The device and principle of operation of a conventional air conditioner
The air conditioner operates in a closed loop based on two functions:
- the transition of a substance from a gaseous state to a liquid with increasing pressure (and vice versa);
- heat release during condensation (transition from gas to liquid) and cooling during evaporation.
In other words, a compressor is used to transfer heat. It changes the pressure of the refrigerant. Usually freon in various compounds acts in this capacity, for example, “R410”. How to fill the air conditioner with freon - read here.
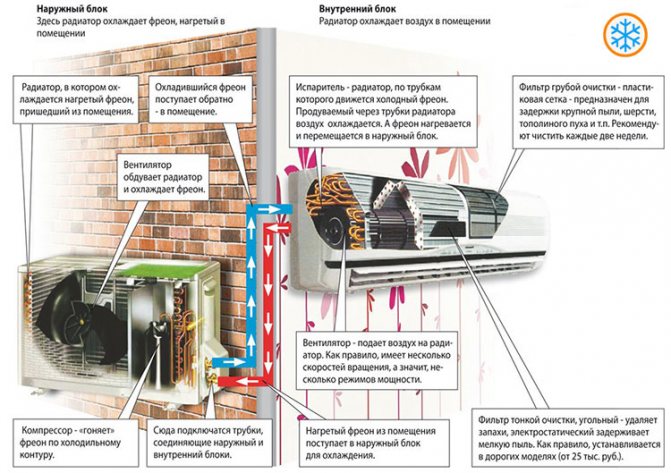
Here is a diagram of the structure of such a system:
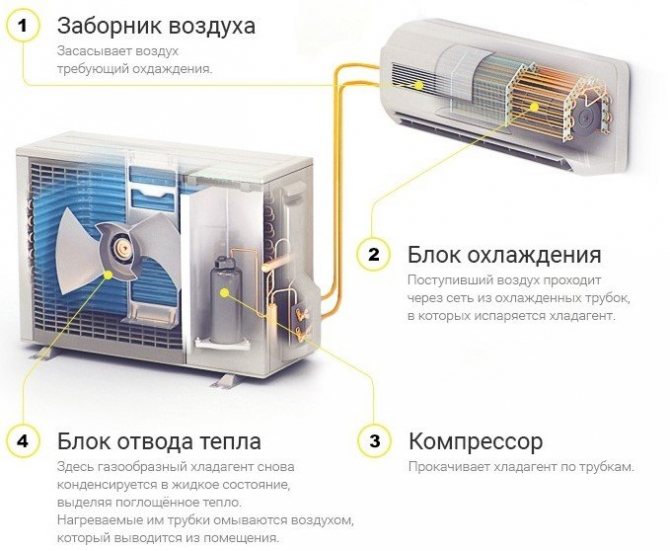
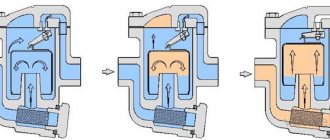
The step-by-step phase of the cycle is as follows:
- A compressor (a small pump with an electric motor) builds up the gas pressure by pumping it from the evaporator (in the room) to the condenser (outside). Due to the increased pressure of the gas, its temperature can rise to 90 degrees Celsius.
When the compressor is started, it runs without lubrication for the first seconds, since oil flows into the crankcase when the engine is not running. Therefore, each next start of the engine increases its overall wear. It is better for the motor if it runs continuously, but this leads to high energy consumption.
- In the condenser, freon begins to give off heat to the environment, because the gas at this moment is hotter than air. The outdoor fan turns on and provides intensive airflow to the heat exchanger, which speeds up the process many times over.
- As a result of cooling, the gas turns into a liquid, but the pressure is still high. The temperature of the liquid is the same, still slightly higher than the ambient temperature.
- Further, the freon passes into a capillary - a thin copper tube wound with a long spiral. Another name for this part is a choke. So the pressure of liquid freon drops to several atmospheres. Part of the liquid immediately turns into a gaseous state.
- Freon ends up in the evaporator. Now the heat exchanger changes from a liquid to a gaseous state, while the freon is cooled together with the heat exchanger grate in the room. A room fan drives air through a chilled grill, quickly drawing cold into the room.
- Then the cycle repeats again - from phases 1 to 5.
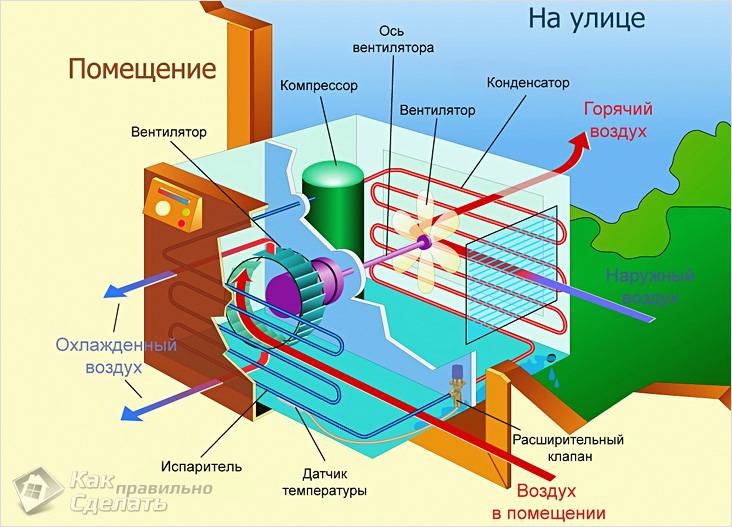
How the air conditioner works in cooling mode is shown in the diagram:
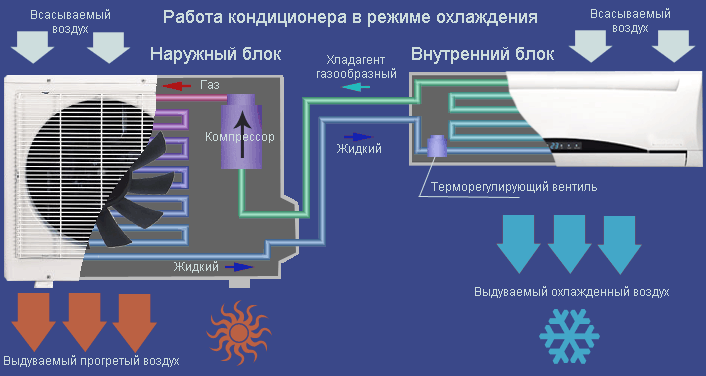

Since the evaporator is very cold and the humidity in the room can be high, drops of water appear on the evaporator - condensation. In fact, it is distilled water. The droplets accumulate and begin to flow down - along the evaporator and below. Of course, water is not needed indoors, so usually a pipe brought out to the street is used to drain the condensate.
The outgoing air flow can be directed with the help of special jalousie planes in the desired direction, both horizontally and vertically. Usually, such control can also be carried out from the remote control. Many models can automatically rotate the louvers to the sides or up and down on a regular basis, pushing cool air through a larger volume.
How to install the air conditioner on your own - read here.
Air conditioner dehumidifier - how it works
This is one of the elements of the system. Its function is to collect the liquid freon flowing out of the condenser and to prevent contamination of the refrigerant. It is located on the freon track, after the condenser and in front of the choke:
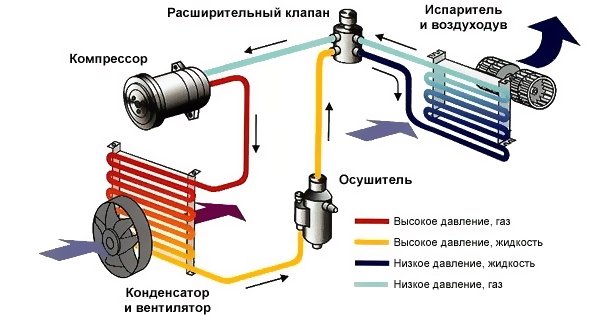

Externally, the desiccant looks like a small tube expanding towards the middle and tapering towards the ends. Inside the tube is a moisture-absorbing mineral "zeolite". There are two grids on the path of freon movement:
- One on the inlet side with large openings to prevent the zeolite granules from entering the condenser.
- The second mesh is on the outlet side. The holes in it are relatively small, like in a tea strainer, so as not to let zeolite particles, metal fragments, and so on into the compressor.
An additional hole is usually made in the dryer. It is used in the assembly and repair of the unit in order to quickly create a vacuum in the system. Otherwise, the throttle having a small diameter would slow down the process of evacuating the air conditioner. Do not open this technological hole, otherwise the device will stop working.
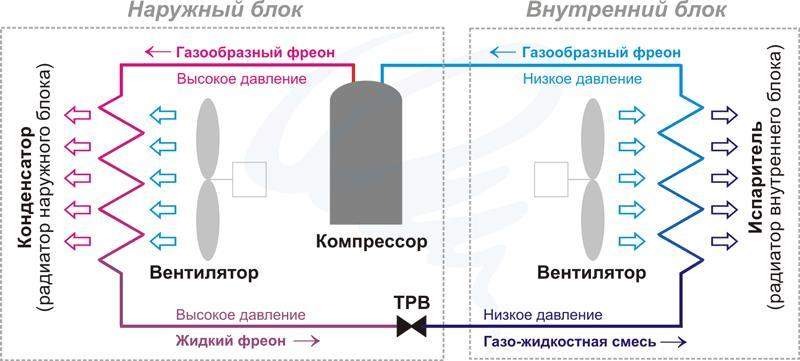
System operation
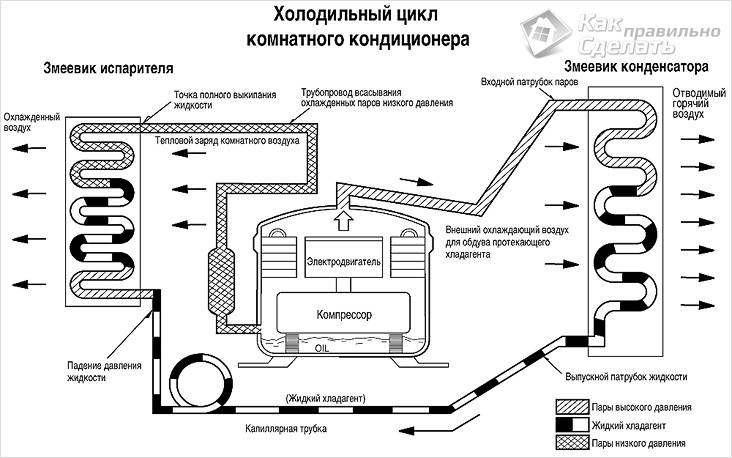

The functioning of the air conditioning system
All parts of the air conditioner (except for the fans) are interconnected with thin copper tubes. In some devices, the tubes are made of aluminum. A coolant circulates through the tubes inside the air conditioner (most often it is freon). The cooler takes either gaseous or liquid form. Fans protect the system from overheating.
When the vaporous freon enters the compression hole, it has a temperature of about 10-15 degrees. In this case, its pressure is 4-5 atmospheres. The refrigerant is compressed in the compressor, the pressure increases 5 times, and the freon temperature rises to 90 degrees.
Very hot freon enters the condenser. There it cools, releasing heat, and smoothly turns into a liquid state. Next, the freon passes the throttle and enters the evaporator. Here, a liquid agent is mixed with a gaseous one. It evaporates and creates cooling. After that, freon enters the compressor again, and the cycle closes. This is how a simple diagram of how an air conditioner works.
Inverter air conditioner
The main purpose of the inverter air conditioner is to save energy and prolong the operating condition of the compressor. In such systems, work does not take place in jerks "on-off", but with a smooth power control. The air conditioner runs continuously, however, not at full strength. This allows the compressor motor to extend its life. In addition, maintaining a stable temperature in the room requires much less energy consumption than with the "ragged rhythm" of a conventional air conditioner.
Compressor speed control is achieved by converting (inverting) the incoming alternating current into direct current, and then back to alternating current, but with a different frequency. The electronics decide how to change the engine speed - decrease or increase, and the speed changes occur smoothly.
But it is important to understand that an inverter air conditioner is more economical only in those places where a conventional air conditioner is turned on only from time to time. With continuous operation, a conventional air conditioner is much more efficient at the same energy consumption, because it does not waste electricity for conversion. Therefore, if your inverter air conditioner operates at full capacity almost continuously, its capacity has been selected incorrectly.
An engineer from Climate Control will tell you what an inverter air conditioner is and whether it is worth overpaying for it:
Installation rules for duct air conditioners
There are conditional installation stages:
- Installation of the outdoor unit. To do this, use a special stand-pocket or mounts.
- Power connection, freon line laying. If the airway system has not yet been installed, do it first.
- Hydro-, thermal insulation of the track. It allows you to extend the life of the device, protects it from external influences.
- Indoor unit installation. It is installed in a false ceiling - it is more difficult than with conventional split systems like CH-S12FTXE-NG, but only the ventilation grilles or diffusers chosen by the user are visible: the integrity of the interior is practically not violated.In addition, one such air conditioner can serve several rooms.
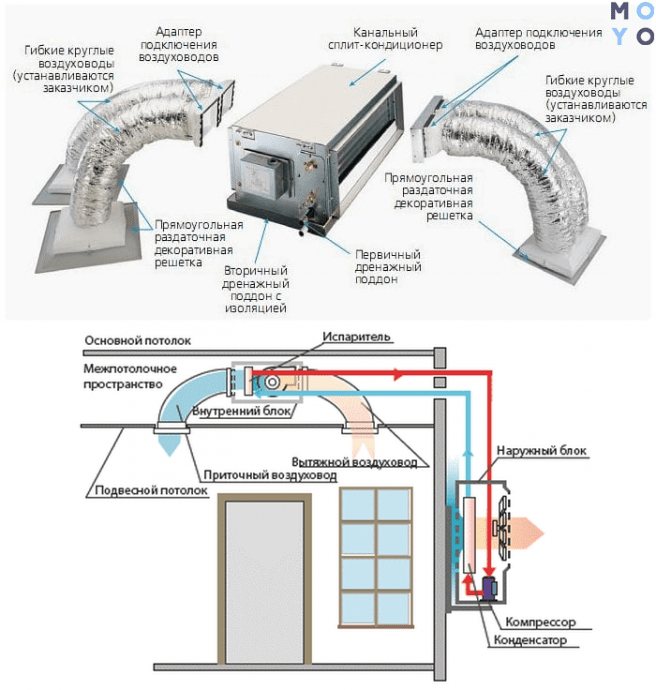

Useful: Functions and operating modes of the air conditioner - an overview of 7 basic and 4 additional options for climate technology
Split system
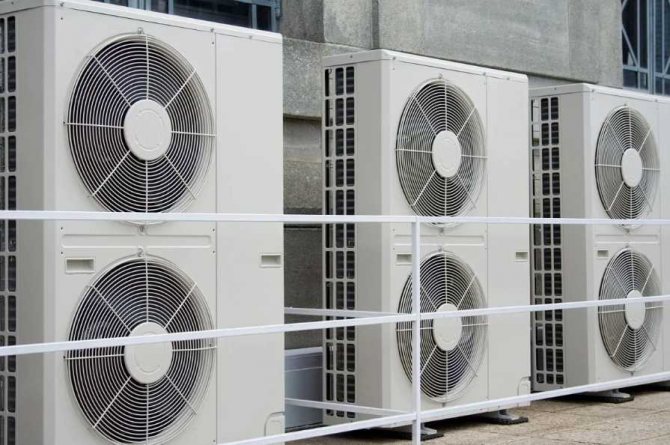
Split means split. In split systems, the condenser and the evaporator are not in a single housing, but can be separated, for example, by a wall. However, they are connected by tubes to exchange refrigerant between them. Usually the outer part of the split system is mounted on the outside on the wall of the building. It contains the following elements:
- compressor;
- capacitor;
- throttle;
- external fan, etc.
The outer part can generate a loud enough noise during operation (up to 45 decibels), which can displease your neighbors.
The inner part is mounted inside the building, it contains:
- evaporator;
- air purification filter;
- thermostat;
- control electronics.
Usually the interior is very quiet.
When installing a split system, special equipment is required to connect the external and internal parts with copper pipes. First of all, it is a vacuum pump, without which it will not be possible to assemble a workable system. The manufacturers do not give a guarantee for units installed by non-certified installers.
Modern split systems are equipped with a compressor start-up control system. This system prevents the engine from starting too quickly after the last shutdown so that it does not overheat.
There are multi-split systems in which not one, but two or more indoor units. But such systems are somewhat more expensive than conventional ones, since they require both a more complex system of connection with an outdoor unit, and a more complex control system for each indoor unit (with a separate thermostat, a remote control unit, and so on).
Most split systems are capable of operating not only for cooling, but also for heating.
The principle of operation of industrial air conditioners
Industrial air conditioning systems do not differ from domestic air conditioning systems, but some are endowed with additional functions, but they are different in type. They are distinguished by increased power and some additional functions, such as humidification, dehumidification, etc.
The main types of industrial air conditioners:
- Multi-zone or VRV systems are a system that is used in buildings with many rooms. Consists of one outdoor unit and several indoor units, each of which is individually configured. Such a system has its own characteristics: it can operate in a mode of different (variable) performance, you can connect a large number of indoor units, and can supply fresh air to rooms or other premises. Two modes, heating and cooling, can be turned on at the same time, there can be a considerable distance from the indoor to the outdoor unit.
- Chillers and fan coil units are, in fact, independent air conditioning units, popular, in recent years, all over the world. A chiller is an air conditioner that cools water, it can heat water (at an outside air temperature of at least -5). He is the main supplier of cold or heat. The fan coil unit is the main consumer of cold, it is, in fact, the indoor unit of the air conditioner, only the cold carrier is the water from the chiller, this is its main difference between the multi-zone system.
- Rooftop (Rooftop). The monoblock, which is mounted on the roof, consists of two sections, one prepares and supplies air to the rooms and the second, compressor-condensate, it contains a refrigeration circuit that cools or heats the air. It is customary to mount such devices on the roofs of shopping and entertainment centers, supermarkets, etc.
- Precision... These are devices that provide accurate temperature and humidity in rooms, they work around the clock and all year round.They have the ability to combine into a single system, with the possibility of dispatching and redundancy of blocks. Used in museums, server rooms, laboratories, etc.
- Central. Purpose - thermal and humidity treatment of air and its subsequent supply to the premises. There are three types: direct-flow central, central with recirculation, central with heat recovery. There are freon and water cooling circuits. Application: warehouses, hangars, cafes, restaurants, theaters, etc.
- Compressor and condensing units. A system consisting of a condenser, fan and compressor. There are two types: the first is made on the basis of a chiller (water-cooled), the second is air-cooled.
It will be interesting for you: The air conditioner squishes and gurgles what to do at the same time


Floor air conditioner
Floor air conditioners are used when it is undesirable or impossible to use a conventional wall model, for example, the room is too small, and the flow of cold air from the wall will immediately fall on people.
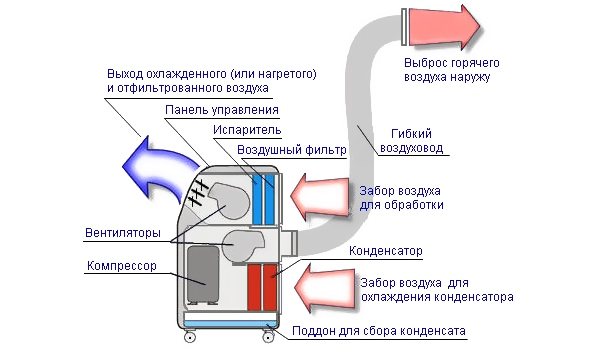

They are of two types: stationary and mobile. And those, and others are not too different from their wall counterparts. Stationary floor air conditioner, as a rule, is made according to the "split" scheme. It also needs to exchange heat with the outside world, as the usual one, therefore it is simply fixed at a height of about half a meter from the floor level, and all other elements are the same. A mobile floor air conditioner is most often just a mobile air conditioner.
Mobile air conditioner: features of work
The device of a mobile air conditioner hardly differs from a stationary one. The main difference is that the entire air conditioner is entirely inside the room. In addition, a thick duct is usually required to pump the outside atmosphere through the condenser. This air duct must be sealed through a window or a special hole in the walls.
The capacity of mobile air conditioners is usually low, since they are designed to cool small rooms. The noisiest part of the air conditioner (condenser + fan + choke) is placed in the dwelling, therefore, with high power of the air conditioner, it will be uncomfortable in the room.
Most of the technical solutions include not only an air cooler, but also a heater. The temperature rise occurs due to the direct heating of the air by heating elements. Moreover, their capacity can be quite large, so check the power grid for suitability for such loads. Models with the ability to work "on heat", as in split systems (with rearrangement of the duct hose and without heating elements), can also be found.
Mobile air conditioners are often equipped with a powerful fan, which allows not only to cool / heat the air in the room, but also to disperse it throughout the structure.
The distilled water generated during the operation of the unit is most often collected in a special container. In order not to run with it every hour, pouring out the accumulated water, it is better to choose a model with a larger capacity. Also, some models, when filling the water tank, simply stop working, giving signals and demanding to drain the liquid.
Mobile air conditioners are useful where there is no reason to install a stationary one. For example, when renting a house, in a summer cottage or during a long business trip. Often, mobile air coolers are purchased for the kitchen so that in summer it is not so hot and stuffy during the operation of all kitchen appliances.
You can learn about mobile air conditioners, their pros and cons from the following video, where the mobile air conditioner ТМ Carrier 51AKP series is considered as an example:
Work principles
Precision type air conditioners absorb cool air from outside, then it is processed in the supply environment, and then it leaves the room with a given temperature, humidity and air speed.
As a result, such precision air conditioners are a kind of hybrid of an atmospheric installation and a room ventilation system. Depending on the type of cooling and the number of circuits, several principles of operation of precision installations are distinguished.
Air block cooled units are designated by a more traditional cooling cycle design, similar to split system operation. Freon under pressure is reduced in the compressor and passes into the condenser already in a liquid state.
Then it moves through the thermostatic expansion valve to the evaporator, where it again turns into a gaseous state and enters the compressor again. As a result, the air cools as it travels through the evaporator and escapes.
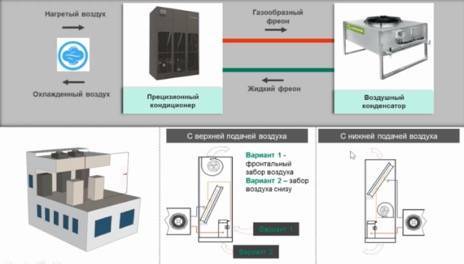

Precision air conditioner with remote air condenser
This type of operation of installations is almost the same as the operation of a product with a cooler. Only the cooling of the device turns out to be not air, but water.
The indoor unit houses a heat exchanger, to which a dry cooler with a water pump is connected outside for cooling. Warm air is transferred through the evaporator and then discharged to the outside thanks to the built-in fan.
If the device is water-cooled, then the air conditioner is usually combined with a chiller (cooling unit)
How does a mobile air conditioner work without an air duct?
A mobile air conditioner without an air duct is actually not an air conditioner, but an air humidifier, and with the need to constantly replenish water supplies. Such a device does not remove heat anywhere, but simply drives air out of the room through a moist spongy material. Some short-term sensation of coolness is possible in the first minutes of work due to the increase in air humidity.
Compared to a conventional air conditioner, it has the following disadvantages:
- The power of such a device cannot be large - due to the limitation of dimensions and noise, as well as the scope of application in small rooms.
- The humidity in the room becomes very high. Accordingly, mold and so on may appear.
- It is necessary to add water to this device all the time, otherwise it may turn off altogether.
How to calculate the power depending on the area of the room
The easiest way to select an air conditioner for the area of the room is to pay attention to the parameters specified by the manufacturer. Usually this information is in the form of numbers - 7, 9 or 12 kBTU. This figure is necessarily contained in the model name. It is quite simple to navigate through them:
- 07 - for a small room, no more than 20sq.m;
- 09 - for rooms from 20 to 26 sq. M;
- 12 - for rooms up to 35 sq.m.
More power is usually not required for domestic premises. To choose the right device, you need to know the area of the room (it is not necessary to remember it by heart, it is enough to read it in the data sheet at home) and compare it with the figure indicated on the package.
Some firms use not only the listed numbers, but also intermediate values - 05, 10, 13, etc. This creates a wide variety of air conditioners and the ability to choose the device exactly for your needs, but complicates the calculations. For such a case, the general formula is suitable:
1 unit = 3sq.m


The larger the area, the more powerful the air conditioner is needed Source zelclimat.ru
This is a simplified calculation, but it will help you avoid confusion when choosing a technique.
Some manufacturers (for example, Mitsubishi) indicate on the packaging the recommended area of the room in square meters, and the calculation of the air conditioner by the area of the room becomes unnecessary.
To convert from one unit to another, use the formula:
1 kBTU = 293W
It deals with the intensity of the cooling, not the consumed electricity.
How does the height of ceilings affect
In the previous section, we were talking only about the area of the room, but completely different ceiling heights can be provided in residential buildings.This affects the volume of air with which the air conditioner will work. Required capacities:
- With a ceiling height of 2.5 to 3m - 100W / sq.m;
- 3-3.5m - 120W / m2 required;
- At 3.5-4m - 140W / sq.m.
Further, this rule remains - every 0.5m of ceiling height requires an additional 20W of cooling capacity of the air conditioner for each square meter. If the power of the device is indicated in units, then it must first be converted to watts. Manufacturers' recommendations usually apply to premises with a ceiling height of 2.5-3m.


A high ceiling requires a more powerful air conditioner Source 2.bp.blogspot.com
Heat sources
The air conditioner parameters are indicated for a room in which the air will not be additionally heated. Additional sources of heat in a closed room are people, animals and household appliances in it.
In fact, each of these objects emits a different amount of heat - a person can actively move or sleep, the most active air heater is a constantly turned on TV. But for simplicity, the calculations use the same value - 300W for each person, animal and household appliance.
Children are taken into account on an equal basis with adults - they move a lot and exchange heat with the environment more intensively. If the number of people in the room is constantly changing, the maximum parameter is taken into account.
Of the animals, only warm-blooded ones are taken into account, for cats, small dogs and rodents, you can "make a discount" and take into account 100W per animal. Pets in terrariums and aquariums do not have a significant effect on the temperature of the house, but you need to take into account the equipment that provides them with air and the optimal temperature. Plants are not included in the calculation of the conditioner.


People are also sources of heat Source mtdata.ru
See also: Specializing in ventilation, air conditioning and lighting
Calculation examples
When calculating the power of the air conditioner by the area of the room, you need to remember that all results will be approximate. There are many factors that are usually not taken into account - the thickness of the walls and the features of the decoration, open windows or doors, the sudden arrival of guests that are a source of heat, etc.
Example # 1
As an example, let's take a room with an area of 24 square meters with a ceiling height of 2.5 m, in which 2 people and a cat live, 2 laptops are turned on during the day. The calculations look like this:
- With such a ceiling height, 100W of cooling energy per square meter is required, i.e. 2 400W for the whole room;
- People, equipment and a cat require another 300W of additional power, i.e. another 1,500W;
- The required power is 3,900 W, i.e. approximately 13kBTU.
At night, when the equipment is turned off and people are sleeping, the power of the device may be excessive (what this threatens will be discussed below).
Example No. 2
Another example of calculating an air conditioner by area is for a small room with an area of 12 sq. M, but with a ceiling height of 3.5 m. A man and a dog live in the room, 3-5 people come every weekend.


A man and a dog - the warmth of friendship is quite tangible Source www.rmim.com.tw
The calculations are as follows:
- For 1 square meter, 140W is required (based on the height of the ceilings), i.e. 1 680W;
- A man and a dog require 300W each, i.e. 600W optional;
- Guests also require 300W, i.e. 900-1 500W when they come;
- The total power is 2,280W (approximately 8 units) for the owner or 3,180-3,780W (approximately 10-12 units) including guests.
Whether it is necessary to take into account people who are not constantly in the room, but come quite regularly, only the owner of the room decides. Manufacturers advise buying equipment with a margin, since it is easier to cope with an excess of capacity than with a lack of it.


The location of the air conditioner also affects the efficiency Source streetclimate.ru
The principle of operation of a window air conditioner
Window air conditioners are popular for the same reason as mobile air conditioners. Usually they do not work all year round, but only in hot weather.This is a very good solution for the kitchen, when you want a little coolness in the summer, and there are no funds to buy an expensive device for cooling a small room.
A similar setup looks like this:
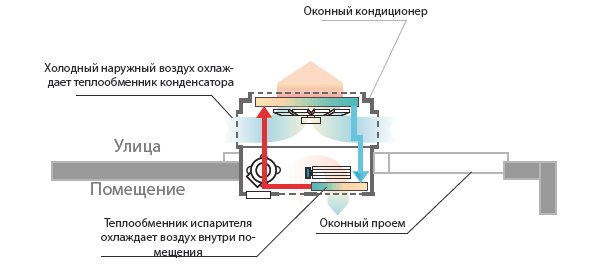

As a rule, they are made according to the "monoblock" scheme and occupy the opening for the window. When choosing a window air conditioner, first check if it is suitable for your particular window (vents). The point is not only in size, but also in the overall strength of the window frame, because the weight of the unit can be considerable, and not every dilapidated window can withstand it.
Keep in mind that most likely there will not be a tight sealed fit of the window air conditioner case, so you will have to solve the issue of insulation from the outside air. Some tenants every summer insert an air conditioner into the window opening and fill the cracks with construction foam, and every autumn they remove the unit to seal the windows for the winter. However, it also happens that the air conditioner is installed, sealed and then takes its place in the window all year round, it just "rests" in winter.
Cheap models may not have a remote control - everything is controlled from the front panel. In this case, this is the right approach - the simpler the better. Less likely to break down complex electronics.
You can clearly see how such an air conditioner works and what happens during its operation in the video:
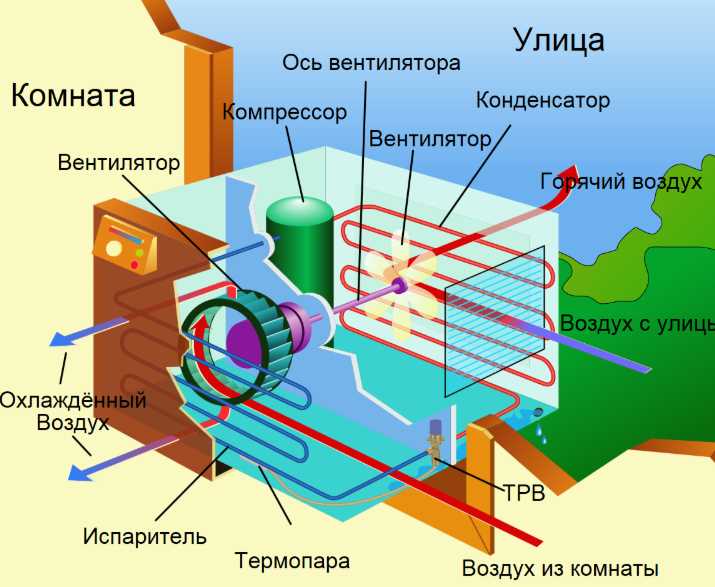
How the air conditioner works
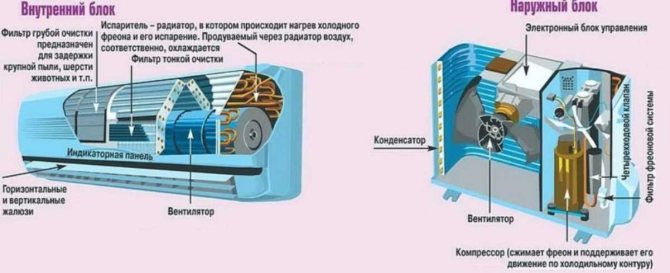
Indoor unit
This part of the device is located inside the room and cools or heats the air there. Now there are so many varieties of indoor units that you can find a model for any interior design.
You will be interested in: Dismantling the air conditioner
Its device:
- plastic case;
- removable front grill;
- coarse filter;
- evaporator;
- radiator;
- display panel (light);
- adjustable fan;
- horizontal curtains (with electric drive);
- vertical curtains;
- fine filter;
- control board;
- condensate container;
- block of fittings for copper connection pipes;
- remote control.
As mentioned above, there are many ways to arrange these modules. In addition, some models have additional functions. These can be: a self-diagnosis function that can independently detect a breakdown, a control function using a smartphone. Another device is equipped with the ability to automatically support operation in a specific mode and a liquid crystal display.
Outdoor unit
The construction of this block is much more complicated, because it is the main one.
And it consists of the following parts:
- Radiator with fan. With the help of these two elements, the freon that flows through the tubes is cooled.
- A compressor that compresses freon and “drives” it in a circle.
- The control board is the “brains” that control everything.
- The valve with the help of which the cold-heat modes are changed.
- External Filter Housing - Provides protection against harmful particles and vandals.
This is basically how domestic and industrial climate control units are arranged and operate. Which one to choose, everyone decides for himself, based on the needs, desires and financial capabilities.
How does the air conditioner work for heating?
Existing air conditioners, capable of heating in winter, are usually equipped with a four-way valve. This valve, switching, makes the refrigerant heat up from the ambient air, and, on the contrary, give off heat to the room. This is a very economical way to warm up a building, since most of the energy is spent not on actually raising the air temperature, but on transferring heat from the street to the house.
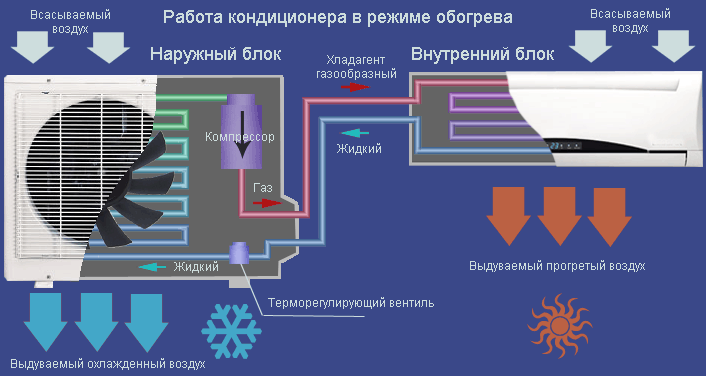

On average, heating a room with an air conditioner is about 3 times more economical than heating a home with electrical appliances that are equipped with heating elements (thermal electric heaters). How to set the air conditioner for warmth is described here:.
However, it should be borne in mind that the colder it is outside the window and the warmer it should be in your room, the less the air conditioner is suitable for this. At a frost of -15 and below, a household air conditioner usually can no longer provide heat transfer from the street to the house, since:
- The air conditioner is originally intended for cooling, therefore, in the heating mode of the dwelling, its efficiency drops along with the ambient temperature.
- The modern environmentally friendly refrigerant is also not suitable for frost.
- It is difficult for the compressor to operate in cold weather - the lubricant becomes too dense.
Many split-systems have automatic switching between the "cold" - "heat" modes, regularly switching to the room cooling mode (with the general "heat" mode), but without the operation of the fan inside the building. This is done to warm up the radiator in the external block of the system so that it does not get covered with ice from condensate and does not lose its ability to efficiently exchange heat.
In split systems, there is also an unpleasant possibility of the drain hose freezing. The water turns into ice and forms a plug inside the hose. Further flow of water from the air conditioner will no longer take place outside, but into the room.
After getting acquainted with all the variety of types of this climatic technology, it will be much easier for you to choose an air conditioner to suit your needs. Of course, in this case it is worth starting from the type of room that needs to be cooled, as well as from the financial capabilities.
Operation of ceiling-type air conditioners
Ceiling air conditioners are split systems with an ultra-thin unit (internal). They are used where the usual ones do not fit for reasons of aesthetics or the specifics of the room.
Subdivided into:
- cassette - ideal for rooms with perfect geometry. Usually used in offices, ventilation ducts are passed above the false ceiling, and the indoor unit is ideally located in the cell of the false ceiling. Not applicable for low ceilings;
- duct - similar to cassette ones, but they have the ability to mix in fresh air. In fact, it is supply and exhaust ventilation. The scattering points in it must be located at the same distance from the outdoor unit;
- wall-ceiling - they are mainly used in rooms with low ceilings, they are effective in rooms with an area of up to 80 m2;
- floor-ceiling - climatic equipment of the combined version, which allows the indoor unit to be placed on the wall near the floor or on the ceiling. The indoor unit is similar to a radiator and is equipped with side shutters. They allow air to be blown out in all directions.