Coolant requirements
You need to immediately understand that there is no ideal coolant. Those types of coolants that exist today can perform their functions only in a certain temperature range. If you go beyond this range, then the characteristics of the quality of the coolant can change dramatically.
The heat carrier for heating must have such properties that will allow for a certain unit of time to transfer as much heat as possible. The viscosity of the coolant largely determines what effect it will have on the pumping of the coolant throughout the heating system for a specific time interval. The higher the viscosity of the coolant, the better characteristics it has.
Physical properties of coolants
If this condition is not met, then the choice of materials will become more limited. In addition to the above properties, the coolant must also have lubricating properties. The choice of materials that are used for the construction of various mechanisms and circulation pumps depends on these characteristics.
In addition, the coolant must be safe based on such characteristics as: ignition temperature, release of toxic substances, flash of vapors. Also, the coolant should not be too expensive, studying the reviews, you can understand that even if the system works efficiently, it will not justify itself from a financial point of view.
A video about how the system is filled with coolant and how the coolant is replaced in the heating system can be viewed below.
Relevance of the procedure and security measures
Do not forget that ethylene glycol is a toxic substance, therefore, when using a water-glycol mixture in climatic heating systems, only structures with a closed circuit are allowed.
When used in a double-circuit boiler, antifreeze can enter the hot water system. It is permissible to work with concentrated glycol only in personal protective equipment - mask, gloves and goggles. In case of accidental leakage, it is necessary to replace the external elements of the system that have come into contact with ethylene glycol.
Manufacturers offer us a choice: trust the professionalism of their technologists and purchase a ready-made composition or save money by diluting concentrated glycol on our own. The range includes antifreeze from the Hot Stream line based on ethylene glycol with a package of carboxylate additives.
Antifreeze is an integral part of any vehicle that has an internal combustion engine. Without coolant, engine parts will not work for a long time, and it is important to choose the right antifreeze, as well as replace it in the car in time.
On sale you can find a diluted version of antifreeze and a concentrated one. A number of drivers do not see the difference in them and make a serious mistake when pouring a coolant concentrate into a car engine. This can lead to serious consequences, especially during the cold season.
How antifreeze works
Water at 0 ° C abruptly and abruptly turns into ice, while expanding by 11%. The pipes cannot withstand this load. The heating system has to be dismantled, including the boiler and all radiators. Water is a good solvent, therefore, even a small amount of antifreeze strongly displaces the crystallization point of water, and there is no jump-like transformation into ice.
Water with the addition of antifreeze at low temperatures slowly thickens, and the expansion of the liquid is insignificant, so the heating system remains intact.
For example, the crystallization of water with 30% antifreeze liquid (propylene glycol) is so slow that there is no need to dilute the coolant to -30 ° C, it is enough to add antifreeze to the design temperature of -12-15 ° C. With a drop in temperature below the calculated one, such a mixture will slowly but surely solidify, and only at -30 ° C can it freeze completely.
How does an antifreeze liquid for a private house heating system work?
In contrast to the water coolant, which begins to freeze already at 0 ° C, the anti-freeze for the heating system begins to freeze at lower temperatures, from -13 ° C to -60 ° C (depending on the antifreeze used and the degree of its dilution), while freezing happens gradually. As the liquid cools, crystals appear in it (crystallization process), then with a further decrease in temperature, more and more crystals appear, and only when a certain freezing point is reached, the liquid completely solidifies.
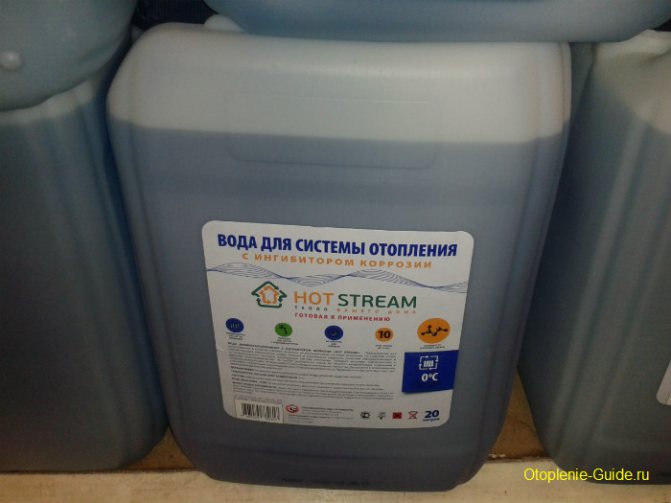

Heating water with Hot Stream corrosion inhibitor. Composition: demineralized water, Arteco additive package (Belgium). ...
Unlike water (which expands strongly when freezing, while a rupture occurs somewhere), the non-freezing liquid practically does not expand in volume (about 0.1-1.5%), which eliminates the rupture of the system.
Features of using water as a heat carrier
Water is a unique and the only liquid in nature that expands both when heated and cooled. Its high density, equal to 917 kg / m3, varies greatly with temperature. This property can do a "disservice" to the owner of the house - if it expands during freezing, the liquid can easily damage the heating system.


Water has a maximum heat capacity (1 kcal / (kg * deg)). This means that when a kilogram of this liquid is heated to a temperature of 90 degrees, and then it is cooled in a heating radiator to 70, as much as 20 kcal of thermal energy will enter this very radiator.
Water as a heat carrier
Water is perhaps the most accessible and cheapest type of heat carrier, besides, it is distinguished by a high level of safety and is unlikely (under any conditions) to pose a serious threat to the health of the owner of the house and his family. And in the event of a leaking working fluid from the heating system, the deficiency can be easily replenished by pouring ordinary tap water.
Interestingly, water is not just a combination of two hydrogen molecules with one oxygen molecule. In fact, it also contains other elements - these are metals, chlorine impurities and various salts. Unfortunately, because of this, water can cause various deposits to appear inside the heating system and even lead to failure over time.
Distilled water
As a working fluid for the heating system, it is advised to use rainwater or its analogue - melt water, because even these fluids have fewer impurities and additives than water from a tap or from a well.
disadvantages
The main disadvantages of water as a heat carrier:
- high corrosive activity;
- scale formation;
- the possibility of destruction of the heating system in just a couple of days if the liquid accidentally freezes;
- fluid change should be done annually.
In the photo - the consequences of freezing water in the battery
The water scale can be slightly reduced. This process is called mitigation. The easiest option is to simply boil water in a metal container without closing the lid. Some connections that have no place in the heating system will settle to the bottom, carbon dioxide will be released.Unfortunately, only some substances can be removed by boiling - for example, unstable calcium or magnesium bicarbonates.
There is also a chemical method for improving the composition of water, which turns soluble salts in a liquid into insoluble. It is carried out using slaked lime, sodium orthophosphate or soda ash. All of these additives are capable of causing precipitation that can be removed by simply filtering the water.
Also, antifreeze, unlike water, is more "scrupulous" in relation to the rules of use - the possibility of its use significantly depends on their observance.
- The pumps required to circulate the coolant must be very powerful, otherwise it will be difficult for the antifreeze to move through the pipes. In some cases, it may be necessary to install an external blower.
- Pipes with a large diameter should be used and the radiators should also be large.
- Air removal devices should not be automatic.
- The gaskets and seals used in the system can only be made of dense and resistant to chemical compounds rubber or made of teflon and paronite.
- When the boiler is turned on, the heating temperature should be increased gradually. In this case, the temperature of the coolant should not exceed 70 degrees.
The power of the heating boiler should be increased gradually after starting.
Antifreeze should never be used in the following cases:
- if the heating system in the house is an open type system;
- if the heating system is galvanized;
- if the heating boiler is capable of heating the antifreeze to more than 70 degrees;
- if oil paint was used as a sealant for the joints in the system, linen winding;
- if ion boilers are used.
Water is the cheapest, most affordable and environmentally friendly heat carrier; an accidental leak from the heating system will not create problems for the health of households. And in the event of such a leak, it is very easy to restore the original volume of water in the heating system - you just need to add the required number of liters to the open expansion tank of the heating system.
Disadvantages:
- water forms scale and reduces heat transfer, as a result of which - energy consumption increases;
- water inevitably leads to corrosion of the heating circuit;
- in the event of a power outage or a drop in gas pressure, at a negative temperature outside, water, having the properties of expanding when freezing, will simply disable the heating system of your house by breaking the heating pipes;
- it is impossible to leave the house unattended in winter, even under unforeseen circumstances, in order to avoid freezing of water (two or three days and an expensive replacement of heating pipes is provided);
- the water must be changed at least once a year, as opposed to the 5-year service life of antifreeze.
Read more: Heating a cottage schemes and nuances of organizing autonomous heating
Water is the only natural liquid that expands both when heated and cooled. Water in its chemical composition has many different impurities of iron, chlorine, salts, and therefore, when heated, salting out occurs on the walls of pipes, on the surfaces of heat exchangers, heating elements, which is the reason for the deterioration of heat transfer and the heating elements may fail due to overheating.
The simplest way to soften water is well known to everyone - thermal (boiling), using a metal container without a lid. In the process of heat treatment, part of the salts will be deposited at the bottom of the container, and carbon dioxide will be removed from the water volume.The disadvantage of the thermal method is that in this way only unstable magnesium and calcium bicarbonates can be removed from the water, and their stable compounds will remain.
The chemical or reagent method is more effective, it allows you to transfer salts contained in water into an insoluble state. For its implementation, slaked lime, soda ash or sodium orthophosphate are used, but in this case it is necessary to know the exact dosage of the reagents. In all operating instructions, manufacturer's recommendations and manuals for installers, it is unanimously stated that heating structures are designed to use a standard coolant in them - distilled water, there are no impurities in it at all, but there are drawbacks - you will have to spend money on the purchase.
Before pouring distilled water into the heating system, it is necessary to thoroughly rinse the heating devices with plain water. It is desirable that special additives be added to the distilled water to help "extend the life" of the heating system. Please note that at temperatures below 0 ° C, it will freeze, expand and cause irreparable damage to the heating system, therefore it is more practical and correct to use antifreeze.
Do not forget that it should not be car antifreeze, transformer oil or ethyl alcohol, but antifreeze specially designed for heating systems. Moreover, we must not forget that antifreeze must be fireproof and not contain additives that interact with the metal of the equipment and are not approved for use in residential premises.
- Before purchasing a heating boiler, make sure that the manufacturer allows it to work in the heating system with this antifreeze, otherwise the factory warranty for the boiler will not be valid.
- Highly concentrated antifreeze is often diluted with water. To obtain antifreeze with a freezing point of -30 ° C, one part of distilled water should be added to two parts of antifreeze. To reach a freezing point of -20 ° C, antifreeze is mixed in half with water. We must not forget that the first available water should not be used to dilute the antifreeze - it must be soft.
- When constructing the heating circuit, do not use galvanized pipes and fittings.
- The heating boiler should not heat the coolant to temperatures exceeding 70 ° C (this is the limiting heating temperature of any antifreeze, it cannot be heated above due to the high temperature expansion inherent in coolants of this group).
- Equip the system with a more powerful circulation pump than would be needed for hot water heating.
- Install a larger expansion tank, the volume of which is at least twice the volume required for the water coolant.
- In the heating system, use pipes of a deliberately larger diameter and volumetric radiators.
- Do not install automatic air vents - only manual ones (for example, Mayevsky taps).
- Seal detachable joints with gaskets made of chemically resistant rubber, paronite or Teflon only. You can use linen roll along with an ethylene glycol resistant sealant (in the case of using an antifreeze based on ethylene glycol).
- Use only gaskets made of chemically resistant materials in all detachable joints. When buying cast iron radiators, it is necessary to disassemble them into sections and replace the existing rubber gaskets with paronite or Teflon ones.
- Before each complete pouring of antifreeze into the system, it is imperative to rinse it with water (the boiler too) - manufacturers of anti-freeze devices recommend completely replacing them in the heating system every 2-3 years;
- you should not set a cold boiler immediately to a high heating temperature of the antifreeze coolant, you need to raise the temperature gradually, giving the coolant time to warm up (non-freezing systems have a lower heat capacity than water).
- In winter, when you turn off a double-circuit boiler in a system with antifreeze for a long time, do not forget to drain the water from the hot water supply circuit, because it can freeze and damage the circuit pipes.
If the temperature in the heating circuit during the cold season does not drop below 5 ° C, then the optimal coolant for such a system is water, from which salt compounds are maximally removed. If there is a possibility of the temperature falling to minus values, then in this case only antifreeze is needed.
- permissible extremely low temperature;
- the composition of the additives and their purpose;
- what interactions with elements of the heating system (made of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, cast iron, plastic, rubber, etc.) can occur when using it;
- the duration of the period of use in the system without replacement;
- safety for human health and the environment (after all, it will have to be merged somewhere).
Heating with antifreeze or water
After reading this section, you will most likely give up antifreeze in your heating system. The main plus of antifreeze is the safety of the system at low temperatures, it is completely crossed out by its minuses.
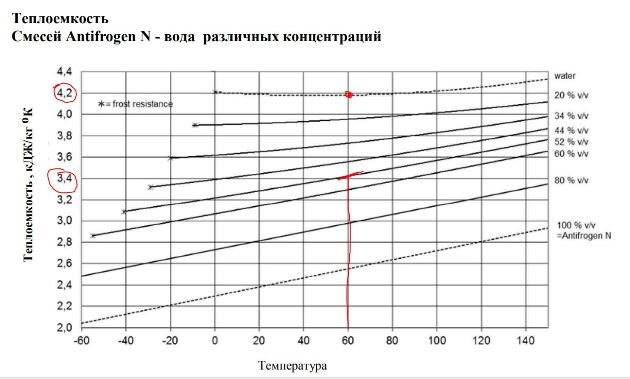
- Low heat capacity of antifreeze. Increase in size radiators by 20-23%
The heat capacity of antifreeze is significantly lower than the heat capacity of water. Diluting water with 35% antifreeze, we lose about 200 W from 1 kW of thermal energy. This means that a 20% increase in the size of pipes, radiators and boiler is required. In terms of a country house of 300 m2, we lose about 60 thousand rubles on increasing the size of the system.

- Antifreeze service life from 5 to 10 yearsOver the years, antifreeze oxidizes and safely destroys brass compounds. After 5 - 10 years, ethylene glycol and propylene glycol must be drained, disposed of and replaced with a new one. You will not only have to buy new antifreeze, but also pay to dispose of the old one. Unfortunately, in our country there is no service for the disposal of ethylene glycol in small volumes, therefore, it will be difficult to find who to hand over this chemistry. I will not consider the idea of pouring antifreeze to a neighbor on the site.
- The use of sectional radiators in systems with antifreeze is unacceptable.Rubber inter-section gaskets oxidize quickly and radiators leak. We use only steel panels. The use of galvanized pipes is also unacceptable. Antifreeze successfully flushes out the zinc, and the pipe remains bare.
- Why is antifreeze useless for a country house?Antifreeze will successfully cope with the task - the heating system will not freeze in winter in your absence, but what to do with the water supply system?Water supply pipes at negative temperatures will freeze faster and with worse consequences, because are laid not only in the floor, but also in the walls. You will have to remove the tiles, beat the screed and change pipes in bathrooms, showers, kitchens, replace the entire piping of the boiler room for water supply. Of course, it will not work to pump antifreeze into the water supply system, as well as to lay all the pipes with heating cables.
Output: Antifreezes are suitable either for heating small summer cottages for temporary residence, or large warehouses, workshops and enterprises. Antifreezes are useless in the heating system of a full-fledged country house.
Antifreeze for the heating system of a country house is needed if:✔ do not plan to live in the house in winter; ✔ in the house there are 1-2 bathrooms with a tee water supply system (without a collector), which can be drained before the onset of cold weather.
It is impossible to leave a full-fledged country house in winter without on-duty heating. In winter, it is necessary to maintain constant standby heating + 10-12 ° С.
The boiler can be controlled remotely via a phone or tablet via an Internet connection or GPS.You can set the air temperature for a specific date and time of arrival, and the boiler will accurately signal possible errors in operation. To maintain the heating system in the event of an accident in the main boiler, a backup electric is often installed, which also turns on automatically. You can order a project of such a boiler room and heating system on our Services page.
This way your engineering systems will be truly protected without antifreeze.
If you liked my article and you are looking for reliable design specialists - call and write to me by mail.
Sometimes the heating system stops functioning in the midst of the heating season. The reasons can be different, from a power outage to a breakdown of any element of the system. If water is used as a coolant, then the lack of heating for a certain amount of time (including depending on the insulation of the house) leads to defrosting of the heating system. Defrosting, as a rule, leads to unfortunate consequences such as burst pipes, radiators, etc. However, this can be avoided if antifreeze is used as the coolant.
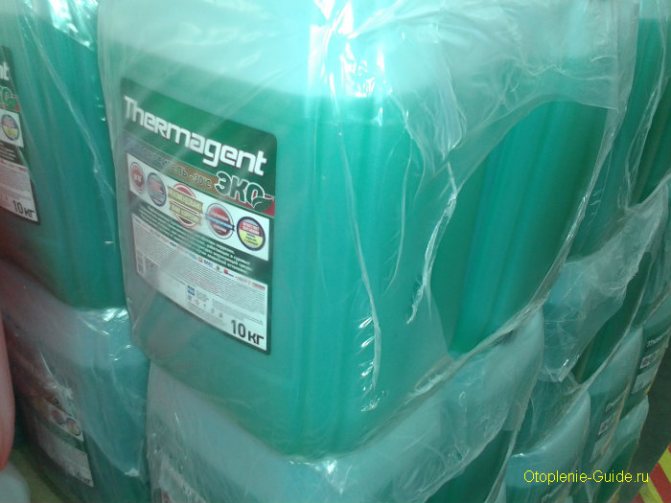


Heat carrier Thermagent Eko, 10 kg.
Antifreeze for the heating system is a liquid, the main purpose of which is to protect the system from defrosting, as well as to reduce the effects of corrosion, scale and various microorganisms.
Note! Manufacturers add special additives to the coolant that prevent the formation of corrosion and scale. However, it should be noted that the effect of the additives, as a rule, lasts a maximum of 5-6 years, after which their effectiveness is greatly reduced and the coolant, while maintaining its anti-freezing properties, will no longer protect the system from the effects of corrosion and scale. After 5-6 years, it is recommended to fill in a new coolant, while pre-flushing the system with water.
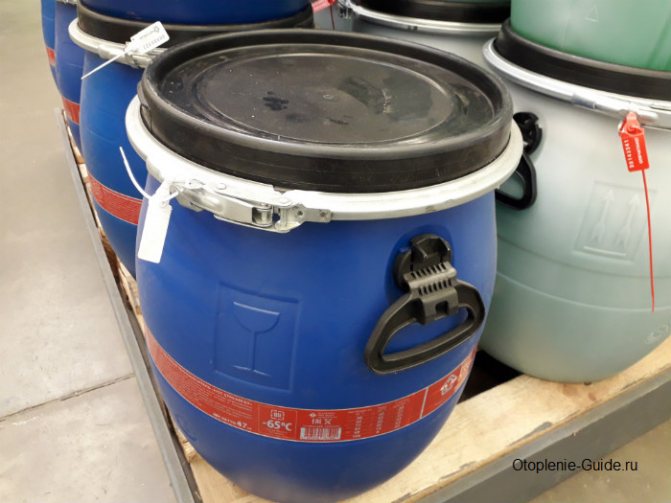


Hot Stream-65, 47 kg. Down to -65 ° C.
What's the difference between green and red antifreeze?
Pure 100% antifreeze is not used as a heat carrier - always in a diluted state: from 20 to 35% antifreeze and 80-65% water, respectively. Only 2 types of antifreeze based on dihydric alcohols are used in heating: ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. Manufacturers produce both a concentrated composition and already diluted for pouring into the heating system. Ethylene glycol is a concentrated red solution and ethylene glycol is a green solution. I will describe their differences below.
Read more: Calculation of the heating system of a private house formulas and examples
Zvir90 ›Blog› How to dilute antifreeze concentrate?
Antifreeze concentrate must be diluted with water before pouring into the radiator, because it is not intended for use as such, but for the preparation of coolants from it with different freezing points. Antifreeze concentrate - almost 100% ethylene glycol (no more than 5% water) with concentrated additives added to it. The temperature of such antifreeze is about minus 13oС. To obtain a coolant with a freezing point of minus 39-40 ° C, the concentrate is diluted with water in a 1: 1 ratio so that the freezing point is minus 30 ° C, in a ratio of 2: 3, and minus 20 ° C in a ratio of 1: 2. It is best to dilute with distilled water, 100% guarantee that no sediment will form either during dilution or during operation. If you are promised that you can dilute with plain water, then it is better to first check by preparing a small volume of antifreeze solution in the ratio you need on your tap water. Let it stand for a day or two and, if there is no turbidity or sediment, prepare the solution and pour it into the radiator.
How to fill in the system correctly?
Crimson solution. A toxic substance used in the auto industry, the production of motor oils, plastic and cellophane. It has an extremely low pour point of -70 ° C.It is mainly used in heating and anti-icing systems of industrial facilities, football fields. It is not recommended to use ethylene glycol in suburban heating systems due to its toxicity.
Green solution, food additive E1520, used in the cosmetics industry. Pour point -50 ° C. 3 times more viscous and 2 times more expensive than ethylene glycol. It is widely used in buildings where there is a risk of system defrosting, but environmental performance is required. In our country, propylene glycol for the heating system is produced from imported raw materials, therefore, it is much more expensive than ethylene glycol.
I got a lot of questions about "glycerin". A glycerin-based heat carrier in the heating system is unacceptable, even in a diluted state.
First, the monstrous kinematic viscosity at negative temperatures (at 0 ° C –9000 m2 / s x 106 - glycerin, 67 m2 / s x 106 - ethylene glycol) - and hence the monstrous pressure loss. It will be difficult to push the glycerin-based coolant through the pipes.
Secondly, the adhesion of organic particles of glycerin to the surface of the boiler heat exchanger, its overheating and complete exit from standing. Dilution of glycerin with alcohols only leads to the formation of explosive compounds.
Any other non-freezing liquids, for example, antifreeze in the heating system, are unacceptable, because do not contain the required amount of anti-corrosion additives. The cost of antifreeze for heating is determined by the quality of these very additives, thanks to which some antifreezes last 5 years and others 10. Over the years, antifreeze in the heating system oxidizes to form acetic acid, which leads to the destruction of brass connections on radiators, so it is important to change the coolant on time.
For household needs, i.e. for heating systems of private houses, antifreezes are produced based on ethylene glycol (monoethylene glycol) and propylene glycol, most of which are offered in Russia - made on the basis of ethylene glycol. This is a toxic substance that is extremely dangerous for humans and its contact with the skin or even more so in the human body is absolutely undesirable.
If the freezing point of antifreeze is -30 ° C, then the concentration of ethylene glycol in such a solution is approximately 44%. At a freezing point of -65 ° C, the concentration reaches 65%, (the remaining 4% are inhibitor additives). This product, considered optimal in terms of thermal performance, never delaminates, does not freeze down to a temperature of -65 ...
-70 ° С, and ethylene glycol practically does not evaporate from it. But in order to perform its main function (heat transfer), antifreeze must not only have satisfactory thermal conductivity, but also not boil in the operating temperature range, not foam, be chemically stable (not form deposits on the surface of the system) and not destroy structural materials.
Various additives help him to solve these problems: metal corrosion inhibitors, anti-foaming agents, etc., which make up about 4% of the solution weight. The use of ethylene glycol-based antifreeze is undesirable in two-circuit heating systems, when there is a possibility of mixing the coolant from the heating circuit into the water supply circuit, as well as in open heating systems (with an open expansion tank), where the coolant may evaporate.


Formulations based on the first type are more common and cheaper than those based on expensive propylene glycol, but they are quite toxic. Working with antifreeze containing ethylene glycol requires mandatory protection of the skin, respiratory system and eyes. Ethylene glycol, which is part of antifreeze, when it enters the human body becomes a "poison" (belongs to the third group of danger), a lethal dose for an adult can be a one-time "intake" of only 100 ml of this substance.
That is why antifreeze on this basis is recommended for use exclusively (!) In closed heating systems (with a closed expansion tank).Another disadvantage of such compositions is that ethylene glycol-based antifreezes are especially sensitive to overheating - with any, even short-term temperature rise above the limit set by the manufacturer for a given brand of non-freezing, its thermal decomposition occurs, insoluble precipitate and acids are formed.
Sediment, if it gets on the surfaces of the heating elements, forms a sludge that worsens heat exchange at the local level and causes overheating with re-formation of sludge, etc. Acids formed as a result of the decomposition of ethylene glycol react chemically with the structural metals of the heating system, causing multiple foci of corrosion.
As a result of the decomposition of the additives, the protective properties of the coolant, previously provided by it for the material of the seals of detachable joints, are sharply reduced, and with high fluidity, this will immediately cause a leak. In addition, overheating increases the foam formation of the antifreeze, which, in turn, adds air to the heating system.
Less dangerous to human life and health. It is important to remember that in the composition of such antifreeze there must be special additives, taking into account the fact that seals in the heating system can be made of various metals, which can be destroyed as a result of the use of an unsuitable component for them.


Non-freezers with propylene glycol are allowed to be used in double-circuit boilers, because their accidental penetration into drinking water, as well as leaks in the places of detachable joints, will not harm people. Propylene glycol coolants, in addition to the general same positive characteristics as ethylene glycol ones, inside the heating system have a lubricating effect, reduce hydrodynamic resistance and facilitate the operation of the secondary circuit pumps.
In some conditions, there is a need to use a heat transfer fluid with a fairly low freezing threshold. Such substances are called antifreezes. Antifreeze based on ethylene glycol accounts for approximately 25% of all heat transfer fluids.
Special additives are introduced into the composition of antifreeze based on ethylene glycol - inhibitors, which slow down the rate of undesirable chemical processes under the influence of ethylene glycol.
The freezing temperature can reach -60 ° C.
To use ethylene glycol, the following factors must be taken into account:
- Viscosity. Ethylene glycol is not used in its pure form; it is mixed with water. Depending on the concentration, the viscosity of the substance also changes. With an increase in viscosity, the speed of movement of the coolant through the pipes also decreases. Because of this, it is necessary to increase the pump performance, which leads to an increase in the cost of generating heat.
- Thermal expansion. The coefficient of thermal expansion of this substance is on average 50% higher than that of water. Therefore, during heating, to prevent pressure build-up in the heating devices, it is necessary to install an expansion tank. The same tank should also serve to feed the coolant when the temperature drops.
- Chemical properties. By its properties, ethylene glycol is aggressive towards some types of materials. For example, when using it, it is necessary to abandon rubber seals. You will need to replace them with paronite. Also, the use of galvanized pipes is not possible. Ethylene glycol dissolves zinc. When deciding to use ethylene glycol as a coolant, it is necessary to carefully study the passports of all installed heating devices for the possibility of its use.
- Filling the system. Filling the system with a water-glycol mixture is possible only with a make-up pump. Taking into account the increased viscosity of the mixture, it is necessary to correctly select the pump parameters. Also, it is necessary to select the material for the tank, from which the pump will fill the heating circuit with a solution.When choosing a pump, it is imperative to take into account the parameters of the liquid that it will pump.
- Toxicity Due to its high toxicity, ethylene glycol is not widely used. For humans, a lethal dose can be 50–500 mg. It is strictly forbidden to use ethylene glycol in open systems. Materials contaminated with ethylene glycol must be replaced.
Read more: Repair of ventilation systems malfunctioning and restoration of work
Positive sides:
- Defrosting the system is almost impossible.
- Good heat capacity.
- Low likelihood of lime scale formation.
- Quite an attractive price.
The negative side is toxicity! This is what prevents ethylene glycol from gradually displacing water from the leading position. Ethylene glycol is deadly.
The most reliable, safe and modern heat carrier is a propylene glycol-based product. It began to be used in the world since the 60s of the last century. In leading European countries, this antifreeze has been used as the main coolant for 20 years. In our country, propylene glycol accounts for only 5%.
When using propylene glycol, the following factors must be taken into account:
- Viscosity. Taking into account the increased viscosity compared to water, when designing a heating system, it is necessary to select a circulation pump with increased capacity. This will ensure the normal rate of heat transfer from the boiler to the heating radiators.
- Chemical properties. In terms of its chemical properties, this antifreeze is close to ethylene glycol. Before starting to use it, you need to make sure that it is possible to use this coolant on the selected equipment. Otherwise, the boiler and the heating system as a whole can be damaged. The use of rubber seals, as well as tow, is also not possible.
- Filling the system. In order to fill the heating circuit with propylene glycol, a recharge pump must be used. At the lowest point of the heating system, it is necessary to provide a place for connecting a booster pump. The system must be filled slowly. In this case, all air valves must be open. This filling method will help to avoid blocking the system with air.
Antifreeze base
Various substances can be used as a basis for the manufacture of antifreeze. The most common are ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, glycerin, and alcohol.
Ethylene glycol heat transfer fluid
Today, ethylene glycol-based antifreeze is the most common antifreeze coolant used in heating systems for private houses. However, it is quickly being replaced by the more advanced and environmentally friendly propylene glycol antifreeze.
Ethylene glycol reliably protects the system from freezing. When the freezing temperature is exceeded, the coolant expands by 1.5-2%, which is not enough for a rupture to occur in any part of the system.
Important! It must be remembered that ethylene glycol-based heat transfer fluid is poisonous and can be hazardous to human health and life. During operation, it is recommended to completely exclude his contact with a person. In particular, this applies to natural circulation heating systems in which there is
open expansion tank
... An open tank must be installed in the attic, but not in the living space. In extreme cases, a gas outlet pipe should be made from the tank, which will divert hazardous vapors to the street.
When working with ethylene glycol, it is necessary to take precautions, in particular to wear goggles and rubber gloves. Ethylene glycol can penetrate the human body through the skin, therefore, if during repair work or filling the system, non-freezing liquid gets on the skin, it should be immediately washed off with warm water and soap.If you get inside the body, you should rinse the stomach and immediately go to the hospital or call an ambulance. It must be remembered that a 100-200 ml dose of ethylene glycol-based antifreeze that has entered the human body can be fatal. Lethargy and depression are clear symptoms of poisoning.
Hot Stream, 20 kg - concentrated antifreeze for the heating system of a country house.
Ethylene glycol is not recommended for use with double-circuit boilers, because antifreeze may enter the hot water circuit.
Storage should be carried out in a tightly closed container away from direct sunlight, electric heaters and foodstuffs. It is highly discouraged to use ethylene glycol-based heat transfer fluid in heating systems of houses where small children live, because the liquid has a sweetish taste and does not have an unpleasant odor, so small children will not be able to determine that it is poison, but, on the contrary, may think that it is some kind of juice or just sweet water!
Important! If there is a leakage of the coolant, then all objects that have gotten or absorbed ethylene glycol (tiles, linoleum, parquet, furniture,
decorative radiator screens
etc.) must be subject to mandatory replacement. Otherwise, they will be a constant source of toxic fumes.
Spent ethylene glycol antifreeze is subject to processing at specialized enterprises; it is prohibited to drain it into the sewer or soil.
Propylene glycol based heat carrier
Due to its relative harmlessness, propylene glycol-based antifreeze is used at facilities with high environmental requirements, where there is a possibility of coolant getting into tap water or other human vital items. As noted above, propylene glycol antifreezes, despite their higher cost, are gradually replacing non-environmentally friendly ethylene glycol antifreezes.
As a heat carrier for heating systems, propylene glycol antifreezes have been used since the 60s of the last century. However, only since the mid-90s, in the countries of Western Europe, the USA and Canada, they began to completely switch to propylene glycol. Currently, Russia is also gradually switching to this safe antifreeze.
The propylene glycol-based heat transfer medium has a high viscosity, which nevertheless does not affect the hydraulic characteristics of the heating system. The fact is that propylene glycol has "lubricating properties" that compensate for its high viscosity.
The density of propylene glycol coolant is lower than that of ethylene glycol, which reduces the load on the circulation pump, and also more efficient circulation of the liquid through the heating system.
In addition, if propylene glycol-based antifreeze leaks, there is no need to change all the "contaminated" items. It is enough only to remove the coolant from the surface of objects and wipe them with a wet cloth.
Compared to ethylene glycol, propylene glycol protects the heating system more reliably from defrosting. Even if the minimum temperature is exceeded, propylene glycol antifreeze does not freeze, but turns into a mushy liquid, while expanding by only 0.1%. With such a volume of expansion, breaking the system is impossible.
The only drawback of this antifreeze is its high cost.
Hot Stream, 10 kg. The temperature of the beginning of crystallization is -30 ° C. Ingredients: ethylene glycol, demineralized water, Arteco additive package (Belgium). ...
Glycerin-based heat carrier
The most widespread glycerine coolants were obtained in the 20s of the last century.It was glycerin that became the basis of the first non-freezing coolants in the USSR, however, due to a number of significant shortcomings, by the beginning of the 40s, glycerin was practically no longer used in heating systems.
Their main disadvantages were poor fluidity and high viscosity levels, which caused the pumps to fail quickly. To solve this problem, they tried to use various additives, mainly poisonous methyl alcohol (methanol), which negatively affected the mental state of workers who had constant contact with it. In addition to the negative impact on human health, methanol boiled already at a temperature of 65 ° C, while evaporating, methanol sharply increased the viscosity of the liquid. In addition, the strong foaming of glycerin leads to the fact that air is constantly circulating in the system, the system is airy.
Another disadvantage of a glycerin-based coolant is that when it is heated for a long time, toxic substances are released, which cause accelerated corrosion of the metal elements of the heating system, as well as corrosion of sealing materials.
At the moment, manufacturers of glycerin-based antifreeze (including with the addition of methyl alcohol) get rid of the above disadvantages by adding special expensive additives. Their cost is much higher than the cost of ethylene glycol and propylene glycol additives. Therefore, when choosing antifreeze for the heating system, one should take into account the fact that the price of high-quality glycerin coolant will always be higher than ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. If the situation is the opposite, it means only one thing: the seller is trying to sell low-quality antifreeze.
Thermagent Eko, 45 kg. Down to -30 ° C.
What kind of coolant to buy?
There are a large number of different brands of heat transfer fluids on the market. All of them are approximately the same in their properties and technical characteristics. In most cases, the different costs are due to marketing and advertising costs. Those. the more popular the brand, the more expensive the product. There are, of course, certain nuances and patented formulations, but as a rule they do not justify the high cost of the product and are exclusively marketing "chips", ie. they do not make some kind of revolution in the heat carrier market and absolutely certainly are not worth overpaying for them.
In turn, we can recommend you the "ThermoStream" heat carrier from a domestic manufacturer - the optimal ratio of price and quality. Nothing superfluous and affordable price.
How to dilute antifreeze?
How to dilute antifreeze concentrate? If the product is certified and released to the market, the packaging will display detailed instructions for proper mixing with distilled water. You need to focus on the climatic zone in which you are at the moment. If you live in regions where the temperature can easily drop below -20 Celsius in winter, it makes sense to achieve a concentration that will withstand 40-degree frosts.
Related article: Contract engine - what it means and how to choose it correctly
There are a number of standard values and recommendations:
- in order for antifreeze to withstand a temperature drop down to -25 degrees, it is required to mix in a 2 to 3 ratio. 2 measuring cups of substrate and 3 cups of distillate. Remember that the boiling point is reduced to 130 degrees Celsius;
- to achieve an indicator of -45 degrees, it is necessary to mix equal proportions, i.e. 1 to 1.
More detailed values will be shown in this table.
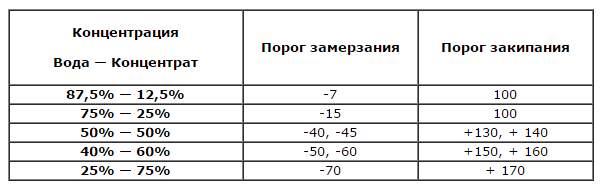

Pay special attention to the boiling point of the finished liquid.... Here, the regularity “the more water, the lower the boiling point” is in full force. Should antifreeze be diluted to critical values? Act according to the conditions in which the vehicle is used.Do not be greedy and overdo it with the "solvent", otherwise the key product will completely lose its useful properties.
Which coolant to choose for heating?
For a heating system, the differences between ethylene glycol and propylene glycol are insignificant, but different freezing temperatures (-70 and -50 ° C) affect the percentage of the substance. To ensure the same crystallization temperature (-25 ° C), almost 2 times less ethylene glycol is required than propylene glycol, but the relationship is not linear.
For example, when the concentration of ethylene glycol in water becomes more than 50%, its characteristics begin to decline. This is due to the ineffective work of anti-corrosion additives, which do not come into contact with water well.
A bit of theory
The coolant consists of ethylene glycol, colorants, various additives and water. Moreover, the water in the antifreeze is about half, depending on this parameter, the performance characteristics of the coolant and the temperature at which it freezes will differ. In the southern regions and in the middle lane, where severe cold is extremely rare, and in winter the car is stored in a warm parking lot or a heated garage, it is economically impractical to use pure antifreeze.
If the level of antifreeze in the expansion tank has dropped slightly, then it is allowed to dilute the coolant with distilled water, with practically no loss of performance. It is only necessary to take into account the initial properties of antifreeze, which is poured into the cooling system. Such dilution is possible both in summer and in winter, while the freezing temperature of the coolant will be minus 20-30 degrees.
Which antifreeze is best for heating a house
The main criterion for choosing antifreeze is safety!
Propylene glycol is used in the food industry. The substance is not toxic. It is used as antifreeze in heating systems of cottages, country houses and premises with constant presence of people.
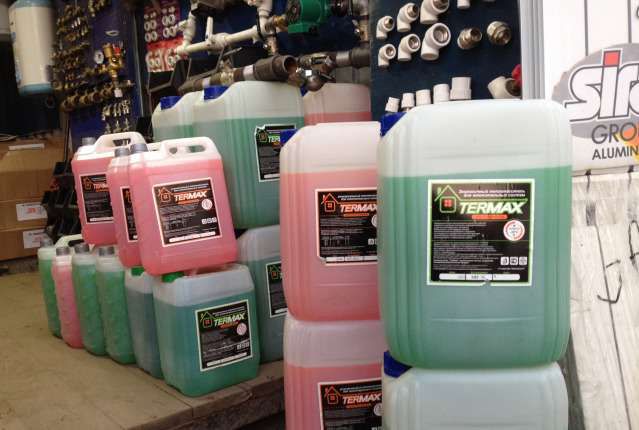


If the building does not require environmental safety, for example, warehouses, garages and production halls, you can safely use ethylene glycol. In all other cases, propylene glycol.
Dilution of antifreeze concentrate
Many antifreeze manufacturers produce refrigerants exclusively in concentrate form. Such substances are based on ethylene or propylene glycol. Special additives are also added. If you take ethylene glycol separately, you can set its crystallization temperature - thirteen degrees below zero. That is why water is added to ethylene glycol to provide a lower crystallization temperature. As a rule, there are instructions on the refrigerant packaging that contain the most appropriate mixing ratio. Almost all modern coolants contain special additives that provide lubrication and corrosion protection to system parts. So, if you add too much water to the concentrate, then the additives will lose their effectiveness, which, of course, will not benefit the car engine.
Calculation of the amount of coolant
Estimated
It is necessary to add up the amount of coolant in the boiler, radiators and pipelines. Data on the amount of coolant in the boiler and batteries can be taken from passports.
The volume of liquid inside the pipe can be calculated using the formula:
- V = S (sectional area of the pipe) x L (length of the pipe).
To simplify calculations, there is a volume table.
Radiator water volume:
- aluminum radiator - 1 section - 0.450 liters;
- bimetallic radiator - 1 section - 0.250 liters;
- old cast iron battery - 1 section - 1,700 liters;
The volume of water in 1 running meter of the pipe:
- ø15 (G ½ ”) - 0.177 liters;
- ø20 (G ¾ ") - 0.310 liters;
- ø25 (G 1.0 ″) - 0.490 liters;
- ø32 (G 1¼ ") - 0.800 liters;
Experienced
To determine the volume empirically, it is necessary to completely fill the heating circuit with water.Then it is necessary to carefully drain the water, measuring the volume with a measuring container.
When filling with water, it is necessary to slightly open the tap installed in the section of the water treatment system. In this case, the air valves must be open. In this way, airing of the system can be avoided.
The water from the heating circuit is drained through the drain valve into the sewerage system or the make-up tank. The system must be filled with propylene glycol using a booster pump.
As with water, the filling must be done at a low speed. Considering the cost of propylene glycol, the systems only need to be drained into the make-up tank.
It is necessary to fill the systems with ethylene glycol with all precautions. Under no circumstances should antifreeze be spilled or spilled on the body. Technically, the procedure for both draining and filling is identical to the procedures using propylene glycol.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lKKW_NrnUug
The frequency of water replacement in the heating circuit is usually one thermal season. For antifreeze, the frequency set by the manufacturer is 5 years.












