Double layer pipes used in gravity sewerage systems. The outer layer of the pipe is a corrugated surface, the numerous ribs of which create high rigidity to resist high loads. The inside of the pipe is made of high quality polyethylene, which has high hydraulic properties and allows water to drain freely and without stagnation. The inner surface is flat, so water does not accumulate in the depressions formed by the ribs. The presence of stiffening ribs favorably distinguishes this type of drainage pipes from analogues and makes their choice a priority for installation in places subject to strong mechanical loads.
What is a rectangular tube?
A rectangular metal pipe is a metal product several meters long. The rectangular pipe has a corresponding cross-section. Its area can be very different. All parameters of such pipes are regulated by special GOSTs - documents emanating from the state. The requirement that all dimensions comply with GOST is associated with the following:
- a pipe manufactured in accordance with GOST will meet safety requirements. If the pipe is made in artisanal conditions, then there is a possibility that the proportions do not meet safety requirements. There is a danger that the product will not withstand the loads and will cause the structure to collapse;
- When calculating pipe loads, it is not required to measure each specific product. Its parameters are set by GOST, therefore, you can take data from this document.
Products are made from various types of steel. Some steel grades do not require additional processing. This is, for example, the so-called stainless steel. Steel, which is afraid of corrosion, must be treated with special solutions or paint.
Pipe bending techniques and their benefits
Bending pipes is a technology where the required turn in the direction of the pipeline is created by physically acting on the workpiece, the method has the following advantages:
- Reduced metal consumption, there are no adapter flanges, couplings and branch pipes in the line.
- Reduced labor costs when installing pipelines compared to welded joints.
- Low hydraulic losses due to constant profile section.
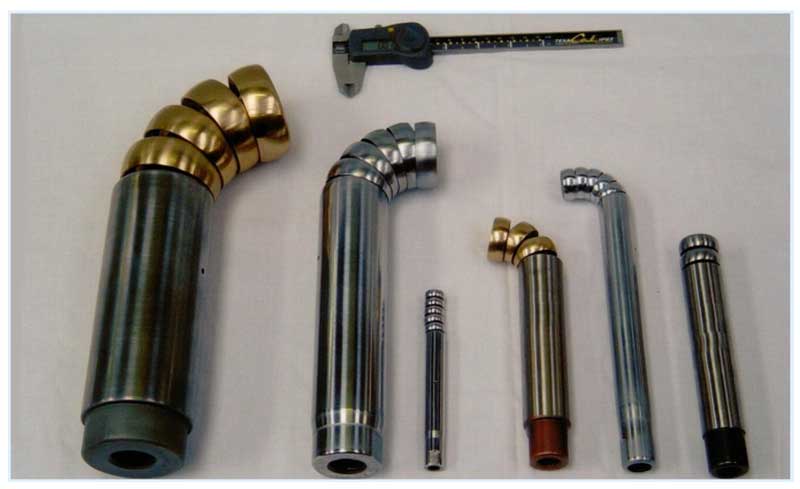

Fig. 3 Dorns for pipe benders
- Unchanging metal structure, its physical and chemical parameters in comparison with welding.
- High quality of sealing, the line has a homogeneous structure without breaks and joints.
- Aesthetic appearance of the highway
There are two main bending technologies - hot and cold, fixtures and methods can be divided into the following categories:
- By the type of physical impact, the pipe bender can be manual and electric with a mechanical or hydraulic drive.
- Bending technology - mandrel (bending with the help of special inner protectors), mandrelless, and rolling machines with rollers.
- By profile - installations for metal-profile rectangular or round products.
Structures from a profile pipe
It was mentioned above that a wide variety of metal structures can be made from rectangular pipes. When making a structure from a metal profile, it is necessary to pay special attention to calculations. Correct calculations will ensure the reliability of the structure.


If we talk about lightweight structures that are not affected by small loads, then calculations here, of course, should be made, but even if there are any errors in them, this is not critical. Errors in the calculations of loads, including those associated with bending of pipes, should not be allowed if serious buildings are being constructed.
When do you need a strength and stability calculation
The calculation of strength and stability is most often needed by construction organizations, because they need to justify their decision, and it is impossible to make a strong margin due to the rise in the cost of the final structure. Complex structures, of course, no one calculates manually, you can use the same SCAD or LIRA CAD for the calculation, but simple structures can be calculated with your own hands.
Instead of manual calculation, you can also use various online calculators, which, as a rule, present several of the simplest design schemes, give you the opportunity to choose a profile (not only a pipe, but also I-beams, channels). By setting the load and specifying the geometric characteristics, a person receives the maximum deflections and values of the shear force and bending moment in the dangerous section.
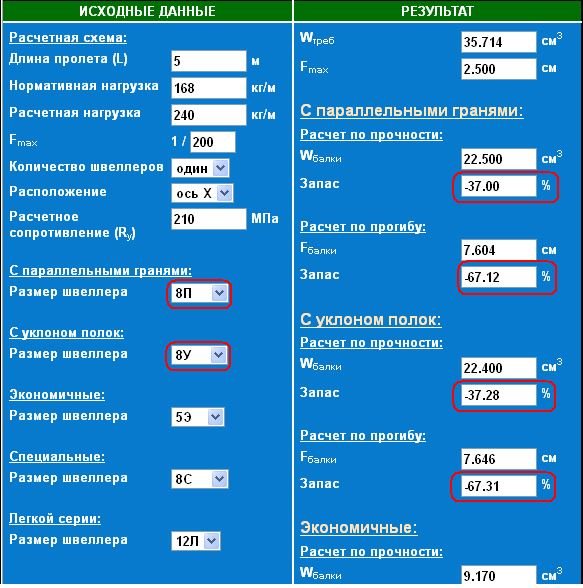

In principle, if you are building a simple canopy over the porch or making a stair railing at home from a profile pipe, then you can do without calculation at all. But it's better to spend a couple of minutes and figure out whether your bearing capacity will be sufficient for a canopy or fence posts.
If you follow the calculation rules exactly, then according to SP 20.13330.2012 you must first determine such loads as:
- constant - meaning the own weight of the structure and other types of loads that will have an impact throughout the entire service life;
- long-term temporary - we are talking about long-term exposure, but over time this load may disappear. For example, the weight of equipment, furniture;
- short-term - as an example, the weight of the snow cover on the roof / porch canopy, wind impact, etc .;
- special ones - those that cannot be predicted, it can be an earthquake, and racks from a pipe by a machine.
According to the same standard, the strength and stability calculation of pipelines is carried out taking into account the most unfavorable combination of loads of all possible. At the same time, such parameters of the pipeline are determined as the wall thickness of the pipe itself and adapters, tees, plugs. The calculation differs depending on whether the pipeline runs underground or above ground.
In everyday life, complicating your life is definitely not worth it. If you are planning a simple construction (a frame for a fence or a shed, a gazebo will be erected from pipes), then it makes no sense to manually calculate the bearing capacity, the load will still be scanty and the margin of safety will be sufficient. Even a 40x50 mm pipe with a head will be enough for a canopy or racks for a future eurofence.
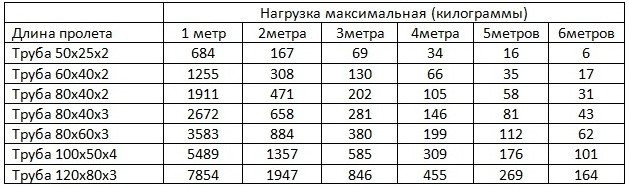
To assess the bearing capacity, you can use ready-made tables, which, depending on the span length, indicate the maximum load that the pipe can withstand. In this case, the own weight of the pipeline has already been taken into account, and the load is presented in the form of a concentrated force applied in the center of the span.
For example, a 40x40 pipe with a wall thickness of 2 mm with a span of 1 m is capable of withstanding a load of 709 kg, but when the span is increased to 6 m, the maximum permissible load is reduced to 5 kg
.
Hence the first important note - do not make the spans too large, this will reduce the permissible load on it. If you need to cover a large distance, it is better to install a pair of posts, you will get an increase in the permissible load on the beam.
Material resistance
Every material has a point of resistance. This is taught in technical educational institutions. Upon reaching the specified point, the material may burst, and the structure, accordingly, crumble.Thus, when the reliability of any building structure is calculated, it is taken into account not only what are the dimensions of the structural elements, but also what material they are made of, what are the features of this material, what kind of bending load it can withstand. The environmental conditions in which the structure will be located are also taken into account.

Strength calculation is carried out according to normal stress. This is due to the fact that stress spreads unevenly over the surface of a rectangular pipe. It will be different at the point of pressure and at the edges of the pipe. This must be understood and taken into account.
It should be added that profile pipes can be tested for bending and in practice. There is special equipment for this. In it, the pipe bends, its stress is recorded. The stress at which the pipe breaks is noted.
The need for practical experimentation is related to the following:
- in practice, there may be deviations from GOSTs. If the building is large-scale, then you should not trust the numbers. Everything needs to be checked empirically;
- if the pipes are not manufactured at the factory, for example, welded from a metal corner, then, based on theoretical calculations, it is impossible to understand what bending stress the pipe will withstand.
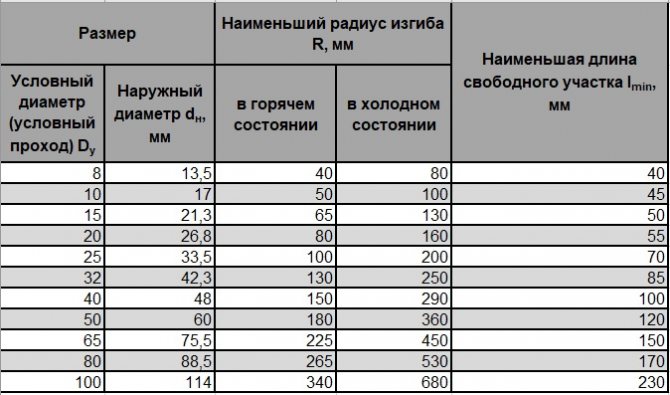
Bending radius of a pipe - devices for obtaining in everyday life and industry
On the construction market, you can find a large number of individual use devices for bending pipes, from the simplest springs to complex electromechanical machines with hydraulic feed.
Manual pipe benders
Pipe benders of this class have a low cost, have a simple design, low weight and dimensions, the process of bending the workpiece occurs due to the physical effort of the worker. According to the principle of operation, manual units produced by the industry can be divided into the following categories.
Lever. Flexion is performed using a large lever to reduce the amount of muscle exerted. In such devices, the workpiece is inserted into a mandrel of a predetermined shape and size (punch), and with the help of a lever, the article is routed around the template surface - as a result, an element of a given profile is obtained. Lever devices provide a 180 degree bend radius and are suitable for small diameter soft metal pipes (up to 1 inch). To obtain roundings of various sizes, replaceable punches are used; to facilitate the work, many models are equipped with a hydraulic drive.


Fig. 7 Hand crossbows
Crossbow. During operation, the workpiece is placed on two rollers or stops, and bending occurs by pressure on its surface between the stops of the punch of a given shape and section. The units have interchangeable punch nozzles and movable stops that allow you to set the bending radius of a steel pipe or non-ferrous metal blanks.
How do you know if the calculations are correct?
Each material, including the metal from which rectangular pipes are made, has an indicator of normal stress. The stress arising in practice should not exceed this indicator. It should also be borne in mind that the elastic force is the less, the greater the load acting on the pipe.
In addition, you need to take into account the M / W formula. Where the bending moment of the axis acts on the bending resistance.
To obtain more accurate calculations, a diagram is depicted, that is, an image of a part that maximally reflects the features of a given part, in this case, a rectangular pipe.
Methods of bending pipes without factory fixtures
In domestic conditions, it is often necessary to bend pipe blanks during construction work or installation of gas pipelines.At the same time, it is economically inexpedient to spend financial resources on the purchase of factory pipe benders for one-time operations; many use simple home-made devices for these purposes.
Steel tubes
Steel is a rather tough and durable material that is very difficult to deform; the main method of changing its configuration is bending in a heated state with a filler with simultaneous physical impact. For pipes made of thin-walled stainless steel, the following technology is used to obtain a long section with a small bend radius:
- Install the workpiece vertically, close it with a cork at one end and pour very fine dry sand inside, after full filling, insert the cork on the other side.
- Find a pipe or a low vertical post of the required diameter and rigidly fix the pipe end to its surface.
- The part is wrapped around the pipe axis by turning the template or going around it.
- After winding, the end is released and the bent part is removed from the template, the plugs are removed and the sand is poured out.
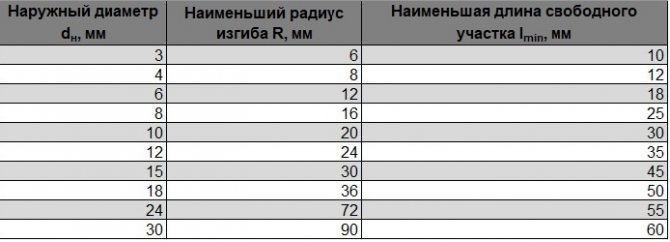
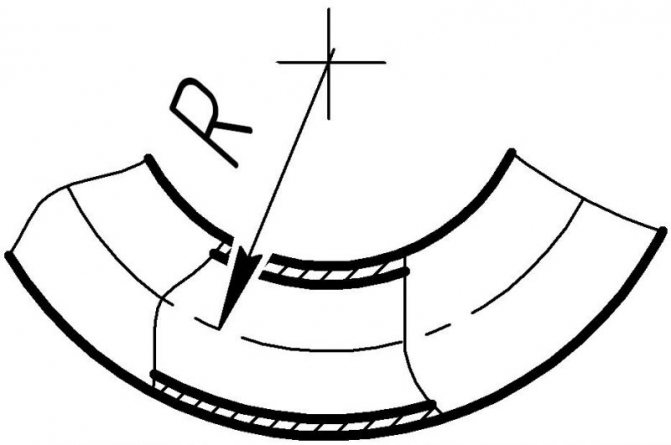
How to calculate the minimum allowable radius
The minimum bending radius of the pipe, at which the critical degree of deformation appears, determines the ratio:
Rmin = 20 ∙ S
In him:
- Rmin means the smallest possible bending radius of the product;
- S indicates the thickness of the pipeline (in mm).
Therefore, the radius along the median pipe axis is: R = Rmin + 0.5 ∙ Dn. Here Dn means the nominal diameter of the round bar.
A prerequisite for correctly calculating the minimum bending radius is the need to take into account the ratio:
CT = S: D
Here:
- CT means the coefficient of thinness of products;
- D indicates the outside diameter of the pipes.
Therefore, the universal formula for calculating the minimum allowable bending radius is:
R = 20 ∙ Kt ∙ D + 0.5 ∙ Dn.
When the specified radius is larger than the value obtained from the above formula, the cold bending method is used. If it is less than the calculated value, the material must be preheated. Otherwise, its walls are deformed during bending.
Consideration should be given to the case when the thinness parameter is 0.03 < Ct <0.2
- Then the minimum allowable bending radius of a hollow bar, without using a special tool, should be: R ≥9.25 ∙ ((0.2-CT) ∙ 0.5).
- When the minimum bend radius is less than the calculated value, then the use of a mandrel is mandatory.
Correction of the bending radius of pipes after removing the load, taking into account the springback (inertia of straightening), is calculated by the formula:
Ri = 0.5 ∙ Ki ∙ Do.
Here:
- Do means the section of the mandrel;
- Ki is the coefficient of elastic deformation for a particular material (according to the reference book).
So:
- For an approximate calculation of the elastic deformation for a steel, copper pipe with a passage of up to 4 cm, the value of the coefficient 1.02 is taken.
- For analogs with an inner diameter of more than 4 cm, this figure will be equal to 1.014.
To know exactly the angle to which the material should be bent, taking into account the radius of gyration of the pipe, the formula is applied:
∆ = ∆c ∙ (1 + 1: Ki)
Here:
- ∆c is the rotation angle of the median axis;
- Ki is the reference spring coefficient.
When the required radius is 2-3 times larger than the section of the hollow rod, the spring coefficient is taken as 40-60.
Watch the video
Calculation of typical schemes
In private construction, complex pipe structures are not used. They are simply too difficult to create, and there is no need for them by and large. So when building with something more complicated than a triangular truss (under the rafter system), you are unlikely to encounter.
In any case, all calculations can be done by hand, if you have not yet forgotten the basics of strength materials and structural mechanics.
Console calculation
The console is an ordinary beam, rigidly fixed on one side.An example would be a fence post or a piece of pipe that you attached to your home to create a canopy over your porch.
In principle, the load can be anything, it can be:
- a single force applied either to the edge of the console or somewhere in the span;
- load evenly distributed along the entire length (or on a separate section of the beam);
- load, the intensity of which varies according to some law;
- also couples of forces can act on the cantilever, causing the beam to bend.
In everyday life, it is most often necessary to deal with the load of a beam with a unit force and a uniformly distributed load (for example, wind load). In the case of a uniformly distributed load, the maximum bending moment will be observed directly at the rigid embedding, and its value can be determined by the formula
where M is the bending moment;
q is the intensity of the uniformly distributed load;
l is the length of the beam.
In the case of a concentrated force applied to the console, there is nothing to count - in order to find out the maximum moment in the beam, it is enough to multiply the value of the force by the shoulder, i.e. the formula will take the form
All these calculations are needed for a single purpose - to check whether the strength of the beam will be sufficient under operational loads, any instruction requires this. When calculating, it is necessary that the obtained value be below the reference value of the ultimate strength, it is desirable that there is a margin of at least 15-20%, it is still difficult to foresee all types of loads.
To determine the maximum stress in the dangerous section, a formula of the form is used
where σ is the stress in the dangerous section;
Mmax - maximum bending moment;
W is the moment of resistance of the section, a reference value, although it can be calculated manually, it is better to just peep its value in the assortment.
Beam on two supports
Another simple use of a pipe is as a lightweight and durable beam. For example, for the device of floors in the house or during the construction of a gazebo. There can also be several loading options here, we will focus only on the simplest ones.
The concentrated force at the center of the span is the simplest way to load a beam. In this case, the dangerous section will be located directly under the point of application of the force, and the value of the bending moment can be determined by the formula.
A slightly more difficult option is a uniformly distributed load (for example, the own weight of the floor). In this case, the maximum bending moment will be equal to
In the case of a beam on 2 supports, its stiffness also becomes important, that is, the maximum displacement under load, so that the stiffness condition is fulfilled, it is necessary that the deflection does not exceed the permissible value (set as part of the beam span length, for example, l / 300).
When a concentrated force acts on a beam, the maximum deflection will be under the point of application of the force, that is, in the center.
The calculation formula has the form
where E is the modulus of elasticity of the material;
I - moment of inertia.
The modulus of elasticity is a reference value, for steel, for example, it is equal to 2 ∙ 105 MPa, and the moment of inertia is indicated in the assortment for each pipe size, so there is no need to calculate it separately and even a humanist can do the calculation with his own hands.
For a uniformly distributed load applied along the entire length of the beam, maximum displacement will be observed in the center. You can define it by the formula
Most often, if, when calculating the strength, all the conditions are met and there is a margin of at least 10%, then there are no problems with rigidity. But occasionally there may be cases when the strength is sufficient, but the deflection exceeds the allowable one. In this case, we simply increase the cross-section, that is, we take the next pipe in the assortment and repeat the calculation until the condition is fulfilled.
Statically indeterminate constructs
In principle, it is also easy to work with such schemes, but at least minimal knowledge in strength materials, structural mechanics is needed.Statically indeterminate schemes are good because they allow you to use the material more economically, but their disadvantage is that the calculation becomes more complicated.
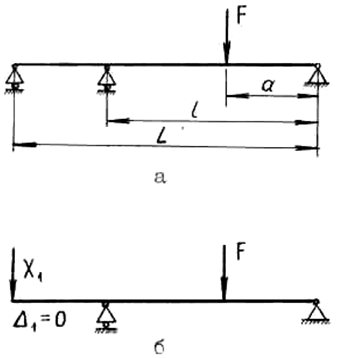

The simplest example - imagine a 6 meter long span, you need to cover it with one beam. Options for solving problem 2:
- just lay the longest beam with the largest possible cross-section. But due to its own weight alone, its strength resource will be almost completely selected, and the price of such a solution will be considerable;
- install a pair of racks in the span, the system will become statically indeterminate, but the permissible load on the beam will increase by an order of magnitude. As a result, you can take a smaller section and save on material without reducing strength and stiffness.
Bendable metal properties
Metal has its own point of resistance, both maximum and minimum.
The maximum load on the structure leads to deformations, unnecessary bends and even kinks. When calculating, we pay attention to the type of pipe, section, dimensions, density, general characteristics. Thanks to this data, it is known how the material will behave under the influence of environmental factors.
We take into account that under pressure on the transverse part of the pipe, stress arises even at points remote from the neutral axis. The zone of the most tangential stress will be the one located near the neutral axis.
During bending, the inner layers in the bent corners contract, decrease in size, and the outer layers stretch, lengthen, but the middle layers retain their original dimensions after the end of the process.


Classification and calculation of the simplest structures
In principle, a structure of any complexity and configuration can be created from pipes, but typical schemes are most often used in everyday life. For example, a beam scheme with rigid pinching at one end can be used as a model for the support of a future fence post or support for a canopy. So, having considered the calculation of 4-5 typical schemes, we can assume that most of the problems in private construction will be solved.
Scope of the pipe depending on the class
Studying the range of rolled products, you may come across such terms as pipe strength group, strength class, quality class, etc. All these indicators allow you to immediately find out the purpose of the product and a number of its characteristics.
Important! Everything that will be discussed below concerns metal pipes. In the case of PVC, polypropylene pipes, of course, it is also possible to determine the strength, stability, but given the relatively mild conditions of their work, it makes no sense to give such a classification.
Since metal pipes operate in a pressure mode, water hammer can periodically occur, the consistency of dimensions and compliance with operational loads is of particular importance.
For example, according to quality groups, 2 types of pipeline can be distinguished:
- class A - mechanical and geometric indicators are controlled;
- class D - resistance to water hammer is also taken into account.
It is also possible to divide rolled pipes into classes depending on the purpose, in this case:
- Class 1 - says that the rental can be used to organize water and gas supply;
- Class 2 - indicates increased resistance to pressure, water hammer. Such rental is already suitable, for example, for the construction of a highway.
Strength classification
Strength classes of pipes are given depending on the ultimate tensile strength of the wall metal. By the marking, one can immediately judge the strength of the pipeline, for example, the designation K64 means the following: the letter K indicates that we are talking about a strength class, the number indicates the ultimate tensile strength (units of kg ∙ s / mm2).
The minimum strength indicator is 34 kg ∙ s / mm2, and the maximum is 65 kg ∙ s / mm2. In this case, the strength class of the pipe is selected based not only on the maximum load on the metal, but the operating conditions are also taken into account.
There are several standards describing the strength requirements for pipes, for example, for rolled products that are used in the construction of gas and oil pipelines, GOST 20295-85 is relevant.
In addition to the classification by strength, division is also introduced depending on the type of pipes:
- type 1 - longitudinal seam (contact welding with high-frequency current is used), diameter is up to 426 mm;
- type 2 - spiral seam;
- type 3 - longitudinal seam.
Pipes can also differ in steel composition, high-strength rolled products are produced from low-alloy steel. Carbon steel is used for the production of rolled products with strength class K34 - K42.
With regard to physical characteristics, for strength class K34, the tensile strength is 33.3 kg ∙ s / mm2, the yield strength is at least 20.6 kg ∙ s / mm2, and the elongation is not more than 24%. For the stronger K60 pipe, these indicators are already 58.8 kg ∙ s / mm2, 41.2 kg ∙ s / mm2 and 16%, respectively.
Design load schemes
The process of calculating any profile begins with the selection of a design schematic model.
Before starting the calculations, collect the load that will act on the floor.
Then a drawing of the diagram is made, taking into account the loading scheme and the beam supports.
Further, using the specified parameters, information from the assortment tables given in GOSTs, the corresponding calculations are made.


For their simplicity and efficiency, you can use online calculators that are equipped with programs with ready-made formulas.
Calculation of the maximum deflection for a beam with two supports
As an example, consider a scheme in which a beam is on two supports, and a concentrated force is applied to it at an arbitrary point. Until the moment the force was applied, the beam was a straight line, however, under the influence of the force, it changed its appearance and, due to deformation, became a curve.
Suppose the XY plane is the plane of symmetry of a beam on two supports. All loads act on the beam in this plane. In this case, it will be a fact that the curve obtained as a result of the action of the force will also be in this plane. This curve is called the elastic line of the beam or the deflection line of the beam. Algebraically solve the elastic line of the beam and calculate the deflection of the beam, the formula of which will be constant for beams with two supports, as follows.
Output
As we found out, there are quite a few popular ways to bend pipes. With a little practice, you can achieve good results. However, it should be remembered that the quality of the bend performed on professional equipment will always be higher.
The video in this article provides additional information on how to bend reinforced plastic pipes. If in the process of performing this operation you have any difficulties, ask questions in the comments, and I will definitely try to help you.
July 22, 2020
If you want to express gratitude, add clarification or objection, ask the author something - add a comment or say thank you!
Load calculation methods
The following methods are used to determine the permissible loads:
- Using an online calculator.
- Based on reference tables.
- According to the formulas of stress during profile deflection.
Before calculations, it is recommended to draw up a drawing of the future frame, to determine the types of loads.
If the part is attached from one end, the element is calculated for bending. When mounted on supports, the deflection is calculated.
Using reference tables
The variant with tables of the already calculated maximum load is the simplest and most convenient for a person unfamiliar with the strength of materials and calculations. They contain ready-made calculation results for specific types of frame elements.
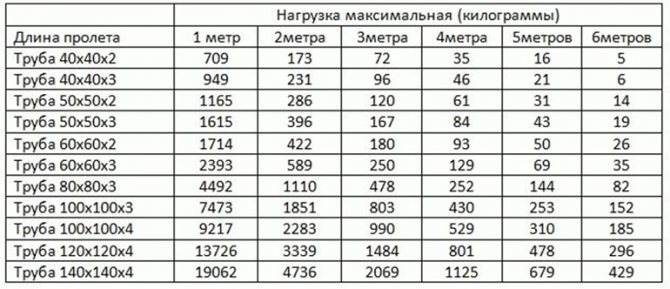
For square profiles

For rectangular beams
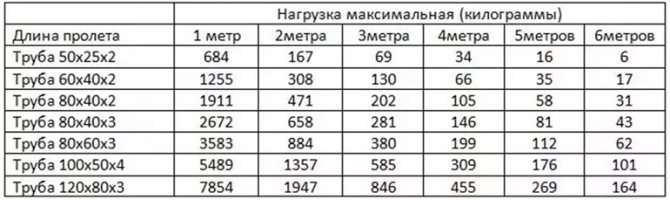

The user immediately sees the limit value that a pipe with certain parameters can withstand for a given span length. Can independently compare and analyze data, choose the best option.
For example, a 40 × 40 square profile with a material thickness of 3 mm in a span of 2 m will withstand 231 kg of weight. If the distance between the supports is increased to 6 m, the permissible load is only 6 kg.
Calculations are made taking into account the weight of the pipe itself, the load value is depicted by the concentrated force applied at the mid-span point.
For independent calculations, data from the GOST reference tables are used. So, the parameter of the moment of inertia of a square profile is taken from GOST 8639-82, of a rectangular section - from GOST 8645-68.
Multifunctionality and basic parameters of pipes with stiffeners
In the process of forming a steel pipe, the dimensions correspond to a given length, the shape during rolling is given to a rectangular (square) with 4 stiffening ribs. The output is a pipe profile. Its configuration stands out among ordinary round pipes. Products from cold-worked rolled products are not significantly different in cost from other varieties. By using cold technology, an aluminum or galvanized profile is produced, it is additionally given anti-corrosion properties.
Helpful advice! It is recommended to look through the prices for finished products in the price lists before buying, taking into account the obvious savings and the cost of delivery to your region.
The increased demand for aluminum profiles is justified by the technical parameters:
- resistance to physical impact;
- low weight with significant dimensions of metal pipes;
- increased strength with sufficient ductility of the metal;
- slight deviations in deformations;
- a wide range of applications;
- affordable prices for the entire aluminum and galvanized assortment, taking into account the standard sizes of pipes.


Profile pipes are rolled into a rectangular shape with four stiffeners
On the territory of the Russian Federation, more than 400 enterprises specialize in the production of profiled and round steel pipes. They differ in the range of cross-sections and wall thicknesses, and their applications are almost limitless.