According to experts, about 15% of the heat can go through the roof and attic of a residential building even with basic insulation. If you do not use insulation at all, then the remaining cold bridges in the winter neutralize the effect of the heating systems. At the same time, modern roof structures and roofing provide ample opportunities for improving the energy efficiency of a building. A properly arranged warm roof will not only provide microclimatic comfort, but also extend the service life of the attic materials.
Constructional features of the insulated roof
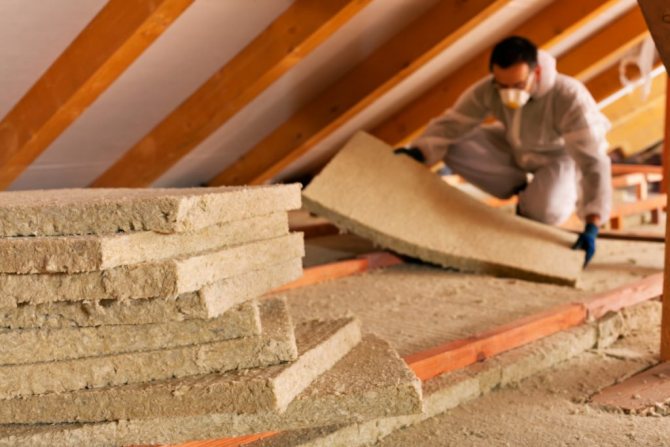
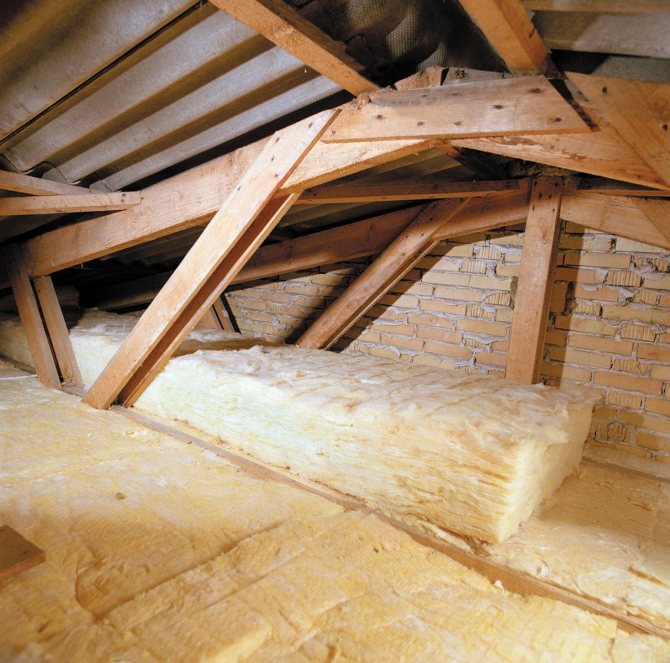
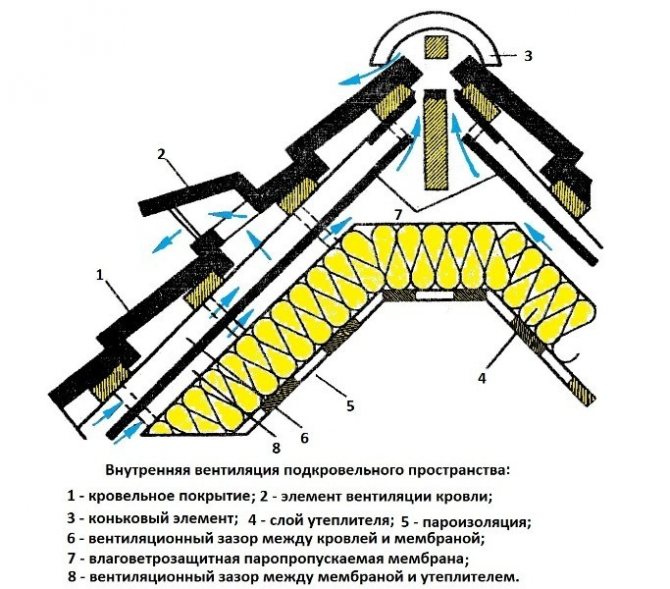
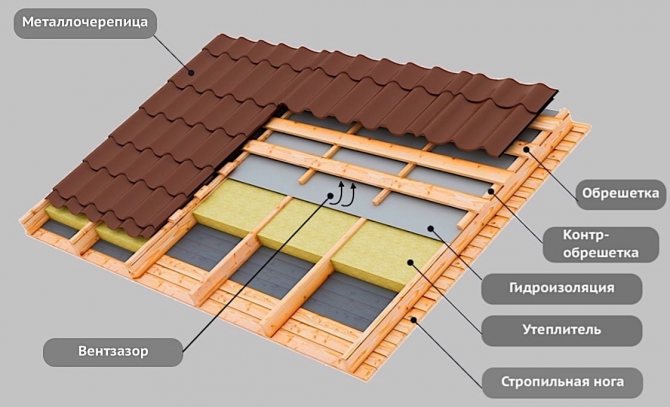
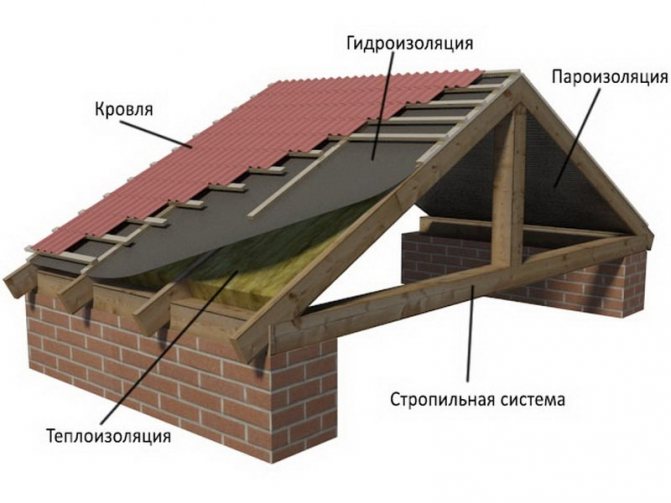
In its pure form, an ordinary pitched roof is a load-bearing frame formed by beams, Mauerlat, support posts and battens on which the roof is laid. The configurations of the rafter system may vary, but the most important thing is that even when assembled and in use, they can be insulated. The insulated roof structure is characterized by the presence of several layers of insulation in the transition areas. The lowest level is the floor that separates the attic from the living space. This is followed by the direct insulation of the slopes from the rear sides and in the layer between the crate and the roofing deck. In addition, the construction of a warm roof provides for technological ventilation zones. They can have a different design, but the task of the ventilation gaps is the same - to exclude the accumulation of condensate in the under-roof and attic space.
Roof icing
As practice shows, the snow on the roof does not carry any danger, except for the additional weight on the roof frame. The danger from snow appears when it begins to melt, as a result of which ice forms.


Do-it-yourself insulation
And because of the ice, icicles and ice plugs appear in the drainage systems. In addition, frost has a negative impact on the quality of the roofing. And this is not the only unpleasant moment for the roof.
The main reason for the formation of ice is the difference in air temperature during the day and at night. In parallel, the melting of snow occurs from the transfer of heat from the dwelling to the attic, and from it to the roof.
For this reason, a warm roof warns against all these problems. Although a lot depends on the material with which the roof is covered.
At this temperature, the air contains an insignificant percentage of humidity, which completely excludes the possibility of precipitation. And, if there is no precipitation, then there is nothing for ice to form.
The choice of thermal insulation material
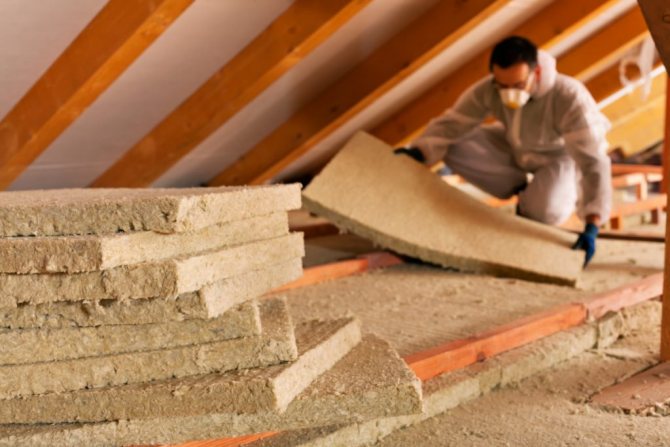


The layout of the insulation will largely determine the effectiveness of the thermal barrier, but if an unsuitable material was initially used, then the highest quality installation will not solve the task of heat saving. Roofers recommend paying attention to the following types of heat insulators:
- Glass wool is a cheap and easy-to-install material with acceptable insulation performance. Its strong point will be the complete elimination of biological degradation processes, and its weak point is the loss of insulating qualities after moistening.
- Basalt slab. It is also a moisture-sensitive insulator, but it is fire-resistant, which is also important for the place of operation in question.
- Mineral wool. A variety of designs and durability can be put among the main advantages of this insulation. A warm roof with mineral wool retains its characteristics for 50 years. But this material should be protected from any contact with moisture.
- Styrofoam.Another option for a budget insulation, which has decent insulating properties, but a lot of structural flaws. Use foam only with good mechanical protection.
- Polyurethane foam. Foam insulation with low thermal conductivity. It is difficult to do without it when spot sealing hard-to-reach cracks and gaps.
Choosing a heater
According to SNiP, the insulation layer for the roof must consist of a non-combustible material, have a density of 20-125 kg / m3 and selective water permeability. In addition, the material must have the following characteristics:
- Good thermal insulation properties.
- Long service life.
- Resistant to atmospheric moisture.
- Good sound insulation performance.
- Biological resistance.
- Ecological cleanliness.
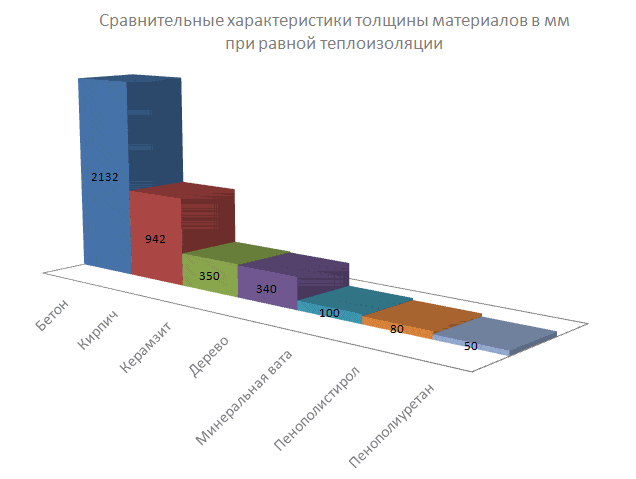

Thickness characteristics for roof insulation.
The most popular in our time are the following heat insulators:
- Extruded polystyrene foam. This material is an effective heat insulator; it is used both for insulating parts of buildings and for insulating roofs in both civil and industrial construction. Due to the homogeneous structure of closed small cells, the product has good thermal insulation properties. The system provides low thermal conductivity and excellent resistance to water vapor. Extruded polystyrene sheets - high compressive strength; they are ideal for places subject to heavy traffic. In addition, this material is environmentally friendly and chemically neutral, it practically does not rot. Plates can be easily cut even with an ordinary knife. Extruded polystyrene foam and DOW can be found today.
- Foam plates. This product has a number of advantages not available to competitors. Here are some of them: a wide range, relatively low cost, low weight, ease of installation, low water absorption capacity (water is not absorbed, but flows down from the material), standard level of thermal conductivity.
- Glass wool. Fiberglass insulation has good performance characteristics. Glass wool slabs provide a quality roof structure. Another plus is that their low density seriously reduces the load on the structure. Soft mats fill uneven surfaces well; they can be used in structures of any configuration and shape.
- Basalt heaters. Basalt slabs are made from basalt fibers, which provide high fire resistance and thermal insulation. The areas of application of this material include sound and heat insulation of light walls, roofs, attics (vertical and inclined), interfloor partitions, attic floors, pipelines, industrial equipment.
- Expanded clay. This material has a natural base. Expanded clay is quite strong and durable. If we compare it with other heat-saving products, for example, with wood, then expanded clay will noticeably benefit in the service life.
For a warm roof, it is preferable to purchase thin insulation with a high degree of thermal insulation. Most often, basalt fiber or glass wool slabs are used in the work.
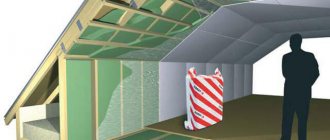
Heat insulator installation
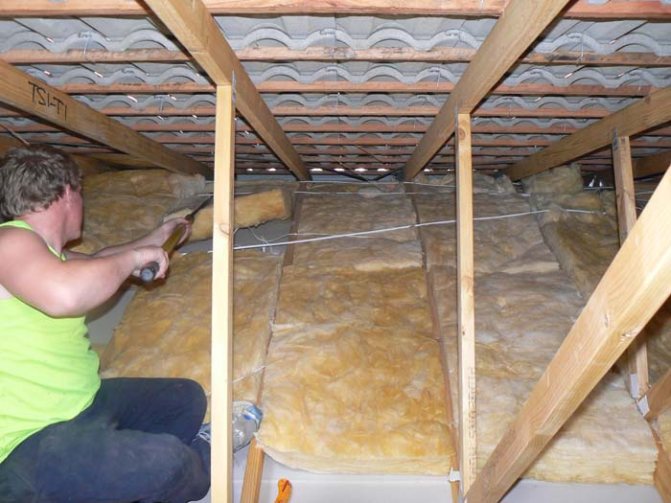


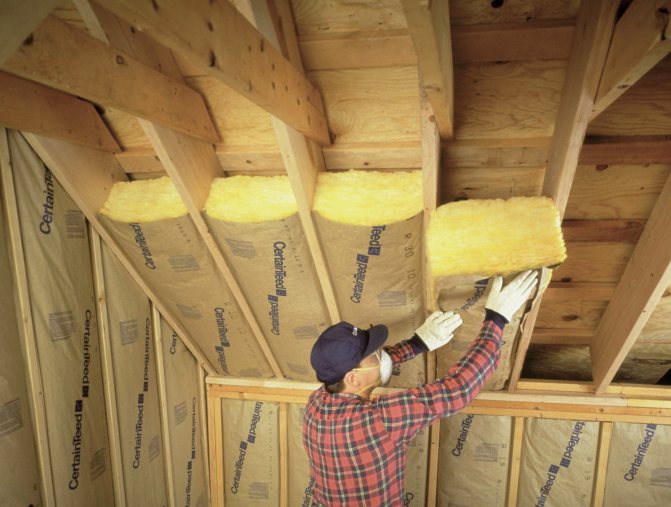
Insulation is built into the construction of the slopes from the inside. Typically, the form of roof insulation is a slab or thick roll material such as mats. Laying is carried out on a prepared surface with profile bearing strips. On the beams of the rafter system, a crate of wooden bars is mounted, to which a heat insulator is subsequently fixed. Fastening can be done with mounting brackets, screws or adhesive. This is not fundamentally important, since the slab or mats should be covered with a counter-grill, the strips of which are nailed to the rafters of the warm roof.Insulation is carried out using the method of solid sheathing with full sealing. Slots, technical gaps and joints are sealed with either moisture-resistant sealants or the aforementioned polyurethane foam. For greater structural reliability, it is advisable to continue the outer crate up to the Mauerlat beams, where the walls of the house begin.
Operating procedure
The insulation technology of the "Pie" type will be the same regardless of the type of building. In this case, all work should be done after the roof has been made and roofing materials have been placed on it.
All work is carried out from the inside:
- First, the waterproofing is laid in one layer. It needs to be fixed to the crate to the bars, using staples for this. The material may sag a little, but not more than 10 cm.
- Next, the insulation is laid. In this case, there should be no gaps between him and the rafters.
- If necessary (if the weather in the region is very harsh), you can lay another layer of insulation. Moreover, its seams should not be next to the seams of the first.
- Now the insulation needs to be covered with a vapor barrier film, for this it can be fixed to the crate using a stapler. In this case, the sheets must be overlapped and connected with construction tape.
- There should be a certain distance between each layer of such a cake so that moisture does not linger in the roof.
- On the inside, such insulation must be covered with sheets of plywood, and if it is used as a living space, it can be covered with a decorative coating.
Laying hydro and vapor barrier
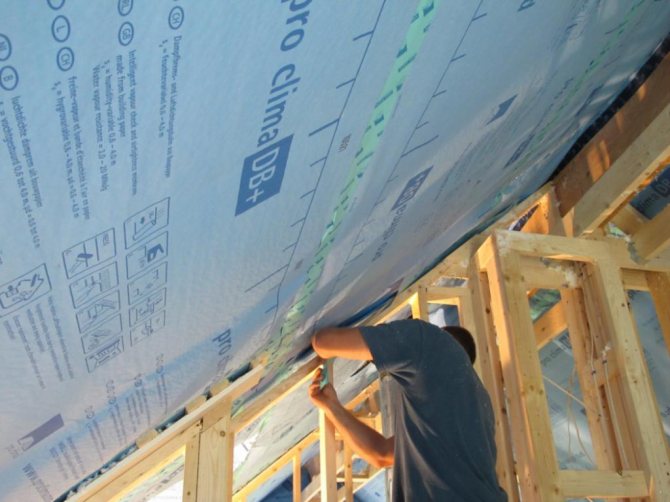


A review of heat insulators showed that without reliable protection from moisture, the material will simply get wet and stop performing its main function. Therefore, the next step is to take care of waterproofing and vapor barrier. For this, membrane film materials are used, which do not require a supporting structure for fastening. In particular, for arranging a warm roof, it is recommended to use Uniflex, Linokrom and Technoelast waterproofers. In some modifications, they also perform the function of a vapor barrier. Laying is done on a surface with a fixed heat insulator by gluing. There are self-adhesive films, but universal building compounds can also be used to fix insulators with a water-repellent effect. Without fail, the film is closed from the outside with strips in increments of 20-30 cm.
Roof insulation in houses without attics
To create a warm roof, I recommend using mineral wool boards. They are made in wedge-shaped and rectangular shapes, making them easy to stack and dock together. Today, there are many ways to fix such plates. For example, you can attach them to screws or nails, mastic or glue, a flat bar or a bar.
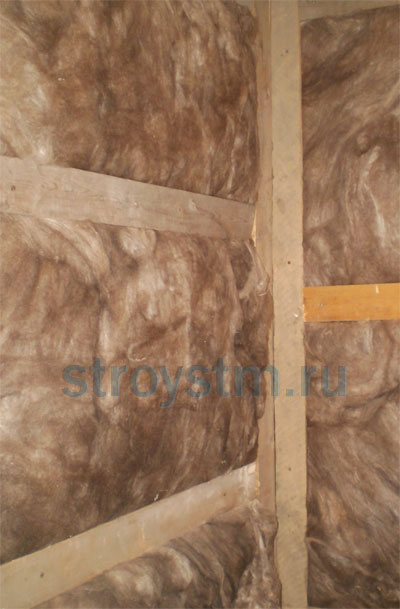


In houses without an attic, I would recommend ceiling insulation, which can be placed both inside and outside the room.
For external roof insulation, use rigid slabs. They must be laid on top of the beams of the supporting structure, thus forming a solid base for the paving slabs. In this case, I recommend that you pay special attention to the supporting structure, it must be strong, otherwise the roof will leak.
I find it more convenient to insulate the roof from the side of the ceiling. This is very easy to accomplish with 25mm thick expanded polystyrene boards, which must be glued to the planks screwed to the ceiling along the walls.
Creating a ventilated gap
Condensation removal from under the roof space is not only a measure of protection of the heat insulator. The wooden rafter system is also sensitive to dampness and if you do not think over the air circulation channels, then in the very first months of operation you can find foci of development of fungus and mold.How to make a warm roof with a ventilation gap? The best option is to use perforated eaves on the overhangs. These are special plastic boxes that are installed along the edges of the slopes, forming a buffer zone with air heat exchange. Thus, effective ventilation of the space from the bottom will be ensured without the risk of rainfall.
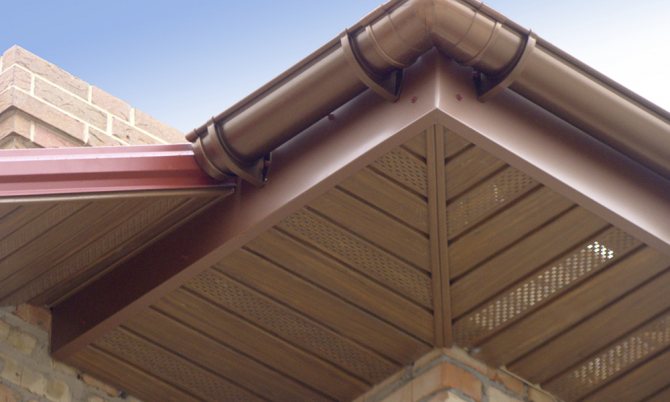


Features of the roofing cake
The most popular option for insulating a roof, and at the same time very easy for self-construction, is considered a "Canadian sandwich".
This technology involves the creation of a multi-layer coating. The arrangement of such a roof does not require the involvement of specialists, the main thing is to observe the correct sequence of laying all layers.
It is important to prevent moisture from entering the insulation. This requires creating conditions under which condensation will not appear. To accomplish this, it is precisely such elements as wind and moisture protection, vapor barrier, hydro-barrier, as well as the creation of small gaps between these layers for ventilation are needed.
You also need to create air circulation in the gaps from bottom to top. Due to this, all the resulting moisture will not fall on the heat-insulating layer, since it will evaporate and be removed due to ventilation in the gaps.
It is important to do this, since mineral wool or any other similar heaters must always remain dry so as not to lose their properties.
Choosing a warm roof
Roof decking can have different heat-saving qualities. The roof in this sense plays a decisive role, but it is far from always possible in principle to use a dense cover with good sealing. For example, bituminous shingles, due to their gravity, are contraindicated for installation on weak rafter systems in many private houses. The way out will be a multi-level warm roof - a roof, the upper level of which is formed by several technological layers. The first layer along the slopes can be laid out with a vapor barrier, and then wind and waterproofers will follow. The task of thermal insulation in this part is not the most important, since the already mounted rear sheathing will be responsible for the regulation of heat flows. In the structure of the roofing system, it is important to provide protection against physical influences, including wind, precipitation, snow, etc.
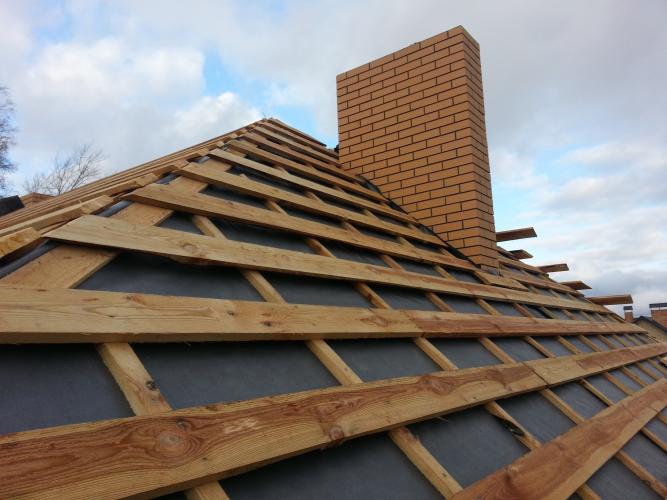


Floor insulation
The main barrier to the outdoor cold from the upper part of the house is the interfloor covering that separates the attic from the lower rooms. In this area, there are many more opportunities for insulation. They should be used to their fullest potential. A layer of expanded clay or sawdust can be poured into the very niche of the warm roof overlap. These are bulk heat insulators, the advantages of which include environmental friendliness and affordable cost. However, expanded clay gives a large weight load, and sawdust is a combustible material and is prone to biological damage. Well, then, already on the surface of the floor, a horizontal crate is mounted, in the cells of which heat-insulating plates are also laid. If the design allows for height, then you can make a double lathing with the location of different insulation fibers in a criss-cross pattern.
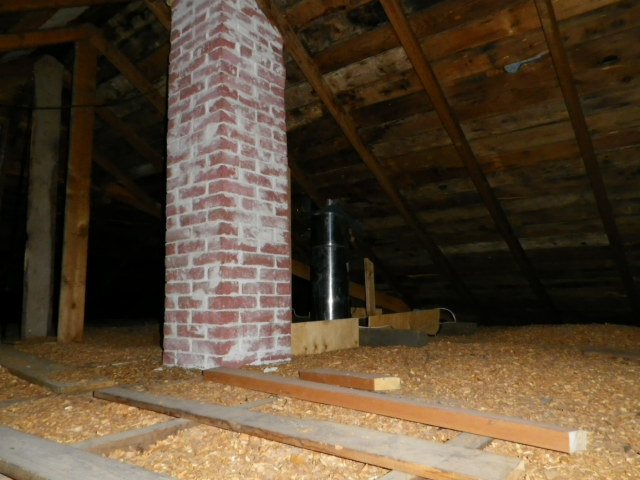


Features of flat roof insulation
In this case, the emphasis is on the use of bulk heat insulators and liquid waterproofing. As for the first, it is not expanded clay with sawdust that should be used, but special lightweight materials like expanded polystyrene crumbs, penoizol or foam glass. But the main feature lies in the structural solution - the creation of a special hatch under the roof covering in the form of a niche 15-20 cm thick. This space is completely filled up with an insulator. Outside, the flat, warm roof structure is covered with molten bitumen using a gas burner.A completely sealed roof deck is formed, which will provide hydro and vapor barrier.


The sequence of works on insulation
Different types of roofs differ in the technology of the process for their insulation.
Flat roof
Insulation cake for a flat roof of a private house
It can be insulated from the outside (on top of the ceiling), from the inside (the principle of a false ceiling), and by both methods at the same time. The main method is external insulation.
The order of work is as follows:
- A vapor barrier is laid on the cleaned and leveled floor slab.
- Then the insulation is laid - more often it is a basalt slab or expanded polystyrene.
- A waterproofing layer from rolls of synthetic materials or classic roofing material is rolled out from above.
- If further operation of the roof is planned, the next layers will be drainage (from expanded clay, for example) and a concrete screed.
- The work is completed with the flooring of the selected roofing material.
Conclusions about the need to use additional methods of heat preservation are taken based on the results of the first winter spent after warming.
Pitched roof
In order to avoid mistakes when performing insulation work, you need to understand the basic principles of the effective and correct action of the resulting insulation "pie".
The main condition for proper insulation of a pitched roof in a private house is the provision of the so-called multi-layer "pie" of waterproofing of the inner space from the outside with simultaneous vapor permeability from the inside. In this case, moisture from possible roof leaks or condensation will not get into the heat-insulating layer. And the water vapor of the attic room will be easily removed through all layers to the outside. At the same time, comfortable humidity values are achieved in the indoor room under the roof. The insulation itself does not get wet, therefore, it does not deform, does not wrinkle and does not lose its declared heat-insulating characteristics.
Correct installation of a vapor-permeable waterproofing membrane is very important. Vapors through it must be discharged from the thermal insulation material to the outside.
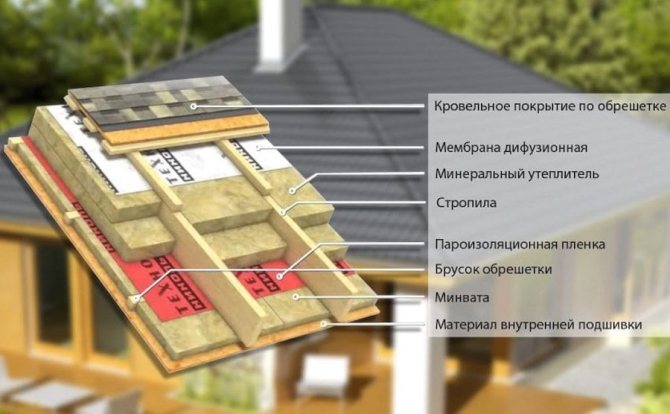
The scheme of the layers of the insulation "pie" sequentially (starting from the inner side) includes: filing (supporting insulation) or decorative trim, vapor barrier, insulation, vapor-permeable waterproofing material.
For natural removal of accidental moisture, it is necessary to provide air gaps (2-3 cm):
- between roofing material and waterproofing;
- between hydro-barrier and thermal insulation;
- between the vapor barrier and the decorative trim of the attic.
In order for the air to circulate freely in the gaps obtained, air vents are left in the overhang (part of the roof protruding beyond the wall line) and under the ridge that ends the roof. They will provide an unobstructed air flow and the same free air removal.
Pie for insulating a pitched roof of a private house
The pitched roof is almost always insulated from the inside. Preparation for work consists in revision of the wooden roof frame, its necessary repair, reinforcement, treatment with impregnation.
Roof insulation in a private house is carried out in stages in the following order:
- Work on this point is carried out in the absence of the original waterproofing under the roof. The rafters themselves cover the water barrier. A construction stapler is used for fixation. Waterproofing must be removed under the overhang - this guarantees the removal of unwanted liquid to the outside. The ideal waterproofing option on the inside of the batten is a superdiffusion membrane. It is not worth saving here, because such an insulation scheme excludes the air cavity adjacent to the waterproofing.
- If the waterproofing is installed under the roof, we create the conditions for obtaining an air gap under it. To do this, a nylon thread or fishing line (fixed with nails) is passed between the rafters repeatedly (10 cm step), retreating 3 cm from the hydro-barrier.The insulation will rest on this artificial web.
- Thermal insulation is placed between the rafters. Expanded polystyrene is inserted tightly, mineral wool is a spur with some compression (for this, the width of the cotton slabs should be one centimeter larger than the opening). With several layers, the slabs are stacked apart with the slabs of another layer, overlapping their joints.
- If necessary, increase the depth of the openings so that the insulation does not protrude beyond the rafters, the latter are built up with additional beams.
- The insulation is attached, or rather, held by a lathing crate or nylon thread.
- Now the vapor barrier canvases are overlapped and fastened with a construction stapler. The joints are glued. Particular care and accuracy will require the space around the chimney or exhaust pipes and the place where the gables fit to the walls.
- The work is completed by the installation of the selected interior decoration - plasterboard, lining, chipboard, plywood. The guide rails and profiles used for the installation of the inner lining provide the necessary air gap between it and the vapor barrier. If further finishing of the attic space is not planned, filing is performed with gaps of up to 10 cm. The used edged board is treated with an antiseptic.