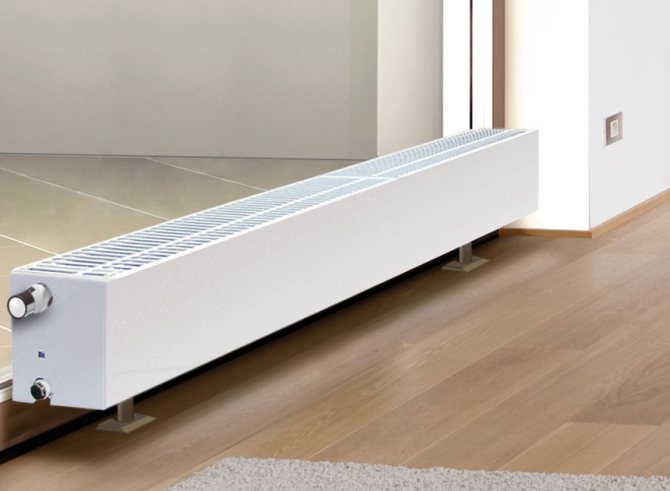
Low heating radiators are in any group of heating devices. This category includes equipment whose height does not exceed 45 cm. Such small batteries are usually looked for for aesthetic reasons: with panoramic glazing or low window sills. Sometimes it is necessary to heat the entire cold wall, in which case this is one of the most effective options. After all, low radiators have low heat transfer, which means that their length will be significant, which is what is needed to heat a cold or "weeping" wall.
It is clear that you want everything to look stylish, but in heating one cannot focus only on aesthetics: technical data are also very important. Therefore, they pay attention to the metal from which they are made. Indeed, it is precisely its properties that largely determine the characteristics of radiators and their area of application.
Aluminum
The lowest aluminum radiators are 245 mm high. The Sira campaign has such models: Alux 80 and Alux 100, Rovall 80 and Rovall 100, Swing. They have a good heat transfer for such miniature products - 89-97 watts. Global has a low radiator - model Gl-200/80 / D. This model is cast, with a working pressure of 16 bar.

The lowest radiator at "Global" Gl-200/80 / D has a height of 200 mm
There are aluminum radiators with a center-to-center distance of 200 mm and from the Russian manufacturer - from] Rifar (Rifar) [/ anchor] - these are Rifar Base 200 and Rifar Forza 200. And the back wall is solid. They can be safely put "back" to the window and not worry about the appearance from the street.
But these are the smallest radiators. There is a large selection of models, the height of which will not be higher than 45 cm. Every company has such dimensions, in almost every line. The center distance of 300 mm, 350 mm or 400 mm is also suitable for the low category.
Advantages, disadvantages


In any line there are low batteries, with a center distance of 300 or 350 mm
Advantages of aluminum radiators: lightweight, have high heat transfer, small capacity (little water is placed), quickly respond to temperature changes.
The most important disadvantage is the reactivity of aluminum and its softness. For normal and long-term operation, a high-quality heat carrier is required: Ph 7-8, working pressure - from 5-6 Bar for extrusion models, up to 10-12 for cast ones. It is imperative that the coolant contains a small amount of oxygen and suspended matter. Oxygen contributes to the oxidation and destruction of aluminum, and suspensions grind off the metal.
But each manufacturer has its own requirements. For example, Chinese Radena aluminum radiators operate at 16 Bar pressure and a heating medium with a Ph of 6.5-9. And the Sira extrusion models have an operating pressure of 16 Bar and a warranty period of 25 years. Perhaps there are other aluminum radiators whose characteristics go far beyond the average: there are too many manufacturers and models here.
When choosing, do not forget about all these technical subtleties: only if the operating conditions coincide with the recommendations of the manufacturers, the heating will work for a long time and without interruptions.
When installing the system, it is worth remembering that aluminum cannot be directly connected to copper (or copper-based alloys). This means that when wiring with copper pipes, it is better to install other radiators. Also, do not use bronze or brass fittings. Galvanized fittings and fittings work well with aluminum.
Application area
Scope: in individual heating there are practically no restrictions, it may only be worth paying attention to the temperature of the coolant, especially if there is a coal or wood-fired boiler in the system. It is risky to put them in apartments. Unless only very reliable and proven, and only if the coolant in the system meets the manufacturer's requirements.
Read about the choice of radiators for an apartment and a house in the article "Aluminum batteries: types, selection, connection"
Calculation of the number of heating batteries
The calculation is made taking into account several factors:
- the area of the heated room, the numbers will be more accurate if you calculate the cubic volume of room air that should be warmed up;
- the area of the outer heating surface, giving off heat to the room, ensuring the circulation of the heat flux;
- working temperature conditions.
If you do not need special precision, you can use the old proven method.
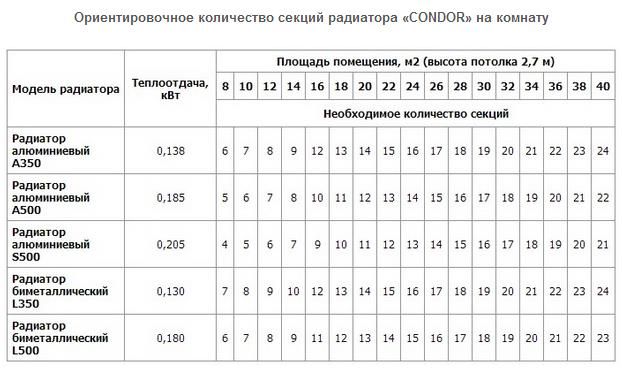

Calculation of radiator sections using the example of CONDOR radiators
Initially, we calculate the area of the apartment, but not the volume.
Then, if the radiators are sectional, we take the required number from the calculation: one section per two square meters.
Now we calculate the total amount and add 10% of the amount received to the result obtained, this is to compensate for losses through windows and doors.
You can read more detailed information in the article "How to independently calculate heating radiators"
Bimetallic
It is customary to call bimetallic radiators heating devices in which the collectors, through which water flows, are made of steel (sometimes stainless, sometimes black). This frame is then fused with an aluminum "jacket" of fins (to increase heat transfer).


Bimetallic very small radiators do not have
Such batteries have a high operating pressure - up to 20-24 bar, can work with almost any coolant (stainless steel collectors work with any), have a fairly high heat transfer. Their disadvantage: often a small cross-section of vertical sea otters, as well as a high price.
The situation here is practically the same as in aluminum ones: some manufacturers have very small radiators with a height of 245-265 mm (the same "Syrah" and "Rifar" have them), and almost all of them have heights from 350 mm to 450 mm.
Advantages, disadvantages
Advantages - high working pressure, compatibility with any metals (aluminum does not come into contact with either the coolant or the supply pipelines). Works with a heating medium in a wide range - Ph 6.5-9 in models with steel collectors and Ph from 5 to 10-11 in models with stainless (Royal Thermo, Calidor, Nova Florida, Radena). Another good quality is the high heat transfer of the section, as well as low inertia (allows you to accurately regulate the temperature in the room using the boiler automation or the temperature controller for the radiator).
Disadvantages - high price, which is due to the high complexity of the technology. And one more drawback: some companies make vertical collectors of small diameter, and they, with a high content of suspended particles in the coolant, can clog. Therefore, it is desirable to install filters at the entrance (and they need to be cleaned regularly).
Application area
This type of radiator has been specially developed for our central heating conditions. Therefore, they need to be installed in high-rise apartments. They will work great in individual heating, but why pay a lot of money for an unnecessary safety factor (almost tenfold)?
Cast iron
Long gone are the days when there was only one type of cast iron batteries. The "Soviet" accordion is far from the only option, there is also a modern style, and in a palace, and in a modern style. There are wall and floor models. Wall-mounted ones are basically the same "accordion" - MS-140 and others, as well as the usual sectional ones of the style familiar today. Floor standing - more often referred to as design radiators. And, unfortunately, they cost a lot. But they look stylish. Read about the types and types of radiators, their manufacturers and technical characteristics here.


Cast iron radiators today are also in a modern style.
"Accordion" is also produced today, and it is in good demand. Called MS-140, MS-110 and MS-90. There are also low models here: with a center distance of 300 mm, and an installation height of 382-388 mm (the height is slightly different for different manufacturers).
There are cast iron radiators in a modern style: they look very much like aluminum and bimetallic ones. In this group, the smallest radiators will also be slightly less than 400 mm.
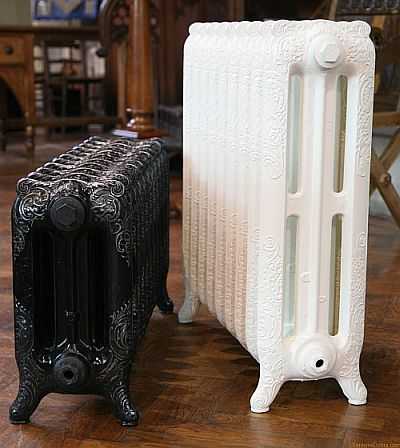


Retro style cast iron radiators are often small
And the third group of cast iron batteries is the design of radiators. Most of them are floor-mounted - on legs. And their sizes are also about the same: around 40 cm (with legs). But some firms have very compact ones:
- BOLTON 220 model with an installation height of 330 mm;
- The Hellas 270 from Viadrus is only 340 mm high.
Perhaps there are other low cast-iron radiators: there are a lot of different proposals, it is impossible to track everything.
Advantages, disadvantages
The undoubted advantages are a long service life, a low price (except for design radiators) and the ability to work with any coolants. Disadvantages - large weight and fragility, difficult to process, not repaired, low operating pressure - 9-10 bar.
There are also properties, which in one case are an advantage, and in the other - a disadvantage:
- Great inertia. Thick walls take a long time to warm up when the system is overclocked. But they cool down for a long time. This feature allows them to smooth out temperature fluctuations when using a conventional coal boiler.
- Large section sections. They hold a lot of water, which again leads to increased system inertia and the use of a more powerful pump in systems with forced circulation. But for systems with natural circulation, low hydraulic resistance of wide collectors is a definite plus.
Application area
All these properties determine the area of use of cast iron radiators, including low ones: they are optimal for individual heating systems (houses, summer cottages, cottages). They stand quite well in high-rise buildings of small number of storeys: where the operating pressure in the system does not exceed 9-10 bar. They do not impose other requirements on the coolant: they do not care whether there is oxygen, how much suspended matter it contains, and what its acidity is. With periodic washing, they will stand for a long time.
Read how to flush the battery here.
Steel tubular
This category has the largest assortment of low radiators. And the low ones here are:
- from 150 mm height for Purmo - Delta Laserline model;
- from 180 mm, Arbonia has almost all models of the "standard" range, there is also a radiator-bench with a height of 180 mm;
- from 190 mm for Zehnder, model Charleston and bench radiators from 400 mm and 410 mm.
- With a center distance of 300 mm from the Russian KZTO.


Tubular radiators are very decorative
At any manufacturer of tubular radiators, you will find those that can be classified as low. They can have from two to six columns of pipes, respectively, they will have different depths - from 50 mm to 250 mm. Each of the models can be installed on the floor or hung on the wall (specify when ordering).
Advantages and disadvantages
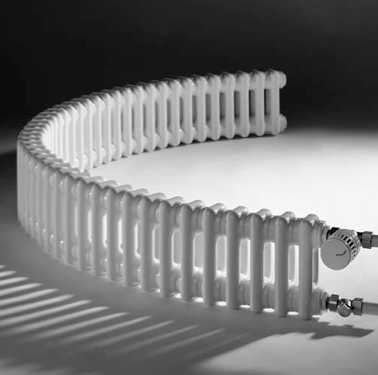

Tubular radiators can be non-linear
The advantages include a large selection of models, with different widths and depths, ease of cleaning, attractive appearance, a large number of decorative options. A large cross-section of pipes creates a small hydraulic resistance, moreover, such radiators are rarely clogged.
Disadvantages are caused by steel: tendency to corrosion, high requirements for the coolant, low operating pressure, short service life - from 5 to 10 years. Exception - Zehnder Charleston Pro
, which is processed from the inside with two compounds. They resist corrosion so well that this option can stand at Ph 5-11. The warranty period is 25 years.
Application area
Basically, tubular radiators are designed for individual heating. Moreover, they can work both in systems with forced and natural gravity. The only requirement is that the system must be of a closed type.
Tips for installing narrow radiators


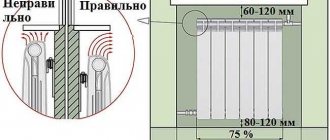
The minimum gap between the wall and the battery must be at least 5 cm
When installing batteries under a window or on a solid wall, it is imperative to observe some nuances.
- If the installation of the structure under the window is unavoidable, it is initially necessary to find the center of the window sill by which to measure the axis of the radiator.
- Consider air convection. Observe the gap between the wall and the battery. This gap should be at least 5 cm.
- If radiators with an air cut-off are installed, they must be at least 5 cm apart.
- When installing low radiators on the wall, it must be borne in mind that the distance from the radiator should be at least 3 cm, and from the floor - 5-10 cm.
- To maintain an attractive design indoors, you can place the radiator in a pre-prepared niche. Communication should be carried out to her in advance.
Radiators should be installed along every wall that faces the outside. This significantly improves the indoor climate.
Narrow horizontal and vertical radiators are considered quite popular among users who own country houses. In such homes, heaters always pay off, creating warmth and comfort at normal energy costs.
Steel panel
Steel panel radiators are low: they are mainly made from 300 mm in height (here it is the height of the radiator, not the center-to-center distance). Any manufacturer has them: both the Russian Prado and the European Purmo and Kermi.
There are also lower ones, but they are rare. So] Purmo [/ anchor] has the Ventil Compact, Purmo Planora and Ramo Compact models. Their height starts from 200 mm (center distance 150 mm). We did not find any other so small.


Steel panel radiators are very low
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of steel radiators include their compact dimensions and the lowest price of one kilowatt of power. In addition, steel is a non-capricious metal that does not conflict with other components of the system.
The main disadvantage is the tendency to corrosion, and hence the exactingness to the coolant: Ph 7-8 and the lack of oxygen (closed systems). The walls of the panels are 1.25 mm or 1.4 mm thick. With a coolant of poor quality, they can corrode in several seasons. There is one more disadvantage, which is due to the design: the small width of the channels through which the coolant circulates. With a large amount of contaminants in the coolant, they quickly become clogged. And flushing such a radiator is a problem. Another disadvantage is the difficulty of cleaning in the presence of plates with convective ribs.
Read more about steel radiators here.
Application area
Normally, panel radiators are in individual closed-type systems (with a closed expansion tank). The circulation of the coolant must be forced: these heaters have a high hydraulic resistance.
They are not recommended to be installed in high-rise apartments, the pressure rarely allows this (working 10 bar). Only in systems that have their own water treatment (independent type of connection) with a mandatory deaeration (air removal) stage.
Battery designs
From the point of view of a constructive solution, all radiators can be divided into:
- Sectional;
- Panel;
- Tubular;
The most common are, of course, sectional models. These are just those vertical "accordions" that we mentioned at the beginning of the article. Aluminum, bimetallic and cheap steel batteries are also a set of sections connected with metal nipples.
Panel radiators are thin flat steel products consisting of rectangular plates, between which there are tubular convectors, which significantly increase the heating efficiency.
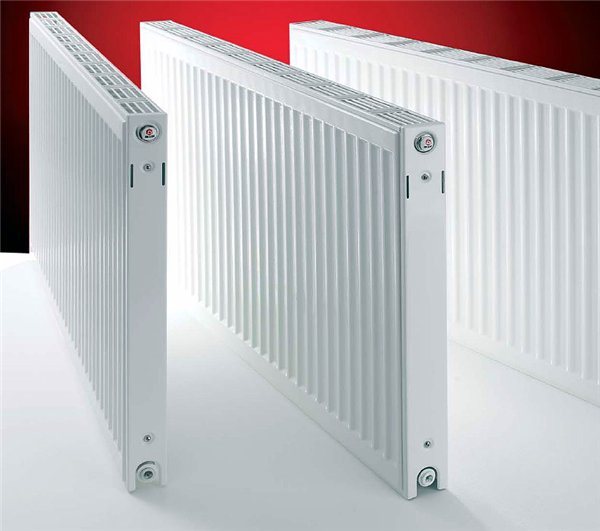


Panel radiators
Tubular batteries are considered the most expensive and reliable. In them, the coolant circulates inside the welded reinforced tubes located vertically. In this way, they are similar to sectional devices, but differ favorably from them in appearance and size.


Tubular radiator
Tubular radiators are available in a variety of colors, high, low and medium varieties, as well as many options with non-standard sizes and configurations. That is why they are used in the majority of luxury luxury cottages and country residences and can be successfully integrated into any of the most sophisticated and sophisticated interiors.
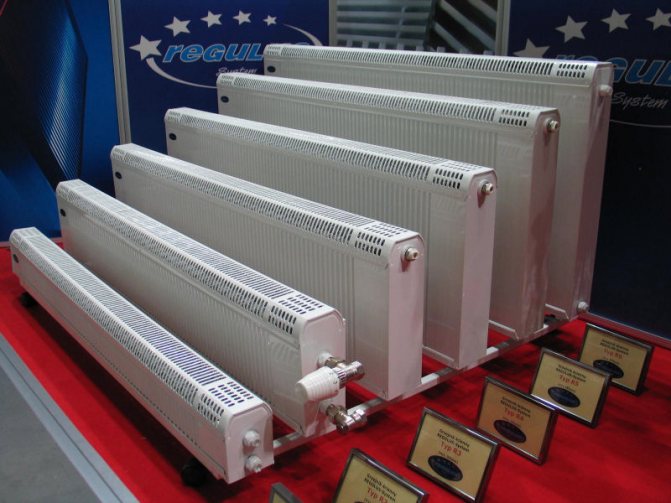
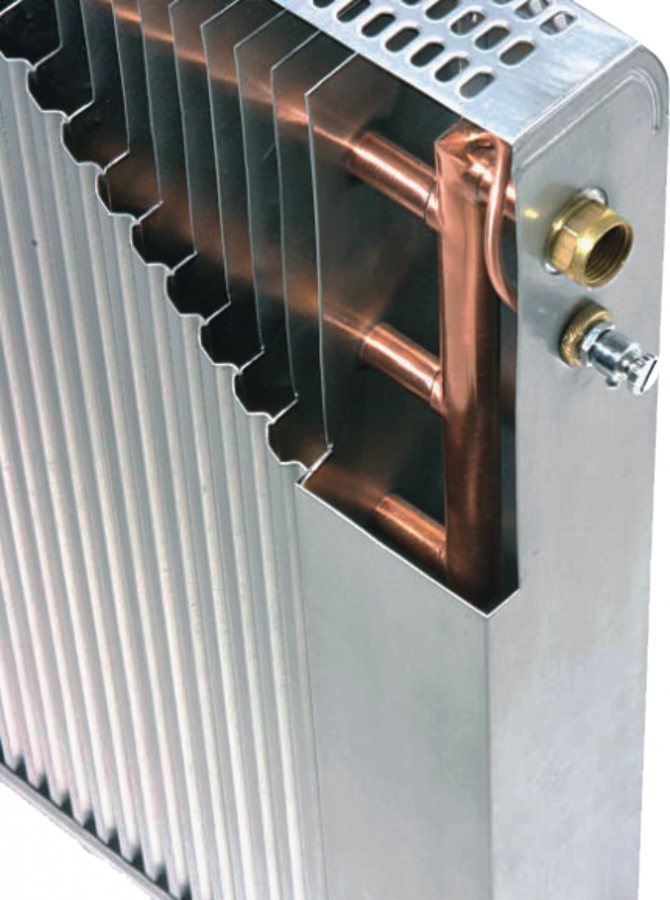
Copper-aluminum radiators
This type of radiators and convectors, with small dimensions, has a high heat transfer. Usually it is a copper tube on which aluminum plates are fixed. This device is hidden in a painted steel casing (sometimes found in stainless steel). Most of the manufacturers on the market produce low copper-aluminum radiators:
- "Thermia" - height from 200 mm, bottom and side connections.
- Regulus-sistem - all models with a height of 215 mm;
- "IsoTerm" - from 215 mm;
- Mars - sectional type with a height of 385 mm.
Read about the manufacturers and models of copper-aluminum and copper radiators here.
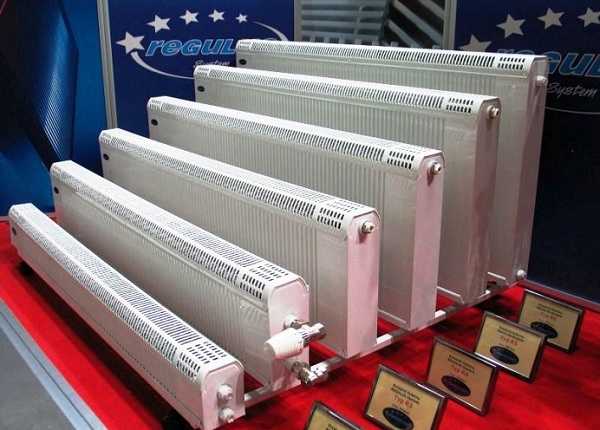


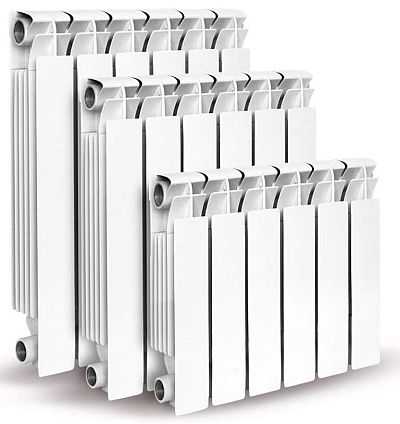
Pictured are copper-aluminum radiators Regulus-sistem
Advantages, disadvantages
The advantage of this type of low radiators is a rather large heat transfer at a small size (a 200mm * 400mm radiator produces 240W). The second good property is that copper does not require a closed system, and Ph should be in the range of 7-9. Quite high working pressure - 16 bar.
But, despite such characteristics, it is not recommended to install in systems with centralized heating: if copper itself reacts little to the quality of the coolant, then it corrodes the solder and leaks appear at the soldering points. And, in addition, copper is incompatible with some metals, and also reacts poorly to a large content of abrasive particles that simply wear it away (copper is soft and gradually grinds off, and this is one of its main disadvantages). Another drawback is the high price, as well as squeaks and rustles that occur when cooling and heating radiators (but this is only for domestic models, European manufacturers have learned to deal with this, ours, not yet).
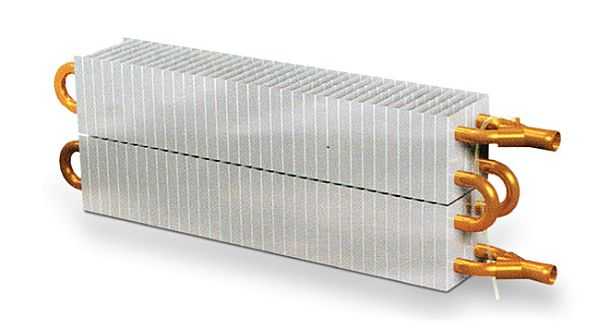

Inside the copper-aluminum radiators there is such or a similar structure.
Application area
And again, these radiators will fit well in individual systems (with forced circulation). But the wiring is desirable from copper, polymer or metal-polymer pipes. In apartments, low copper-aluminum radiators will work normally, provided that the requirements for the coolant and working pressure are met. It is also necessary to install an inlet filter.
Some features of the installation and operation of narrow and high heating radiators
If you count buy narrow and high heating radiators, then the choice will be limited in depth and width. Most models look like one section or a radiator spacing up to 2 m high and about 120-130 mm wide with one-sided pipes relative to the collector. When choosing, it should be borne in mind that the installation and operation of such devices has a number of features that must be taken into account at the design level:
- radiators with a height of about two meters makes sense to use in rooms with a ceiling height of 3.5 meters or more, or in cases where the design and configuration of the room does not make it possible to place horizontal devices;
- it is desirable that a high circulation rate of the coolant is maintained in the heating system, otherwise the top of the radiators will always be much warmer than the bottom, and with a vertical arrangement, this effect is significantly enhanced;
- high type radiators are effectively used as “thermal frames” next to French glazing when it is not possible to equip underfloor heating with convectors;
- thermal efficiency of narrow high radiators is calculated taking into account the height of the room, therefore the formulas used when calculating the “squares of the area of the room” in this case do not give the correct result;
- radiators with bottom connection to the heating system start with 4 sections.
It is necessary to carefully study the prospects for the use of the room, since it will be technically difficult to make changes to the heating system later. Narrow heating radiators fulfill their functions in full, if you rely on correct calculations and assess the prospects for using the room with changes in design.
Skirting heating
This type of heating devices appeared in our country not so long ago. These are very similar devices to copper-aluminum radiators: the same copper tube on which copper or aluminum convective plates are put. They just have a different connection method, layout and other dimensions. Heating elements can be inserted into heating modules (tubes with plates) or they can be assembled into closed circuits through which the coolant circulates. They are located along the floor along the perimeter of the walls, covered with metal decorative overlays. In width - about 3 cm, in height 12-20 cm, depending on the power. Precisely low radiators.


This is what plinth heating looks like. No more other heaters
Advantages, disadvantages
The advantage is that most of the heat (70-80%) is transferred by thermal radiation. From the heat that rises from warm skirting boards, the walls are heated first. They then begin to radiate heat. Therefore, a more uniform temperature is observed in the room, and warm air does not accumulate at the top.
Another plus is the very compact size and at the same time quite high heat transfer: one meter produces 180-280 watts at average temperatures. In addition, they are not striking and provide a wide scope for design decisions.
Minus one - high price.
Application area
They are excellent in individual heating systems. It is possible to install electric warm skirting boards in the apartments. Connection to centralized heating requires a complex system: for optimal operation, the difference between the supply and return pipelines should not exceed 5oC, therefore each circuit should be no more than 12-14 meters in length, and a mixing unit must be installed to maintain normal temperature.
What to do if the top of the radiator is cold
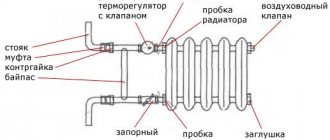
If the top of the heat exchanger is colder than the bottom, this is a clear sign of an air lock. With proper installation, it is assembled near the Mayevsky crane. The removal process is very simple.
This is Mayevsky's crane.
At the top, you need to find an air vent (in the figure on the right). It has a rotating part with a hole, the hole diameter is no more than the thickness of the needle. There should be a bolt in the center of the cap. Algorithm of action:
- turn the cap with the hole down;
- substitute the cup;
- unscrew the bolt half a turn;
- we release the air and wait for 100 ml of water to merge;
- we tighten the bolt back.
You may need to repeat the procedure again. The radiator will then heat up evenly. This procedure must be done every year at the very beginning of the heating season. It is important to release the air when the heating is already running.