Many of you have observed the appearance of droplets of moisture on surfaces - on cold water pipes, bath walls, windows, and also when things are moved from frost to room temperature. This can be explained simply: the object cools the surrounding air, provoking the formation of condensation.
The appearance of moisture occurs due to the difference in temperature inside and outside the room. This physical phenomenon is inextricably linked with the concept of "dew point". Let's figure out what the term means, consider its meaning in house insulation and give examples of self-calculation.
What it is?
Let's start with the basics - let's turn to the school physics course. So what is a dew point? This is the name of the temperature at which air begins to transform into liquid. As a result, droplets of moisture form on the surface - condensation, which can subsequently transform into frost, fog or evaporate.
An elementary example is a kettle on the stove. When the water starts to boil, condensation will appear on the surface of the lid. In this case, the temperature of the heated teapot lid will correspond to the dew point.
Another example: foggy windows in an apartment. Here the dew point indicates that there is high humidity inside the room, respectively, with a large difference between the internal and external temperatures (winter period), condensation forms on the windows.
Hence, we can conclude that the dew point is a kind of indicator of air humidity. Considering that we are talking about a temperature phenomenon, dew point is measured in degrees Celsius.
Physical term
The constantly growing and developing market for construction products presents a wide range of materials for thermal insulation. It is necessary to approach the choice of thermal insulation for industrial and residential premises properly and pay attention to the indicator in question during construction.

Due to incorrect measurement of the dew point, the walls often fog up, mold appears, and sometimes the destruction of structures
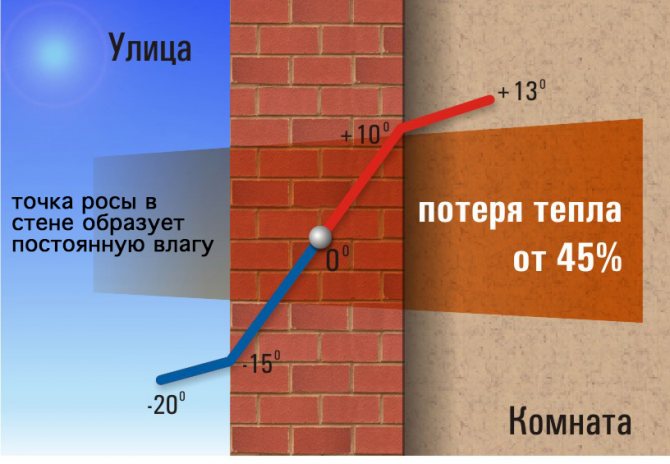
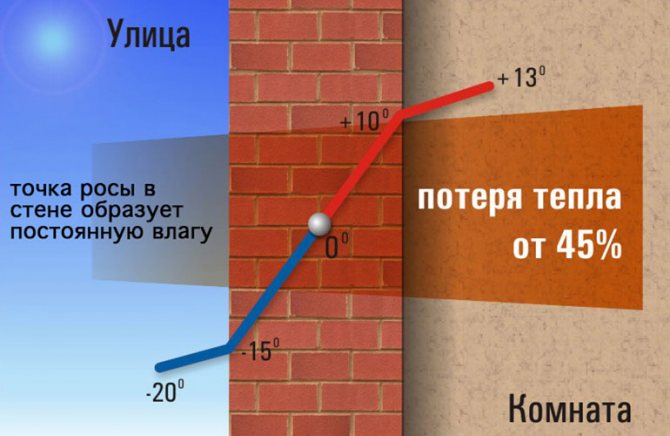
The border of the transition from a low temperature outside the walls to a higher temperature inside the heated structures with possible condensation formation, experts consider the dew point. Water droplets will appear on any surface in the room that is close to or below the dew point temperature. The simplest example: in the middle of some rooms, in cold weather, condensation drips on the window panes.
The main factors affecting the determination of the value are:
- climatic factors (temperature value and air humidity outside);
- temperature values inside;
- humidity indicator inside;
- the value of the thickness of the walls;
- vapor permeability of thermal insulation used in construction;
- the presence of heating and ventilation systems;
- purpose of structures.

Correct dew point determination is essential in construction
All physical phenomena that are studied in the school physics course surround us without breaks for lunch, sleep and holidays. All life is physics, one way or another already mastered by humanity and still completely unexplored. For example, many natural phenomena recognized by physicists have found their scientific embodiment in the practical activity of man.
Here is the morning dew - the beauty of a summer morning. But from the same dew that falls in residential premises due to improperly installed windows, broken hydro and thermal insulation, you can get a huge number of problems.And certain parameters, when moisture falls on the surrounding surfaces, have received a beautiful name - dew point.
Air humidity


Understanding the definition of the dew point, we noted that the phenomenon directly depends on the humidity of the air. Given this feature, it makes sense to focus on this issue in more detail.
What is air humidity? This is the liquid content in the surrounding atmosphere. The quantity can be absolute or relative.
Absolute humidity - the actual moisture content in one cubic meter of air. This indicator is usually denoted by the Latin symbol F... You can calculate the absolute humidity using the formula:
F = M:Vwhere:
- M - the actual mass of moisture;
- V - air volume.
- F - moisture content, expressed in G / m3.
Relative humidity - a value showing the real moisture content in the atmosphere in relation to the nominally permissible values at temperature indicators. The unit of measurement is expressed as the percentage that announcers use when reporting the weather forecast.
It is the relative humidity that is tied to the concept of the dew point.
If we talk about the dew point, there are several interesting facts:
- This value never exceeds the actual air temperature.
- The dew point temperature is directly related to the moisture content in the air.
- The highest point can be observed in the tropical climate, the lowest in the arctic.
- 100 % the relative humidity of the atmosphere leads to the formation of condensation.
- The highest dew point can be observed before the passage of the cold atmospheric front.
These nuances will help you better understand the capricious definition.
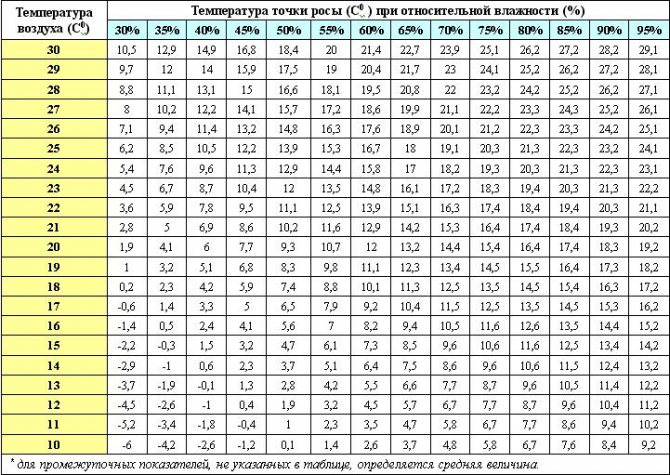
| Dew point, ° C | Human perception | Relative humidity (at 32 ° C),% |
| more than 26 | extremely high perception, deadly for asthma patients | 65 and up |
| 24—26 | extremely uncomfortable state | 62 |
| 21—23 | very humid and uncomfortable | 52—60 |
| 18—20 | unpleasantly perceived by most people | 44—52 |
| 16—17 | comfortable for most, but the upper limit of humidity is felt | 37—46 |
| 13—15 | comfortable | 38—41 |
| 10—12 | very comfortable | 31—37 |
| less than 10 | a little dry for some | 30 |
Determination of loads of heating systems
It is important to know how much heat can be given off by devices in the heating system of the house. Calculation of the heat load on the heating of the building allows you to avoid overspending on the installation of unnecessary elements of the system On the other hand, it delivers the right amount of calories to the room. The total indicator of the thermal power of the system is made up of the load parameters:
- thermal heating structures;
- forced ventilation and hot water supply systems;
- floor heating elements in the house;
- different technological needs.
When calculating for the correct determination, it is important to take into account literally all additional parameters:
- type of heated building (residential, non-residential);
- whether or not they have hot water supply, air conditioning, etc.
- the number and purpose of special rooms (bathhouse, sauna, greenhouse, etc.)
- architectural features with or without basements;
- roof structure;
- number of storeys of the building;
- dimensions of door, balcony and window openings, etc.
- standard temperature indicators for a specific type of room;
- operational characteristics of building materials, their thermal conductivity.
The number of people living or permanently staying in the house also affects the calculation of heating. The technique takes into account the expected moisture and temperature released in the process of vital activity.
Thus, in the standard version, the definition of heat output consists of:
- finding the estimated maximum flow of heat energy emitted by radiators;
- specific heat consumption per unit of time;
- determination of the total consumption of heat power during the heating season.
Additional calculations
The hydraulic calculation of the heating system will help to calculate the resistance that arises when passing through pipes, batteries heated to a high temperature of the coolant. There are various calculation methods for the natural and forced movement of the coolant. Today pump heating is considered the most efficient. It depends on the characteristics of the pump that drives water through the system:
- pressure of the head of the liquid in the system (Pa);
- productivity (l / min).
Calculation of a circulation pump for a heating system gives two important characteristics: head and capacity, according to which the pressure equipment is selected. Calculations show with what pressure the pump is needed to overcome the resistance of the moving heat carrier.
The calculation of the diameter of pipes for heating a private house is carried out according to the scheme, after determining the method of their wiring, piping the boiler and connecting to heating radiators. For a two-line version, you need to know the distances from the batteries to the boiler. The measured result (m) is doubled (forward and backward line). When choosing a pipe section for a medium-sized building, they are guided by indicators from 20 to 32 (mm). It is taken into account that with an increase in the working section of the pipe, the cost of the entire heating system also increases.
Calculation adjustments
- Heating calculation for the area of the room is adjusted according to the average power of the radiators. As a rule, in the passport for the devices, a characteristic is given for the maximum temperature of the carrier - up to 90 ° C and 70 ° C on the return line. In practice, the operating parameters are 55 ° and 45 ° C, respectively. Therefore, the calculations are being refined.
- Before calculating the power of the heat flow in the batteries, they are determined with the mode of their operation. At a low water temperature, sections will need 2 times more.
- When deciding how to calculate heating in a private house, keep in mind that when radiators are diagonally connected with a coolant supplied from above, heat losses are minimal. With lateral supply - maximum (about 22%).
Attention! If you do not know how to calculate heating in a cottage or private house, rely on our specialists. always offers the best solution to the problem, both financially and qualitatively.
Everyday meaning


Many residents of private and apartment buildings have never thought about the dew point. This is quite understandable: the inner walls of the premises are always warm, condensation never appears here. Moisture droplets can appear on the windows when there is severe frost outside the window.
This balance will be maintained until the tenants decide on additional insulation of the house or apartment from the inside. In this case, the temperature difference will change, moisture will begin to accumulate under the insulation layer. At the same time, the type and cost of the insulation will not matter.
If we are talking about natural materials, the following problems will appear:
- bloating;
- mold;
- bundle.
Concrete and brick structures will gradually begin to deteriorate.
To avoid these problems, the dew point should be on the insulation layer, which is located on the outside of the wall. A logical question arises: "How to find the desired point?"
Find out why the windows in the house are sweating >>>
Existing methods for calculating home heating
The required performance of the heating system is determined by several methods. Some are quite simple, others require the use of software and specific devices (thermal imagers).


- You can independently calculate the heating by the area of the room: the calculator (a set of special calculation algorithms) allows you to do this with an acceptable accuracy. For climatic conditions of middle latitude, the normative value of the power of heating devices is 60-100 W per 1 sq. building. In the northern regions, this figure is higher.
- The calculation of heating by the volume of the room is more specific.It takes into account all three dimensions of the room, which is especially important for heating rooms with ceilings of 3 m and higher. An important value is the norm-determined heating performance of 1 cubic meter of room volume. For the Central European part of Russia, this is a coefficient of 41. It varies depending on the region. The required heat output of the radiators is found as the product of the room volume by 41 (or by another value). Calculations are carried out in the same dimensional units: meters and kW.
- Based on the material of manufacture, the average power values of the heating battery section are taken: 160 W (for cast iron), 200 W (for aluminum), 180 W (for bimetallic products).
The simplest calculation method
For preliminary calculations of water heating, a simple method is used:
- The area of the heated room is calculated
- Its numerical value is multiplied by the climatic power.
- The resulting work is divided by 10.
The algorithm is the simplest (the minimum number of initial data is taken), but quite accurate. The boiler is selected with a power reserve in cases when it is planned in the future to increase the number of connections (consumers) and heating areas, as well as a possible abnormal temperature drop. This is an average of 25%.
When determining the total area of heated rooms, all rooms in which at least one wall is in contact with the outside are taken into account. Calculation of the heating system for a private house is impossible without correcting for the climate of the region. The maximum climatic power factor for the northern regions (up to 2.2 kW), the minimum for the south of the country (0.8 kW).
Where is the dew point


Dew point location (TR) can be identified independently by visual inspection of the wall. Let's consider various situations with examples.
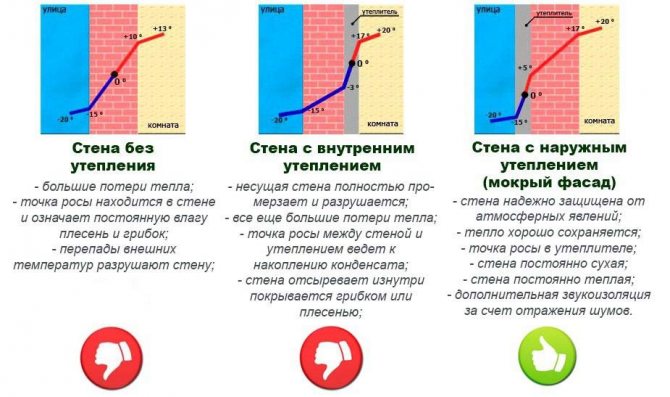
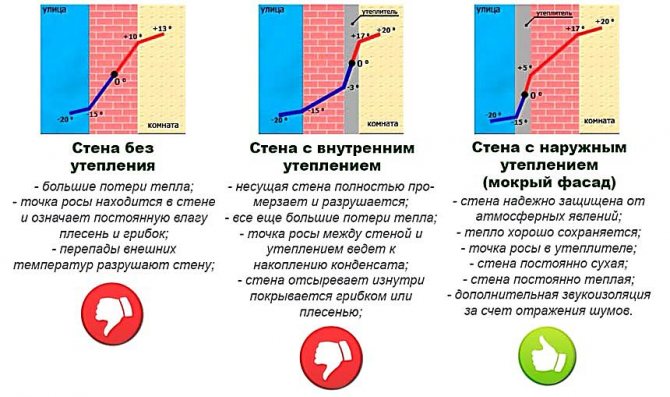
- Uninsulated walls... Here, the point can be in the middle of the structure, shifting to the inner surface during sharp cold snaps. In the first case, the inner surface will be dry if TR constantly shifted closer to the inner side, the surface will be damp throughout the cold season.
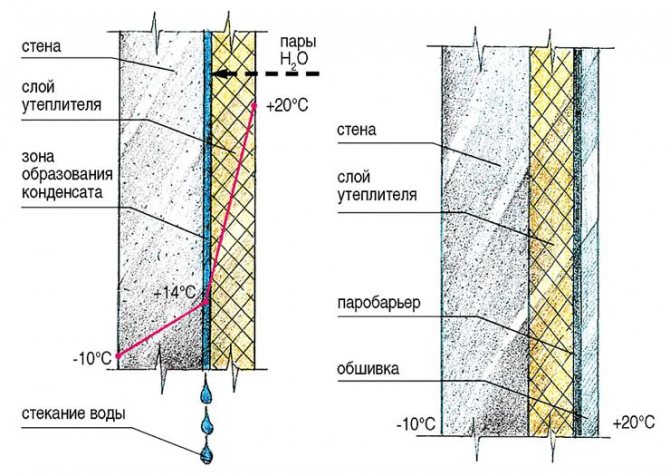
- With external insulation. If the work is done correctly, the dew point will fall on the insulation layer, and condensation will form here. This indicates correct construction calculations. If the layer of insulation is incorrectly calculated, TR can be located anywhere in the thickness of the wall.
- With internal insulation. Here the point will invariably be shifted towards the interior of the room. It can be located in the central part of the wall, directly under the insulation. The surface of the wall or the middle of the insulating layer will be partially damp. In this case, the material will be wet throughout the winter.
From the examples given, it can be seen that the dew point does not have an exact position and can shift with temperature changes.
Calculating the power of a heating radiator: calculator and battery material
The calculation of radiators begins with the selection of the heating devices themselves. For batteries with a battery, this is not necessary, since the system is electronic, but for standard heating you will have to use a formula or calculator. Batteries are distinguished from behind manufacturer material. Each option has its own power. Much depends on the required number of sections and the dimensions of the heating devices.


Types of radiators:
- Bimetallic;
- Aluminum;
- Steel;
- Cast iron.
For bimetallic radiators, 2 types of metal are used: aluminum and steel. The inner base is constructed from durable steel. The outer side is made of aluminum. It provides a good increase in the heat transfer of the device. The result is a reliable system with good power. The heat transfer is influenced by the center spacing and a specific radiator model.
The power of Rifar radiators is 204 W with a center distance of 50 cm. Other manufacturers provide products with lower performance.
For an aluminum radiator, the thermal power is similar to that of bimetallic devices.Typically, this indicator with an center-to-center distance of 50 cm is 180-190 W. More expensive devices have power up to 210 watts.
Aluminum is often used for individual heating in a private house. The design of the devices is quite simple, but the devices are distinguished by excellent heat dissipation. Such radiators are not resistant to water hammer, therefore they cannot be used for central heating.
When calculating the power of a bimetallic and aluminum radiator, the indicator of one section is taken into account, since the devices have a monolithic structure. For steel compositions, the calculation is performed for the entire battery at certain dimensions. The choice of such devices should be carried out taking into account their row.
The heat transfer measurement of cast iron radiators ranges from 120 to 150 W. In some cases, the power can reach 180 watts. Cast iron is corrosion resistant and can be operated at a pressure of 10 bar. They can be used in any building.
Cons of cast iron products:
- Heavy - 70 kg weigh 10 sections with a distance of 50 cm;
- Complicated installation due to severity;
- It takes a long time to warm up and uses more heat.
When choosing which battery to buy, take into account the power of one section. This is how the device with the required number of compartments is defined. With a center-to-center distance of 50 cm, the power of the structure is 175 W. And at a distance of 30 cm, the indicator is measured as 120 W.
Consequences of incorrect calculations


If a calculation error is made during the construction of a building, warm air leaving the room will collide with cold air and convert into condensation. As a result, droplets of moisture will appear on surfaces that are below the dew point.
The winter period in most regions of the country lasts a long time, is accompanied by consistently low temperatures, so the walls will be constantly wet.
This phenomenon can cause a lot of trouble for residents.
- The level of comfort in living quarters will decrease.
- High indoor air humidity will provoke chronic respiratory diseases.
- Damp wall structures are an ideal environment for mold growth.
Homes affected by wall fungus begin to collapse.
You can correct the situation on your own. To do this, you need to bring the dew point to the outside of the wall.
The best option is to insulate the house from the outside. This will help reduce the magnitude of the temperature difference and remove TR out. The thicker the insulating outer layer, the less likely it is that the dew point will fall on the wall structures.
Features of calculating heating
It is often stated that 100 watts is enough for 1 square meter. But these indicators are superficial. They leave out a lot of factors worth knowing about.
Required data for calculation:
- Room area.
- The number of external walls. They cool the premises.
- Cardinal points. The sunny or shaded side is important.
- Winter wind rose. Where it is windy enough in winter, the room will be cold. All data is taken into account by the calculator.
- The climate of the region is minimal temperatures. It is enough to take the average indicators.
- Wall masonry - how many bricks were used, whether there is insulation.
- Window. Consider their area, insulation, type.
- Number of doors. It is worth remembering that they take away heat and bring in cold.
- Battery tie-in diagram.
In addition, the capacity of one radiator section is always taken into account. Thanks to this, you can find out how many radiators to hang in one line. The calculator greatly simplifies the calculations, since many data are unchanged.
How to calculate with minimum error?


To determine the dew point temperature, you do not need to rely on intuition and act "by eye". There are formulas that will allow you to accurately determine the temperature of condensation.
For calculations, the following mathematical formula is usually used:
TP = (B F (T, RH)): (A-F (T, RH)) hence F (T, RH) = A T: (B + T) + LN (RH: 100)
Here:
- TR - the required value;
- A – 17,27;
- B – 237,7;
- T - internal temperature;
- RH - value of relative humidity;
- LN Is the natural logarithm.
Calculate the dew point under the following conditions: internal temperature - 21 0C, air humidity - 60 %.
First, the function is calculated F (T,RH)... Substitute the desired values and get the following: 17.27 x 21: (237.7 + 21) + LN (60: 100) = 1.401894 + (-0.51083) = 0.891068.
Determine the dew point temperature: (237.7 x 0.891068): (17.27 x 0.891068) = 211.087: 16.37893 = 12.93167 ° C
In addition, you can use special tables (regulatory document SP 23-101-2004) or an online calculator offered by some construction sites.
Dew point device
To determine TR you can use special devices for measuring air humidity. A condensation hygrometer will help you find the value you are looking for. The device is easy to use, and the principle of operation is based on a built-in mirror surface that reacts to the ambient temperature.
The primary measurement determines the temperature of the mirror. Condensation forms on the surface and the measurement is repeated. The difference in values will show the absolute or relative humidity of the air. Precise instrument settings help you determine the dew point for any surface.