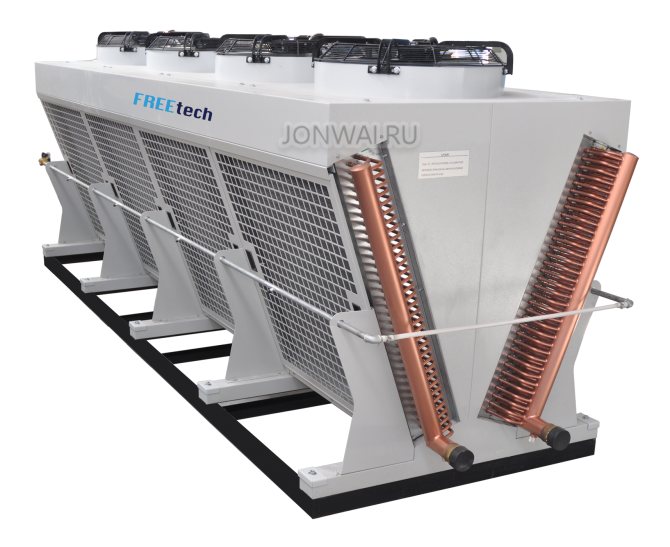
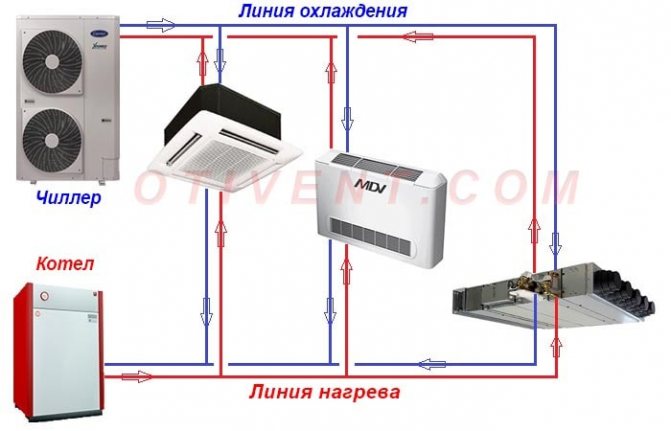
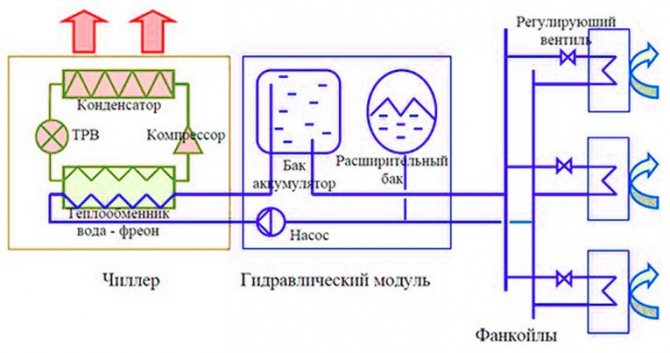
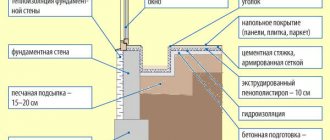
A chiller is a type of refrigeration unit that is used for air conditioning in large rooms. Chillers act as central air conditioners. But if in air conditioners freon directly cools the air, then with chillers everything is somewhat different.
The chiller cools the filling water or non-freezing liquids. Here, thermal energy is transported using ordinary water. To prevent it from freezing, an antifreeze mixture can be used.
This type of climatic equipment is a rather massive structure. The chiller cooler consists of three parts:
- capacitor;
- compressor;
- evaporator.
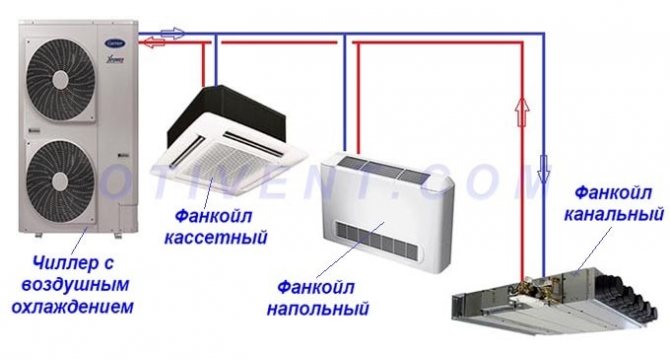
At the moment, the chiller-fan coil system has become widespread. This is a modern air conditioning system that makes it possible to establish and regulate the microclimate in several separate rooms at once. The operation of the system is as follows: the chiller cools (heats up) the coolant, then feeds it to the fan coil through a special pipeline. Thus, the chiller is able not only to cool, but also to heat the room.
The main components of the chiller-fan coil system are similar to the air conditioner device, - the outdoor unit (chiller), the indoor unit (fan coil) and the refrigerant pipelines connecting them, but water flows through the pipes instead of freon, and there may be several indoor units, it depends on cooling capacity of the chiller.
Chiller and its differences from a fan coil unit
The term chiller comes from the English chiller, which literally means "cooling machine". Where and how is this unit used? Almost everywhere. It cools the filling water or non-freezing liquids. The installation is essential for industries such as mechanical engineering, metalworking, food processing, winemaking and others, as well as where air conditioning systems operate.
This type of climatic equipment is a rather bulky apparatus. The chiller cooler, both domestic and industrial, consists of three parts:
- capacitor;
- compressor;
- evaporator.

Summary
Euler circles are a very useful technique for solving problems and establishing logical connections, and at the same time an entertaining and interesting way to spend time and train your brain. So, if you want to combine business with pleasure and work your head, we suggest taking our Neurobics course, which includes a variety of tasks, including Euler's circles, the effectiveness of which is scientifically substantiated and confirmed by many years of practice.
We also advise you to read:
- Eugenics: in simple words about the most important
- How to Switch to Creativity: Right Brain Workout by Betty Edwards
- Golden ratio
- 7 popular pseudosciences
- Learn to Learn: Some Tips from Coursera's LH2L Course
- Mathematical thinking
- Cognitive development. Part 1
- TRIZ exercises in pedagogy
- Logical paradoxes
- Solving non-standard Fermi problems
Keywords: 1Cognitive science
Principle of operation
The principle of operation is to convert the energy of the cooled liquid into a vapor state. The heat from the liquid is taken off in the evaporator and in the vapor state it is transferred to the compressor. Then it goes to the chiller motor, cooling its winding. The refrigerant is then cooled in the condenser by air currents, converted to liquid and returned to the evaporator. The cycle is repeated anew.


Finding an Euler cycle in a graph
Fleury's algorithm
Main source: M. Fleury.
Deux problèmes de Géométrie de situation (French) // Journal de mathématiques élémentaires. - Paris: C. Delagrave, 1883. - Vol. 2, livr. 2nd ser .. - P.257-261.
The algorithm was proposed by Fleury in 1883.
Consider a graph G = (V, E) {\ displaystyle G = (V, E)}. We start from some vertex p ∈ V {\ displaystyle p \ in V} and each time we cross out the passed edge. We do not go along an edge if the removal of this edge leads to a partition of the graph into two connected components (not counting isolated vertices), i.e. it is necessary to check whether the edge is a bridge or not.
This algorithm is ineffective: the running time of the original algorithm O
(|
E
| 2). Using a more efficient bridge search algorithm [4], the execution time can be reduced to O (| E | (log | E |) 3 log log | E |) {\ displaystyle O (| E | (\ log | E |) ^ {3} \ log \ log | E |)}, however this is still slower than other algorithms.
The algorithm can be extended to directed graphs.
Loop Based Algorithm
We will consider the most general case - the case of an oriented multigraph, possibly with loops. We also assume that there is an Euler cycle in the graph (and consists of at least one vertex). To find the Euler cycle, we will use the fact that the Euler cycle is the union of all simple cycles of the graph. Therefore, our task is to efficiently find all the cycles and effectively combine them into one.
This can be implemented, for example, recursively:
procedure find_all_cycles (v) var array cycles 1. while there is a cycle passing through v, we find it add all the vertices of the found cycle to the cycles array (keeping the traversal order) remove the cycle from the graph 2. go through the elements of the cycles array each element of cycles
add to the response from each element and recursively call ourselves: find_all_cycles (cycles)
It is enough to call this procedure from any vertex of the graph, and it will find all the cycles in the graph, remove them from the graph and combine them into one Euler cycle.
To find the loop in step 1, we use depth-first search.
The complexity of the obtained algorithm is (M), that is, linear with respect to the number of edges M in this graph.
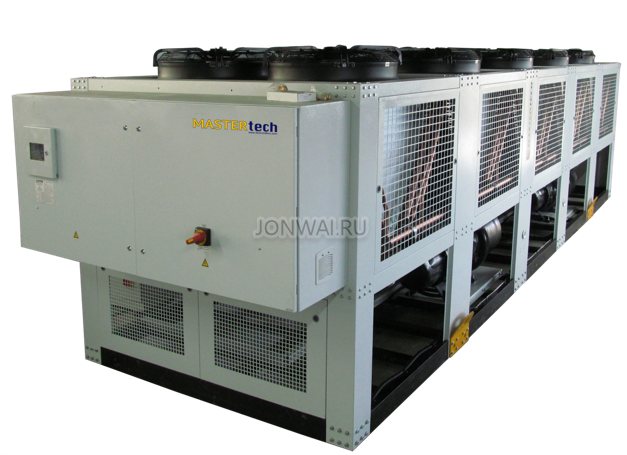
Chiller types
Industrial chillers come in different types. They can be classified into four groups according to different criteria.
- By the type of cooler.
- Fan type.
- By the way of cooling.
- According to the features that the chiller design has.
Chillers are air-cooled or water-cooled. An air cooler is similar in principle to a conventional air conditioner, where a fan blows a stream to air-cool the condenser. In a cooler where water is cooled, the design is simpler, the unit itself is smaller and lower in cost than air. But the air one is self-sufficient and works autonomously, and the water one requires the supply of water from the outside using a special additional installation.
What is the second wonderful limit
The Swiss mathematician Jacob Bernoulli (1655–1705) derived the number e when he was trying to solve a financial question. In particular, he tried to understand how interest should be calculated on the amount of the deposit in the bank so that it would be most profitable for the owner of the money.
He also tried to figure out if there is a limit on the income earned as a percentage, or if it will increase indefinitely.
In solving this problem, he used the sequence limit, namely the second remarkable limit. The formula for calculating the number e can be written as follows (where n is a number tending to infinity):
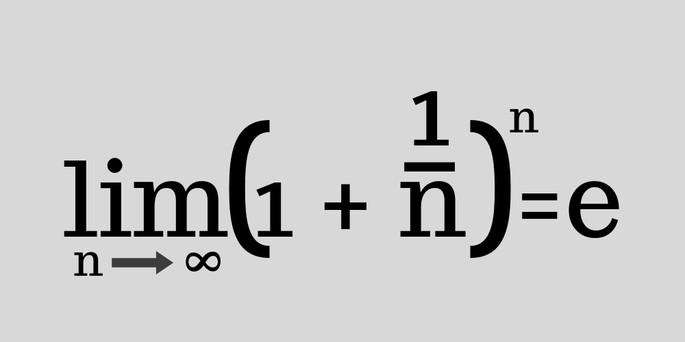
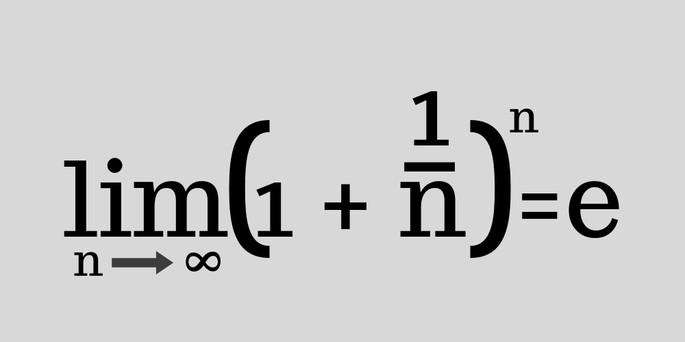
Second wonderful limit
That is, the number e is equal to the limit, where n tends to infinity, from 1, plus 1, divided by n, and raise everything to the power n.
If you substitute some very large number in this formula instead of n, you can get a very good approximation to e. For example, substitute 1.000.000 and calculate on the calculator:
(1 + 1/1000000) ^ 1000000 = 2.7182804691
As you can see, with n = 1.000.000 we got a pretty good approximation, with the correct 5 decimal places.
Chiller characteristics
The main characteristic of a cooling machine is its capacity. It can vary between 5 kW - 9000 kW.Low-power ones are suitable for offices, more powerful ones are used in industry and manufacturing.
Other characteristics
| Characteristic | The values |
| Model | Depends on the manufacturer |
| Cooling capacity | Measured in kW, it can be from 10 to several thousand |
| Rated power | Also measured in kW, has values in the range from 30 to 200 |
| Dimensions (edit) | From 500 to 4000 mm in width, length and height |
| Weight | 100 to 2000 kg |
| Compressor, evaporator, condenser type and body color | Depends on the manufacturer |
A typical example of Euler circles
To better understand how the Euler circles "work", we recommend that you familiarize yourself with a typical example. Pay attention to the following figure:
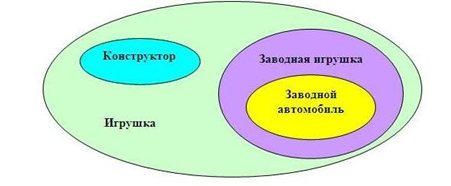

In the figure, the largest set is marked in green, representing all the options for toys. One of them is constructors (blue oval). Constructors are a separate set in and of themselves, but at the same time, they are part of the overall set of toys.
Clockwork toys (purple oval) also belong to the set of toys, but they have nothing to do with the set of the constructor. But a clockwork car (yellow oval), even if it is an independent phenomenon, is considered one of the subsets of clockwork toys.
A similar scheme is used to construct and solve many tasks (including tasks for the development of cognitive abilities) that involve Euler's circles. Let's take a look at one such problem (by the way, it was this one that was included in the demo test of the Unified State Exam in Informatics and ICT in 2011).
Chiller capacity
Power and efficiency are not only the number of kW, but the aggregate in the sum of various terms. When calculating the capacity of the chiller, the following indicators are taken into account:
- Heat entering windows through fences.
- Heat from people in the room.
- Heat energy generated by lighting and other equipment.
All heat inflows are summed up, and thus the total heat load that the room is carrying is determined. Then the loads of all rooms served by the chiller are summed up.
Since the cooling process is accompanied by the release of condensate, and the moisture content of the air changes, the power is calculated according to a special formula, providing up to 20% of the power reserve.


How to determine the number e?
Besides the second remarkable limit, there are other ways to determine the number e:
- through the sum of the series;
- through the Moivre-Stirling formula;
- others.
The sum of the series
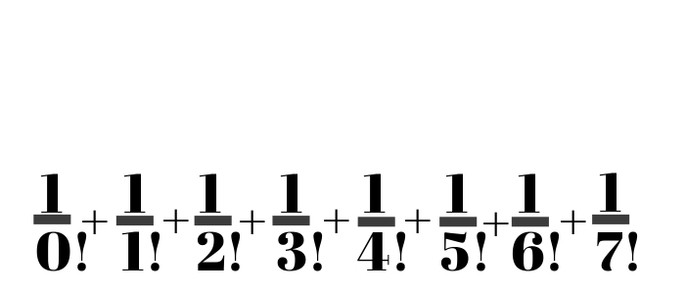
It is believed that this method was used by Euler himself when he calculated e.
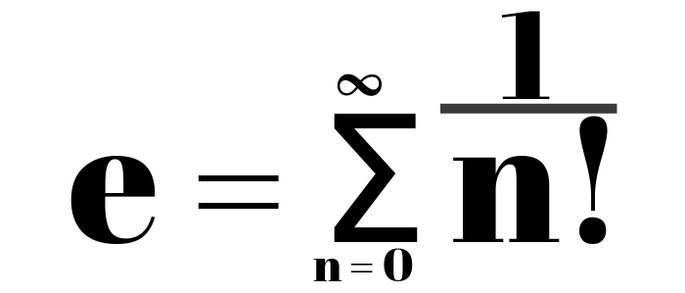
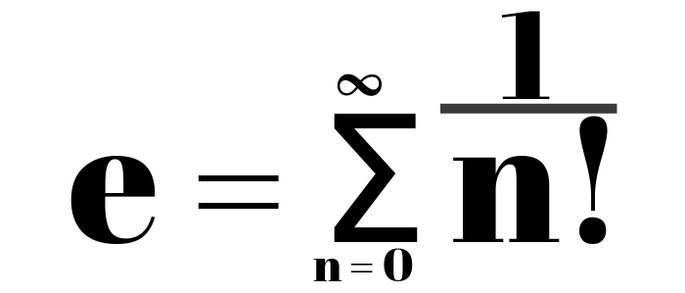
You can get an approximation of e by calculating the first 7 parts of this sum:

And these calculations gave us the following result:
This method gave us exactly 4 decimal places and is fairly easy to remember.
Moivre - Stirling formula
Also called simply Stirling's formula:
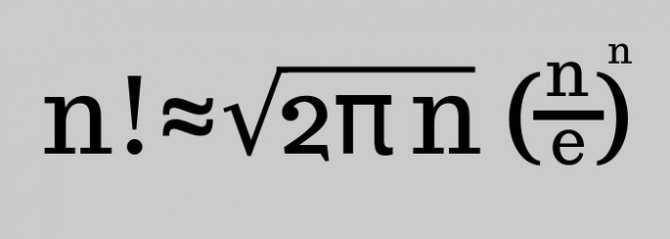
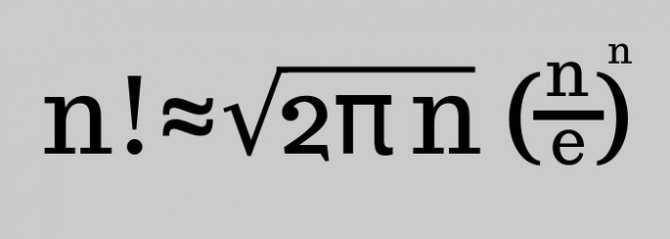
And in this case, the larger n, the more accurate the result will be.
Chiller cost
The cost of a refrigeration unit is made up of several parameters. The price is influenced by both technical indicators and the name of the manufacturer's brand. Also taken into account:
- additional power steps;
- complete set of pipes for connecting the unit with fan coil units;
- The material from which the pipes are made (metal or plastic);
- axial fan configuration (standard or modified blade configuration);
- > additions in the form of drainage, heated trays and others.
After evaluating all the parameters of the room, calculating the required power according to the formula, you can choose the best option for the chiller, not only in terms of performance, but also at the price, which includes the cost of maintenance.
Interesting Facts
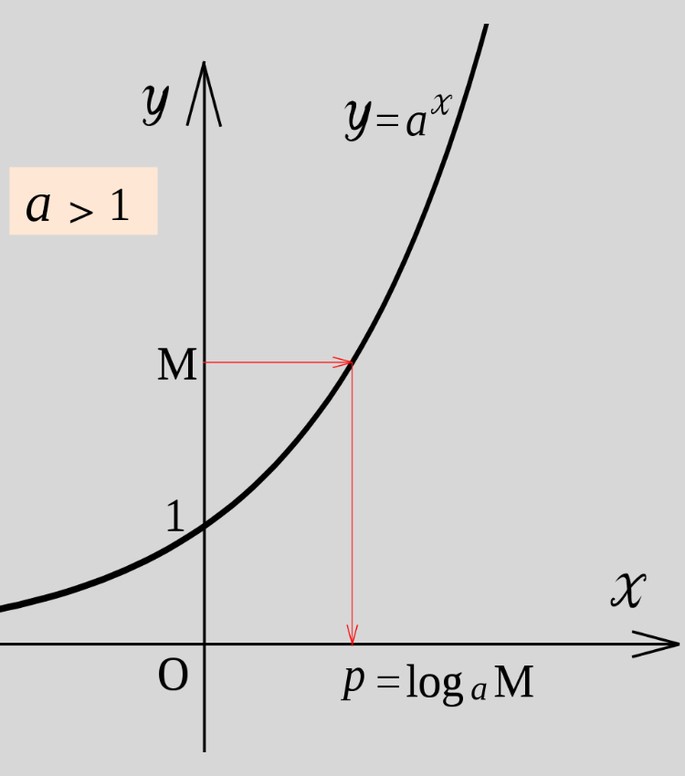
The exponential function is also called the exponential function.
The exponential function is a function of the form y = a ×, where a is a given number (base), x is a variable.
And if base = e, with variable x, then mathematically, the logarithm is written as ln, not as log.And it's called the natural logarithm (base e logarithm):
The logarithmic function that is inverse to the exponential function y = a ×, a> 0, a ≠ 1, is written as.
The derivative and antiderivative of an exponential function are equal to itself, i.e. (e ×) ’= e ×, but (a ×)’ = (a ×) * ln (a).
Jacob Bernoulli was assisted in the calculations by his brother Johann. One of the craters on the moon bears their name.
The nuances of choosing a chiller
Tip 1. If you are going to place the cooler indoors, do not forget to measure the width of the doorway beforehand. It often happens that the purchased unit simply does not fit into the door, which becomes a serious problem for its installation.
Advice 2. It is necessary to ensure sufficient air exchange in the installation room, which corresponds to the parameters and characteristics of the unit producing free cooling.
Advice 3. If the chiller is installed outdoors, on the street, be sure to consider the following issues:
- protection of the unit from external influences and vandalism;
- the possibility of using anti-freezing liquids.
Advice 4. Before buying, even at the selection stage, you need to accurately determine the flow rate of the cooled water (liquid) in order to calculate the pressure required for its cooling.
Tip 5. When choosing an installation filled with antifreeze liquid, you need to calculate the capacity of the water-cooling evaporator.
Existence of the Euler cycle and the Euler path
In an undirected graph
According to the theorem proved by Euler, an Euler cycle exists if and only if the graph is connected or will be connected if all isolated vertices are removed from it, and there are no vertices of odd degree in it.
An Euler path in a graph exists if and only if the graph is connected and contains at most two vertices of odd degree. [1] [2] Due to the handshake lemma, the number of vertices with an odd degree must be even. This means that the Euler path exists only when this number is zero or two. Moreover, when it is equal to zero, the Euler path degenerates into an Euler cycle.
In a directed graph
A directed graph G = (V, A) {\ displaystyle G = (V, A)} contains an Euler cycle if and only if it is strongly connected or among its strongly connected components only one contains edges (and all the others are isolated vertices) and for each vertex of the graph, its inward degree indeg (⋅) {\ displaystyle \ mathrm {indeg} (\ cdot)} is equal to its outdeg (⋅) {\ displaystyle \ mathrm {outdeg} (\ cdot)}, that is, in a vertex enters as many edges as it leaves: indeg (v) = outdeg (v) ∀ v ∈ V {\ displaystyle \ mathrm {indeg} (v) = \ mathrm {outdeg} (v) \ quad \ forall v \ in V}.
Since the Euler cycle is a special case of the Euler path, it is obvious that the directed graph G = (V, A) {\ displaystyle G = (V, A)} contains an Euler path if and only if it contains either an Euler cycle or an Euler a path that is not a cycle. A directed graph G = (V, A) {\ displaystyle G = (V, A)} contains a non-cycle Euler path if and only if there are two vertices p ∈ V {\ displaystyle p \ in V} and q ∈ V {\ displaystyle q \ in V} (the initial and final vertices of the path, respectively) such that their half-degrees of entry and half-degrees of exit are related by the equalities indeg (q) = outdeg (q) + 1 {\ displaystyle \ mathrm {indeg} (q ) = \ mathrm {outdeg} (q) +1} and indeg (p) = outdeg (p) - 1 {\ displaystyle \ mathrm {indeg} (p) = \ mathrm {outdeg} (p) -1} and all other vertices have the same half-degree of outcome and approach: outdeg (v) = indeg (v) ∀ v ∈ V ∖ {p, q} {\ displaystyle \ mathrm {outdeg} (v) = \ mathrm {indeg} (v) \ quad \ forall v \ in V \ setminus \ {p, q \}} [3].
Question answer
Question:
What do chillers work on?
Answer:
The main working medium of the chiller is the refrigerant. Freon is most often used as a refrigerant. It circulates along the circuit of the device and evaporates in the heat exchanger due to the heat received from the cooled liquid. Cold transfer is carried out using a coolant (water, ethylene glycol).
Refrigerant circulation is provided by a compressor, the smooth operation of which depends on many factors. Thus, the operation of the chiller is impossible without refrigerant and refrigerant.
Question:
What is better freecooler (cooling tower) or chiller?
Answer:
The freecooler provides cooling of water or other refrigerant in the radiator to the level of heat in the ambient air. For this, fans are used. Freecooling technology does not include a compressor module. Thanks to this feature, they consume much less electricity than chillers.
Disadvantages of freecoolers: the impossibility of their full use in hot weather, since the cooling occurs to the air temperature level. Freecoolers can be easily integrated into existing air conditioning units, so they can be conveniently used in combination with chillers that operate independently of the outside temperature.
Question:
Which chillers are better water or air chillers?
Answer:
By the type of condenser cooling, chillers can be water or air. Devices that use water for these purposes are suitable for operation throughout the year. They are more compact, can be installed inside a building, but they are much more expensive than equipment where the temperature is reduced by a directed air flow.
Air installations are offered at a low price, but their installation requires vast areas to accommodate all units and modules. For example, the cooling system is often installed outdoors. This allows more rational use of space inside the building, but reduces the functionality of such equipment.
Question:
What is the difference between chillers with and without a heat pump?
Answer:
Devices in which a heat pump is installed can not only cool, but can also heat the surrounding space or provide hot water. This useful function allows such installations to be used for heating large public or industrial premises. Equipping with a heat pump increases the cost of the equipment, but significantly expands its functionality.
Question:
What is the principle of operation of absorption chillers?
Answer:
Absorbed devices use waste heat in factories as the main energy. In such systems, the main working substance contains several components. The solution consists of an absorbent and a refrigerant. The absorber is lithium bromide, and the refrigerant is water. It enters the low pressure evaporator, from where it leaves cooled and absorbed by lithium bromide. The liquid is concentrated in a condenser and then the refrigerant is piped to the end users. Absorbed chillers do not have a compressor module and therefore consume a minimum of electricity.
Question:
What is the cost of modern chillers?
Answer:
The cost of modern chillers depends on their design features and power. These are industrial air conditioning systems that are designed to service large industrial or public buildings, so the price of new units starts at 100 thousand rubles. The cheapest are low-power mini chillers, and the most expensive ones have an output power measured in thousands of kW, and their cost is several million rubles. Many suppliers, upon request of the customer, provide a cost estimate after specifying the main required characteristics and functions.
Important equipment features
The refrigeration unit, which is designed to heat and cool heat transfer fluids in the main air conditioning system, is called a chiller. Heat carriers can be fan coil units or supply-type mechanisms.
The service life of a chiller is highly dependent on the technical characteristics of the product. It is also of great importance whether the rules for the operation of this equipment are followed.
The main features of the chiller include the following.
- This system is flexible. In it, the distance between the fan coil units and the chiller is limited only by the pump power and can be hundreds of meters.
- Thanks to this equipment, you will be able to save money.
- The equipment can be used at any time of the year.
- It is possible to automatically maintain the set parameters in each room.
- By using shut-off valves, the risk of flooding is minimized.
- The equipment makes almost no noise during operation.
- The refrigerant is safe and environmentally friendly.
- Construction pluses - flexibility of planning, small expenses of usable area for equipment placement.
The choice of a chiller should be approached with all responsibility. In order not to be mistaken, it is important to know what types of chillers exist, as well as what the device and basic principles of operation of such installations are.
The chiller device is somewhat different from that of a conventional refrigerator or air conditioning system. The chiller does not lower the air temperature. It lowers the temperature of the substances used to move the cold. This equipment can cool, for example, glycol solution or water. Then the liquid goes where the cold is needed.
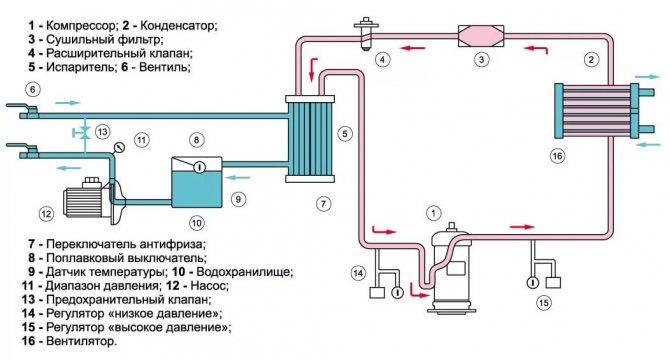
The chiller has the following functional elements:
- air condenser;
- storage capacity;
- high and low pressure switches;
- compressor mechanism;
- plate heat exchanger;
- pressure gauges for liquid;
- filter drier;
- thermostatic valve;
- flow switch;
- pump;
- receiver.
The exact set of components depends on the hardware modification.
Pros and cons of SCR with door closers
The obvious advantage of air conditioning with fan coil units is the precise maintenance of the desired temperature in different rooms. Multi-zone systems allow very wide regulation of microclimate parameters within one building. Other pluses compared to conventional air conditioners:
- the cost of equipment for 2-3 rooms will be clearly less than the price of a multi-split system of identical power;
- sources of heat and cold are located in a technical room or on the street, outdoor units do not clutter up the facade;
- fan coil units can be installed 50… 200 meters from the chiller;
- communications between the units are made of inexpensive plastic pipes - low pressure polyethylene or polypropylene (the latter must be soldered);
- in the event of an accident and leakage, it is easier to make repairs, replenish the system with purified water.
Do not think that the chiller-fan coil type SCR is applicable only in industrial buildings. Daikin, Carrier and Gree brands produce small two-fan chillers with a capacity of 3 ... 10 kW, which are quite suitable for private houses.
Disadvantages of fan coil units:
- SLE for 2 rooms is still more expensive than two separate split systems;
- decent size and weight of the chiller unit;
- qualified installation and start-up of equipment is required;
- the equipment will have to be serviced, the masters will be called in every year.


On an industrial scale, the main competitors of water SCR are freon VRF systems operating on the "split" principle. Up to 50 indoor units can be connected to the external vapor compression module only. The cost of the equipment is about the same, but fan coil units benefit from the ease of laying highways and the lower price of plastic pipes compared to copper ones. A separate story is the leakage of freon from a huge system, which is not easy to find and eliminate.
Chiller heat exchanger freon-water
The heat exchanger for the chiller is designed in such a way that there are two circuits inside it:
- Freon circulates in the first circuit;
- In the second, a liquid (for example, water).
Both circuits of the heat exchanger are in contact with each other through the metal walls, but freon and water, of course, do not mix with each other. For greater efficiency, movement occurs towards each other.


In the freon-water heat exchanger, the following occurs:
- Liquid freon through the expansion valve (thermostatic expansion valve) enters its own heat exchanger circuit. In the process, it expands, as a result, heat is removed from the walls, cooling them and heating freon.
- Water passes along its own heat exchanger circuit and its temperature drops due to the cooled walls, which were cooled by freon.
- Further, freon is carried away to the compressor, and cold water - for its intended purpose (for cooling something).
- The cycle repeats itself.
Fan coil design
The English name of the fan coil apparatus literally means "coil fan" and indicates a structural similarity with the long-known AVO heaters (air heating units). In appearance and device, fan coils also resemble the internal blocks of a split system, only instead of freon, water or an anti-freeze liquid is used.


On the left in the photo is the internal module of the split system, on the right is the AVO heating unit
A fan coil unit consists of the following elements:
- a body equipped with air grilles or nozzles;
- heat exchanger - copper tube coil with numerous plates;
- fan, usually centrifugal;
- coarse air filter;
- solenoid valve - regulator of the fluid flow through the heat exchange radiator;
- manual air release valve;
- electronic control board.
A condensate collection tank is installed under the heat exchanger. The latter is discharged through a tube to the street or to a sewer receiver. If the unit is installed at a considerable distance from the discharge point, the condensate is pumped over by a drain pump.
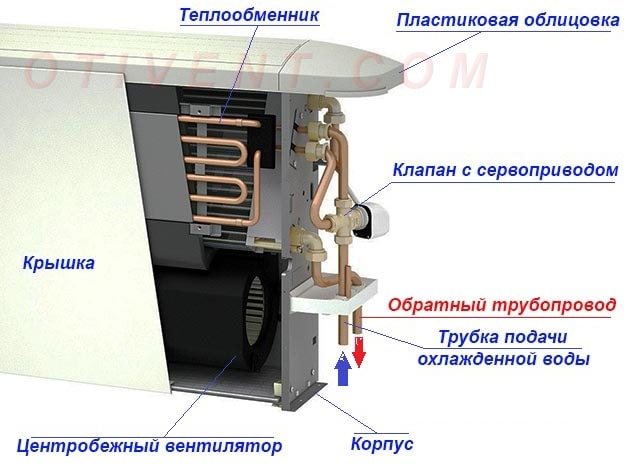

Console fan coil device - sectional diagram