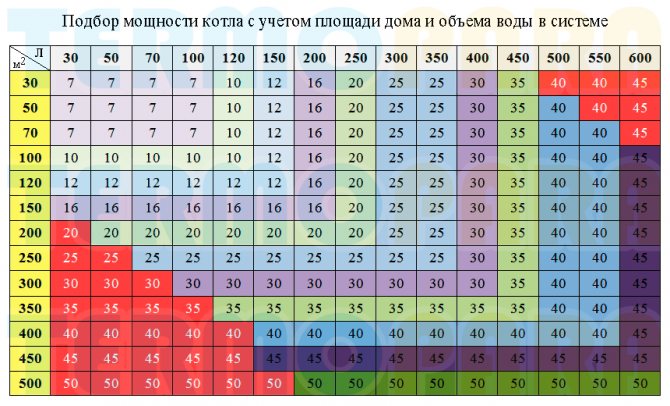
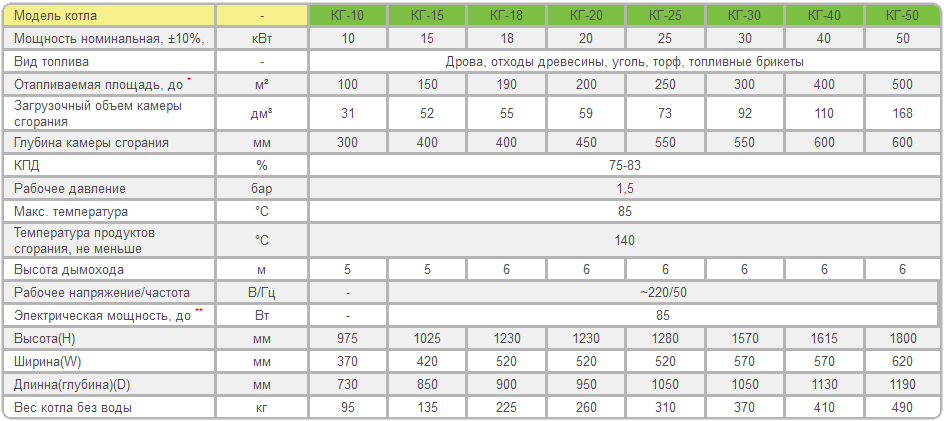
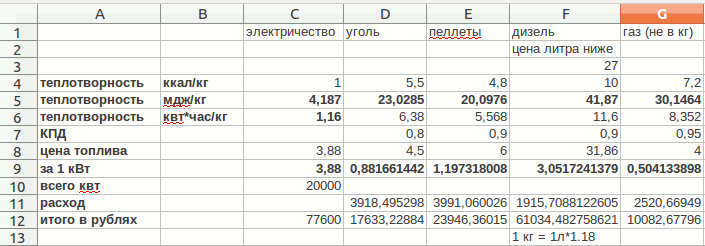
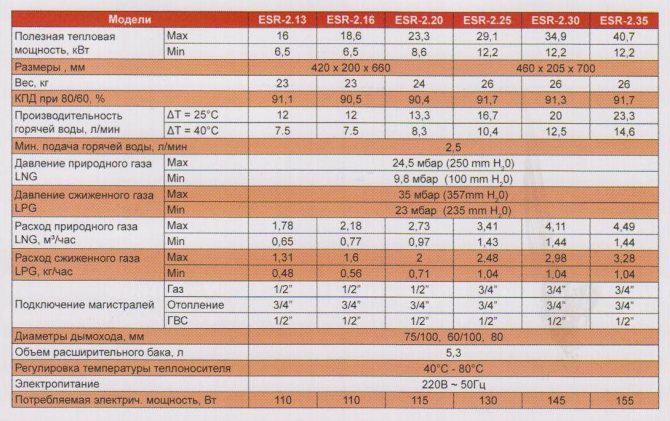
With the help of hydraulic calculation, you can correctly select the diameters and lengths of pipes, correctly and quickly balance the system with the help of radiator valves. The results of this calculation will also help you choose the right circulation pump.
As a result of the hydraulic calculation, it is necessary to obtain the following data:
m is the flow rate of the heating agent for the entire heating system, kg / s;
ΔP is the head loss in the heating system;
ΔP1, ΔP2 ... ΔPn, are the pressure losses from the boiler (pump) to each radiator (from the first to the nth);
Heat carrier consumption
The coolant flow rate is calculated by the formula:
,
where Q is the total power of the heating system, kW; taken from the calculation of the heat loss of the building
Cp - specific heat capacity of water, kJ / (kg * deg. C); for simplified calculations, we take it equal to 4.19 kJ / (kg * deg. C)
ΔPt is the temperature difference at the inlet and outlet; usually we take the supply and return of the boiler
Heating agent consumption calculator (only for water)
Q = kW; Δt = oC; m = l / s
In the same way, you can calculate the flow rate of the coolant at any section of the pipe. The sections are selected so that the water speed is the same in the pipe. Thus, the division into sections occurs before the tee, or before the reduction. It is necessary to sum up in terms of power all radiators to which the coolant flows through each section of the pipe. Then substitute the value into the formula above. These calculations need to be done for the pipes in front of each radiator.
The simplest formula for calculating the required heat energy for heating
For an approximate calculation, there is an elementary formula: W = S × Wsp, where
W is the power of the unit;
S - the size of the building area in m², taking into account all rooms for heating;
Wsp is a standard indicator of specific power, which is used when calculating in a specific climatic region.
The standard value for specific output is based on experience with a variety of heating systems.
The average statistical information is ascertained from the housing and communal services employee in your region. After that, multiply this value by the total area of the building, and you will get the average indicator of the required boiler power.
A convenient online calculator for self-calculating the power of a heating boiler directly on our website!
Coolant speed
Then, using the obtained values of the coolant flow rate, it is necessary to calculate for each section of pipes in front of the radiators the speed of movement of water in pipes according to the formula:
,
where V is the speed of movement of the coolant, m / s;
m - coolant flow through the pipe section, kg / s
ρ is the density of water, kg / cubic meter. can be taken equal to 1000 kg / cubic meter.
f - cross-sectional area of the pipe, sq.m. can be calculated using the formula: π * r2, where r is the inner diameter divided by 2
Coolant speed calculator
m = l / s; pipe mm by mm; V = m / s
Calculation of unit performance for an apartment
The power of the boiler for heating apartments is calculated taking into account the same rate: for every 10 "squares" of the area, 1 kW of thermal energy is required. But in this case, the correction is made in accordance with other parameters.
First of all, take into account the presence / absence of a cold room at the bottom of the apartment or on top of it:
- when a warm apartment is located on a floor below or above, a coefficient of 0.7 is applied;
- if there is an unheated room, no adjustment is needed;
- when the attic or basement is heated, the correction is 0.9.

Before determining the power of the boiler, it is necessary to calculate the number of external walls facing the street, and more heat will be required for a corner apartment, therefore:
- when there is only one outer wall - the applied coefficient is 1.1;
- if it is one - 1.2;
- when the 3 outer walls are 1.3.
Fence surfaces in contact with the street are the main areas through which heat escapes. It is advisable to take into account the quality of glazing of window openings. Correction is not made in the presence of double-glazed windows. If the windows are old wooden, the result of the previous calculations is multiplied by 1.2.
When calculating power, both the location of the apartment and the planning of the installation of a double-circuit unit in order to provide hot water supply are important.
Loss of pressure on local resistances
Local resistance in a pipe section is resistance at fittings, valves, equipment, etc. Head losses on local resistances are calculated by the formula:
where Δpms. - loss of pressure on local resistances, Pa;
Σξ - the sum of the coefficients of local resistances on the site; local resistance coefficients are specified by the manufacturer for each fitting
V is the speed of the coolant in the pipeline, m / s;
ρ is the density of the heat carrier, kg / m3.
Dissipation factor
The dissipation factor is one of the important indicators of heat transfer between a living space and the environment. Depending on how well the house is insulated. there are such indicators that are used in the most accurate calculation formula:
- 3.0 - 4.0 is the dissipation factor for structures that do not have any thermal insulation at all. Most often, in such cases, we are talking about temporary huts made of corrugated iron or wood.
- A coefficient from 2.9 to 2.0 is typical for buildings with a low level of thermal insulation. We mean houses with thin walls (for example, one brick) without insulation, with ordinary wooden frames and a simple roof.
- The average level of thermal insulation and the coefficient from 1.9 to 1.0 are assigned to houses with double plastic windows, insulation of external walls or double masonry, as well as with an insulated roof or attic.
- The lowest dissipation coefficient, from 0.6 to 0.9, is typical for houses built using modern materials and technologies. In such houses, the walls, roof and floor are insulated, good windows are installed and the ventilation system is well thought out.
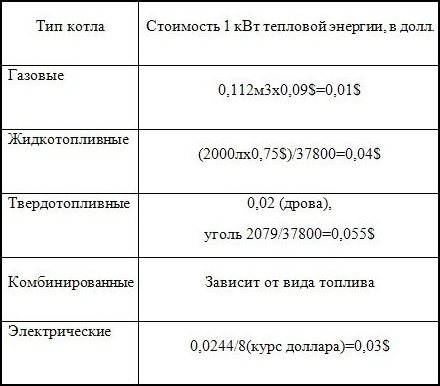

Table for calculating the cost of heating in a private house
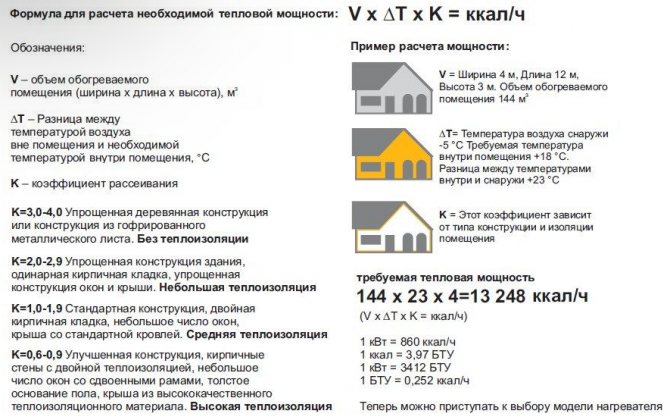
The formula in which the value of the dissipation coefficient is applied is one of the most accurate and allows you to calculate the heat loss of a particular structure. It looks like this:
In the formula, Qt is the level of heat loss, V is the volume of the room (the product of length, width and height), Pt is the temperature difference (to calculate, it is necessary to subtract the minimum air temperature that can be at this latitude from the desired temperature in the room), k Is the dissipation factor.
Let's substitute the numbers in our formula and try to find out the heat loss of a house with a volume of 300 m³ (10 m * 10 m * 3 m) with an average level of thermal insulation at a desired air temperature of + 20 ° C and a minimum winter temperature of -20 ° C.
Having this figure, we can find out how much power the boiler is needed for such a house. To do this, the resulting value of heat loss should be multiplied by the safety factor, which is usually equal to from 1.15 to 1.2 (the same 15-20%). We get that:
Having rounded the resulting number down, we find out the required number. To heat a house with the conditions set by us, you will need a 38 kW boiler.
Such a formula will allow you to very accurately determine the power of a gas boiler required for a particular house.Also today, a wide variety of calculators and programs have been developed that allow you to take into account the data of each individual structure.
Heating a private house with your own hands - tips for choosing the type of system and type of boiler Requirements for installing a gas boiler: what is necessary and useful to know about the connection procedure? How to correctly and without errors calculate heating radiators for a house Water supply system of a private house from a well: recommendations for creating
Hydraulic calculation results
As a result, it is necessary to sum up the resistances of all sections to each radiator and compare with the reference values. In order for the pump built into the gas boiler to provide heat to all radiators, the pressure loss on the longest branch should not exceed 20,000 Pa. The speed of movement of the coolant in any area should be in the range of 0.25 - 1.5 m / s. At a speed above 1.5 m / s, noise may appear in the pipes, and a minimum speed of 0.25 m / s is recommended according to SNiP 2.04.05-91 in order to avoid airing the pipes.
In order to withstand the above conditions, it is enough to choose the right pipe diameters. This can be done according to the table.
| Trumpet | Minimum power, kW | Maximum power, kW |
| Reinforced plastic pipe 16 mm | 2,8 | 4,5 |
| Reinforced plastic pipe 20 mm | 5 | 8 |
| Metal-plastic pipe 26 mm | 8 | 13 |
| Reinforced plastic pipe 32 mm | 13 | 21 |
| Polypropylene pipe 20 mm | 4 | 7 |
| Polypropylene pipe 25 mm | 6 | 11 |
| Polypropylene pipe 32 mm | 10 | 18 |
| Polypropylene pipe 40 mm | 16 | 28 |
It indicates the total power of the radiators that the pipe provides with heat.
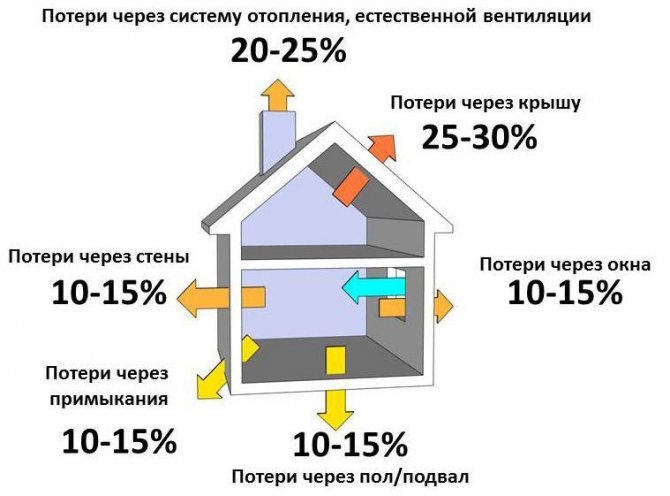
Influence of heat loss on heating quality
In order to ensure high-quality heating of the household, it is necessary that the heat supply system can fully replenish the heat losses. It leaves the buildings through the roof, floor, windows and walls. For this reason, before calculating the power of the boiler for heating a house, one should take into account the degree of thermal insulation of these housing elements.
Some real estate owners prefer to seriously deal with the issue of assessing heat loss and order the corresponding calculations from specialists. Then, based on the results of calculations, they can select a boiler for the area of the house, taking into account other parameters of the heating structure.
When performing the appropriate calculations, one should take into account the materials from which the walls, floor, ceiling are built, their thickness and the degree of thermal insulation. It also matters which windows and doors are installed, whether the supply ventilation system is equipped and its performance. In a word, this process is not easy.
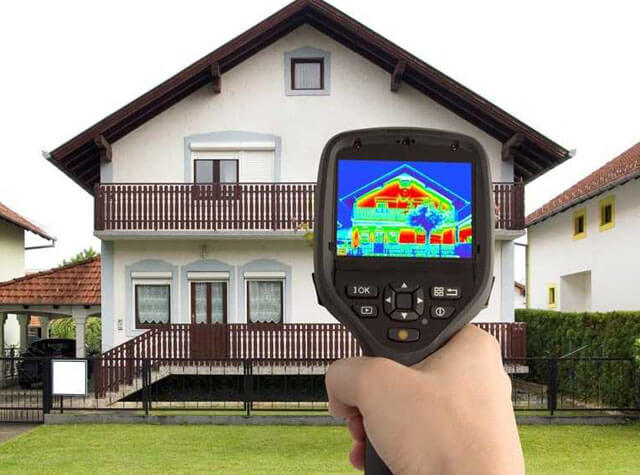


There is another way to find out the heat loss. You can clearly see the amount of heat lost by a building or room using a device such as a thermal imager. It is small in size and the actual heat losses are visible on its screen. At the same time, it is possible to find out in which zones the outflow is the largest and take measures to eliminate it.
Often, real estate owners are interested in whether it is necessary for an apartment or for a private house when calculating a solid fuel boiler or other type of heating unit to do this with a margin. According to experts, the daily work of such equipment at the limit of its capabilities negatively affects the duration of its service.
Therefore, you should purchase a device with a performance margin, which should be 15 - 20% of the design power - it will be enough to provide conditions for operation.


At the same time, the selection of a boiler by power with a significant margin is economically unprofitable, since the greater this characteristic of the device, the more expensive it is. In this case, the difference is significant. For this reason, if an increase in the heated area is not planned, it is not worth purchasing a unit with a large power reserve.
Quick selection of pipe diameters according to the table
For houses up to 250 sq.m. provided that there is a pump of 6 and radiator thermal valves, you can not do a full hydraulic calculation. You can select the diameters from the table below. In short sections, the power can be slightly exceeded. Calculations were made for a coolant Δt = 10oC and v = 0.5m / s.
| Trumpet | Radiator power, kW |
| Pipe 14x2 mm | 1.6 |
| Pipe 16x2 mm | 2,4 |
| Pipe 16x2.2 mm | 2,2 |
| Pipe 18x2 mm | 3,23 |
| Pipe 20x2 mm | 4,2 |
| Pipe 20x2.8 mm | 3,4 |
| Pipe 25x3.5 mm | 5,3 |
| Pipe 26х3 mm | 6,6 |
| Pipe 32х3 mm | 11,1 |
| Pipe 32x4.4 mm | 8,9 |
| Pipe 40x5.5 mm | 13,8 |
Discuss this article, leave feedback on Google+ | Vkontakte | Facebook
Accounting for the region where the house is located
Heating housing located in the south of the country will require less heat energy than those located to the north. Correction factors are also used to account for the region.
Their value has a range, since weather conditions differ somewhat within the same climatic zone. If the house is built closer to its northern border, they take a larger coefficient, and if to the southern borders, a smaller one. The absence or presence of a strong wind load must also be taken into account.
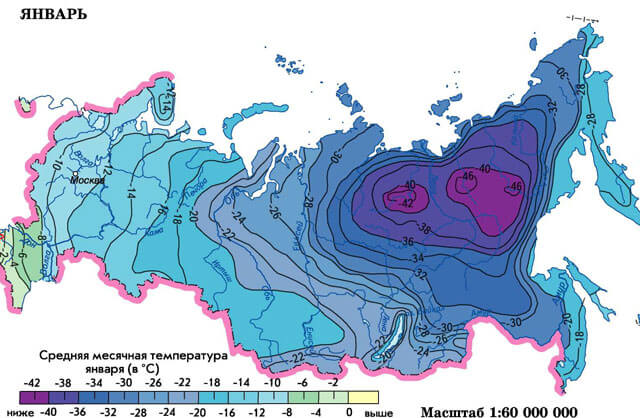

In Russia, the middle band is taken as a standard, for which the size of the amendment is 1 - 1.1, but when approaching the northern border, the power of the unit is increased. For the Moscow region, the result of calculating the power of the boiler room is multiplied by a factor of 1.2 - 1.5. As for the northern regions, then for them the result is adjusted for an amendment equal to 1.5-2.0. For the southern zones, reduction factors of 0.7 - 0.9 are used.
For example, a house is located in the north of the Moscow region, then 18 kW is multiplied by 1.5 and you get 27 kW.
If we compare 27 kW with the initial result, when the power was 14 kW, then you can see that this parameter has almost doubled.
Expansion tank of an open heating system calculation and installation rules
Expansion tanks are used in all schemes of individual heating systems. The main purpose of the expansion tank is to compensate for the volume of the heating system caused by the thermal expansion of the coolant.
Features of the tank of an open heating system
The fact is that the volume of the coolant increases with increasing pressure, and if no additional capacity is provided where the excess volume could fit, then the pressure in the heating system can increase by so much that a breakthrough occurs. To eliminate the overpressure of the system, an expansion tank is used.
In addition, the expansion tank of an open heating system is different from tanks intended for closed systems. Closed systems use non-vented tanks. In an open system, the use of such a tank is impossible, since the excess pressure in the tank will create a large resistance to the circulation of the coolant. Therefore, open tanks are used for open heating systems.
Hence, there is a big drawback of open heating systems - this is the evaporation of the coolant from the tank. As a result, it is periodically necessary to control the level of the coolant in the tank and, if necessary, replenish the losses.
In addition, for open heating systems, it is important not only that the tank can communicate with the atmosphere, but also the correct calculation of the tank volume and proper installation and connection to the heating system
Calculation of the volume of an open expansion tank
Traditionally, the volume of an expansion tank is defined as 5% of the volume of the entire heating system. This is due to the fact that when the water temperature rises to 80 degrees, its volume increases by approximately 4%. Adding to this a small space so that water does not overflow over the edges of the tank for another 1%, in total we obtain the volume of the expansion tank as a percentage of the volume of the entire heating system.
If a different coolant is used in an open system, then the volume of the tank should be adjusted based on the thermal expansion of the applied coolant.
Most of the difficulties arise with calculating the volume of the coolant in the heating system. To calculate the volume of the system, it is necessary to sum up the internal volume of all elements of the radiator, heating and boiler piping system.The volume of the system can also be determined indirectly by the power of the boiler, based on the fact that 1 kW of boiler power is needed to heat 15 liters of coolant.
Installation and connection of an open expansion tank
Unlike a closed expansion tank, there are certain rules for an open one.
The most important rule is that the tank should be located above the entire heating system. Otherwise, according to the principle of communicating vessels, water will flow out of it.
This circumstance often leads to the refusal of the device of an open-type heating system, tk. it is not always possible to conveniently install the expansion tank.
The second important feature is that the tank must be connected to the return line. The fact is that on the return line the water temperature is lower, and, therefore, the water will evaporate more slowly.
In addition, given the low return water temperature, the expansion tank can be connected to the system using a transparent hose, which makes it easier to control the amount of water in the system.
Additionally, the expansion tank can be provided with special branch pipes to prevent overflow and control the water level in the tank.
Open and closed heating systems
Open tanks are used for heating systems where the coolant circulates by gravity. The container is usually cylindrical or rectangular with an open top, the connection to the heating system is through an outlet at the bottom.
There are many more disadvantages of using open tanks:
- requires regular maintenance;
- heat loss in the system is quite high;
- the inner walls of the tank are corroded;
- during installation, additional pipe laying is required;
- installation is carried out in the attic, which requires additional reinforcement of the floors due to the large weight of the tank.
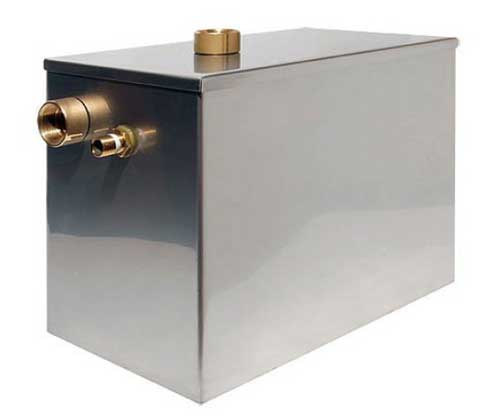


An example of an open-type stainless steel expansion tank
Closed tanks can be used for any heating system, but they are usually required for forced heating. The tank is closed, that is, contact between the coolant and the ambient air is excluded. In addition, sealed tanks can be equipped with automatic or manual valves, pressure gauges to measure the pressure in the system.
The advantages of such equipment are many:
- the tank can be installed in a boiler room, it does not require frost protection;
- the pressure level in the system can be quite high;
- the tank is more protected from corrosion, its service life is long;
- the coolant does not evaporate;
- there is no heat loss;
- maintenance of the system is simpler, there is no need to monitor the pressure, water level.
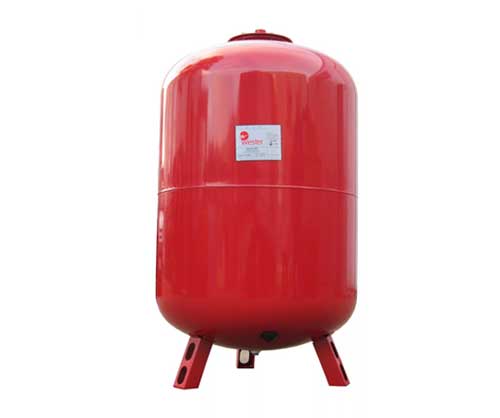


Closed expansion tank WESTER
Closed diaphragm tank
For the membrane system, a sealed tank is used, the functioning of which is similar to a conventional closed one. The principle of operation is very simple - when heated, the coolant expands, "excess" water enters one compartment of the tank, putting pressure on the elastic membrane. When cooling down, the pressure decreases, the air from the second container pushes cool water back into the system, that is, it circulates.
The membrane can be removable or non-removable, it does not come into contact with the inner walls of the device. If the diaphragm is damaged, it must be replaced as the tank stops functioning.
Among the advantages of using such equipment, it should be noted:
- compact size of the tank;
- the coolant does not evaporate;
- the heat loss of the system is minimal;
- the system is protected against corrosion;
- it is possible to work with high pressure without fear of damaging the system.
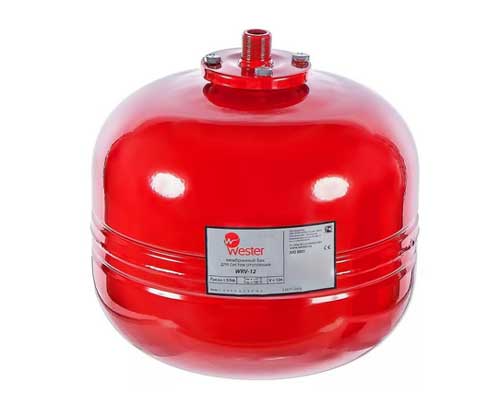


Diaphragm expansion tank