Classification of heat supply systems

In science, there are many options for systematizing communications, depending on the parameter under study. For us, first of all, it is important that there is an open and closed heat supply system. It can also be centralized (within a quarter, district, settlement or even an entire region) and decentralized (individual or local). According to the quality of water supply, systems are divided into municipal and industrial. The total number of classifications is much wider, but they do not apply to the topic under consideration.


Features of an open system
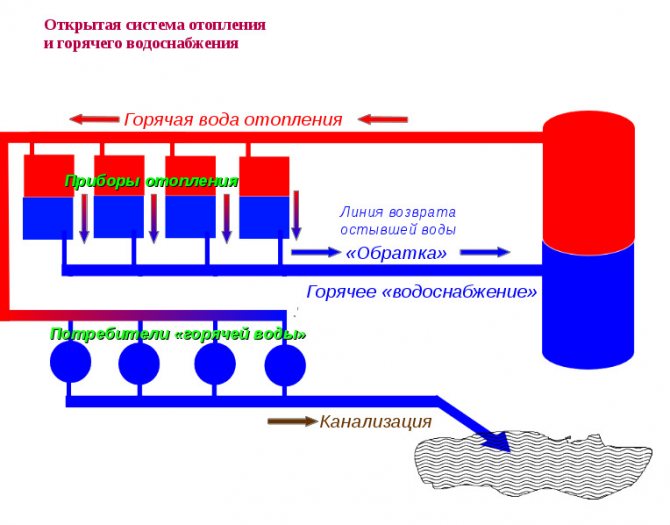
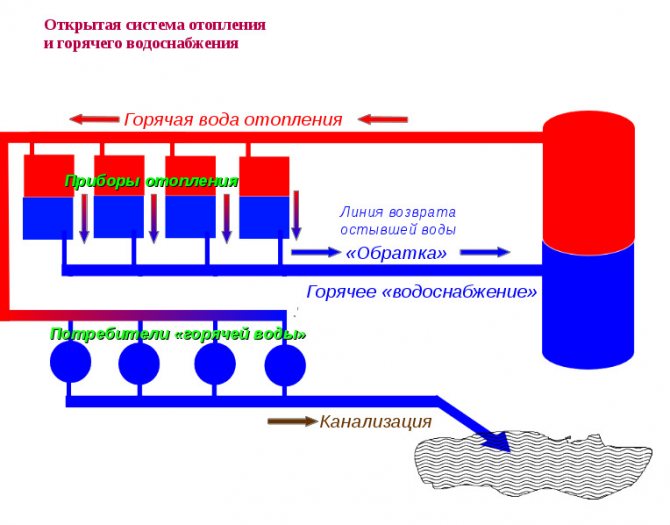
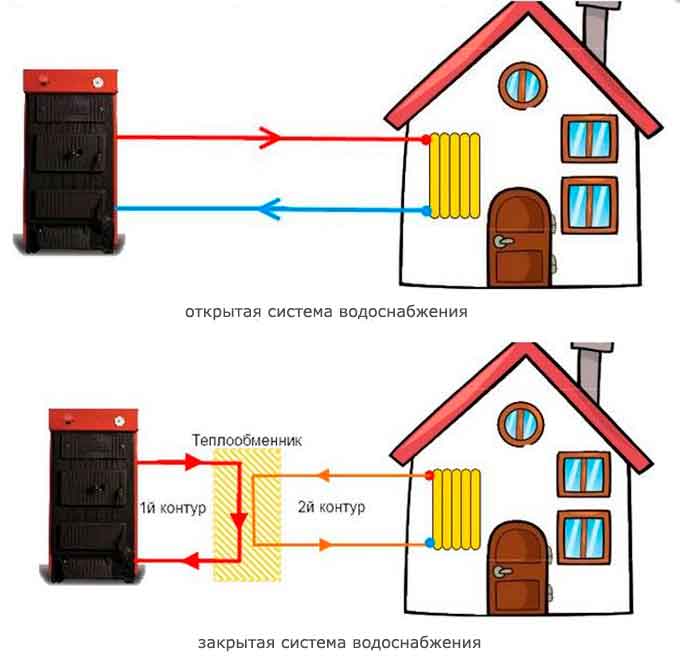
It is characterized by the circulation of the coolant obtained from the general communications. An open hot water supply system is when water enters the batteries from the DHW main pipe. From the same source from where the hot water goes to the residents' taps.
The system is based on natural circulation. Due to physical phenomena, the cooling water, acquiring a large mass, will displace the hot stream, giving it acceleration. In some cases (in large systems), the circulation is pumped by pumps.
Open type heating is usually installed in high-rise buildings. The main plus here is that there is no need for special mechanisms or devices for heating the coolant. For private households, such a system will be unnecessarily expensive, because the heating pipe will have to be connected to some high-rise building or dig a hole to dock with the highway.
Main advantages
Let's list the main advantages:
- energy independence and centralized supply;
- smooth circulation of the carrier in the system without sudden pressure surges;
- ability to work in case of emergency due to redundant DHW lines.
However, an open heating system is not ideal.
disadvantages
The main disadvantages include:
- high heat loss and, accordingly, unnecessary costs for heating water;
- dependence on the performance of large highways, in the event of an emergency, the supply of hot water supply may stop in a large number of houses;
- water quality decreases due to defects in the mains, in particular, rusty pipes;
- branched open systems require constant monitoring and careful calculations of delivery volumes, heating temperatures and pressures.
Consider an alternative.
Typical errors in connecting a heated towel rail
Bottom connection (example of incorrect design)
Side connection (example of incorrect design)
The heated towel rail is located below the lower outlet. A device connected with such a violation works until a certain height difference "lower outlet - bottom of the heated towel rail" is exceeded, then the circulation stops.
It is undesirable to lower the device below the taps for two reasons:
- The water that has cooled and sank down is trapped by the bottom of the device and the pipe (stagnant zone - from the bottom of the heated towel rail to the bottom outlet) and is poorly pushed back into the riser, since lighter hot water presses on it.
- In the resulting "holes" from the pipes, dirt from the riser will accumulate. In the future, with low water quality, you can get a clogged pipe, as well as sub-sludge corrosion, if the dirt collector falls on a metal pipe section or on the device itself.
Side connection (example of incorrect design)
Side connection (example of incorrect design)
The top tube forms a rise (above the dotted line in the illustrations), in which there is air. The circulation in the appliance stops.Theoretically, operation is possible if there is an automatic drain valve for air at the highest point of the pipe (however, they leak regularly) or a Mayevsky crane.
Side connection with offset bypass (example of incorrect design)
Lateral connection with narrowed bypass (example of incorrect design)
The performance of the side connection with an offset or narrowed bypass and bottom flow depends on the circulation rate in the riser.
At a low or normal circulation rate, the device does not work, since the pressure in the lower branch due to displacement / narrowing of the bypass is greater than in the upper one. The circulation pump tends to supply water through the lower outlet, and the "gravity pump" inside the device tends to lower the water cooling down in the heated towel rail. Mutually opposite flows inhibit each other, and the circulation stops.
We offer you to familiarize yourself with the Boiler from the pipe with your own hands
If the riser has not yet been mutilated by its neighbors, and there is a powerful circulation pump in the basement, then it happens that the pump wins, and a circular circulation starts in the device. On the left collector, hot water rises up, on the right, cooling water goes down, gradually mixing with hot water in the left collector through horizontal bridges.
The diagonal connection in this situation is no better than the side connection.
Bottom connection with narrowed bypass (example of incorrect design)
One of the most common mistakes is that it is so tempting to run pipes in the floor screed without the tedious chipping of the walls ...
A device connected with such a violation can only work with a very good circulation rate in the riser. But, as a rule, such a connection is inoperative, because the circulating pressure first needs to raise the water from the pit up into the device, and then raise the cooled and heavier water from the same pit up to the outlet of the riser.
Also, in the resulting pits, dirt from the riser will accumulate. In the future, with low water quality, pipes clogged with sludge can be obtained.
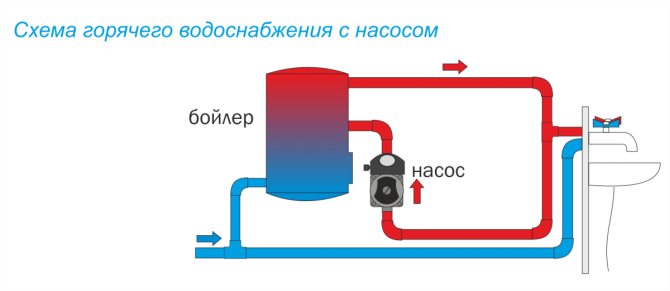
Closed DHW system
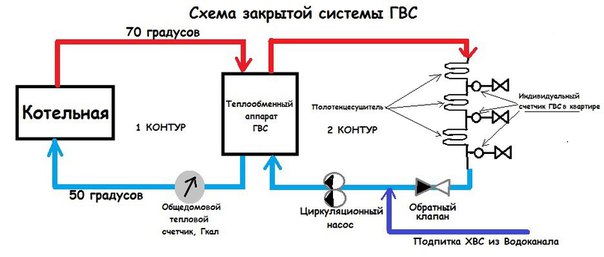

Requires own heater in the apartment. The dead-end DHW system works on the principle of taking cold water from a common pipeline, which then passes through special equipment that carries out heating. A closed hot water system is a more economical solution. The tenant will be able to independently regulate the heating temperature.
What types of heaters are there
The most common are two main options. Consider certain types of water heating equipment.
Flow devices
An example of this type is an ordinary gas water heater. The principle of operation is aimed at instantaneous heating of the water passing through the water heater. The inconvenience of working with such a device is due to the fact that it must be turned on every time you need to use hot water. In this case, the crane should work at this moment. Modern speakers turn on automatically, but the gas wick must burn constantly.
Heating devices
Storage tanks are becoming a more economical solution. Such a device is larger than a column. It contains a container in which volumes of water are accumulated and gradually heated to the desired temperature. At the same time, heating in the tank is maintained with insignificant energy consumption. The downside of the equipment is that it takes a long time to reach an acceptable temperature level. Boilers are usually powered by electricity.
A bit of history: old types of heated towel rails
Twenty years ago, a heated towel rail "from the developer" was a monolithic riser pipe bent in the form of the letters P or M.The heated towel rail served as a compensation loop and neutralized linear thermal expansion on the riser.
U- and M-shaped heated towel rail as part of the riser
New heated towel rail, which is part of the riser (correct)
Despite the unsightly appearance, this type had undeniable advantages: it was constantly hot, did not introduce any noticeable hydraulic resistance and did not allow the residents to disrupt the operation of the hot water riser in any way.
However, time passed, and tenants in the old housing stock, changed the old and ugly heated towel rail for a new and shiny one.
The installation was successful if the diameter of the heated towel rail corresponded to the diameter of the riser, and the connection was made without constrictions and shut-off valves (taps).
New heated towel rail that is part of the riser (incorrect)
Attentive readers will notice that four extra narrowings from the fittings used have appeared in the riser.
Internal section of a fitting for metal-polymer pipes


New heated towel rail, which is part of the riser (strictly prohibited)
In addition to the narrowings already mentioned above, shut-off valves have been added. When any of them are shut off in the riser, the circulation completely stops, the pressure in the apartments following the direction of supply drops, the riser quickly cools down in the absence of a draw-off, when you open the mixers, you have to drain cold water for a long time. Not the most pleasant picture, which also promises a showdown with neighbors!
It is important to remember: the installation of shut-off and control valves on risers is strictly prohibited!
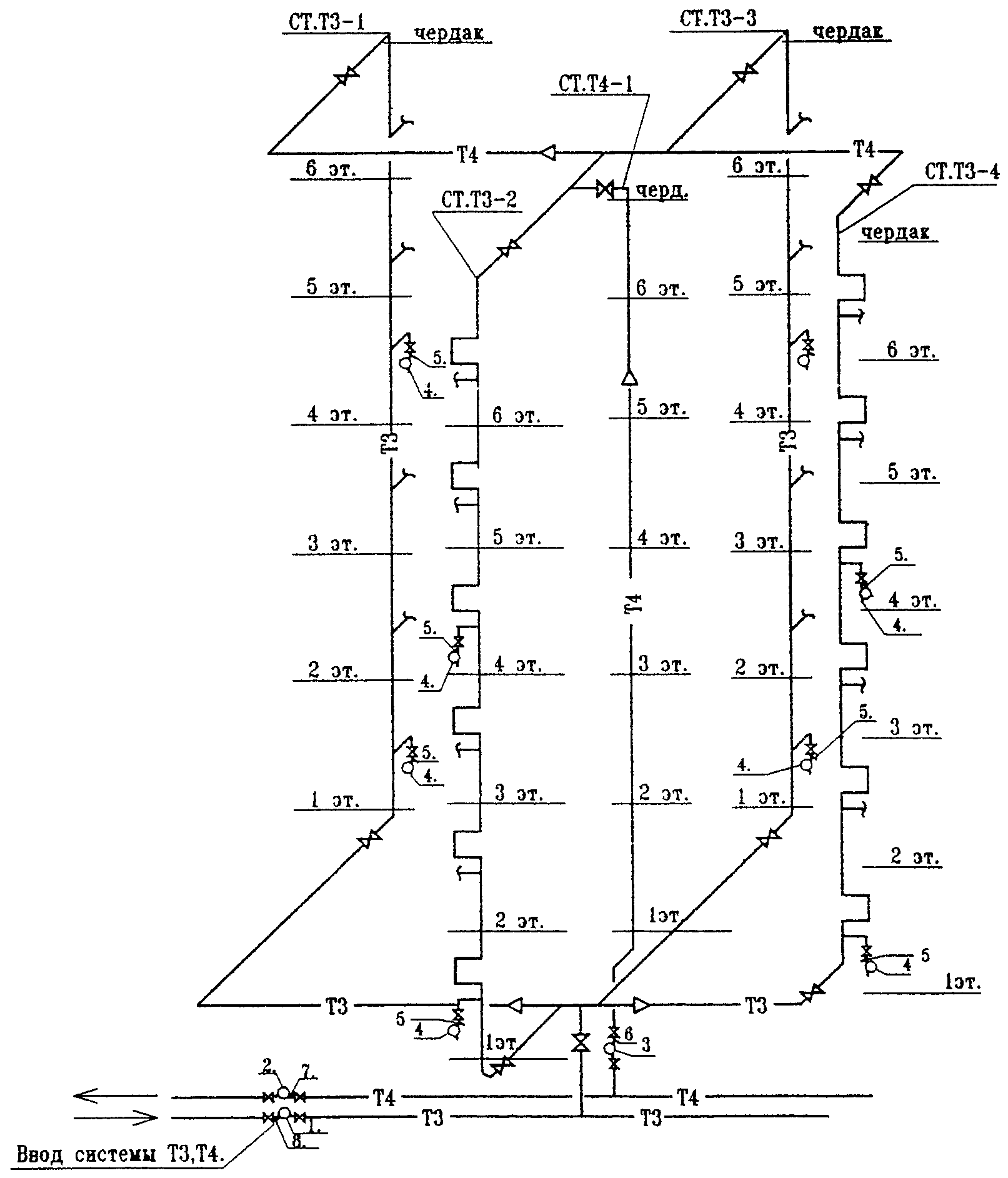
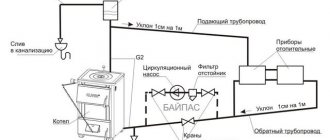
Calculation and recirculation procedure
In order for the DHW system to be designed correctly, the following must be borne in mind.
- The drawing indicates the circulation rings. They are closed at the thermal node.
- There are 2 pipelines: supply and circulation.
- On the longest section of the DHW route, zones of maximum circulating heat consumption are noted.
- The diameter of the pipes cannot be less than 1.5 cm. Moreover, they should be 1-2 sizes larger than the diameter of those in the supply section. This is done to avoid air pockets.
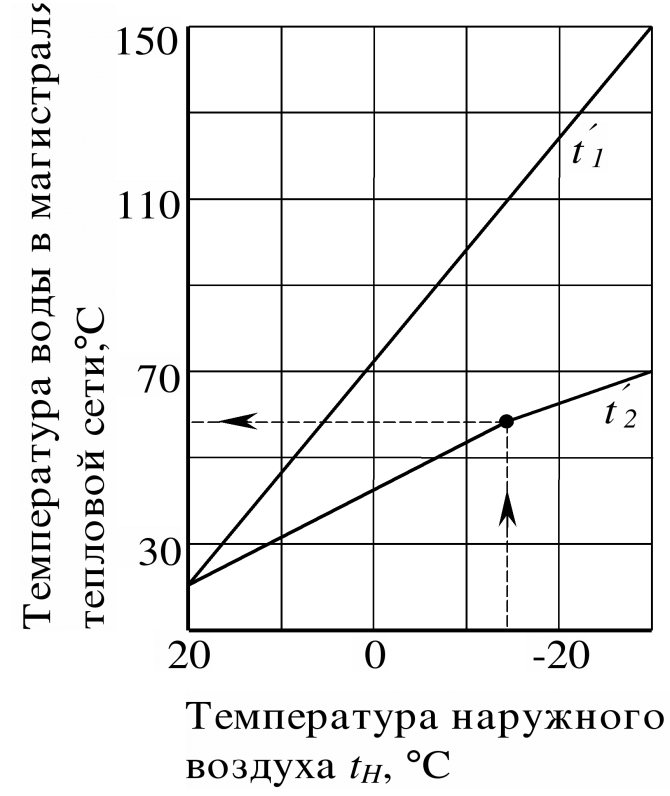
When calculating a heating installation, it must be borne in mind that an open system will be effective only with a small distance from the intake point and with frequent opening of the valve supplying boiling water. Otherwise, the consumer will receive cooled water.
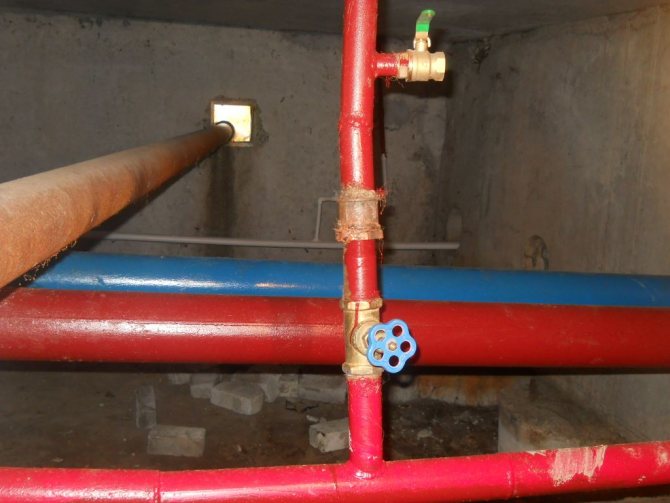
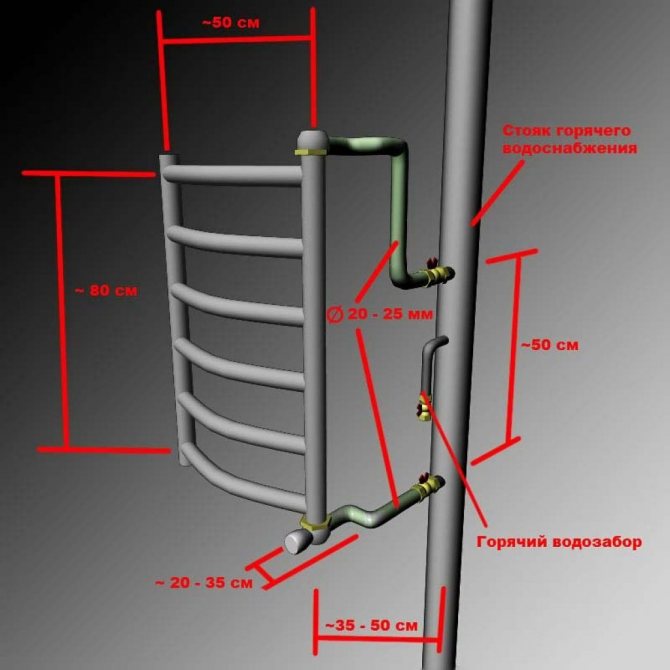
Outlets from the riser and bypass for heated towel rails
When the hot water is turned off, the heated towel rail cools down, as the circulation is disturbed, and when it is turned on again, an air lock occurs. Only a heating system fitter can fix the malfunction. If this problem applies to all apartments in a multi-storey building. Call the plumber. This is an obvious jamb of the management company.
The dead-end circuit has one hot water supply pipe without a return outlet. If the water is not used for a long time, it cools down. In order for the heated towel rail to heat up, you need to open the tap and drain the water until it is hot.
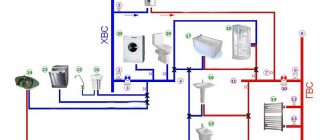
Now in multi-storey buildings they make distribution risers for hot water supply to the bathroom, to the kitchen, and to heat the towel dryer. At the bottom end, they are connected at one point with a pipe supplying hot water.
The upper ends are bridged and cut into a pipe that circulates chilled water back to the boiler. It is called the return line. With constant circulation, the water temperature in both pipes is approximately the same. With this scheme, the towel dryer can be included both in the supply pipe and in the return pipe. It will work properly if there is hot water circulation.
Over time, developers began to use more modern technologies and instead of a compensation loop, they began to make two branches from the riser to connect a heated towel rail at the choice of the residents themselves.
In this case, there is always a bypass between the taps - a closing section of a pipe with a diameter equal to the diameter of the riser or one step less.
The bypass at the heated towel rail solves several problems:
- 1. Maintaining a normal circulation rate throughout the hot water riser. Forced circulation in the riser ensures the supply of uniformly hot water (according to standards - at least 60 ° C) to any apartment, on any floor, regardless of its distance from the start of supply to the riser, the time of day and the presence or absence of water intake in the apartments of the tenants.
- 2. Only a part of the total heat carrier (water) flow passes through one heated towel rail. Another part goes by, saving more heat for the next bathrooms, because one or two dozen heated towel rails can work from one riser.
- 3. It is possible to completely turn off the heated towel rail or adjust its temperature by residents without negative consequences for the rest of the apartments. The possibility of temperature regulation requires the installation of an additional control valve on one of the outlets, since it is impossible to regulate anything with a ball valve.
But even here there is a problem: the height of the bends from the floor, the distance between them, the diameter and type of bypass are not standardized in any way. This leads to massive problems when connecting heated towel rails, they will be discussed below.
1. Unbiased and unconstrained bypass. The bends are welded directly to the riser pipe. Between the taps, the geometry of the riser (this is the diameter of the pipe and its direction) remains unchanged. You can often hear "oh, but I don't have a bypass!" - but in reality, the bypass is just part of the riser.
Unbiased and unconstrained by-pass (galvanized riser)
Unbiased and unconstrained bypass (stainless steel riser)
2. Unbiased narrowed bypass. Between the taps, the diameter of the riser is reduced by one standard size of the pipe (for example, for a 1 ”riser, the bypass is 3/4”), the riser itself remains straight. Perhaps the most common option, which, alas, brings a lot of problems under certain conditions.
Unbiased narrowed by-pass (galvanized riser)
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the washing machine from the bottom during washing: first steps, elimination of breakage
3. Offset narrowed or unconstrained bypass. Between the taps, the riser section is shifted towards the heated towel rail, and the offset section can be further narrowed by one diameter step. Also a problematic option in very many cases.
Offset unconstrained by-pass (galvanized riser)
And here are the approximate coefficients of water flow into the heated towel rail for different bypass configurations. Remember that they are valid only when choosing a uniquely working connection diagram from the options presented below.
- Offset bypass: 0.33-0.4.
- Displaced and at the same time narrowed by one step in diameter bypass: 0.48-0.52.
- Unbiased narrowed bypass: 0.4.
That is, shifting the bypass in terms of efficiency is almost equivalent to its narrowing.
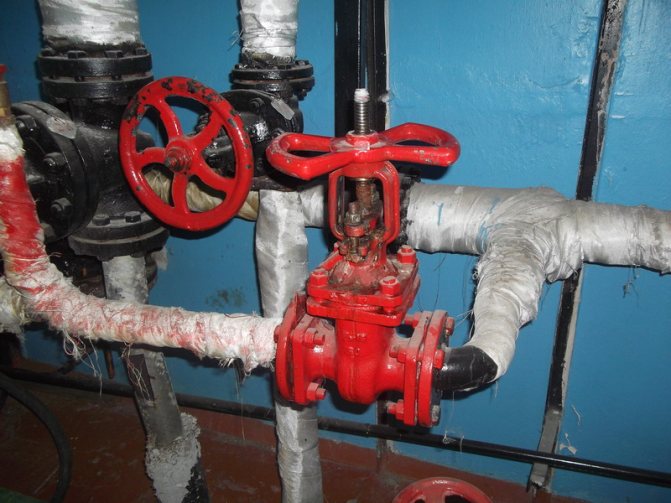
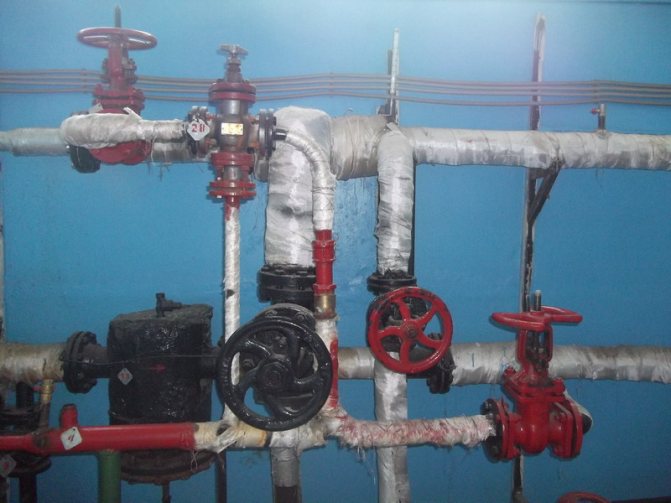
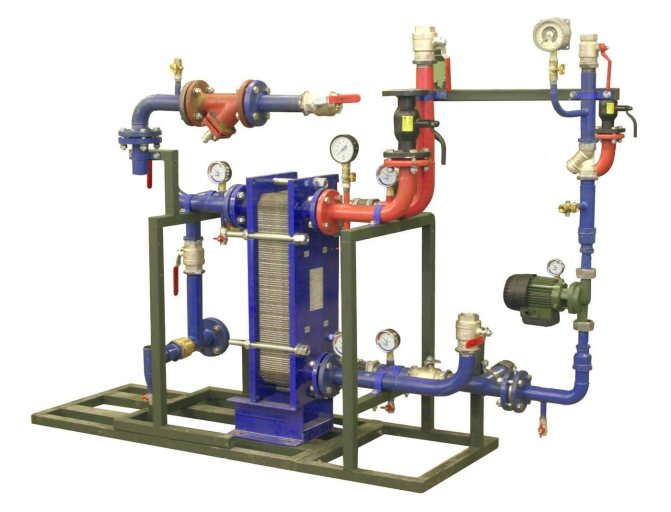
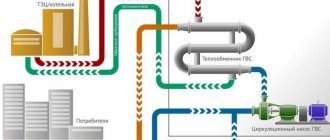
Use of heat points
This is a separate room. It should contain thermal power plants connected to the heating network. Heat exchangers for hot water supply of an apartment building must have tools for regulating consumption, distributing hot water supply to apartments, and setting up the equipment itself.
An individual heating point in an apartment building is usually located in the basement. Previously, the system was installed in attics. In the event of a breakthrough, streams of boiling water spilled over the room and flooded the apartments. If the emergency happened at night, it could lead to serious injury or even death.
An alternative option is to build a heating point in a separate building next to the building.The purpose of the equipment is to transform the coolant, regulate the supply of hot water or heat, distribute the resource among apartments and turn off its supply.
Water heating equipment
A standard water heater can be used for domestic hot water or heating. In the event of equipment breakdown, utility rates will not be reduced. Repair work will also fall on the shoulders of consumers, who are obliged to monitor its good condition.
Thermal energy component
He is responsible for heating cold water. And counters are not installed on the component. Before calculating the heat energy for DHW, the following parameters must be taken into account:
- DHW tariff;
- system operating costs;
- the cost of transferring the heat carrier;
- calculation of heat loss.
The payment for ordinary water supply is also taken into account, calculated on the basis of consumption (RUB / m3).