The heating system is one of the most important life support systems for the home. Each house uses a certain heating system, but not every user knows what an elevator heating unit is and how it works, its purpose and the possibilities that are provided with its use.

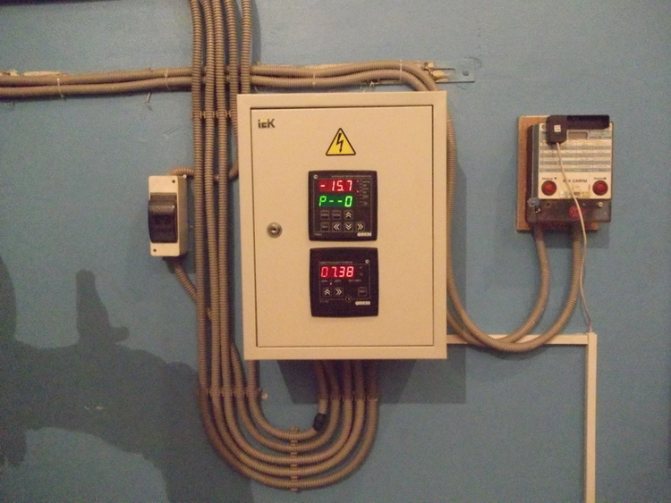
Electric heating elevator
Heating system device
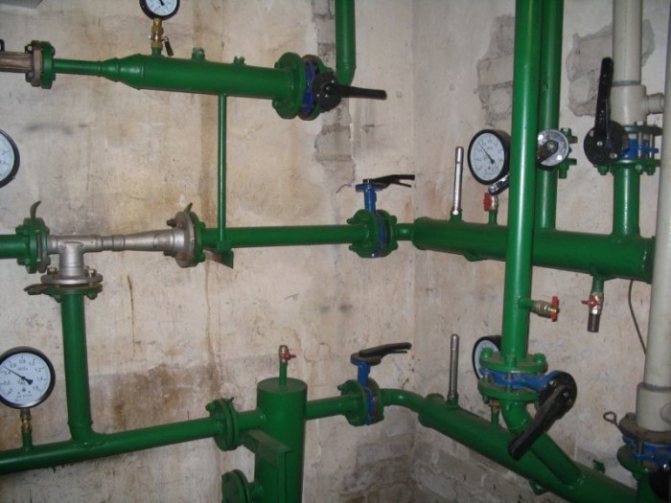
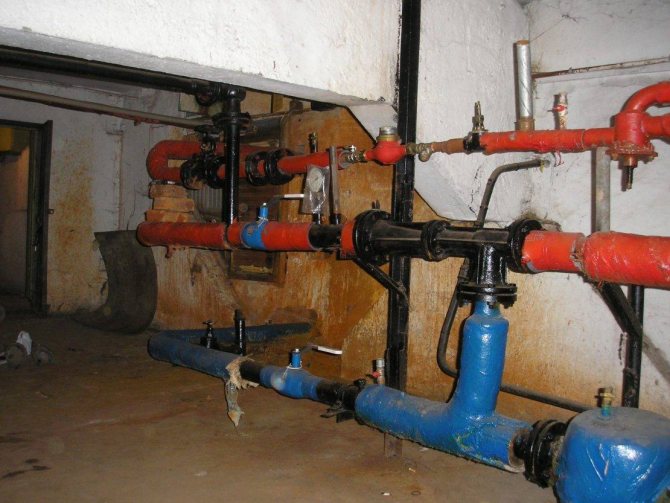
A heating unit is a way of connecting a home heating system to the mains. The structure of a heating unit in a typical apartment building built in the Soviet years includes: a mud sump, shut-off valves, control devices, the elevator itself, etc.
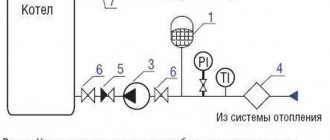
The elevator unit is placed in a separate ITP room (individual heating point). There must certainly be a shut-off valve in order to disconnect the in-house system from the main heating supply, if necessary. In order to avoid blockages and blockages in the system itself and in the devices of the internal house pipeline, it is necessary to isolate the dirt coming along with hot water from the main heating network, for this a mud sump is installed. The diameter of the sump is usually from 159 to 200 millimeters, all incoming dirt (solid particles, scale) collects and settles in it. The sump, in turn, needs timely and regular cleaning.
Control devices are thermometers and manometers that measure temperature and pressure in the elevator unit.


The main elements of the device
The elevator includes the following parts: nozzle, suction and mixing chamber, diffuser. In addition, this includes its piping, including measuring thermometers and manometers, shut-off valves.
Manufacturers also produce an adjustable elevator heating unit, which is able to change the nozzle diameter by means of an electric drive. This is necessary to control the heating of the heat carrier. The mixing ratio of superheated and cooled water in such a system changes, whereas in a conventional elevator this is not provided. This reduces the heat loss of the building and, accordingly, the cost of heating it.
The design of such an elevator with automatic regulation includes an actuator that guarantees constancy in the operation of the heating system at a low consumption of the heat carrier.
The structure of the cone-shaped nozzle consists of a guide device, a toothed roller and a throttle needle. The movement of the roller is provided by means of an electric motor or manually. The roller imparts movement to the throttle needle, which changes the lumen of the elevator assembly.
This makes it possible to change the consumption of the coolant. Therefore, it is possible to increase the water consumption within 15-45%, decrease it or completely block the nozzle.
When the lumen of the nozzle decreases, this leads to the fact that the flow rate of the water through the pipes and its mixing ratio increase significantly. As a result, the temperature of the coolant decreases.
It should be noted that foreign analogs have a fairly large adjustment range. However, this is not necessary. Domestic elevators have less such a range, but in practical use it is quite enough for various cases.
Alternative
New technologies also find their application in the utilities sector, as well as in the heating system. An automated heating system control unit is an alternative to a conventional elevator. Although it is more expensive, it is more ergonomic and economical.
The automated unit is designed to control the temperature and flow rate of the heat carrier inside the system, depending on the outside temperature. However, for its functioning, electricity is needed, sometimes of high power.
Of course, innovative technologies demonstrate more advantages in ensuring the required temperature regime of the heating system. Nevertheless, elevator units are also in wide demand in this area.
The device and principle of operation of the heating elevator
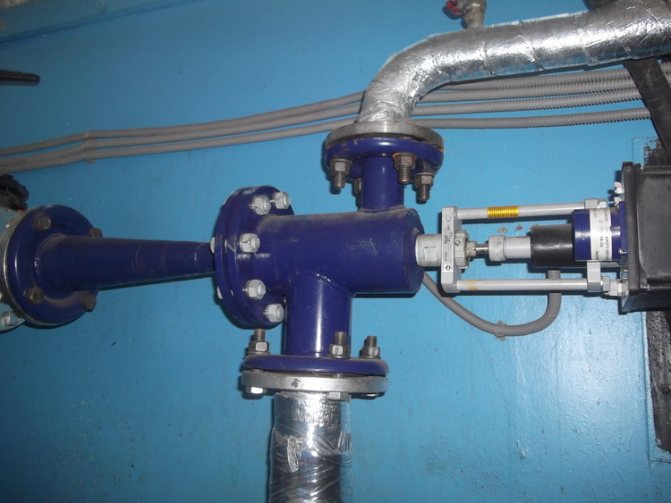
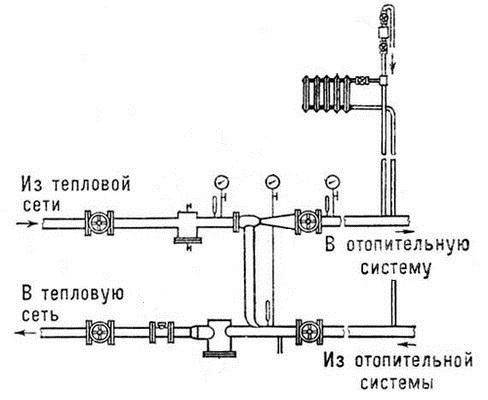
At the entry point of the heating network pipeline, usually in the basement, a knot that connects the supply and return pipes is striking. This is an elevator - a mixing unit for heating a house. The elevator is manufactured in the form of a cast iron or steel structure equipped with three flanges. This is an ordinary heating elevator, its principle of operation is based on the laws of physics. Inside the elevator there is a nozzle, a receiving chamber, a mixing neck and a diffuser. The receiving chamber is connected to the "return" by means of a flange. Superheated water enters the elevator inlet and flows into the nozzle. Due to the narrowing of the nozzle, the flow rate increases and the pressure decreases (Bernoulli's law). Water from the "return" is sucked into the area of reduced pressure and mixed in the mixing chamber of the elevator. The water reduces the temperature to the desired level and at the same time decreases the pressure. The elevator works simultaneously as a circulation pump and a mixer. This is, in brief, the principle of operation of an elevator in the heating system of a building or structure.
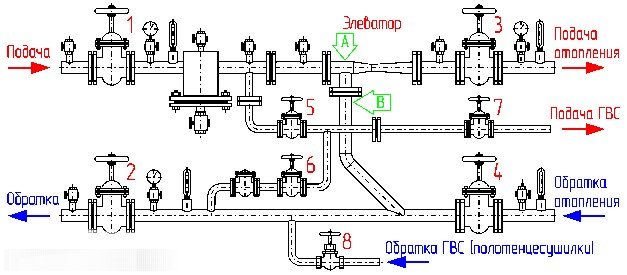
Heating unit diagram
The adjustment of the coolant supply is carried out by the elevator heating units of the house. The elevator is the main element of the heating unit; it needs strapping. The control equipment is sensitive to contamination, therefore, mud filters are included in the piping, which are connected to the "supply" and "return".
The elevator trim includes:
- mud filters;
- pressure gauges (inlet and outlet);
- temperature sensors (thermometers at the inlet of the elevator, at the outlet and at the "return");
- gate valves (for preventive or emergency work).
This is the simplest version of the circuit for adjusting the temperature of the coolant, but it is often used as the basic device of the heating unit. The basic unit for elevator heating of any buildings and structures, provides regulation of the temperature and pressure of the coolant in the circuit.
The advantages of using it for heating large buildings, houses and high-rise buildings:
- reliability due to the simplicity of the design;
- low cost of assembly and component parts;
- absolute non-volatility;
- significant savings in heat carrier consumption up to 30%.
But in the presence of indisputable advantages of using an elevator for heating systems, the disadvantages of using this device should also be noted:
- the calculation is done individually for each system;
- you need a mandatory pressure drop in the heating system of the facility;
- if the elevator is not adjustable, it is not possible to change the parameters of the heating circuit.
Elevator with automatic adjustment
Currently, there are elevator designs in which, with the help of electronic adjustment, the nozzle cross-section can be changed. Such an elevator has a mechanism that moves the throttle needle. It changes the lumen of the nozzle and, as a result, the flow rate of the coolant changes. Changing the clearance changes the speed of movement of the water. As a result, the mixing ratio of hot water and water from the "return" changes, thereby changing the temperature of the coolant in the "supply". Now it is clear why water pressure is needed in the heating system.
The elevator regulates the flow and pressure of the heating medium, and its pressure drives the flow in the heating circuit.
Functioning principle
The best example that a heating elevator will show how it works would be a multi-storey building.It is in the basement of a multi-storey building that you can find an elevator among all the elements.
First of all, we will consider what kind of drawing the elevator heating unit has in this case. There are two pipelines: supply (it is through it that hot water goes to the house) and return (cooled water returns to the boiler room).

Elevator heating unit diagram
From the heat chamber, water enters the basement of the house; there is always a shut-off valve at the entrance. Usually these are gate valves, but sometimes in those systems that are more thoughtful, they put steel ball valves.
As the standards show, there are several thermal modes in boiler rooms:
- 150/70 degrees;
- 130/70 degrees;
- 95 (90) / 70 degrees.
When the water heats up to a temperature not higher than 95 degrees, the heat will be distributed through the heating system using a collector. But at temperatures above normal - above 95 degrees, everything becomes much more complicated. Water of this temperature cannot be supplied, so it must be reduced. This is precisely the function of the elevator heating unit. We also note that cooling water in this way is the simplest and cheapest way.
Site search otoplenie-doma.org
Why do you need a heating unit
The heat point is located at the entrance of the heating main into the house. Its main purpose is to change the parameters of the coolant. To put it more clearly, the heating unit reduces the temperature and pressure of the coolant before it enters your radiator or convector. This is necessary not only so that you do not burn yourself from touching the heating device, but also to extend the service life of all equipment of the heating system.
This is especially important if the heating inside the house is divorced using polypropylene or metal-plastic pipes. There are regulated operating modes of heating units:
These figures show the maximum and minimum temperature of the coolant in the heating main.
Also, according to modern requirements, a heat meter should be installed at each heating unit. Now let's move on to the design of the heating units.
The purpose of the elevator in the heating system
The heat carrier leaving the boiler room or CHP plant has a high temperature - from 105 to 150 ° С. Naturally, it is unacceptable to supply water with such a temperature to the heating system.


Regulatory documents limit this temperature to a limit of 95 ° C and here's why:
- for safety reasons: you can get burns from touching the batteries;
- not all radiators can function at high temperatures, not to mention polymer pipes.
The operation of the heating elevator allows the temperature of the supply water to be reduced to the normalized level. You may ask - why can't you immediately send water with the required parameters to the houses? The answer lies in the plane of economic feasibility, the supply of a superheated coolant makes it possible to transfer a much larger amount of heat with the same volume of water. If the temperature is reduced, then it will be necessary to increase the flow rate of the coolant, and then the diameters of pipelines of heating networks will significantly increase.


So, the work of the elevator unit installed in the heating point consists in lowering the water temperature by mixing the cooled coolant from the return line into the supply pipeline. It should be noted that this element is considered obsolete, although it is still widely used today. Now, when installing heat points, mixing units with three-way valves or plate heat exchangers are used.
Determination of the value of the heating unit


An elevator is a non-volatile independent device that performs the functions of water-jet pumping equipment. The heating unit lowers the pressure, the temperature of the heat carrier, mixing in the chilled water from the heating system.
The equipment is capable of transferring a coolant heated to the highest possible temperatures, which is beneficial from an economic point of view. A ton of water, heated to +150 C, has thermal energy much greater than a ton of coolant with a temperature of only +90 C.
Principles of operation and a detailed diagram of the heating unit
To understand how equipment works, you need to understand its design. The layout of the elevator heating unit is not complicated. The device is a metal tee with connecting flanges at the ends.
The design features are as follows:
- the left branch pipe is a nozzle that tapers towards the end to the calculated diameter;
- behind the nozzle is a cylindrical mixing chamber;
- the lower branch pipe is needed to connect the water reverse circulation pipeline;
- the right branch pipe is an expansion diffuser that transports the hot coolant to the network.
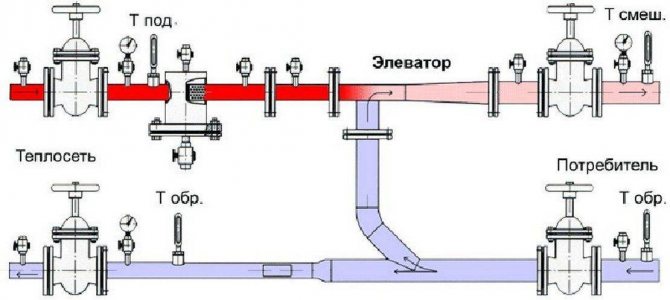

Despite the simple device of the elevator of the heating unit, the principle of operation of the unit is much more complicated:
- The coolant heated to a high temperature moves through the nozzle into the nozzle, then under pressure the transport speed increases, and the water quickly flows through the nozzle into the chamber. The water-jet pump effect maintains a predetermined flow rate of the coolant in the system.
- When water passes through the chamber, the pressure decreases, and the jet passes through the diffuser, providing a vacuum in the mixing chamber. Then, under high pressure, the coolant moves the liquid returned from the heating line through the jumper. The pressure is created by the ejection effect due to the vacuum, which maintains the flow of the supplied heat carrier.
- In the mixing chamber, the temperature regime of the flows decreases to +95 C, this is the optimal indicator for transportation through the heating system of the house.
Understanding what a heating unit in an apartment building is, the principle of operation of an elevator and its capabilities, it is important to maintain the recommended pressure drop in the supply and return pipelines. The difference is necessary to overcome the hydraulic resistance of the network in the house and the device itself
The elevator unit of the heating system is integrated into the network as follows:
- the left branch pipe is connected to the supply line;
- lower - to pipes with return transportation;
- shut-off valves are mounted on both sides, supplemented with a dirt filter to prevent blockage of the unit.
The whole circuit is equipped with manometers, heat meters, thermometers. For better flow resistance, a jumper is cut into the return line at an angle of 45 degrees.
Advantages and disadvantages of heating units
A non-volatile heating elevator is inexpensive, does not need to be connected to the power supply, and works flawlessly with any kind of coolant. These properties ensured the demand for equipment in houses with central heating, where a heat carrier of a high degree of heating is supplied.


Disadvantages of using:
- Maintaining the differential pressure of water in the return flow and supply pipelines.
- Each line requires specific calculations and parameters of the heating unit. At the slightest change in fluid temperature, you will have to adjust the nozzle holes, install a new nozzle.
- It is not possible to smoothly regulate the intensity and heating of the transported coolant.
Units with adjustable bore section, manual or electric drive of the gear transmission located in the antechamber are on sale. But in this case, the device loses its non-volatility.
general description
Before dealing with the diagram of the elevator heating unit, it must be said that, by its design, the elevator is a kind of circulation pump, which is located in the heating system along with pressure meters and shut-off valves.
Thermal elevator units perform a number of functions in their work.To begin with, this electronic device distributes the pressure in the heating system so that water is delivered to consumers in the heating batteries at a certain pressure and temperature. During the circulation through the pipes from the boiler room to multi-storey buildings, the volume of the heat carrier in the circuit almost doubles. This can only happen if there is a supply of water in a separate sealed container.
Most often, a heat carrier is supplied from the boiler room, with a temperature of about 110-160 ℃. For domestic needs, in terms of safety, these high temperature readings are unacceptable. The maximum temperature regime of the coolant in the circuit cannot be more than 90 ℃.
From this video we learn the principle of operation of the elevator heating unit:
It is also noteworthy that the SNiP currently indicates the temperature standard of the coolant in the range of 65 ℃. But in order to save resources, there is an active discussion on reducing this standard to 55 ℃. Taking into account the opinion of experts, the consumer will not feel a significant difference, and as a disinfection, the thermal carrier will need to be heated to 75 ℃ once a day. However, these changes in SNiP have not yet been adopted, since there is no exact opinion on the effectiveness and feasibility of this decision.
The diagram of the elevator unit of the heating system makes it possible to bring the temperature regime of the heat carrier up to standard requirements.
This device allows you to prevent the following consequences:
- if the wiring is made of propylene or plastic pipes, then it is not designed for the supply of a hot heat carrier;
- not all heating pipes are designed for prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures under high pressure - these conditions will lead to their rapid failure;
- very hot radiators can cause burns if handled carelessly.
The main malfunctions of the elevator unit
Even a device as simple as an elevator unit can malfunction. Malfunctions can be determined by analyzing the readings of the manometers at the control points of the elevator unit:
- Malfunctions are often caused by clogging of pipelines with dirt and solid particles in the water. If there is a drop in pressure in the heating system, which is much higher up to the sump, then this malfunction is caused by clogging of the sump, which is in the supply pipeline. The dirt is discharged through the drain channels of the sump, cleaning the nets and internal surfaces of the device
- If the pressure in the heating system jumps, then possible causes may be corrosion or a clogged nozzle. If the nozzle breaks down, the pressure in the heating expansion vessel may exceed the permissible value.
- A case is possible in which the pressure in the heating system rises, and the manometers before and after the sump in the "return" show different values. In this case, you need to clean the "return" sump. The drain taps on it are opened, the mesh is cleaned, and dirt is removed from the inside.
- When the size of the nozzle changes due to corrosion, a vertical misalignment of the heating circuit occurs. The batteries will be hot at the bottom, and insufficiently heated on the upper floors. Replacing the nozzle with a nozzle with a calculated diameter will eliminate this problem.
Advantages and disadvantages
The widest distribution of elevators in heat supply networks is due to the stable operation of these elements even with a change in the thermal regime of the coolant supply. In addition, the main advantages of using elevators are:
- Simplicity of design.
- Reliability in work.
- Energy independence.
In addition, the elevators in the CSO are practically maintenance-free. Correctness of work depends solely on competent installation and correctly selected nozzle diameter.
Important! The calculation of the elevator unit of the heating system, which includes the selection of pipe diameters, nozzle cross-section and the dimensions of the device itself, is carried out only in a specialized design organization.
Wiring diagrams for the elevator unit of the heating system


The processes of heating water for hot water supply (DHW) and heating systems are in some way interconnected with each other.
Due to the fact that the temperature of the water in the hot water supply under any conditions must be maintained within the range of 60 - 65 degrees, at positive outside temperatures, a hotter coolant can enter the elevator than required.
At the same time, there is an overconsumption of heat at the level of 5% - 13%. To avoid this phenomenon, three schemes for connecting the elevator unit are used:
- with a water flow regulator;
- with an adjustable nozzle;
- with a regulating pump.
With water flow regulator
When this condition is met, it is possible to avoid floor misalignment, which occurs in one-pipe systems in the event of a decrease in the flow rate of the coolant.
However, the elevator + flow regulator is not able to maintain the temperature downstream of this device at an acceptable level when there are deviations from the normal temperature schedule.
With adjustable nozzle
The cross-sectional area of the nozzle outlet is regulated by a needle inserted into it. At the same time, the mixing coefficient increases and, accordingly, the temperature of the coolant after the elevator decreases.
The disadvantage of this scheme is that when the needle is inserted into the hole of the cone, the hydraulic resistance of the latter increases, as a result of which the flow rate of the coolant, and, accordingly, the amount of supplied heat, decreases.

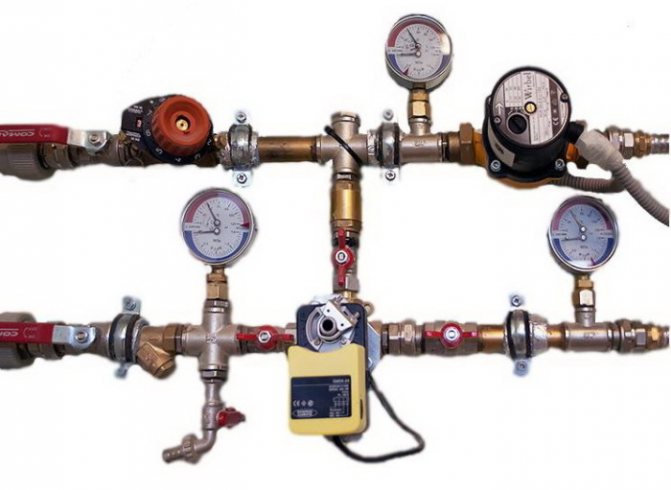
Schematic diagram of an adjustable elevator unit
With control pump
The pump is mounted on the mixing line of the elevator unit or parallel to it. In addition to it, regulators of the heat carrier flow and its temperature are mounted. This solution is very effective because it allows you to:
- regulate the temperature of the coolant at any outside temperature, and not only at positive;
- maintain the circulation of the coolant in the internal network when the external network is stopped.
The disadvantages of the scheme include high cost, complexity and increased operating costs due to the power supply of the pump.
Possible problems and malfunctions
Despite the durability of the devices, sometimes the elevator heating unit malfunctions. Hot water and high pressure quickly find weak points and provoke breakdowns.
This inevitably happens when individual assemblies are of poor quality, the calculation of the nozzle diameter is incorrect, and also due to the formation of blockages.
Noise
The heating elevator can generate noise when operating. If this is observed, it means that cracks or scuffs have formed in the outlet of the nozzle during operation.
The reason for the appearance of irregularities lies in the distortion of the nozzle caused by the supply of a coolant under high pressure. This happens if the excess head is not throttled by the flow regulator.
Temperature mismatch
The quality operation of the elevator can be questioned even when the temperature at the inlet and outlet is too different from the temperature schedule. This is most likely due to the oversized nozzle diameter.
Incorrect water flow
A defective throttle will result in a change in water flow from the design value.
Such a violation can be easily identified by the change in temperature in the incoming and outgoing piping systems. The problem is solved by repairing the flow regulator (throttle).
Defective structural elements
If the scheme for connecting the heating system to the external heating main has an independent form, then the reason for the poor-quality operation of the elevator unit can be caused by faulty pumps, water heating units, shut-off and safety valves,all kinds of leaks in pipelines and equipment, malfunctioning regulators.
The main reasons that negatively affect the circuit and the principle of operation of pumps include the destruction of elastic couplings in the joints of the pump and electric motor shafts, wear of ball bearings and destruction of seats for them, the formation of fistulas and cracks on the body, aging of oil seals. Most of the faults listed can be fixed by repair.
The problem of fistulas and cracks in the case is solved by replacing it.
Unsatisfactory operation of water heaters is observed when the tightness of the pipes is broken, their destruction occurs or the tube bundle sticks together. The solution to the problem is to replace the pipes.
Blockages
Blockages are one of the common causes of poor heat supply. Their formation is associated with the ingress of dirt into the system when the dirt filters are faulty. Increase the problem and build up of corrosion products inside the pipes.
The level of clogging of the filters can be determined by the readings of the pressure gauges installed in front of the filter and after it. A significant pressure drop will confirm or disprove the assumption about the degree of debris. To clean the filters, it is enough to drain the dirt through the drain devices located in the lower part of the housing.
Any malfunctions of pipelines and heating equipment must be eliminated immediately.
Minor remarks that do not affect the operation of the heating system are mandatory registered in special documentation, they are included in the plan for current or major repairs. Repair and elimination of comments occurs in the summer before the start of the next heating season.
Elevator unit - an element of the heating system, which allows to reduce the temperature of the heat carrier coming from the CHP to the optimal level. The heating elevator mixes the high-temperature heat carrier from the CHPP and the cooled heat carrier from the return line of the heating system of the apartment building. By regulating the volume of the coolant in two streams, the optimal temperature for the heating system of the house is achieved.
The temperature of the coolant in the external heating pipelines reaches + 130 ° С - + 150 ° С (if the water supply comes from large CHPPs), or + 95 ° С - + 105 ° С (from small CHPPs, local boiler houses).
Using water of this temperature is impossible for several reasons:
- The water temperature in the heating mains from the CHP is high. But with poor thermal insulation of the system and a sharp drop in air temperature, its sharp drops are possible.
- Such differences negatively affect the life of the internal heating system of residential buildings. For example, cast iron radiators, which are often used in the internal circuit of heating systems, can crack from a sharp temperature drop;
- Recently, they have been widely used in heating systems for residential buildings. Plastic pipes at temperatures above + 95 ° C deform, and also leak or crack. (Propylene can withstand temperatures at + 100 ° C, but on condition that such a temperature does not last long);
- Touching pipes heated to more than + 90 ° C can cause burns.
Note! According to SNiP-s, the temperature of the coolant in buildings where people are located should be no more than + 95 ° C at the supply and no more than + 70 ° C at the return.
Therefore, for heating residential buildings, a dependent connection scheme is rarely used, according to which the coolant from the heating network enters directly into the house heating system. In most cases, this is simply not possible.
More often we are dealing with a two-circuit system, the so-called independent connection scheme.
In this case, the water from the CHPP or the boiler house enters the heat exchanger, in which, due to the mixing of water from the external circuit and the internal circuit, the latter is heated to a temperature acceptable for use.
It is here that an elevator heating unit is used, as a device that mixes hot and cold flow to an acceptable temperature necessary and sufficient for operation in the internal system.
The elevator unit, despite its simplicity of design, performs 2 functions - under the influence of pressure drops, it works as a pump and a water mixer. Therefore, in some sources, this device is called a water-jet heating elevator or a mixing pump.
DHW from an individual heating point
The simplest and most common is the scheme with a single-stage parallel connection of hot water heaters (Fig. 10). They are connected to the same heating network as the heating systems of the buildings. Water from the external water supply network is supplied to the DHW heater. In it, it is heated by network water coming from a heat source.
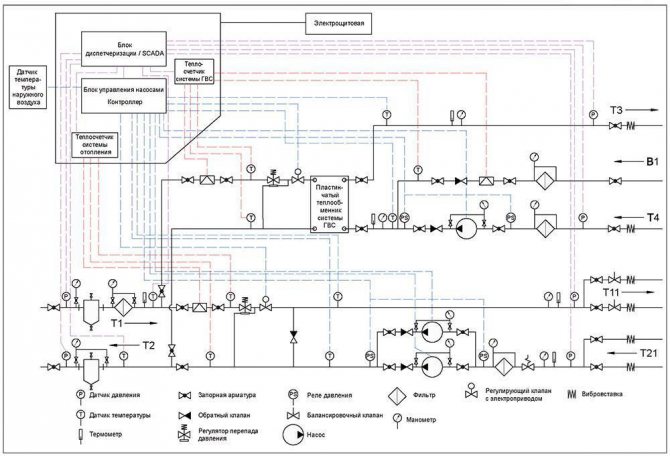

Fig. 10. Scheme with dependent connection of the heating system to the external network and single-stage parallel connection of the DHW heat exchanger
The cooled network water is returned to the heat source. After the hot water supply heater, the heated tap water enters the DHW system. If the devices in this system are closed (for example, at night), then hot water is fed back to the DHW heat exchanger through the circulation pipe.
In addition, a two-stage hot water heating system is used. In it, in winter, cold tap water is first heated in the first stage heat exchanger (from 5 to 30 ° C) with a coolant from the return pipe of the heating system, and then water from the supply pipe of the external network is used for the final heating of the water to the required temperature (60 ° C) ... The idea is to use waste heat energy from the return line from the heating system for heating. At the same time, the consumption of network water for heating water in the hot water supply is reduced. In the summer, heating takes place according to a one-stage scheme.
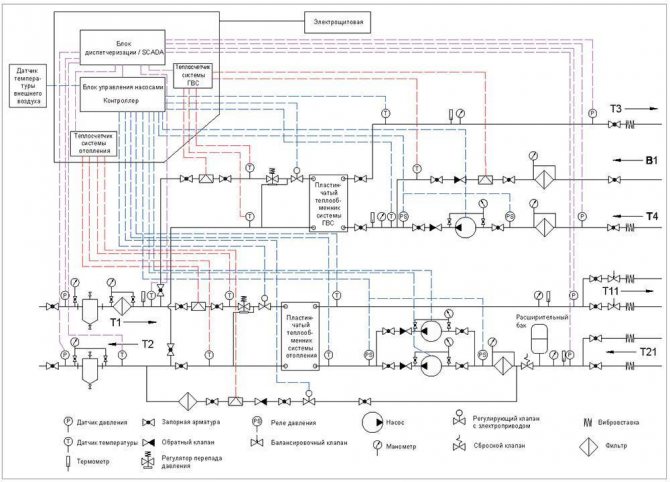

Fig. 11. Diagram of an individual heating point with independent connection of the heating system to the heating network and parallel connection of the DHW system
For multi-storey high-rise (more than 20 storeys) housing construction, schemes with independent connection of the heating system to the heating network and parallel connection of hot water supply are mainly used (Fig. 11). This solution allows you to divide the heating and hot water supply systems of the building into several independent hydraulic zones, when one IHP is located in the basement and ensures the operation of the lower part of the building, for example, from the 1st to the 12th floor, and on the technical floor of the building there is exactly the same heating point for 13 - 24 floors. In this case, heating and DHW are easier to regulate in the event of a change in heat load, and also have less inertia in terms of hydraulic mode and balancing.
The principle of operation of the elevator heating unit and the diagram
With the help of an elevator, the temperature of the overheated water is lowered to the calculated one, after which the prepared coolant is sent to the heating devices. The principle of operation of the elevator unit is based on mixing in it the superheated coolant from the supply pipeline with cooled water from the return pipe.
The diagram of the elevator unit below clearly shows that the elevator performs 2 functions at once, which makes it possible to increase the overall efficiency of the heating system:
- Works as a circulation pump;
- Performs mixing function;
The advantage of the elevator is its simple design and, despite this, high efficiency. Its cost is low. It does not require an electrical connection to operate.
The disadvantages of this element are also worth mentioning:
- There is no possibility of regulating the outlet water temperature;
- The pressure difference between the supply and return pipelines should not be outside the range of 0.8-2 bar;
- Only an accurate calculation of every detail of the elevator guarantees its efficient operation;
Today, elevators are still widely used in heating units of residential buildings, since their efficiency does not depend on changes in thermal and hydraulic regimes in heating networks. In addition, the elevator unit does not require constant supervision, and to adjust it, it is enough to choose the correct diameter of the nozzle. It is worth remembering that the entire selection of elements of the elevator unit should be trusted only by specialists who have the appropriate permissions.
The principle of operation of centralized heating
The general scheme is quite simple: a boiler room or a CHP plant heats water, supplies it to the main heat pipes, and then to heating points - residential buildings, institutions, and so on. When moving through the pipes, the water cools somewhat and at the end point its temperature is lower. To compensate for the cooling, the boiler room heats the water to a higher value. The amount of heating depends on the outside temperature and the temperature schedule.
For example, with a 130/70 schedule at an outside temperature of 0 C, the parameter of the water supplied to the main line is 76 degrees. And at -22 C - not less than 115. The latter fits well into the framework of physical laws, since the pipes are a closed vessel, and the coolant moves under pressure.
Obviously, such overheated water cannot be supplied to the system, since the overheating effect arises. At the same time, the materials of pipelines and radiators wear out, the surface of the batteries overheats up to the risk of burns, and plastic pipes, in principle, are not designed for a coolant temperature above 90 degrees.
For normal heating, several more conditions must be met.
- First, the pressure and speed of movement of the water. If it is small, then overheated water is supplied to the nearest apartments, and too cold water is supplied to the distant ones, especially the corner ones, as a result of which the house is heated unevenly.
- Secondly, a certain volume of coolant is required for proper heating. The heating unit receives about 5–6 cubic meters from the mains, while the system requires 12–13.


It is for the solution of all of the above issues that the heating elevator is used. The photo shows a sample.
Purpose and functions of the node
Water in district heating networks reaches a temperature of 150 ° C and moves along external mains under a pressure of 6-10 bar. Why are such high parameters of the coolant supported:
- So that high-temperature boilers or other heat-and-power equipment function with maximum efficiency.
- To deliver heated water to areas remote from the boiler house or CHP, network pumps must create a decent head. Then, at the heating inputs of nearby buildings, the pressure reaches 10 Bar (pressure test - 12 Bar).
- The transportation of the superheated coolant is economically profitable. A ton of water, brought to 150 degrees, contains significantly more heat energy than a similar volume at 90 degrees.
Reference. The coolant in the pipes does not turn into steam, since it is under pressure, which keeps the water in a liquid state of aggregation.
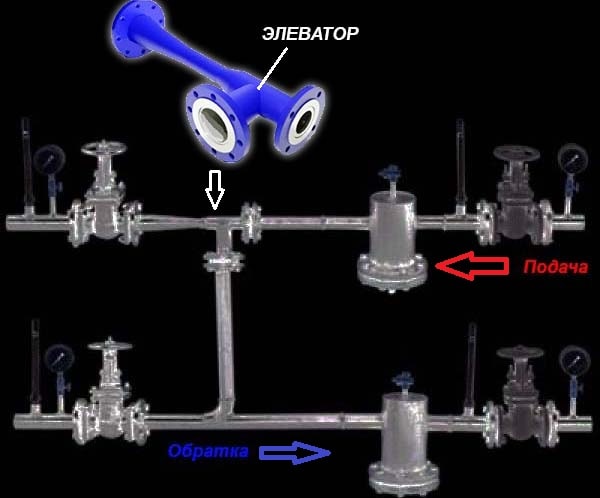

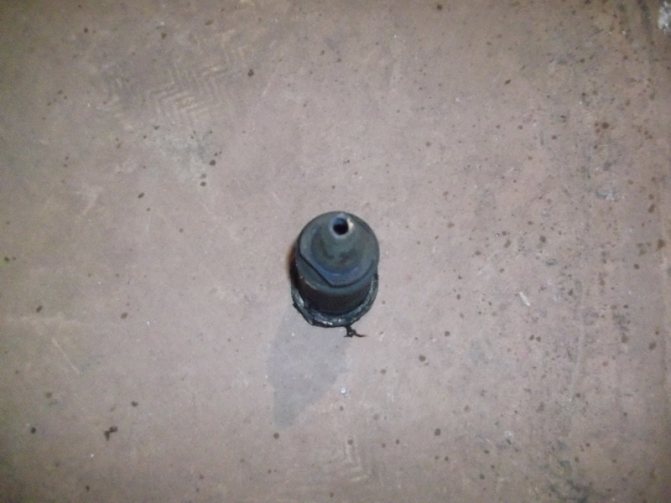
The detail is straightforward - seemingly an ordinary tee with flanges
According to the current regulatory documents, the temperature of the coolant supplied to the water heating system of a residential or office building should not exceed 95 ° C. And the pressure of 8-10 atmospheres is too high for an internal heating network. This means that the indicated water parameters need to be adjusted downward.
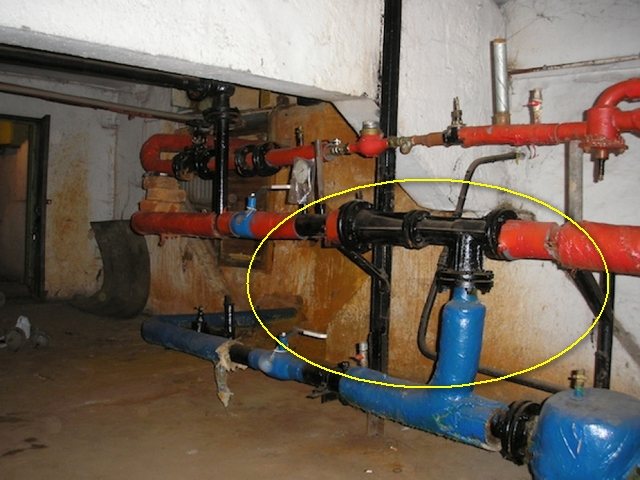
An elevator is a non-volatile device that reduces the pressure and temperature of the incoming heating medium by mixing in chilled water from the heating system.The element shown above in the photo is part of the heating unit diagram, installed between the supply and return pipelines.
The third function of the elevator is to ensure the circulation of water in the house circuit (usually a one-pipe system). That is why this element is of interest - with its external simplicity, it combines 3 devices - a pressure regulator, a mixing unit and a water-jet circulation pump.


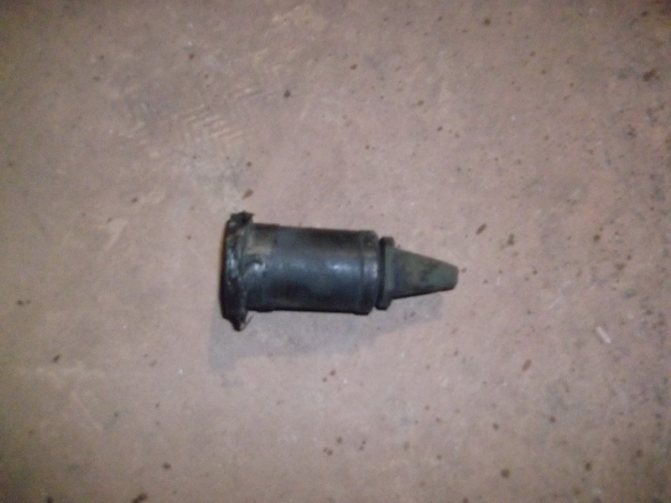
Elevator element with replaceable nozzle
The principle of operation of the elevator unit
The mixing elevator serves as a device for cooling the superheated water received from the heating system to a standard temperature before supplying it to the in-house heating system. The principle of its lowering consists in mixing water of elevated temperature from the supply pipeline and cooled down from the return pipeline.
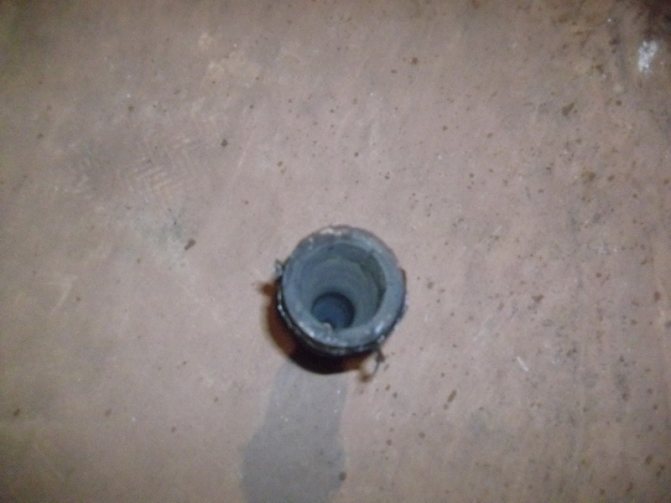
The elevator consists of several main parts. This is a suction manifold (inlet from the supply), a nozzle (throttle), a mixing chamber (the middle part of the elevator, where two flows are mixed and the pressure is equalized), a receiving chamber (mixing from the return), and a diffuser (outlet from the elevator directly to the network with a steady pressure ).
The nozzle is a constriction device located in the steel body of the elevator device. From it, hot water at high speed and with reduced pressure enters the mixing chamber, where water is mixed from the heating network and the return pipeline by suction. In other words, hot water from the main heating network enters the elevator, in which it passes through the converting nozzle at high speed and already reduced pressure, mixes with water from the return pipeline, and then, at a lower temperature, moves into the building pipeline. How the nozzle of a mechanical elevator looks directly can be seen in the photo below.
This structure of the elevator has an actuator to ensure its stable performance, consisting of a guiding device and a throttle needle, which is driven by a toothed roller. The action of the throttle needle regulates the flow rate of the coolant.


How does the elevator work
Studying the diagram of the elevator unit of the heating system, namely, what it is and how it functions, one cannot fail to note the similarity of the finished structure with water pumps. At the same time, the operation does not require obtaining energy from other systems, and reliability can be observed in specific situations.
The main part of the device from the outside looks like a hydraulic tee installed on the return line. Through a simple tee, the coolant would calmly enter the return line, bypassing the radiators. Such a heating unit scheme would be impractical.
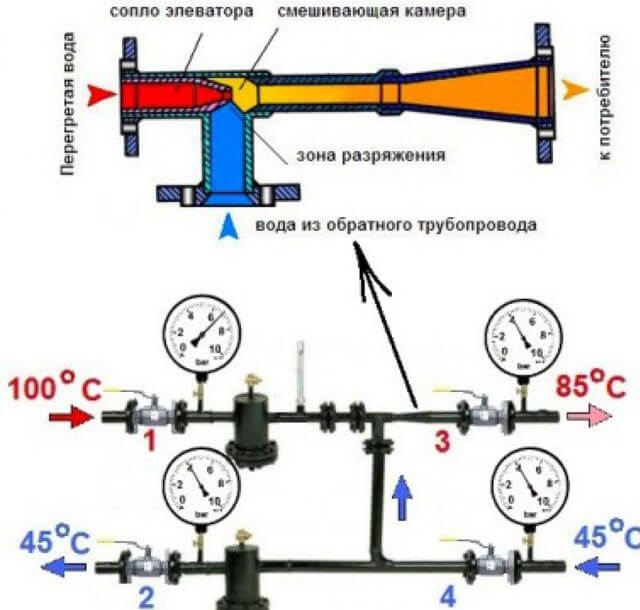

In the usual diagram of the elevator unit of the heating system, there are the following parts:
- A pre-chamber and a feed pipe with a nozzle of a certain section installed at the end. Through it, the coolant is supplied from the return branch.
- A diffuser is integrated at the outlet. It is designed to transfer water to consumers.
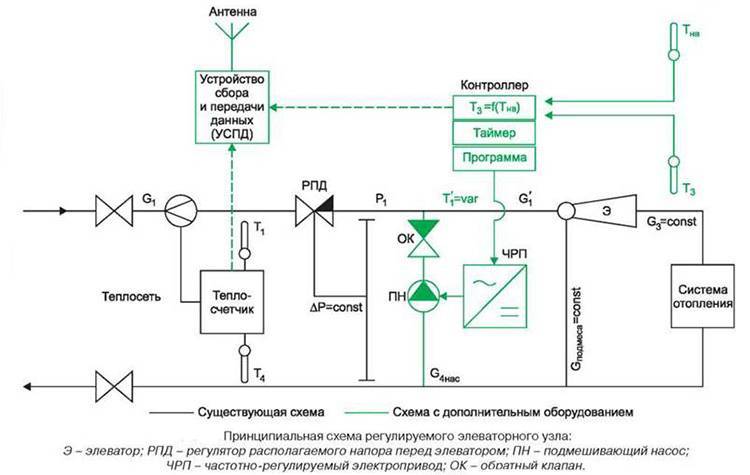
At the moment, you can find nodes where the nozzle cross-section is adjusted by an electric drive. Thanks to this, it is possible to automatically adjust the acceptable temperature of the heating medium.
The selection of a circuit for a heating unit with an electric drive is made on the basis that it is possible to change the mixing coefficient of the coolant within 2-5 units. This cannot be achieved in elevators in which the nozzle section cannot be changed.It turns out that systems with an adjustable nozzle make it possible to significantly reduce heating costs, which is very important in houses with central meters.
The role of the elevator assembly
Heating of domestic apartment buildings is carried out by means of a centralized heating system. For this purpose, small thermal power plants and boiler houses are being built in small and large cities. Each of these facilities generates heat for several houses or neighborhoods. The disadvantage of such a system is the significant heat loss.
The principle of the node
The boundary of a building is the outer walls and the top surface of the highest ceiling, basement in basement buildings, or ground level in buildings without basements. In the case of compact buildings, the boundary between the individual objects is the contact plane of the top wall, and if there is a joint between the two walls, the boundary between the buildings passes through the center.
Installation boundaries of the building, depending on the type of installation, for example, fitting, inspection hatches, shut-off valves for water, gas, heating, etc. Construction equipment includes all installations built into a permanent building, such as sanitary, electrical, alarm, computer, telecommunications, fire fighting and conventional construction equipment such as built-in furniture.
If the path of the coolant is too long, it is impossible to regulate the temperature of the transported liquid. For this reason, every house must be equipped with an elevator unit. This will solve many problems: it will significantly reduce heat consumption, prevent accidents that may arise as a result of a power outage or equipment failure.
This issue becomes especially relevant in the autumn and spring seasons. The heating medium is heated in accordance with established standards, but its temperature depends on the outside air temperature.
Thus, a hotter coolant enters the nearest houses, in comparison with those that are located further away. It is for this reason that the elevator unit of the central heating system is so necessary. It will dilute the superheated coolant with cold water and thereby compensate for heat loss.

Calculation of the heating elevator
It should be noted that the calculation of a water-jet pump, which is an elevator, is considered rather cumbersome, we will try to present it in an accessible form. So, for the selection of the unit, two main characteristics of the elevators are important for us - the internal size of the mixing chamber and the flow diameter of the nozzle. The size of the chamber is determined by the formula:
Here:
- dr is the required diameter, cm;
- Gpr - reduced amount of mixed water, t / h.
In turn, the reduced flow rate is calculated as follows:
In this formula:
- τcm - temperature of the mixture going for heating, ° С;
- τ20 is the temperature of the cooled coolant in the return line, ° С;
- h2 - resistance of the heating system, m. water. Art .;
- Q is the required heat consumption, kcal / h.
To select the elevator unit of the heating system according to the size of the nozzle, you need to calculate it using the formula:
Here:
- dr is the diameter of the mixing chamber, cm;
- Gпр - reduced consumption of mixed water, t / h;
- u is the dimensionless injection (mixing) coefficient.
The first 2 parameters are already known, it remains only to find the value of the mixing ratio:
In this formula:
- τ1 is the temperature of the superheated coolant at the inlet to the elevator;
- τcm, τ20 - the same as in the previous formulas.
Note. To calculate the nozzle, you need to take the coefficient u equal to 1.15u '.
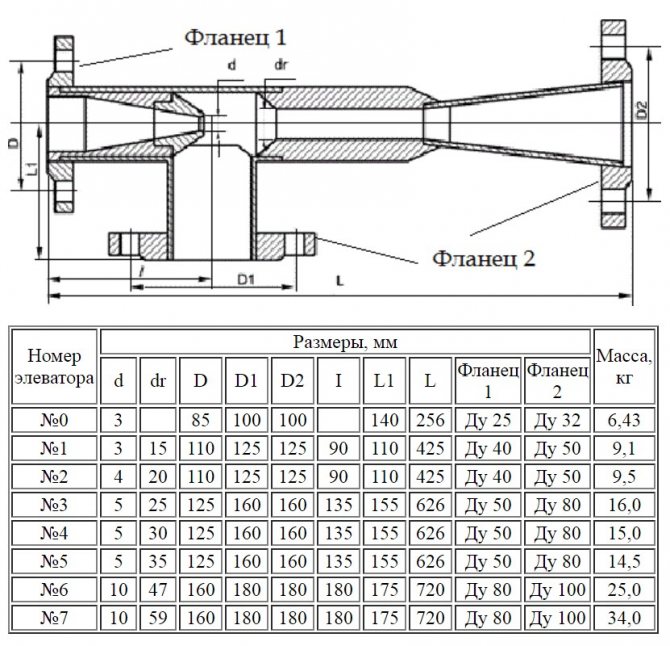
Based on the results obtained, the unit is selected according to two main characteristics. The standard sizes of elevators are designated by numbers from 1 to 7, it is necessary to take the one that is closest to the design parameters.
Three-way valve
If it is necessary to divide the heat carrier flow between two consumers, a three-way valve for heating is used, which can operate in two modes:
- permanent mode;
- variable hydraulic mode.
The three-way valve is installed in those places of the heating circuit where it may be necessary to divide or completely shut off the water flow. The material of the tap is steel, cast iron or brass. There is a shut-off device inside the valve, which can be spherical, cylindrical or conical. The tap resembles a tee and, depending on the connection, the three-way valve on the heating system can function as a mixer. The mixing ratio can be varied over a wide range.
The ball valve is used mainly for:
- temperature control of warm floors;
- battery temperature regulation;
- distribution of the coolant in two directions.
There are two types of three-way valves - shut-off and control valves. In principle, they are practically equivalent, but it is more difficult to smoothly regulate the temperature with three-way shut-off valves.
- How to pour water into an open and closed heating system?
- Popular floor-standing gas boiler of Russian production
- How to properly bleed air from a heating radiator?
- Expansion tank for closed-type heating: device and principle of operation
- Gas double-circuit wall-mounted boiler Navien: error codes in case of malfunction
Recommended reading
Expansion membrane tank of the heating system: design and function Heating thermostat - the principle of operation of different types of Bypass in the heating system - what is it and why is it needed? How to correctly select an expansion tank for heating?
2016–2017 - Leading portal for heating. All rights reserved and protected by law
Copying of site materials is prohibited. Any copyright infringement entails legal liability. Contacts
What is an elevator and how is it used
According to sanitary standards, the temperature of the medium entering the heating system of the house should not exceed 95 degrees C. And water can be supplied to the main pipeline within 130-150 degrees C. It becomes necessary to reduce the heating of the media to the desired value. There are several reasons for this:
- if the apartments are equipped with cast iron radiators, they may become unusable. Cast iron does not tolerate significant temperature changes. Due to the high, it can become fragile, which leads to leakage, and sometimes even to an explosion of batteries;
- people due to such temperatures inside metal radiators and pipes can get burns (especially for children);
- plastic pipes, which are now often used, withstand a maximum of 90 degrees. C, that is, with a hotter coolant, they can melt. And even at their maximum loads, they have a one-year manufacturer's warranty.
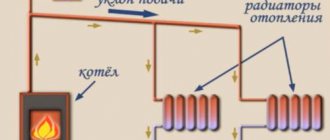
The heat carrier is supplied to the heating system of the house through the supply pipeline. And the water that has given off the heat is diverted back to the boiler room. The carrier is heated with a certain thermal reserve in order to transfer heat through pipes in cold weather.
From the heat chamber, it enters the basement of the house, where there are shut-off valves at the entrance. It is a gate valve or steel ball valves. You can purchase shut-off valves below by following the link.
If the heating of the coolant does not exceed 95 degrees C, it is distributed through the pipes of the house system with the help of collectors and balancing taps. If the temperature is higher (130-150 degrees C), it must be cooled. Therefore, the heating control unit includes an elevator, in which this happens.
Such a device is the most inexpensive and simplest way to cool water so that its temperature is acceptable for the system inside the building. In a private house, the heating mixing unit is also part of the heating.For example, when water is supplied for floor heating, it is cooled from 70-80 degrees C, coming from the boiler, to the required 50-55 degrees C.
Elevator with adjustable nozzle
With the help of the latest models of elevators equipped with automation, you can significantly save heat. This is achieved by regulating the temperature of the coolant in the zone of its outlet. To achieve this goal, you can lower the temperature in apartments at night or in the daytime, when most people are at work, study, etc.


The economical elevator unit differs from the conventional version by the presence of an adjustable nozzle. These parts can have different designs and levels of adjustment. The mixing ratio of a device with an adjustable nozzle varies from 2 to 6. As practice has shown, this is quite enough for the heating system of a residential building.
The cost of equipment with automatic adjustment is much higher than the price of conventional elevators. But they are more economical, functional and efficient.