What is the difference between polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam?
Water absorption (%) - a parameter that determines how much water a material can absorb:
These figures indicate that polystyrene foam can absorb only 400 grams of water during the specified period, while polystyrene is capable of more - 4 liters.
Blocking heat from passing through a wall in the same house can help reduce heating costs. The low thermal conductivity provides an economic benefit as it becomes possible to reduce the thickness of the material. The lower parameter of thermal conductivity of polystyrene makes it a unique material, capable of better than other similar products keep warm:
- 0.036–0.050 W / (m · K) - foam;
- 0.028 W / (m K) - expanded polystyrene.
Density - mass parameter, allowing to determine the weight of 1 m 3 of material in kilograms:
- 15–35 kg / m 3 - polystyrene;
- 28–45 kg / m 3 - expanded polystyrene.
To understand how the above parameters compare favorably with the materials in question from other construction products, you can familiarize yourself with the following figures:
- 0.058 W / (m K), 368 kg / m 3 - wood;
- 0.05 W / (m K), 1200 kg / m 3 - foam concrete;
- 0.2 W / (m K), 1800 kg / m 3 - brick.
Strength (limit) - a parameter, the value of which can be found out if you put the material on any supports so that they hold it along the edges, and then begin to apply pressure to the middle of the product until it breaks. As a result, the required values can be obtained for each of the materials:
- 0.07-0.2 kgf / m 2 - foam;
- 0.4-1.0 kgf / m 2 - expanded polystyrene.
Strength (compression) - a parameter due to the effect of a pressure force on a material placed on a flat plane until its thickness is reduced by 10%. The high strength of expanded polystyrene determines it as the most resistant material:
- 0.05–0.20 MPa - foam;
- 0.25-0.50 MPa - expanded polystyrene.
Working temperatures - both materials can be used in approximately the same temperature conditions: from -50 ° C to +75 ° C.
Life time - the undoubted leader of the two materials under consideration is expanded polystyrene, since it is several orders of magnitude more durable than polystyrene. Its lifespan is at least 50 years, while foam can retain its properties for no more than 25 years.
Against the background of polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam looks like a more practical product that has a number of advantages, which include:
- high strength;
- resistance to moisture;
- lower thermal conductivity;
- durability.
At the same time, expanded polystyrene is somewhat inferior to polystyrene, since it is definitely heavier and, although not much, is more expensive.
Valuable properties of foam
This polymer is obtained by pressure foaming of polystyrene granules, which increase in volume up to 50 times. They are dried and stabilized and then baked in contour molds. With the help of hot metal threads, the resulting blocks are cut into convenient briquettes in the form of slabs with the required dimensions.
Polyfoam has many advantages:
- low weight with a density of 50 kg / m3,
- ease of use,
- moisture resistance,
- excellent heat retention,
- lack of reaction to the action of ethers, alcohols, hydrocarbons and some other chemical compounds,
- the lowest cost in the line of synthetic insulation.
It should be noted and disadvantages:
- the foam does not deteriorate when water enters, but the granules disintegrate, and the material loses its thermal insulation characteristics,
- it is inappropriate to use a vapor-proof material in humid rooms that require a high-quality ventilation system,
- quickly dissolves in hydrocarbons, esters and acetone,
- insufficient strength and increased fragility.
In the composition of only some types of foam, there are fire retardants that reduce the degree of its flammability.
Manufacturers promise 20-50 years of insulation, although it depends on the conditions of use and is about 20 years.
Extruded polystyrene - what is it?
EPPS is an improved version and a great alternative to foam. The production technology of the material also involves the use of a blowing agent. But then the granules are placed in molds for drying under high pressure with the addition of modifying additives that improve the properties of the material. During extrusion, closed and very tightly adjacent cells are created, so the new insulation is not able to get wet.
Extruded polystyrene foam has excellent performance characteristics, for example:
- effectively retains heat (the thermal conductivity index can reach 0.043 W / m K),
- operated at a temperature of -50 - +70 0С,
- repels water (absorption coefficient - up to 0.4% of the total volume, in accordance with the requirements of GOST-17177.94),
- does not deteriorate in contact with household and building substances - bitumen, soap, soda, gypsum, cement,
- reduces the level of external noise by 30 dB.
High resistance to deformation allows the use of polystyrene boards in the insulation of attic floors and ceilings.
The disadvantages of the material include:
- sensitivity to ultraviolet irradiation,
- low vapor permeability, which makes it difficult to ventilate a damp room,
- destruction under the influence of building solvents,
- flammability.
According to the assurances of manufacturers, extruded expanded polystyrene is ready to serve faithfully for half a century. None of the thermal insulation materials can boast of such a period.
The video talks about the extraordinarily attractive properties of extruded polystyrene foam:
There is a variety - extruded polystyrene XPS (what it is, special reference books explain). The multifunctional thermal insulation Extruded Polystyrene Foam is extruded from an initial version of polystyrene. This material is used for the manufacture of extrusion boards.
Historical reference
The discovery of expanded polystyrene took place about 50 years ago in Germany, where it almost immediately began to be used in construction. During the time that has passed since this discovery, studies of its qualities, properties and merits have not stopped. In particular, the Germans tested polystyrene foam, which was extracted from houses built 40 years ago.
The studies carried out made it possible to determine that expanded polystyrene retained its properties by almost 90%, and this once again confirms the durability of this material.
Comparison of foam and extruded polystyrene foam
Extruded polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam are among the most popular thermal insulation materials on the market. These heaters, it would seem, at different prices, have similar technical characteristics, and it is sometimes very difficult to choose a suitable option for use.
Foam plates PSB-S25
In this article, we will figure out which is better - polystyrene or expanded polystyrene, and what is the significant difference between these materials. A comparison of their technical characteristics and operational properties will be made.
Varieties of expanded polystyrene
The vast majority of polystyrene foam is produced from polystyrene. Widespread and well-known in our country for a long time, polystyrene is no exception. Therefore, it is incorrect to compare which is better, foam or polystyrene.
However, foam sheets are commercially available that differ in appearance and structure. The reason for this is different production technologies. There are two main types of Styrofoam:
- Pressless is the most common. It is with this variety that Styrofoam is usually associated.During its invention, this material received the trade name "styropor". It is produced by polymerizing styrene with the addition of a pore-forming agent. The high tendency to pore formation made it possible to achieve the content of flesh in the gas composition up to 98%. All gas is enclosed in microscopic polystyrene cells.
- Extrusion - produced by extrusion, that is, by pressure treatment at an elevated temperature with the addition of a blowing agent and subsequent extrusion from the extruder.

The porosity in these materials is different
The main visual difference between styrofoam and extruded polystyrene foam is the structure of porosity. Extrusion makes it possible to achieve cells with a size of several tenths of a millimeter, and classic polystyrene has significantly enlarged spherical granules during steam processing, which are easily separated from each other.
See the same: technical characteristics of expanded polystyrene.
It is impossible to unequivocally determine which is better, extruded polystyrene foam or foam obtained by the non-pressing method. Each material has its own characteristics that determine its application.
Pressless material
The relatively large size of the granules of classic foam is determined by the technology of its manufacture.
Simplified the production process can be described by the following algorithm:
- The starting material is styrene granules. At the first stage, the initial saturation of the granules with gas is carried out, for this it is dissolved in the polymer mass. Traditional technology uses natural gas for this purpose. The use of pentane, isopentane, or mixtures thereof is widespread. They are highly volatile liquids, the vapors of which are used in production. The process was named suspension polymerization, since these liquids are perfectly soluble in styrene, but insoluble in polystyrene. Special fire-resistant modifications of the material are also produced, in which carbon dioxide acts as a granule filler. Sometimes vacuum technology can be used, in which there is no gas filler.
- In the second step, the pellets are steamed. Alternative processes can use water or air treatment. In the process of such exposure, the granules begin to grow significantly and can increase in size up to 30 times.
- At the final stage, the granules are sintered while simultaneously filling the shape of the future product.
Polyfoam or expanded polystyrene, their differences and which one is better
Wall insulation has become very important for most people, in the winter it is to protect the house from the cold, and in the summer - from the heat. The quality of insulation will depend on the heat-insulating material, the more effective it is, the better it will be able to retain heat in the room.
Currently, there is a large selection of materials for insulating the walls of the house from the outside, more and more of them appear on the construction market every year. Experts advise to insulate the walls of the house with certain materials, such as polystyrene and expanded polystyrene. It is difficult for ordinary consumers to figure out what is the difference between these two names and which one is better, because at first glance they are very similar.
What to choose as insulation?
The process of wall insulation with foam.
It is impossible to unequivocally answer the question which is warmer, polystyrene or expanded polystyrene. These insulating materials have almost the same low thermal conductivity and have a lot in common, but their application depends on the specific problem. Foam plastic is widely used for exterior decoration of premises, since it is environmentally friendly and retains heat well. Its cost is also significantly lower and more affordable than other materials.
For interior decoration of walls and rooms with high air humidity, it is more appropriate to use expanded polystyrene, since it is more airtight and resistant to stress. The cost of expanded polystyrene is much higher than that of polystyrene, but if all the necessary requirements for installation and operation are met, it has a longer service life (at least half a century).
The final choice in favor of a particular material is made after considering the scope and nature of the work and drawing up an approximate cost estimate.
Polyfoam, its characteristics and advantages
This heat-insulating material is produced from polystyrene by foaming and in finished form in it. 98% air, it is a classic type of insulation. Polystyrene granules are treated with dry steam and at the moment of thermal expansion they adhere to each other, resulting in micropores in the finished material. For a long time, people began to use it for thermal insulation at home, use the material to insulate walls, floors, roofs. Such protection not only saves from the cold in winter, but also serves as a kind of protection for the walls of the building.
Due to the basic characteristics of foam, many believe that it is best suited as insulation. Its main qualities can be attribute the following properties.
- It is 98% air.
- Its thermal conductivity ranges from 0.038 to 0.050 W / m K, which is significantly lower than that of wood or brick. For example, wood in terms of thermal conductivity exceeds polystyrene by 3 times, and brick by 17 times.
- Only 2-3cm of foam can make a complete soundproofing of the building.
- They do not absorb moisture more than 3% of its mass and at the same time its thermal insulation properties remain unchanged.
- The light weight makes it easier to work with the material, it is easy to install, no special tools are required for cutting.
- It is non-toxic, odorless, does not generate dust during operation, therefore, protective equipment is not needed during operation.
- Polyfoam is resistant to cement, gypsum, alkalis, water-based paints, but is afraid of acetone and benzene.
- In contact with an open fire, it ignites, but quickly extinguishes.
- The material is environmentally friendly, safe to use and dispose of, it is also widely used in the food industry and as packaging for many goods, including for children.
Styrofoam also has disadvantages, it very fragile material, which in bad weather complicates the work with it, as well as the transportation of insulation.
Despite the fact that foam appeared a long time ago and now there are many new and modern materials, it has not lost its relevance. Its low price is also attractive to many, which makes it possible to use foam in many types of construction work.
Expanded polystyrene (penoplex)
The extrusion method produces extruded polystyrene foam, the method forces the polymer to first melt, after which a viscous mass is formed. From the solid state granules turn into viscous-viscous, as a result of which a single liquid-phase substance with a solid and durable microstructure is obtained.
Extruded polystyrene foam looks like a mass of closed cells, inside which there is gas, it is much stronger than foam. Polystyrene foam cells are impermeable, they do not have micropores, like foam plastic, so water or gas cannot penetrate into the cells. The cells of expanded polystyrene look like a solid mass, air or water can penetrate only from the cut side of the side surfaces. In general condition, the material cannot absorb moisture, steam and much more from the outside.
We often call expanded polystyrene foam polystyrene, since the domestic brand of extruded polystyrene foam is produced with this name, in fact, they are the same thermal insulation material... The polispen brand is also widespread, it is used in various industries: agriculture, in the construction of runways, when laying oil and gas pipelines, with it they make a heat-insulating layer in civil and industrial building structures.
Since the moment of mass production, penoplex has become widely used in construction as a high-strength heat-insulating material. It is always used for work outside, since it is not suitable for internal insulation, expanded polystyrene at high temperatures can release styrene. Main characteristics material are:
- Increased compressive and fold strength.
- High density foam.
- Does not crumble, unlike styrofoam.
- Thermal conductivity 0.028 W / m K.
- It absorbs moisture no more than 3% of its mass, this indicator does not affect its thermal insulation, strength and structure.
- Has excellent sound insulation.
- Penoplex is not afraid of insects and rodents.
- Does not rot and burns poorly.
Styrofoam or expanded polystyrene, which is better
Comparing both heaters, we can say that they very similar to each other... Having carefully studied their main characteristics, we can say for sure that foams have a higher degree of strength, moisture resistance and air permeability. Due to its density, the insulation has the best thermal insulation qualities, but without special processing it is more flammable than polystyrene.
Compared to penoplex, foam loses in density, insulates less from noise. Polyfoam retains heat better due to its looseness, but this property protects it from moisture worse. Styrofoam always needs to be covered with other materials in order for it to serve for a long time.
If you compare the price of one and the other insulation, then penoplex will cost more than polystyrene, which means that more money will have to be spent on all construction work. When choosing polystyrene, you need to know which brand you need to purchase, they have differences in their characteristics.
Before buying, you need to compare all the basic properties of the two materials, know in advance where they will be used for insulation and make your choice correctly.
What is Styrofoam
In fact, the two concepts of foam and polystyrene foam represent the same material, but produced using different technologies. As a result, both of them acquire differences in technical characteristics. The starting material for both foam and polystyrene foam are polymers based on:
- polyvinyl chloride;
- polyurethane;
- phenol formaldehyde;
- polystyrene;
- combinations of urea and formaldehyde.
In everyday life, the most common type of foam, called polystyrene, is produced without such a technological stage as pressing. This material was first obtained at the BASF factories in the middle of the last century, where it was first named "styrofoam" or PSB-1 foam.
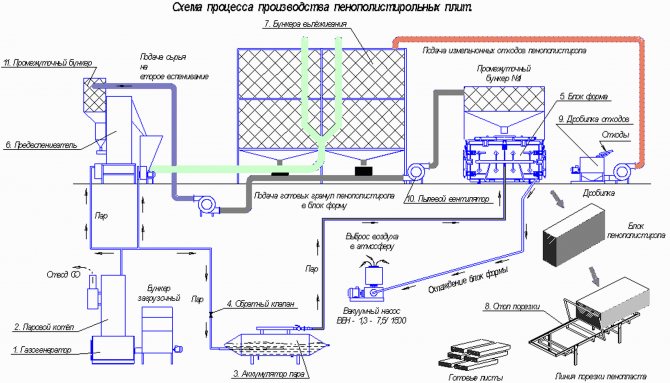
Manufacturing technology
Granular styrofoam is produced using pentane, a substance that promotes the formation of tiny pores filled with gas.


Raw material for the production of foam
At the same time, styrene itself in the total mass of the material contains no more than 2%, the rest is gas. In production, the foam is pure white in color and is extremely lightweight due to the fact that it consists practically of air. And it is precisely this circumstance that became the reason for the use of foam as an insulating material, since there is no better insulation in nature better than air.
The entire production process for obtaining foam includes several operations:
- Primary foaming of granular styrene under the influence of hot steam.


Foaming polystyrene
- Placement of foam in a drying chamber.
- Extract of chilled foamed granules.
- Secondary foaming.
- Cooling of the resulting mass.
- Cutting products according to the specified parameters.
Foaming of granules can be performed several times, depending on the required density of the finished product.
How epps is made - extruded polystyrene foam
The technological process for the production of raw materials for foam and extruded polystyrene is the same. Differences begin at the foaming stage, where special additives are introduced into the raw material.
The process takes place under the influence of high temperature steam in a special device called an extruder, where the mass under the influence of steam acquires a homogeneous and smooth consistency that can take any shape.
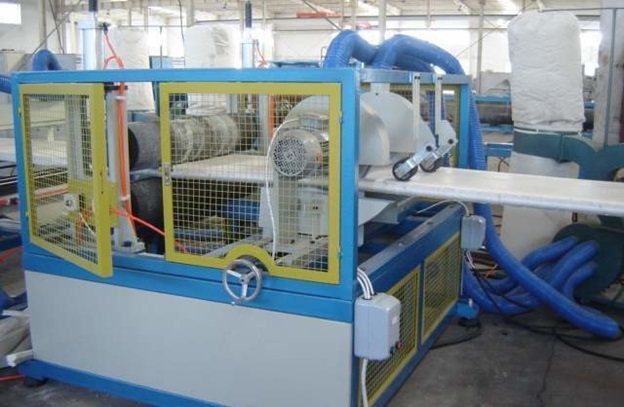


Production of extruded polystyrene foam (foam)
Through a special hole in the extruder under high pressure, the liquid mass is squeezed out into prepared forms. Finished products, after cooling, have the necessary density, rigidity and, at the same time, plasticity. On sale you can find insulation called penoplex, which is nothing more than extruded polystyrene foam.
The difference between concepts such as foam and extruded polystyrene foam lies in the production technology, as a result of which the materials acquire different technical properties and characteristics.
The modern variety of technological production methods often contributes to the emergence of difficulties for homeowners when choosing materials for construction and household needs. Experts have noted a tendency according to which the variety of commercial offers is correlated with the complexity of the material selection process. "Styrofoam or expanded polystyrene, which is better?" - this question has become the most frequent when visiting the construction market, and the purpose of this article is to compare foam and expanded polystyrene.
Content
- Styrofoam and expanded polystyrene. Video production technology
- Physical characteristics of foam and polystyrene foam. Differences
- Thermal conductivity of foam and polystyrene foam
- Styrofoam and expanded polystyrene. Temperature resistance
- Disadvantages of Styrofoam and Styrofoam Video
Styrofoam and expanded polystyrene. Manufacturing technology
Given the related origin of these materials (both are considered modified versions of polystyrene), the relevance of the issue is beyond doubt. The most common misconception about seemingly related materials is the myth that both materials, be it expanded polystyrene or polystyrene, are the same material with the same functional and performance characteristics, but this article is intended to debunk unfounded myths.


The difference between these materials can be judged in connection with a significant difference in technological production options, which from the very beginning provide the prerequisites for distinguishing between foam and polystyrene foam.
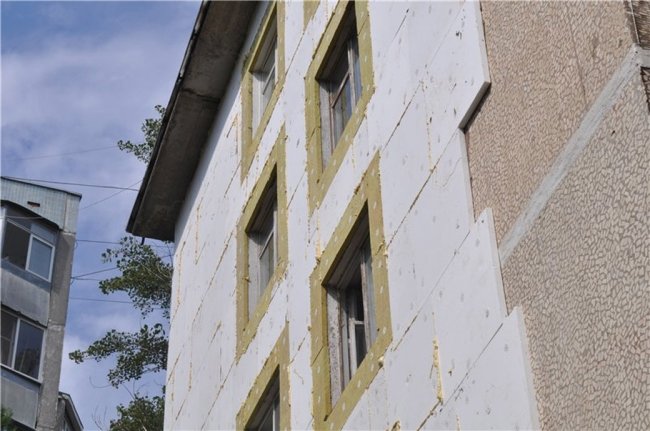


The technological solution for polystyrene involves the processing of the initial polystyrene granules by means of dry steam, which promotes the expansion of the porous structure of polystyrene under the influence of high temperatures and a high level of adhesion of the expanded granules. As a result, a plastic mass is formed, obtained in the process of foaming.

Technological features of the production of expanded polystyrene are fundamentally different from those in the manufacture of polystyrene and is an extrusion process, the essence of which is to melt the granules of raw materials to form a viscous consistency and then push the molten initial substance through a standard caliber hole. The result of this production manipulation is a material with a single structure and strong molecular bonds.
Physical characteristics of foam and polystyrene foam. Differences
The next difference according to all the rules of logic arises from the previous one, which consists in the differences in the technological stages of manufacturing. The manufacturing method directly determines the physical differences between expanded polystyrene and expanded polystyrene. The physics of these materials is very simple.
As discussed in the previous story, polystyrene foam is a single molecular structure, unlike foam, which is produced by the adhesion of related particles. As a result, the conclusion suggests itself that when checking the performance properties, the foam can crumble, which is impossible to say about expanded polystyrene, which takes on the deformations of the building associated with fluctuations in temperature indicators, changes in humidity levels and shrinkage phenomena.
In addition, the use of polystyrene is appropriate for warming and soundproofing flat surface planes that are not affected by mechanical factors of various levels, since its deformation and irreversible violation of integrity are not excluded. Thus, all of the above indicates that the strength characteristics of expanded polystyrene are 5-6 times higher than those of foam.
The structure of the foam, represented by interconnected micropores, is prone to destruction under the influence of moisture, since the granules, as they settle, lose their initial bond strength.
The exact opposite situation develops in the operation of expanded polystyrene. Its closed-cell structure creates conditions for maximum impermeability of substances from the environment, which cannot be said about the foam, which freely passes water vapor from the external space into the room, which subsequently condenses and accumulates in the form of excess moisture.
As for the permeability to moisture and sound waves, it can be argued that the indicated indicators are higher for foam, which also follows from the peculiarities of the technological production process.


Thermal conductivity of foam and polystyrene foam
Speaking about the characteristics of polystyrene and expanded polystyrene, one should not forget about the thermal conductivity, which is the main parameter of the quality of materials intended for thermal insulation work. The thermal conductivity of polystyrene and expanded polystyrene is recognized as a fixed indicator, which significantly differs among the substances analyzed in this text. The thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam is at a lower level, which is due to a more durable structure. This indicator for foam is almost twice that of a competitor, which suggests that the ability of foam to retain heat is several times lower than that of expanded polystyrene.
Styrofoam and expanded polystyrene. Temperature resistance
Comparative characteristics of extruded polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam show that the resistance to thermal effects of the material obtained as a result of extrusion exceeds the ability of the foam plastic to withstand the onslaught of temperature changes. This drawback becomes especially noticeable when finishing the facades of buildings located on the south side with expanded polystyrene foam.
Due to the low intermolecular interaction, which characterizes the structure of the foam, and the low level of resistance to high temperatures, there is reason to fear for the structural integrity of the material. An unfavorable circumstance in this situation is the painting of the wall in a dark color. All this contributes to the fact that in the hot summer period, the plane, finished with expanded polystyrene foam, heats up to 50-60 degrees. This is the threshold temperature at which the foam loses its original structure and begins to melt.Extruded polystyrene foam is devoid of such disadvantages due to the technological features of production. And this was the reason for the rejection of foam when decorating the facades of buildings.


Disadvantages of Styrofoam and Styrofoam
But, oddly enough, the structural features of expanded polystyrene do not affect the level of biodegradation and evaporation of harmful substances with an increase in the permissible heating temperature. According to this parameter, the analyzed materials are similar, and, apparently, this property is their common disadvantage. Both materials are subject to destructive changes, during which the styrene monomer is released. The low level of maximum permissible concentrations of styrene in the room indicates a high range of toxic mechanisms of action of the monomer when it enters the body.


But, despite this, the concentration of styrene is often noted in the room, which is several times higher than the maximum permissible indicators, and, apparently, this is due to the ability of styrene to cumulate indoors and in the human body.
Thus, the stability of extruded polystyrene foam is one third higher than that of the competitor, with the exception of biodegradation indicators. But, in fairness, it is worth noting that the cost of the material made in the extrusion process is 3-4 times higher than the price range of expanded polystyrene foam or the so-called polystyrene foam.


Author: Sergey and Svetlana Khudentsov
10
Scope of foam and expanded polystyrene
Considering that the foam is the same expanded polystyrene, but of a higher density, the area of its use in construction is mainly reduced to the insulation of structural elements of buildings and structures. For example, non-extruded polymer material is quite often used for thermal insulation of facades, given its high thermal insulation properties, ability to adhesion.
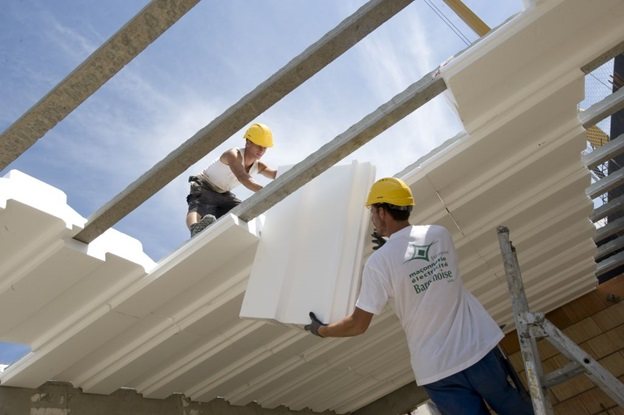


Roof insulation with polystyrene
But with penoplex it is good to insulate basements, foundation and basement elements of buildings, loggias and balconies. At a thinner thickness, it retains all the thermal insulation properties inherent in thicker foam.
At the same time, it is not recommended to insulate with these materials indoors, especially in residential premises, due to the fact that during production the insulation is treated with anti-combustion compounds that can be released into the environment throughout the entire period of operation. In some countries of Europe and America, the use of foam as a heat-insulating material is not allowed. The reason is the release of toxic substances during a fire.
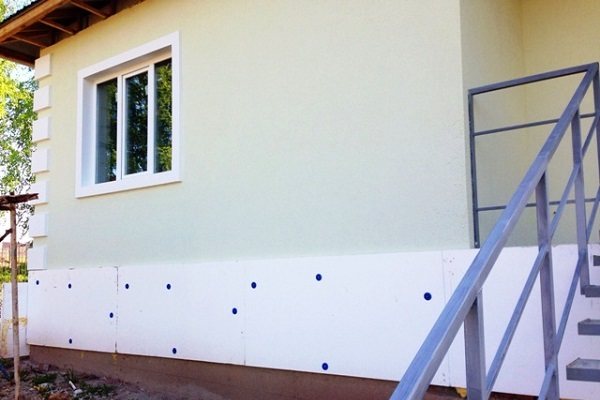


Basement insulation
Extruded styrene foam is used in the production of decorative interior products.
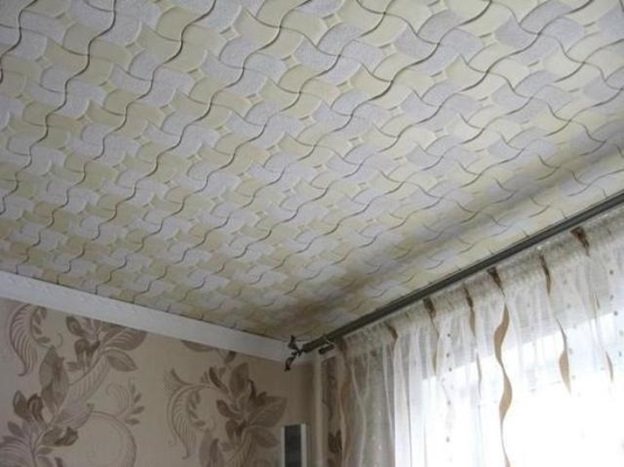


Polystyrene tiles as a finishing material in the interior of premises
In the medical industry, expanded polystyrene, just like polystyrene, is used as a material for the manufacture of packaging.
These materials serve as insulation in household appliances, industrial refrigerators, buoys, floats, life jackets are made from them, they fill the compartments of ships, which ensures their ability to float.
In the food industry, packaging for products and fragile items is made from extruded styrene foam.


Styrofoam in the production of food packaging
Polymer materials obtained without pressing or by extrusion are used in different fields, and when the question arises what to choose, you need to know what is the difference and the properties of these materials.
What is the difference between polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam
Both materials have a lot in common. Considering that the foam is essentially the same expanded polystyrene, however, they have significant differences due to the technology of their production. Consider first the positive and negative properties of foam.The positive characteristics of this material include:
- Low cost of finished products, which is one and a half times lower than the price of extrusion material.
- Long service life provided that installation and operating conditions are observed.
- High degree of thermal insulation with proper installation and further operation. Light weight for easy transportation and installation.
- The structure of the material, if used in dry conditions, does not develop fungi, mold and other microorganisms.
- It is easily processed (cut, sawn, broken) with any available tools and even hands. It does not require providing the worker with protective equipment, since it is an environmentally safe material - it does not emit harmful odors and dust, does not prick. This is confirmed by the production of disposable tableware and toys for children from polystyrene.


Foam application
- It can also be used as sound insulation, when a three-centimeter slab of polymer material is able to completely drown out sounds.
- Temperature range of polystyrene use, without loss of thermal insulation properties and mechanical strength, from -60 ° Ϲ to + 95 ° C. Practically does not absorb moisture.
- Does not support combustion. Extinguishes within 4-5 seconds after contact with an open flame.
The negative properties of foam include its non-contact with solvents and relative fragility. In the event of a fire in a room where Styrofoam has been used, the toxic smoke can cause death. Domestic rodents often live in the porous material.


Polyfoam is not a hindrance to mice
Comparison of foam and extruded polystyrene material
Quite often, when choosing a heater, consumers ask themselves what is better than polystyrene or expanded polystyrene, what is the difference between these heaters, which is warmer, easier to install and more economical. To understand, you need to consider the technical characteristics of both materials:
- The thermal conductivity of foam is 0.04 W / mK, for foam -0.032 W / mK.
- The mechanical strength of the foam is inferior to the extrusion material.
- The density of the foam is 20-30 kg / cm3, of the foam is 30-45kg / cm3.
- Vapor permeability 0.022 and 0.005 mg / mchPa, respectively, for foam and foam.
- Due to the higher density, which is achieved by better molecular bonding, the mechanical compressive and flexural strength of the extruded polystyrene insulation is higher, as well as the ability to withstand a wider range of temperature differences.
- Polyfoam can absorb no more than 3% of water from its mass, penoplex - no more than 0.4%. If you choose a material for warming a bath, it is better to dwell on the second option.
- The shrinkage of the foam is much greater than that of polystyrene. The first is afraid of sunlight and heavy mechanical stress. The second is more resistant to both UV radiation and stress. Therefore, polystyrene foam products can be used to insulate facades with subsequent plastering, when installing a warm floor, which cannot be said about ordinary foam.
In terms of flammability, both materials are equally susceptible to fire, but when flame retardants are added to the styrene formulation at the manufacturing stage, neither the foam nor the extruded polystyrene sustain open combustion. Both have the property of self-extinguishing if they are not in the center of the fire.
If there is a choice of insulation, and you do not know which is better - to buy extruded polystyrene foam or to stay like a cheaper foam, take into account all the characteristics of the materials.
Insulation description and terminology
The possibilities of using polymers in construction have long been of great interest, since there was a chance to reduce the costs of erecting buildings without losing their operational properties. This approach would support large volumes of construction, as polymer elements can be produced in significant quantities.
Styrofoam was invented in the middle of the twentieth century. Almost immediately, the industrial production of an innovative material was launched as heat-insulating panels for construction needs. The growth in popularity of this insulation was facilitated by following benefits:
- Low density and easy installation. The weight of the sheets is so small that it is easy and cheap to transport them. Working with the material is quite simple. The sheet can be easily held at the desired height. The high machinability also makes construction work easier. The most common cutting is with a razor tool and heated metal wire.
- Low liquid absorption. Contrary to popular belief, fiber-free foam practically does not absorb moisture. Even when the material is completely immersed in water, the volume of absorbed liquid does not exceed 0.4%. Tests for the impact of groundwater showed an even better result - no more than 0.1%.
- Environmental friendliness. According to the European Chemicals Agency, the foam has no carcinogenic, mutagenic or other toxic effects. And in accordance with the British scale of environmental impact, it has the highest safety class.
- High durability. The studies carried out show that the service life of the material can exceed 80 years when used under conditions of significant temperature and humidity changes.
- Biological stability. The material does not support the development of fungi and microorganisms. It is of no interest or nutritional value to rodents.
- Good sound insulation properties. Styrofoam used in interfloor ceilings and walls provides effective attenuation of sound waves generated by construction work, impacts, furniture movement and vibrations of household appliances.
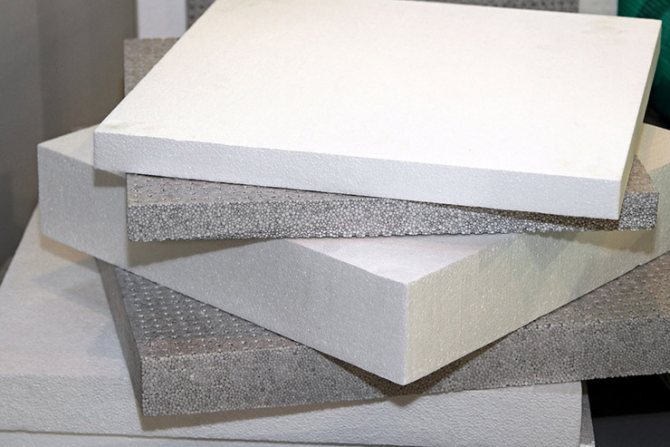


There are several types of polymers that belong to foam.
Foams include several different foamed plastics. The most popular are the following polymers:
- polystyrene;
- polyvinyl chloride;
- polyurethane;
- phenol-formaldehyde resins;
- urea-formaldehyde resins.
For use in certain conditions and for solving specific problems, the material is made from the corresponding plastic.
In addition, differences in the processing technology of raw materials make it possible to obtain a product with the desired properties:
- density;
- strength;
- resistance to various influences.
In this video, you will learn the pros and cons of Styrofoam: