You have equipped a ventilation system, but the house still has nothing to breathe, and even damp? So, it's time to think about how to get rid of condensate in the ventilation pipe and prevent its formation in the future. Agree, it is better to solve the problem right away than to endure discomfort for a long time.
We will show you what to do so that you do not have to spend money on replacing ventilation pipes and fighting mold in living rooms. From our proposed article, you will learn how best to prevent and exclude condensation. Our recommendations will help independent home craftsmen.
What is condensation and what harm does it cause?
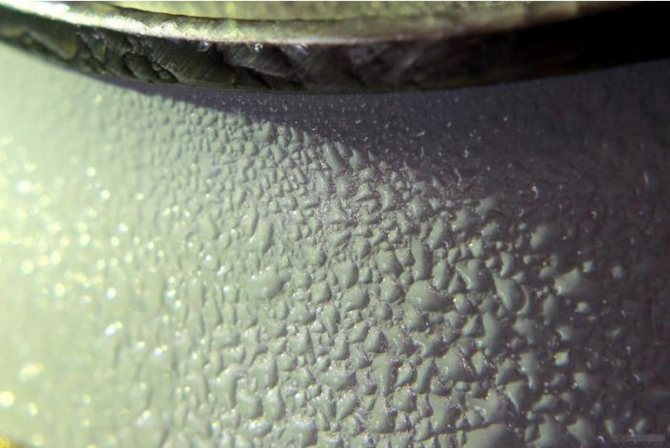
Water is present in the air in a vapor state. When cooled, the steam is converted into liquid water and settles on the inner surfaces of the air ducts in the form of drops, which can drain off, forming rivulets and puddles.
Reasons for the formation of condensation:
- errors in the design and installation of the ventilation system;
- high humidity in the premises;
- the proximity of water bodies;
- large temperature difference inside and outside the house.
Of concern should be not only puddles on the floor, but also rust on the pipes, a decrease in the flow of fresh air, the accumulation of moisture in the walls and ceilings through which the air ducts are laid.

Condensation in the ventilation system leads to an increase in air humidity in the house itself, with effects such as fogging of windows
Condensation is a source of dampness in your home. It serves as a breeding ground for mold and other microorganisms that negatively affect human health. Under the influence of ventilation condensate, metal air ducts are destroyed. Even concrete walls can “feel” the harmful effects of high humidity.
Condensate removal methods
Eliminating condensation from indoor ventilation is the primary task of residents, since high humidity in the premises is fraught with a violation of the microclimate.


Too humid air in a house or apartment leads to the formation of mold and fungi, which are dangerous for people prone to respiratory diseases (allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma).
The appearance of a specific smell in rooms is another consequence of the increased air humidity.
Condensation on the pipes is undesirable in itself, since the liquid contains aggressive components that negatively affect metal and concrete structures. There are many ways to deal with condensation.
Ventilation duct insulation
This method is relevant for private low-rise buildings, where the owners have every right to interfere with the building's internal engineering systems. To insulate air ducts that remove air from the premises from the kitchen, bathroom and living rooms, it may be necessary to temporarily dismantle wall partitions and other non-bearing structures in order to get to the ventilation ducts.
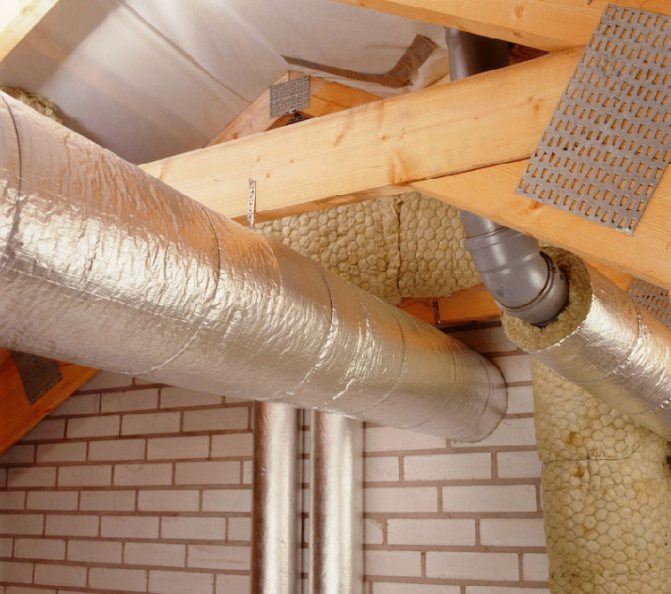


If this can be done, then it is better to use standard insulating materials for sealing and insulating ventilation ducts:
- mineral wool;
- foamed polyethylene;
- Styrofoam;
- polyurethane foam.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with: How to properly bend a polypropylene pipe at home and avoid deformation
Depending on the shape of the pipelines and their location, you can use roll insulation, or polyurethane foam shell, which protects the round metal duct pipes.
It is important! The insulating layer must be fastened as tightly as possible so that a gap does not form between the pipe and the insulation layer.
When insulating air ducts, special attention should be paid to areas on the so-called.dew point - the section of transition from the heated room to the attic and exit to the roof. It is also necessary to pay attention to the tightness at the joints of the pipes.
The section of the pipe that comes out of a warm room must be wrapped with insulation, the thickness of which should not be less than 100 mm. On the outer section of the duct - the head of the pipe - a deflector must be installed, which improves traction and protects the duct from atmospheric moisture.
Condensate drainage
Sometimes the owners of the house do not have the opportunity, time and desire to interfere with the ventilation system and insulate the air duct, and in other cases, the insulation does not give the desired result.
In such a situation, it is possible to reconstruct the ventilation system to mechanically remove moisture from the system. To do this, the air duct pipe, which takes air from the premises to the street, is turned in the opposite direction (90 degrees) after preliminary disassembly.
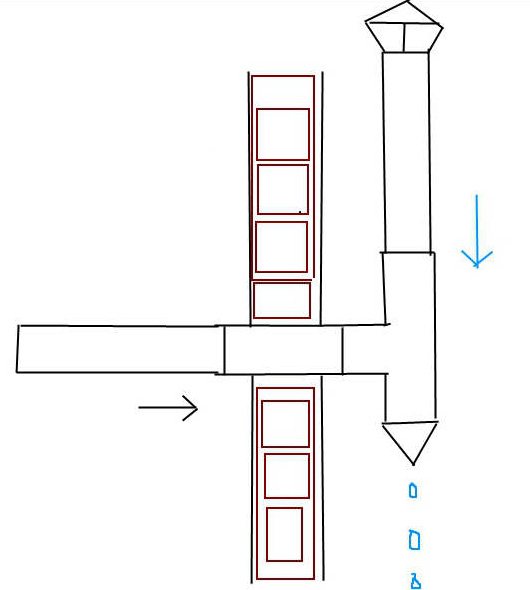

Having installed the pipe in a vertical position, another pipe is installed on top of it, leading to the roof. The section of the pipe, turned downward, will serve to drain condensate, which will simply drain outward. If desired, a conical element can be put on the head of the lower pipe, which serves as a kind of wrench.
Attention! It is possible to install an additional branch pipe, of the type that is in the autonomous boiler heating systems. To do this, you can connect a small flexible tube to the pipe and lead it to the drainage system.
Forced ventilation
If the ventilation system in the house is outdated, then the methods described above for dealing with condensation may not work. In this case, it is recommended to install a new supply ventilation in the house, preserving the old one.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with: How to make scaffolding from a profile - drawings and instructions
A plug is placed on the air duct of the old system, and an exhaust fan is installed in the window or wall in the kitchen, providing forced circulation. The device will extract air from the room along with microscopic droplets of moisture.
To supply fresh air to the house, you can additionally install wall inlet valves. They are usually cut into the walls next to the heating radiators so that the air masses coming from the street are heated and do not affect the temperature regime.
Removal of condensate outside the ventilation ducts
The collection of condensate in the vertical and inclined sections of the air ducts is carried out in their lower part. On horizontal air ducts, condensate collection can be organized almost anywhere, except for areas laid in the walls.
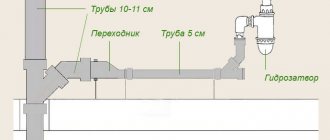
A socket-tee is installed in the ventilation pipe so that the branch is directed downward. The outlet is equipped with a special container - a condensate trap.
Various types of condensate traps for ventilation can be found commercially. They differ in design and materials of manufacture. They can be transparent, which makes it easier to control the filling, but more often they are made of stainless or galvanized steel.
When filling with condensate, containers with a screw lid are emptied manually, which is not always convenient. Moreover, at an outdoor air temperature of -20 ° C and below, condensation forms especially abundantly and the tank is filled in a short period of time.


Before installing the condensate collector, the lowest point in the air duct system is determined, but with their horizontal arrangement, the condensate trap can be installed in almost any convenient place
In this case, a conical watering can is a good option. It is easy to connect a hose to it and drain the condensate into the drain. If it is necessary to organize the drainage of liquid in a hard-to-reach place, a model with a watering can is also used.
When organizing the collection and drainage of condensate, the configuration of the ventilation system is taken into account. With multiple pipe bends, you will have to install not one, but several condensate traps.
Sorbents - moisture-retaining substances - also help to collect and remove condensate. They look like cassettes and are installed in the filtration section of the supply air duct. Periodically, the sorbent must be removed for drying, after which it is again ready for use.
Condensate removal is seen as a temporary measure, primarily due to the possibility of ice plugs in winter. Warming of branch channels helps to radically solve the problem.
How to avoid condensation in ventilation
To avoid the formation of condensation in the air ducts, the ventilation system needs to ventilate the room more often. With an increase in the flow of fresh air, the humidity in the rooms decreases. It is also advisable to limit the number of pots with indoor flowers, do not allow pots to boil on the stove with open lids for a long time, clean the channels in a timely manner and wipe wet surfaces.
In addition, it is necessary to check the health of the ventilation system. It is carried out in calm weather in the following way:
- remove the ventilation grill;
- bring a lighted match to the hole and observe the movement of the fire;
- in the absence of traction, the channels are cleaned;
- replace the grate. The tight and tight connection of the grille must be constantly monitored.
High humidity and low temperatures outside can cause severe humidification of the system. It is possible to reduce the formation of condensation in such weather by slightly opening the window sash for a long time.
Requirements for thermal insulation materials
For the insulation of air ducts in the ventilation system, materials are required with the following properties:
- low thermal conductivity;
- vapor tightness;
- fire resistance;
- noise absorbing ability;
- biostability.
The coefficient of thermal conductivity is the most important parameter of a thermal insulation material.


Even with the correct installation of all elements of the ventilation system, condensate drainage is not always effective, since it may freeze and form an ice plug
The second most important indicator is vapor permeability. Many materials used for thermal insulation of ventilation have the ability to release moisture accumulated under them when the maximum voltage for them is exceeded.
By filling the pores of the material, moisture increases its thermal conductivity, thereby reducing the effectiveness of insulation. To prevent this from happening, a waterproofing coating is mounted on top of the heat insulator - a membrane capable of letting steam out, blocking its access to the inside.
Fire resistance determines how fireproof the thermal insulation will be. There are 6 fire resistance classes in total.
For air ducts, a zero-grade insulation is required, that is, having the highest fire resistance, and therefore the most fireproof. With multilayer thermal insulation and the fulfillment of a number of additional conditions, the use of materials of the first class of fire resistance is allowed
The air flow passing through the air ducts creates noise. In forced ventilation systems, a running fan also makes noise and vibrates. Damping devices and gaskets are used to prevent noise and vibrations from being transmitted through rigid structures and from spreading through living quarters.
But most heat-insulating materials also have sound-insulating properties and, in addition to their main function, help to protect the house from unpleasant acoustic effects.


Mineral wool is one of the most popular thermal insulation materials in low-rise construction and is also used for thermal insulation of air ducts.
The materials used should not be a favorable environment for the vital activity of insects, molds, rotting bacteria and other harmful microorganisms.
Penetrating through the air ducts into living quarters, they can cause disease, and also damage the material itself, which may require its premature replacement. There are microorganisms whose waste products are so aggressive that they can burn through steel sheets 1.5 mm thick.
The materials used in the arrangement of ventilation communications must comply with sanitary and hygienic standards. The insulation should not release substances that are dangerous to humans and the environment. Environmental friendliness means the absence of the threat of contamination of the natural environment during disposal.
Examples of insulation errors
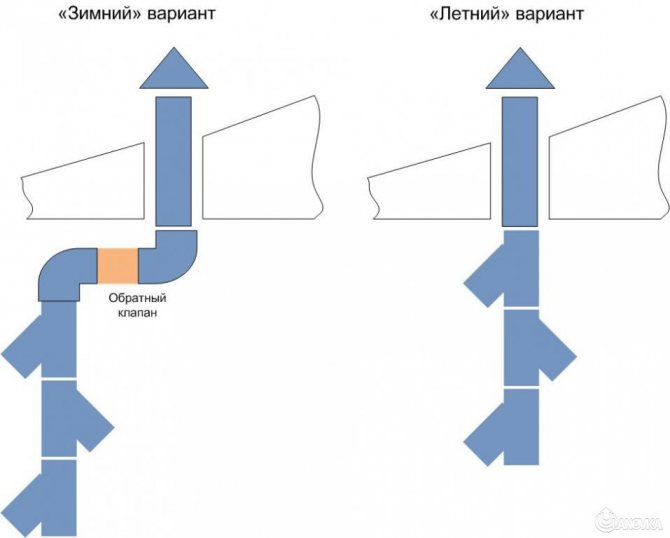

Winter ventilation duct configuration
Example # 1
The bathroom has no windows, its size is 2 x 2.5 m. Ventilation is made in the form of a PVC exhaust pipe with a cross section of 110 mm. Through the wooden ceiling, the ventilation duct goes to the attic (2.5 m long), and then to the street. Moreover, the section of the ventilation pipe in the attic is insulated. Vent pipe in the bathroom with a built-in fan with a non-return valve. In winter, condensation begins to drip in the ventilation system. How to solve the problem?
It all lies in the wrong insulation. It was necessary to correctly calculate the "dew point". Even if the pipe in the attic is insulated, it remains open in the ceiling, a temperature drop occurs and, as a result, condensation forms. Therefore, it is recommended to insulate it with heat-insulating materials, starting from the ceiling and ending with its exit to the street. Some owners also insulate the street part of the air ducts, which is also correct.
Example # 2
In older buildings, the ventilation system is represented by an asbestos pipe running through the attic to the street. At subzero temperatures, you can find that dripping from the ventilation, and in some cases, the water drains off in buckets. Many owners are wondering if insulation will help? After all, all the same, cold air cools down and turns into condensation.
In private houses, starting from the overlap, wrap the pipe with insulation so that the thickness is 100 mm, a deflector should be installed at the end of the ventilation pipe. If the house is multi-storey, then asbestos-cement pipes, like galvanized ones, have a space between themselves, which is not sealed. Therefore, cold air cools this area, forming condensation in the supply ventilation.
To eliminate the problem, it is necessary to make spacers, install the formwork and fill with cement. This method of combating condensation prevents cold wind masses from entering the ventilation. Air ducts in such houses are located in a brick pipe, it is necessary to investigate it. If necessary, use mortar to seal the gaps between the bricks. Next, wrap the air duct with a heater. These simple methods help eliminate condensation in ventilation.
Allowable thermal insulation options
The above requirements are met by many mineral fiber materials, hydrocarbon polymers, foam elastomers, including:
- mineral wool;
- polyvinyl chloride;
- expanded polystyrene;
- polyurethane.
Foam elastomers are produced by extrusion and vulcanization. They have a porous structure, and the pores are bubbly, that is, closed, which reduces moisture absorption and makes them vapor-impermeable. Insulation materials such as polyurethane and polyvinyl chloride are obtained by polymerization of hydrocarbons.
Heat insulators are supplied on sale in the form of rolls, sheets (mats), hollow cylinders (shells). Roll materials and shells are suitable for thermal insulation of pipes and round ducts. Rectangular air ducts can be insulated with sheet material.


The air duct is insulated in all areas located in unheated rooms and ventilation ducts passing through walls, ceilings and roofs require special attention
Sheets and rolls of insulation are highly flexible, easy to shape, one side of them can be smooth. Due to the combination of these properties, the installation of thermal insulation is greatly facilitated. Many materials are not only fire-resistant, but also self-extinguishing, which increases fire safety.
Insulation is chosen taking into account the conditions of the environment in which it will be used, including the operating temperature. For central Russia, materials that can withstand ambient temperatures in the range from -30 ° C to 60 ° C are suitable for thermal insulation of ventilation systems.
A polyethylene (PE) film and a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) membrane are used as waterproofing protection. The insulated ventilation ducts are closed from external damage with boxes sheathed with a board, plywood or aluminum sheets.
Where does the condensate in the chimney come from?
You saw condensation in the chimney - what to do, it happens to everyone. You can even say that there is simply no chimney without condensation.
The following factors influence the process of condensation formation:
- Fuel moisture level. Moreover, absolutely dry fuel simply does not exist. A portion of water vapor is contained even in natural gas; moreover, during combustion, this fuel decomposes into carbon dioxide and water vapor. Therefore, condensation in the chimney of a gas boiler is quite common.
- The temperature of the flue gases and the chimney itself - if it is less than 100 degrees Celsius, then the air in the chimney itself will be the source of water vapor. At the same time, at the start, any heater generates exhaust gases with an insufficiently high temperature, which pass through an insufficiently heated pipe.
- Weak draft in the chimney duct - if the speed of movement of exhaust gases through the air ducts is insufficient, the risk of vapor transfer to water increases. At high speed (thrust), the vapors simply fly out of the pipe, without having time to thicken and transform into liquid.


- There is a large difference in temperature between the pipe and the environment - in this case, water vapor condenses on the outer surface of the chimney, as well as in its end part. This effect is exacerbated with every seasonal cold snap.
Features of the insulation of the duct from the inside
It is necessary to insulate all air ducts outside the heated premises, including areas in the walls. Insulation of both external and internal surfaces of air ducts is possible.
If the insulation is carried out from the inside, already at the design stage, an increase in the duct cross-section is envisaged in accordance with the thickness of the heat-insulating layer. Otherwise, its bandwidth will decrease.
Mineral wool fibers are strengthened with adhesives. This is to prevent the fibers from peeling off by the air blast. The glue used for this purpose should not affect the level of fire resistance of the insulation and its environmental friendliness.


In order not to decrease the aeration properties of the ventilation duct, it is better to carry out insulation from the inside according to the "pipe-in-pipe" scheme. This is how a chimney sandwich is constructed. If there is no time and desire to do them yourself, you can buy ready-made
The thermal insulation laid on the inside should not increase aerodynamic resistance, slowing down the movement of air masses. That is, it is necessary to make its surface smooth.
Due to additional requirements for internal thermal insulation, its use is often impractical. Including if you have to insulate an already built ventilation system with a given cross-section of air ducts. In such cases, the air ducts are insulated from the outside.
The procedure for installing thermal insulation outside
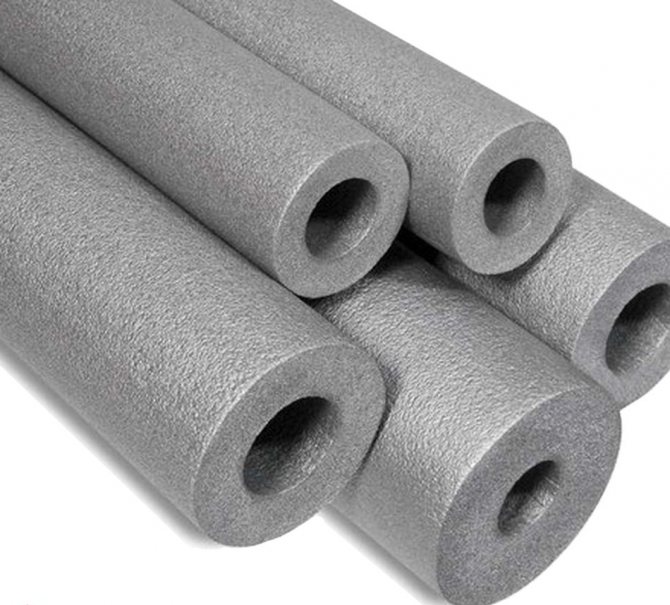
The most economical thermal insulation material for a private house is the time-tested mineral wool. It comes in rolls of various widths and can have one or two outer foil layers.


The thermal insulation material is installed overlapped on the ventilation pipe so that there are no unprotected areas, the joints are glued on top with adhesive tape
When determining the thickness of the heat-insulating layer, they are guided by SNiP 2.04.14–88. Heat engineers perform complex calculations taking into account the diameters of the pipes, the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the used heat-insulating material.
They take into account the average annual air temperature and even possible heat loss through joints and fasteners, as well as other parameters, most of which can be found in reference books and the above SNiP.
Speaking specifically about mineral wool, then when insulating ventilation systems in private houses located in central Russia, roll material with a thickness of 100 mm is usually used. You can buy 50 mm mineral wool and wrap the pipe twice.
To determine the required width of the insulation, measure the diameter of the pipe, add the thickness of the mineral wool multiplied by two to the obtained value. Multiply the resulting amount by 3.14 (pi).
Getting started, prepare in advance a rubber spatula, a construction knife, a stapler, aluminum tape 7-8 cm wide, a marker and measuring tools - a square, a ruler and a tape measure (preferably metal). Be sure to wear protective clothing.
A day without precipitation is chosen for work in the open air. Otherwise, the mineral wool may get wet. The roll is unrolled, marked and cut to obtain the desired size cut. Separate the foil along the edge so that the pipe can be wrapped with an overlap of mineral wool and cover the connecting seam with a foil layer.


In hard-to-reach places, a modern type of heat insulator is used - the so-called shell, which must be selected taking into account the outer diameter of the pipe
Then the connecting seam with a step of 10 cm is fixed with a stapler and glued with tape along the entire length. To fix the insulation to the pipe, both special fasteners and ordinary wire are used.
To protect the joints of the air ducts, the insulation is cut into fragments of the appropriate shape and size. Do not forget to clean the pipe from dirt before insulation.
Insulation can also be performed using segmented heaters. The monolithic casing is in the form of a pipe and is threaded onto the duct. It is mainly used during the installation of a ventilation system "from scratch".
Having measured the geometric parameters of the duct, a casing is selected that is suitable in size and stretched along the entire length of the pipe. Foil is wound over and fixed with stainless steel or copper clamps.
The collapsible shell consists of two semi-cylinders, which are applied to the pipe from both sides and fixed. On the sections passing through the wall, it is difficult to wrap the pipe in a roll of insulation, and it is much easier to put on the shell. The collapsible shell can be put on an existing air duct.
How to permanently get rid of the appearance of condensation in the ventilation pipe? - Prof Pipes
If any type of ventilation system is improperly installed, condensation will form in the ventilation in a private house. This is fraught with serious consequences - wet walls, dampness in the house. Over time, the formation of molds occurs, which destroys structures, makes surfaces visually unattractive and harms human health.
How to get rid of condensation in ventilation pipes?
The difference in temperature between the air ducts and the air pumped through them provokes an abundant release of condensate of water vapor, which settles both on the inner and outer surfaces of the supply and exhaust ducts.
As a result, one of the most important tasks of designers and assemblers of air exchange systems is to remove condensate from ventilation. Therefore, in this article we will consider the main methods for leveling condensation processes and the most common technologies for removing liquid from ventilation ducts.
Condensation in the ventilation system
Reasons for the appearance of condensation in the ventilation ducts
Condensation in ventilation is most often explained by the following reasons:
- Firstly, the difference in temperature between the supply flow and the ventilated room. And the greater this difference, the higher the intensity of the process of condensation of water vapor.
- Secondly, breakdowns of the air exchange system itself. With insufficient inflow or weak exhaust, excess water vapor will not "leave" from the ventilation ducts, but will settle on the walls of the air ducts.
- Thirdly, condensation in the ventilation system can appear even if the thermal insulation of the air ducts is broken. Contact of a cold pipe with relatively warm air provokes an immediate thickening of water vapor deposited on its walls.
- Fourthly, the appearance of condensation can provoke an operational failure - flooding of the canal with ground, melt or rainwater, a breakthrough in the water supply system, the consequence of which was the oversaturation of the room with water vapor, and so on.
- Fifth, the reason for the excess moisture in the ventilation may be a defect in the structure of the ventilated room, namely, a violation of waterproofing, insufficient thermal insulation of the building, and so on.
In a word, we figured out the root causes due to which condensation appears on the ventilation pipes. Now all that remains is to develop measures to counter this process, trying to either eliminate the root cause, or reduce the intensity of the process.
How to get rid of condensate in the ventilation system - an overview of techniques
To get rid of moisture, it is enough to prevent the process of thickening of water vapor (by violating the conditions for the formation of condensate) or to reduce its intensity.
Condensation control by example
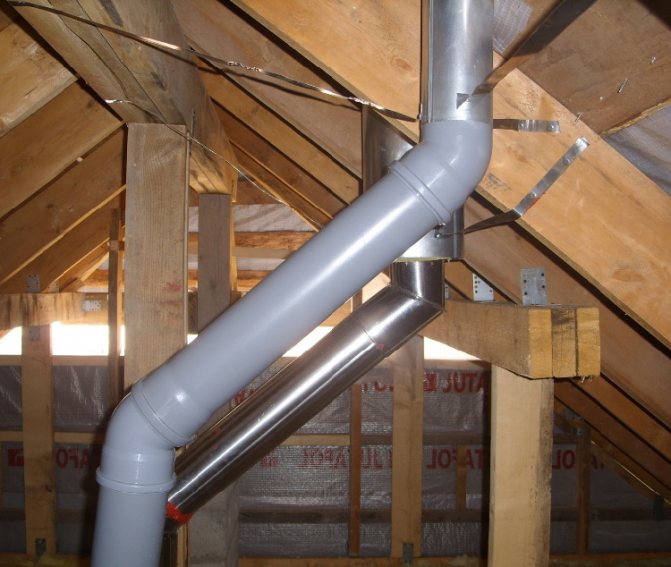
Let's consider a specific situation. The one-story private house has a ventilation system that provides air exchange in the bathroom and kitchen. Metal ventilation pipes are connected to these rooms.
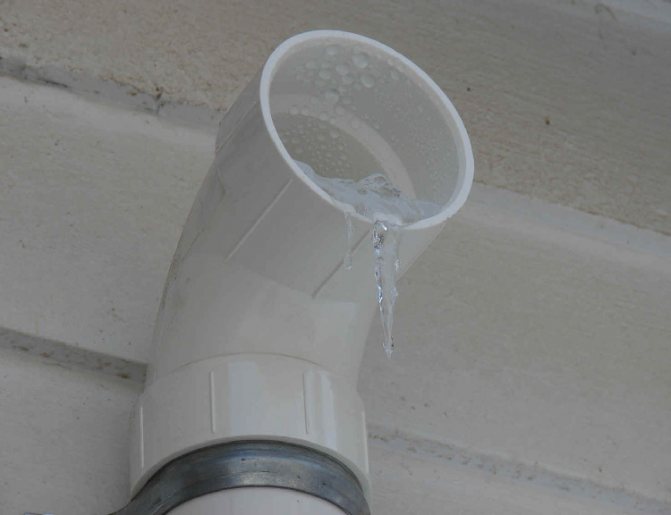
They are laid in the attic with a subsequent exit to the roof. With daily temperature fluctuations, condensation forms in the pipes. But especially its large amount is observed in winter, when water drips from the hood, collecting in a puddle.


Attics are usually not heated, so ventilation pipes laid in this room need to be insulated along their entire length.
The problem is solved comprehensively. Insulation of the exhaust and supply pipes is in progress. The pipes are insulated from the entrance to the ceiling to the exit to the outside. In areas passing through an unheated attic space, pipes are insulated with rolled mineral wool 70-100 mm thick.
In the places of passage through the ceiling and overlap, shells are used. At the lowest point, a tee with a condenser collector is installed.
If the ventilation ducts do not pass through the roof, but through the wall, a section in the wall is insulated with the help of a shell. Outside the house, a 90-degree tee is installed on the ventilation pipe, a condensate trap and an umbrella (deflector) are mounted.
Reasons for damage to the system
Most people, even after moving to a new place of residence and living there for years, often do not think about some kind of pipes laid inside the walls. Often they find out that there is a ventilation duct in their home only when some trouble happens to the hood. And then they wonder for a long time why this very trouble happened. And it could have happened for several reasons:
- The main reason for the appearance of condensation is a sharp temperature difference, the collision of cold air currents from the street and warm, humid domestic ones. The greater the difference in temperature, the more the pipes “cry”. It is not for nothing that people usually begin to complain about condensation when the hood is turned on in the off-season.
- The system from the very beginning was arranged incorrectly and malfunctioned from which condensation began to form. Typically, moisture appears due to weak exhaust or insufficient air flow, due to which water vapor is retained in the pipe and settles in droplets there.
- The reasons may go deeper into oversight when building a house. The foundation is damp or the walls and floor are poorly insulated.
- Another version is excessive humidity in the room.
- Condensation forms in response to flooding of a house or from a breakdown in water supply.
- Condensation appears if the thermal insulation of the pipe is poor. The situation described in the first paragraph occurs - a collision of temperatures, a conflict between the coldness of the pipe and the heat of the air passing through it.
- The problem of the hood is caused by its clogging. Over time, dust and other debris gets inside the channel, its amount increases until it turns into an obstacle to air exchange. Place a piece of paper against the ventilation grill - if the duct is not clogged, the paper will stick tightly to the grill due to the airflow. Worst of all, if the piece of paper abruptly flies off the grate, it means that exhaust air from neighbors enters the house.
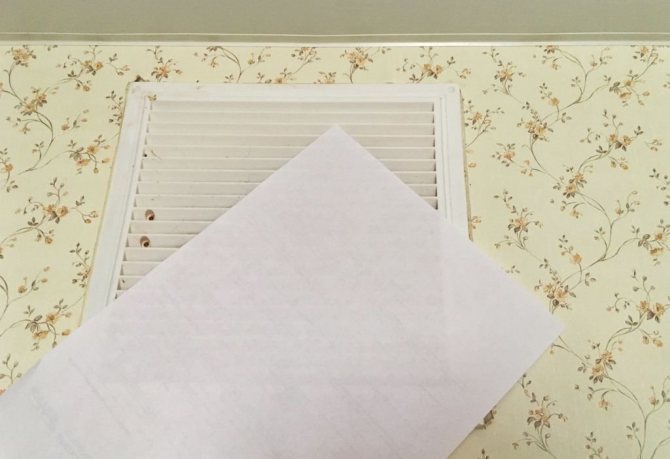


By attaching paper to the ventilation grill, you can check the operation of the exhaust system
Construction of a new ventilation system
Due to errors in design and installation, when using low-quality pipes, all measures to combat condensate may be in vain.
In this case, it is economically expedient to drown out the old and equip a new ventilation system that would cope with its functions of removing contaminated air and supplying fresh air masses.
Design is carried out only after analyzing air exchange processes and calculations in accordance with the standards specified in SNiP, based on the characteristics of the ventilated premises and the number of residents. It may be necessary to abandon natural ventilation in favor of forced ventilation with a change in the configuration of ventilation ducts and the installation of equipment for heating the supply air.
What is the reason for the appearance of condensation
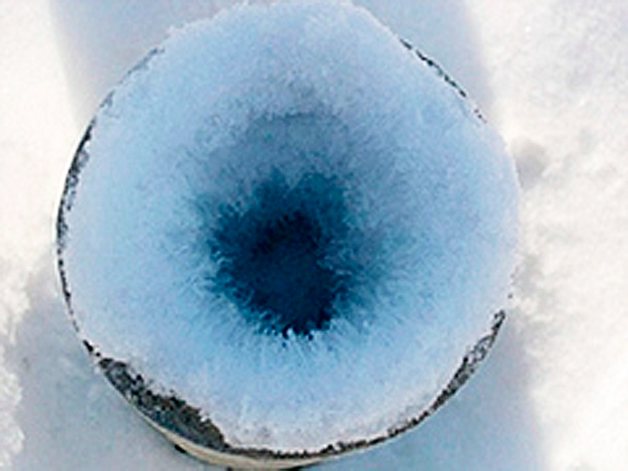


Such ventilation will definitely give not just condensation, but water will pour
Condensation - the formation of moisture on the inside of the pipe. Water droplets seep through numerous joints, resulting in walls and ceilings being constantly wet. In winter, the lumen may disappear in the pipe due to freezing of water, thus, there will be no air circulation in the ventilation duct. The reasons why ventilation flows in a private house are as follows:
- lack of thermal insulation on the ventilation pipes;
- incorrect insulation of pipes was made;
- during the installation of ventilation, defective materials were purchased;
- poor insulation of the floor and walls, ice;
- the house was erected on a damp foundation;
- water in the basement of the house;
- ventilation pipes clogged with debris over time;
- faults in the water supply in the house;
- temperature difference outside and inside the house;
- incorrect installation of the hood.
The reasons can also be constant sources of fumes - drying wet linen in the house, especially the area where the house was built, for example, near a lake, a river. In any case, if it drips from the ventilation, then you need to take action.