Any building must ensure the maximum safety of the people in it. One of the most dangerous situations is a fire. The spread of fire between floors occurs most often through the ventilation system, and therefore the problem of fire resistance of air ducts is one of the most urgent tasks of fire prevention.
We welcome our regular reader and offer him an article on what fire protection of air ducts is, why it is needed and how it is performed.
What is
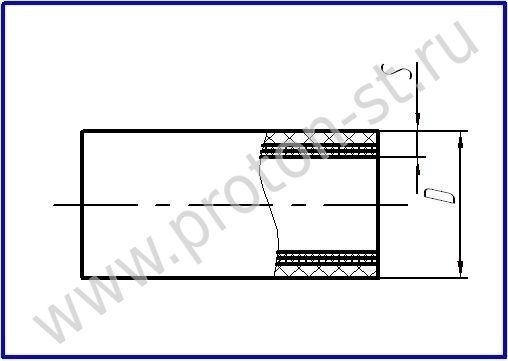
Fire protection for air ducts is a passive means of protection against fire and consists in creating heat-insulating protection (screen) on the surface of ventilation pipelines with high heat and fire resistance.
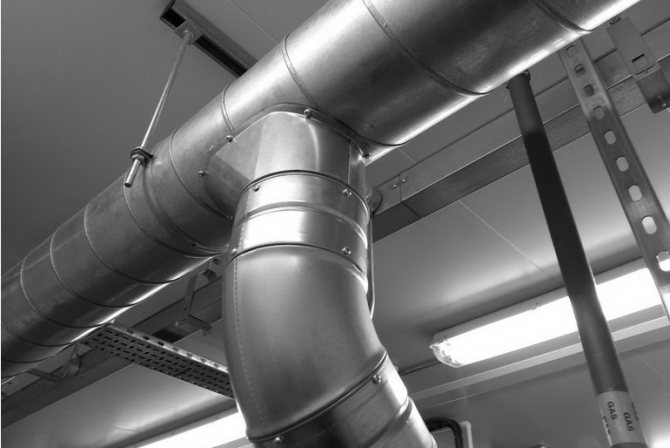

The screen must, for a specified time, protect:
- near sources of ignition - an air duct from destruction and, if possible, from heating;
- in the above and below rooms, walls, ceilings - combustible structures and materials adjacent to the air duct pipes, from secondary combustion.
Fire protection is carried out by applying special compounds or thermal insulation with various products made of non-combustible materials (mineral wool, asbestos, sometimes ceramic materials - for example, expanded clay concrete, brick).
Fire resistance limit of building structures
To give an approximate estimate of the fire resistance limit of specific structures, during their development and design, the following points should be followed:
- The fire resistance threshold of laminated fences is comparable in terms of thermal insulation ability, and, in most cases, exceeds the set of stability limits for individual layers. This indicates that a greater number of layers of the enclosing structure does not reduce the fire resistance. In some cases, additional layers may not play a significant role, for example, sheet metal cladding on the side that is not heated;
- Fencing structures with an air gap, on average, are 10% more refractory than their counterparts without it. Moreover, its efficiency increases in proportion to the distance from the heating source, regardless of the thickness;
- The asymmetrical arrangement of the layers affects the fire resistance depending on the direction of the heat flow. It is recommended to place non-combustible materials with low thermal conductivity in the most fire hazardous place;
- The increased humidity of structures slows down heating, increases fire resistance, except for those cases when the material becomes more fragile with increasing humidity (which is especially important for products made of concrete or asbestos cement);
- Fire resistance decreases at high loads - structures with the maximum stressed section serve as an indicator for determining the limit of fire resistance;
- The period of exposure to heat also affects the material's ability to withstand high temperatures in a fire;
- Structures whose heat resistance cannot be determined usually have a higher heat resistance limit of similar statically determinate structures. It is also important to take into account the additional forces resulting from thermal deformations;
- The fire resistance of a structure does not depend on the flammability of the materials of which it is composed. So, thin-walled metal profiles have a minimum fire resistance, while wooden structures have a higher rate with the same ratio of the heated section perimeter to the area and impact force, ultimate strength or yield strength.
Attention! Combustible materials used in the design of a building, instead of hardly combustible or non-combustible, can greatly reduce the fire resistance of the entire structure. This is especially true when the burnout rate exceeds the heating rate.
Why ventilation is dangerous during a fire
The ventilation system in the event of a fire creates two types of danger:
- distribution of smoky air through the air ducts. The uninitiated people underestimate the danger of smoke - and according to statistics, most of those injured and killed during the fire died of suffocation. But this article will not talk about the prevention of smoke;
- spread of fire and secondary ignition of combustible structures and materials from contact with the hot walls of the air duct.
In most public, industrial and office buildings, natural ventilation is used (that is, without the use of fans) or mixed (some of the systems are equipped with fans). In private and apartment buildings, only natural ventilation is usually used.


The air ducts of any ventilation system are practically not blocked by any valves and gates (in modern systems, special fire dampers are installed, but there is always a possibility that the valves will not work, and modern systems are not installed everywhere).
In large modern buildings, there are smoke removal systems - separate exhaust ventilation removes combustion products from places of fire and from adjacent rooms, supply ventilation pumps air and creates excess pressure in staircases and elevator shafts and prevents them from smoke.
Hot air from the fire zone will rush upward, heat the air ducts, carry away sparks and flames - and cause secondary fires on the upper floors, attics, and roofs.
Fire-fighting polypropylene fire-resistant pipe AntiFire (Antifire)
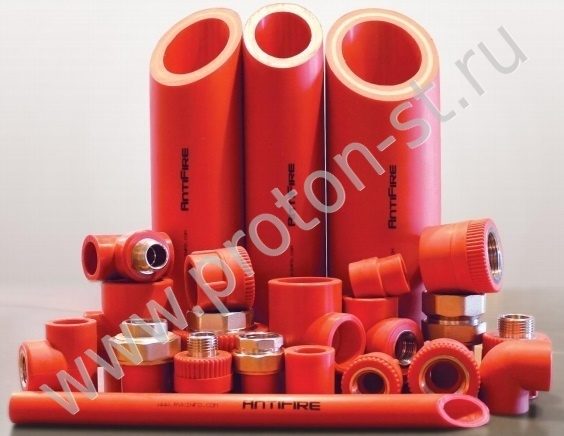


Regulatory document
| Certificate of the official representative of "RVC" |
|
Table: specifications and dimensions
| Name | Outer diameter D (mm) | Wall thickness S (mm) | Quantity in a pack (PC.) | The cost(rub.) |
| Fire-fighting plastic polypropylene PP-R fire-resistant pipe AntiFire red DN 20 SDR 7.4 red pipe L = 4m | 20 | 2.8 | 50 | price per meter |
| Fire-resistant plastic polypropylene PP-R fire-resistant pipe AntiFire (Antifire) red DN 25 SDR 7.4 red pipe L = 4m | 25 | 3.5 | 35 | price per meter |
| Fire-fighting plastic polypropylene PP-R fire-resistant pipe AntiFire (Antifire) red DN 32 SDR 7.4 red pipe L = 4m | 32 | 4.4 | 20 | price per meter |
| Fire-resistant plastic polypropylene PP-R fire-resistant pipe AntiFire red DN 40 SDR 7.4 red pipe L = 4m | 40 | 5.5 | 15 | price per meter |
| Fire-resistant plastic polypropylene PP-R fire-resistant pipe AntiFire red DN 50 SDR 7.4 red pipe L = 4m | 50 | 6.9 | 8 | price per meter |
| Fire-fighting plastic polypropylene PP-R fire-resistant pipe AntiFire (Antifire) red DN 63 SDR 7.4 red pipe L = 4m | 63 | 8.6 | 5 | price per meter |
| Fire-fighting plastic polypropylene PP-R fire-resistant pipe AntiFire (Antifire) red DN 75 SDR 7.4 red pipe L = 4m | 75 | 13.3 | 4 | price per meter |
| Fire-resistant plastic polypropylene PP-R fire-resistant pipe AntiFire red DN 90 SDR 7.4 red pipe L = 4m | 90 | 12.3 | 2 | price per meter |
| Fire-resistant plastic polypropylene PP-R fire-resistant pipe AntiFire red DN 100 SDR 7.4 red pipe L = 4m | 110 | 15.1 | 2 | price per meter |
Related products
| Fireproof fire-resistant fittings AntiFire (Antifire) | Optional equipment | Fire equipment |
Back to section Fire fighting equipment >>
Return to Product catalog >>
Which premises need protection in the first place
First of all, they need fire protection:
- warehouses of fuels and lubricants;
- production using open fire or molten metals and minerals, welding, plasma cutting, electric furnaces for various purposes;
- places with a large crowd of people - shopping centers, shops; entertainment establishments (theaters, cinemas, entertainment complexes, sports facilities); office buildings, household buildings in industrial enterprises, children's and educational institutions; catering establishments4
- underground structures.
At the household level, first of all, they need to protect the premises with heating devices (especially with the use of open fire) - rooms with stoves and fireplaces, baths, kitchens, boiler rooms and the premises and attics located above them. However, all air vents should be protected - fires occur for other reasons (cigarettes, pranks, short circuits).
Do not forget about high-quality and correct thermal insulation and sufficient fire resistance of chimneys, especially in places of passage through walls, ceilings and roofs.
The principle of operation of fire couplings
The principle of operation is based on the ability of a fire retardant material to thermal expansion (swelling) tens of times with a sharp rise in ambient temperature. In a real fire and as the temperature rises, the polymer pipe softens (melting point ≤ +180 ° C) or even burns out. Due to the violent thermal expansion of the fire retardant material, "foam coke" is formed, which fills not only the entire inner cavity of the coupling, pinching the melting plastic pipe, but also the hole in the wall or floor through which the pipes were laid. Swelling coefficient not less than 95 (950%), bulk density 1500 kg / m3.
Watch the video "The principle of operation of the fire clutch" OGNEZA-PM "
Methods and materials for protection
Fire protection methods:
- insulation using sheet and roll materials made of mineral wool;
- application of special intumescent paints;
- application of refractory mastics;
- device of a fire-retardant barrier made of heat insulators;
- combined method - the use of paints and roll materials.
For the fire protection of a forced ventilation system (using a fan), vibration-resistant soundproof materials are required, since the ventilation units generate noise and vibration.
The thickness of the metal for ventilation ducts must be at least 0.8 mm; grilles and diffusers in the system must be installed in metal.
Basalt mats, slabs, sheets
For fire protection, mats and sheets of mineral wool, vermiculite boards, foil sheets, self-adhesive basalt fibers, asbestos-cement, gypsum fiber boards are used. Medium in price and affordable for self-assembly method of isolation. For installation, use screws, washers, pins, wire, clamps. They increase the dimensions and weight of the pipes, it is impossible to carry out work if the pipe is tightly adjacent to the wall or located in a corner. There are a lot of types and varieties of plates and mats.
Fire retardant paint
Special paints, varnishes and enamels are used that swell under the influence of high temperatures. The resulting layer has high thermal insulation properties.
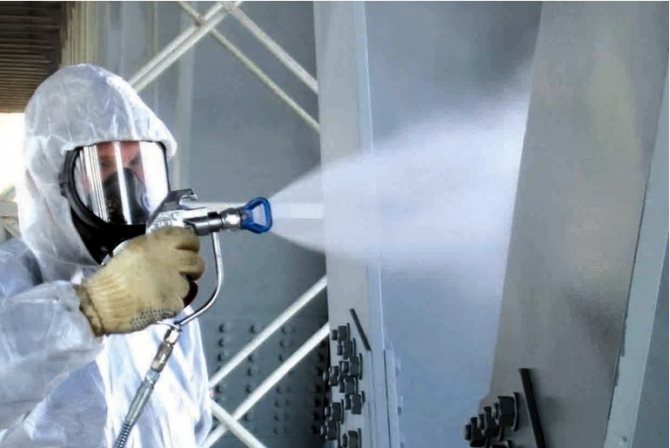


Easy and quick to apply.It can be applied in hard-to-reach places, where thicker insulation does not fit - for example, if the pipes are laid against the wall and in the corner of the room. The complexity of this method is about 5 times less than the use of mineral mats or mastics. Disadvantages: Less effective thermal insulation than other methods. Most of the compositions are of considerable value.
Fire barrier
To create a fire barrier, plaster on a grid, a brick box or concrete coating are used. These methods are already unpopular. Plaster makes the structure very heavy, requires strengthening of fasteners. Brick boxes are sometimes used in private housing construction.
Concreting used to be used in the construction of industrial and residential buildings, now it is practically not used.
For concrete and brick boxes, a foundation is required.
Refractory mastic
All kinds of pastes and mastics based on phosphates, liquid glass (silicates), mineral or asbestos fibers, nepheline mineral are applied in a thick layer to the surface of the air ducts. Coating thickness - from 10 to 50 mm. An effective method of fire protection, moreover, it is inexpensive and fairly easy and with not too much labor costs.
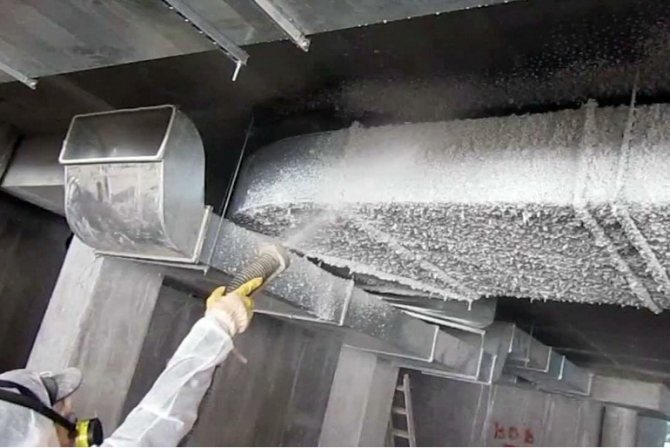


The application of pastes requires the use of specialized equipment available only to organizations. The coating is unstable to moisture and precipitation - the wet layer cracks during temperature changes. Significantly increase the mass of structures and require reinforcement of fasteners. Do not coat the walls of air ducts adjacent to walls.
Where to buy materials
Your life and the life of your loved ones depend on the quality of the materials used, so you should not buy materials for fire protection in the markets and in small shops - almost certainly the quality does not meet the standards. You need to buy in large building supermarkets, with a check and a certificate. The likelihood of buying a fake in this case will be minimal.
The approximate price of rolled foil mats 50 mm thick - from 200 rubles; 80 mm - from 250 rubles.
Air duct insulation device against condensation
A serious problem in the operation of ventilation and air conditioning systems is the formation of condensation on the surface of air ducts transporting colder air than the air in the room.
Condensation on air ducts, especially in rooms with high humidity, causes the formation of water droplets that can damage floors, walls and ceilings. Condensation gradually becomes the cause of the duct failure.
Condensation can be avoided by providing an insulating layer of sufficient thickness so that the temperature of the outer surface of the insulation is not lower than the room temperature. A feature of such insulation is the need for a surface vapor barrier layer, the purpose of which is to protect the insulation from moisture ingress into it. Most often, foil insulating coatings are used for this purpose. Basalt fiber, foamed rubber and polyethylene, fiberglass can be used as the basis of the insulating layer.
All joints of the foil-clad insulating layer must be carefully glued with foil-clad tape. For additional fixation of roll insulation, wire or steel tape is used.
Design and installation
Any work on fire protection of public and residential buildings is carried out by specialized organizations with the presence of a project. However, no one forbids additionally isolating the ventilation duct in their apartment. Fire protection of ventilation systems in private housing construction is practically not controlled by anyone.
Carrying out fire protection is advisable in the following cases:
- if the dwelling has two or more floors, including the used basement;
- if the ventilation ducts in a one-story house run close to the chimneys of the heating system. In a small one-story house, fire protection of ventilation ducts in the attic is a matter of your desire.
You can independently apply intumescent paint or insulate with mineral wool boards. Working with asbestos-cement or gypsum-fiber boards is laborious; the use of asbestos-cement in residential premises is not allowed.
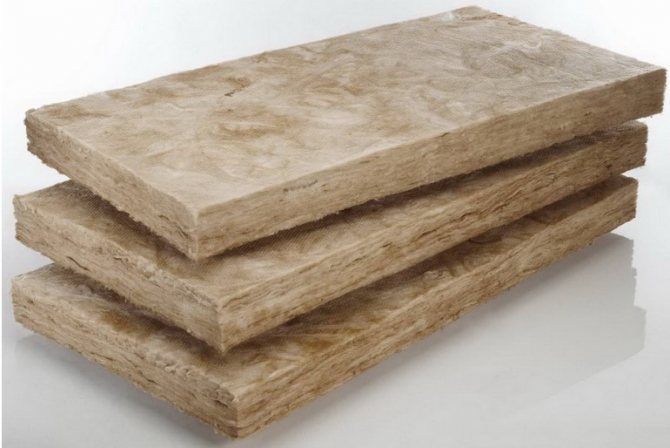


Before carrying out work, you should complete a project or make a drawing, think over a method of fastening, calculate the number of all components.
Most often, basalt mats are used at home.
Installation technology:
- it is necessary to degrease, rinse and degrease the surface of the air ducts (using acetone). Do not forget to open the windows - you can work only with a sufficient supply of fresh air and as quickly as possible;
- mats are cut along the perimeter of the duct, taking into account an overlap of 100 mm;
- special glue for sticking mineral wool cloths is kneaded, protruding elements of the air duct (for example, joints, clamps) are smeared;
- first of all, protruding parts, brackets, joints are glued. the foil will be on the outside of the mat; pieces of mat are glued with an overlap of 100 mm;
- an even part of the duct is coated and glued;
- at the joints of mats and protruding parts, mineral wool slabs should have an overlap, if necessary, the joints are glued with aluminum foil;
- it is advisable (but not necessary) to fix the mats from above with wire, clamps, metal brackets.
Watch the technology in more detail on our video:
Fire protection of metal structures
Fire protection is necessary not only for wooden elements, but also for the protection of metal structures. Metal is a non-combustible material, but this does not mean that its structure does not undergo changes under the influence of fire. High temperature reduces the strength of the metal and introduces critical changes that can lead to an emergency. To protect metal structures, mineral wool, special non-combustible materials, fire-fighting agents and paints that prevent combustion are used.
Mineral technical insulation for fire protection is able to withstand prolonged exposure to fire and ensure the safe use of the equipment. Due to these properties, it has a wide range of uses. With the help of mineral wool insulation, technical communications, air ducts and cable lines, metal structures and elements are protected, pipes and industrial equipment are insulated. Various types of materials are used for pipelines: the outer shell and foil-lined mats, stitched on the basis of basalt wool.
Mineral technical insulation with fire-retardant properties is a basalt fiber piercing material with a foil layer. Basalt insulation for fire protection of metal structures and air ducts is resistant to moisture, non-combustible and has fire-resistant properties. It can be used for thermal, acoustic and fire protection, as it has high heat and sound insulation properties and belongs to fireproof, environmentally friendly materials. They make stitched mats for fire protection from basalt rocks. Slabs are obtained from the melt of basalt rock into super-thin fibers at a high temperature. They are then pressed and formed into mats.
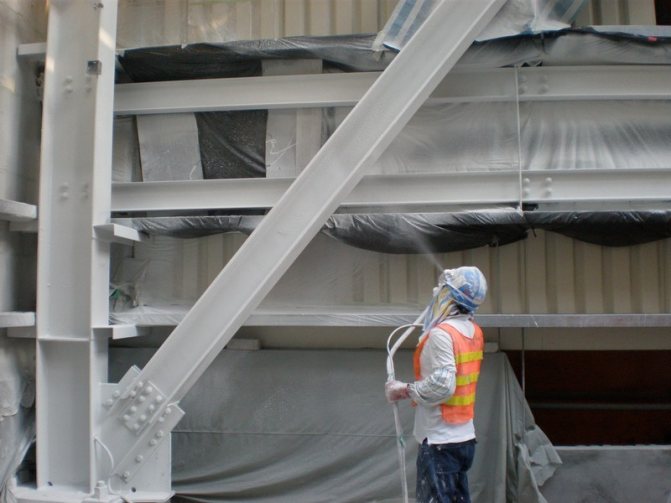


Photo 2. Fire protection of metal structures
Technical insulation and fire protection functions
- Thermal insulation, basalt wool has a low thermal conductivity, it allows you to reduce heat loss and absorb radiated heat.
- Fire protection. Stone fibers are non-combustible material, they do not support combustion and make it possible to organize the protection of equipment, structures made of any materials, including wood, from the effects of fire.
- Moisture protection, building insulation, fire protection of metal structures protects the pipeline from moisture and prevents corrosion processes, which means it helps to extend the service life of the protected elements.
- Soundproofing. Basalt mats and other technical insulation materials reduce operating noise and help ensure a comfortable environment in industrial environments.
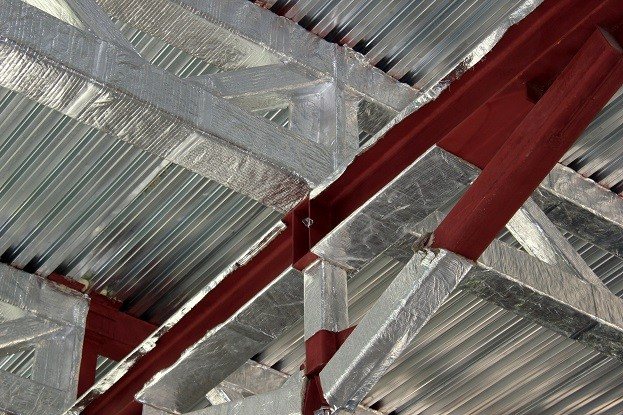


Photo 3. Protection of structures from fire