Home / Gas boilers
Back to
Published: 22.04.
Reading time: 4 minutes
0
158
Double-circuit gas boilers for heating and hot water are heat supply sources that are installed in individual housing stock: cottages or private houses.
As a rule, such units are capable of operating on two types of fuel: main and liquefied gas and can be both wall-mounted and floor-mounted. Among the sources of heating, such designs are most popular.
This is due to the fact that gas in Russia is still the cheapest energy source in domestic heat supply schemes, and the device of such boilers is capable of providing 100% automatic mode.
- 1 Types and features of double-circuit gas units
- 2 Design of a double-circuit gas boiler
- 3 How it works
- 4 Advantages and disadvantages of double-circuit devices
- 5 Characteristics of heat exchangers 5.1 Models with bithermic heat exchanger
- 5.2 Models with instantaneous heater
Types and features of double-circuit gas units
Double-circuit floor-standing gas boilers are available with a mini-boiler room. The user who purchased such a unit does not need to additionally purchase: a pump, fan, expansion tank, air vent, as well as primary sensors of the automation system.
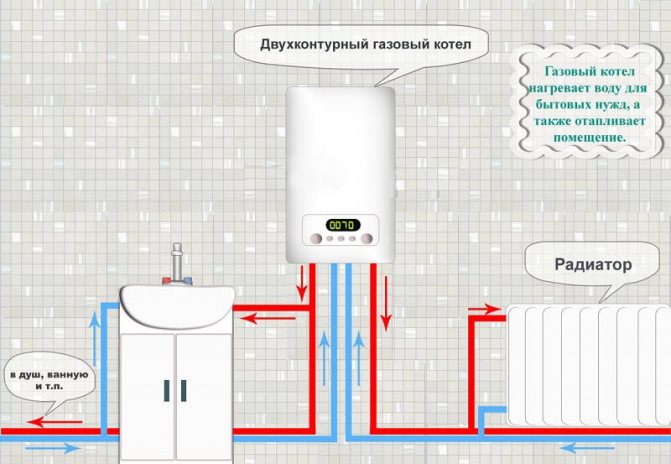
All this is supplied in a set by the manufacturer and is effectively configured for boiler operation. In some cases, even a coaxial chimney is supplied with the unit.
The Russian market for boiler equipment is oversaturated with various modifications of units, in order to navigate them, they are grouped according to the following parameters:
- Design type: convection and condensation, the latter method is characterized by the highest efficiency, but the device costs much more and has a more complex maintenance process.
- Thermal output (kW), indicated separately for DHW and heating loads.
- Installation option: floor or wall.
- Type of combustion chamber: open with natural chimney and closed, with forced movement of the gas mixture in the combustion chamber, provided by a fan and a coaxial chimney.
- Burner ignition type: piezo ignition or electric ignition.
In contrast to single-circuit heating units, double-circuit ones differ in the principle of distributing hot water from a gas boiler.
It is necessary to select this equipment taking into account the characteristics of the heat exchanger capable of providing the DHW load and guaranteeing several operating modes of the boiler "winter-summer".
Ways to connect the DHW subsystem to the heat supply system
- Hot water is supplied to the consumer directly from the general heating system. With this connection, the quality of water in the tap and inside the radiator (battery) heating is the same. That is, people consume directly coolant
... In this case, the heat supply system itself is called
open
(that is, through
open
taps from the heat supply system, the coolant flows out).
- Cold drinking water taken from the water supply system is heated in an additional heat exchanger with network water, after which it is supplied to the consumer. Hot water and heat carrier are separated, hot water consumed by people practically does not differ from cold water in terms of its drinking quality (hot water pipes rust faster than cold water pipes). In this case, the heat supply system is called closed
, since it transfers only heat to consumers, but not a coolant.
- Hot water is heated in a boiler room or central heating point, after which it is supplied to the consumer separately from the heat supply system. Such a hot water system is called independent
... It is most often used in low-rise buildings, if the installation of indoor heaters is economically unjustified or impossible; however, it does not have the disadvantages of an open system in terms of low water quality. Another advantage of this system is the possibility of separate maintenance and repair of hot water and heat supply pipelines.
The design of a double-circuit gas boiler
A double-circuit gas boiler for heating has a special design of the combustion chamber, in which there are two heating circuits - heating and hot water supply.
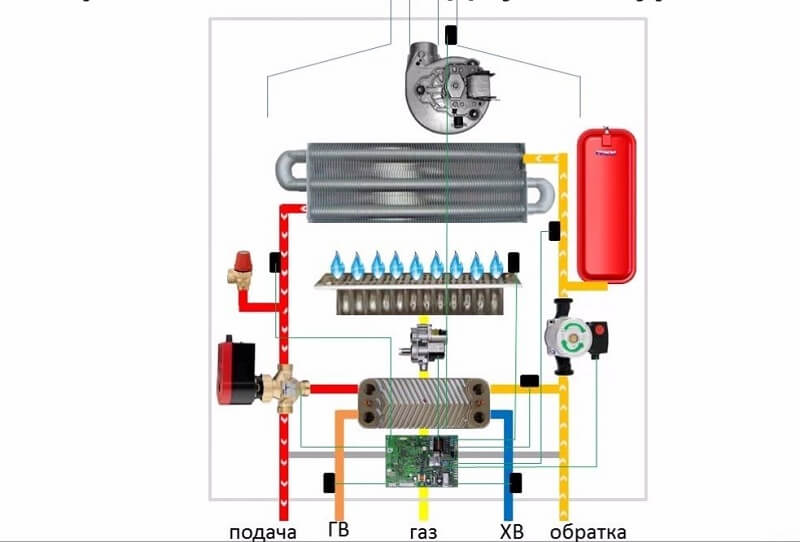

In order to ensure their work, the unit is made of the following elements:
- The burner device is the head element of the boiler, which ensures the creation of a gas-air mixture in ratios that ensure complete combustion of the fuel.
- The firebox or combustion chamber serves to transfer the released thermal energy from gas combustion to the coolant in the heating and hot water circuits.
- An electric pump circulates water through the heating circuit.
- A blower fan for closed-type furnaces supplies air to the flare mouth for complete combustion of fuel. In addition, it creates the necessary pressure of the flue gases for its discharge through the coaxial flue gas system into the surrounding space.
- The safety group is equipped with a safety valve, an air vent and primary sensors of the automatic regulation and safety system.
- The three-way valve switches the flow of the heating medium in the heating and DHW circuits.
- Basic heating heat exchanger.
- DHW heat exchanger for heating cold water.
- Coolant supply and outlet pipes to the heating circuit.
- Sump and water purification filter.
- Expansion tank, storage.
In certain modifications of double-circuit gas boilers, a paired heat exchanger is installed, in which the coolant between the heating circuits is switched inside the body. In this case, the principle of operation of such a unit does not change.
Principle of operation
The thermal regime for a gas boiler is set using modern weather-dependent automation, which is adjusted according to the outside air temperature, and therefore the principle of its operation is simplified as much as possible. The start-up and operation of the unit is controlled by a microprocessor.
At this time, when the water in the heating circuit reaches the set temperature, the burner switches to modulation or, in other words, standby mode. The heat cycle resumes when the water temperature in the circuit drops below user-set modes.
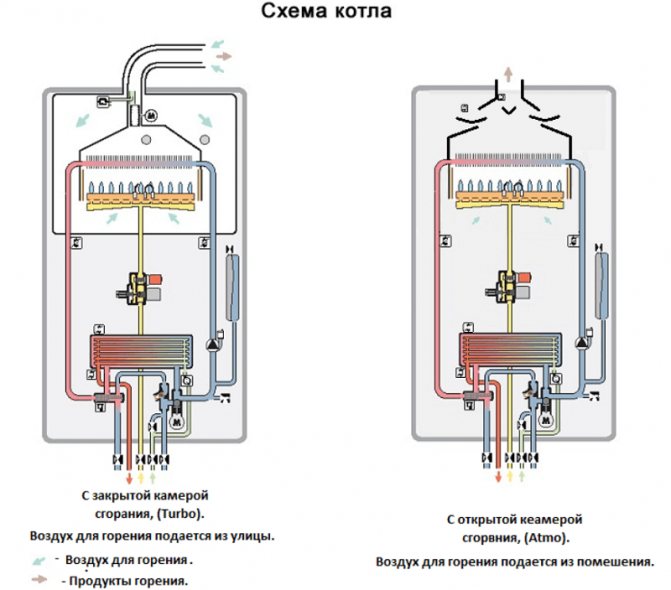

A fan built into the structure in closed models supplies primary air to the furnace to ensure complete combustion of the gas and creates an aerodynamic mode of movement of flue gases sufficient for complete removal of exhaust flue gases into the atmosphere.
When there is a weak pressure of hot water in the heating circuit, a centrifugal pump is installed, which directs the coolant to the final heating point in the house and returns it back to the boiler.
An electromechanical three-way valve switches the heating medium between DHW and heating circuits. When the user turns on the hot water tap on the mixer, the three-way tap directs the coolant along a small circuit, as a result, hot water is heated in high-speed heating mode.
The heating system does not work during this period. After turning off the tap on the mixer, the three-way valve switches the coolant to heating.
Recirculation via indirect boiler
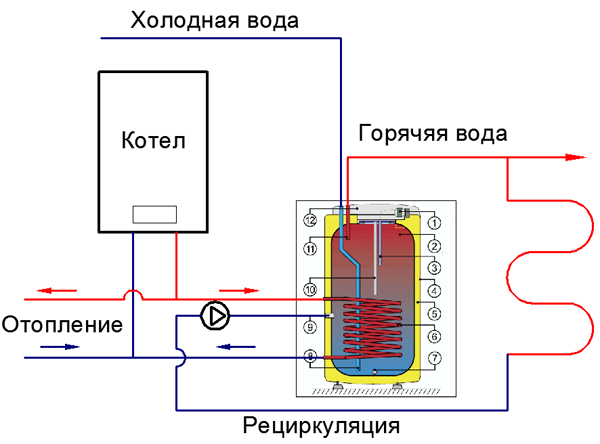

A single-circuit boiler with an external indirect heating boiler is the most optimal option for organizing recirculation, which is often used in conditions of fairly intensive hot water consumption. In such a bundle, hot water recirculation is usually used.
Such a system allows the simultaneous use of two or more showers, a bath, a Jacuzzi. In their own homes, an indirect heating boiler is usually installed, having a volume of one hundred to one thousand liters.
In such a system, water is heated by passing through the boiler, a large-sized tank with a tubular spiral. The heating system coolant circulates along the spiral of the boiler, which thus heats the water in the boiler. In this system, in contrast to the variants of an instantaneous or storage water heater, the heating boiler operates all year round.
Most boilers with indirect heating have a tank made of enamelled steel. And some premium models have an inner tank material, which is stainless steel.
Advantages and disadvantages of double-circuit devices
Today, double-circuit gas boilers are among the most energy efficient heating equipment. However, they have both advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of a double-circuit boiler:
- Low specific gas consumption for generating a unit of thermal energy, modern units have an efficiency of 90-92%.
- Compactness and light weight, in connection with which most of the double-circuit units are produced in a wall-mounted version, which allows them to be placed even in small-sized kitchens.
- Universal heat supply system. There is no need to purchase additional accessories and adjust them to the parameters of the boiler.
- In the warm season, such a device works perfectly for heating hot water, which makes it possible to rationally use the heat source throughout the year.
Disadvantages of a double-circuit boiler:
- With a large water intake, it is impossible to qualitatively ensure the simultaneous operation of two circuits: heating and hot water supply on a gas boiler.
- Limited thermal power models.
- The compactness of the combustion chamber is not always capable of providing the required mode of operation of the boiler for DHW, especially when the taps are located remotely.
- Susceptibility to the quality of the source water, which causes premature failure. The DHW plate heat exchanger works very poorly on hard water.
- Many users attribute its increased cost to the disadvantages of a double-circuit boiler. But experts say the opposite, in comparison with the options when it is necessary to additionally purchase an indirect heating boiler or install a gas water heater.
DHW recirculation on a double-circuit boiler.
DHW recirculation on a double-circuit boiler.
Message minimaxpo »08 Nov 2012, 17:10
Re: DHW recirculation on a double-circuit boiler.
Message BAXI-Valuyskikh »08 Nov 2012, 17:45
Re: DHW recirculation on a double-circuit boiler.
Message BAXI-Ural »08 Nov 2012, 19:46
Re: DHW recirculation on a double-circuit boiler.
Message RADAR »08 Nov 2012, 20:41
Re: DHW recirculation on a double-circuit boiler.
Message Gdalex »08 Nov 2012, 22:19
Re: DHW recirculation on a double-circuit boiler.
Message RADAR »08 Nov 2012, 22:24
Re: DHW recirculation on a double-circuit boiler.
Message Bahus »08 Nov 2012, 23:24
Re: DHW recirculation on a double-circuit boiler.
Message minimaxpo »09 Nov 2012, 11:32
Re: DHW recirculation on a double-circuit boiler.
Message minimaxpo »09 Nov 2012, 11:33
Can it be adjusted?
Re: DHW recirculation on a double-circuit boiler.
Message BAXI-Ural »09 Nov 2012, 11:41
Can it be adjusted?
Heat exchanger characteristics
In modern double-circuit boilers, two types of boilers are mainly used - bithermal and flow-through. The first one is used more with a small hot water consumption. Flow-through heaters have a developed heating surface, which ensures a high heating rate of water and its large volumes.
Models with bithermic heat exchanger
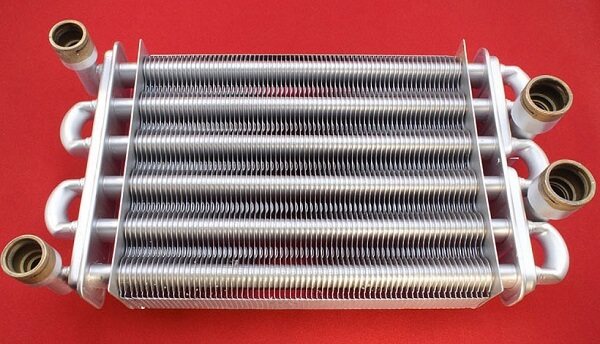

Heating of the coolant in a gas boiler equipped with a bithermal heat exchanger occurs due to the circulation of the coolant through copper channels, the sections of which are made with a complex configuration inside the body.
A heating medium circulates through the external channels, inside the tubes - heated water for hot water supply. The heat exchanger receives heat from an operating gas burner.
The principle of operation of the bithermal heat exchanger:
- In heating mode at a low temperature of the coolant in the circuit, the electromechanical gas flow valve supplies gas to the nozzle, which is ignited by the piezo igniter.
- The fuel burns out, and the released heat is transferred through the walls of the heat exchanger to the coolant.
- When the set water temperature is reached, the gas supply to the double-circuit gas boiler stops and turns on automatically when it drops.
- When the user opens a hot water tap on the mixer, tap water will begin to flow into the DHW heating circuit of the bithermal heater. The heat carrier enters a small DHW circulation loop and heats up cold water at a rate.
- After the DHW tap is closed, the valve redirects the coolant to the heating circuit.
Instantaneous heater models
The principle of operation of boilers operating on gas fuel, in the design of which a separate flow-through heat exchanger for hot water supply is installed, is that the coolant for heating and hot water is heated in separate buildings.
In a DHW instantaneous heat exchanger, tap water is heated by a heating medium, which is switched by a three-way valve.
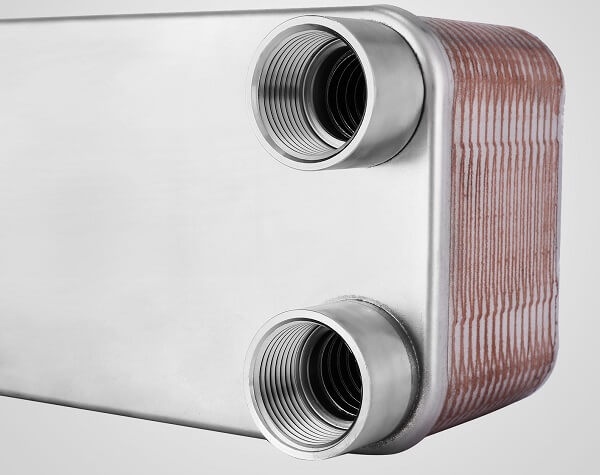


At this moment, the water in the heating circuit of the in-house heating system continues to circulate through a separate heat exchanger, naturally without receiving heat. In order for the system to work reliably, a circulation electric pump and two separate expansion tanks for each circuit are integrated into it.
This scheme is more efficient in terms of specific indicators of fuel, is capable of providing a large load on hot water supply, and is not so sensitive to the quality of the source water. In addition, the heating surfaces of the heat exchangers are designed in such a way as to ensure maximum heat removal from the combustion chamber.
For example, in the hot water supply circuit, the flows of the coolant and cold water are directed according to the counterflow principle, which allows the temperature in the heating circuit to be removed as much as possible and reduces the scale formation processes on the internal heating surfaces of the heat exchanger.
What it is?
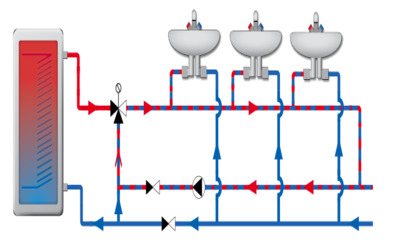

Recirculation is heating circuit piping system, as well as DHW lines, designed for the constant movement of heat carrier or hot water.
It is designed to increase the efficiency of using boilers, as well as to improve the comfort of residents when using hot water.
For example, with a remote location of the hot water supply tap from the boiler, the water in the pipes cools down quickly. You have to skip it for a long time until the temperature rises to the desired value.
If recirculation is used, water is constantly moving from the boiler to the draw-off point and vice versa. It does not cool down, which makes it possible to use DHW immediately, without waiting.
In heating systems, circulation ensures optimal thermal conditions. A hot coolant enters the heating circuit, which passes through a cascade of radiators and gives up its thermal energy.
Returning to the boiler, the cooled coolant heats up again and enters the heating circuit for a new cycle. The efficiency of heating, uniform heat transfer at the initial and final points of the circuit, depends on the speed of water movement.
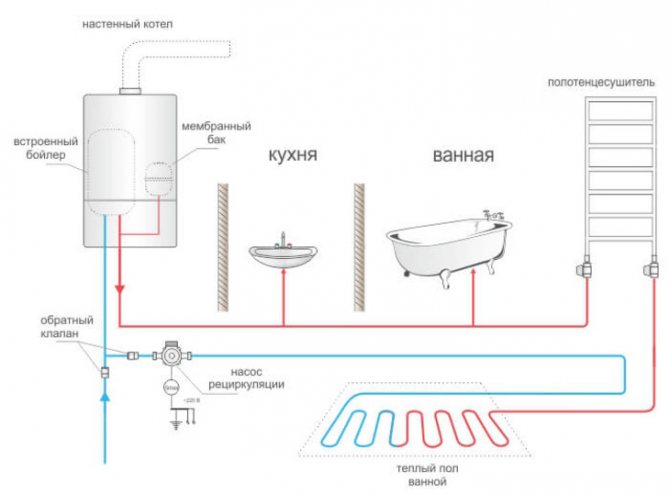
In a private house
Recirculation of hot water in a private house performed by piping the boiler or, less commonly, a heating boiler.
There are single- and double-circuit models that can only prepare a coolant for heating, or simultaneously supply a coolant and hot water for domestic needs. In addition, there are volatile and non-volatile boiler models.
The first ones are capable of working without being connected to the power supply network and only need a fuel supply. The latter need to be connected to the power supply. They are equipped with their own circulation pumps, which ensure the movement of the coolant along the heating circuit.
Usually, the circulation of the coolant is provided by the boiler itself. For hot water recirculation, an additional piping equipped with a circulation pump is used.
It is connected to the boiler, carried to the most distant consumption device, and returned back to the boiler. There is an additional consumption of electricity to power the pump, but there is a noticeable saving of water, and the convenience of using hot water supply increases.

In a multi-storey building
Modern DHW circuits use a boiler system, in which the network hot water is not supplied to the apartments. The water is heated indirectly in a boiler, from which hot water is supplied to the heated towel rail and hot water supply system.
Each apartment in a multi-storey building is one of the sections of the general recycling scheme. Its feature is the vertical movement of water - from the bottom point to the top floor, and back. As a rule, circulation is organized along the line of heated towel rails.
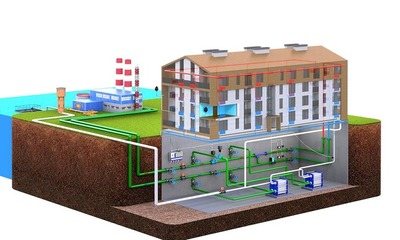

It is powered from the DHW pipeline, so the water in the boiler never cools down and maintains its operating temperature.
Hot water rises through the riser, connects to the heated towel rail and goes back to the boiler.
But, it is impossible to organize its own circulation for each draw-off point (kitchen sink, washbasin or bathtub), therefore, the water in the outlets from the riser often cools.
The solution to this problem can be the installation of your own boiler and the installation of a recirculation loop. This is an effective measure if the apartment is large and the appliances are located far from the storage tank.











