A well-designed heating system will provide housing with the required temperature and will be comfortable in all rooms in any weather. But in order to transfer heat to the air space of living quarters, you need to know the required number of batteries, right?
Calculating this will help the calculation of heating radiators, based on calculations of the thermal power required from the installed heating devices.
Have you ever done such a calculation and are you afraid to make mistakes? We will help you figure out the formulas - the article discusses a detailed calculation algorithm, the values of individual coefficients used in the calculation process are analyzed.
To make it easier for you to understand the intricacies of the calculation, we have selected thematic photographs and useful videos that explain the principle of calculating the power of heating devices.
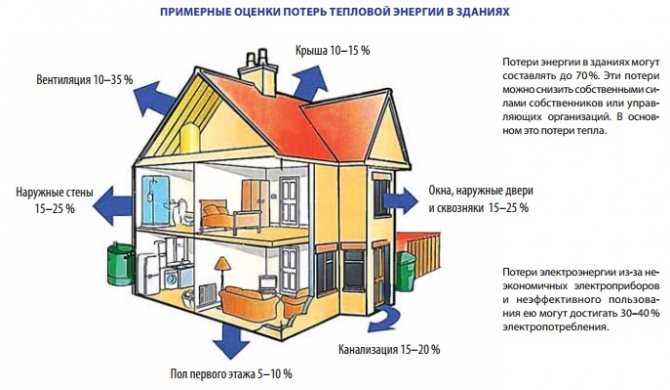
Simplified calculation of heat loss compensation
Any calculations are based on certain principles. The basis for calculating the required thermal power of batteries is the understanding that well-functioning heating devices must fully compensate for the heat losses that arise during their operation due to the characteristics of the heated premises.
For living rooms located in a well-insulated house, located, in turn, in a temperate climatic zone, in some cases, a simplified calculation of compensation for thermal leaks is suitable.
For such premises, calculations are based on a standard power of 41 W required for heating 1 cubic meter. living space.
In order for the heat energy emitted by heating devices to be directed specifically to heating the premises, it is necessary to insulate walls, attics, windows and floors.
The formula for determining the thermal power of radiators required to maintain optimal living conditions in a room is as follows:
Q = 41 x V,
Where V - the volume of the heated room in cubic meters.
The resulting four-digit result can be expressed in kilowatts, reducing it from the calculation of 1 kW = 1000 W.
How much does the cooling radiator weigh?


Here I found such information, rummaging through the open spaces of Ineta, I think it will be useful to everyone.
Complete power unit (with gearbox and transfer case)
GAZ-67 engine with gearbox and transfer case (transfer case is integrated into gearbox) - 248 kg GAZ-69 engine with gearbox and transfer case - 280 kg GAZ-66 engine with gearbox and transfer case - 380 kg ZIL-130 engine (431410) with gearbox and parking brake - 640 kg Engine UAZ-3151 (UMZ-4179) with gearbox and transfer case - 240 kg Engine
GAZ-66 engine - 275 kg ZIL-130 engine (431410) - 500 kg UAZ-3151 (UMZ-4179) engine - 165 with clutch Mitsubishi 4D56 engine - 215 kg Mitsubishi 4G64 engine - 195 kg Mitsubishi 4M40 engine - 270 kg Mitsubishi engine 6G72 - 225 kg Nissan TD27 engine - 250 kg Nissan RD28 engine - 255 kg Nissan TD42 engine - 365 kg Toyota 1HDFTE engine - 365 kg HUYNDAI D4BH engine - 220 kg VAZ 21214-1000260-32 engine - 134.5 kg VAZ 21213- engine 1000 260-00 - 124 kg VAZ 2121 engine - 114 kg
GAZ-66 gearbox - 56 kg
ZIL-130 (431410) gearbox without parking brake - 98 kg GAZ-69 gearbox - 28 kg UAZ 3151 gearbox - 36 kg Mitsubishi V5MT1 gearbox (manual transmission) with SuperSelect transfer case - 110 kg Mitsubishi V4AW3 gearbox (automatic transmission) with SuperSelect transfer case - 140 kg VAZ-2121 gearbox (with clutch housing) - 32 kg
Transfer case GAZ-66 - 49 kg, with brake 57 transfer case UAZ-3151 with brake - 37 Transfer case GAZ-69 - 43 Transfer case VAZ-2121 - 27.6 kg
Cooling system radiator
Radiator ZIL-130 (431410) - 21 kg Radiator GAZ-53 - 21 kg Radiator VAZ-2121 - 7 kg Radiator GAZ-24 - 10 kg Radiator GAZ-69 - 16 kg
Frame GAZ-69 - 125 Frame GAZ-66 - 290 Frame UAZ-3151 - 112
Fuel tank 21213 with sensor - 4.8 kg Fuel tank Gazelle, GAZ-3307, GAZ-66 100l universal - 14 kg Fuel tank UAZ-3303 onboard - 9.1 kg
Fuel tank UAZ-469 left assembly 7.2 kg
complete body (1 complete set)
GAZ-69 body - 409 GAZ-66 cab assembly - 360 VAZ-2121 body assembly - 520 UAZ-3151 body assembly - 475 UAZ Patriot body assembly - 760 UAZ Hunter body (rear swing door) assembly - 590 Body UAZ-31514-84 (with a metal roof, soft seats, folding tailgate) - 587 kg UAZ-3303 cab (onboard) assembled (with seats) - 268 UAZ-3741 body (manufactured goods non-glazed van) - 592 UAZ cab- 39094 Farmer (5-seater double cab) - 610 Body UAZ 3962 (nurse, glazed, with folding benches) - 765 bare body (frame, 3 complete set)
Body with a frame Pajero II V24W shorty (frame, 3 complete set) -415 kg Body frame painted UAZ Patriot - 420 Boat UAZ 31512 (469), under the awning - 249 Body frame UAZ Hunter (rear swing door) - 241
Body frame UAZ-31514 (tailgate folding) - 249 Cab UAZ-3303 (side) frame - 160 Body frame UAZ-3741 (manufactured goods non-glazed van) - 400 Cab UAZ-39094 Farmer (5-seater double cab, frame) - 180 Body frame UAZ 3962 (nurse, glazed, with folding benches) - 400 Removable roof
Roof UAZ 3151-40 under the tailgate with upholstery and glazing - 91 kg Roof UAZ 3151-95 under the rear hinged door with upholstery and glazing - 83 kg
Hood without noise insulation MMC Pajero II without nostril - 17.7 kg Hood GAZ-69 - 12 kg Hood VAZ-2121 - 15 kg Hood UAZ-3163 (Patriot) - 15.8 kg Hood UAZ-469 - 13.1 kg
Front wing MMC Pajero II dorestyle, without extender (fender) - 4.8 kg Front wing VAZ-2121 - 5.8 kg Wing UAZ 469 - 4.3 kg Wing UAZ Patriot 3163 - 5.2 kg
Trunk door VAZ-21214 (bare) - 8.5 kg
Trunk door UAZ-3162 (bare) - 22 kg
Door UAZ-3160, front Patriot (bare) - 17.7 kg Door VAZ-21214 (bare) - 14.4 kg Windshield
Windshield MMC Pajero II - 11.5 kg
Rear axle complete with brakes
Rear axle GAZ-66 - 250 Rear axle GAZ-69 - 90 Rear axle UAZ-31512 (collective farm) - 100 Rear axle UAZ-3151 (military) - 122 Axle VOLVO Laplander 170 Axle rear MMC Pajero 9.5 ″ (spring suspension) - 115 Rear axle MMC Pajero 8 ″ (spring suspension) - 95 Rear axle MMMC Pajero 8 ″ (leaf spring suspension, LSD) with oil, parking brake cables - 93 Rear axle VAZ-2121 - 60 kg
Front axle GAZ-66 330 kg Front axle GAZ-69 120 kg Front axle UAZ-31512 (collective farm) - 120 kg Front axle UAZ-3151 (military) - 140 kg Front axle VAZ-2121 (with front wheel drive) - 32 kg
cardan gear GAZ-66 - 36 kg cardan shafts UAZ-3151 - 15 kg
Wheel (standard, factory)
Wheel with GAZ-69 tire - 30 Wheel with GAZ-67 tire - 29 Wheel with UAZ-3151 tire - 39 Wheel with GAZ-66 tire - 118 Wheel with VAZ-2121 tire - 21
wheel disk (factory)
steel VAZ-2121 16 "- 8.7 kg steel VAZ-2123 15" - 9.0 kg steel UAZ-452-3101015-01 15 "- 11.7 kg steel UAZ-452-3101015 16" - 13.1 kg cast MMC Pajero II 7 × 15 ″ - 9.5 kg
Posted by aron878, 11 April 2012 in Tech Support
Recommended posts
Create an account or log in to leave a comment
Comments can be posted only by registered users
Create an account
Register a new account in our community. It's not hard!


From this moment, a number of difficulties begin and a question arises for connoisseurs how much a vaz cooling radiator weighs, because often the user does not understand where to look for the answer. Instructions and videos are available in an international format for citizens of any country over the age of 18.
Video quality: HDRip
The video was uploaded to the admin from the user Agapit: for urgent viewing on the portal.
To give the correct answer to the question, you need to watch the video. After viewing, you do not need to seek help from specialists. Detailed instructions will help you solve your problems. Happy viewing.
Humor in the subject: - Mikhalych, give the key to 173.211.101.14! - Catch: NUYik98ULAase3
iobogrev.ru
https://youtu.be/UA-Hog-YN8w
A practical example of calculating heat output
Initial data:
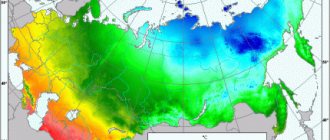
- A corner room without a balcony on the second floor of a two-story cinder block plastered house in a windless region of Western Siberia.
- Room length 5.30 m X width 4.30 m = area 22.79 sq. M.
- Window width 1.30 m X height 1.70 m = area 2.21 sq. M.
- Room height = 2.95 m.
Calculation sequence:
| Room area in sq.m .: | S = 22.79 |
| Window orientation - south: | R = 1.0 |
| The number of external walls is two: | K = 1.2 |
| Insulation of external walls - standard: | U = 1.0 |
| Minimum temperature - down to -35 ° C: | T = 1.3 |
| Room height - up to 3 m: | H = 1.05 |
| Upstairs room - not insulated attic: | W = 1.0 |
| Frames - single-chamber double-glazed windows: | G = 1.0 |
| The ratio of the area of the window and the room - up to 0.1: | X = 0.8 |
| Radiator position - under the windowsill: | Y = 1.0 |
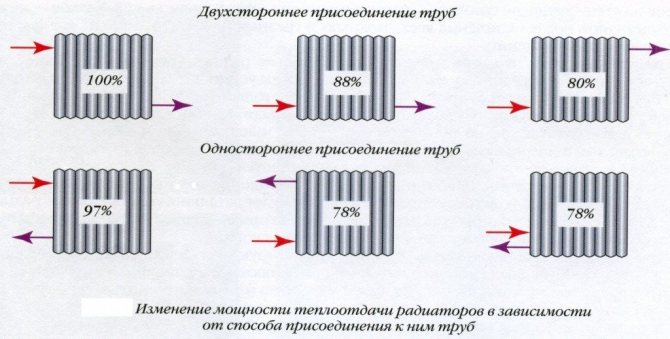
| Radiator Connection - Diagonal: | Z = 1.0 |
| Total (don't forget to multiply by 100): | Q = 2 986 Watt |
Below is a description of how to calculate the number of radiator sections and the required number of batteries. It is based on the results obtained for the thermal power, taking into account the dimensions of the proposed installation sites for heating devices.
Regardless of the outcome, it is recommended to equip not only window niches with radiators in corner rooms. The batteries should be installed near “blind” external walls or near corners, which are exposed to the greatest freezing due to the outdoor cold.
LET'S CALCULATE
Knowing that 100 watts of heat is needed per square meter of room area, you can easily calculate the number of required radiators.
Therefore, first you need to accurately determine the area of the room where the batteries will be installed.
The height of the ceilings, as well as the number of doors and windows, must be taken into account - after all, these are openings through which heat evaporates most quickly. Therefore, the material from which the doors and windows are made is also taken into account.
The lowest temperature in your area and the temperature of the heating medium at the same time are now determined.
All nuances are calculated using the coefficients that are entered in the SNiP. Taking into account these coefficients, you can also calculate the heating power.
A quick calculation is done by simply multiplying the area of the room by 100 watts.
But this will not be accurate. Coefficients are used for correction and.
POWER ADJUSTMENT FACTORS
There are two of them: decreasing and increasing.
Derating factors are applied as follows:
- If plastic multi-chamber double-glazed windows are installed on the windows, then the indicator is multiplied by 0.2.
- If the ceiling height is less than the standard (3 m), then a reduction factor is applied.
- It is defined as the ratio of the actual height to the standard height. Example - the ceiling height is 2.7 m. This means that the coefficient is calculated using the formula: 2.7 / 3 = 0.9.
- If the heating boiler operates with increased power, then every 10 degrees of heat energy generated by it, the power of the heating radiators is reduced by 15%.
Power increase factors are taken into account in the following situations:
- If the ceiling height is higher than the standard size, then the coefficient is calculated using the same formula.
- If the apartment is corner, then a coefficient of 1.8 is applied to increase the power of heating devices.
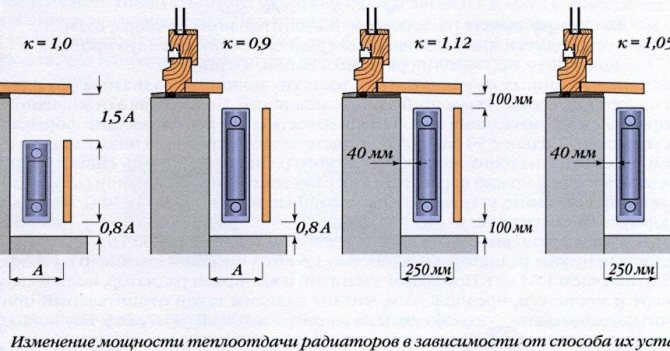
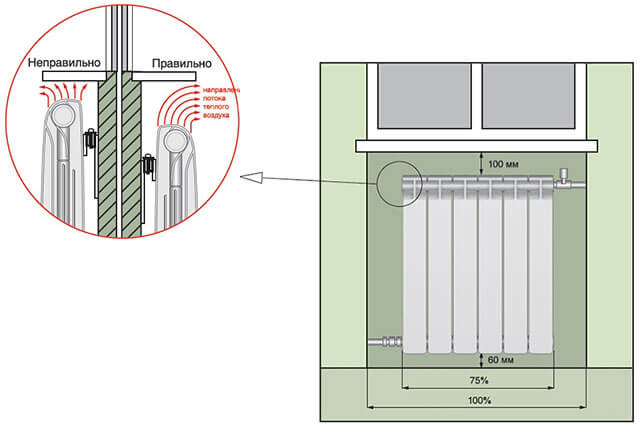
- If the radiators have a bottom connection, then 8% is added to the calculated value.
- If the heating boiler lowers the temperature of the coolant on the coldest days, then for every 10 degrees of decrease, an increase in the capacity of the batteries by 17% is necessary.
- If sometimes the temperature outside reaches critical levels, then you will have to double the heating power.
Specific thermal power of battery sections
Even before performing a general calculation of the required heat transfer of heating devices, it is necessary to decide which collapsible batteries from which material will be installed in the premises.
The selection should be based on the characteristics of the heating system (internal pressure, heating medium temperature). At the same time, one should not forget about the greatly differing cost of purchased products.
How to correctly calculate the required number of different batteries for heating will be discussed further.
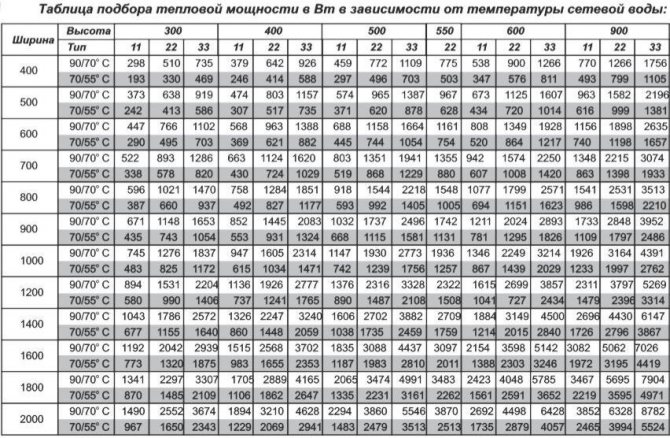
With a coolant of 70 ° C, standard 500 mm radiator sections made of dissimilar materials have unequal specific heat output “q”.
- Cast iron - q = 160 Watt (specific power of one cast-iron section). Radiators made of this metal are suitable for any heating system.
- Steel - q = 85 Watt... Steel tubular radiators can withstand the harshest operating conditions.Their sections are beautiful in their metallic luster, but have the least heat dissipation.
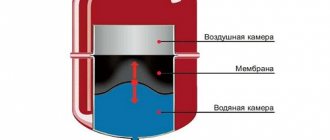
- Aluminum - q = 200 Watt... Lightweight, aesthetic aluminum radiators should be installed only in autonomous heating systems, in which the pressure is less than 7 atmospheres. But in terms of heat transfer, their sections have no equal.
- Bimetal - q = 180 Watt... The insides of the bimetallic radiators are made of steel, and the heat-dissipating surface is made of aluminum. These batteries will withstand all kinds of pressure and temperature conditions. The specific thermal power of the bimetal sections is also at a height.
The given values of q are rather arbitrary and are used for preliminary calculations. More accurate figures are contained in the passports of purchased heating devices.
Image gallery
Photo from
The advantages of the sectional assembly principle
Basic rules for assembling heating devices
Obsolete Cast Iron Battery Sections
Powder coated colored sections
Varieties of radiators
Today, the most popular heating scheme consists of three main elements: a heating boiler (solid fuel, gas, electric or alternative subspecies), pipes and radiators through which the coolant (antifreeze or water) is transported. At first glance, everything looks very simple. The batteries are installed under the window and heat the room. But there are several nuances here. The radiator power must correspond to the square of the room.
All calculations of this type must be carried out in accordance with the norms of SNiP. The procedure is quite complex and is performed exclusively by specialists in this field. But if you use a few tips, then such calculations can be done independently.
Many varieties of steel radiators can be found on the market today. The main ones are:
- cast iron radiators;
- aluminum radiators (several subspecies);
- steel radiators (tubular or panel scheme);
- bimetallic radiators.
In this video, you will learn how to calculate the power of a radiator:
Steel batteries
Such options are not very popular today, even taking into account the aesthetically beautiful external design. The walls of the batteries are very thin, so they quickly heat up and cool down. At high pressure, the welds may break and the radiator will leak. Also, cheaper models that do not have a special anti-corrosion coating can rust quickly. As a rule, manufacturers do not provide a long-term warranty for such products.
In most cases, steel radiators consist of one solid plate, so it will not work to change the heat transfer by adjusting the number of sections. It is necessary to build on the quadrature and choose components according to the installed passport capacity. In some models of the tubular type, you can change the number of sections, but this is more an exception. You won't be able to do such work on your own, you will need to order the work from the master.


Typically, steel radiators consist of 1 slab
Cast iron models
This option is familiar to many, since it was precisely such batteries that were installed from the time of the Soviet Union until the beginning of the twentieth century. People also call them "accordions". Although they don't look pretty, they have a long lifespan. Each edge of the battery has a heat dissipation rate of 160 W. The number of sections is not limited in any way, so the radiator can be assembled in parts. Today you can see modern analogues of cast iron radiators on the market.
At the same time, they do not lose their initial advantages:
- high heat capacity, due to which the temperature is maintained for a long time, and the heat output is quite high;
- if the entire system is properly assembled, then the cast iron elements will not be "afraid" of water hammer and temperature changes;
- the walls are quite thick, they will not rust.
Any liquid can act as a heat carrier, so they are good for both an autonomous heating system and a centralized one. But they also have some disadvantages.Firstly, the poor appearance and the complexity of the installation. Secondly, cast iron is a rather fragile material and point water hammering may not withstand. In addition, the large mass of such batteries will not allow them to be installed on any wall.


These batteries have a high heat exchange rate.
Aluminum products
Aluminum radiators appeared relatively recently, but in a short time they managed to gain popularity among buyers. They have excellent heat dissipation, they have an attractive appearance and are quite easy to install and operate. But when choosing them, you need to pay attention to some nuances.
Aluminum models can withstand temperatures up to 100 ° C and pressures up to 15 atmospheres. In this case, the heat transfer of one section can reach 200 W. Also, with a weight of one section of about 2 kg, they do not require large volumes of coolant (up to 500 ml). Today on the market there are products with the possibility of dividing sections and one-piece structures with an already calculated capacity.
They also have their disadvantages:
- Aluminum radiators can undergo oxygen corrosion, so they can only be installed on autonomous heating systems, since they are very demanding on the coolant.
- Some models, consisting of a solid canvas, under certain conditions can leak in the area of the connecting elements, while they cannot be replaced, it will be necessary to change the entire battery.
Of all the possible variations, aluminum radiators are the highest quality and most reliable products, in the production of which the technology of anodic oxidation of metal was used. They are almost completely free from oxygen corrosion. The appearance of such products, regardless of the production technology, is the same. In this regard, you need to pay particular attention to the technical documentation when choosing.
Bimetallic materials
Today such products are ideal in all respects. In terms of reliability, they are not inferior to cast-iron counterparts, and their heat transfer is at the level of aluminum radiators. This is due to their design features.
The structure consists of two steel collectors (upper and lower) and connecting channels between them. All elements are connected to each other with high quality couplings. Thanks to the outer aluminum shell, heat dissipation remains at a high level. The inner part of the pipes is made of metal that does not corrode or has an anti-corrosion coating. The aluminum container for heat exchange is not subject to corrosion, since it does not come into contact with the coolant.
The design has a high level of reliability and a fairly high heat dissipation.
Bimetallic batteries are not afraid of temperature and pressure surges. They are more effective precisely at high pressures, since they are useless in a system with natural circulation. If we talk about the shortcomings, then we can only note the high cost.
Calculation of the number of radiator sections
Collapsible radiators made of any material are good in that individual sections can be added or subtracted to achieve their design thermal power.
To determine the required number of "N" sections of batteries from the selected material, follow the formula:
N = Q / q,
Where:
- Q = the previously calculated required heat output of the devices for heating the room,
- q = heat specific power of a separate section of the batteries intended for installation.
Having calculated the total required number of radiator sections in the room, you need to understand how many batteries you need to install. This calculation is based on a comparison of the dimensions of the proposed installation sites for heating devices and the dimensions of the batteries, taking into account the supply.


battery elements are connected by nipples with multidirectional external threads using a radiator wrench, at the same time gaskets are installed in the joints
For preliminary calculations, you can arm yourself with data on the width of the sections of different radiators:
- cast iron = 93 mm,
- aluminum = 80 mm,
- bimetallic = 82 mm.
In the manufacture of collapsible radiators from steel pipes, manufacturers do not adhere to certain standards. If you want to put such batteries, you should approach the issue individually.
You can also use our free online calculator to calculate the number of sections:
WE CALCULATE THE VOLUME OF SPACE
For a panel house with a standard ceiling height, as mentioned above, the heat is calculated based on the requirement of 41 W per 1 m3. But if the house is new, there are brick windows, double glazed windows, and the outside wall is insulated, then you need 34 watts per m3.
The formula for calculating the number of radiation sections is as follows: the volume (area multiplied by the ceiling height) is multiplied by 41 or 34 (depending on the type of house), which is divided by the Heater section of the manufacturer's certificate.
For example: Room area 18 m2, ceiling height 2, 6 m.
The house has a typical panel building. The heat transfer of one section of the radiator is 170 W.
18X2.6X41 / 170 = 11.2. So, we need 11 radiator parts. This ensures that the room is not corner and there is no balcony, otherwise it is better to place 12 pieces.
Improving the efficiency of heat transfer
When the room is heated by a radiator, the external wall also intensively heats up in the area behind the battery. This leads to additional unnecessary heat loss.
It is proposed to shield the heater from the outer wall with a heat-reflecting screen to improve the efficiency of heat transfer from the radiator.
The market offers a variety of modern insulating materials with a heat-reflecting foil surface. The foil protects the warm air warmed up by the battery from contact with the cold wall and directs it inside the room.
For correct operation, the boundaries of the installed reflector must exceed the dimensions of the radiator and protrude 2-3 cm on each side. The gap between the heater and the thermal protection surface should be 3-5 cm.
For the manufacture of a heat-reflecting screen, you can advise isospan, penofol, alufom. A rectangle of the required dimensions is cut out of the purchased roll and fixed on the wall at the place where the radiator is installed.
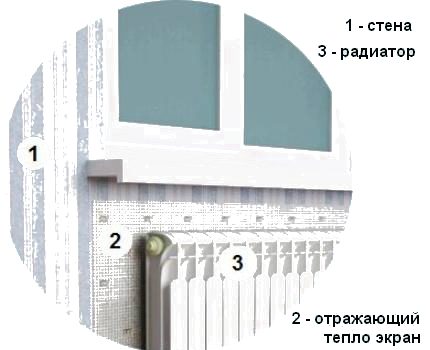

It is best to fix the screen that reflects the heat of the heater on the wall with silicone glue or with liquid nails
It is recommended to separate the insulation sheet from the outer wall with a small air gap, for example, using a thin plastic grating.
If the reflector is joined from several pieces of insulating material, the joints on the foil side must be glued with metallized adhesive tape.
WE MAKE THE CALCULATION OF THE PIPELINE CORRECT
How to calculate heating in a private house, and which pipes are best suited?
Pipes for a heating system are always selected individually, depending on the type of heating selected, but there are certain tips that are relevant for all types of systems.
In systems with natural circulation, pipes with an increased cross-section are usually used - at least DU32, and the most common options are within the range of DU40-DU50.
This allows you to significantly reduce the resistance to the coolant with a slight slope. For the installation of radiators installed using bends, pipes DU20 are used.
A very common mistake when choosing is the confusion between the cross-sectional diameter and the outer diameter of the pipe (for more details: "The optimal pipe diameter for heating a private house"). For example, a DN32 polypropylene pipe usually has an outer diameter of about 40 mm.
Systems equipped with a circulation pump are best equipped with pipes with an outer diameter of 25 mm, which allows heating a building of average dimensions (about
Weight of standard heaters
Both traditional and designer pieces are united by the material of manufacture, which is cast iron.
And now everywhere there are regularly serving classic accordion-shaped radiators installed:
- in schools and preschool educational institutions;
- in outpatient departments and hospitals;
- in the premises of the housing stock - apartments, private households, hostels;
- in public and state institutions.
Usually these are models MS-140 or MS-90, since in past years there were no other mass-produced heating devices. Cast iron products NM-150, RKSH, Minsk-1110 and others are presented in small series, but today they are no longer produced. So what is the weight of one section of an old-style cast iron battery? And in this case, there is no exact figure. This is explained by the fact that this value depends on the parameters of the section.
For example, a battery of the MC-140 series can be of two modifications, depending on the center distance, which is 300 or 500 millimeters. If we are talking about the MC-140-300 model, then the average weight of the section is about 5.7 kilograms, and when about the MC-140-500 device, then 7.1 kilograms.
You can often find a product of the MC-90 series, in which the weight of a cast-iron radiator section is 6.5 kilograms with a distance between the axes of 500 millimeters. The difference between the MC-90 and 140 models lies in the different depths of the sections.
Can we assume that the weight of the radiators of these popular series, equal to 6.5, 5.7 and 7.1 kilograms, is final? The answer is no, and there is an explanation for this. The fact is that the current GOST 8690-94, which is a regulatory document regulating the production of batteries from cast iron alloys, indicates their main dimensions.
Regarding how much the section of the old-style cast-iron battery weighs, this standard indicates the specific gravity - 49.5 kg / kW. This standard value applies to radiators that are intended for operation in heating systems with a coolant temperature not exceeding 150 degrees at an excess operating pressure of a maximum of 0.9 MPa (9 kgf / cm²).
In the production of heating devices, manufacturers must ensure that the products comply with these values, but GOST does not regulate how much one section of the cast-iron battery weighs. As a result, the mass of radiators manufactured in different factories is different.
Today, the most famous are the products of several industrial enterprises that produce modifications of the MC-140 series and devices of their own design. Among them: the Belarusian plant of heating equipment, the Russian "Descartes" and "Santekhlit" and others.
The advantages of cast iron
If you do not take into account how much the cast iron battery weighs, a whole range of advantages of this type of heating device can be noted
, which include:
- corrosion resistance;
- resistance to chemically aggressive media - the material is undemanding to the characteristics of the coolant;
- durability;
- high rates of thermal radiation - the more the number of sections, the higher the heat transfer of the heating device.
The appearance of standard cast iron batteries is simple and concise, but today manufacturers also offer antique radiators. The advantages of such models include a stylish and respectable appearance.
Various radiator options
Specifications
The power of a heating device is an indicator of its thermal efficiency. When calculating the heating system, the heating needs of the house are taken into account. It is important to know the capacity of 1 section of a cast-iron radiator in order to determine the size of the batteries for each heated room. Incorrect calculations lead to the fact that the room will not warm up qualitatively, or vice versa - it will often have to be ventilated, removing excess heat.
For an ordinary standard cast iron radiator, the power of 1 link is 170 watts.Cast iron batteries can withstand heating over 100 ° C and successfully operate at an operating pressure of 9 atm. This allows the use of products of this type as part of central and autonomous heating networks.
Modern models
Manufacturers offer lightweight versions of gray cast iron batteries. If the weight of 1 link of the Soviet radiator MC140 is 7.12 kg, then 1 section of the Czech-made Viadrus STYL 500 model weighs 3.8 kg, and its internal volume is 0.8 liters. This means that a Czech radiator of 10 links filled with a coolant will have a mass of (3.8 + 0.8) × 10 = 46 kg. This is 40% less than the mass of a filled MC 140 battery with the same number of cells.
Lightweight cast iron heating devices are also produced in Russia. Under the EXEMET brand, MODERN batteries are produced, 1 section of which weighs 3.3, and its internal volume is 0.6 liters. These tubular cast iron radiators are characterized by relatively low heat transfer, which requires an increase in the number of links. The heaters are designed for floor standing installation.
Vintage cast iron radiators are growing in popularity. These are floor models made using art casting technology. Due to the volumetric complex patterns, the weight of the cast-iron radiator section is significantly increased, it reaches 12 or more kilograms.
Vintage cast iron floor standing radiator
Life time
Houses built before the revolution still have cast iron radiators installed over 100 years ago. Modern heating devices made of this material are also designed for decades of maintenance-free operation.
Durability is due to the strength of cast iron, resistance to heat and pressure. Cast iron heaters do not rust during the period when the coolant is drained from the network and the inner surface of the batteries is in contact with air.
Dimensions (edit)
The weight of a cast iron radiator section depends on its height, configuration and wall thickness.
Manufacturers offer models with different characteristics
:
- battery depth is 70 to 140 mm as standard;
- link width varies from 35 to 93 mm;
- section volume - from 0.45 to 1.5 liters, depending on the size;
- standard heater height - 370-588 mm;
- center distance - 350 or 500 mm.
What does the weight of the battery matter?
It is necessary to have information on how much a cast-iron heating radiator weighs for a number of reasons. For example, if batteries are purchased for installation in an entire private household, it is required to calculate the carrying capacity of a machine transporting heating devices, and you should also decide on the number of movers who will bring them into the house.
For clarity, you can compare the weight of cast-iron radiators of outdated samples and modern analogues made of other materials:
- one section of standard batteries made of cast iron with an inter-axle distance of 500 mm weighs 5.5 - 7.2 kilograms, and with an inter-axle parameter of 300 mm - from 4.0 to 5.4 kilograms;
- the weight of the rib of non-standard cast-iron heating devices ranges from 3.7 to 14.5 kilograms;
- the section of the aluminum battery weighs 1.45 kilograms with an center gap of 500 millimeters, and 1.2 kilograms at 350 millimeters;
- bimetallic devices with a center distance equal to 500 mm weigh 1.92 kg / section, and at 350 mm, 1.36 kg / section.
When carrying out repairs and replacement of heating equipment in a house, it is important for its owners to know how much the old cast-iron battery weighs in order to decide whether it will be possible to independently take out the old multi-section radiator to the street, since it is necessary to calculate their own strength. But there is no such data.
The reason is that there are different models in operation. Moreover, they have the same purpose, but different weight. In addition, devices are sold on the domestic market that differ in size and variety of shapes.
Today, for example, there are more than several dozen names of traditional cast iron batteries, and it is difficult to count models made in a designer style. At the same time, such a parameter as the weight of one section of a cast-iron radiator is very different.
Pressure
Usually, the accompanying documentation contains the characteristics of aluminum radiators, indicating the operating and pressure pressure (the last parameter is an order of magnitude higher). Sometimes, there may be indications of maximum pressure, which often causes confusion. You need to know that it is at the operating pressure that the battery will operate. Aluminum devices have a working pressure of 10-15 atm.
Central heating has a pressure of 10-15 atm., And heating lines - almost 30 atm. For this reason, it is not recommended to install aluminum radiators in apartments with central heating. As for private houses with autonomous heating, domestic-made boilers produce a pressure of no more than 1.4 atm. (this parameter is sometimes indicated in bars, which is the same). German-made boilers have a higher working pressure - almost 10 bar: this is suitable for the use of aluminum radiators.

Pressure parameters are equally important. As a rule, at the end of the heating season, the water is drained from the system. To restart the heating, it is necessary to check the tightness of the entire circuit. This is achieved by pressure testing, that is, testing in the mode of increased pressure (usually it is 1.5-2 times higher than the performance indicators). Traditionally, the pressure test can reach 20-30 atm. Most often, this procedure is carried out in centralized networks.
The large difference in operating pressure for apartment buildings and private houses is due to the different number of floors. The pressure helps determine the level to which the water is reaching. So, one atmosphere is capable of raising water to a height of 10 meters. This is quite enough for a three-story house, but not enough for a four-story house. Utilities rarely adhere to the declared coolant supply regime. In some cases, due to exceeding the norms, even the most durable expensive devices fail.
Therefore, it is desirable that the installed aluminum batteries have a certain pressure margin. This will allow them to withstand pressure surges in the system. Having a pressure reserve, you can not worry about the health and efficiency of the batteries. The characteristics of aluminum radiators indicated by different manufacturers may differ. In addition to designation units such as bar and atmosphere, sometimes megapascals (MPa) are also found. To convert to bar, 1 MPa is multiplied by 10.
Dependence of heat transfer on material
The best materials for the manufacture of radiators are metals, because they have the best coefficient of thermal conductivity. The higher this indicator, the better the material transfers heat from the hot coolant to the ambient air.
The table below contains the heat transfer coefficients of metals used in the manufacture of heating devices:
As can be seen from the table, copper is the most advantageous from this point of view - it transfers heat better than others. However, with such advantages, it is very "inconvenient" in terms of manufacturing and operation:
- easily damaged;
- quickly oxidizes;
- chemically active.
Aluminum
Aluminum is used more often than copper, although its thermal conductivity is half that. It heats up quickly, is lightweight, and can be used to make products of almost any shape. But it has the same disadvantages as copper. In addition, when aluminum comes into contact with other metals, corrosion quickly begins.
Cast iron
For a long time, cast iron heating batteries have enjoyed well-deserved popularity. This metal is durable, inexpensive and corrosion resistant. Its disadvantages include only great weight and fragility. But the large weight of the batteries in some cases is good for them. In networks with solid fuel boilers, a large thermal inertia due to the weight of the radiators helps smooth out the inherent fluctuations in the temperature of the coolant and maintain the temperature in the room after the fuel has burned out.
Steel
The thermal conductivity of steel is even lower. In addition, it is subject to intense corrosion, which significantly reduces the service life of such radiators. But the relatively low price and ease of manufacture of panel radiators attracts many manufacturers.Radiators of this type are two interconnected steel plates with stamped channels for the movement of the coolant.
Bimetallic devices
Each of the materials considered has its own advantages and disadvantages - there is no ideal metal for making a radiator. But by combining two different metals, good results can be achieved. Recently popular bimetallic radiators are made of steel and aluminum. The aluminum outer part of the appliance is excellent at transferring heat from the sturdy inner made of steel. As a result, their heat transfer is much higher than that of cast iron or steel. The table shows the amount of heat transfer from heating radiators of one standard size:
Dependence of heat transfer on the shape
For the quality of heat transfer, in addition to the material from which the radiator is made, its shape is of great importance.
For example, the simplest panel radiator measuring 0.5 m by 0.5 m has a thermal power of about 380 W. So, if it is equipped with additional ribs and the area is increased, the heat transfer will increase by one and a half times: up to 570 W. Without increasing the temperature of the coolant, its speed, without changing the size of the channels - only by increasing the surface area in contact with the surrounding air.
Therefore, all manufacturers strive to increase the heat transfer of their products precisely according to this principle - they are looking for a form that will more efficiently transfer the energy of the coolant without additional costs.
How to increase heat dissipation
There are several simple ways to increase the heat transfer of the heating battery:
- Install heat-reflecting material behind the radiator. You can attach a thin metallized or foil insulation to the wall behind it. It should fit snugly against the wall and be at least 1 cm away from the radiator housing to ensure good air circulation.
- Clean the case from dust, which inevitably accumulates on it even in the "cleanest" apartment.
- Excess paint layers greatly reduce the heat transfer of the heating device. Therefore, if you are going to repaint it, remove the old paint before work. (It is written here how to do it correctly).
- Do not cover radiators with solid floor-length curtains. They block the normal air circulation, and mainly the space near the window is heated.
- Check if air has accumulated in the radiator. It will be understandable if its upper and lower parts differ significantly in temperature. To remove air, a Mayevsky tap is used, which should be on each heating device.
- If temperature regulators are installed on the battery, check their position and serviceability.
In addition to simple methods that are feasible during the heating season, in the summer you can try to solve the problem radically:
- Flush the battery and heat supply pipelines. The coolant inevitably contains some contamination. Especially the central heating "sins" this. These contaminants settle in the pipes and internal channels of radiators and gradually reduce their diameter, making it difficult for the coolant to pass and transfer its heat to the body. This procedure is recommended to be carried out before each heating season. (This article describes various ways to flush the heating system.)
- Change the radiator connection or its location if they were not made efficiently enough, and this allows the room and the design of the heating network.
- Increase the number of sections in the heating battery. All types of radiators, except for panel and tubular radiators, make it easy to carry out this operation by increasing the size of heating devices.
- In an apartment building, the reason for the decrease in heat transfer may not be the shortcomings of your heating devices, but the neighbors.For example, they can build up their batteries so much that the coolant in them will cool much more than the architects and builders foresaw, and come to your apartment cold. In this case, you will have to contact the managing organization to check the condition of the riser and, then, to the mayor's office to take measures to the negligent neighbor.
Installation tips
Some tips for using and installing cast iron batteries:
- If you decide to install a cast iron heating system in your house or apartment, then you can be sure that the large weight does not affect the operation process in any way. It all depends on the correct and quality installation.
- The power of cast iron batteries can be increased and decreased by adding or removing additional sections.
- Since the battery is lightweight, it must be securely attached to the wall.
- To extend the battery life and maintain good thermal conductivity, it is recommended to flush the cast iron radiators every season.
It is not recommended to install cast-iron radiators on your own, but if you nevertheless decide on this, then you should study all the information on this matter. Installation work on the installation of cast iron batteries requires special skills and verified actions. Inaccuracies in operation can lead to serious accidents.
The most correct decision in this matter is to seek the services of professionals. They will help determine not only the installation, but also the choice of the heating device, depending on the room where it will be located.
Watch a video in which an experienced user explains the techniques for assembling cast iron radiators:
teplo.guru