Production
These two materials are completely synthetic, but they are made using different technologies. For the production of foam, a polystyrene or formaldehyde base is used. Substances are added to it that form a foam.
These substances use air to create foam. As a result, a huge number of bubbles are formed, filled with a synthetic base. The whole process takes place under normal conditions without elevated temperatures or pressures.
After the end of the reaction, small polystyrene or formaldehyde balls remain. To make polystyrene, elements with a diameter of 3-5 mm are selected and subjected to the influence of the press. As a result, slabs of different thickness from 1–2 cm to 10 and more are obtained.
As for the penoplex, it is made from ready-made polystyrene balls. The finished mass is loaded into a pressure oven called an extruder. Everything melts there, decreases in size and floats onto the prepared base. The result is a slab that is slightly thinner than the foam would make.
Styrofoam characteristics
This material is 98% air and only 2% is polystyrene itself. As everyone knows, air is the worst conductor of heat, so it has excellent thermal insulation characteristics.

It is used to insulate almost all parts of the house, with the exception of the floor. What are the advantages of using this material:
- Absolutely non-absorbent.
- Microorganisms do not live on the synthetic surface.
- Poorly supports the combustion process.
- Very lightweight.
- Cheap.
- You can insulate houses from different materials.
- Long service life.
- It absorbs sound well (noise isolator).
- Ease of installation.
Despite such a number of positive aspects, there are also several significant disadvantages. Pressed polystyrene foam practically does not allow moisture to pass through. This disadvantage should not be neglected if the house is made of wood or other breathable material. Moisture will accumulate between the insulation and the wall, causing rotting.
If this material is chosen for insulating the facade of such a house, then in addition, forced ventilation should be used or a ventilated facade should be installed.
In addition, although the material does not support combustion, it releases toxic substances into the environment under the influence of high temperature. In order for the foam insulation to last as long as possible, it must be protected from sunlight.
Otherwise, the plate will fall apart into a huge number of small balls. Without a good protective coating, it is easy to break or puncture. Styrofoam is most often laid under plaster or siding. It is contraindicated to paint this material. He is very afraid of solvents.
Foam melting point
Main Heaters Extruded, extruded polystyrene foam
Extruded polystyrene foam resistant to the action of most solutions of salts, acids and alkalis, oils, alcohols and alcohol dyes used in construction work. When interacting with cements and gases, the extruded polystyrene foam is not destroyed or damaged.
Along with this, it must be protected from the action of organic solvents: gasoline, kerosene, diesel fuel, aldehydes, ketones and ethers.
It is not recommended to store extruded polystyrene foam for a long time in the sun, because under the influence of sunlight, the surface layer of expanded polystyrene becomes brittle and crumbles.
Extruded polystyrene foam is created from granular polystyrene.The polystyrene granulate is loaded into an extruder, where it is first melted, and later the melt is pressed under pressure through a die. Since at the same time with the granulate, a porophore is also loaded into the extruder (a pore former, for example, a mixture of carbon dioxide CO2 and light freons), closed pores with a size of 0.1-0.2 mm are formed in polystyrene. Closed pores make the extruded polystyrene foam impermeable to dripping liquid, steam, dust and other substances.
Some sellers of heaters specializing in the sale of extruded polystyrene foam argue that expanded polystyrene by and large and extruded polystyrene foam in particular is almost a panacea for all troubles in the field of thermal insulation. It goes without saying that this is not the case. But it should be borne in mind that in some cases, such a conclusion may be honest. Of course, any type of thermal insulation materials has its pros and cons and, accordingly, has specific areas of application, in which its advantages are manifested to the fullest.
For example, the low vapor permeability of extruded polystyrene foam can be viewed as an advantage over such insulation as mineral wool. they say that thermal insulation is not blown by the wind, does not allow moisture to pass through and does not require additional waterproofing.
But, if you look at the situation differently, the same property is a disadvantage. Insulation of the wall with extruded polystyrene foam will transform the room into a warm bath with high humidity. Such a wall does not breathe.
How to be, what to choose?
You decide. It is fundamentally important only to know the properties of the selected heat-insulating materials and to understand how these properties will affect the indoor microclimate. And it is imperative to take into account in which room the insulation will work. It may happen that a given specific property of the thermal insulation material is irrelevant for that particular room. The above is true not only for extruded polystyrene foam and not only for expanded polystyrene in general, but also for any other heat-insulating materials.
Extruded polystyrene foam prices are very reasonable. And despite the fact that the price of expanded polystyrene is its undoubted advantage, one should not focus on low cost. There is no need to consider the price of extruded polystyrene foam in isolation from its other properties. You can be sure that expanded polystyrene has many other advantages ...
So certain types of extruded polystyrene foam are able to withstand a load of up to 35 thousand kilograms per square meter. And in this sense, extruded polystyrene foam is beyond any doubt superior to the hardest mineral wool boards.
Manufacturers of thermal insulation materials claim that extruded polystyrene foam is hardly flammable and has a tendency to self-extinguish. There is no reason not to believe them. In addition to polystyrene granules, the formulation of modern extruded polystyrene foam without fail includes additives that beat off extruded polystyrene foam from burning.
But one should not delude oneself due to the fact that expanded polystyrene is a polymer and, like most of the compounds of this glorious kind, it easily melts.
It should not be interpreted that at the end of melting, its pores stick together and the property of extruded polystyrene foam to thermally insulate something disappears completely. Proceeding from this, by the way, extruded polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam, by and large, under no circumstances are used for thermal insulation in the broad sense of the word. Some explanations are needed here.
The term thermal insulation, in contrast to the term insulation, is broader. Insulate is indicative of not allowing freezing.Imagine an object that is to be in an environment of negative temperatures, to which it is not adapted. It needs to be insulated. And in this case, expanded polystyrene fully cope with the functions assigned to it.
But quite often the opposite situation appears - some object heats up very much and it is necessary not to allow it to cool down or to heat up what is about. And here the situation for extruded polystyrene foam is not so encouraging.
According to various data and for various polystyrenes, its melting point is in the range of 250-300 ° C. Along with this, expanded polystyrene melts more rapidly than a monolithic piece of polystyrene, which is harder to heat up. But already at 250 ° C, in addition, the most refractory polystyrenes begin to smell and not at all of violets.
Experts will explain to us, they say, the polymer begins to decompose. And what is formed during the decomposition of polystyrene can be assumed. For example, styrene vapors can be released - a kind of byaka with a benzene ring in the right side. It must be admitted that this compound is quite unnecessary for health. And only that would be good - styrene itself can decompose at high temperatures. And no matter what stands out in the investigation, it will definitely not be necessary.
In other words, if it is necessary to insulate a warm object with a temperature of 200 or more degrees, extruded polystyrene foam is obviously not suitable for this work.
Is it not good or not?
It is not entirely correct to pose the question like this. You just need to understand that any heat-insulating material has its own areas of application and not to use it where it cannot fully work.
Extruded polystyrene foam is used as thermal insulation ...
Similar news
Penoplex characteristics
Since this material is made on the basis of polystyrene balls, like polystyrene, some of their characteristics are similar:
- Resistant to moisture.
- Light weight.
- Good noise isolator.
- Long service life, with a protective coating.
- Easy to assemble.
- Does not allow steam to pass through.
But there are also differences. Penoplex is more dense, so it is needed less than foam for external insulation. For example, a 3–4 cm thick foam board has the same effect as a 10 cm thick foam board.


Penoplex supports combustion. To eliminate this defect, a fire retardant coating is used, but then poisonous substances are released when heated. For the price, this material is much more expensive than expanded polystyrene, but it is more resistant to external mechanical damage.
Output
Both polystyrene and penoplex have excellent heat and sound insulation performance. Their main difference is the price and resistance to mechanical damage. If the owner of the house plans to cover a layer of insulation with plaster or siding, then more, a budget option (polystyrene) will help to save a little the family budget.
If there is enough money, then it is better to choose Penoplex. The thickness of the insulation will be less, and it is also protected by a special coating against insects and rodents.
Below in the video you can see how to insulate a frame house with foam polystyrene.
The most famous insulation yesterday was polystyrene, but today there is also a newer generation material on the market, penoplex, which has slightly different properties, although both of them are made from the same raw material.
Manufacturers recommend both the one and the other material for high-quality and reliable thermal insulation. To understand what to prefer for insulation in a particular case, we propose to make a comparison.
Material properties


Penoplex advantages.
Both materials can be easily ignited. However, the lighter foam belongs to the category of normally combustible (G3), and dense foam is to highly combustible building materials (G4).Manufacturers eliminate the inherent disadvantage of plastics by treating polystyrene foam with fire retardants, which makes them more resistant to fire. But the result of the treatment with fire retardants was the deterioration of the environmental performance of the materials: they turned into self-extinguishing, while they began to emit toxic substances into the atmosphere.
Polyfoam and polystyrene foam are considered almost eternal materials. Their manufacturers focus on this, but the statement about an unlimited resource can only be partially true, since polystyrene foam is sensitive to such a factor as environmental impact. They themselves need protection from ultraviolet radiation, temperature changes, the chemical composition of the air, etc. Therefore, it should be noted that penoplex or polystyrene can show their effectiveness only after they are covered with other materials. By the way, a layer of plaster applied to them provides sufficient insulation from external influences of expanded polystyrene.


The advantages of polystyrene.
An important factor that makes it possible to use the material when insulating surfaces in an environment with high humidity is the high moisture resistance of foam. Mineral wool, which surpasses this expanded polystyrene in terms of noise and heat insulation, is completely unsuitable for laying on a basement or foundation. Due to its properties, penoplex is practically airtight. In contrast, foam cannot serve as a reliable barrier to free air circulation.
Having considered the characteristics possessed by polystyrene and polystyrene foam, it can be concluded that the differences between both materials are in the degree of their strength, moisture resistance and air permeability. The main differences between one material and another can be listed in a short list. Penoplex:
- more dense, which worsens the thermal insulation properties;
- moisture resistant;
- more flammable without special processing;
- less environmentally friendly (as a result of processing with fire retardants).
At the same time, Styrofoam:
- less dense;
- retains heat better due to its looseness;
- because of it, it protects against moisture worse;
- does not isolate from noise;
- effective only when covered with denser materials.
For the rest of the indicators, both are approximately equal. Expanded polystyrene is easy to transport, handle and install. Builders must consider all of these circumstances before finding the most suitable application for a material.
Penoplex and polystyrene: what's the difference?
Production
Both materials make polystyrene, but the production process is completely different:
When processing polystyrene granules with steam, their the volume increases almost fifty times, they stick together. The result is an airy material with micropores and voids between the granules.
If they are pressed well, then the density of such foam is high, and accordingly, the quality characteristics increase. Another name for the material - expanded polystyrene.
Manufactured by extrusion. Under conditions of high temperature and high pressure, a material appears that has a very uniform dense structure with good consistency. The material is called differently extruded polystyrene foam.
Penoplex is much denser than polystyrene, therefore, it weighs more, so it can withstand heavy loads.
Thermal conductivity
Since the foam granules foamed during the production process do not adhere too tightly to each other, its properties, as a heat insulator, much lowerthan penoplex.
The latter has a much smaller pore, since the material is much more strongly compressed.
For an equal degree of protection from the cold, foam will have to be purchased 25 percent more than foam.
Moisture permeability and vapor permeability
Penoplex is more moisture resistant. Its water absorption rate is approximately 0.35 percent, versus two percent for foam. Although the foam granules do not absorb water into themselves, it is quite capable of penetrating into the gaps between them. As a result, the foam may be slightly saturated with a small amount of moisture. Polyfoam is more vapor-permeable than Penoplex insulation, in which this indicator is practically zero. In principle, both materials have extremely low vapor permeability.
Strength
Polyfoam is more fragile, because it consists of small particles that are interconnected, it crumbles easily due to a little effort.
Penoplex almost six times stronger, it is extremely difficult to break it. In addition, polystyrene is afraid of kinks, it breaks, its analogue bends much better. If we compare the indicators of materials in terms of the degree of compressive strength, then they are incomparably higher for foam.
Styrofoam properties
Expanded polystyrene (foam) is a gas-containing material obtained from polystyrene and its derivatives, consisting of sintered granules with pores and voids between the granules. The strength of a material directly depends on its apparent density: the denser, the stronger.
Polyfoam is used in construction as a heater, heat insulator, low-combustible (subject to processing with fire retardants) material for the design of facades.
What are the main properties of expanded polystyrene?
The main properties of expanded polystyrene include:
- low vapor permeability;
- water absorption (depending on the density of the material), preventing the accumulation of moisture near the walls, moving the dew point inside the material (all together allows you to effectively use foam in structures with external wet insulation);
- resistance to mold, fungus, microorganisms and moss (colony formation was not recorded);
- non-nutritious for rodents (however, they can use foam as a material for bedding or for grinding teeth);
- durability (no loss of quality for at least 60 years, in favorable conditions from 80 years);
- the coefficient of thermal expansion is from 5-10 to 7-10 (i.e. from 0.05 to 0.07 mm per 1m and 1 C), which should be taken into account when designing buildings in places with strong temperature jumps.
At what temperature does the foam melt?
The operating temperature of expanded polystyrene is from -180 to +80 C, for a short time up to 95 C (withstands contact with hot bitumen). The melting point of expanded polystyrene will be 120 C (at this moment, irreversible depolymerization occurs). The processed foam can have different exact heat resistance data related to the type of impregnation used in production.
The processing option used by us has a flammability class G1 and does not collapse when exposed to temperature by more than 65%.
What kind of load can polystyrene foam withstand?
Expanded polystyrene withstands the load in accordance with its density class (and directly related strength) and an infinite number of load cycles, if they do not exceed 80% of the maximum possible compressive strength for a given block. In the studies, materials with a density of no higher than 20-25 kg / m3 were used; this version of a lightweight structure is most convenient to use and gives a low load on the supporting elements.
There are only four orders of columns in architecture Gustave Flaubert
Insulation of various structures
In principle, both heaters have a wide range of applications, but when insulating external walls, it is sometimes advisable to purchase inexpensive and breathable foam, and when arranging a loggia, penoplex.
The latter material is distinguished by its strength, which allows it to be used for thermal insulation of floors, when insulating pipes (due to good plasticity), and even when insulating the basement or foundation of a house. But, as mentioned above, penoplex is much more expensive, and in some cases the additional costs are simply not practical.
Exterior walls of the house
Polyfoam, which is applied to external surfaces, must not only be protected from ultraviolet radiation, but also take into account that this material does not allow steam to pass through.Otherwise, the isolated part of the wall will become a breeding ground for various bacteria.
Therefore, it is not worth treating houses made of wood with foam.
It should also be borne in mind that this material flammable, it can spread combustion and independently increase the fire, while releasing toxins hazardous to human health. That is, if simple polystyrene is used outside during the construction of a building, it should at least be insulated with special care.
When used for insulation of external walls of foam, you can use it not only as insulation, but also as a building material for some auxiliary structural elements.
In addition, penoplex is not so much afraid of moisture, it is more biologically stable than its competitor, and rodents do not like to live in it. True, it also does not differ in high fire safety, although, unlike foam, it simply burns without supporting and without spreading the fire any further.
For detailed instructions on insulating external walls with foam, read here.
In general, polystyrene is actively replacing polystyrene with external insulation of walls more and more often. In Europe, foam plastic is not used at all for the exterior decoration of buildings; in other countries, including ours, it is also increasingly being replaced by foam plastic.
Internal walls of the house
Concerning the issues of active energy saving, experts in this field are increasingly recommending that to reduce heat loss to carry out thorough thermal insulation of the walls, using modern heaters. These are both polystyrene and penoplex, and both are equally suitable for this purpose, having excellent thermal insulation properties.

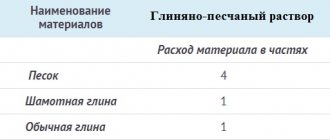
Polyfoam is inexpensive and very easy to install, you can carry out work on the insulation of your house on your own, without involving specialists. It is used to insulate warehouses where non-combustible materials are stored, technical buildings, and other buildings.
Penoplex is more resistant to mechanical damage, its plates do not crumble, but insulation will cost them, as already mentioned, more expensive.
Sometimes it is required to create additional sound insulation indoors, for this they take three-centimeter penoplex, the foam will have to be applied much thicker. By the way, this will reduce the overall space of the room, which is important, especially in a small apartment, which is not very large anyway.
With what material to decorate the walls in the apartment, read our article.
Any of the two materials can be used to insulate the balcony. The loggia should be insulated with a simple five-centimeter foam; you do not need to buy expensive materials for these works.
If the winters are very cold, you can take a thicker foam, up to ten centimeters. But if the balcony is small, you can purchase penoplex for this purpose.
The floor is insulated only with penoplex, since the foam is too fragile, it has a low density, so you cannot put a screed on it. Penoplex, on the other hand, will withstand high loads, and the floor will be not only warm, but also durable.
This material is used to create a system called "warm floor", where thermal insulation plays a key role, since it reduces heat transfer in two directions at once (top and bottom). Penoplex floor insulation is effective even at high humidity, constant mechanical stress.
Attics and roofs
When insulating the roof inside both materials are suitable, but if you need to make the floor in the attic warmer, you should still choose Penoplex. By the way, in the attic space, you can not put other materials on top and walk directly on the penoplex.
To insulate the roof, they also use foam boards, which are carefully on top covered with a waterproofing layer... If the roof is cold, the inside of it is insulated with foam, and the outside with foam, while leaving enough space for ventilation.
Thus, both of the materials described above can be used for thermal insulation, depending on what needs to be insulated. Penoplex is suitable for outdoor decoration, for floors and roofs, but it is much more expensive, and sometimes foam is enough.
You can watch the process of external wall insulation in the video:
Non-flammable foam will keep you warm
FEEL THE DIFFERENCE
Polyfoam of the TIZOREN brand is intended for thermal insulation of foundations, walls, roofs, interfloor floors of buildings and residential buildings. It is irreplaceable in the production of building envelopes for thermal insulation of industrial, office buildings and structures. And also all types of pipelines, fittings, valves, industrial equipment, sandwich panels.
What kind of material is this, and why is it fundamentally different from the well-known polystyrene foam, previously used only for packaging, including for household appliances?
It is important that TIZOREN can withstand heating up to 300 degrees (ordinary foam - 110-130 degrees), and when exposed to open fire, it does not burn, but turns into carbon, charred.
We carried out the experiment using an ordinary lighter. As long as the flame touches the TIZOREN bar, its surface only darkens and turns into a carbon state. A completely different picture - when tested by fire with ordinary polystyrene foam - it ignites itself, and continues to burn, even if the original source of the flame is extinguished. The difference in fire resistance is clearly visible in the photographs.
Polyfoam of the TIZOREN brand has been tested at the All-Russian Research Institute of Fire Protection (MES). It was assigned the G1 index. This means that it can legally be used as internal insulation, external wall and roof insulation. At the same time, TIZOREN foam does not contain and does not emit toxic products.
LET'S COMPARE EVERYTHING INDEPENDENTLY
There are three main types of insulation on the market today: mineral wool, polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam. The latter are known to non-specialists under the name "foam". We have already found out the cardinal difference in fire resistance between conventional foams and foams of the TIZOREN brand, by experiment with a lighter. We will only add that the absolute majority of those killed in the old-type Perm club "Lame Horse", insulated with foam plastic, did not even die of fire, but suffocated by the poisonous products of its combustion.
But that's not all. Today, even the so-called "elite" housing in the center of Vladimir is being built, insulated with materials, in the old fashioned way called polystyrene. High temperature shrinks this obsolete material, and in the event of a local fire, which can be liquidated without much visible consequences, a void forms inside the wall, which is simply technically impossible to fill. With the arrival of cold weather, this area begins to freeze, then a fungus appears there, and this spot will begin to creep in all directions.
Polyfoam of a new type, brand TIZOREN, does not change its shape and volume due to high temperatures, and even in case of damage to the insulation it does not get wet, but continues to perform its functions, maintaining its thermal insulation properties.
The walls of most buildings are still insulated with mineral wool slabs. They say that they learned how to make it resistant to moisture. However, under an electron microscope it is perfectly visible that mineral wool is, figuratively speaking, a "haystack" - a mass of fibers intertwined with each other. In principle, it is impossible to achieve that it stops taking moisture from the environment. Gaining moisture, mineral wool immediately loses its insulating properties. In frost - freezes, then thaws. On the vertical surface of the wall, sloping roof - it sags and sags.As a result, it turns out that there is mineral wool at the bottom, and an empty "pocket" is formed at the top. Under the finishing materials (the same siding), this trouble is not visible, it makes itself felt when more and more money starts to go to heating.
Another advantage of TIZOREN is that it is possible to mount heat-insulating panels from it in any weather; this does not affect the properties of the thermal insulation of the wall. But the mineral wool gets wet and begins to deteriorate in the rain and snow even before the construction of the house is completed.
And what is the difference between TIZOREN and polyurethane foam?
Along with the positive properties (environmental friendliness, long service life), polyurethane foam has serious disadvantages, among which is the high cost, which makes this type of thermal insulation inaccessible to an ordinary person who is building his own house. It is too expensive to insulate walls and roofs.
At a temperature of 140 degrees, polyurethane foam, as they say, "floats", and when exposed to open fire, it burns. The next problem is that one of the components used to obtain polyurethane foam is produced only in Germany. This means that there is a dependence on fluctuations in exchange rates, customs regulations and even the international situation. Heat-resistant foam is made entirely from Russian raw materials, which automatically means lower cost and reliability of supply.
TYROSENE "LIVES" LONGER THAN METAL
With the same density, TIZOREN foam has twice the strength than FRP-1 phenol-resole foam. From lightweight and durable TIZOREN, equipped with a protective foil layer, you can make box-shaped air ducts, thermal insulation for pipes, sandwich panels for housing construction, and insulate existing buildings with plates from it. The operating cost of such thermal insulation is 2.5 times less than that of traditional materials.
Polyfoam of the TIZOREN brand does not promote corrosion when applied to metal, therefore, for thermal insulation it is possible to use steel pipes with little or no preliminary cleaning from rust. In the workshop, centralizers, polyethylene or any other outer shell are put on a metal pipe, and a mixture is poured into the annular space, which foams and polymerizes. Thermal insulation for pipes does not require replacement, since its service life is longer than the service life of the pipe itself.
Another method involves the production of shells of various diameters in pre-made forms, as well as shells for shaped products, etc. After that, the shell is delivered to the construction site, where it is attached to the pipe and insulated from the outside.
Butt joints in both methods can be cast with existing foam in the field in pre-prepared molding casings. In the production of thermal insulation with the use of TIZOREN filling foam, the resulting foam waste is not sent to a landfill, but is used as a filler-heater for building structures and pipes.
AVAILABILITY, EFFICIENCY, SAFETY
Entrepreneurs from the Krasnodar Territory, who are building Olympic facilities in Sochi-2014, as well as from Perm and Moscow, have already shown interest in TIZOREN's material. Having applied the material from Kosterevo at two sites, the customers were very satisfied, they are going to order a new batch and, possibly, organize production on site.
To date, TIZOREN polystyrene is included in the "Register of new equipment used in the construction (reconstruction) of objects of the city order in Moscow and the Moscow region". This is a very important stage for the release of new material to the consumer. This document officially confirms the ability for designers to include TIZOREN in the design documentation of facilities under construction and reconstruction. A sanitary and epidemiological conclusion was also received for this material.
There is a long way to go from the development of a new material to its industrial production: laboratory research, the organization of pilot production, then - scaling the process, calculating the possibility of mass production. Now at the production site of LLC NPO Transpolymer in the city of Kosterevo, an experimental industrial batch of TIZOREN foam has been received, in February this material will be launched into mass production. everyone will be able to buy for a house and a summer residence.
WHAT ELSE IS TYROSENE capable of:
- provides the ability to carry out technological processes with the specified parameters,
- will create a safe and comfortable environment for service personnel in production,
- ensures the transport of heat from the source to the consumer,
- prevents freezing of cold water in pipelines during the winter season,
- allows you to store liquefied and natural gases in isothermal storage,
- provides a reduction in energy consumption for heating buildings and structures.
USEFUL ADDRESS
OOONPO "Transpolymer"
Vladimir region, Kosterevo, st. Pistsova, 50, bldg. 8/9, 3. Tel .: (49243) 4-39-13, fax: (49243) 4-26-59. post office
Let's analyze two materials


Penoplex and polystyrene have common properties, since they are produced from the same primary raw materials. At the same time, extruded polystyrene foam is produced using a new technology, which gives it distinctive qualities. To determine what is best for insulating houses and apartments, it is worthwhile to study in detail what is the difference between the two thermal insulation materials.
Appearance and description
At first glance, extruded polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam are similar. Taking a closer look, it will be possible to understand how Penoplex differs. Polyfoam is polystyrene foam balls, pressed into plates. Inside, the cavities are filled with air, which makes the material lightweight and allows you to retain heat. The EPSP production method involves the melting of polystyrene balls, so a denser, compressed material is obtained at the output, which in appearance looks like frozen polyurethane foam.
Penoplex and expanded polystyrene differ in color: the first has an orange tint, the second is white.
Types of materials
Polyfoam is of different types: polyethylene, polyurethane, polyvinyl chloride and polystyrene. For thermal insulation, it is the last type that is used - from polystyrene balls. Penoplex is made of different types. It is possible to purchase finished products for insulation of roofs, walls, foundations, etc. Manufacturers offer special lines for certain types of insulation. Polyfoam and penoplex have different thicknesses, which affects performance. To choose the right insulation, you should familiarize yourself with all the parameters.
Differences in production technology
Based on this data alone, it would be almost impossible to choose a material that would be better than another for specific tasks. Therefore, a comparison of 2 types of expanded polystyrene will help developers make the right choice when buying.
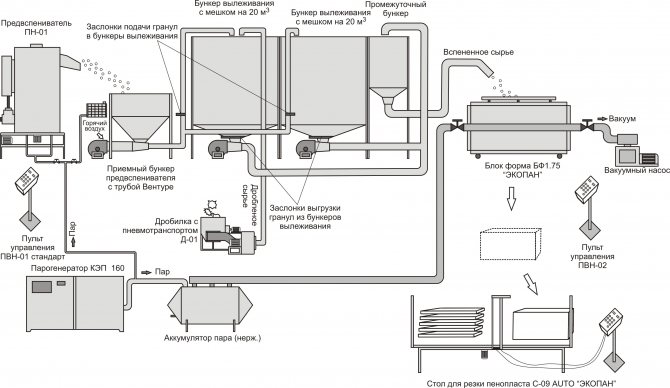

Foam production scheme.
Both polystyrene and polystyrene foam are mainly used as insulation materials, for this they have similar properties, but each of the materials has features predetermined by different production technologies. These nuances should be taken into account when using expanded polystyrene in construction.
Polyfoam is obtained by foaming polystyrene without forced pressurization. During the production process using pentane and steam, polystyrene granules are increased by at least 50 times. The polymer content in it does not exceed 2%, and the rest of the volume falls on air.This determines the high thermal insulation characteristics of the material, but such expanded polystyrene, due to its fragility, is not able to withstand even small mechanical loads.
Penoplex is obtained under pressure and at high temperature (extrusion), has a high density, which worsens its vapor permeability, in comparison with foam. Nevertheless, it is a more durable material - good insulation for structures subjected to various mechanical loads: walls, foundations and even runways.
Useful and harmful properties
Those who use penoplex or expanded polystyrene for thermal insulation are interested in the question of possible harm to human health. Subject to the production technology, materials become safe. The installation does not require the use of personal protective equipment. If the service life of expanded polystyrene is exceeded, decomposition of the foam may begin with the release of harmful substances, for example, styrene, ammonia, benzene, which can adversely affect others. The real threat is the use of substandard material. In Moscow and other large cities, there is a large number of heaters offers. In order not to be mistaken, you should carefully study the accompanying documentation, consumer reviews, price compliance.


It is important to note that Styrofoam and Styrofoam are susceptible to fire. As a result of smoldering, heaters emit harmful substances that are dangerous to humans. Manufacturers are working to reduce the flammability level through additional processing and the addition of antiprenes to the composition of materials.
The useful properties of heaters are obvious - a warm house with a comfortable atmosphere inside. Penoplex and polystyrene perfectly retain heat, provide sound insulation. At the same time, working with them is convenient and simple. The processing of materials is simple, even an inexperienced person can cope with the insulation.
Self-tested: foam flammability
The market for thermal insulation materials is small, and therefore the competition within it is enormous. It would seem that only two heaters could peacefully coexist, but no. "HIM" is accused of almost all mortal sins, but the main reason is that "HE" is on fire and, in case of trouble, "HE" will certainly burn out everything and everyone, because "HIM" is used in the manufacture of napalm! You guessed it - it's about styrofoam. We checked in practice how things are around its flammability.
Subjects
For our first experiments with foams, we chose a representative from each of the most common types in Belarus. Among the "experimental" were:
- expanded polystyrene made by non-pressing molding (sample no. 1), molded (sample no. 2), as well as two types of insulation with low thermal conductivity - with surface treatment of granules (sample no. 3) and made from Neopor raw materials (sample no. 4);
- extruded polystyrene foam from the only Belarusian manufacturer (sample No. 5), as well as copies of two Russian ones - not "untwisted" (sample No. 6) and an eminent manufacturer (sample No. 7);
- urea-formaldehyde foam, aka penoizol (sample No. 8);
- polyurethane foam (sample No. 9).
In spite of all, their main competitor is mineral wool (sample no. 10).


Test program
Polyfoam is accused of high flammability and inability to withstand open fire. Skeptics say that if a spark hits the surface of the material, the insulation will certainly burn out. We will simulate a mini-fire - spill gasoline over the surface, set it on fire and see what happens to the material. If the arguments of the competitors are correct, then the insulation will simply burn out. If the manufacturers are right, then the foam will have to go out. It's simple - either pan or disappear.
So, we have ten samples, approximately the same density and size, a canister of gasoline, a measuring vessel with which we will dose all participants an equal amount of flammable liquid (5 ml each), a fire source (aka matches) and a laser thermometer, with which we will measure the temperature on the surface. The burning time will be assessed using a chronometer, and the degree of damage - visually and using a ruler. Before testing, we kept each sample under the same conditions for an equal amount of time.
Foam insulation
Combustion of all representatives of the class of expanded polystyrene is characterized by common signs - this is a rapid loss in volume, a fairly high smoke and melting. All samples have the property of self-extinguishing and did not support self-combustion. So, sooner or later, the "test subjects" died out, and, therefore, in the absence of an external source of fire, the material can be conditionally considered safe.
Sample of material made by the method press-free molding, burned through, forming a hole, albeit small in area. On the surface, the sample was deformed only in the part where the flammable liquid was burning, not spreading the combustion over the entire surface. The areas exposed to fire were melted, but their own combustion in the molten state did not occur. The burning time was 44 seconds. The recorded maximum surface temperature is 306 ° C.
Molded polystyrene foam characterized by more intense combustion, higher flame height, but lower volume loss and fusion. The sample did not burn through and through, being marked by a slightly more operational attenuation. Burning duration - 35 seconds. The recorded maximum surface temperature is 256 ° C.
Expanded polystyrene with surface treatment of granules distinguished itself by high smoke and a large number of melts on the surface. The damage area turned out to be larger than the area over which the flammable liquid was spreading - areas where there was no gasoline were also exposed to fire. The sample was burnt through, while about 1/5 of its lower surface was melted. Total volume losses are the highest among competitors. Burning duration - 52 seconds. The recorded maximum surface temperature is 297 ° C.
Expanded polystyrene from Neopor raw materials uniform attenuation over the surface, slightly larger surface of gasoline spreading, is characteristic. When burning, the material melts, and the melt itself does not burn. Burning duration - 37 seconds. The maximum surface temperature is 262 ° C. The best result among expanded polystyrene.
Extrusion
In a group extruded polystyrene foam in our experiment "competition" was due only to the manufacturer. Two representatives on the test with Russian roots (and one of them is a very well-known brand), but the main sample - so far the only Belarusian one - was noted for a larger surface area over which the liquid spread, which is due to the low water absorption of the material. When burning, the material emitted a hiss and was quickly extinguished. Perhaps this is the characteristic work of fire retardants, which must be used in the production of building foam. The total duration of burning was 50 seconds, however, already 26 seconds after we set fire to gasoline on the surface of the material, the combustion practically stopped - only a small part of it burned out at the edge of the product. There is a minimum of damage and all of them are only on the surface on which there was a flammable liquid. The recorded maximum temperature is 240 ° C.
Sample of extruded polystyrene foam unnamed Russian manufacturer also confirmed low water absorption - the liquid spread over almost the entire surface. This representative of polystyrene "distinguished" by greater smoke and rapid decay - combustion stopped after 23 seconds. Sample damage was minimal. Volume losses - no more than 1/5 of the original. The recorded maximum temperature is 329 ° C.
Branded extruded polystyrene foam a well-known Russian manufacturer surprised us extremely unpleasantly. As soon as gasoline appeared on the surface, the insulation entered into a violent chemical reaction with it, which was accompanied by hiss and the formation of bubbles.Obviously, this specimen's resistance to the chemical attack of solvents is just a myth. None of the tested samples showed such a violent reaction.
The burning of the "eminent" sample continued to amaze us unpleasantly. There is no question of any self-extinguishing property. The sample ignited with a "blue flame" and even after the catalyst (flammable liquid) had burned out, combustion continued with equal success. They burned like molten parts of the insulation, which formed flaming black puddles on our "test bench", and parts of the insulation that were not melted under the influence of burning gasoline. The burning lasted 4 minutes 40 seconds and was stopped artificially. The almost completely melted foam continued to burn, significantly affecting the base on which it was laid. Fact - if the base turned out to be made of a combustible material, the foam would certainly set it on fire. The recorded maximum temperature is 334 ° C. The burning was accompanied by increased smoke, and small black "flakes" rose into the air. The ingestion of such in the respiratory tract would hardly be harmless. The loss in volume is maximum. The sample would have burned completely if we had not interfered with the combustion process.
The famous extruded foam is the worst result.
Exotics and competitors
Urea-formaldehyde foam and polyurethane foam, in the opinion of experts, are undervalued materials in our market. And if penoizol (urea foam, which we are used to calling by the name of a Russian manufacturer) finds only limited use in construction, then polyurethane foam, according to builders, could become much more widespread. Be that as it may, both of these materials are exotic for our market.
Combustion of penoizol flowed only in the area where the liquid got into. The material was characterized by minimal volume loss. Despite the long (55 seconds) burning time, the process itself was "reluctant". The combustion was not accompanied by increased smokiness, but there was a specific and unpleasant smell. The maximum surface temperature is 356 ° C.
Polyurethane foam proved to be the leader in combustion temperature among all tested samples. Throughout the experiment, the flame temperature did not fall below 300 ° C. The maximum even exceeded four hundred. A large amount of smoke and soot is emitted during combustion. The insulation was marked by a small shrinkage in volume, but a larger surface area on which deformation occurred. By the way, the damage turned out to be only superficial - the material darkened, but did not significantly lose in volume. No melts typical of foamed polystyrene were observed. But the smoke turned out to be extremely caustic. Indoors, this is guaranteed suffocation in a matter of seconds. We dare to assume that the content of toxic substances in such a carbon monoxide "cocktail" will go off scale. Burning duration - 39 seconds.
The competing mineral wool immediately marked by high absorption of liquid, and in our case, highly flammable. Gasoline did not spread over the surface, but was completely absorbed into the material. Burning lasted 2 minutes and 1 second, while it was happening not so much on the surface as "deep". Extinction is uniform. No visible damage. The surface was blackened, sparking of red-hot mineral fibers was noticeable during combustion. At the same time, the stone wool was "marked" with high smoke, which was clearly not caused by gasoline. We assumed that the binder burned out, which is often used as phenol-formaldehyde resins. The maximum surface temperature is 388 ° C, while the main temperature range is from 250 and above.
| Sample / Material | Burning duration, s | Combustion temperature, °FROM | Smokiness | Self-burning | Nature of damage, notes |
| 1. Expanded polystyrene without pressing | 44 | 306 | moderate | not | Over the spreading area of the igniter, through and through |
| 2. Expanded polystyrene molded | 35 | 256 | moderate | not | Over the spreading area of the igniter |
| 3. Non-pressing expanded polystyrene foam with low thermal conductivity (surface treatment of granules) | 52 | 297 | increased | not | On an area larger than the spreading area of the igniter |
| 4. Expressed polystyrene foam with low thermal conductivity (from Neopor raw materials) | 37 | 262 | moderate | not | Over the spreading area of the igniter |
| 5. Expanded polystyrene extruded (made in Belarus) | 50 | 240 | moderate | not | Over the spreading area of the igniter |
| 6. Extruded expanded polystyrene (manufacturer Russia) | 23 | 329 | increased | not | Over the spreading area of the igniter |
| 7. Extruded expanded polystyrene (manufacturer Russia, brand) | 280 | 334 | high | Yes | All over the surface, the sample is burnt. Violent chemical reaction on surfaces under the influence of gasoline |
| 8. Foam plastics based on urea-formaldehyde resin | 55 | 356 | low | not | Over the spreading area of the igniter |
| 9. Polyurethane foam | 39 | >400 | high | not | More spreading area of the igniter, pungent smoke |
| 10. Mineral wool | 121 | 388 | high | not | Over the spreading area of the igniter |
Outcome
All types of foams are susceptible to fire. Foamed polystyrene significantly lose in volume (the degree of damage to the sample regulated by STB is no more than 80%), smoke abundantly and melts. The melt of the granules burns for some time, however, due to the obvious self-extinguishing property, it quickly extinguishes. In this case, there is no flame spread over the surface or volume. The most susceptible to deformation is expanded polystyrene made by the method of pressless molding, and its counterpart with surface treatment of granules with carbon-containing additives. The molded one showed the best result. "Silver" - for foam from Neopor raw materials.


Not taking into account the clearly disastrous sample of the eminent Russian manufacturer, we can conclude that extruded foam has a minimum burning time and a clear self-extinguishing property. As soon as the flammable liquid on the surface of the material burned out, combustion ceased. The material is resistant to deformation and shrinkage under the influence of fire, almost does not melt and does not sin with excessive soot.
The famous Russian styrofoam would have burned out completely if we hadn't intervened. Obviously, the use of fire retardants in its manufacture is out of the question. It burns not only in a molten state, but also in its original form under the influence of even a minimal source of fire. It is likely that such a foam can ignite from sparks. Absolute failure.


Exotic types of foam and mineral wool keep combustion to a minimum. Despite the absence of significant damage and deformation, the samples were marked by significant drawbacks - prolonged burning (mineral wool), maximum temperature (polyurethane foam) and an unpleasant odor (penoizol).


Instead of a resume
Each of our readers is able to analyze the information presented himself and draw a conclusion. Well, we will continue our experiments. Follow the announcements!
Still have questions? Do you disagree with something? Have a story to tell? Call the editorial office. Write, e-mail edition
comparison table
It is difficult for many to decide which material to use for insulation: foam or foam.
What better help to solve the comparative table of heaters.
| Properties | Styrofoam | Penoplex |
| Density (kg / m³) | 11-40 | 25-47 |
| Compressive strength (MPa) | 0,05-0,16 | 0,2 |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| Water absorption (%) | 1-2 | 0,5 |
| Thermal conductivity (W / m • ° С) | 0,029-0,032 | 0,039 |
| Fire resistance | G3-G4 | G1-G4 |
Indicators vary depending on the type of insulation chosen. The exact information on the characteristics of the purchased thermal insulation material is indicated in the technical documentation.
What is better to apply where
The scope of use of both heaters is wide.It is important to correctly determine which material is best to use in each specific case.
Professionals recommend using different insulation for the following situations:
- Insulate the walls from the outside with extruded polystyrene foam, since it is less susceptible to combustion, has a longer service life and is considered biologically sustainable.
- For internal insulation, both materials can be used, but using foam is cheaper. The only drawback is a decrease in the usable space inside the room.
- When insulating the floor, only foam is used, since foam is not suitable for this purpose due to its excessive fragility.
- The roof can be insulated with both materials. Combination of polystyrene and polystyrene foam is possible. The combination of internal insulation with expanded polystyrene and external insulation with expanded polystyrene is considered effective.
Extruded and regular polystyrene foam are considered the most common materials for thermal insulation.
Which is better, everyone decides for himself, based on the characteristics of a particular situation and financial capabilities.
Polyfoam or Penoplex - which is better?
When choosing a heater with a minimum coefficient of thermal conductivity and increased resistance to moisture, foam or Penoplex is usually chosen. They are produced in slabs, have a simple installation technology and are in many ways similar in properties. Therefore, a reasonable question arises - which is better than Penoplex or foam?
Polyfoam and Penoplex are foam materials made on the basis of expanded polystyrene. The difference is that Penoplex is produced by an extrusion method under high pressure, therefore it has a porous structure with high density and approximately the same granule size, while foam is produced under normal conditions.
To reduce the flammability of the material during the production process, special compositions based on fire retardants are added. As a result, the environmental friendliness of the material is violated, since toxic gases begin to evolve under the influence of high temperatures.
Application
- lightweight filler of compartments that ensure the unsinkability of ships (more often small ones)
- material for making floats, life jackets and bibs
- material for the manufacture of medical containers, including for the transportation of donor organs
- heat insulator and sound insulator in construction.
- constructional building and finishing material (form-building and decorative elements).
- heat insulator in household appliances (for example, in refrigerators)
- packaging for various goods (especially fragile), including food
- material of models used in casting (metals) according to gasified models.
Material cost analysis
TOP 3 best products according to customers' opinion
In our catalog you can buy Penoplex 50 mm. in Moscow at a cost that is more profitable than the average market.
Polyfoam Mosstroy-31 1000x1000x50 mm (density 15) - heat-insulating moisture-resistant pl.
The thickest insulated panels Penoplex 100 mm. used in areas with low temperature display.
Polyfoam Mosstroy-31 1000x1000x100 mm (density 15) - heat-insulating moisture-resistant p.
This material is universal, it can significantly increase the level of thermal insulation.
Polyfoam Mosstroy-31 1000x1000x100 mm (density 25) - heat-insulating moisture-resistant plates.
Penoplex 30mm is available in our catalog, the quality of which is confirmed by certification. We are.
Polyfoam Mosstroy-31 1000x1000x30 mm (density 15) - heat-insulating moisture-resistant plates d.
Insulation Penoplex Foundation is optimal for use in loaded structures with protective c.
Polyfoam Mosstroy-31 1000x1000x100 mm (density 25 F) - heat-insulating moisture-resistant boards.
Polyfoam 1000x1000x30 mm (density 25 F) - heat-insulating moisture-resistant plates.
Polyfoam Mosstroy-31 1000x1000x50 mm (density 25 F) - heat-insulating moisture-resistant plates.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Styrofoam
pros
- Low coefficient of thermal conductivity.
- Long shelf life and operation, which is 20-30 years.
- High resistance to high humidity.
- Installation is possible without laying a vapor barrier layer.
- Light weight, allowing the use of insulation even in frame structures.
- Retains the geometry of the sheets throughout the entire service life.
- Increases the level of soundproofing of premises.
- Not susceptible to the negative effects of bacteria, mold and microorganisms.
- The lowest price compared to other types of insulation.
- Ease of processing and shaping the sheets.
Minuses
- Increased flammability.
- The fragility of the boards, requiring careful transportation and installation.
- The insulation is susceptible to rodents.
- The need to provide an almost perfectly flat surface to prevent damage to the sheets.
Spheres of application of polystyrene
The use of foam is justified in the following cases:
- it is required to ensure the minimum weight of the structure;
- the minimum budget for the insulation of the structure;
- high-quality sound insulation is required;
- the thickness of the insulation layer is not critical to achieve the required level of thermal insulation;
- it is required to insulate the facade, loggia or balcony without the use of a vapor barrier layer.
Foam operating temperatures
The foam plastic retains its operational characteristics at temperatures from +80 to -180 degrees. It is important to note that the foam is able to withstand direct exposure to temperatures above 110 degrees for a short time. The maximum temperature that the material can withstand for several minutes without losing its basic properties is 95 degrees. The recommended maximum temperature is 80 degrees, at which the material will not undergo deformation.
Polyfoam, provided that it is laid, will be able to serve in compliance with all requirements without losing its original characteristics for more than 30 years. The durability of the material is due to its resistance to deformation, mechanical stress, and resistance to biological effects.
Polyfoam retains heat well. The laying of expanded polystyrene in the outer walls of residential buildings allows several times to reduce heat loss.According to research and testing, expanded polystyrene with a thickness of only 12 cm in its heat-saving properties is equivalent to:
- 0.5 m thick timber wall;
- 2-meter brick wall;
- 4-meter reinforced concrete wall.
Advantages and disadvantages of Penoplex
pros
- High strength of the material due to the size of the cells up to 0.2 mm, allowing it to be used in loaded structures.
- Increased resistance to the negative effects of fungus, mold and insects.
- The minimum degree of moisture absorption.
- The service life is up to 50 years.
- Small thickness of slabs while maintaining a minimum coefficient of thermal conductivity.
- Possibility of using for insulation of external and internal structures.
- Simple technology of installation and formation of sealed joints due to the special shape of the ends of the plates.
- Ease of material handling.
- Optimal sound insulation of insulated structures is provided.
Minuses
- Increased flammability.
- The material loses its properties when used under direct exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Scopes of Penoplex
Depending on the density, Penoplex is suitable for insulating the following structures:
- pitched and flat loaded and unloaded roofs with a density from 28 to 33 kg / m 3;
- internal partitions, walls from the inside and outside, if the density of the insulation is in the range of 25-33 kg / m 3;
- the facade of the building and the foundation, it is recommended to use slabs with a density of 29-35 kg / m 3;
- for insulation of heavily loaded structures, such as highways, runways, foundations of multi-storey buildings, slabs with a density of 35-45 kg / m 3 are suitable.
Polyfoam (expanded polystyrene foam) for insulation
Polyfoam (expanded polystyrene foam) for insulation
Expanded polystyrene is a heat-insulating material obtained by foaming polystyrene during heat treatment. Expanded polystyrene has the form of granules with a size of 2-8 mm. They are made of suspension expandable polystyrene with the addition of a fire retardant. The formation of such a material occurs by the method of steam impact due to the sintering of granules with each other. The main purpose of expanded polystyrene is thermal insulation of enclosing structures - walls, roofs, ceilings, floors, as well as industrial equipment in the absence of contact with the interior and the temperature of the insulated surface is not higher than 80 ° C. Since polystyrene is safe (subject to manufacturing technology and using high-quality raw materials), expanded polystyrene inherits this property. The structure of expanded polystyrene provides its unique heat-insulating properties, it is water-resistant, it is characterized by stable performance during operation in regions with a harsh and humid climate, has high mechanical strength, and weakly absorbs moisture. And the high density of expanded polystyrene in the building elements and the special design of the connecting locks exclude violations of thermal conductivity, both at the stage of installation and during the operation of the building. Expanded polystyrene is not radioactive, and also does not contain substances that feed microorganisms, therefore it is not susceptible to rodents, mold, fungi and bacteria. If expanded polystyrene is exposed to a flame for a short time, it melts around the fire source, but does not ignite, and, accordingly, the fire does not spread, but a poisonous gas is released. If another material (wood) is burning, and expanded polystyrene is present in the structural elements, then one of the main damaging factors is the poisonous gas released by expanded polystyrene. For fatal poisoning, two breaths are enough. According to the results of fire tests carried out at the VNIIPO EMERCOM of the Russian Federation, the following data were obtained: the fire resistance limit of the wall is 2.5 hours, the fire propagation rate is zero. The special properties of closed-cell polystyrene foam, such as stability and durability, resistance to moisture and soil organisms, as well as good thermal insulation, lead to the possibility of using foam plates as a frost protection layer in the construction of roads and railways. Since 1972, a new construction method has been developed in Norway: the use of expanded polystyrene blocks as a load-distributing substrate at the entrances to roads and bridges in areas with poorly bearing soil properties. In such areas, over time, there is a strong subsidence of certain parts of the carriageway, which entails costly repair measures. The solution to the problem was the use of expanded polystyrene blocks, which, with a minimum bulk density of 20 kg / m³, have the durability required for such an application. The blocks of expanded polystyrene are protected from slipping by means of toothed plates and are stacked on top of each other to a height of 10 meters. Thereafter, a 10 cm thick concrete layer with steel fabric reinforcement is applied, followed by a bitumen coating. Water absorption Unlike other materials, expanded polystyrene is not hygroscopic. Even under water, it absorbs a small amount of moisture. Influence of temperature The use of expanded polystyrene has practically no lower temperature limit. Dimensional stability When the temperature changes by 17oC, the length change is equal to 1%, i.e. 1 mm / m.Sound insulation Thanks to the protected composite insulation system, very good sound insulation from outside noise can be achieved. Flat roof The insulating material is laid loosely, depending on the roof structure, hot or cold glued or mechanically attached to the subfloor. In this case, the insulating plates and the seal are laid freely and supplied with a load (for example, a reinforcing mesh) or fixed with special dowels. Sloped roof To insulate sloped roofs, polystyrene foam is used to fill the space between the rafters or to be laid directly on the rafters. Such insulating systems make it possible to efficiently perform and provide reliable thermal insulation for a long time. Internal wall insulation The most economical method of internal insulation of external walls and ceiling surfaces is the use of composite panels. These boards consist of rigid polystyrene foam combined with gypsum board or wood chip boards. Foundation structures The use of heavy-grade polystyrene foam in northern countries with severe winters and permafrost is especially important as an insulating material to protect foundations and pipelines laid in the soil. PSK GK supplies all types of polystyrene for insulation of buildings and premises from the companies Mosoblstroy-25 (Mosstroy-31). Always in stock! Call us!
/upload/iblock/068/0688ad241e53e4ea18fb577474df1c07.jpg
1.00
/ catalog / izolyatsia / teplo / yacheistyy_penopolistirol_-penoplast / penoplast_-penopolistirol_vspenennyy-_dlya_izolyatsii /
Comparison of material characteristics


| Characteristics | Styrofoam | Penoplex |
| Thermal conductivity, W / m ∙ K | 0,036-0,050 | 0,028-0,034 |
| Water absorption per day,% | 2 | 0,2 |
| Flexural strength, MPa | 0,07-0,20 | 0,4-1 |
| Compressive strength, MPa | 0,05-0,2 | 0,25-0,50 |
| Density, kg / m3 | 15 to 35 | 28 to 45 |
| Temperature at which the insulation is allowed to operate, ° С. | -50 to +70 | -50 to +70 |
| Water vapor permeability, mg / m ∙ h ∙ Pa | absent | 0,018 |
| Material thickness, cm | 30-100 | 2-10 |
Melting and softening temperature of plastics, operating temperature of plastics
Recently, plastics and plastics are widely used in industry and everyday life. Therefore, it often occurs the problem of choosing a specific plastic for the given temperature conditions of its operation... When choosing a plastic, it is necessary to take into account the range of its operating temperature or the temperature of the beginning of softening and melting of the plastic. The table below contains all the data required for this.
The table shows the density values ρ ... melting point of plastic t pl ... Vicat softening temperature t size ... brittleness temperature t xp ... as well as the operating temperature range t slave in which the operation of plastics is allowed.
The values in the table are for more than 270 types of plastic. For each plastic, at least one temperature is indicated, which makes it possible to assess the permissible temperature conditions for its operation. The following types of plastics and plastics are considered: polyolefins, polystyrene, fluoroplastics, PVC, polyacrylates, phenolic plastics, foams, ABS plastics. polyurethanes, resins and compounds, anti-friction self-lubricating plastics, fiberglass, etc.
Polyolefins include plastics and plastics such as polyethylene, polypropylene and copolymers based on them. The melting point of polyethylene has a value of 105-135 ° C depending on the density, and the operating temperature range of this plastic is from -60 to 100 ° C. High-strength low-pressure polyethylene can be operated at very low temperatures: the brittleness temperature of this plastic is minus 140 ° C.
The melting point of polypropylene is in the range of 164-170 ° C. At low temperatures, this plastic becomes brittle from minus 8 ° C. Among other representatives of polyolefins, it is necessary to note a high temperature resistant plastic based on templain.This plastic can withstand temperatures up to 180-200 ° C and has a frost resistance of -60-40 ° C.
It should be noted the modes of operation of plastics based on PVC and abs-plastics. PVC-based foams have an operating temperature of -70 to 70 ° C, depending on the brand. The softening point of abs plastic is 95-117 ° C.
Plastics with a high melting point include fluoroplastics and polyamides, as well as heat-resistant plastic niplon. For example, the melting point of PTFE is 327 ° C. (for fluoroplastic-4 and 4D). Polyamides (caprolon, caprolite) have a softening point of 190-200 ° C, and the melting point of such plastic is 215-220 ° C. Glass and carbon fiber niplon has a melting point above 300 ° C.
Of all the variety of polymers for operation at high temperatures, plastics based on organosilicon resins are suitable. The maximum operating temperature of such plastic can reach 700 ° C.
Density and characteristic temperatures of plastic and plastics
No comments yet!