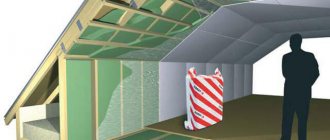
Is it worth insulating the roof at all in a particular house?
Before you start choosing a material and installing a heat insulator, you need to decide whether insulation is required or you can and should do without it.
The main thing here is to make a fundamental decision - the attic will be used as a "not insulated" storage room for various small things, or it is still planned to make a living room there.
Insulate the roof along the rafters only in the second case, when arranging the attic. Snow lying on the roof must be insulated from the attic heat, otherwise it will begin to melt and turn into ice, followed by damage to the roofing materials.
But in a situation with a non-residential attic, the overlap between the living rooms in the house and the under-roof space should be insulated. Otherwise, it will cease to perform the functions assigned to it and, plus, corrosive processes may begin on the rafters.
Thermal insulation "from above"
Thermal insulation can be laid from the inside, but this option is only suitable for rooms with high ceilings and is quite difficult and time consuming. At the same time, the flooring of insulating material in the attic and the insulation of the roof are simple processes.
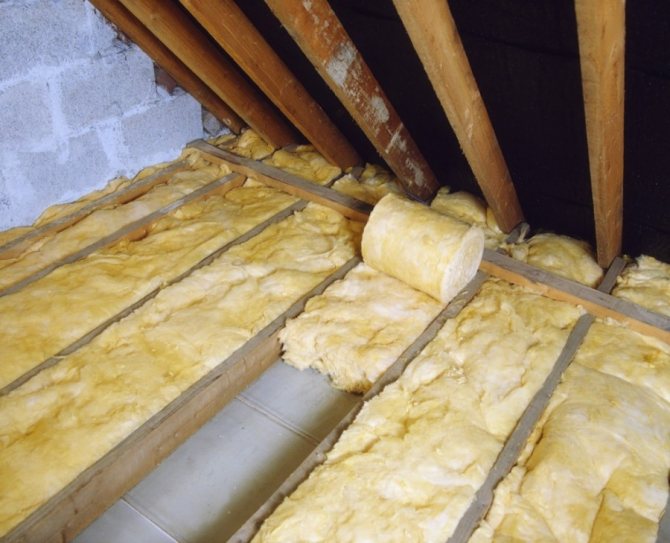

The choice of insulation and the method of its installation depend only on the slope of the roof and the used roofing material.
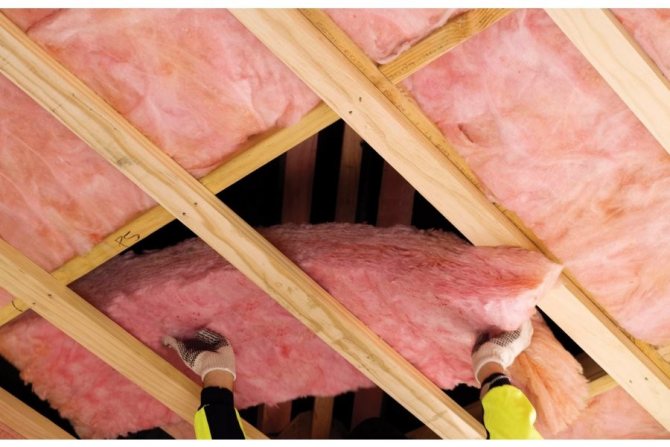


Material selection
There are a lot of options for materials for insulating the roof between the rafters in the domestic market of heat-insulating materials:
- Polyfoam (extruded polystyrene foam) - excellent indicators of water absorption and thermal conductivity, but due to its rigidity it is not very suitable for roofs.
- Polyurethane foam - thermal conductivity is comparable to the first material, but there is more water absorption (you cannot do without arranging a high-quality waterproofing layer).
- Penoizol is a carbamide-formaldehyde foam in the form of a polyurethane foam (after foaming, it fills all holes and cracks, but under the influence of water and steam it quickly loses all its thermal insulation qualities and, moreover, is easily destroyed even by light pressure).
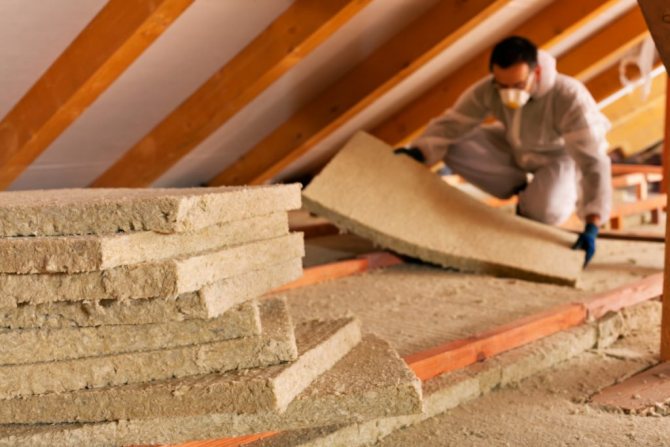
- Mineral wool (from basalt, glass or slag) - fibers obtained by extraction from mineral raw materials or industrial waste.
The main problem with all polymer heat insulators is their flammability.
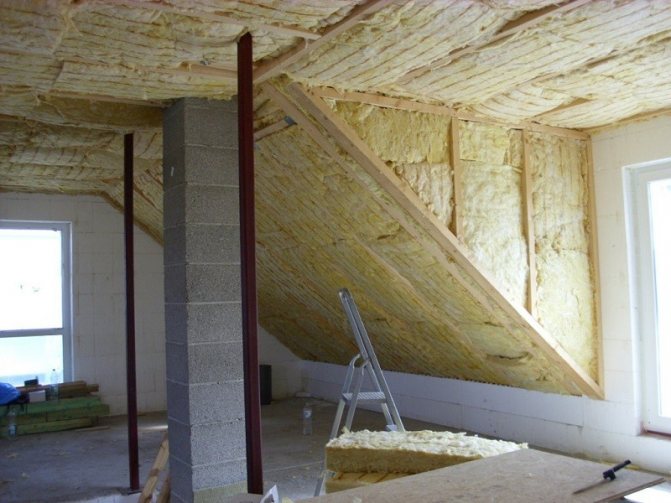
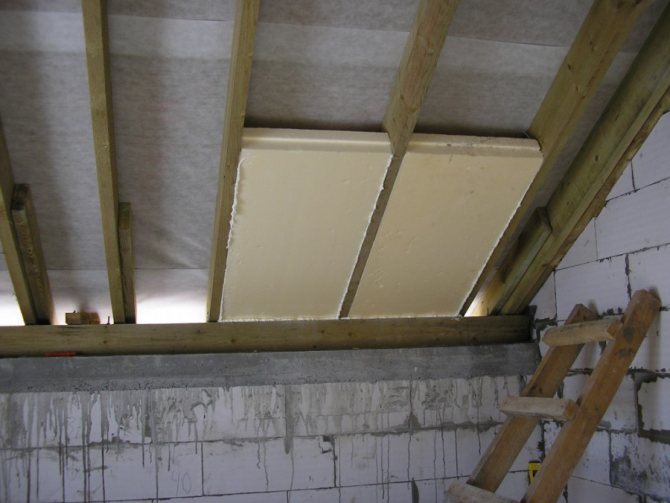
Polyfoam tolerates moisture well, but it is tough in work and it will leave cracks at the rafters. Therefore, it is the last option, stone (basalt) mineral wool, with the best thermal conductivity among all mineral wool, is the most optimal choice for roof insulation along the rafters.
The main thing is to qualitatively perform its vapor-waterproofing so that moisture cannot get close to it. And it is easy to work with it, and with proper installation, any crevices for drafts are excluded.
Roof insulation materials
In general, all thermal insulation materials can be divided into:
- porous (or porous-fibrous), which contain communicating gas cavities.
- cellular, which contain insulated gas cavities: polyurethane foam; expanded polystyrene; polyethylene foam; foamed rubber.
It is customary to use the following types of insulation:
- Polyfoam (expanded polystyrene), which with a big stretch can be called a heat-insulating material due to the complexity of high-quality insulation.
- Minvatu. Mineral wool insulation can contain staple fiberglass or rock. From experience I will say that the material with stone inclusions, namely basalt insulation, has the highest quality thermal insulation properties.
note
In my work, I never use and do not recommend using foam or fiberglass-based mineral wool. We insulate only with basalt stone rock heaters, because we are solely responsible for the work performed and guarantee their maximum quality.
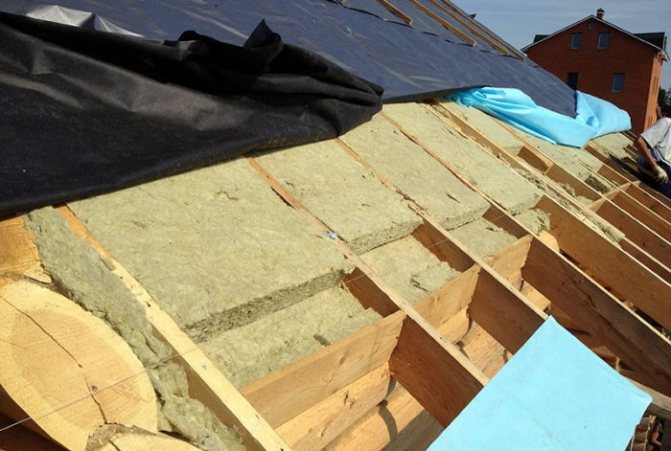
Correct inter-rafter insulation technology
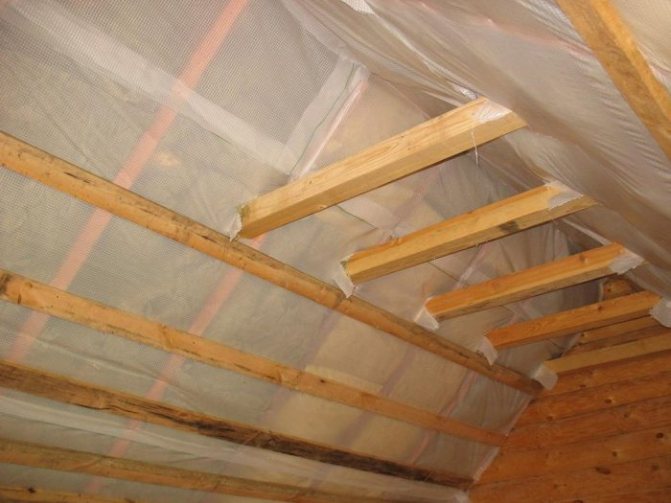
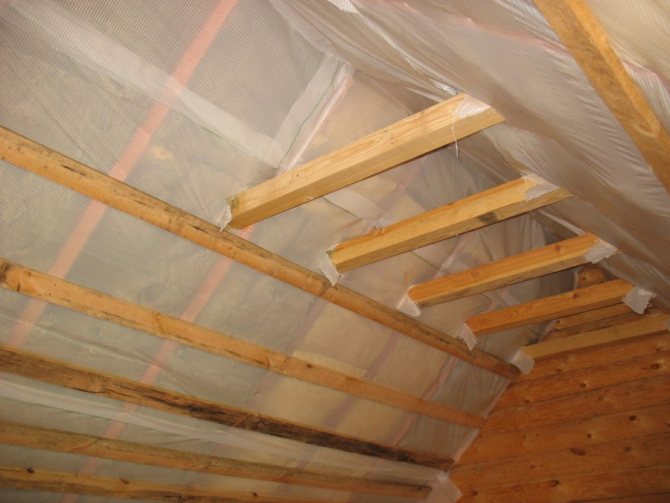
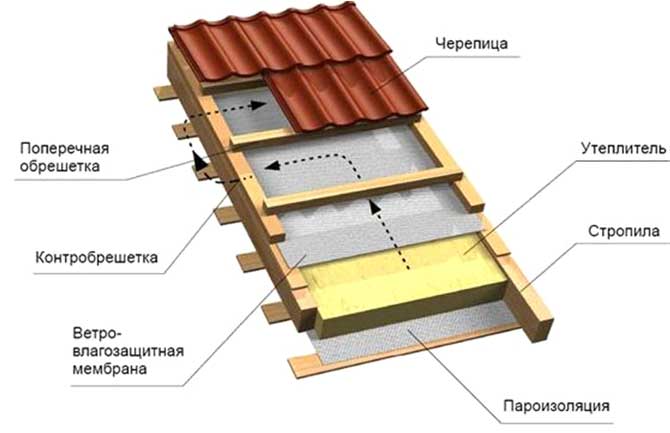
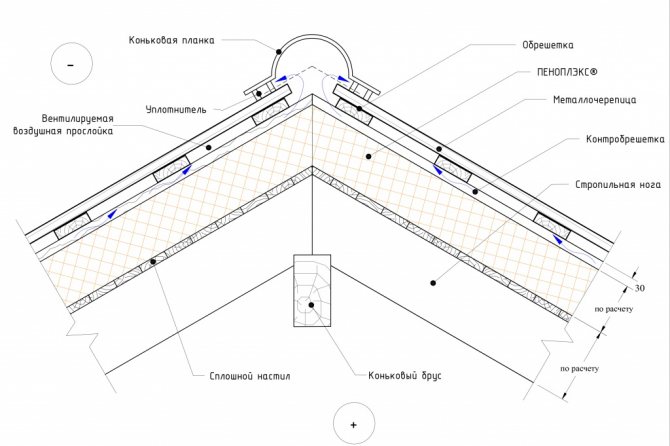
Upon completion of laying the mineral wool between the stacks, a "puff cake" should be obtained, in which layers successively go out from the attic:
- Decor (plasterboard or lining).
- Ventilation gap.
- Vapor barrier (cotton wool must be protected from steam).
- Minvata.
- A waterproofing pad that releases steam to the outside, but does not let water through to the mineral wool.
- Second ventilation gap
- Roof material.
It is most convenient to carry out work on roof insulation even at the stage of arranging the roof during the construction of a house, otherwise then you will have to remove the roofing material.
Features of basalt heaters
Basalt heaters - belong to the group of mineral wool heaters and are made from various stone rocks.
Stone wool is made up of the finest fibers, chaotically interconnected and forming cells filled with air, therefore, the material is characterized by low density and increased content inside the air.
The advantages of basalt insulation
- High thermal insulation qualities. Heat exchange between the cold and warm sides of the structure is noticeably reduced.
- Quite good soundproofing of the premises.
- Durability and easy installation. Basalt heaters are not afraid of temperature effects and do not shrink.
- Basalts have an incombustibility class NG (fireproof frame). This means that by winning 15-30 minutes against the fire, many lives can be saved.
- This is the most common thermal insulation in Russia. Factories producing basalt insulation are scattered throughout the country in great variety.
- Basalt insulation is the most environmentally friendly compared to other heaters.
- Hydrophobic qualities. Stone wool fibers are naturally water-repellent; in addition, specialized additives are used in the production that can enhance their water-repellent properties.
note
And yet, you must understand that at any stage of construction, if water is available to the mineral wool insulation, soon the mineral wool will stop working, since basalt will crumple under the influence of water and lose its thermal insulation properties.
For this, steam and waterproofing is used.
More about steam and waterproofing
Work outside
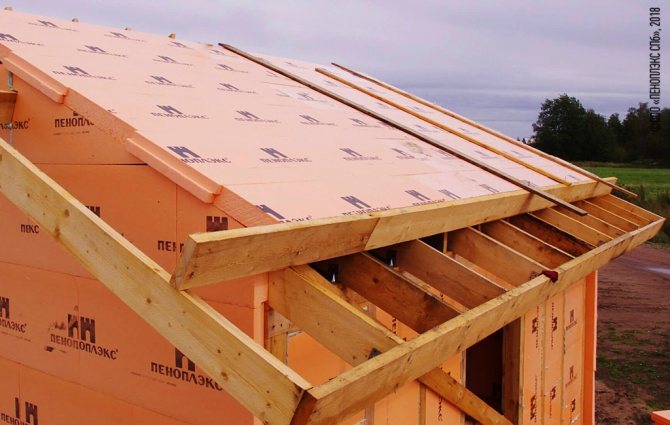
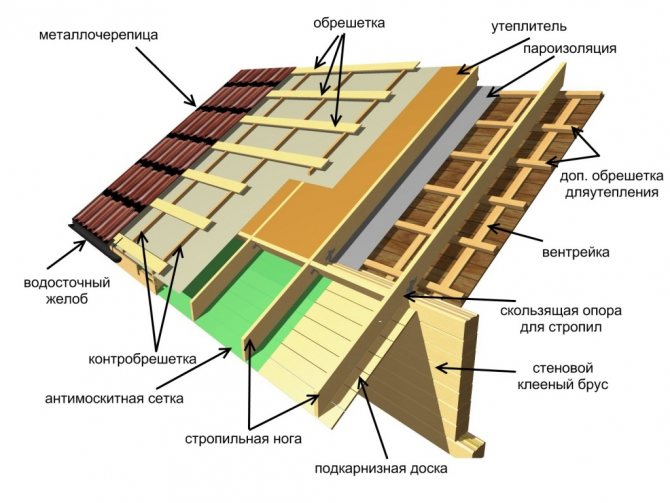
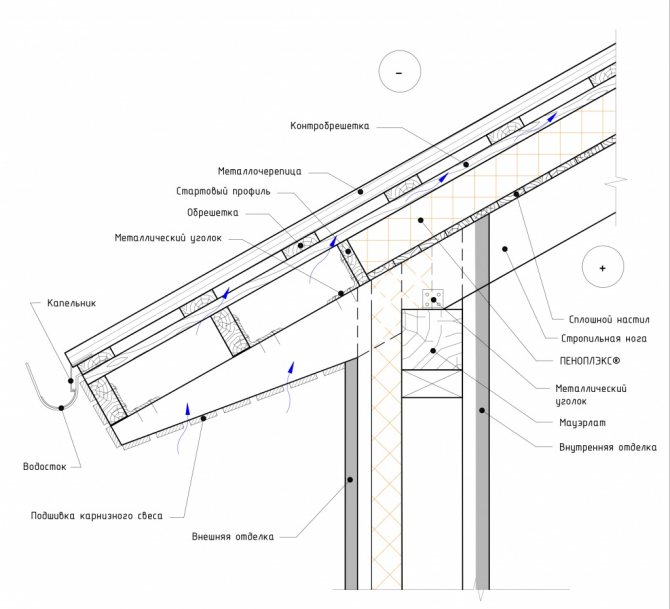
After the installation of the system is completed, even before the installation of the roof itself, waterproofing should be installed from a special superdiffusion membrane. The main thing is not to confuse her sides. Outside, it spreads with a moisture-proof layer. Laying is done from the eaves up, the canvases overlap by 10-15 cm and all joints will need to be glued with construction tape. To attach the film to the rafters, it is most convenient to use a construction stapler, or you will have to work with a hammer. The main thing is that the carnations are galvanized.
It is not recommended to stretch the waterproofing film on the rafters. With a decrease in temperatures, it will begin to shrink a little and will simply be damaged in the places of fasteners, and the canvases may also disperse with the formation of gaps.
Next, a crate is packed over the superdiffusion membrane. It will require 2.5-5 cm wooden slats, depending on the planned ventilation space and the type of roofing material. Galvanized self-tapping screws are quite suitable as fasteners. At the end, the roofing is installed on top of the crate.
If the insulation is carried out in the attic with the roof already laid and if the waterproofing was missed during its installation, then it will be necessary to remove the roofing material and lay the film. Otherwise, the under-roof insulation will get wet and lose all its thermal insulation properties.
If the membranes are laid from the inside and the rafters are wrapped around them, then they will simply begin to rot from an excess of moisture.
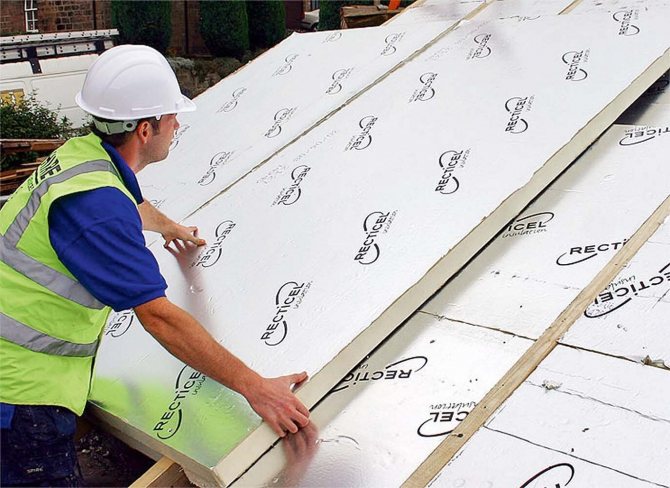
The considered technology involves the use of sheet roofing materials (slate, metal, corrugated board). To insulate the soft roof on the rafters, you will need to nail moisture-resistant plywood on top of the sheathing, and the topcoat should already be attached to it.
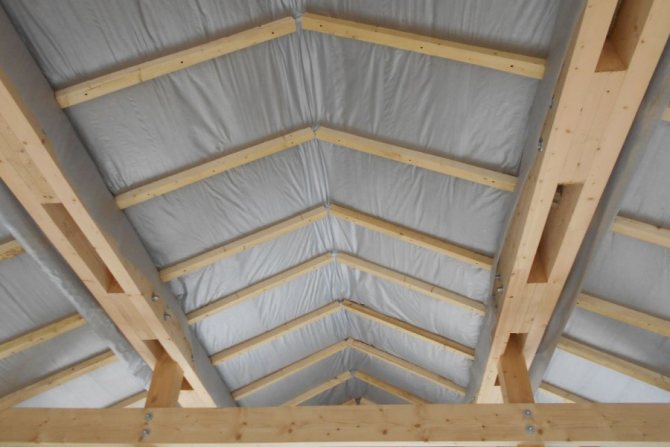
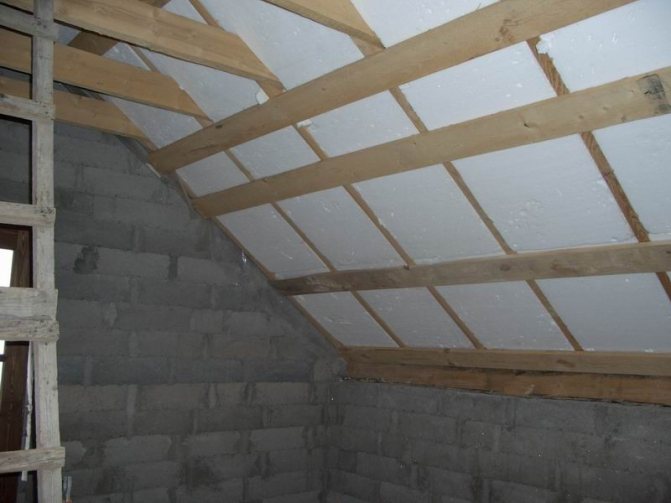
Insulation between the rafters
The traditional way to insulate a sloped roof is to position the insulation between the rafters. In this case, you can arrange a flat ceiling of the attic room.
Before starting insulation, you need to mount a waterproof film over the rafters. It will protect the premises from possible precipitation and will allow work to be carried out in any weather. It is better to choose a diffusion membrane. When installing a microperforated or anti-condensation coating, a two-sided gap is arranged. Condensation often forms on the films. Its hit on the insulation:
- will increase the coefficient of thermal conductivity;
- will lead to deterioration of insulation;
- promotes the development of mold;
- will reduce the bearing capacity of the roofing elements.
The insulation is not laid to the full height of the rafter leg. A gap of 2-3 cm is sufficient for air flow and natural drying.
With this technology, low density insulation is often used. For proper operation, such heaters need to be additionally fastened, which leads to overspending of the frame material.
Often, soft insulation shrinks during operation. Deformations occur both in width and height. As a result, some areas become bare, becoming defenseless against the cold.


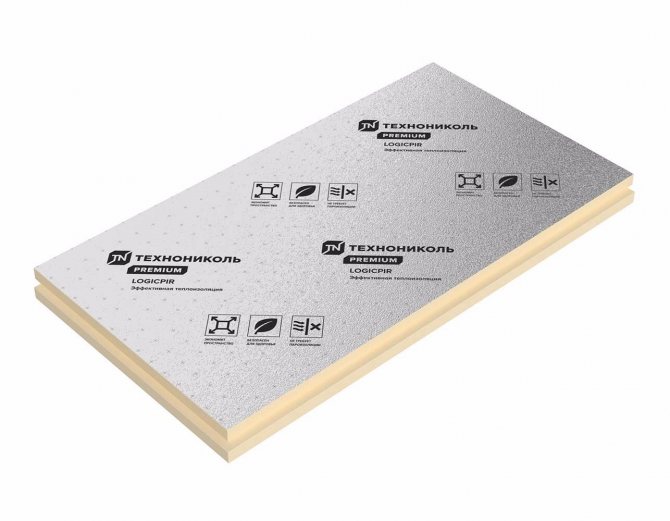
It is not recommended to use insulation in the form of dense materials: foam, polyurethane foam. Due to dimensional instability, gaps are formed between the rafters and the slabs. The use of polyurethane foam does not save the situation. Blowdowns are formed.
Mineral wool insulation Stone (basalt) wool Glass wool
Mineral wool of a slab type is best suited for insulation inside the rafters. When laying, the joints of the slabs are shifted by half the width of the product. In this case, the appearance of cold bridges is prevented.
The dressing of the seams is also important for multi-layered styling. The next product should overlap the seams of the previous flooring. For multi-layer laying, products of maximum thickness are used. For example, for insulation with a layer of 150 mm, it is better to take a material of 100 and 50 mm than three plates of 50 mm each.
When the slope angle is less than 30 °, an additional frame is arranged for insulation. It will prevent slabs from slipping and caking. The frame keeps the boards in the assembly position during their entire service life.
The accepted width of the slabs should be 1-1.5 cm greater than the clear distance between the rafters. In this case, a tight abutment will be ensured. With a smaller width, gaps will appear due to defects in wood or oversight of builders. Large thickness contributes to the deformation of the board and its bending.
Inside the insulation of pitched roofs on wooden rafters, there should be no air gaps and cracks. The layers should be tightly adjacent to each other. This also applies to interlayer spaces and joints. Professionals lay the slabs by cutting them into two trapezoidal pieces.
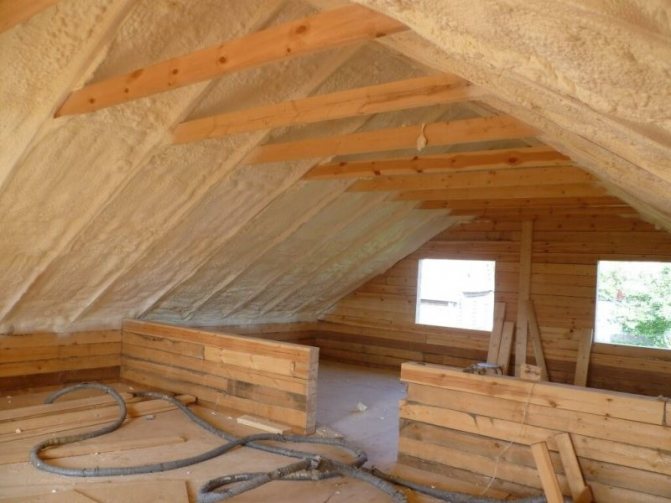
Polyurethane foam (PPU)
Another innovative way of insulation is polyurethane foam. It is possible to arrange the coating both after waterproofing and after installing the roof covering.
The application process takes place by spraying. The work is carried out using special equipment.Protection is mandatory for the employee in the form of:
- suit;
- masks;
- respirator.
Foam is applied both in the gap between the rafters and on the supporting elements of the roof. They must first be treated with antiseptics or anti-corrosion solution. Foam:
- clogs the smallest blows and cracks;
- hides bolt holes;
- covers all metal elements, protecting them from corrosion.
The continuous layer excludes the penetration of drafts and moisture. Low thermal conductivity allows you to reduce the consumption of heating the under-roof space.
The second innovative continuous coating material is ecowool. The name itself speaks of environmental friendliness and safety of use.
Ecowool
The composition includes fire retardants and antiseptics. The first ones prevent the fire of the layer, the second ones spread inside fungi and mold. The bulk of the composition is waste paper and cardboard production waste.
Laying is done dry and wet. In dry installation, the rafters are sewn up from the inside with facing material. The material is placed in the resulting boxes. In the wet method, wet cotton wool is applied to the surface under pressure. High adhesion of the material allows you to cover the surface with a dense, uniform layer.
Works inside
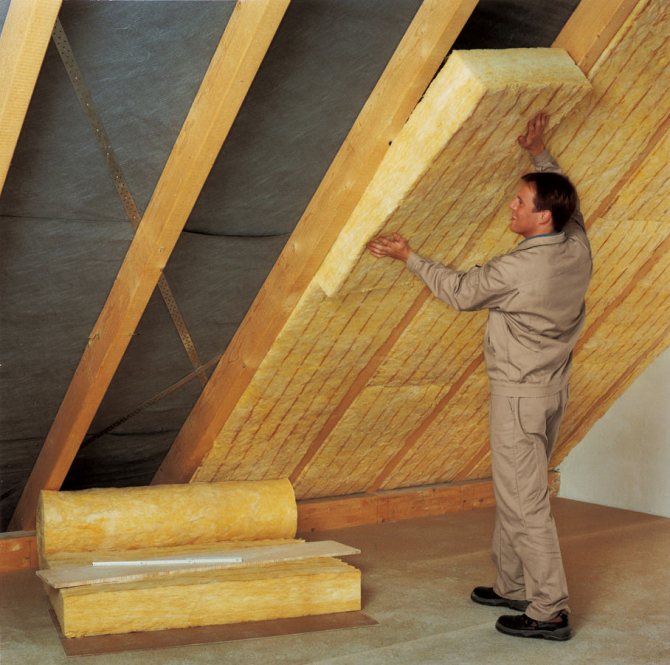
After arranging the roof, the laying of mineral wool between the rafters inside the attic begins. Minvata must be unpacked, allowed to lie down a little and straighten out, and then cut into pieces equal to the inter-rafter distance with the addition of 3-4 cm.
The material should be pressed with little effort between the rafters to fill the entire space.
On top of the mineral wool, a vapor barrier film is stuffed to the rafters, using the same technology as outside. Then again a gap is made for ventilation, on the crate of which the internal decor of the ceiling and walls of the attic is mounted.
It can be drywall for further finishing or lining for painting.
Features of roof insulation
An important layer, of course, remains waterproofing. Immediately after it, we will begin to insulate. The most important parameter of the insulation is the coefficient of its thermal conductivity. It is worth choosing a material with a lower value, because the lower it is, the more heat it will retain in the house.
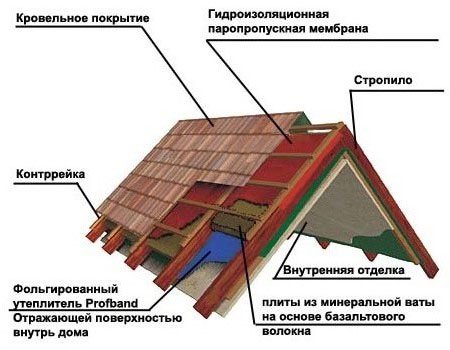

Attic insulation scheme from the outside and inside
Besides thermal conductivity, there is another important characteristic - rigidity. The insulation will lie in an inclined plane parallel to the roof, and it may slide over time. Do not forget that we will lay it in the space between the rafters, where it will have to maintain its original dimensions. If you choose a material that is not quite rigid, over time, “cold bridges” will appear, and soon icicles and ice will appear on the roof. The interior decoration of the attic may also suffer. It will not be possible to increase the rigidity in any way, so you should immediately choose a suitable insulation.
In the matter of choosing a material for thermal insulation, it is necessary to choose a middle ground, because the tougher the material, the less heat it retains. It is not so difficult to choose the right material, plates or mats made of glass wool and expanded polystyrene, as well as mineral wool, have balanced qualities of thermal conductivity and rigidity.
Features of the process of thermal insulation of the roof
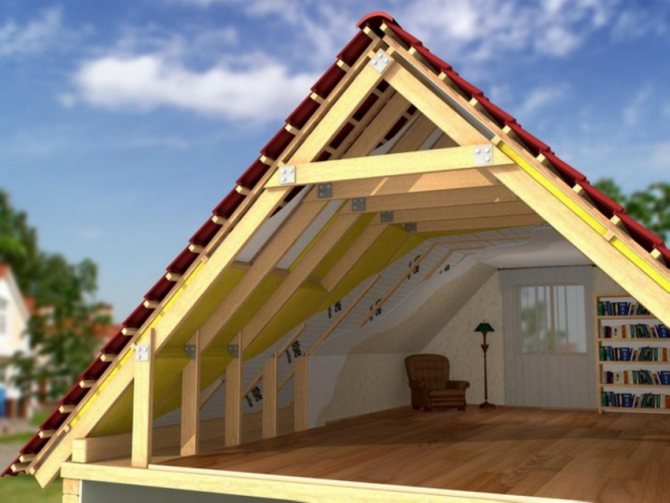


For all the seeming lightness, roof insulation is a complex and time-consuming process. There are several reasons for this:
- Firstly, the roof is the lightest building element, which is contraindicated to make it heavier. However, when arranging an attic space, you need to be sure of sufficient thermal insulation properties of the roof. These indicators should be on a par with the load-bearing walls;
- Secondly, the peculiarity of the operation of the roofing "pie" affects.Its outer part constantly interacts with an unfavorable external environment (including humidity). The inner, lower part is also exposed to moisture and indoor microclimate. Therefore, due to the temperature difference, there is a risk of condensation in. It enhances its increased vaporization characteristic of residential premises.
Therefore, special requirements are imposed on materials for roof insulation. According to their characteristics, they should be:
- as light as possible, to eliminate the increased load on the rafter system;
- have a higher class of resistance to moisture. It will not be possible to completely avoid the process of condensation formation in any case;
- meet the fire safety requirements - be non-flammable or at least non-combustible;
- have the effect of noise absorption. Correctly selected material drowns out both noises from the street and, for example, the sound of rain on the surface of the roof;
- have minimal thermal conductivity. The main purpose of the insulation is to maintain a comfortable temperature in the room, even in the cold season.
The insulation technology can be used for both attic and semi-attic attic spaces. Depending on the region and the average temperature in winter, the required thickness of the insulation layer will differ. The lower the temperature drops in the cold season, the thicker the layer must be mounted.
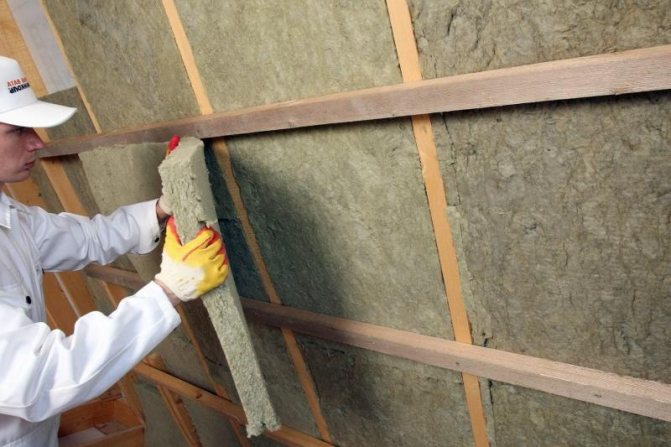


Expert opinion
Konstantin Alexandrovich
In order to live in the attic all year round, it is required to insulate not only the upper part of the roof, but also the slopes, side ceilings and joints with the load-bearing walls. All necessary calculations and layer thicknesses are described in SNiP II-3-79. The most suitable option is a material with a thermal conductivity of no more than 0.04 W / m C.
When choosing a material, you should pay attention to its crease. Good insulation does not sag under its own weight. This parameter is important when arranging the roof, because the rafter system is tilted, and the load on the insulation will be constant. After a few years, the sheet, which is quickly removed, slides to the base, which is why the ridge will have a “bare”, non-insulated zone. Heat will be lost through it, losses can reach up to 40%. The best choice is material marked "for pitched roofs".