Why it is not recommended to pour antifreeze into the heating system

Varieties of automotive antifreeze
Before pouring antifreeze into the heating system, you need to find out its exact composition. In the vast majority of cases, it includes ethylene glycol. This substance is extremely toxic to humans. In the liquid state, one should beware of contact with eyes and exposed skin. But antifreeze, which turns into steam due to exposure to high temperatures, when overheating or a small leak of the coolant occurs, is much more dangerous.
But is it possible to pour antifreeze into the heating system in this case? Subject to all safety rules and requirements, the use of automotive antifreeze is allowed. However, in this case, it is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of the system operation:
- Antifreeze has a higher viscosity than water. Therefore, it is necessary to replace the circulation pump with a more powerful one - by 15-20%;
- High degree of fluidity. A small microcrack or loose connection in the pipeline is enough for the antifreeze for heating the house to begin to penetrate into the room. Be sure to replace all rubber gaskets with paronite;
- Can antifreeze be poured into an open-type heating with a leaky tank? No, this is strictly prohibited;
- The heating rate of the coolant with the addition of antifreeze will be lower than that of plain distilled water. This must be taken into account when choosing the temperature regime of the system;
- You can not pour antifreeze for heating systems in a concentrated form. This can damage the pump and damage the boiler. You can find out the ratio of automotive antifreeze to water on the label.
What other problems can you face after pouring an anti-freeze liquid? First of all, its quality. If the manufacturing technology is not followed after prolonged thermal exposure to the antifreeze solution, third-party substances appear in it in the form of white flakes. They negatively affect the state of the heating system, can cause a decrease in the throughput of the pipeline and the transfer of energy by the heat exchanger.
Antifreeze can corrode polypropylene pipes. It cannot be used in such pipelines.
What to choose: water or antifreeze for heating systems
This is a question often asked by homeowners. But today in private homes, antifreeze for heating systems is used much less often than water. There are several reasons for this, first of all, the different physicochemical properties of these coolants. Therefore, an antifreeze heating system must be designed differently from a water heating system.
Comparative characteristics of water and antifreeze
The advantages of using water as a coolant are obvious: availability, high specific heat capacity and low cost (not free, because water should be poured into the system not from the tap, but distilled water, or after appropriate water treatment).
The main disadvantage is that water freezes at zero degrees, while expanding and tearing the elements of the heating system. Antifreezes freeze at very low temperatures (down to -70 C). However, they have some unpleasant features.
- Their specific heat capacity is 10-15% lower than that of water: they heat up more slowly and give off heat worse, so a more powerful boiler will be required.
- They are denser (10-20%) and more viscous (30-50%) than water. Consequently, you will need a powerful pump for circulating the coolant, large diameter pipes and more powerful heating radiators for antifreeze.
- When heated, they expand 30-40% more than water. This means that you will need a closed expansion tank 2 times larger in volume.
- Non-freezing joints have no surface tension and are 50% more fluid than water. With the smallest flaws in the sealing of the joints, antifreeze begins to leak, especially when the system cools down, when the diameters of the pipeline elements decrease. Therefore, the heating system should have the minimum possible number of joints, and they should be available for inspection and repair at any time.
Characteristics of popular heat transfer fluids
Therefore, a heating system designed for water is not suitable for the use of anti-freezing liquids. If you plan to use antifreeze to heat the house, then the system must be designed in advance, and it will cost significantly more.
Properties and features of the use of antifreeze in heating systems
For private heating systems, you can find on sale two types of non-freezers: aqueous solutions of ethylene glycol and propylene glycol.
Glycols, in contrast to water, pass into the solid phase gradually with decreasing temperature: the range from the temperature of the onset of crystallization to complete solidification is 10-15 ° C.
In this range, the liquid gradually thickens, turns into a gel-like "sludge", but does not increase in volume. Glycols are sold in two “formats”:
- Concentrate with a crystallization onset temperature of -65 ° C. It is assumed that the buyer himself will dilute it with softened water to the required parameters. Only ethylene glycol antifreezes are sold in the form of a concentrate.
- Ready-to-use solutions with a freezing point of -30 ° C.
The homeowner can further dilute the concentrate to save the concentrate to obtain a freezing point of -20 or -15 ° C. Antifreeze should not be thinned more than 50% - this reduces its protective properties.
All anti-freezing fluids contain additives. Their purpose:
- protection of metal elements of the system from corrosion;
- dissolution of scale and sediments;
- protection against destruction of rubber seals;
- protection against foaming.
Each brand of antifreeze has its own set of additives; there is no universal composition. Therefore, when choosing an anti-freeze, you should familiarize yourself with the types of additives and their purpose.
Antifreeze in the heating system of a house is very susceptible to overheating: when the critical temperature is exceeded (each brand has its own), ethylene glycol and additives decompose, forming acids and solid precipitates.
Carbon deposits appear on the heating elements of the boilers, the sealing elements are destroyed, and intense corrosion begins. When the additives overheat and decompose, foaming begins, and it leads to the airing of the system.
For these reasons, manufacturers of heating boilers strongly recommend against using antifreezes in the system, especially ethylene glycol.
Also, you cannot use galvanized pipes: antifreeze corrodes the zinc coating, white flakes are formed - an insoluble precipitate.
Gas boiler burner destruction caused by antifreeze
The heating system is filled with antifreeze through the expansion tank. The coolant should be changed every 4-5 years.
Ethylene glycol based antifreeze
Ethylene glycol antifreezes are more common due to their relatively low cost.
However, ethylene glycol is a very toxic substance even in diluted form, therefore, non-freezing liquids based on it are strictly forbidden to use in open heating systems, where poison evaporates from the expansion tank into the surrounding space, and in double-circuit systems, where ethylene glycol can get into hot water taps.
Important! Non-frosting on ethylene glycol is colored red, so their entry into the DHW system can be easily detected.
Propylene glycol based antifreeze
This is a newer and more expensive generation of antifreezes. They are completely harmless, and food propylene glycol is even used in confectionery products under the guise of food additive E1520. Non-freezing on propylene glycol is less aggressive to metal and sealing elements. Due to their harmlessness, they are recommended for use in two-circuit systems.
Important! Propylene glycol antifreezes are colored green.
Green and red anti-freeze liquids
Is it possible to pour antifreeze into the heating system
Antifreeze antifreeze antifreeze is produced on the basis of ethylene glycol, but it is not intended for heating systems. Its additives are designed for the operating conditions of automobile engines, and act destructively on the elements of the heating system.
It is necessary to switch from water to antifreeze for home heating systems due to the threat of prolonged power outages, which is important for areas remote from large cities.
An alternative is the presence of backup power sources in the house, as well as the use of solid fuel boilers (fired by wood, coal, pellets).
But if the transition to non-freezing is inevitable, then it is better to entrust the design and installation of such a system to professionals so as not to damage expensive equipment.
: how to choose antifreeze for heating
Preparation of the solution and its filling


Flushing and filling pipes with antifreeze
In order to add antifreeze to the heating system of a house, you need to correctly select its composition. All manufacturers produce ready-to-fill fluids. The temperature at which crystallization occurs is indicated in the name. For example - A40-M (-40 ° C). It is important to know that ready-made antifreeze cannot be diluted with water. To do this, you need to use special concentrates, 95% consisting of ethylene glycol.
Preparing a solution of antifreeze for heating
For the correct filling of antifreeze into the heating system, it is best to use a concentrate. This has the added benefit of allowing you to choose the ratio of antifreeze to distilled water yourself. In addition, you can more often find a fake of an already prepared solution than a concentrate.
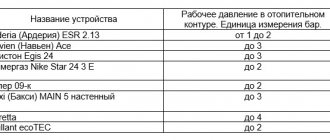
First, it is necessary to determine the minimum temperature at which the effect of coolant crystallization will not be observed. To do this, you need to know the ratio of antifreeze for heating a house to water. They are presented in the table.
| Concentrate to water ratio | Freezing temperature, ° С |
| 1:1 | -40 |
| 2:3 | -30 |
| 1:2 | -20 |
But first you need to check if this antifreeze can be poured into the heating system. To do this, make a solution in a small transparent container (glass) and leave it for several days at room temperature. After this period, no sediment or foaming should be observed in the liquid. If this is present, the quality of the concentrate is very low.
When antifreeze leaks from the heating system, you must first ventilate the room, eliminate the accident and thoroughly wash the places where it got.
Pouring antifreeze into the heating system


It is best to cut off the top of the container for pouring.
Having decided that this particular brand of antifreeze can be poured into the heating, they begin to prepare the system. First, all the coolant is drained. If antifreeze was poured into the pipeline before, it should never be mixed with a new solution.
Then the following actions are performed:
- Thorough flushing of pipes and radiators. Before adding an antifreeze solution to the heating system of the house, you need to remove all internal contamination. It is best to perform several circuses until the water is completely clear;
- Checking all connections and pipe joints. It is imperative to replace the rubber gaskets;
- Pressure testing - is necessary to check the system for a possible increase in normal pressure.In this way, you can identify elements with hidden defects;
- Pouring antifreeze for the heating system using a special pump.
During this procedure, you must follow all safety rules. The room must be well ventilated - all windows and doors are open. Be sure to use a protective suit, respirator and rubber gloves. If, while pouring antifreeze into the heating system, it gets on an open area of the skin, you should immediately rinse it with water. In the event of a chemical burn, consult a doctor.
The lower the concentration of antifreeze, the lower the likelihood of getting a chemical burn.
Filling a closed heating system
Here it is most convenient to carry out the filling process using a pump connected to the system make-up connection. If there is no pump, then the grueling job of pouring antifreeze through the highest point awaits you by unscrewing the automatic air vent. It is also desirable that an assistant be involved in the operation. Its task is to release air from the batteries while you are pumping antifreeze into the boiler room. Before starting work, make sure that:
- all shut-off valves are open;
- the boiler shut-off valves are closed;
- the concentrate is diluted according to the instructions;
- Mayevsky's relief valves are closed;
- the shut-off valve of the diaphragm expansion vessel is open.


The process begins by pumping antifreeze until the pressure gauge shows a pressure of 1.4-1.5 bar. After that, you need to give a signal to the assistant to gradually release air from the radiators, starting from the lowest ones. At this time, you need to monitor the pressure drop of the manometer and slowly pump up the coolant so that it does not fall below 1 bar.


Note. In closed heating systems, there must be a spring-type check valve on the make-up insert, otherwise it will be difficult to pump antifreeze or water there.
When all the air has been successfully released, the antifreeze is pumped again to a pressure of 1.5 bar. Then it is necessary to alternately open the taps that cut off the boiler - first on the return, and then on the supply line. Open the second tap slowly so that the air has time to escape through the automatic air vent located on the boiler safety group. In this case, the pressure will begin to fall again, you will have to immediately pump up antifreeze.


When starting the heat generator and heating the coolant, you need to follow the readings of the pressure gauge. As a result, they should not exceed 1.8 bar at operating temperature. The last stage is re-venting air from the heaters and adjusting the pressure. It is necessary to work with Mayevsky's taps carefully and carefully so as not to burn yourself and not spill antifreeze, especially when you have poured ethylene glycol into the system.
Advice. At the end of the process, carefully inspect all connections and equipment for antifreeze leaks. If these are found, it is not necessary to empty all pipelines again, you can cut off a separate branch or a radiator with fittings, and after elimination, again raise the pressure and bleed the air.
What is it


Antifreeze or antifreeze is an anti-freeze liquid that is poured into the expansion tank of a car. It is also used in heating systems. In translation, our language means "anti-freeze". That is why it is also called anti-freeze. That is, this liquid does not freeze at negative temperatures, it also cools the engine during operation and protects its elements from corrosion.
Anti-freeze production does not have a negative impact on nature. The composition of factory antifreeze often includes ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, glycerin mixtures
, as well as monohydric alcohols and other substances that are based on water. Sometimes more flavorings are added. Note that making antifreeze at home is quite easy. How exactly? Read on!
Filling an open heating system
For open systems, it is necessary to choose exactly the propylene glycol substance, as the most harmless, because the open-type expansion tank communicates directly with the atmosphere, and since it is located inside the building (usually in the attic), vapors of antifreeze liquid can leak into the rooms, albeit in insignificant volume.


Filling an open heating system with coolant
It is believed that the "non-freezing" bay in open systems is meaningless. To prevent evaporation of the coolant, the system should be converted to a closed one.
Diluted and fully prepared antifreeze is added through the make-up valve using a pump or through an expansion tank. Each Mayevsky valve located on the batteries must be in the open position. The taps close gradually as the volume of the expansion tank is filled. Then the non-freezing coolant must be topped up, bringing its content to approximately one third of the tank.
Before pumping antifreeze into the heating system, it is necessary to check that each element of the shut-off and control structure is not closed.
After turning on and first warming up the heater, bleed air through the radiators. When the level of hot antifreeze in the tank drops, it must be topped up to about half of its volume.