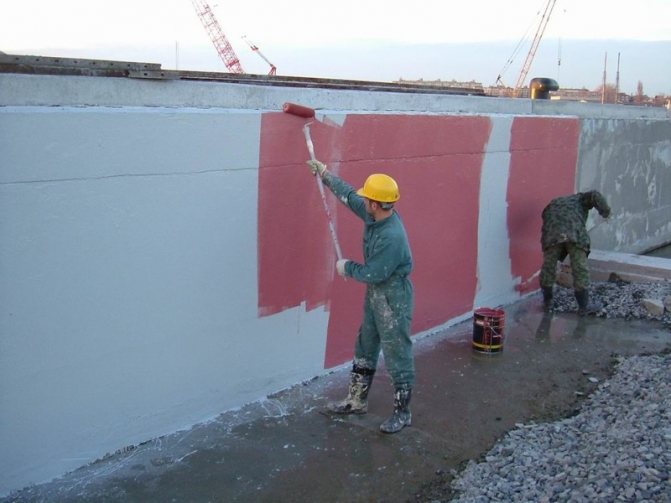
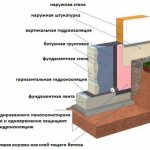
The concrete base of the building requires close attention during construction, not only with respect to resisting loads, but also taking measures to protect against moisture penetration into the structure of the material. The use of a specific foundation waterproofing technology assumes an understanding of the processes of soil moisture impact on the foundation structure.
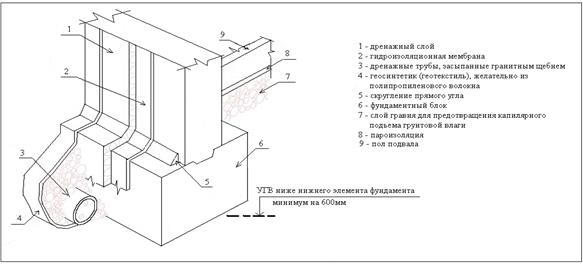
Strip foundation waterproofing scheme.
Feature of protection of building structures from water
Waterproofing works must be carried out regardless of whether there is groundwater on the building site or not. If, during the study of the hydrogeology of the territory, the presence of groundwater is detected, it is recommended to make drainage in addition to waterproofing. So it is possible to exclude the risk of flooding the site due to seasonal fluctuations in the level of groundwater. If the water available in the soil is below the level of the base of the building all year round, this will have a positive effect on the condition of the supporting structures. But building structures are also negatively affected by atmospheric / surface waters. Therefore, the blind area around the object must be done.
Waterproofing is made in such a way that it rises along the surface of a vertical wall to a height of at least 20 centimeters. For brick and wooden structures, moisture protection rises to the foundation up to 20-25 centimeters above the ground. If the floor of the building is laid on wooden structures, then it is allowed to bring the insulation to the surface up to 15 centimeters.
The way to protect the foundation and basement of buildings can be the manufacture of their structural elements from special hydro-concrete, which includes several brands. Grades of hydro-concrete are selected depending on the characteristics of the operation of the structure. This building material can be used for the construction of port structures, swimming pools, underground bunkers, etc. Hydroconcrete perfectly withstands pressure and non-pressure water, as well as the action of aggressive chemicals dissolved in water.
Hydroconcrete is successfully used for the construction of buildings located on hills or mountain slopes. In a rainy period in such an area, the load of the soil on the foundation of the building can significantly increase and the area of contact of water with the foundation of the building object increases. Therefore, hydro-concrete in such cases allows you to solve many problems of the stability of the foundation to water and soil pressure.
There are other ways to effectively protect buildings from moisture and water, which differ in the method of applying the moisture-resistant material and the place of its application. offers waterproofing services on very favorable terms. We employ real professionals who are able to solve the most complex problems of protecting building structures from water.
In order for the foundation to serve for a long time and, moreover, to protect the basement, basement and the house from dampness, it first of all requires protection itself - from ground, rain and melt water. Moreover, not only the underground part of the foundation needs protection, but also the aboveground one - the basement. Waterproofing should not only resist the flow of water during spring melting snow or heavy rains, but also - just as important! - protect the walls of the foundation from capillary moisture, prevent water absorption by its surfaces.
Waterproofing is usually performed in both planes - vertical and horizontal.
There are three types of waterproofing that correspond to the types of water exposure:
§ unpressurized
§ anti-pressure
§ anti-capillary
Non-pressure waterproofing of basements is carried out against the temporary effects of moisture in atmospheric precipitation, seasonal top water and in drained floors, ceilings.
Anti-pressure - to protect enclosing structures (floors, walls, foundations) from hydrostatic groundwater backwater.
Anti-capillary - for waterproofing walls and floors of buildings in the zone of capillary rise of ground moisture.
According to the device method, waterproofing is distinguished:
Pasting (made of roll materials, for example, glass-proof, waterproof, roofing material, izol, brizol),
Coating (hot bitumen, hot bitumen mastics, solvent-thinned bitumen),
Hard (cement or asphalt plaster in several coats on hot or cold bituminous mastics, well-fired clay bricks),
· Shell (metal).
To create a horizontal layer of waterproofing, roll materials are laid under the base of the foundation and in the places of its articulation with the walls of the house. On the surface of the base, leveled with mortar, or in its thickness (10-15 cm above the blind area), waterproofing is laid from two layers of roofing tar (or from any new waterproofing material) on glue mastic or from a layer of cement.
In basement buildings, the first layer of horizontal waterproofing is placed between the foundation and the basement, the second is 10-15 cm below the ceiling within the basement wall and 15-20 cm above the blind area.
Basement waterproofing or basements of old buildings should be combined with bioflora and salt removal measures.
Protection against capillary ground moisture of the walls of buildings is mandatory even when the groundwater is below the basement.
Vertical waterproofing is arranged to protect the basement walls from getting wet with water. The type of waterproofing, the materials for its device are chosen depending on the moisture content of the soil, on the level and pressure of groundwater, and their aggressiveness.
With a high location of the groundwater horizon (above the basement floor), special measures may be required to strengthen the structure of the foundations and waterproofing, up to the installation of sealed metal shells. At the same time, measures are taken to lower the groundwater level (GWL) - drainage, etc. Events.
If the groundwater level is below the mark of the felling floor and does not rise above it (Fig. 28a), but moisture can penetrate into the basement through the capillaries, then the floor and plaster of the walls are made of tiles or cement-sand mortar with iron, and from the outside the foundations are covered with waterproofing mastic. In this case, building sediments that develop after the flooring and plastering of the walls in the basement can damage them. However, due to the relatively low penetration of moisture through individual cracks, this has little effect on the moisture regime of the basements. In addition, such cracks can easily be repaired from the basement side.
If the water table is or can rise above the basement floor mark, it is necessary to perform continuous waterproofing under the floor and along the walls above the mark of its maximum position. Such waterproofing is subjected to hydrostatic pressure directed towards the insulated room. To keep the waterproofing in a given design position, it is pressed with a special structure capable of absorbing the specified pressure.
If the GWL rises above the basement floor by no more than 0.5 m (Fig. 28b), then either a low brickwork outside or a surcharge concrete layer inside the room is sufficient to keep it in its design position. In other cases, special bending structures are required.Depending on the nature of this structure, a distinction is made between external and internal waterproofing.
Below, in Fig. 28 and 29, various cases of waterproofing basements are shown (Fig. 28 - waterproofing from the outside of the basement wall; Fig. 29 - from the inside).
Fig. 28 External waterproofing of foundations
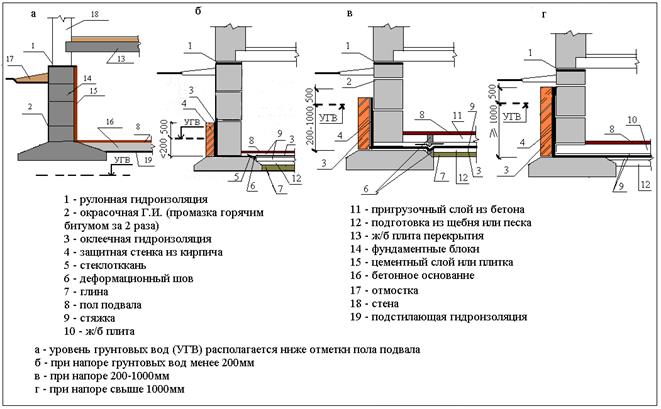
Fig. 29 Internal waterproofing of the foundation


External waterproofing is arranged before the foundation is erected, internal - after. External waterproofing is more reliable, since it has fewer bends (fractures) compared to the internal one, during the construction of which it is necessary to make bends in all rooms in the places where the floor joins the walls, the walls turn and in the doorways of the basements. The weak point of the internal waterproofing is the reentry corner, where two angled walls converge from the floors.
One of the ways to isolate the underground parts of a building or structure from surface water (atmospheric precipitation) is to install a blind area outside the building with a slope of 1-2%.
To date, there are many new modern materials for waterproofing. For example, geotextiles (Fig. 30), liquid glass, etc. Liquid glass - unlike bitumen - does not lose its properties over time. However, the cost of the foundation increases dramatically. But if you are building on damp ground, then perhaps this particular option may be preferable for you. It is better to save the foundation once and for all once and for all than to regularly save the whole house.
Fig. 30 A variant of the device for external vertical waterproofing of the foundation using materials of a new generation

But there are even more effective methods for protecting foundations. For example, the penetrating waterproofing method. Special compounds are applied to the wet surface of the foundation. Getting into microcracks and pores filled with moisture, these substances crystallize and clog them. Moreover, with the formation of new cracks, the process spontaneously resumes. This miraculous effect continues as long as the free active substances of the protective compounds remain in the treated surface. We can say that with their help, the foundation acquires the ability to heal itself for a long time.
Today, there are many new modern methods of waterproofing foundations. For example, injection, diffusion or surface impregnation. When injected, "crystallization barrier" materials can be used. Among polymer-cement waterproofing materials, the so-called "flexible cement membranes" occupy an important place. Noteworthy is the use of waterproofing mats containing sodium bentonite clay, which are laid along the outer perimeter of the insulated surface as a “wall in the ground”.
Until the end of the 19th century, waterproofing of buried premises was carried out in the form of a "clay castle" - a layer of crumpled and densely compacted clay 26.7-30.5 cm thick. It was arranged under the floor and around the underground walls and foundations of buildings. "Clay castle" protected foundations, walls or glued insulation from direct contact with groundwater (including aggressive) and thereby increased the service life of the underground part of the structure. The “clay castles” were replaced by products in the form of bentonite clay. Bentonites are highly dispersed rocks with a montmorillonite content of at least 60%. On the domestic market there are Nabento insulating mats (Akzo Nobel concern), as well as Bentomat panels and Voltex mats (). In the starting material, bentonite is in the form of granules, enclosed in a geotextile, aero-textile, polyethylene or polypropylene shell, in a shell made of biodegradable cardboard.In working condition (after contact with water), bentonite, while remaining in a closed volume, swells and turns into a gel state, which has a very low water permeability, but sufficient vapor permeability.
Currently, bentonite derivatives are added to other waterproofing materials, such as thermoplastic and rubber-bitumen. The materials are produced and used in the following forms: powder, which is applied by spraying; boards on a cardboard base; rolls on various bases, bentonite and rubber sheets; fabric mats. Of all waterproofing materials, bentonite, as well as cement, are the least toxic and cause minimal damage to the environment. A clay based waterproofing membrane has the ability to self-heal cracks. But for this it is necessary that the material adheres tightly to the concrete. Clay is extremely sensitive to weather conditions and should be protected during application. If it rains or the water table rises and the material is moistened before backfilling, hydration is carried out ahead of time and the waterproofing ability disappears, since the increase in volume has occurred in an open space. Bentonite coatings should not be used in areas where there is a free flow of groundwater, since in this case they will be washed out.
- see what is not written and add from here
? Insulation of foundations
The desire for comfort and the high cost of electricity makes modern builders think about the need for thermal insulation of the foundations of houses. According to existing estimates, heat losses through foundations account for a significant share of the total energy load on heating and air conditioning of a building - more than 20%. In many countries, foundation insulation is a mandatory procedure regulated by state regulations. It is expected that this tendency will be duly spread in Russia as well. Nowadays, many homeowners with basements insulate them, giving them additional space for living. In this case, they usually insulate the basement walls around the perimeter.
Thermal insulation in direct contact with the soil is subjected to harsh operating conditions, including prolonged exposure to water, high soil moisture and repeated exposure to freeze-thaw cycles. These natural factors can drastically reduce the effectiveness of thermal insulation. Therefore, thermal insulation in contact with the soil should be inert to the effects of soil and water, and the thermal insulation characteristics should not decrease when exposed to them. Rigid extruded polystyrene foam (XPS) rigid slabs are used to insulate walls and floors in underground structures. XPS material has a very low thermal conductivity that remains stable for many years. The material is waterproof, therefore, invulnerable to prolonged contact with soil moisture. In this case, the thermal conductivity of the material does not increase in the presence of moisture, because XPS material has a closed cell system. It is resistant to common acids contained in the soil, does not support the growth of mold and mildew, does not corrode or decay. All these qualities make XPS boards a material suitable for long-term underground use.
Freezing has little effect on XPS thermal insulation material, which stays dry or, more accurately, does not absorb moisture from the environment. On the other hand, moisture-wicking insulation cannot perform its function properly. This is an important factor when choosing thermal insulation for locations where freeze-thaw cycles are common.Independent research demonstrates that only XPS can be used for thermal insulation of underground facilities in humid environments with multiple freeze-thaw cycles.
There are four ways to insulate basement walls (basement floors): insulation from the inside, outside, between walls, or on both sides at the same time.
From the point of view of building physics, the most logical placement of thermal insulation is outside. A layer of thermal insulation, placed on the outside of the wall and outside in relation to the waterproofing, keeps the basement walls at a constant (almost room) temperature. The walls act as a thermal reservoir, smoothing out possible temperature fluctuations in the interior. At the same time, thermal insulation does not interfere with the natural diffusion of water vapor from the interior of the underground structure to the outside and excludes the conditions for the formation of condensation on the inner surface. Another advantage of external thermal insulation is the simultaneous protection of the walls of the underground part from the direct effect of frost heaving forces. Frost heaving is an increase in the volume of water-saturated soil during its freezing, which occurs due to freezing of moisture in the soil and the formation of ice lenses.
In the case of external insulation, there is a need for mechanical protection of the insulation itself during the construction period, this task is successfully solved with the help of insulation having high compressive strength, as well as with the help of modern profiled membranes, which play the role of mechanical protection and a wall drainage layer in the structure of the foundation wall ... Another problem is the formation of "cold bridges" through the layer of facing bricks. According to some estimates, the heat loss in this case can be so significant that it can negate the effectiveness of the thermal insulation layer.
Fig. 2. "Cold bridges" through facing bricks reduce the effectiveness of thermal insulation
Fig. 1. a) thermal insulation from the inside: the most economical method, which is used more often than others. Has the greatest moisture problems; b) thermal insulation outside: the most attractive location from the point of view of building physics. Practical problems with "cold bridges" are characteristic; c) insulation in the middle of the wall: the most expensive and most difficult method to implement, reducing moisture problems; d) thermal insulation on both sides: has similar problems with thermal insulation on the outside. Additional costs for the device of the inner layer.
These factors can force one to look for alternative approaches to thermal insulation of underground structures, first of all - to thermal insulation from the inner side of the wall. Unfortunately, this method has a significant drawback: in the cold season, the outer walls of the underground structure are in the zone of negative temperatures.
It is known that when protecting a structure from diffusion of water vapor (from the interior to the outside through the walls), one of the measures involves the location of dense materials in multilayer walls, always closer to the inner surface, and more porous materials closer to the outer. This requirement is not met when performing insulation from the inside of the room. Thermal insulation, installed from the inside and covered with a vapor barrier film from the interior side, prevents the natural diffusion of moisture from the interior and promotes the formation of condensation. This usually causes mold, odor and corrosion problems. Thus, it turns out that if the walls of an underground structure are designed and arranged in such a way that they have the ability to release excess moisture into the interior (regardless of which side the thermal insulation is placed on), then it is necessary to abandon the vapor barrier film in the interior.However, the rejection of the vapor barrier film from the interior side also does not solve the problem: water vapor will migrate outward, creating conditions for moisture condensation on the inner wall surface, mold and other problems.
Since most interior insulation materials are breathable, they allow air to pass from the interior to the outer walls. When insulating from the inside, the structures of the walls of underground structures will be cold in winter (reinforced concrete in direct contact with cold ground), and the contact of warm air with a cold outer wall will cause condensation to form between the insulation and the wall. Therefore, for thermal insulation of the walls of underground structures, a material with minimal water absorption and vapor permeability should be used, which would prevent the contact of indoor air with the cold surfaces of the underground structure.
The higher the vapor permeability of the materials of the walls of the underground part of the building, the more intensive the drying process of the inner surface of the wall and, therefore, the less risk of accumulation of excessive moisture. However, in the cold Russian climate and / or in buildings with high relative humidity during the cold season, the upper part of the wall of an underground structure can become so cold that vapor-permeable thermal insulation will allow a significant amount of moisture from outside to enter the room. In such a situation, you can use semi-permeable vapor barrier films or an additional layer of external thermal insulation.
When insulating walls from the inside, the most energy-saving option is a combination of extruded polystyrene foam and a layer of fibrous thermal insulation (mineral wool or fiberglass), which is laid over a wooden frame. In this case, the vapor barrier film is not mounted on top of the fibrous thermal insulation. The structure is then sheathed with plasterboard and prepared for subsequent finishing.
Fig. 3. Variant of combined insulation from the inside
The floors of underground structures are thermally insulated, most often, with rigid plates of extruded polystyrene. Most often, the floor is insulated under the slab. Floor insulation under the slab is necessary if there are heated floors in the basement. In addition, this option of thermal insulation of the floor creates additional comfort and protects against the damaging effects of moisture, including protection against moisture condensation in the summer.
On top of the insulation boards, it is necessary to lay a reinforced polyethylene film, which will act as a vapor barrier. Do not place a sand cushion between the vapor barrier and the concrete slab. A layer of sand placed between the slab and the film can become saturated with moisture, which subsequently cannot evaporate into the soil due to the presence of a vapor barrier. In this case, moisture evaporation can only take place in the upward direction, through the plate. This usually leads to deterioration of the floor covering in the interior.
The Heck system provides for thermal insulation of underground and basement parts of buildings with special fiber panels, reinforced and covered with sealing sludge. Due to temperature gradients and steam partial pressures, the moisture flow is directed from the inside, that is, the wall “dries out” without the formation of condensation on the inner surface. - add logical to the written
rice…. insulation of the foundation using electric cables
Materials (edit)
Currently, the construction market represents materials for waterproofing of a wide variety of groups. All of them should be used only taking into account the characteristics of the construction site and the territory where it is located. The cost of waterproofing can vary.There are inexpensive materials, for example, bituminous mastics, and there are also quite expensive solutions. But this does not mean that preference should be given to those materials that are more expensive. It all depends on the specific conditions in which the building will be used.
Professional waterproofing works can be performed using various materials:
Purpose of waterproofing
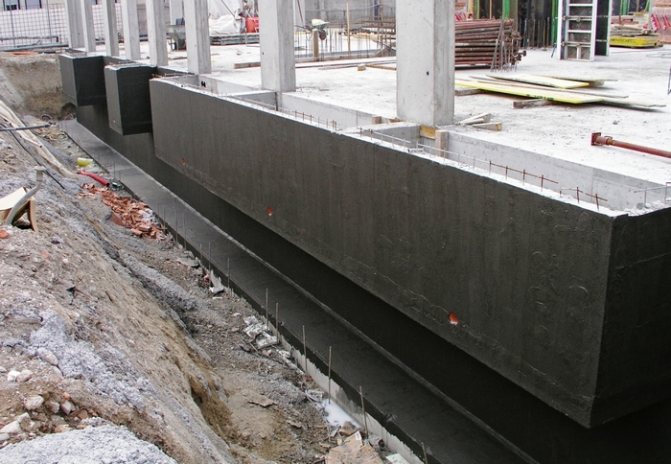


All engineers and builders are unanimous in the opinion that protection of the foundation from soil and surface moisture is simply necessary.
First, let's figure out what waterproofing is for. All engineers and builders are unanimous in the opinion that protection of the foundation from soil and surface moisture is simply necessary. Why is this protection needed? The thing is that any moisture that penetrates into the smallest cracks in the base structure can significantly reduce the strength of the foundation. So:
- Capillary moisture entering concrete structures through small cracks destroys the base from the inside. This is especially true of concrete with a loose structure, inside of which water is constantly moving through the capillaries. This contributes to the constant exchange of salts and a decrease in the strength of the concrete.
- It is no secret that water corrodes metal parts in the base structure. So, steel reinforcement under the influence of corrosion increases in diameter several times. Thus, it simply rips open the foundation from the inside.
Important: the negative impact of moisture on the foundation of the house leads to a sharp decrease in the strength of the base, deformation of structures and cracking of the entire structure. Correctly performed waterproofing of the foundation minimizes the likelihood of such situations occurring.
Since groundwater has a different composition, they are divided into different types according to the degree of aggressiveness to concrete structures and metal products. Therefore, for a base located in an aggressive environment, not only waterproofing for the foundation is needed, but also the use of special waterproof concrete grades (according to SNiP, the grade must be at least 4). The aggressiveness of groundwater is determined based on the composition data obtained in the laboratory during the analysis of the sample.
Roll materials
- Technoelast is a multifunctional bio-resistant roofing and waterproofing material of high quality and increased reliability. It is manufactured using a unique technology by the method of double-sided application of a special insulating compound (bitumen, SBS thermoplastic or its modifications and filler) on a fiberglass or polyester base. The price per m2 of waterproofing made with Technoelast does not exceed 450-550 rubles. Materials such as sand, asbestos, etc. are used as a powder.
- Bipole is a high quality waterproofing material made on the basis of fiberglass, fiberglass or polyester. Bitumen plays the role of a binder here. The material has high strength characteristics and provides reliable surface insulation.
- Gidrostekloizol. It is made of fiberglass impregnated with a mixture of bitumen and fillers. Polymer films are used as a protective layer. It is fixed on building structures by fusion or by means of glue.
- Hydroizol. This is an asbestos canvas impregnated with bitumen. This material has excellent biological resistance.
- Metalloizol. Double-sided material based on metal foil treated with bitumen mastic. It is highly durable but short-lived.
- Folgoizol. This is the same metal insulation, only a layer of bitumen is applied to one side.
- Bikrost. The basis of this material can be fiberglass or polyester impregnated with bitumen. Protected on both sides by coarse and fine-grained powder made from sand, shale and other minerals. Distinguish between roofing and lining bikrost.
- Linocrom.Made on an organic basis with bitumen as a binder. Protected with plastic foil or mineral powder. It is used for waterproofing roofs and foundations.
There is a number of roll-bitumen materials that are easy to apply to the structure and low cost. To find out the price per m2 of waterproofing work with these materials, call the managers by phone.
Where to start?
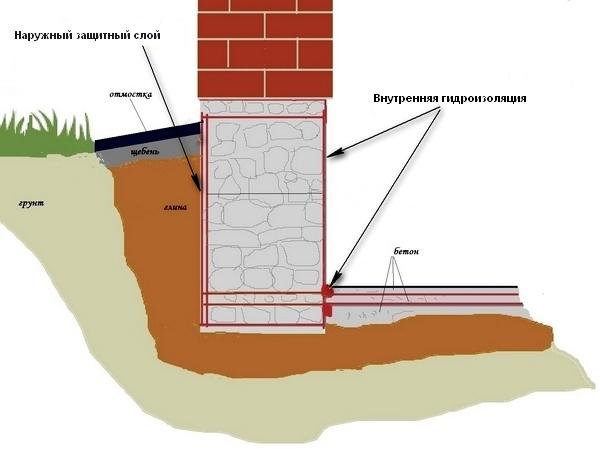

To fully understand the meaning of the waterproofing work of the foundation of the assignment, it is necessary to distinguish between the external and internal protection of the building foundation.
- Outer protective layer erected on the outer area of the foundation, its task is to prevent the penetration of groundwater, moisture discharged from the roof into the foundation cavity. In addition, for certain types of foundations, for example, slab, external insulation is arranged not only along the vertical side surfaces, but also under the slab itself - so that moisture does not seep and destroy the slab.
- Internal waterproofing mostly arranged for tape and grillage types foundations for buildings in which the device is planned basement room.
Depending on the technology of building the foundation and the device of the protective layer outside work is carried out in the following order:
- clearing the space around the concrete base;
- removal of excess concrete, sagging, chips;
- sealing seams and cracks;
- priming the surface with a deep penetration primer;
- applying protective layers of waterproofing material or installing a roll coating;
- assessment of surface quality, elimination of problem areas, re-coating, if required by technology.
- device of soil filling.
Lubricants
The coating compositions include materials based on bitumen. Application method - cold or hot. They are characterized by good adhesion to any building structure.
Prices for waterproofing work can be found on the website, which offers various services to protect buildings and structures from surface, atmospheric and ground waters. The price for the work on applying waterproofing depends on the area of the structures to be treated and the technology for manufacturing the protective layer.
Today the specialists of our company are ready to carry out design work, as well as the installation of any kind of waterproofing. We work directly with suppliers of building materials, purchasing products at favorable prices for the end consumer. The experience of our specialists allows us to manufacture drainage and waterproofing in a short time with high quality. This is another advantage to take advantage of.
DIY waterproofing
Do-it-yourself foundation waterproofing can be arranged in several ways. The simplest and most reliable method to protect the walls of the foundation and its base is the use of waterproofing mixtures of penetrating action.
... The advantages of penetrating concrete additives are
in the ease of preparation of waterproofing from water and the ability to exclude contact with more toxic and easily soiled bituminous compounds.
By turning into a crystalline substance, they prevent the penetration of moisture and corrosive substances to corrode the material. Concrete becomes stronger and more resistant to chemical and water attack. Its susceptibility to these substances becomes 4 times less. Frost resistance is significantly increased.
Foundation waterproofing materials
Penetrating mixture "Pronitrate Mix"
is added to water for preparation of concrete solution (in the ratio of dry mixture: water - 1: 1.5). The solution itself is kneaded using standard technology. The consumption of the product is 4 kg / m3 of concrete.
Penetrating waterproofing tools and equipment:
- gloves;
- Master OK;
- bucket;
- concrete mixer;
- shovel.
Diy foundation waterproofing scheme using Penetrate
Penetrat Hydro system
applied to walls outside or inside the room, providing a surface and penetrating waterproof layer.
The use of the product is preceded by a thorough preparation of the surface, which aims at maximum adhesion of the drug and its deep penetration. The system consumption is 200-300 g / m2 of surface.
Preparation of the wall for processing by the GS "Penetrat Hydro":
- removal of mortar and building material residues from the surface;
- cutting seams with a jackhammer to a depth of 10-20 mm;
- thorough cleaning of dirt and dust residues; - saturation with water (5 liters of water per 1 m2 of surface);
- application of the system until a mirror-like surface is obtained (in 2 coats, with an interval of 24 hours between coats).
Do-it-yourself foundation waterproofing is ready!
Further finishing of the wall is possible one week after the completion of processing.
Compliance with the basic requirements for waterproofing works allows you to get a building that is resistant to melt and groundwater. The use of high-quality protective compounds "Penetrat" leads to the maximum waterproofing effect in the construction of building structures, as well as the processing of finished surfaces. Read more about the use of GS Pronitrat Mix and GS Penetrat Seam. here
.
Restoration of waterproofing
Do-it-yourself restoration of waterproofing is possible, but still, in order to fully assess the scale of the work, as well as to choose the right type of waterproofing, based on the current situation, it is better to contact the specialists.
Remember the incorrectly selected recovery method, if it gives the desired result, then the success from it will be short-term.
Before starting work, the entire surface of the building is thoroughly inspected.
Areas with loose cement are cleaned, if necessary, if rusted reinforcement elements are identified, corrosion is also removed and the metal is treated with a special protective compound. The floor and walls that have been attacked by microorganisms, such as fungus or mold, undergo a complex disinfection process, are treated with antifungal compounds.
In the presence of water, the liquid is completely pumped out, and the walls, floor and other surfaces of the object are thoroughly dried.
Regardless of the method chosen, work begins with cleaning the object of materials that have become unusable. Only a complete cleaning, including the removal of paint residues, glue and other substances, guarantees a high adhesion of the waterproofing to the surface.
In the case when it comes to the foundation, a lot of time and effort will be spent on earthworks, the base must be completely exposed, and then buried again.
Experts recommend eliminating changes in the direction of groundwater or their excessive formation with the help of a drainage system, sometimes only a layer of protection may not be enough. In addition, the drainage system located under the house is silted up, which also leads to disastrous consequences.
Methods
It is important to divide the main methods of recovery into externally and internally.
Working outside the structure is a better option. Thus, we eliminate the problem itself, that is, we remove the water pressure (by the drainage method) and protect the concrete base from contact with water. The room will not allow water to penetrate into the structure, but the outer shell will still be destroyed.
The most popular and effective ways:
Outside:
- Two-component sprayed waterproofing Liquid rubber;
- Two-component sprayed waterproofing Polyurea;
- Roll (membrane) or welded waterproofing.
From the inside:
- Penetrating waterproofing;
- Injection waterproofing;
- Waterproofing with pressure sealants (seams, cracks);
- Coating waterproofing on cement-mineral compositions.
The longest lasting and highest quality insulation is provided by Liquid Rubber.It is applied to any surface by spraying, forming a seamless uniform elastic coating.
High elasticity prevents the formation of tears during deformation or shear of structural elements. Liquid rubber also provides 100% grip. Thanks to the technology of cold spraying, the substance lays down in an even layer and covers every millimeter of the object. Also among the advantages is the ability to process objects of any shape.
After coating, a layer is formed on the surface that resembles plastic or very hard rubber. Often, for reliable waterproofing, it is sufficient to apply liquid rubber in one layer.
Polyurea has the same characteristics, but is less elastic, thus not allowed for use in dynamic units and where there is a possibility of shrinkage or movement of the structure.
Unlike Liquid Rubber, Polyurea has a different color range.
Examples of our work:
You can isolate water using roll materials. The popularity of this method is due to its relatively low cost in comparison with other technologies.
However, the method has a number of nuances. To implement the plan, free access to the surface is necessary, for example, if the foundation of the object is reliably hidden, and the adjacent territory is landscaped, then work is impossible.
Also, roll materials require a flat surface, but even if there is one, they do not provide 100% adhesion.
The disadvantage of this method lies in the presence of seams, this complicates the process of creating a single coating and requires additional sealing of the joints.
Experts recommend waterproofing at least two layers, with mixing joints. It is not recommended to use this method again, because if it did not help the first time, the likelihood that it will help the second time is negligible.
Roll waterproofing is divided into two main methods: fusion and membrane (using TPO or PVC membranes).
The main disadvantages of these materials are the presence of seams, the difficulty in working with multiple abutments, the need for a flat surface and the lack of adhesion to the base.
Examples of our work:


The injection method, widely used in Europe, is gaining popularity in the Russian service market. Restoration in this way is performed only by professionals.
It consists in drilling holes in staggered rows. Then the resulting holes are filled with an acrylate gel composition using special equipment operating under a pressure of 240 atmospheres.
The substance is able to penetrate into various crevices and cracks as effectively as water. Due to its unique properties, a hydro-barrier is formed.
Injection waterproofing can be performed both in the form of a barrier or screen at the ground-wall / foundation contact, as well as in the following structures:
- Waterproofing cracks, cold joints, expansion joints;
- Waterproofing the base of the structure.
The drilling of cavities is carried out with special equipment with utmost care so as not to damage the already weakened structure. The size of the hole is 1-2 cm, the frequency of location is about 30 cm. It is important to understand that before performing the injections, a full-fledged project is drawn up, taking into account all the features of the object.
The project specifies the walls that will be processed, with numbered holes indicated on them. The plan must necessarily contain information about the amount of solution used and its manufacturers.
Special efforts are required for waterproofing old buildings. In significantly worn out lime masonry, it is recommended to make a number of cuts and insert polymer or metal sheets into them. The holes for forming the barrier in the form of sheets are made with a special diamond tool.The service life of the structure can be extended by using an insert in the form of a sheet of heavy-duty stainless steel, but it must cover the entire plane of the object.
An example of our work:


Wooden foundation ↑
The foundation made of wooden piles must be treated with an anti-corrosion solution. But it should be borne in mind that the wooden foundation does not tolerate drainage and other measures that lower the level of groundwater. The fact is that wooden piles do not rot only if they are completely in the water. If this does not happen, their service may decrease.


Wooden foundation for a log house
Exterior wall waterproofing
We prepare tools and materials for work:
- Bituminous mastic. It is better to buy it in metal buckets.
- Bitumen-based primer.
- Reliable respirator, goggles, gloves.
- Thinner, paint brush and roller.
Having prepared the tools for work, apply a primer to a clean surface and wait for it to dry. With a very thin layer, the color will be black. It is necessary to repeat the operation.
We are waiting for the walls to dry completely. We dilute a very thick mastic with white spirit and mix the solution. At very low temperatures, the mastic is heated to a liquid state.
With a roller or brush, we process the surfaces around the perimeter. After applying a layer, let it dry. The mastic dries completely within 24 hours, at low temperatures the process will slightly increase. Then we apply the second coat. We leave it for a few days and then fill up the trench. Before that, if funds are available, you can perform thermal insulation of the basement.
For this, it is better to use expanded polystyrene, but any insulation can be used.
This method will allow you to maintain a normal temperature in the basement, without heating costs.
This video provides visual information on the implementation of work on the waterproofing of the basement. Thanks to this, you can perform operations while watching a video.