hour. To avoid confusion, calories are easily converted to watts using the simplest calculation (1 W = 859.8 cal / hour).
The heat from the battery heats the room as a result of three processes:
Room heating process
Each model of heating devices uses all types of heating, but in different proportions. For example, a radiator is considered to be those batteries that transfer 25% of thermal energy to the surrounding space by means of radiation. But now the term "radiator" has begun to call any heating device, regardless of the main heating method.
Sizes and capacity of sections
Bimetallic radiators due to steel inserts are more compact than aluminum, cast iron, steel models. To some extent, this is not bad, the smaller the section is in size, the less coolant is required for heating, which means that in operation the battery is more economical in terms of heat energy consumption. However, too narrow pipes are more quickly clogged with debris and rubbish, which are inevitable companions in modern heating networks.
Garbage and dirt in the radiator
Good models of bimetal radiators have the thickness of the steel cores inside like the walls of a regular water pipe. The heat transfer of the battery depends on the capacity of the sections, and the center distance directly affects the capacity parameters:
From the given data, it follows that bimetal radiators require a small amount of coolant. For example, a heater of ten sections 35 cm high and 80 cm wide can only hold 1.6 liters. Despite this, the strength of the heat flow is sufficient to warm up the air in a room with an area of 14 square meters. It is worth considering that a battery of this size weighs almost twice as much as its aluminum counterparts - 14 kg.
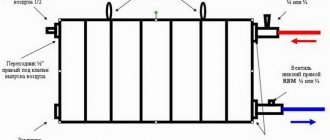
The overwhelming majority of bimetal batteries can be purchased in specialized stores in one section and assemble a radiator of exactly the size required by the room. This is convenient, although there are one-piece models with a fixed number of sections (usually no more than 14 pieces). Each part has four holes: two in and two out. Their dimensions may differ from the model of the heater. To make bimetal radiators easier to assemble, two holes are made with a right-hand thread, and two with a left one.
Assembly of bimetallic heating radiators
How to choose the right number of sections
The heat transfer of bimetallic heating devices is indicated in the data sheet. All the necessary calculations are made on the basis of this data. In cases where the value of heat transfer is not indicated in the documents, these data can be viewed on the official websites of the manufacturer or used in the calculations with the average value. For each individual room, its own calculation must be carried out.
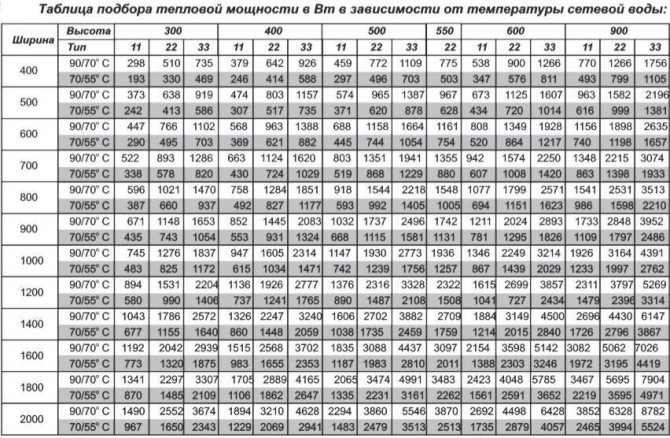
To calculate the required number of bimetal sections, several factors must be taken into account. The heat transfer parameters of a bimetal are slightly higher than those of cast iron (taking into account the same operating conditions. For example, let the coolant temperature be 90 ° C, then the power of one section from bimetal is 200 W, from cast iron - 180 W).
Radiator heating power calculation table
If you are going to change the cast-iron radiator to a bimetallic one, then with the same dimensions, the new battery will heat a little better than the old one. And this is good. It should be borne in mind that over time, the heat transfer will be slightly less due to the occurrence of blockages inside the pipes. Batteries become clogged with deposits that form from metal contact with water.
Therefore, if you still decide to replace, then calmly take the same number of sections.Sometimes batteries are installed with a small margin in one or two sections. This is done to avoid loss of heat transfer due to clogging. But if you are purchasing batteries for a new room, you cannot do without calculations.
Calculation by dimensions
The heat dissipation of radiators depends on the volume of the room to be heated. The larger the room, the more sections you need. Therefore, the simplest calculation is by the area of the room.
For plumbing, there are special standards strictly regulated by SNiP. Batteries are no exception. For buildings in a zone with a temperate climate, the standard heating power is 100 W for each square meter of the room. Having calculated the area of the room, multiplying the width by the length, it is also necessary to multiply the resulting value by 100. This will give the total heat transfer of the battery. It remains only to divide it into the parameters of the heat transfer of the bimetal.
Formula for calculating the number of sections by room size
For a room of 3x4 m. The calculation will look like this: K = 3x4x100 / 200 = 6 pcs. The formula is extremely simple, but it allows you to calculate only an approximate number of bimetal sections. These calculations do not take into account such important parameters as:
- ceiling height (the formula is more or less accurate for ceilings not higher than 3 m.);
- location of the room (north side, corner of the house);
- the number of window and door openings;
- the degree of insulation of external walls.
How much should the battery heat?
Volume calculation
Calculating the heat dissipation of a battery by the volume of a room is a little more complicated. To do this, you need to know the width, length and height of the room, as well as the heating standards established for one m 3 - 41 W.
What heat transfer should bimetallic radiators have for a 3x4 m room, taking into account the ceiling height of 2.7 m: V = 3x4x2.7 = 32.4 m 3. Having received the volume, it is easy to calculate the heat transfer of the battery: P = 32.4x41 = 1328.4 W.
As a result, the number of sections (taking into account the thermal power of the battery at a high-temperature mode of 200 W) will be equal to: K = 1328.4 / 200 = 6.64 pcs. The resulting number, if not an integer, is always rounded up. Based on more accurate calculations, 7 sections will be needed, not 6.
Correction factors
Despite the same values in the data sheet, the actual heat dissipation of the radiators may differ depending on the operating conditions. Considering that the above formulas are accurate only for houses with average insulation indicators and for areas with a temperate climate, under other conditions it is necessary to amend the calculations.
Correction factors when calculating the number of sections of heating batteries
For this, the value obtained during the calculations is additionally multiplied by a coefficient:
- corner and north rooms - 1.3;
- regions with extreme frosts (Far North) - 1.6;
- screen or box - add another 25%, niche - 7%;
- for each window in the room, the total heat transfer for the room increases by 100 W, for each door - 200 W;
- cottage - 1.5;
Important! The latter coefficient is used extremely rarely when calculating bimetallic radiators, because such heating devices are almost never installed in private houses due to their high cost.
Bimetallic radiators
Effective heat dissipation
The heat output values for radiators are indicated in the data sheet or on the manufacturers' websites. They are suitable for specific parameters of heating systems. The thermal head of the system is an important characteristic that cannot be ignored when making the necessary calculations. Typically, the value of heat transfer for 1 section is given for a thermal head of 60 ° C, which corresponds to the high-temperature regime of the heating system with a water temperature of 90 ° C. Such parameters are now found in old houses. For new buildings, more modern technologies are already being used, which no longer require a high thermal head. Its value for the heating system is 30 and 50 ° C.
Heating system temperature graph
Due to the different values of the thermal head in the data sheet and in fact, it is necessary to recalculate the power of the sections. In most cases, it turns out to be lower than stated. The heat transfer value is multiplied by the real value of the thermal head and divided by what is indicated in the documents.
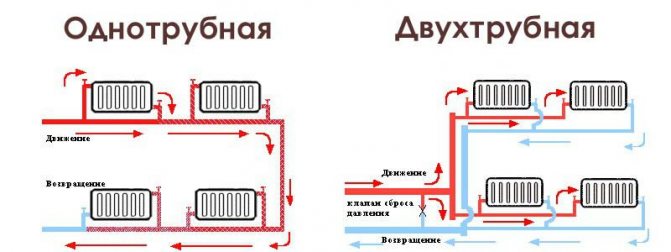
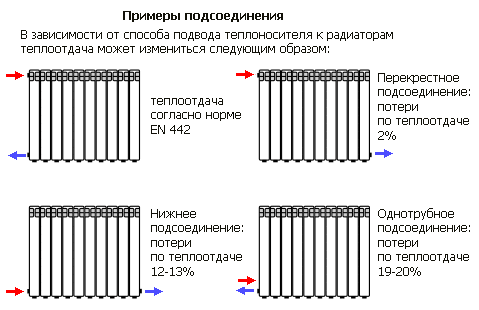
Effective heat dissipation of radiators, depending on the installation and connection method
The output parameters of one section of a bimetallic heating battery directly affect its dimensions and ability to heat the room. It is impossible to make accurate calculations without knowing the value of the heat transfer of the bimetal.
klimat-vdome.ru
Heat transfer calculation
First of all, it is recommended to pay attention to the available data sheet, which is attached to each product of this type. In it you can find the necessary information regarding the heat output of one section of the product. These figures require significant adjustments. The heat dissipation of bimetallic radiators, like aluminum ones, has excellent power ratings, while the judgment is based on the well-known fact that copper products have an excellent heat dissipation level, just like aluminum ones. They have a high thermal conductivity, while heat transfer depends on many other factors.
Jpg "alt =" Calculation of the heat transfer coefficient "width =" 544 "height =" 146 ">
The heat dissipation of the heating radiator is multiplied by the correction factor adopted depending on the DT value
The figure indicated in the passport is correct only if the difference between the supply and processing temperatures is 70 ° C.
Using the formula, calculations are made as follows:
The instruction may have various designations. Often, only a difference of 70 ° C is mentioned and no more.
Area calculation
This is the simplest technique that allows you to roughly estimate the number of sections required to heat a room. On the basis of many calculations, norms have been derived for the average heating power of one square of the area. To take into account the climatic features of the region, two norms were prescribed in SNiP:
- for regions of central Russia, from 60 W to 100 W is required;
- for areas above 60 °, the heating rate per square meter is 150-200 watts.
Why is there such a wide range in the norms? In order to be able to take into account the materials of the walls and the degree of insulation. For concrete houses, the maximum values are taken; for brick houses, average values can be used. For insulated houses - the minimum. Another important detail: these standards are calculated for an average ceiling height - no higher than 2.7 meters.
Knowing the area of the room, you multiply its rate of heat consumption, which is most suitable for your conditions. You get the general heat loss of the room. In the technical data for the selected radiator model, find the heat output of one section. Divide the total heat loss by the power, you get their amount. It is not difficult, but to make it clearer, we will give an example.
An example of calculating the number of radiator sections by the area of the room
Corner room 16 m2, in the middle lane, in a brick house. Batteries with a thermal power of 140 watts will be installed.
For a brick house, we take heat loss in the middle of the range. Since the room is corner, it is better to take a higher value. Let it be 95 watts. Then it turns out that 16 m2 * 95 W = 1520 W is required to heat the room.
Now we count the quantity: 1520 W / 140 W = 10.86 pcs. We round it up, it turns out 11 pcs. So many radiator sections will need to be installed.
The calculation of radiators per area is simple, but far from ideal: the height of the ceilings is not taken into account at all. With a non-standard height, a different technique is used: by volume.
Calculation methodology
As a result, it turns out that the declared heat transfer of the batteries and the power is slightly lower than the real one, which is indicated in the documentation.For the correct choice of equipment, it is necessary to clearly understand the difference in these numbers. The components used will also play a secondary role, be it a copper or bimetallic element. To verify the data, a reduction factor should be used that is applicable to the original power rating of the device as indicated in the documentation.
The calculation is done with the following sequence:
- To begin with, it is necessary to develop the optimal temperature regime in the premises and the main coolant.
- Fill in the collected information and calculate the delta as the average of the indicator.
- Find the most approximate indicator in the attached table.
- The resulting figure is multiplied by the one given in the documentation.
- The calculation of the required number of heating devices is made.
It is also worth considering that the heating season sometimes comes earlier than usual and the device must be ready for use. For bimetallic equipment, the calculation will be as follows: 200 W x 0.48 - 96 W. If the area of the room is 10 m2, then you will need at least a thousand watts of heat or 1000/96 = 10.4 = 11 batteries or sections (rounding always goes up). In any case, there is always the opportunity to seek help from professionals who will help make the necessary calculations, and will tell you in detail how and why this is done. Good luck in your endeavors!
The main elements of a standard heating system are radiators that provide uniform heating of the premises, so their installation must be carried out in accordance with all requirements. Today, consumers have access to a varied selection of models, the differences of which are both in form and in materials of manufacture. Over time, cast iron radiators have not outlived their usefulness, and still continue to occupy stable positions in the apartments and homes of users.
This material, as before, remains one of the most reliable and durable. Given the fact that modern cast iron models have changed their appearance, becoming more modern and elegant, they continue to be bought. For this reason, it is worth considering how their heat transfer should be calculated so that a constant comfortable temperature is maintained in the premises.
Standard power ratings
As a rule, if the battery consists of separate sections, then its total capacity is increased by adding them. That is why, when choosing a cast-iron radiator, it is always necessary to focus on individual sections. And the power depends directly on the capacity of the product - the larger the volume of the coolant, the more kW the device will produce.
Today, manufacturers produce radiators with different section sizes, so the power can range from 0.075 to 0.30 kW. The most common are 150 watt products.
But the device will give out such an indicator only if the temperature difference is observed - room and coolant. The difference in values should be within 50 ° C - if the room is 18-20 ° C, the water temperature in the heating system should not be less than 70 ° C.
On average, to heat a room with an area of 15 m², a cast iron radiator is required, the design of which consists of 10 sections with a capacity of 0.15 kW.
When installing cast-iron radiators, it must be borne in mind that within 80% of heat transfer they carry out by the convective method and about 20% by means of infrared radiation. This determines their location - near the window or under it. Due to the increased air circulation, heat transfer will be significantly improved.
Varieties and benefits
Today on the heating equipment market there are radiators of various types:
- single-channel;
- two-channel;
- three-channel;
- with rectangular sections;
- with a retro-style exterior.
Also, products can be of domestic and foreign production, the main differences of which are:
- heat transfer is the same, but the volume of sections for imported models is smaller;
- cost - domestic devices are much cheaper;
- surface - foreign devices are distinguished by a smoother surface, which reduces hydraulic resistance.
Cast iron radiators have less heat transfer than aluminum devices, but this drawback is offset by their slower cooling, as well as reliability and longer service life. Bimetallic devices are characterized by similar heat dissipation, but their corrosion resistance is poor.
dekormyhome.ru
Cast iron radiators are still one of the most common means of heating in domestic apartments. They can deservedly be called veterans of the heating front - after all, this type of heating device was invented back in 1857 by the French scientist Franz San Galli. Since then, they have been widely used for space heating and are still relevant today.
Such popularity of cast iron batteries can be explained very simply - they are convenient, efficient and their cost is low.
Power calculation
What does it depend on
- Room area
- in order for the radiator to effectively heat a given volume, it must have a certain heat transfer, which directly depends on the number of sections included in it. The power is calculated in a standard way: 1 kW - for 10 m² of the room, respectively - 100 watts are required for 1 m².
- Factors
- however, not everything is so simple, and the above calculation is approximate, you should take into account various nuances that affect heat loss:
Advice: the heat transfer of the radiator should be calculated taking into account all the negative factors that imply the penetration of cold air into the room.
- To find out the heat transfer of one heating device, you should know the power of the MC 140 cast-iron radiator section and add up their number. This indicator is standard for most manufacturers and is equal to 150 W, but depending on the shape and quality of the device, it may vary slightly.
Heat carrier
Another indicator that needs to be considered is the temperature of the circulating fluid.
Therefore, the standard capacity of the section takes into account two temperature indicators:
- indoor mode;
- temperature inside the heating system, depending on the degree of heating of the heat carrier.
Thermal power is determined by the difference between these indicators. And if, at a coolant temperature of 70 ° C, the difference was 50, we can say that the power of 1 section of the MC 140 cast-iron radiator is exactly 150 W.
First of all, this is due to the fact that it is precisely such a temperature regime that is taken into account, at which a constant air temperature in the room will always be maintained at 20 ° C. In addition, heating takes place taking into account the properties of cast iron, which do not differ in high heat transfer rates.
Easy way to calculate
If everything is complicated with the calculations, you can resort to a simpler method and take advantage of many years of experience for those who already use such radiators. A 10-section radiator is required for a 15 m² room.
However, it should be borne in mind that in this case there should be one window in the room. For each subsequent section, it will be necessary to add more sections, the amount depends on the design of the window opening itself, the material from which it is made, the number of chambers in the glass unit and other factors. But, as a rule, 1 or 2 more sections are added, as a result, the price of the equipment increases.
Advice: when the area of the room exceeds 20 m², there should be several radiators. Moreover, they should be installed in different places, since even having increased a certain number of sections, the situation will not improve.
The main qualities of cast iron radiators
Selection is done in two ways:
- convection;
- radiant energy.
They are capable of creating a thermal curtain, therefore it is recommended to install them under windows, from where the cold comes.
However, the power of one section of the MC 140 cast-iron radiator is not the main indicator of the device's reliability. For example, aluminum and bimetallic radiators are more heat dissipated, but they have a much shorter service life.
Perhaps this was the reason that cast iron models are still in demand. You must admit that you will not find aluminum batteries in any old building, but there are as many cast-iron batteries installed in the past centuries.
The opinion of many people agrees that a large amount of heat carrier required for them is very uneconomical and leads to excessive consumption of energy required to heat it. But this is just a delusion, the more coolant is contained in the device, the more it gives off heat.
In addition, if for some reason the supply of the coolant stops, the cast-iron battery will retain heat transfer for a long time, which is explained both by the properties of the material and the large volume of hot water that it contains. The only drawback of devices is their high inertness, which contributes to too slow heating, all other problems are quite solvable.
Right choice
- The performance of heating devices should be 10% of the area of the room if the height of its ceiling is less than 3 m.
- If it is higher, then add 30%.
- For the end room, add another 30%.
Required calculations
An example of heat transfer from an aluminum product.
After determining the heat loss, you need to determine the performance of the device (how many kW in a steel radiator or other devices should be).
- For example, you need to heat a room with an area of 15 m² and a ceiling height of 3 m.
- We find its volume: 15 ∙ 3 = 45 m³.
- The instruction says that for heating 1 m³ in the conditions of Central Russia, 41 W of thermal performance is needed.
- This means that we multiply the volume of the room by this figure: 45 ∙ 41 = 1845 W. A heating radiator should have such a power.
Note! If the dwelling is located in a region with severe winters, the resulting figure must be multiplied by 1.2 (heat loss coefficient). The final figure will be 2214 watts.
Number of ribs
Next, you need to calculate the number of sections in the battery. The instructions for the products indicate the parameter of each of their ribs.
From it you will find out how many kW in one section of a bimetallic radiator and an aluminum analogue is 150-200 watts. Let's take the maximum parameter and divide by it the total required power in our example: 2214: 200 = 11.07. This means that a battery of 11 sections is needed to heat the room.
Output
During its long operation, cast-iron models of radiators have shown themselves only on the good side. Today, not only standard models of such devices are in demand, but also modern ones.
The only drawback is a large mass, so they can be installed with their own hands only on a main wall or on the floor. The video in this article will allow you to find additional information on the above topic.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
In the last decade, new models of heating equipment, including radiators, have appeared on the domestic market, but cast iron products are still in demand among consumers. They are produced by both Russian and foreign manufacturers. The cast iron heating radiators shown in the photo are one of the elements of arranging the heat supply of an apartment or your own house.
What is heat dissipation and power of radiators
The power of cast iron heating radiators and their heat transfer are among the main characteristics of any device that provides room heating. Usually, manufacturers of equipment for heating structures indicate this parameter for one section of the battery, and the required number is calculated based on the size of the room and the required one.
In addition, other factors are taken into account, such as, for example, the volume of the room, the presence of windows and doors, the degree of insulation, the peculiarities of climatic conditions, etc. depends on the material of their manufacture. It should be noted that cast iron loses in this matter to aluminum and steel. The thermal conductivity of this material is 2 times lower than that of aluminum. But this disadvantage is compensated by the low inertness of cast iron, which gains heat and gives it away for a long time.
In closed heating systems with forced circulation, the efficiency of aluminum batteries will be much higher, but subject to the presence of an intense flow of coolant. With regard to open structures, cast iron has more advantages with natural circulation.
The approximate power of one section of a cast-iron radiator is 160 watts, while for aluminum and bimetallic devices, the same parameter is within 200 watts. Therefore, under equal operating conditions, a cast iron battery must have a large number of sections.
A Few Tips and Preliminary Notes
The heat transfer from the heater depends on the temperature of the heating medium. There are two types of heating:

Radiator connection diagram.
- High temperature. Plus one: heating devices can be small. Cons - low efficiency, small adjustment margin, the possibility of burns, decomposition of organic dust at high temperatures. Then people breathe in the products of this decomposition. For these reasons, high temperature heating is not recommended for use.
- Low temperature. Safer, more economical, more comfortable. The conclusion suggests itself: a large and warm heater is better than a small and hot one. When calculating, they are usually guided by a temperature of 70 ° C.
In rooms with an area of more than 25 m2, it is advisable to install not one, but several heating devices: air circulation will improve, heat will be more evenly distributed throughout the room. If there are several windows in the room, it is better to place heating devices under each of them.
The power of one separate section of a bimetallic radiator usually ranges from 170 to 220 watts. The specified data can be obtained from the seller or from the passport of the heater.
The procedure for calculating the number of sections
There are different methods for performing technical calculations for radiators. Accurate algorithms allow calculations to be made taking into account many factors, including the size and placement of the room in the building. You can also use a simplified formula that will allow you to find out the desired value with sufficient accuracy. So, you can calculate the number of sections by multiplying the area of the room by 100 and dividing the result by the power of the section of the cast-iron radiator in cotton wool. At the same time, experts recommend:
- in the event that the total is a fractional number, round it up. The heat reserve is better than its lack;
- when the room has not one, but several windows, install two batteries, dividing the required number of sections between them. As a result, not only the service life of the radiators increases, but also their maintainability. Batteries will be a good barrier to cold air coming from windows;
- with a ceiling height in the room of more than 3 meters and the presence of two external walls in order to compensate for heat losses, it is advisable to add a couple of sections and thereby increase the power of the cast-iron heating radiator.
Dimensions and weight of cast iron heating radiators
The parameters of cast-iron radiators using the example of the domestic product MC-140 are as follows:
- height - 59 centimeters;
- section width - 9.3 centimeters;
- section depth - 14 centimeters;
- section capacity - 1.4 liters;
- weight - 7 kilograms;
- section power 160 watts.
From the side of real estate owners, you can hear complaints that it is quite difficult to transfer and install radiators, consisting of 10 sections, the weight of which reaches 70 kilograms, but I am glad that such work in an apartment or house is done once, so it is necessary to calculate correctly.
Since the amount of coolant in such a battery is only 14 liters, then when heat energy comes from the boiler of an autonomous heating system, then you will have to pay for extra kilowatts of electricity or cubic meters of gas.
Limiting temperature and volume of the coolant
Bimetallic radiators withstand water temperatures up to 90 degrees Celsius. And aluminum - the temperature of the coolant up to 110 degrees C. The volume of the coolant is calculated by multiplying the number of sections by the capacity of one of them. It depends on the height of the device and the thickness of the shell. For aluminum sections, this value is 250-460 ml.
The capacity of sections of bimetallic heating equipment is less than that of aluminum. The standard values are on average as follows: for a battery with a center distance of 200 mm, the capacity of the coolant channel is 0.1-0.16 liters. For devices with a distance between the axes of 350 mm - 0.15-0.2 liters.
The products of each manufacturer differ in parameters and technical characteristics, this applies to any type of heaters. For example, in an aluminum radiator Profi 500 it is only 0.28 liters, while a 10-section radiator will take 2.8 liters.
Service life of cast iron radiators
In terms of such indicators as the duration of operation and sensitivity to temperature and quality of the coolant, cast iron radiators are ahead of other types of batteries. Which is quite understandable: cast iron is characterized by resistance to abrasive wear and by the fact that it does not enter into any chemical reactions with the materials from which pipes and elements of heating boilers are made.
The dimensions of the channels passing through the cast iron batteries are sufficient to ensure that the devices are minimally clogged. As a result, they do not require cleaning work. According to experts, modern cast iron radiators can last from 30 to 40 years. But one cannot fail to say about the big drawback of this product - it is poor tolerance to water shocks.
Working and pressure test
Among the technical characteristics, in addition to the fact that the power of cast-iron heating radiators is important, mention should be made of pressure indicators. Typically, the working pressure of the heat transfer fluid is 6-9 atmospheres. Any types of batteries with such a pressure parameter can cope without problems. The nominal pressure for cast iron products is exactly 9 atmospheres.
In addition to the working pressure, the concept of "pressure" pressure is used, reflecting its maximum allowable value that occurs during the initial start-up of the heating system. For the cast iron model MS-140, it is 15 atmospheres.
According to the regulations, in the process of starting the heating system, it is necessary to check the ability to smoothly start the centrifugal pumps, which should function in automatic mode, but in reality everything is far from being as it should be.
Unfortunately, in most homes, automation is either missing or faulty. But the instruction for carrying out this type of work provides that the initial start-up should be performed with the valve closed. It is allowed to open smoothly only after equalization of the pressure in the heating medium supply line.
But utility workers do not always follow instructions. As a result, in case of violation of the regulations, a water hammer occurs. With it, a significant pressure jump leads to an excess of the permissible pressure value and one of the batteries located along the path of the coolant is not able to withstand such a load. As a result, the service life of the device is significantly reduced.
Coolant quality for cast iron radiators
As previously noted, for cast iron radiators, the quality of the heat transfer fluid does not matter. These devices do not care about pH or other characteristics. At the same time, foreign impurities, such as stones and other debris, present in municipal heating systems, pass without hindrance through sufficiently wide channels of the batteries and are transported further. Often they end up in narrow holes of steel inserts in bimetallic radiators from neighbors. Naturally, over time, the power of the cast-iron radiator section decreases.
If an autonomous heating system is used in a private house, it does not matter what kind of coolant will be used - water, antifreeze or antifreeze. Before using water as a heat carrier, the property owner needs to prepare it, otherwise the heating boiler, hydraulic group or heat exchanger will quickly fail (read: ""). The output of the heating unit may also drop.