Characteristics of the substance
Propylene glycol is a dihydric alcohol, usually a colorless viscous liquid. It has a faint smell and a sweetish taste.
Propylene glycol, unlike its closest analogue, ethylene glycol, is considered a non-toxic substance, it is widely used in the perfumery and even in the food industry - in this case it is designated as E-1520.
The chemical formula of propylene glycol is C3H6 (OH) 2. The substance is extremely fluid in structure and can slowly seep through micro-holes and cracks. The ignition temperature is quite high, it is + 421 ° C.
201301230949_0–2

How interchangeable are modern coolants?
It depends on three parameters: heat transfer efficiency, corrosivity, service life. Any "correct" (ie meeting at least the requirements of the old GOST) antifreeze performs these functions. To the direct question "Is it possible to mix different coolants?" no serious manufacturer will answer directly. At best, you will hear “undesirable”. Why? Because additives, with a general understanding of the formulations, each uses his own, with a different degree of chemical purity (and hence cost), i.e. the devil is in the details. So no one undertakes to predict how different packages will behave.
How to choose a coolant for your car in a store?
First of all, we look at the price. Normal coolant should not cost less than 60 rubles. per kilogram. The brand should be "heard" - you should not play the lottery. Important: the color of the coolant does not matter! All coolants are initially colorless. Giving them one color or another is a whim and a right of the manufacturer. That is why liquids of the same color can be completely different in composition, while multi-colored ones, on the contrary, can turn out to be the same. Color has nothing to do with the chemical composition of coolants.
A good but tricky way to purchase a product that is known to be of high quality is to check that it has at least one vehicle manufacturer's approval. You can find out on the official website of this manufacturer.
Antifreeze: what hides the hood of a car
Advantages and Disadvantages of Propylene Glycol as a Heat Transfer Fluid
You can clearly identify the advantages and disadvantages of propylene glycol by comparing it with water (which is also a heat transfer fluid in some heating systems):
- the density of dihydric alcohol is 1037 kg / m³, which is more than that of water (1000 kg / m³): the difference is 3.7%;
- the substance begins to boil at +187 ° С, and water at +100 ° С, the difference is 87%;
- alcohol freezes at -60 ° C, water already at 0 ° C;
- the specific heat capacity is equal to 2483 J / (kg · K), almost 2 times lower than that of water (4.187 J / (kg · K));
- thermal conductivity - 0.218 W / (m · K), which is three times lower than that of water 0.6 W / (m · K);
- dynamic viscosity of alcohol - 56 mPa · s, eight hundred times more than that of water (0.894 mPa · s).
Several conclusions can be drawn from this list.
- The density of propylene glycol is higher than that of water, so the static load and pressure in the heating system will also increase.
- A high boiling point of +187 ° C is not such an advantage. The specific heat of propylene glycol is two times lower than that of water. This means that you can bring these two liquids to a boil with the same amount of heat. Their temperature will reach its extreme point almost simultaneously, only water will boil at +100 ° C, and alcohol at +187 ° C.
- The freezing point of propylene glycol is noticeably lower.In addition, it practically does not expand during cooling, and this does not damage the heating system.
- A low specific heat capacity is a clear advantage, hence the rapid heating of the heating system, however, propylene glycol is able to accumulate little heat - and this is already a disadvantage.
- High dynamic viscosity will add a load to the circulation pump, which moves the coolant through pipes and radiators.
However, in some situations, propylene glycol will do its job better than water:
- if you do not use the water heating system in winter and do not drain the water, the system may fail (even after complete draining, the water will still remain in the pipes, causing corrosion) - and propylene glycol can be used all year round and not drained in winter;
- antifreeze, which is based on propylene glycol, does not cause corrosion and does not form scale.
Such antifreezes also have disadvantages:
- the cost is higher than that of water;
- a complete fluid change is required every five years;
- there should be no parts in the heating system that contain zinc - propylene glycol quickly dissolves them;
- Propylene glycol is extremely fluid and can penetrate through small joints in the heating system.
Many manufacturers dilute antifreeze with water to correct some of the disadvantages of propylene glycol. What will it give:
- the cost of antifreeze will become noticeably lower;
- the viscosity will decrease;
- the heat capacity will increase;
- the heat transfer rate will increase;
- the boiling point will drop, but most boilers are still not designed for 160 ° C;
- freezing point is from -30 to -40 ° C degrees;
- antifreeze based on propylene glycol with water expands slightly, so the destruction of the heating system will not occur.
Operating rules for complexes with glycerin antifreeze
Glycerine coolants have a long service life, subject to the basic rules:
- 1 Do not overheat antifreeze. Otherwise, anti-corrosion impurities in the basis of its composition can decompose and form deposits on the surface of the heating elements, which impairs the operation of the heating system as a whole;
- 2Low coefficient of surface tension of the composition helps to reduce swelling of the seals. To reduce the likelihood of leaks, it is necessary to make additional tightening at the junction of different elements;
- 3 At low temperatures, the coolant in the pipes will have a viscous state with individual crystals of the substance. When starting up the equipment, you must first turn on the minimum speed of the heater and increase it gradually. Such a start-up will avoid premature boiler failure. The heated composition will have all its original properties.
A source
How to use propylene glycol fluids correctly
Propylene glycol based heat transfer fluids have a similar chemical composition, which differs in the percentage of alcohol. Most often, such compositions are named by the manufacturer's name.
If propylene glycol antifreeze contains about 30%, it freezes at -13 ° C, 35% alcohol solution crystallizes at -20 ° C, 40% at -25 ° C, 75% solution at -65 ° FROM.
When replacing water with a propylene glycol-based composition, it is necessary to take into account some of the properties of antifreeze.
- Lower heat capacity and thermal conductivity. The number of radiators should be increased, as well as a more powerful boiler should be purchased. Heating systems are often installed in private houses that operate at half their capacity - in this case, you can do without replacing the boiler.
- High viscosity. Make sure the pipes have an inner diameter of at least 25 mm and install a larger circulation pump.
- Greater expansion ratio.If the expansion tank is less than 10 liters, then a larger one will need to be replaced.
- High fluidity. It is worth reducing the number of threaded connections, tie-ins and squeegees, and also provide free access to existing connections in case of leaks.
If the technical parameters of the existing heating meet the new requirements, you can proceed to the preparatory work:
- to seal squeegees, connections, tie-ins;
- completely drain the water from the heating system and rinse with caustic soda, it will remove rust and scale;
- remove all zinc parts;
- additives can be added to antifreeze that will protect copper parts;
- check the dirt trap twice as often;
- check the solution every two years for alcohol concentration;
- complete change of antifreeze every five years.
It is always worth flushing the system thoroughly if you are going to switch to another coolant.
Selection and use of glycerin coolant


Glycerine coolant is presented on the market by manufacturers Gulfstream, Eco-30, Teplocom, PRIMOCLIMA, Olga. Compositions of different brands differ in color and type of impurities.
For the convenience of consumers, antifreezes are sold packaged in cans of 10 or 20 kg, as well as in barrels of 50 kg. To fill a heating system with a volume of 100 liters, about 115 kg of coolant will be required.
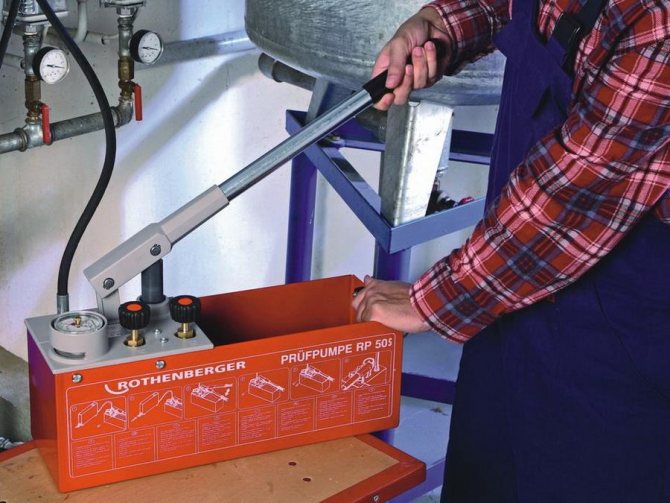
When injecting the composition, specialized equipment is required. It is recommended to involve specialists to fill the heating complex. First of all, all heating equipment is cleaned.
To fill the complex with antifreeze, you will need a pump, a hose, a pressure gauge, a large container for the coolant and equipment for subsequent pressure testing. After filling the heating complex, it is pressure tested.
Water
Benefits:
- environmentally friendly substance;
- sufficiently high heat capacity;
- circulates freely through the system;
- always at hand;
- extremely low cost.
Disadvantages:
- freezes at temperatures below 0 ° С;
- lack of operation in winter requires draining the system, which leads to corrosion;
- water hardness manifests itself at temperatures above 80 ° C, then decomposition of carbonate salts begins and scale deposits on the walls of the system, which reduces heat transfer and can break the system due to overheating.
What is ANTIFREEZE ???
To protect heating and cooling systems from defrosting in the 20s of the twentieth century, the first low-freezing coolant appeared, called Antifreeze (from the Greek anti - against and English freeze - to freeze).
The first coolant - antifreeze was made on the basis of glycerin - three atomic alcohol. Such coolants in a 35:65 mixture of water and glycerin had a freezing point of 40 ° C and a boiling point of + 280 ° C. The problem and disadvantage of such antifreezes is their high viscosity and insufficient fluidity. They tried to solve this problem with the help of ethanol, methanol, salts, etc. until in the 30s they found a full-fledged replacement for glycerin and two atomic alcohol, ethylene glycol, became the basis of coolants. In the USSR, as in the rest of the world, by 1937, ethylene glycol-based coolants practically replaced glycerin and methanol antifreezes.
Glycerin-based heat carrier
Benefits:
- environmentally friendly;
- not dangerous by inhalation of vapors;
- does not cause poisoning if accidentally ingested;
- inert to galvanized parts;
- cheaper than propylene glycol-based coolant.
Disadvantages:
- the mass of the glycerin coolant gives an additional load on the equipment;
- the viscosity is higher than that of glycol solutions;
- thermally unstable;
- foams strongly, the risk of airing the system increases;
- when used, the requirements for gaskets (seals) and parts are increased.
Antifreeze base
Various substances can be used as a basis for the manufacture of antifreeze.The most common are ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, glycerin, and alcohol.
Ethylene glycol heat carrier
Today, ethylene glycol-based antifreeze is the most common antifreeze coolant used in heating systems for private houses. However, it is quickly being replaced by the more advanced and environmentally friendly propylene glycol antifreeze.
Ethylene glycol reliably protects the system from freezing. When the freezing temperature is exceeded, the coolant expands by 1.5-2%, which is not enough for a rupture to occur in any part of the system.
Important! It must be remembered that ethylene glycol-based heat transfer fluid is poisonous and can be hazardous to human health and life. During operation, it is recommended to completely exclude his contact with a person. This applies in particular to natural circulation heating systems with an open expansion vessel. An open tank must be installed in the attic, but not in the living space. In extreme cases, a gas outlet pipe should be made from the tank, which will divert hazardous vapors to the street.
When working with ethylene glycol, it is necessary to take precautions, in particular to wear goggles and rubber gloves. Ethylene glycol can penetrate the human body through the skin, therefore, if during repair work or filling the system, non-freezing liquid gets on the skin, wash it off immediately with warm water and soap. If you get inside the body, you should rinse the stomach and immediately go to the hospital or call an ambulance. It must be remembered that a 100-200 ml dose of ethylene glycol-based antifreeze that has entered the human body can be fatal. Lethargy and depression are clear symptoms of poisoning.
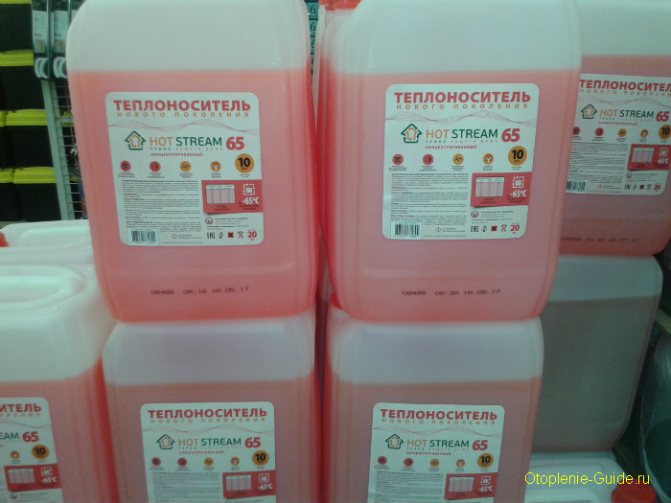


Hot Stream, 20 kg - concentrated antifreeze for the heating system of a country house.
Ethylene glycol is not recommended for use with double-circuit boilers, because antifreeze may enter the hot water circuit.
Storage should be carried out in a tightly closed container away from direct sunlight, electric heaters and foodstuffs. It is highly discouraged to use ethylene glycol-based heat transfer fluid in heating systems of houses where small children live, because the liquid has a sweetish taste and does not have an unpleasant odor, so small children will not be able to determine that it is poison, but, on the contrary, may think that it is some kind of juice or just sweet water!
Important! If there is a leakage of the coolant, then all objects that have gotten or absorbed ethylene glycol (tiles, linoleum, parquet, furniture, decorative radiator screens, etc.) must be subject to mandatory replacement. Otherwise, they will be a constant source of toxic fumes.
Spent ethylene glycol antifreeze is subject to processing at specialized enterprises; it is prohibited to drain it into the sewer or soil.
Propylene glycol based heat transfer fluid
Due to its relative harmlessness, propylene glycol-based antifreeze is used at facilities with high environmental requirements, where there is a possibility of coolant getting into tap water or other human vital items. As noted above, propylene glycol antifreezes, despite their higher cost, are gradually replacing non-environmentally friendly ethylene glycol antifreezes.
As a heat carrier for heating systems, propylene glycol antifreezes have been used since the 60s of the last century. However, only since the mid-90s, in the countries of Western Europe, the USA and Canada, they began to completely switch to propylene glycol. Currently, Russia is also gradually switching to this safe antifreeze.
The propylene glycol-based heat transfer medium has a high viscosity, which nevertheless does not affect the hydraulic characteristics of the heating system. The fact is that propylene glycol has "lubricating properties" that compensate for its high viscosity.
The density of propylene glycol coolant is lower than that of ethylene glycol, which reduces the load on the circulation pump, and also more efficient circulation of the liquid through the heating system.
In addition, if propylene glycol-based antifreeze leaks, there is no need to change all the "contaminated" items. It is enough only to remove the coolant from the surface of objects and wipe them with a wet cloth.
Compared to ethylene glycol, propylene glycol more reliably protects the heating system from defrosting. Even if the minimum temperature is exceeded, propylene glycol antifreeze does not freeze, but turns into a mushy liquid, while expanding by only 0.1%. With such a volume of expansion, breaking the system is impossible.
The only drawback of this antifreeze is its high cost.


Hot Stream, 10 kg. The temperature of the beginning of crystallization is -30 ° C. Ingredients: ethylene glycol, demineralized water, Arteco additive package (Belgium). ...
Glycerin-based heat carrier
The most widespread glycerin coolants were obtained in the 20s of the last century. It was glycerin that became the basis of the first non-freezing coolants in the USSR, however, due to a number of significant shortcomings, by the beginning of the 40s, glycerin was practically no longer used in heating systems.
Their main disadvantages were poor fluidity and high viscosity levels, which caused the pumps to fail quickly. To solve this problem, they tried to use various additives, mainly poisonous methyl alcohol (methanol), which negatively affected the mental state of workers who had constant contact with it. In addition to the negative impact on human health, methanol boiled already at a temperature of 65 ° C, while evaporating, methanol sharply increased the viscosity of the liquid. In addition, the strong foaming of glycerin leads to the fact that air is constantly circulating in the system, the system is airy.
Another disadvantage of a glycerin-based coolant is that when it is heated for a long time, toxic substances are released, which cause accelerated corrosion of the metal elements of the heating system, as well as corrosion of sealing materials.
At the moment, manufacturers of glycerin-based antifreeze (including with the addition of methyl alcohol) get rid of the above disadvantages by adding special expensive additives. Their cost is much higher than the cost of ethylene glycol and propylene glycol additives. Therefore, when choosing antifreeze for the heating system, it should be borne in mind that the price of high-quality glycerin coolant will always be higher than ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. If the situation is the opposite, it means only one thing: the seller is trying to sell low-quality antifreeze.
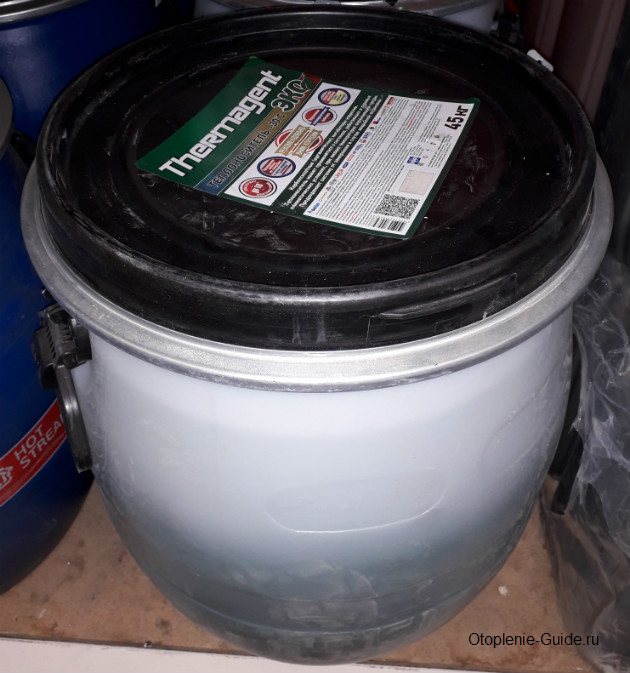


Thermagent Eko, 45 kg. Down to -30 ° C.
Ethylene glycol heat carrier
Benefits:
- the system is not defrosting;
- good thermophysical properties;
- slight deposits of salts and scale;
- average cost.
Disadvantages:
- belongs to the third class of danger, has a narcotic effect on the body, is toxic;
- quickly absorbed into the body, is able to penetrate the skin and by inhalation;
- does not have an unpleasant odor;
- poses an environmental hazard;
Component Specifications
Pure glycerin is a transparent liquid and belongs to trihydric alcohols. Mixes well with water or alcohols in any proportions. Under industrial conditions, the substance is synthesized from propylene.Under natural conditions, it is found in the base of oils or fats. Has the following technical characteristics:
- Colorless;
- Odorless;
- Transparent;
- Melts at 18 ° C, boils at 290 ° C;
- The density of the substance is 1.27 g / cm³;
- The refractive index is 1.473.
Propylene glycol based heat transfer fluid
Benefits:
- insures the system against rupture;
- the volume during freezing increases by only 0.1%;
- provides the highest level of safety after water;
- not dangerous even with prolonged inhalation of vapors;
- non-corrosive;
- good thermophysical properties;
- possesses bactericidal and sterilizing properties.
Disadvantages:
- high cost (pays off with minimal repair costs, safety and the ability not to connect to central heating systems).
Why is the glycerin mixture so bad - antifreeze ???
Indeed, 90 years ago, the first antifreezes were based on glycerin. But, since they had an extremely high viscosity, which the pumps could not cope with, the circulation in the cooling and heating systems was insufficient; they had to be diluted with various alcohols, including methyl alcohol. Glycerin thermally NOT stable, with prolonged heating (even up to 80-130 ° C), it decomposes with the formation of acrolein and acetone, which lower the flash point to 112 ° C, and acetone vapors are explosive. As a result, there were constant problems with machinery, pumping equipment, poisoning by vapors of people and a high fire hazard.
After the invention of ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, the global industry unequivocally rejected glycerin as the basis for coolants. And at present there is not a single large world or domestic manufacturer that has switched to the production of glycerin-based antifreezes and coolants, except, of course, "woe to inventors" who do not think about the consequences of using such antifreezes, they need to be sold with maximum profit for themselves.
Today, many antifreezes are presented on the Russian market, there are also high-quality ones among them, which have long proven themselves from the best side and their manufacturers keep a high bar in terms of the quality of their products. But, there is a lot of cheap, glycerin and counterfeit antifreezes that can damage your expensive heating system - beware such counterfeits and antifreeze.
Remember the proverb - "Stingy person, pays twice", do not fall for this bait.
What is the difference between G12 and G11, G12 and G13
The main types of antifreeze such as G11, G12 and G13 differ in the type of additives used: organic and inorganic.


General information about antifreezes, what is the difference between them and how to select the right coolant
Cooling liquid class G11 inorganic origin
with a small set of additives, the presence of phosphates and nitrates. Such antifreeze is created using silicate technology. Silicate additives cover the inner surface of the system with a continuous protective layer, regardless of the presence of areas of corrosion. Although such a layer is
protects already existing foci of corrosion from destruction
... Such antifreeze has low stability, impaired heat transfer and a small line of operation, after being used up, which precipitates, forming an abrasive and thereby damaging.
Due to the fact that G11 antifreeze creates a layer similar to scale in a kettle, it is not suitable for cooling modern cars with radiators with thin channels. In addition, the boiling point of such a coolant is 105 ° C, and the service lines are no more than 2 years or 50-80 thousand km. mileage.
Often antifreeze G11 turns green
or
blue colors
... This coolant is used
for cars manufactured before 1996
years and machines with a large volume of the cooling system.
G11 does not work well with aluminum radiators and blocks, as its additives cannot properly protect this metal at high temperatures.
In Europe, the authoritative specification of antifreeze classes belongs to the Volkswagen concern, therefore the corresponding marking VW TL 774-C provides for the use of inorganic additives in antifreeze and has the designation G 11. Specification VW TL 774-D provides for the presence of carbo-acid additives on an organic basis and is marked as G 12. The classes G12 + and G12 ++ are marked with the VW TL 774-F and VW TL 774-G standards, and the most complex and expensive G13 antifreeze is regulated by the VW TL 774-J standard. Although other manufacturers such as Ford or Toyota have their own quality standards. By the way, there is no difference between antifreeze and antifreeze. Antifreeze is one of the brands of Russian mineral antifreeze, which is not designed to work in motors with an aluminum block.
It is categorically impossible to mix organic and inorganic antifreezes, since a coagulation process will occur and, as a result, a precipitate in the form of flakes will appear!
And fluid classes G12, G12 + and G13 varieties of organic antifreezes
Long Life.
Used in cooling systems of modern cars
manufactured since 1996 G12 and G12 + based on ethylene glycol but only
G12 plus assumes hybrid technology
production in which silicate technology was combined with carboxylate technology. In 2008, the G12 ++ class also appeared, in such a liquid, an organic base is combined with a small amount of mineral additives (called
lobrids
Lobrid or SOAT coolants). In hybrid antifreezes, organic additives are mixed together with inorganic additives (silicates, nitrites and phosphates can be used). This combination of technologies made it possible to eliminate the main disadvantage of G12 antifreeze - not only to eliminate corrosion when it has already appeared, but also to take preventive action.
G12 +, unlike G12 or G13, can be mixed with G11 or G12 liquid, but still such a "mix" is not recommended.
Cooling liquid class G13
the beginning is produced from 2012 and is calculated
for automobile engines operating in extreme conditions
... From a technological point of view, it does not differ from the G12, the only difference is that
made with propylene glycol
, which is less poisonous, decomposes faster, which means
is less harmful to the environment
when recycled and its price is much higher than G12 antifreeze. It was invented based on the requirements for increasing environmental standards. Antifreeze G13, as a rule, is purple or pink, although in fact it can be painted in any color, since this is just a dye, on which its characteristics do not depend, different manufacturers can produce coolant with different colors and shades.
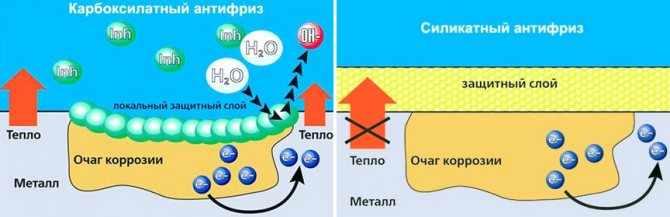

The difference in the action of carboxylate and silicate antifreeze
2.1 Water or antifreeze
For any type of engineering systems, the choice is between ordinary boiler or demineralized water and special liquids with a low crystallization temperature - antifreezes. As a basis for industrial antifreezes, aqueous solutions of various compounds are used - salts of inorganic acids, glycerin, glycols or ether.
First, we will consider in detail the feasibility of using water as a working fluid for engineering systems. This is the most affordable, environmentally friendly and efficient in terms of heat transfer option, which has several significant disadvantages. The water contains impurities of salts, chlorine, iron, alkali and alkaline earth metals. In addition to its high corrosiveness, which can actually be reduced due to demineralization and the introduction of special additives, water has a high freezing point. As a result, the climate system must constantly be in the zone of positive operating temperatures, otherwise this will lead to the destruction of the system due to the volumetric expansion of the liquid during freezing.To use it as a working fluid in heating systems, demineralization and the introduction of special anti-corrosion additives are required.
What to advise pouring into the heating, cooling or air conditioning system ???
Among the highest quality antifreezes on the Russian market, one should mention the German antifreeze - "Antifrogen N" (manufactured by Hoehst, Germany). Russian antifreeze - "Hot Stream" (produced since 2004 in the Moscow region of Klimovsk), as well as one of the first and best domestic coolants household antifreeze - "Hot Blood". Household brand antifreeze «Hot Blood"(Hot Blood)are the product of a unique patented technology. These coolants have been produced for 18 years (since 1997) our Moscow.
Which antifreeze to buy and pour into the heating or air conditioning system is up to you. Therefore, for the sake of your health and reliable operation of the heating system, use only high-quality household antifreezes that have many years of experience in use and have State quality certificates.